A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
In vitro Digestion of Emulsions in a Single Droplet via Multi Subphase Exchange of Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids
In This Article
Summary
A pendant drop surface film balance implemented with a multi-subphase exchange, nicknamed the OCTOPUS, allows for mimicking digestive conditions by the sequential subphase exchange of the original bulk solution with simulated gastrointestinal fluids. The simulated in vitro digestion is monitored by recording in situ the interfacial tension of the digested interfacial layer.
Abstract
Emulsions are currently being used to encapsulate and deliver nutrients and drugs to tackle different gastrointestinal conditions such as obesity, nutrient fortification, food allergies, and digestive diseases. The ability of an emulsion to provide the desired functionality, namely, reaching a specific site within the gastrointestinal tract, inhibiting/retarding lipolysis, or facilitating digestibility, ultimately depends on its susceptibility to enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. In oil-in-water emulsions, lipid droplets are surrounded by interfacial layers, where the emulsifiers stabilize the emulsion and protect the encapsulated compound. Achieving a tailored digestibility of emulsions depends on their initial composition but also requires monitoring the evolution of those interfacial layers as they are subjected to different phases of gastrointestinal digestion. A pendant drop surface film balance implemented with a multi-subphase exchange allows for simulating the in vitro digestion of emulsions in a single aqueous droplet immersed in oil by applying a customized static digestion model. The transit through the gastrointestinal tract is mimicked by the subphase exchange of the original droplet bulk solution with artificial media, mimicking the physiological conditions of each compartment/step of the gastrointestinal tract. The dynamic evolution of the interfacial tension is recorded in situ throughout the whole simulated gastrointestinal digestion. The mechanical properties of digested interfaces, such as interfacial dilatational elasticity and viscosity, are measured after each digestion phase (oral, gastric, small intestine). The composition of each digestive media can be tuned to account for the particularities of the digestive conditions, including gastrointestinal pathologies and infant digestive media. The specific interfacial mechanisms affecting proteolysis and lipolysis are identified, providing tools to modulate digestion by the interfacial engineering of emulsions. The obtained results can be manipulated for designing novel food matrices with tailored functionalities such as low allergenicity, controlled energy intake, and decreased digestibility.
Introduction
Understanding how fat is digested, which involves emulsion digestion, is important to rationally design products with tailored functionality1. The substrate for fat digestion is an emulsion since fat is emulsified upon consumption by mechanical action and mixing with biosurfactants in the mouth and stomach. Also, most of the fat consumed by humans is already emulsified (such as milk products), and in the case of infants or some elderly people, this is the only form of consumption. Hence, the design of emulsion-based products with specific digestion profiles is very important in nutrition1. Moreover, emulsions can encapsulate and deliver nutrients, drugs, or lipophilic bioactives2 to tackle different gastrointestinal conditions such as obesity3, nutrient fortification, food allergies, and digestive diseases. In oil-in-water emulsions, lipid droplets are surrounded by interfacial layers of emulsifiers such as proteins, surfactants, polymers, particles, and mixtures4. The role of emulsifiers is twofold: stabilize the emulsion5 and protect/transport the encapsulated compound to a specific site. Achieving a tailored digestibility of emulsions depends on their initial composition but also requires monitoring the continuous evolution of this interface during the transit through the gastrointestinal tract (Figure 1).
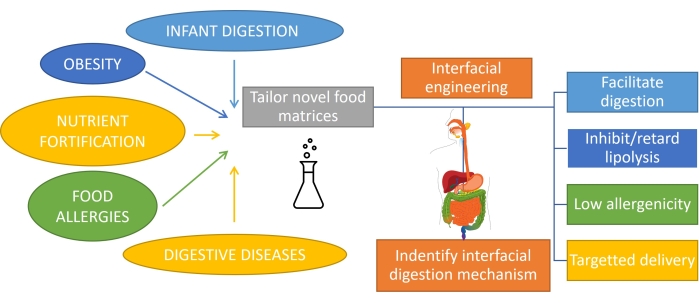
Figure 1: Applying interfacial engineering of emulsions to tackle some of the main gastrointestinal conditions. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Lipid digestion is ultimately an interfacial process because it requires the adsorption of lipases (gastric or pancreatic) onto the oil-water interface of emulsified lipid droplets through the interfacial layer to reach and hydrolyze the triglycerides contained in the oil into free fatty acids and monoacylglycerides6. This is schematized in Figure 2. Gastric lipase competes with pepsin and phospholipids in the stomach for the oil-water interface (Figure 2, gastric digestion). Then, pancreatic lipase/colipase compete with trypsin/chymotrypsin, phospholipids, bile salts, and digestive products in the small intestine. Proteases can alter the interfacial coverage, preventing or favoring lipase adsorption, while bile salts are highly surface active and displace most of the remaining emulsifier to promote lipase adsorption (Figure 2, intestinal digestion). Eventually, the rate and extent of lipolysis depend on the interfacial properties of the initial/gastric digested emulsion, such as the thickness, inter/intramolecular connections, and electrostatic and steric interactions. Accordingly, monitoring the evolution of the interfacial layer as it is digested offers an experimental platform to identify interfacial mechanisms and events affecting lipase adsorption and, hence, lipid digestion.
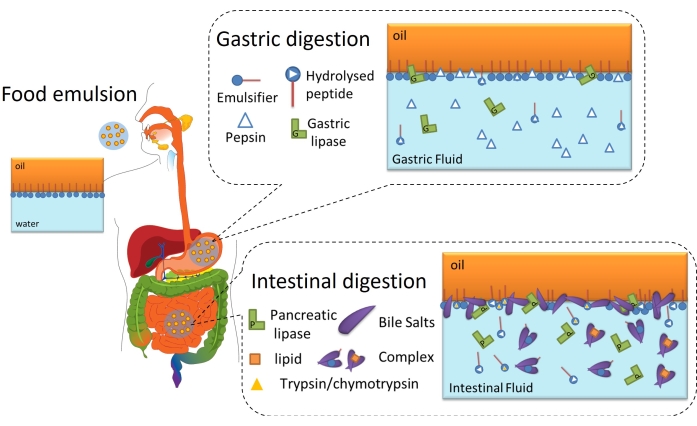
Figure 2: Schematic diagram illustrating the role of interfaces in gastrointestinal lipid digestion. Pepsin hydrolysis alters interfacial composition at the gastric phase, while gastric lipase hydrolyzes triglycerides. In the small intestine, trypsin/chymotrypsin further hydrolyze the interfacial film, while lipolysis proceeds by the adsorption of BS/lipases, the hydrolysis of triglycerides, and the desorption of lipolytic products by solubilization in the BS micelles/complex. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The pendant drop equipment at the University of Granada (UGR) is implemented with a patented technology, the coaxial double capillary, that enables subphase exchange of the bulk solution7. The capillary, which holds the pendant drop, consists of an arrangement of two coaxial capillaries that are independently connected to each channel of a double microinjector. Each microinjector can operate independently, allowing the exchange of the dropped content by through-flow7. Accordingly, the subphase exchange consists of the simultaneous injection of the new solution with the inner capillary and the extraction of the bulk solution with the outer capillary using the same flow rate. This process allows the replacement of the bulk solution with no disturbance of the interfacial area or the volume of the droplet. This procedure was later upgraded to a multi-subphase exchange, which allows up to eight sequential subphase exchanges of the droplet bulk solution8. This enables the simulation of the digestive process in a single aqueous droplet suspended in lipidic media by sequentially exchanging the bulk solution with artificial media mimicking the different compartments (mouth, stomach, small intestine). The whole setup is represented in Figure 3, including the details of the components. The syringes in the microinjector are connected to the eight vias valves, each connecting to a microcentrifuge tube containing the artificial digestive fluid with components described in Figure 2.
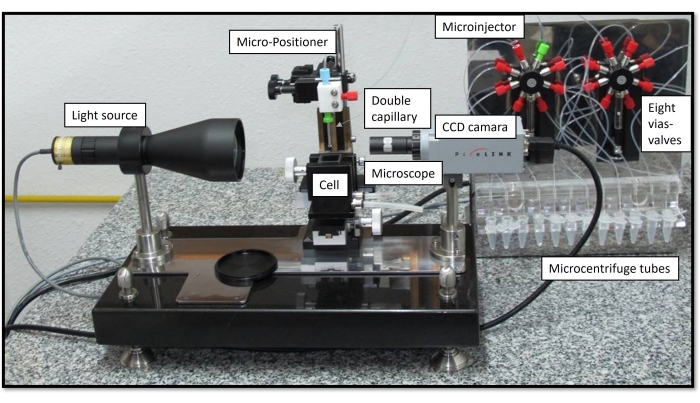
Figure 3: General view of the OCTOPUS with all components. The CCD camera, microscope, micro-positioner, thermostabilized cell, and double capillary connected independently to a double microinjector with two syringes connected to eight vias valves. Each syringe connects with capillary, four microcentrifuge tubes with sample and one discharge. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 4A shows how each of the artificial digestive fluids is injected into the pendant drop by subphase exchange through the double capillary. Each digestive compound detailed in Figure 2 can be applied simultaneously/sequentially, simulating the passage through the gastrointestinal tract. The artificial digestive fluids contain different enzymes and biosurfactants, which alter the interfacial tension of the initial emulsifier, as schematized in Figure 4B. The software DINATEN (see Table of Materials), also developed at the UGR, records the evolution of the interfacial tension in real time as the initial interfacial layer is digested in vitro. Also, after each digestive phase, the dilatational elasticity of the interfacial layer is computed by imposing periodic oscillations of volume/interfacial area onto the stabilized interfacial layer and recording the response of the interfacial tension. The period/frequency and the amplitude of the oscillation can be varied, and image processing with the software CONTACTO provides the dilatational rheological parameters8.
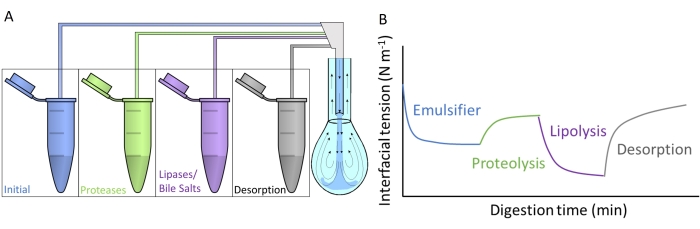
Figure 4: Examples of digestion profiles. (A) The initial emulsifier layer is subjected to artificial digestive media placed in the microcentrifuge by sequential subphase exchange of the different solutions into the pendant drop. (B) The general evolution of the interfacial tension (y-axis) of the initial emulsifier as a function of time (x-axis) as it is digested in vitro by the various enzymes/biosurfactants in the artificial media. A final subphase exchange with plain intestinal fluid measures the desorption of digested lipid by solubilization in mixed micelles. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
This study presents the general protocol designed to measure in vitro digestion of interfacial layers with pendant drop equipment9. The initial interfacial layer is subjected sequentially to conditions mimicking the passage through the gastrointestinal tract, as depicted in Figure 2. These different digestive media are injected into the pendant drop by subphase exchange of the different solutions contained in the microcentrifuge tubes (Figure 4A). The composition of these media can be customized depending on the gastrointestinal conditions that will be evaluated, namely, gastric/intestinal proteolysis/lipolysis, allowing for measuring cumulative effects and sinergies10. The experimental conditions used to mimic the digestion process in each compartment follow the international consensus protocol published by INFOGEST detailing the pH and amounts of electrolytes and enzymes11. The experimental device based on pendant drop allows recording of the interfacial tension in situ throughout the simulated digestion process. The dilatational rheology of the interfacial layer is computed at the end of each digestive step. In this way, each emulsifier offers a digestion profile illustrating the properties of the digested interfaces, as depicted in Figure 4B. This allows the extraction of conclusions regarding its susceptibility or resistance to the different stages of the digestive process. In general, the artificial digestive media contains acid/basic pH, electrolytes, proteases (gastric and intestinal), lipases (gastric and intestinal), bile salts, and phospholipids, which are dissolved in their respective digestive fluids (gastric or intestinal). Figure 4B shows a generic profile of the evolution of an emulsifier's interfacial tension, first subjected to protease action, followed by lipases. In general, proteolysis of the interfacial layer promotes an increase in the interfacial tension owing to the desorption of hydrolyzed peptides9,12, while lipolysis results in a very steep reduction in the interfacial tension due to the adsorption of bile salts and lipases13. A final subphase exchange with intestinal fluid depletes the bulk solution of unadsorbed/digested material and promotes the desorption of soluble compounds and the solubilization of digested lipids in mixed micelles. This is quantified by the increased interfacial tension recorded (Figure 4B).
In summary, the experimental design implemented in the pendant drop to simulate in vitro digestion in a single droplet allows for measuring cumulative effects and synergies as the digestion process is applied sequentially to the initial interfacial layer10. The composition of each digestive media can be easily tuned to account for the particularities of the digestive conditions, including gastrointestinal pathologies or infant digestive media14. Then, identification of the interfacial mechanisms affecting proteolysis and lipolysis can be used to modulate digestion by the interfacial engineering of emulsions. The obtained results can be applied in designing novel food matrices with tailored functionalities such as low allergenicity, controlled energy intake, and decreased digestibility15,16,17,18,19.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Cleaning sequence for all glassware used in surface science experimentation
- Scrub the glassware with a concentrated cleaning solution (see Table of Materials) diluted in water (10%).
- Rinse thoroughly with a sequence of tap water, propanol, distilled water, and ultrapure water. Dry in a cabin and store in a closed cabinet until use.
2. Sample preparation
- Prepare artificial digestive media according to INFOGEST standardized protocols11,20 (see Table of Materials). For details, see Table 1 and include small adaptations to the requirements of the interfacial work to prevent surface active contamination and the dilution of samples (1:10)10.
- Prepare the emulsifier solution following the steps below.
- Prepare 0.01 L of a concentrated solution of (1 kg·L−1) emulsifier or a mixture of emulsifiers (see Table of Materials) in an initial buffer (Table 1) and keep under mild agitation overnight.
- Dilute to 0.1 kg·L−1 (or as required) to saturate the interface; reach a pseudo plateau in the interfacial tension after 1 h of adsorption at a constant interfacial area following the previously published report21.
- Keep under mild agitation for 15 min before use.
- Purify the oil phase.
- Prepare a mixture of vegetable oil (sunflower, olive, triolein, etc. )and magnesium metasilicate resins (see Table of Materials) in a proportion of 2:1 w/w in a large beaker. Keep under mild mechanical agitation for at least 3 h.
- Centrifuge the mixture at 8,000 x g for 30 min at room temperature in a commercial centrifuge (see Table of Materials).
- Filter the oil mixture under vacuum with a syringe filter (0.2 µm pore size) (see Table of Materials). Store in clean amber bottles sealed and bubbled with nitrogen until use.
3. Calibration and cleaning of the OCTOPUS
- Rinse all the tubing with ultrapure water by setting a sequence of cleaning both syringes and all valves through a capillary (valves 6/4) and to the external exit (valve 8-blue color). Perform this by pressing the clean button in the left dialog (Supplementary Figure 1A).
- Check the surface tension7 of water at room temperature by forming a water droplet and measuring in real time for 5 min (Supplementary Figure 1B, C).
- Set the differential density to air-water (0.9982 kg·L−1) in the left dialog, Supplementary Figure 1B.
- Fill the clean cuvette (optical glass) with 0.002 L of clean vegetable oil and place it in the cuvette holder in the thermostatic cell (Figure 3).
- Set the thermostat and allow for temperature equilibration at 37 °C.
- Check the interfacial tension of water-oil at room temperature7.
- Set the differential density to vegetable oil-water (olive oil: 0.800 kg·L−1) (Supplementary Figure 1C).
- Inject 40 µL at a rate of 0.5 µL·s−1 and measure in real time every second until the end of the injection. This is a simple dynamic process (Supplementary Figure 1B, D).
- Plot the interfacial tension as a function of droplet volume in a data sheet.
- Check that the droplet volume range provides a value for the interfacial tension independent of the droplet volume. Plot the interfacial area as a function of droplet volume.
- Program a process containing two steps (Supplementary Figure 1B and Supplementary Figure 2A) following the steps below.
- With an inner syringe, inject a volume contained within this range of constant interfacial tension.
- Maintain the interfacial area constant at the value selected in step 3.5.4 and record the interfacial tension for 5 min7.
4. Programming one experimental process in DINATEN for each digestive step
NOTE: For the process parameters, see Supplementary Figure 1B.
- Perform the initial control.
- For drop formation, inject 10 µL (±5 µL) of emulsifier solution into the capillary (valve 6) (Supplementary Figure 2A).
- Record the adsorption at a constant interfacial area21 of 20 mm2 (±10 mm2) for 1 h (Supplementary Figure 2B).
- Record the dilatational rheology8 (Supplementary Figure 2C).
- Set the amplitude of oscillation to 1.25 µL, period 10 s.
- Record the adsorption at the selected interfacial area (step 4.1.2) for 10 s.
- Repeat step 4.1.3 at different periods: 5 s, 20 s, 50 s, and 100 s.
- Record gastric digestion.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area for 10 s.
- Subphase exchange7 with liquid in valve 2 (sSGF) and gastric enzymes (Table 1) (Supplementary Figure 2D).
- Fill the left syringe from valve 2. Inject 125 µL into valve 6-capillary with the left syringe at 5 µL·s−1.
- Extract 125 µL from the capillary with the right syringe at 5 µL·s−1. Unload the right syringe to exit valve 8. Repeat steps 4.2.2.1-4.2.2.2 10 times to assure complete exchange.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 1 h (Supplementary Figure 2B).
- Record the dilatational rheology8 (Supplementary Figure 2C).
- Set the amplitude of oscillation to 1.25 µL, period 10 s.
- Record the adsorption of the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 10 s. Repeat at different periods: 5 s, 20 s, 50 s, 100 s.
- Record intestinal digestion.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 10 s (Supplementary Figure 2B).
- Subphase exchange7 with liquid in valve 3 (sSIF) and intestinal enzymes/bile salts/phospholipids (Table 1) (Supplementary Figure 2D).
- Fill the left syringe from valve 2. Inject 125 µL into valve 6-capillary with the left syringe at 5 µL·s−1. Extract 125 µL from the capillary with the right syringe at 5 µL·s−1.
- Unload the right syringe to exit valve 8. Repeat steps 4.3.2.1-4.3.2.2 10 times to assure complete exchange.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 1 h.
- Record the dilatational rheology8 (Supplementary Figure 2C).
- Set the amplitude of oscillation to 1.25 µL, period 10 s.
- Record the adsorption at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 10 s.
- Repeat at different periods: 5 s, 20 s, 50 s, 100 s.
- Record the desorption following the steps below.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 10 s (Supplementary Figure 2B).
- Subphase exchange7 with liquid in valve 5 (sSIF) (Table 1, Supplementary Figure 2D).
- Fill the left syringe from valve 5. Inject 125 µL into valve 5-capillary with the left syringe at 5 µL·s−1.
- Extract 125 µL from the capillary with the right syringe at 5 µL·s−1. Unload the right syringe to exit valve 8. Repeat steps 4.4.2.1-4.4.2.2 10 times to assure complete exchange.
- Record the adsorption21 at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 1 h (Supplementary Figure 2B).
- Record the dilatational rheology8 (Supplementary Figure 2C).
- Maintain the amplitude of 1.25 µL, period 10 s.
- Record the adsorption at the selected interfacial area in step 4.1.2 for 10 s.
- Repeat step 4.4.4 at different periods: 5 s, 20 s, 50 s, 100 s.
5. Setting up the experiment
- Fill the microcentrifuge tubes with the artificial digestion media and connect each of them to the respective valve by the corresponding tubing.
- Fill the tubing in valves 2-5 by cleaning from valve 2, valve 3, valve 4, and valve 5 to the external exit (valve 8) (Supplementary Figure 1A).
- Fill the tubing in valve 1 by cleaning from valve 1 to valve 6-capillary 5 times.
- Place the capillary into the oil phase. Load the left syringe with valve 1 (initial solution, Table 1).
- Start sequentially processing step 4.1-initial, step 4.2-gastric, step 4.3-intestines, and step 4.4-desorption, saving the data at the end of each process.
6. Calculation of the dilatational rheological parameters with the image processing software CONTACTO8
NOTE: For details, see Maldonado-Valderrama et al.8.
- Load the images corresponding to the area oscillation at a given frequency and amplitude (Supplementary Figure 3A).
- Press Rheology (Supplementary Figure 3B) and obtain the dilatational parameters (Supplementary Figure 3C).
- Copy-paste the results into the data spread sheet.
7. Plotting the experimental results
- Recalculate the time column in each of the steps of the digestion process by adding the last data of the time of the previous step.
- Plot the interfacial tension versus additive time for each of the steps of the digestion process used.
- Plot the final interfacial tension/dilatational elasticity and viscosity obtained at the end of each step versus the digestion phase: initial, gastric digestion, duodenal digestion, and desorption.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
This section shows different examples of digestion profiles measured with the OCTOPUS. The general appearance of the simulated digestion profile matches is shown in Figure 4B. The interfacial tension is usually represented against time in the digestion profile. The different phases/digestion steps considered are represented in different colors. The first phase forms the initial layer and corresponds to the adsorption phase of the emulsifier or protein/surfactant/polymer, depending on each ca...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
This article describes a generalized protocol to measure in vitro digestion of interfacial layers by using pendant drop equipment. The protocol can be adjusted to the specific requirements of the experiment by tuning the composition of the digestive buffers, which are based on the INFOGEST11,20 harmonized protocol to facilitate comparison with literature. The digestive enzymes and biosurfactants can be added individually, sequentially, or together. This ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by projects RTI2018-101309-B-C21 and PID2020-631-116615RAI00, funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by "ERDF A way of making Europe". This work was (partially) supported by the Biocolloid and Fluid Physics Group (ref. PAI-FQM115) of the University of Granada (Spain).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Alpha-chymotrypsin from bovine pancreas | Sigma-Aldrich | C4129 | Enzyme |
| Beta-lactoglobulin | Sigma-Aldrich | L0130 | Emulsfier |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | 9048-46-8 | Emulsfier |
| CaCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | 10043-52-4 | Electrolyte |
| Centrifuge | Kronton instruments | Centrikon T-124 | For separating oil and resins |
| Citrus pectin | Sigma-Aldrich | P9135 | Emulsfier |
| co-lipase FROM PORCINE PANCREAS | Sigma | C3028 | Enzyme |
| CONTACTO | University of Granada (UGR) | https://core.ugr.es/dinaten/, last access: 07/18/2022 | |
| DINATEN | University of Granada (UGR) | https://core.ugr.es/dinaten/, last access: 07/18/2022 | |
| Gastric lipase | Lipolytech | RGE15-1G | Enzyme |
| Human Serum Albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | 70024-90-7 | Emulsifier |
| INFOGEST | http://www.proteomics.ch/IVD/ | ||
| Lipase from porcine pancreas, type II | Sigma-Aldrich | L33126 | Enzyme |
| Magnesium metasilicate resins | Fluka | 1343-88-0 | Resins to purify oil |
| Micro 90 | International products | M-9051-04 | Cleaner |
| NaCl | Sigma | 7647-14-5 | Electrolyte |
| NaH2PO4 | Scharlau | 10049-21-5 | To prepare buffer |
| OCTOPUS | Producciones Científicas y Técnicas S.L. (Gójar, Spain) | Pendandt Drop Equipment implemented with multi subphase exchange | |
| Olive oil | Sigma-Aldrich | 1514 | oil |
| Pancreatic from porcine pancreas | Sigma | P7545-25 g | Enzyme |
| Pepsin | Sigma-Aldrich | P6887 | Enzyme |
| Pluronic F127 | Sigma | P2443 | Emulsifier |
| Pluronic F68 | Sigma | P1300 | Emulsfier |
| Sodium deoxycholate | Sigma | Bile salts | |
| Sodium glycodeoxycholate | Sigma | C9910 | Bile salts |
| Sodium taurocholate | Sigma | 86339 | Bile salts |
| Syringe Filter | Millex-DP | SLGP033R | Syringe Filter 0.22 µm pore size polyethersulfone |
| Trypsin | Sigma-Aldrich | T1426 | Enzyme |
References
- McClements, D. J. The biophysics of digestion: Lipids. Current Opinion in Food Science. 21, 1-6 (2018).
- McClements, D. J., Li, Y. Structured emulsion-based delivery systems: Controlling the digestion and release of lipophilic food components. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 159 (2), 213-228 (2010).
- Corstens, M. N., et al. Food-grade micro-encapsulation systems that may induce satiety via delayed lipolysis: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 57 (10), 2218-2244 (2017).
- Aguilera-Garrido, A., del Castillo-Santaella, T., Galisteo-González, F., Gálvez-Ruiz, M. J., Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Investigating the role of hyaluronic acid in improving curcumin bioaccessibility from nanoemulsions. Food Chemistry. 351, 129301(2021).
- Rodríguez Patino, J. M., Carrera Sánchez, C., Rodríguez Niño, M. R. Implications of interfacial characteristics of food foaming agents in foam formulations. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 140 (2), 95-113 (2008).
- Wilde, P. J., Chu, B. S. Interfacial & colloidal aspects of lipid digestion. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 165 (1), 14-22 (2011).
- Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A., Wege, H. A., Holgado-Terriza, J. A., Neumann, A. W. Axisymmetric drop shape analysis as penetration Langmuir balance. Review of Scientific Instruments. 70 (5), 2438-2444 (1999).
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Muros-Cobos, J. L., Holgado-Terriza, J. A., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A. Bile salts at the air-water interface: Adsorption and desorption. Colloids and surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 120, 176-183 (2014).
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Terriza, J. A. H., Torcello-Gómez, A., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A. In vitro digestion of interfacial protein structures. Soft Matter. 9, 1043-1053 (2013).
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Probing in vitro digestion at oil-water interfaces. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science. 39, 51-60 (2019).
- Brodkorb, A., et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nature Protocols. 14 (4), 991-1014 (2019).
- del Castillo-Santaella, T., Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Molina-Bolivar, J. A., Galisteo-Gonzalez, F. Effect of cross-linker glutaraldehyde on gastric digestion of emulsified albumin. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 145, 899-905 (2016).
- Macierzanka, A., Torcello-Gómez, A., Jungnickel, C., Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Bile salts in digestion and transport of lipids. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 274, 102045(2019).
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Torcello-Gómez, A., del Castillo-Santaella, T., Holgado-Terriza, J. A., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A. Subphase exchange experiments with the pendant drop technique. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 222, 488-501 (2015).
- Bellesi, F. A., Ruiz-Henestrosa, V. M. P., Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Del Castillo Santaella, T., Pilosof, A. M. R. Comparative interfacial in vitro digestion of protein and polysaccharide oil/water films. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 161, 547-554 (2018).
- Del Castillo-Santaella, T., Sanmartín, E., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A., Arboleya, J. C., Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Improved digestibility of β-lactoglobulin by pulsed light processing: A dilatational and shear study. Soft Matter. 10 (48), 9702-9714 (2014).
- Infantes-Garcia, M. R., et al. In vitro gastric lipid digestion of emulsions with mixed emulsifiers: Correlation between lipolysis kinetics and interfacial characteristics. Food Hydrocolloids. 128, 107576(2022).
- del Castillo-Santaella, T., Cebrián, R., Maqueda, M., Gálvez-Ruiz, M. J., Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Assessing in vitro digestibility of food biopreservative AS-48. Food Chemistry. 246, 249-257 (2018).
- Torcello-Gómez, A., Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Jódar-Reyes, A. B., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A., Martín-Rodríguez, A. Pluronic-covered oil-water interfaces under simulated duodenal conditions. Food Hydrocolloids. 34, 54-61 (2014).
- Minekus, M., et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food - an international consensus. Food & Function. 5 (6), 1113-1124 (2014).
- Wege, H. A., Holgado-Terriza, J. A., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M. A. Development of a constant surface pressure penetration langmuir balance based on axisymmetric drop shape analysis. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 249 (2), 263-273 (2002).
- del Castillo-Santaella, T., et al. Hyaluronic acid and human/bovine serum albumin shelled nanocapsules: Interaction with mucins and in vitro digestibility of interfacial films. Food Chemistry. 383, 132330(2022).
- Aguilera-Garrido, A., et al. Applications of serum albumins in delivery systems: Differences in interfacial behaviour and interacting abilities with polysaccharides. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 290 (5), 102365(2021).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved