A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
A Mass Spectrometry-Based Approach to Identify Phosphoprotein Phosphatases and their Interactors
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a protocol for the enrichment of endogenous phosphoprotein phosphatases and their interacting proteins from cells and tissues and their identification and quantification by mass spectrometry-based proteomics.
Abstract
Most cellular processes are regulated by dynamic protein phosphorylation. More than three-quarters of proteins are phosphorylated, and phosphoprotein phosphatases (PPPs) coordinate over 90% of all cellular serine/threonine dephosphorylation. Deregulation of protein phosphorylation has been implicated in the pathophysiology of various diseases, including cancer and neurodegeneration. Despite their widespread activity, the molecular mechanisms controlling PPPs and those controlled by PPPs are poorly characterized. Here, a proteomic approach termed phosphatase inhibitor beads and mass spectrometry (PIB-MS) is described to identify and quantify PPPs, their posttranslational modifications, and their interactors in as little as 12 h using any cell line or tissue. PIB-MS utilizes a non-selective PPP inhibitor, microcystin-LR (MCLR), immobilized on sepharose beads to capture and enrich endogenous PPPs and their associated proteins (termed the PPPome). This method does not require the exogenous expression of tagged versions of PPPs or the use of specific antibodies. PIB-MS offers an innovative way to study the evolutionarily conserved PPPs and expand our current understanding of dephosphorylation signaling.
Introduction
Protein phosphorylation controls most cellular processes, including but not limited to the response to DNA damage, growth factor signaling, and the passage through mitosis1,2,3. In mammalian cells, the majority of proteins are phosphorylated at one or more serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues at some point in time, with phosphoserines and phosphothreonines comprising approximately 98% of all phosphorylation sites2,3. While kinases have been extensively studied in cellular signaling, the role of PPPs in the regulation of dynamic cellular processes is still emerging.
Phosphorylation dynamics are controlled by the dynamic interplay between kinases and phosphatases. In mammalian cells, there are more than 400 protein kinases that catalyze serine/threonine phosphorylation. Over 90% of these sites are dephosphorylated by phosphoprotein phosphatases (PPPs), a small family of enzymes that consists of PP1, PP2A, PP2B, PP4-7, PPT, and PPZ2,3. PP1 and PP2A are responsible for the majority of phosphoserine and phosphothreonine dephosphorylation within a cell2,3,4. The notable difference in number between kinases and phosphatases and the lack of specificity of PPP catalytic subunits in vitro led to the belief that kinases are the main determinant of phosphorylation2,3. However, multiple studies have shown phosphatases to establish substrate specificity through the formation of multimeric holoenzymes5,6,7,8,9. For example, PP1 is a heterodimer that consists of a catalytic subunit and, at a given time, one out of the more than 150 regulatory subunits6,7,8. Conversely, PP2A is a heterotrimer that is formed of a scaffolding (A), a regulatory (B), and a catalytic (C) subunit2,3,9. There are four distinct families of PP2A regulatory subunits (B55, B56, PR72, and striatin), each with multiple genes, splice variants, and localization patterns2,3,9. The multimeric nature of PPPs fills the gap in the number of kinases and PPP catalytic subunits. However, it creates analytical challenges for studying PPP signaling. To comprehensively analyze PPP signaling, it is critical to investigate the various holoenzymes within a cell or tissue. Great advances have been made in studying the human kinome through the use of kinase inhibitor beads, termed multiplex inhibitor beads or kinobeads, a chemical proteomic strategy where kinase inhibitors are immobilized on beads and mass spectrometry is used to identify enriched kinases and their interactors10,11,12,13.
We have established a similar approach to study PPP biology. This technique involves affinity capture of PPP catalytic subunits using beads with an immobilized, non-selective PPP inhibitor called microcystin-LR (MCLR) termed phosphatase inhibitor beads (PIBs)14,15. Unlike other methods that require the endogenous tagging or expression of exogenous PPP subunits that could alter protein activity or localization, PIB-MS allows for the enrichment of endogenous PPP catalytic subunits, their associated regulatory and scaffolding subunits, and interacting proteins (termed the PPPome) from cells and tissues at a given time point or under specific treatment conditions. MCLR inhibits PP1, PP2A, PP4-6, PPT, and PPZ at nanomolar concentrations, making PIBs highly effective at enriching for the PPPome16. This method can be scaled for use on any starting material from cells to clinical samples. Here, we describe in detail the use of PIBs and mass spectrometry (PIB-MS) to efficiently capture, identify, and quantify the endogenous PPPome and its modification states.

Figure 1: Visual summary of the PIB-MS protocol. In a PIB-MS experiment, samples can be obtained in various forms, from cells to tumors. The sample is collected, lysed, and homogenized prior to PPP enrichment. To enrich for PPPs, the lysate is incubated with PIBs with or without a PPP-inhibitor, such as MCLR. The PIBs are then washed, and PPPs are eluted in denaturing conditions. The samples are prepared for mass spectrometry analysis by the removal of detergents through SP3 protein enrichment, tryptic digestion, and desalting. Samples can then be optionally TMT-labeled prior to mass spectrometry analysis. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
PIB-MS involves lysis and clarification of cells or tissues, incubation of the lysate with PIBs, elution, and analysis of the eluate via western blotting or mass spectrometry-based approaches (Figure 1). The addition of free MCLR can be used as a control to distinguish specific PIB binders from non-specific interactors. For most applications, a label-free approach can be used to directly identify proteins in eluates. In cases where greater precision in quantification or the identification of low-abundance species is needed, further processing with tandem mass-tag (TMT) labeling can be used to increase coverage and decrease input.
Protocol
NOTE: The generation of PIBs is done as described by Moorhead et al., where 1 mg of microcystin and about 6 mL of sepharose are coupled to generate PIBs with a binding capacity of up to 5 mg/mL17.
1. Sample preparation
NOTE: A typical starting amount for PIB-MS is 1 mg of total protein per condition. For this experiment, approximately 2.5 x 106 HeLa cells were used to extract 1 mg of protein. This calculation should be performed for each cell line or tissue being used in an experiment18. If the sample is limited and 1 mg cannot be obtained, the amount of input can be reduced with a minor loss of PPP subunit detection. Alternatively, TMT labeling can be employed to allow the mixing of all conditions in one sample, increasing the sensitivity of detection as shown in Step 9.
- Collect tissue samples or cell pellets. For cell pellets, collect cells by centrifugation at 277 x g for 2 min at room temperature (RT), remove media, and wash the cells with 5 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cell pellets may be stored at -80 °C for several months.
- Prepare lysis buffer (500 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 0.5% Triton X-100 (vol/vol), 5 mM beta-glycerophosphoric acid disodium salt pentahydrate, 1:500 (vol/vol) protease inhibitor cocktail III) and keep on ice. Make enough to lyse and wash all the samples. If starting with 1 mg of protein per condition, make about 3 mL of buffer per sample for lysis and washes.
NOTE: The lysis buffer noted in this step is a mild detergent solution, which may not be sufficient to solubilize insoluble membrane or cytoskeletal-associated proteins. Other detergents could be explored to improve solubilization. A range of NaCl and Triton-X-100 concentrations were tested, and the above concentrations were found to be optimal for low background and high phosphatase subunit binding. - Add chilled lysis buffer to the samples. For lysis of 1 mg of protein, use 1 mL of buffer. If the sample is frozen, add lysis buffer and let the sample thaw on ice in the buffer.
- For cells, homogenize the samples via sonification, keeping the cells on ice between pulses. Sonicate the samples at 15% amplitude with three 15 s pulses. This may vary based on the sonicator used (see Table of Materials).
- For tissues, homogenize the samples first using a Dounce tissue grinder to grind the tissue until liquified before sonicating as described in Step 1.3.1.
- Clarify the homogenized sample of insoluble debris by centrifugation at 21,130 x g for 15 min at 4 °C. Then, without disturbing the formed pellets or lipids that have collected on the side of the tubes, transfer the lysates to new tubes. Remove 100 µL of the pre-enrichment sample of the clarified lysate if desired and store at -20 °C. Be sure to keep the lysates on ice.
- Determine the total protein content in each sample by performing a protein quantification assay, such as a bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA), on a small aliquot of each sample, according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure the lysates are kept on ice during the BCA assay.
- After performing the BCA assay, transfer an equivalent amount of protein to new tubes and dilute with lysis buffer to ensure each tube has the same concentration of protein (e.g., 1 mg/mL). If the experiment requires a PPP inhibitor control, prepare two aliquots of each sample that have the same protein content and proceed to Step 1.7. If PPP inhibitor controls are not needed, skip to Step 2. Ensure samples are kept on ice.
NOTE: It is critical that equal protein concentrations are used per condition in a PIB-MS analysis. PPP inhibitor controls are used to distinguish specific binders to PIBs from the non-specific background. - For the PPP inhibitor control, treat one sample with free MCLR (1 µM) and the other one with an equal volume of DMSO as a control. Vortex the samples gently and incubate them on ice for 15 min.
NOTE: MCLR treatment of the lysates blocks the binding of PPP catalytic subunits but not proteins that bind non-specifically to PIBs in the samples. Be cautious when handling MCLR as it is toxic. Refer to handling precautions in the Table of Materials.
2. Preparation of PIBs
- Determine the amount of PIBs needed for the experiment. For 1 mg of protein, 1-3 µg of PPPs and interacting proteins can be obtained; use at least 10 µL of solid PIBs resin per sample to minimize bead loss. The binding capacity of PIBs is 3-5 mg/mL14,17.
- Transfer the appropriate amount of PIBs to a 1.5 mL tube and wash them 3x with 0.5 mL of lysis buffer by gently vortexing and then centrifuging at 376 x g for 30 s at RT in between washes. Avoid pipetting up the beads when removing lysis buffer between washes.
- Make a 50% PIB/buffer solution (vol/vol) by adding an appropriate amount of lysis buffer to the washed PIBs. Gently pipet up and down and swirl the pipet tip in the slurry to resuspend the PIBs.
- Transfer 20 µL of the slurry to a new 1.5 mL tube already containing 0.5 mL of lysis buffer. The lysis buffer in the tube helps in expelling the beads from the pipet tip. Do this until there are enough tubes containing an equal amount of PIBs for each sample.
- Spin the tubes at 376 x g for 30 s at RT. Make sure all tubes contain an equal amount of bead resin. Discard any supernatant, only leaving solid resin and a maximum of 50 µL of lysis buffer in each tube.
3. Incubation of PIBs with lysates
- Transfer the lysates from Step 1.6. or Step 1.7. to the appropriately labeled tube containing PIBs from Step 2. Rotate the lysate at 8 rpm with the PIBs for 1 h at 4 °C.
4. Washing of PIBs
- Centrifuge the PIBs at 376 x g for 30 s at 4 °C to collect the beads. Remove and discard the supernatant, saving a 100 µL aliquot for post-enrichment analysis, if desired.
- Wash the PIBs 3x by adding 0.5 mL of lysis buffer to the beads, inverting the tubes (vortexing not recommended), collecting the beads by centrifugation at 376 x g for 30 s at 4 °C, and removing the lysis buffer from the settled beads, being careful not to disrupt the bead pellet.
5. Elution of PPPs from the PIBs
- After the final wash, remove as much of the lysis buffer as possible without pipetting up any of the PIBs. Make elution buffer containing 2% SDS (vol/vol) and elute the PPPs from the PIBs by adding enough volume of elution buffer to be 4x-5x the volume of PIBs. For example, if 10 µL of PIBs are used, use 50 µL of elution buffer. Incubate the PIBs with the elution buffer at 65 °C for 1 h to elute the PPPs from the PIBs.
- After elution, collect the eluate by centrifuging the tubes at 376 x g for 30 s at RT and pipetting the eluate into a separate tube, being careful not to transfer any PIBs. Use the eluate for western blot analysis or for mass spectrometry analyses. Eluates can be stored at -20 °C for up to several months.
- To regenerate the PIBs for further use, incubate the beads in 2% SDS (vol/vol), rotating at 8 rpm at RT for 1 h. Wash them 3x-5x in 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) with rotation for 30 min per wash. After all washes, store PIBs in 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) storage buffer with sodium azide (0.05% wt/vol).
- Analyze the eluates by western blotting or mass spectrometry. The mass spectrometry analysis of PIB eluates is described below.
6. Removal of detergents
NOTE: Various approaches can be used to remove detergent from eluate samples for MS analysis. We found that single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample-preparation (SP3), described by Hughes et al., works well19.
- Add 0.5 µL of SP3 beads to 50 µL of eluate from Step 5.2 above. Use SP3 beads at a ratio of 10:1 (µg:µg) or at least 0.5 µg/µL (stock solution is 50 µg/µL). Gently vortex the beads and eluate.
- Add one elution volume of 100% ethanol to the bead-eluate mixture (e.g., if 50 µL of the eluate was used, use 50 µL of 100% ethanol). Incubate the samples for 5 min in a thermomixer set to shake at 1000 rpm at 24 °C.
- To collect all the beads, place them in a magnetic tube rack. Once the beads collect, discard the supernatant and wash the beads with 0.5 mL of 80% ethanol (vol/vol) 3x. For washing, resuspend the beads by vortexing, collect the beads by placing them in the magnetic tube rack, and discard the supernatant between washes.
- Wash the beads one more time with 0.5 mL of 100% acetonitrile (ACN) to remove all traces of ethanol, removing as much ACN as possible.
7. Digestion of proteins
- Make a 1:100 dilution of trypsin (final concentration of 0.004 µg/µL) in 166 mM HEPES (pH 8.5) and add 30 µL of this trypsin solution to each tube with the beads, resuspending by vortexing.
- Incubate the SP3-trypsin bead mixture in the thermomixer at 1000 rpm at 37 °C for 5 h or overnight at 30 °C. Place the tubes in the magnetic rack to collect the beads and remove the digests to new tubes.
- For label-free analysis, quench the reaction by adding 20% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (vol/vol) to a final concentration of 0.2% TFA (vol/vol). Check that the pH of each sample is between 2-3 with a pH paper. If not, add small additional aliquots of 20% TFA until this is achieved. The samples must be appropriately acidified prior to desalting. Continue to Step 8.
- For TMT labeling of the samples, do not acidify and continue to Step 9.
8. Desalting the digest
- Prepare a stage tip for each sample by packing a 200 µL of MS solvent compatible tip with C18 resin as described by Rappsilber et al.20. Use a blunt-ended needle to press two C18 material disks, ensuring that the disks remain in the needle. Transfer the disks into the MS solvent compatible tip using a thin wire plunger to expel the discs from the needle.
NOTE: It is critical to use MS solvent compatible tips from this point in the protocol since other pipet tips may leach chemicals into the samples that can be detected via mass spectrometry. - Equilibrate each stage tip with 30 µL of 100% MeOH, then with 30 µL of 60% MeOH (vol/vol), followed by 30 µL of 0.1% TFA (vol/vol). Push each solution through the stage tip with a syringe. Attach a pipet tip to the end of a syringe with a transparent film to increase contact between the syringe and stage tip if needed. Be sure to never let the C18 material inside the stage tip to go dry.
- Add acidified peptide digest from step 7.3 to the labeled stage tip and push through the stage tip with a syringe, again being careful not to let the stage tip go completely dry.
- Wash each sample 2x with 30 µL of 0.1% TFA (vol/vol). Elute the peptides from each stage tip by adding 30 µL of 60% MeOH (vol/vol) to each stage tip and expelling it all from the tip with syringe pressure into a new, labeled tube. This is the only step where the C18 material is completely dried.
- Dry each sample by vacuum centrifugation. Dried peptides can be stored at -20°C for several months. The samples are now ready for label-free mass spectrometry analysis. Use only half of the sample for analysis on the mass spectrometer and the other half for reinjection if needed. Ensure the use of an appropriate mass spectrometer method for analysis.
9. TMT labeling
NOTE: Tandem-mass tag labeling is used to multiplex samples for quantitative analysis. A 0.8 mg vial of TMT reagent is sufficient for labeling up to 0.8 mg of protein21. In a PIB pulldown experiment starting with 1 mg of protein, 1-3 µg of phosphoprotein subunits are obtained. The protocol below is optimal for up to 10 µg of protein.
- Reconstitute one 0.8 mg vial of TMT reagent in 80 µL of anhydrous ACN.
- Label each sample from Step 7.4 with a different TMT label for up to 18 channels. Be sure to note which TMT label is added to each sample. Add 2 µL of the TMT reagent and 2 µL of ACN to the peptide digest, vortex gently to mix, centrifuge at 376 x g for 30 s at RT to collect the sample, and incubate at RT for 1 h to label the sample.
- To test the TMT labeling efficiency, make a label check sample by combining 1 µL of each labeling reaction in a 0.5 mL tube containing 9 µL of LC-MS grade water and 1 µL of 10% hydroxylamine (vol/vol) to quench the reaction. Place the remaining unquenched labeled samples in a -80 °C freezer. Samples can be stored for several days while the labeling efficiency is evaluated.
- Acidify the TMT label check sample by adding 30 µL of 0.1% TFA (vol/vol). Check that the pH is between 2-3. If not, add 20% TFA (vol/vol) until this pH is achieved. Desalt the label check sample via stage tipping, as described in Steps 8.1.-8.5.
- Analyze the TMT label check sample on the mass spectrometer to evaluate labeling efficiency. Filter the search results to a 1% false discovery rate (FDR) on the peptide level and determine the labeling efficiency21,22.
- Fully TMT-labeled peptides have TMT reagent at the N-terminus and at all lysines. Quantify the TMT reporter ion intensities and compare their total sum across all channels. The sample is sufficiently labeled when >95% of all peptides are labeled and the TMT reporter ion sum intensities are comparable
NOTE: Besides incomplete labeling, differences in summed TMT reporter ion intensities could be the result of inaccurate pipetting of the 1 µL test sample. It could also reflect a true biological observation, in which case all replicates should display the same behavior. - Remove the unquenched samples from -80 °C storage and thaw them. If they are not fully labeled, add 1 µL of the appropriate TMT reagent to the sample as noted above, incubate for 1 h, and repeat the TMT label check. If the samples are fully labeled, continue to Step 9.8.
- When fully labeled, add 2 µL of 10% hydroxylamine (vol/vol) to the TMT reactions to quench the labeling. Incubate the samples at RT for 15 min. Once quenched, the samples can be stored at -80 °C for several months.
- Combine all quenched TMT channels and add 2 µL of 20% TFA (vol/vol) to acidify the reaction. Check the pH of the combined reaction, ensuring it is between pH 2-3. If not, add small aliquots of 20% TFA until the desired pH is reached. This is critical for proper desalting.
- Remove ACN by vacuum centrifugation for 30 min and desalt the sample as described below.
10. Desalting the TMT-labeled combined sample
- Use an SPE C18 desalting plate with the appropriate protein capacity (2 mg sorbent is usually sufficient for this application) to desalt the combined TMT reagent. Equilibrate the well with 200 µL of 60% MeOH (vol/vol) and 200 µL of 10% MeOH/0.1% TFA (vol/vol).
- Load the acidified TMT-labeled peptides from Step 9.10. onto the desalting plate. Wash the sample wells 2x with 200 µL of 10% MeOH/0.1% TFA (vol/vol).
- Elute the peptides with 100 µL of 60% MeOH (vol/vol). Dry the samples by vacuum centrifugation. The dried, TMT-labeled sample can be stored at -80 °C for several months.
- For mass spectrometry analysis of the TMT labeled sample, inject half of the sample and save the other half if reinjection is required.
NOTE: Injection amounts on the mass spectrometry will vary depending on the specific column, instrument setup, and sample type.
11. Data analysis
NOTE: Methods of data filtering and analysis vary and are beyond the scope of this protocol, but the following notes on analysis are included to provide guidance specific to the type of data resulting from this protocol.
- Search raw mass spectrometry data against a species-specific proteome database based on the origin of the sample cells or tissue used. Here, Comet was used as a search algorithm23.
- Filter the search results with a 1% FDR by adjusting the search algorithm-specific parameters22. For label-free quantification, use MS1 peak area measurements to quantify the data. For TMT-labeled samples, use MSn-derived reporter ion intensities for quantification. For statistical significance, analyze the samples in biological triplicates.
- To de novo identify PPP subunits and their interactors, ensure that triplicate biological samples of MCLR-inhibited and DMSO-treated samples are compared. To compare the PPPome under different conditions or upon drug treatment, ensure that biological triplicates of each condition or drug treatment were generated.
- Filter the data so that only proteins with a total peptide count >1 in at least two of three DMSO control-treated samples are present. MCLR competition does not always compete off all catalytic subunit binding. Also, some PPP catalytic subunits might non-specifically stick to the sepharose resin. To account for either possibility while filtering out proteins that non-specifically bind to the resin, remove proteins with a total peptide count in the MCLR-treated condition higher than that for any PPP catalytic subunit.
- Exclude common contaminants, such as keratin, collagen, 40S and 60S ribosomal proteins, and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins that are not PPP subunits, from the analysis14.
- Import filtered data into Perseus by clicking Generic Matrix Upload in the Load section24,25. Log2 transform the data by going to Basic > Transform, selecting the data, and specifying the transformation function, in this case log2(x).
- Impute missing values from a normal distribution by going to Imputation > Replace Missing Values from Normal Distribution, selecting the data, and specifying the width (default 0.3) and the down shift (default 1.8) for the calculation. Perform quantile normalization by going to Normalize > Quantile Normalization.
- Calculate log2 ratios and Student's T-test p-values for the respective conditions. First, annotate the data by going to Annot. Rows > Categorical Annotation Rows. Perform the T-test by going to Tests > Two-sample Tests, and selecting the groups to compare, the test to perform, and the method for multiple hypothesis testing correction as used for truncation.
NOTE: For de novo identification, a protein is considered a PPP-interacting protein if its abundance is statistically significant in the MCLR-treated versus DMSO condition, with a log2-fold change greater than the minimum fold change of any specifically-bound known PPP subunit.
Results
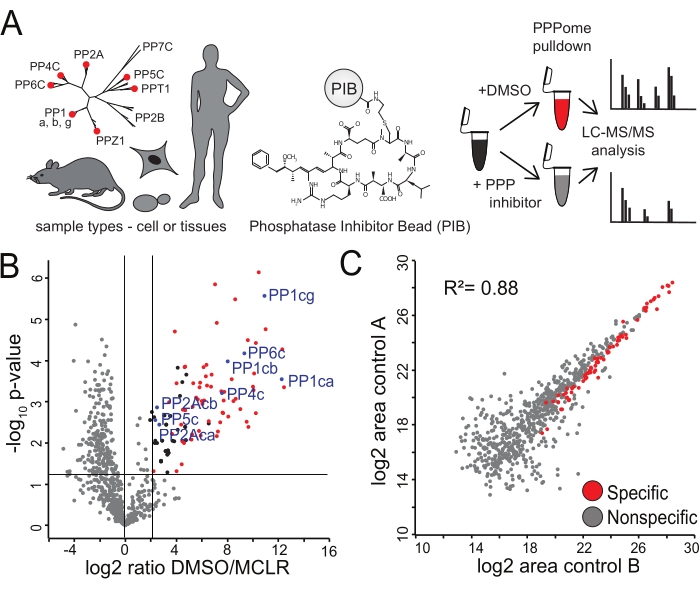
Figure 2: Identification of specific PIBs binders. (A) A variety of tissue types or cells can be analyzed via PIB-MS. HeLa cells in biological triplicate were either treated with DMSO or the PPP-inhibitor MCLR, incubated with PIBs, and analyzed via LC-MS/MS. (B) Volcano plot of PIB-MS anal...
Discussion
PIB-MS is a chemical proteomics approach used to quantitatively profile the PPPome from various sample sources in a single analysis. Much work has been done using kinase inhibitor beads to study the kinome and how it changes in cancer and other disease states10,11,12,13. Yet, the study of the PPPome lags behind. We anticipate that this approach is able to fill this gap and shed light on the reg...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose and no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
A.N.K. acknowledges support from NIH R33 CA225458 and R35 GM119455. We thank the Kettenbach and Gerber labs for their helpful discussion.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetonitrile (ACN) | Honeywell | AH015-4 | CAUTION: ACN is flammable and toxic; wear gloves, and work in a chemical fume hood. |
| Anhydrous Acetonitrile | Sigma-Aldrich | 271004-100ML | CAUTION: ACN is flammable and toxic; wear gloves, and work in a chemical fume hood. |
| Benchtop centrifuge | Eppendorf | model no. 5424 | |
| Beta-glycerophosphoric acid, disodium salt pentahydrate | Acros Organics | 410991000 | |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | model no. 5810 R 15 amp version | |
| Distilled water | |||
| DMSO | Fisher Scientific | BP231-100 | |
| Dounce tissue grinder | Fisherbrand Pellet Pestles | 12-141-363 | |
| Empore solid phase extraction disk, C18 | CDS Analytical | 76333-132 | |
| Eppendorf tubes, 1.5 mL | Eppendorf | 22363204 | CRITICAL: Other tubes may leach polymer into sample, contaminating the analysis. |
| Eppendorf tubes, 2 mL | Eppendorf | 22363352 | CRITICAL: Other tubes may leach polymer into sample, contaminating the analysis. |
| Extraction plate manifold | Waters | WAT097944 | |
| Falcon tubes, 50 mL | VWR | 21008 | |
| Generic blunt end needle and plunger | |||
| Generic magnetic separation rack | |||
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | H3375 | |
| Hydrogen chloride (HCl) | VWR Chemicals BDH | BDH3028 | CAUTION: HCl is corrosive; wear gloves and work in a chemical fume hood. |
| Hydroxylamine solution 50% (wt/vol) | Sigma-Aldrich | 467804 | |
| Incubator, 65 °C | VWR | model no. 1380FM | |
| Koptec Pure Ethanol, 200 Proof | Decon Labs | V1001 | |
| Methanol for HPLC (MeOH) | Sigma-Aldrich | 34860-4L-R | CAUTION: MeOH is flammable and toxic; wear gloves, and work in a chemical fume hood. |
| Microcystin LR (MCLR) | Cayman Chemical | 10007188 | CAUTION: MCLR is toxic; wear gloves when handling and avoid skin contact. |
| PBS, 1× without calcium and magnesium, pH 7.4 ± 0.1 | Corning | 21-040-CV | |
| pH test strips, such as MilliporeSigma MColorpHast pH test strips and indicator papers | Fisher Scientific | M1095310001 | |
| PIBs | For protocol for the generation of PIBs, see Moorhead et al., 2007. | ||
| Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit | Thermo Scientific | 23225 | |
| Pipette tips, 10 μL | Eppendorf | 22491504 | CRITICAL: Other tips may leach polymer into samples, contaminating the analysis. |
| Pipette tips, 1000 μL | Eppendorf | 22491555 | CRITICAL: Other tips may leach polymer into samples, contaminating the analysis. |
| Pipette tips, 200 μL | Eppendorf | 22491539 | CRITICAL: Other tips may leach polymer into samples, contaminating the analysis. |
| plastic syringe, 10 mL | BD | 309604 | |
| Protease inhibitor cocktail III | Research Products International | P50700-1 | |
| Q Exactive Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer, Oribtrap Fusion, Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, or Orbitrap Eclipse Tribrid Mass Spectrometer | Thermo Scientific | ||
| Refrigerated benchtop centrifuge | Eppendorf | model no. 5424 R | |
| Rotator (Labquake Shaker Rotisserie) | Thermo Scientific | 13-687-12Q | 8 rpm rotation |
| Sample collection plate, 96- well, 1 mL | Waters | WAT058957 | |
| SDS | Fisher Scientific | BP1311-1 | |
| Sequencing grade modified trypsin | Promega | V511C | |
| Sodium azide | EMD Chemicals | SX0299-1 | CAUTION: Sodium azide is explosive and toxic; wear gloves, work in a chemical fume hood and avoid contact with metals. |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Fisher Chemical | S27110 | |
| Sonicator (Branson digital sonifier) | model no. SFX 250 | ||
| SPE C18 desalting plate | Waters | 186001828BA | |
| SpeedBeads magnetic carboxylate modified particles (SP3 beads) | Cytiva | 6.51521E+13 | |
| Thermomixer | Eppendorf | model no. 5350 | |
| TMT10plex Isobaric Label Reagent Set plus TMT11-131C Label Reagent, 3 × 0.8 mg per tag | ThermoFisher | A37725 | |
| Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) | Honeywell | T6508-25ML | CAUTION: TFA is corrosive and will irritate skin on contact. Wear gloves and eye protection, and work in a chemical fume hood. |
| Tris Base | Research Products International | T60040 | |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma-Aldrich | T9284 | |
| Vacuum centrifuge and vapor trap | Thermo Scientific | model nos. SpeedVac SPD120 and RVT5105 | |
| Vortexer (Vortex-Genie 2) | Scientific Industries | ||
| Water LC-MS | Honeywell | LC365-4 |
References
- Nilsson, J. Protein phosphatases in the regulation of mitosis. Journal of Cell Biology. 218 (2), 395-409 (2019).
- Brautigan, D. L. Protein Ser/Thr phosphatases--the ugly ducklings of cell signalling. The FEBS Journal. 280 (2), 324-345 (2013).
- Brautigan, D. L., Shenolikar, S. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases: keys to unlocking regulators and substrates. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 87, 921-964 (2018).
- Janssens, V., Goris, J. Protein phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochemical Journal. 353, 417-439 (2001).
- Virshup, D. M., Shenolikar, S. From promiscuity to precision: protein phosphatases get a makeover. Molecular Cell. 33 (5), 537-545 (2009).
- Bollen, M., Peti, W., Ragusa, M. J., Beullens, M. The extended PP1 toolkit: designed to create specificity. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 35 (8), 450-458 (2010).
- Qian, J., Winkler, C., Bollen, M. 4D-networking by mitotic phosphatases. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 25 (6), 697-703 (2013).
- Heroes, E., et al. The PP1 binding code: a molecular-lego strategy that governs specificity. The FEBS Journal. 280 (2), 584-595 (2013).
- Eichhorn, P. J., Creyghton, M. P., Bernards, R. Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1795 (1), 1-15 (2009).
- Bantscheff, M., et al. Quantitative chemical proteomics reveals mechanisms of action of clinical ABL kinase inhibitors. Nature Biotechnology. 25 (9), 1035-1044 (2007).
- Klaeger, S., et al. Chemical proteomics reveals ferrochelatase as a common off-target of kinase inhibitors. ACS Chemical Biology. 11 (5), 1245-1254 (2016).
- Duncan, J. S., et al. Dynamic reprogramming of the kinome in response to targeted MEK inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell. 149 (2), 307-321 (2012).
- Cooper, M. J., et al. Application of multiplexed kinase inhibitor beads to study kinome adaptations in drug-resistant leukemia. PLoS ONE. 8 (6), 66755 (2013).
- Lyons, S. P., et al. A quantitative chemical proteomic strategy for profiling phosphoprotein phosphatases from yeast to humans. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics. 17 (12), 2448-2461 (2018).
- Nasa, I., et al. Quantitative kinase and phosphatase profiling reveal that CDK1 phosphorylates PP2Ac to promote mitotic entry. Science Signaling. 13 (648), (2020).
- Swingle, M., Ni, L., Honkanen, R. E. Small-molecule inhibitors of ser/thr protein phosphatases: specificity, use and common forms of abuse. Methods in Molecular Biology. 365, 23-38 (2007).
- Moorhead, G. B. G., Haystead, T. A. J., MacKintosh, C. Synthesis and use of the protein phosphatase affinity matrices microcystin-sepharose and microcystin-biotin-sepharose. Methods in Molecular Biology. 365, 39-45 (2007).
- Brauer, B. L., Wiredu, K., Mitchell, S., Moorhead, G. B., Gerber, S. A., Kettenbach, A. N. Affinity-based profiling of endogenous phosphoprotein phosphatases by mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols. 16 (10), 4919-4943 (2021).
- Hughes, C. S., Moggridge, S., Müller, T., Sorensen, P. H., Morin, G. B., Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nature Protocols. 14 (1), 68-85 (2019).
- Rappsilber, J., Mann, M., Ishihama, Y. Protocol for micro-purification, enrichment, pre-fractionation and storage of peptides for proteomics using StageTips. Nature Protocols. 2 (8), 1896-1906 (2007).
- Zecha, J., et al. TMT labeling for the masses: A robust and cost-efficient, in-solution labeling approach. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics. 18 (7), 1468-1478 (2019).
- Elias, J. E., Gygi, S. P. Target-decoy search strategy for increased confidence in large-scale protein identifications by mass spectrometry. Nature Methods. 4 (3), 207-214 (2007).
- Eng, J. K., Jahan, T. A., Hoopmann, M. R. Comet: an open-source MS/MS sequence database search tool. Proteomics. 13 (1), 22-24 (2013).
- Tyanova, S., et al. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nature Methods. 13 (9), 731-740 (2016).
- Yu, S. H., Ferretti, D., Schessner, J. P., Rudolph, J. D., Borner, G. H. H., Cox, J. Expanding the Perseus software for omics data analysis With custom plugins. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. 71 (1), 1-29 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved