A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Evaluating the Effect of Pesticides on the Larvae of the Solitary Bees
In This Article
Summary
The present protocol explains a method to feed pesticide-contaminated provisions to the larvae of the solitary bees, Osmia excavata. The procedure examines the ecotoxicity of the pesticide to the larvae of the solitary bees.
Abstract
Current ecological risk assessments of pesticides on pollinators have primarily considered only laboratory conditions. For the larvae of solitary bees, ingestion of provisions contaminated with pesticides may increase the mortality rate of the larvae, decrease the collection rate and the population of adult solitary bees in the next year from a demographic perspective. But there are limited studies on the effects of pesticides on the larvae of solitary bees. Therefore, understanding how pesticides influence the larvae of solitary bees should be considered an integral part of pesticide ecological risk assessment. This study presents a method to expose the larvae of solitary bee, Osmia excavata, to lethal or sublethal doses of pesticide, tracking larval weight gain, developmental duration, eclosion ability, and food consumption efficiency conversion of ingested food. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this method, the larvae of O. excavata were fed with provisions containing acute lethal and sublethal doses of chlorpyrifos. Then, the above indexes of the treated larvae were investigated. This technique helps to predict and mitigate the risk of pesticides to pollinators.
Introduction
Pollinators play a critical role in the ecosystem services of modern global agriculture. While honey bees (Apis mellifera; Hymenoptera: Apidae) have traditionally been considered as the essential economic pollinators of crops, recent research suggests that Osmia (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae) is also very important in improving pollination for certain crops, increasing fruit size and number of seeds, and reducing the proportion of asymmetric fruit in commercial orchards in different parts of the world1. Osmia excavata has been considered an ideal species for apple pollination, mainly in Asia, like in north and northwest China and Japan2,3,4. It can provide pollination services for certain crops with similar or sometimes with greater efficiency. In this respect, they have been shown to replace or work in synergy with the honey bees4,5,6.
The biological characteristics of O. excavata are unique compared with social bees. Its univoltine, solitary, and nesting activity occurs mainly in spring and early summer. The nests of O. excavata are usually found in preexisting holes, typically in deadwood, hollow plants, straw tubes, and bamboo stem in the natural condition3. The adult O. excavata emerges from its cocoon to mate, gather pollen, and build a nest to lay eggs, which begin to hatch a week later. The fertilized eggs develop into females, while the unfertilized eggs develop into males3. Females are distributed in the bottom of the bee tube, and the corresponding provisions are more significant. In contrast, males were in the proximity of tube exit with minor provisions7, so the males come out first, and the females come out later. The female mixes pollen with a small amount of nectar into a moist blob, the only food source for each larva in the cell8.
Several studies have reported a decrease in the population of pollinating insects9,10. The extensive use of pesticides has been identified as one of the main factors for reducing pollinator abundance and diversity and may also endanger pollination services11,12. To reduce and mitigate the adverse effects of pesticides, it is necessary to conduct a pesticide risk assessment for pollinators. Some countries have established regulatory frameworks to ensure safety to bees from the pesticides used13,14. Recent studies have shown that Osmia was more susceptible to pesticides than honey bees1,15.
Interestingly, most risk assessments were focused on adult honey bees11,12; little research has been conducted on O. excavata, especially the larvae. Furthermore, the mortality of Osmia directly caused by pesticides is most commonly considered16. Still, the chronic toxicities such as larval weight gain, developmental duration, feeding patterns, eclosion ability, subsequent adult behavior, and fecundity may have the same harm as the acute lethal toxicities and are often ignored because of a lack of an effective experimental method for the solitary bees17.
Up to now, two methods are used to evaluate the effects of pesticides on the larvae of solitary bees: (1) an appropriate amount of pesticide was applied in the localized spot of provisions without removing the egg of solitary bees1,18,19,20; (2) replacing provisions with artificial pollen-nectar mixtures containing a specific amount of pesticide21. However, there are some limitations to the above two methods. The former can only measure acute toxicity, but not chronic toxicity because the larvae ingested the entire dose in a short period of time; the latter would lead to a high mortality rate because of human manipulation1. Here, the immersion method was described to study the ecotoxicity of pesticides to O. excavata under highly controlled research conditionsby simulating the behavior of larval feeding on residual pesticide in the provisions in the real environment. The method of this study solves the disadvantages of the above two methods and is suitable for measuring the effects of a hazardous substance on acute and chronic toxicity.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Preparation of the feeding tube
- Punch a hole (~0.3 mm diameter) into the lid of a 2 mL centrifuge tube using an electric winding iron (see Table of Materials). Use such a centrifuge tube to maintain an O. excavata larva and its provision mass.
2. Preparation of pesticide
- Dissolve the technical-grade pesticide (see Table of Materials) in acetone to acquire stock solutions of 1 x 104 µg a.i. mL-1. Then, perform gradient dilutions of the solution to more than five concentrations.
NOTE: Chlorpyrifos at 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2, 6.4 µg a.i. mL-1 were used in this study.
3. Preparation of the provisions
- Acquire plastic bee tubes containing provisions (see Table of Materials) and newly hatched larvae of O. excavata from a mass-rearing program.
NOTE: No pesticides were used from 20 days before flowering to the entire flowering period; chemical analysis results showed that commonly used pesticide contents in randomly selected fifty provisions were both below the minimum test levels. - Separate provisions and larvae gently using a soft brush. Select female larvae based on provision size and cell position within the nest9. Then, place uniform-sized provisions and selected female larvae in Petri dishes (60 mm diameter) and set them aside for use.
NOTE: Fifty provisions were randomly selected to analyze the contents of commonly used pesticides: chlorpyrifos, imidacloprid, fendifenuron, phoxim, avermectin. The soft brush parameters are (a) diameter of the brush: 0.3 mm, (b) length of the brush: 2 cm, (c) length of the pen: 18 cm.
4. Provision treatment with pesticide
- Soak the selected evenly sized provisions (from step 3.2) in diluted pesticide (from step 2.1; chlorpyrifos at 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2, 6.4 µg a.i. mL-1) for 10 s using a cage. Soak the control check (CK) in 0.2% solvent (acetone in this study).
NOTE: There are three replicates per concentration treatment, and each replicate consisted of 60 provisions. The difference of dosage of each provision can be reduced by selecting evenly sized provisions. - Measure the volume of pesticide solution before and after treating the provisions with the pesticide. Then, calculate the immersed volume of insecticide in each treatment, including 60 mass provisions (Supplementary Table 1). Place the provisions in separate centrifugal tubes with holes (from step 1.1) after air-drying on a sterile worktable.
NOTE: Before the experiment, put the cages containing the provisions into the pesticide solution, and then measure the volume of pesticide solution before and after soaking to eliminate the error. - Transfer female larvae individually to the surface of naturally dried provisions using a soft brush.
NOTE: One larva in one tube.
5. Growth conditions
- Rear the larvae of O. excavata in a growth chamber in the dark, 65%-75% relative humidity, and 25 ± 2 °C16.
6. Examination of the results
- The acute lethal toxicity test
- Measure the mortality of the larvae after placing them onto the treated and the control (CK) provisions for 48 h.
NOTE: The death criteria: when the larvae did not respond to mild touch using a soft brush under black-light lamps22. Black-light lamps were used to simulate the dark growth conditions of larvae and avoid the influence of light on the larvae when checking growth indicators. For eliminating human error, the mortalities with and without removal of larvae from the provisions after 48 h in control groups were also measured. - Weigh 60 provisions before and after 48 h of insect rearing trials to determine the amount of provision consumed by each larva.
- Calculate the dose of pesticide at each concentration consumed by each larva according to the percentage of provision eaten and the pesticide content in each provision.
NOTE: The equation for dose calculation is23:
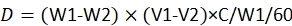
where, D is the consumed dose of pesticide by each larva; W1 is the weight of 60 provisions before infusion of pesticide; W2 is the remaining weight of 60 provisions after 48 h; V1 is the volume of pesticide before immersion for 60 provisions; V2 is the volume of pesticide after immersion for 60 provisions; C is the concentration of the pesticide.
- Measure the mortality of the larvae after placing them onto the treated and the control (CK) provisions for 48 h.
- The sublethal toxicity test
- Weigh the larvae before rearing trials and after 14 days of treatments to determine the larval weight gain.
- Observe O. excavata daily during cocooning under black-light lamps to measure the larval development duration.
- Weigh the remaining portions of provisions after 14 days of feeding on treated and CK provisions to calculate the consumption and the efficiency of conversion of ingested food (ECI)24.
- Examine the number of eclosions by sniping the cocoons using a small scissor when the control bees emerge into adults.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The contents of commonly used pesticides, chlorpyrifos, imidacloprid, fendifenuron, phoxim, avermectin in provisions were less than the limit of quantification (0.01-0.02 mg kg-1) in the control group; these results excluded the influence of pesticide residues on each treatment. The mortality with and without removing larvae from provisions after 48 h in control groups was evaluated; the results showed no significant differences (Table 1), indicating a minor human error.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
For adult pollinators, there are two main methods for measuring the ecotoxicity of pesticides. One is the contact method, in which the pesticide is applied to the prothorax of the adult insects; the other is the gastric toxicity method, in which the adult pollinators are fed with honey water containing pesticide25,26. In recent years, it has been found that the pollination effect and eclosion rate of O. excavata are relatively low27
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0200400), Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (2017CXGC0214), Bee Industry Innovation Team of Shandong Province, Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CXGC2019G01), and Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CXGC2021B13).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Abamectin | Jinan Lvba Pesticide Co. Ltd | ||
| Black-light lamps | Kanghua Medical Device Co., Ltd | ||
| Centrifugal tube box with 100 Wells | Shanghai Rebus Network Technology Co., Ltd | ||
| Centrifuge tube | Shanghai Rebus Network Technology Co., Ltd | 2 mL; Serve as bee tube | |
| Electric soldering iron | Kunshan Kaipai Hardware Electromechanical Co., Ltd | ||
| Electronic scale | Sartorius Scientific Instruments (Beijing) Co., Ltd | 3137510295 | |
| Graduated cylinder | Anhui Weiss Experimental Equipment Co. Ltd | ||
| Petri dishes (60 mm diameter) | Qingdao jindian biochemical equipment co., LTD | ||
| Pollen provision | Yantai Bifeng Agricultural Science and Technology Co. Ltd | ||
| Soft brush | Wengang Wenhai painting material factory | ||
| Solitary bees | Yantai Bifeng Agricultural Science and Technology Co. Ltd |
References
- Sgolastra, F., Tosi, S., Medrzycki, P., Porrini, C., Burgio, G. Toxicity of spirotetramat on solitary bee larvae, Osmia cornuta (hymenoptera: megachilidae), in laboratory conditions. Journal of Apicultural Science. 59 (2), 73-83 (2015).
- Wei, S. G., Wang, R., Smirle, M. J., Xu, H. L. Release of Osmia excavata and Osmia jacoti (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae) for apple pollination. TheCanadian Entomologist. 134 (3), 369-380 (2002).
- Men, X. Y., et al. Biological characteristics and pollination service of Mason bee. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology. 55 (6), 973-983 (2018).
- Bosch, J., Kemp, W. P., Trostle, G. E. Bee population returns and cherry yields in an orchard pollinated with Osmia lignaria (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Journal of Economic Entomology. 99 (2), 408-413 (2006).
- Winfree, R., Williams, N. M., Dushoff, J., Kremen, C. Native bees provide insurance against ongoing honey bee losses. Ecology Letters. 10 (11), 1105-1113 (2007).
- Garibaldi, L. A., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Winfree, R. Wild pollinators enhance fruit set of crops regardless of honey bee abundance. Science. 339 (6127), 1608-1611 (2013).
- Bosch, J., Sgolastra, F., Kemp, W. P. Life cycle ecophysiology of Osmia. mason bees used as crop pollinators. Bee Pollination in Agricultural Ecosystems. James, R. R., Pitts-Singer, T. L. , Oxford University Press. Oxford, UK. 83-104 (2008).
- Liu, L., et al. Population investigation and restriction factors analyses of Osmia excavata Alfken in Jiaodong. Apiculture of China. 69 (9), 68-71 (2018).
- Biesmeijer, J. C., Roberts, S. P. M., Reemer, M. Parallel declines in pollinators and insect-pollinated plants in Britain and the Netherlands. Science. 313 (5785), 351-354 (2006).
- Potts, S. G., Biesmeijer, J. C., Kremen, C. Global pollinator declines: trends, impacts and drivers. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 25 (6), 345-353 (2010).
- Chen, L., Yan, Q., Zhang, J., Yuan, S., Liu, X. Joint toxicity of acetamiprid and co-applied pesticide adjuvants on honeybees under semi-field and laboratory conditions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 38 (9), 1940-1946 (2019).
- Sgolastra, F., Medrzycki, P., Bortolotti, L., Renzi, M. T., Bosch, J. Synergistic mortality between a neonicotinoid insecticide and an ergosterol-biosynthesis-inhibiting fungicide in three bee species. Pest Management Science. 73 (6), 1236-1243 (2017).
- Bireley, R., et al. Preface: Workshop on pesticide exposure assessment paradigm for non-Apis bees. Environmental Entomology. 48 (1), 1-3 (2019).
- European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Guidance Document on the risk assessment of plant protection products on bees (Apis mellifera, Bombus spp. and solitary bees). EFSA Journal. 11 (7), 3295(2013).
- Rundlof, M., et al. Seed coating with a neonicotinoid insecticide negatively affects wild bees. Nature. 521 (7550), 77-80 (2015).
- Yuan, R., et al. Toxicity and hazard assessment of six neonicotinoid insecticides on Osmia excavata (hymenoptera:megachilidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica. 61 (8), 950-956 (2018).
- Lin, Z., Meng, F., Zheng, H., Zhou, T., Hu, F. Effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on honeybee health. Acta Entomologica Sinica. 57 (5), 607-615 (2014).
- Gradish, A. E., Scott-Dupree, C. D., Cutler, G. C. Susceptibility of Megachile rotundata to insecticides used in wild blueberry production in Atlantic Canada. Journal of Pest Science. 85, 133-140 (2012).
- Hodgson, E. W., Pitts-Singer, T. L., Barbour, J. D. Effects of the insect growth regulator, novaluron on immature alfalfa leafcutting bees, Megachile rotundata. Journal of Insect Science. 11, 43(2011).
- Konrad, R., Ferry, N., Gatehouse, A. M. R., Babendreier, D. Potential effects of oilseed rape expressing oryzacystatin-1 (OC-1) and of purified insecticidal proteins on larvae of the solitary bee Osmia bicornis. PLoS ONE. 3 (7), 2664(2008).
- Abbott, V. A., Nadeau, J. L., Higo, H. A., Winston, M. L. Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Osmia lignaria and clothianidin on Megachile rotundata (Hymenoptera: megachilidae). Journal of Economic Entomology. 101, 784-796 (2008).
- Yan, Z., Wang, Z. Sublethal effect of abamectin on 3rd instar larvae of Prodenia litura. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops. 32 (10), 1945-1950 (2011).
- Song, Y., et al. Comparative ecotoxicity of insecticides with different modes of action to Osmia excavata (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 212 (5), 112015(2021).
- Chen, F. J., Wu, G., Ge, F., Parajulee, M. N., Shrestha, R. B. Effects of elevated CO2 and transgenic Bt cotton on plant chemistry, performance, and feeding of an insect herbivore, the cotton bollworm. Entomologia Experimentalis Et Applicata. 115 (2), 341-350 (2005).
- Cang, T., et al. Toxicity and safety evaluation of pesticides commonly used in strawberry production to bees. Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences. (4), 785-787 (2009).
- Cang, T., et al. Acute toxicity and safety assessment of chiral fipronil against Apis mellifera and Trichogramma ostriniae. Ecotoxicology. 7 (3), 326-330 (2012).
- Liu, X., Pan, W. Measures to ensure pollination effect and cocoon recovery rate of Osmia excavata in apple orchard. Northwest Horticulture. (3), 20-21 (2017).
- Meikle, W. G., Adamczyk, J. J., Weiss, M., Ross, J., Beren, E. Sublethal concentrations of clothianidin affect honey bee colony growth and hive CO2 concentration. Scientific Reports. 11 (1), 4364(2021).
- Meikle, W. G., Adamczyk, J. J., Weiss, M., Ross, J., Beren, E. Sublethal concentrations of clothianidin affect honey bee colony behavior and interact with landscapes to affect colony growth. BioRxiv. , (2020).
- Wang, Y. F., et al. Combination effects of three neonicotinoid pesticides on physiology and survival of honey bees (Apis mellifera L). Journal of Environmental Entomology. 41 (3), 612-618 (2019).
- Kopit, A. M., Pitts-Singer, T. L. Routes of pesticide exposure in solitary, cavity-nesting bees. Environmental Entomology. 47 (3), 499-510 (2018).
- Cheng, Y., et al. Chronic oral toxicity of chlorpyrifos and imidacloprid to adult honey bees (Apis mellifera L). Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology. 11 (2), 715-719 (2016).
- Li, M., Ma, C., Xiao, L., Li, Z., Su, S. Effects of chlorpyrifos on behavior response of Apis mellifera and Apis cerana. Apicultural Science Association of China. , (2016).
- Cresswell, J. E. A meta-analysis of experiments testing the effects of a neonicotinoid insecticide (imidacloprid) on honey bees. Ecotoxicology. 20 (1), 149-157 (2011).
- Nauen, R., Ebbinghaus-Kintscher, U., Schmuck, R. Toxicity and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor interaction of imidacloprid and its metabolites in Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera; Apidae). Pest Management Science. 57 (7), 577-586 (2001).
- Colin, M. E., et al. A method to quantify and analyze the foraging activity of honey bees: relevance to the sublethal effects induced by systemic insecticides. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 47 (3), 387-395 (2004).
- Decourtye, A., et al. Comparative sublethal toxicity of nine pesticides on olfactory learning performances of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology. 48 (2), 242-250 (2005).
- Williamson, S. M., Wright, G. A. Exposure to multiple cholinergic pesticides impairs olfactory learning and memory in honeybees. Journal of Experimental Biology. 216 (10), 1799-1807 (2013).
- Henry, M., et al. A common pesticide decreases foraging success and survival in honey bees. Science. 336 (6079), 348-350 (2012).
- Matsumoto, T. Reduction in homing flights in the honey bee Apis mellifera after a sublethal dose of neonicotinoid insecticides. Bulletin of Insectology. 66 (1), 1-9 (2013).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved