A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Microdissection and Whole Mount Scanning Electron Microscopy Visualization of Mouse Choroid Plexus
In This Article
Summary
The choroid plexus (CP), an understudied tissue in neuroscience, plays a key role in health and disease of the central nervous system. This protocol describes a microdissection technique for isolating the CP and the use of scanning electron microscopy to obtain an overall view of its cellular structure.
Abstract
The choroid plexus (CP), a highly vascularized structure protruding into the ventricles of the brain, is one of the most understudied tissues in neuroscience. As it is becoming increasingly clear that this tiny structure plays a crucial role in health and disease of the central nervous system (CNS), it is of utmost importance to properly dissect the CP out of the brain ventricles in a way that allows downstream processing, ranging from functional to structural analysis. Here, isolation of the lateral and fourth brain ventricle mouse CP without the need for specialized tools or equipment is described. This isolation technique preserves the viability, function, and structure of cells within the CP. On account of its high vascularization, the CP can be visualized floating inside the ventricular cavities of the brain using a binocular microscope. However, transcardial perfusion required for downstream analysis can complicate the identification of the CP tissue. Depending on the further processing steps (e.g., RNA and protein analysis), this can be solved by visualizing the CP via transcardial perfusion with bromophenol blue. After isolation, the CP can be processed using several techniques, including RNA, protein, or single cell analysis, to gain further understanding on the function of this special brain structure. Here, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on whole mount CP is used to get an overall view of the structure.
Introduction
Tight barriers separate the central nervous system (CNS) from the periphery, including the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier. These barriers protect the CNS against external insults and ensure a balanced and controlled microenvironment1,2,3. While the BBB has been extensively studied over time, the blood-CSF barrier located at the choroid plexus (CP) has only gained increasing research interest during the last decade. This latter barrier can be found in the four ventricles of the brain (Figure 1A, B) and is characterized by a single layer of choroid plexus epithelial (CPE) cells surrounding a central stroma, leaky capillaries, fibroblasts, and a lymphoid and myeloid cell population (Figure 1C)4,5,6. The CPE cells are firmly interconnected by tight junctions, thus preventing leakage from the underlying fenestrated blood capillaries into the CSF and brain. Additionally, transport across the CPE cells is regulated by a number of inward and outward transport systems that manage the influx of beneficial compounds (e.g., nutrients and hormones) from the blood to the CSF and the efflux of harmful molecules (e.g., metabolic waste, excess neurotransmitters) in the other direction1,6. To be able to exert their active transport function, the CPE cells contain numerous mitochondria in their cytoplasm7. Moreover, the CP is the main source of CSF and acts as the gatekeeper of the brain by the presence of resident inflammatory cells1. Due to its unique location between the blood and the brain, the CP is also perfectly positioned to carry out immune surveillance8.
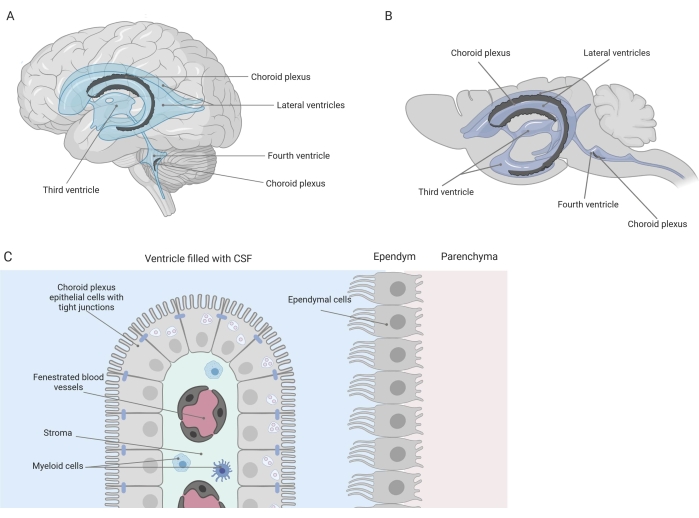
Figure 1: Schematic overview of the location and composition of the choroid plexus (CP). (A,B) CP tissue is found within the two lateral, the third, and the fourth ventricles of (A) human and (B) mouse brains. (C) The CP tissue consists of a single layer of tightly connected cuboidal CP epithelium (CPE) cells surrounding fenestrated capillaries, loose connective tissue, and lymphoid and myeloid cells, and forms the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (adapted and modified from reference23). Figure created with Biorender.com. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Over the past decade, increasing evidence, including several reports from our research group, have revealed that the CP plays a central role in health and disease9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18. For example, it is known that the aging blood-CSF barrier displays morphological alterations in, among others, the nuclei, microvilli, and the basement membrane1,19. Additionally, in the context of Alzheimer's disease, the overall barrier integrity is compromised and all of these age-related changes appear to be even more pronounced1,8,20. In addition to morphological changes, the transcriptome, proteome, and secretome of the CP are altered during disease12,21,22,23. Thus, advanced knowledge of the CP is essential to better understand its role in neurological diseases and potentially develop new therapeutic strategies.
An efficient method for accurate microdissection of the CP out of the brain ventricles is the first invaluable step to allow proper investigation of this tiny brain structure. On account of its highly vascularized nature (Figure 2B), the CP floating inside the ventricular cavities of the brain can be identified using a binocular microscope. However, transcardial perfusion is often required for downstream analysis, complicating the proper identification and isolation of the CP tissue (Figure 2C). If the further processing steps allow (e.g., in the case of RNA and protein analysis), the CP can be visualized via transcardial perfusion with bromophenol blue (Figure 2A). Several publications already describe the isolation of the CP from rat24 and mouse pup brains25. Here, a microdissection isolation technique is described to isolate the CP from adult mice. Importantly, this isolation technique preserves the viability, function, and structure of the cells within the CP. The isolation of the CP floating in the fourth and lateral ventricles is described here. In short, the mice are terminally anesthetized and, if necessary, transcardially perfused. However, it should be noted that perfusion can damage the structure of the cells within the CP. Consequently, if the sample is to be analyzed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM), or focused ion beam SEM (FIB-SEM), perfusion should not be performed. Next, the whole brain is isolated, and forceps are used to sagittally hemisect the brain. From here, the CPs floating in the lateral ventricles can be identified and dissected, while the CP from the fourth ventricle can be isolated from the cerebellar side of the brain.

Figure 2: Visualization of the (A-C) fourth and (D-F) lateral ventricle choroid plexus (CP) after (A,D) bromophenol blue perfusion, (B,E) no perfusion, and (C,F) perfusion with PBS/heparin. The images are taken with a stereo microscope (8x-32x magnification). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Once the CP is properly dissected out of the brain ventricles, a whole repertoire of techniques can be applied to gain further understanding on the function of this structure. For example, flow cytometry or single cell RNA sequencing can be performed to quantify and phenotypically analyze the infiltrating inflammatory cells under certain disease conditions26,27. In addition to the cellular composition, the molecular composition of the CP can be analyzed to assess the presence of cytokines and chemokines via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunoblot, or through simultaneous analysis of multiple cytokines using the cytokine bead array28. Moreover, transcriptome, vascular, immune cell histology, and secretome analyses can be performed on the microdissected CP explants29. Here, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) on whole mount CP is used to obtain an overall view of the CP structure. SEM uses a beam of focused electrons to scan over the surface and create an image of the surface's topography and composition. Since the wavelength of electrons is much smaller than that of light, the resolution of SEM is in the nanometer range and superior to that of a light microscope. Consequently, morphological studies on the subcellular level can be performed via SEM. Briefly, the dissected CP is immediately transferred into a glutaraldehyde-containing fixative for an overnight fixation, followed by osmication and uranyl acetate staining. The samples are then treated with lead aspartate stain, dehydrated, and ultimately embedded for imaging.
Thus, this protocol facilitates the efficient isolation of the CP from the mouse brain ventricles, which can be further analyzed using a variety of downstream techniques to investigate its structure and function.
Protocol
All animal experiments described in this study were conducted according to the national (Belgian Law 14/08/1986 and 22/12/2003, Belgian Royal Decree 06/04/2010) and European legislation (EU Directives 2010/63/EU, 86/609/EEC). All experiments on mice and animal protocols were approved by the ethics committee of Ghent University (permit numbers LA1400091 and EC 2017-026).
1. Preparation
- Anesthetics: Prepare a terminal anesthetic. For instance, a sodium pentobarbital (≥100 mg/kg) solution in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) can be prepared.
- Transcardial perfusion solution: Prepare 10 mL (per mouse) of PBS/heparin (containing 0.2% heparin) solution supplemented with 0.5% bromophenol blue.
NOTE: If the downstream processing steps allow (e.g., in the case of RNA and protein analysis), the choroid plexus (CP) can be visualized via transcardial perfusion with bromophenol blue. If bromophenol blue is not compatible with the further processing steps (e.g., for imaging), use PBS/heparin to perfuse. - Prepare the solutions required for SEM analysis.
- Prepare 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4). Prepare a solution of 2% paraformaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer. Make 20 mL of this solution per sample.
- Prepare 2% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer (5 mL per sample).
- Prepare 50%, 70%, 85%, and 100% EtOH solutions. Prepare 5 mL of each EtOH solution per sample.
2. Microdissection of the choroid plexus out of the lateral and fourth ventricle
NOTE: Female, 9-week-old C57BL/6 mice were used in this study. However, the described isolation technique is independent of the strain, sex, and age of the adult mouse.
- Isolate the mouse brain.
- Intraperitoneally inject a lethal dose of a short-acting barbiturate (>100 mg/kg, prepared in step 1.1) using a 26G needle to terminally anesthetize the mouse. Check the foot reflex of the mouse by pinching its rear paw with forceps.
- When there is no foot reflex, place the terminally anesthetized animal in the dorsal decubitus position and fix the mouse by pinning the limbs on a plate.
NOTE: If transcardial perfusion of the mice is not needed, depending on the downstream analysis method (e.g., for SEM imaging), proceed to step 2.1.7. However, if perfusion is needed to remove blood cells or other components in the blood, the CP can be visualized as a blue structure floating in the brain ventricles via perfusion with bromophenol blue. - Disinfect the chest by spraying 70% ethanol. Place a sterile drape around the surgical area. Make an incision of ~4 cm just under the diaphragm using a carbon steel surgical blade (see Table of Materials).
- Open the skin and expose the chest using surgical scissors. Cut the diaphragm completely open.
- Separate the thorax to expose the lungs and the beating heart.
- Transcardially perfuse the mice with 10 mL of the perfusion solution at a rate of 4.5 mL/min, using a perfusion pump (see Table of Materials). The perfusion will take ~2 min. Insert a 26G needle in the left ventricle to pump the solution into the systemic circuit. In addition, make a cut with surgical scissors in the right atrium so that blood can go out of the circulation.
NOTE: A perfusion pump is preferred over manual administration of the fluid, as it will deliver the fluids at a precisely programmed rate and ensure that the shearing forces caused by the perfusion are not too strong. Excessive shearing forces will compromise the viability and structure of cells within the CP. Additionally, the perfusion flow rate recommended here is optimal to perfuse adult mice from 7 weeks onward. If younger mice are used, a lower flow rate should be used. It is also important to dab away the blood that comes out of the right atrium in order to preserve a clean surgical site. - Decapitate the mouse.
NOTE: Pay caution to cut off the head as low as possible to the shoulder to preserve the brain structure. If the cut is too high, the cerebellum can be damaged. - After decapitation, cut open the scalp by a making an incision from between the ears to superior to the eyes. Pull the skin laterally to expose the skull. Then, cut open the skull by following the squamosal sutures, toward the nasal part.
NOTE: It is important to gently remove the skull to maintain the brain integrity. - Place the brain in an ice-cold Petri dish and add 1 mL of ice-cold 1x PBS on the brain tissue.
NOTE:Coating of the dish is not needed.
- Isolate the CP floating in the fourth ventricle.
- Gently cut off the cerebellum from the cerebrum with a scalpel. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, while the cerebellum is a much smaller part at the back of the brain. If necessary, remove remaining brain stem tissue parts from the cerebellum.
- Rotate the brain so that the cutting line is facing upward. Ensure that the fourth ventricle cavity is now visible in the middle of the section, with the CP floating at the dorsal site. If necessary, open up the ventricle a bit by pulling open the connective tissue with sharp forceps. In this way, the CP will be more visible and easier to reach.
- Gently tear the CP out of the ventricle wall using tiny sharp forceps.
NOTE It is important to only touch and take out the CP in this step in order to not contaminate the sample with the surrounding tissue. Opening up the ventricles as described in step 2.2.2 will facilitate step 2.2.3.
- Isolate the CP protruding out of the lateral ventricle.
- Use tiny sharp forceps to sagittally cut the brain into two hemispheres.
- Rotate the brain so that the cutting line is facing upward. To reveal the lateral ventricle, gently pull away the cortex from the thalamus.
- Retract the hippocampus to the midsagittal cutting line. The lateral ventricle is now visible with the CP lying at the bottom of the ventricle. If necessary, open up the ventricle a bit by pulling open the connective tissue with sharp forceps. In this way, the CP will be more visible and easier to reach.
- Use tiny sharp forceps to gently tear the CP out of the ventricle wall.
NOTE: It is important to only touch and take out the CP in this step in order to not contaminate the sample with the surrounding tissue. Opening up the ventricles as described in step 2.3.4 will facilitate step 2.3.5. Use necessary caution in this step to preserve the structure of the CP as much as possible. It is easiest to start pulling the CP in the rostral to caudal direction.
3. Morphological analysis of CP tissue using scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
CAUTION: Toxic solutions are used in the following processing steps. It is recommended to perform the sample preparation in a fume hood.
- Perform sample preparation for SEM as described below.
- Transfer the fresh isolated CP into freshly made fixation solution containing 2% paraformaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4). Incubate overnight at 4 °C.
NOTE: As the CP tissue is very fragile and thin, the tissue should be put in small specimen baskets (see Table of Materials) to transfer it between buffers. In this way, the structure of the tissue will be better preserved. A cacodylate-based fixative is used over a PBS-based one, as the strong cacodylate buffer can counter the low pH of glutaraldehyde in the EM fixative. - Wash the sample 3x for 5 min each with 3-5 mL of 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4).
- Post-fix the samples in 3-5 mL of 2% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer for 30 min. Wash the samples 3x for 5 min each with 3-5 mL of ultrapure water.
- Dehydrate the samples in a series of ice-cold solutions of increasing EtOH concentrations (50%, 70%, 85%, 100%), for 15 min per EtOH solution. Use a critical point dryer to properly point dry the sample.
NOTE Changing from liquid to gas phase affects the surface tension, causing damage to the surface structure. The critical point drying step allows for the preservation of the surface structure. - Position the sample carefully on a specimen mount provided with a carbon sticker (see Table of Materials).
- Coat the samples with a thin layer (2-5 nm) of platinum. To do so, mount a platinum source in a vacuum system between two high-current electrical terminals and heat the platinum to its evaporation temperature. A fine stream of platinum is deposited on the sample.
NOTE: A more detailed protocol for this step is provided in reference30. Besides platinum, gold or gold/palladium can also be used.
- Transfer the fresh isolated CP into freshly made fixation solution containing 2% paraformaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M Na-cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4). Incubate overnight at 4 °C.
- Visualize the CP samples with SEM (see Table of Materials). The visualization procedure of CP tissue via SEM is similar to that of other types of tissues and depends on the used software and instruments. A step by step SEM protocol with an accompanying video is available in reference31 or reference30.
Results
The described protocol facilitates the efficient isolation of the CP from the mouse brain lateral (Figure 2A-C) and fourth (Figure 2D-F) ventricles. After isolating the whole brain, forceps are used to sagittally hemisect the brain and identify the CPs floating in the lateral ventricles. The CP from the fourth ventricle can be isolated from the cerebellar side of the brain. Perfusion with bromo...
Discussion
Here, a method to isolate the choroid plexus (CP) out of the lateral ventricle and the fourth ventricle of a mouse brain is described. This whole mounting method of the CP facilitates further analysis using a repertoire of techniques to get a complete view of the CP morphology, cellular composition, transcriptome, proteome, and secretome. Such analyses are crucial to gain a better understanding of this remarkable structure protruding from the ventricles of the brain. This knowledge is of immense research interest, as it ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Belgian Foundation of Alzheimer's Research (SAO; project number: 20200032), the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO Vlaanderen; project numbers: 1268823N, 11D0520N, 1195021N) and the Baillet Latour Fund. We thank the VIB BioImaging Core for training, support, and access to the instrument park.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 26G x 1/2 needle | Henke Sass Wolf | 4710004512 | |
| Aluminium specimen mounts | EM Sciences | 75220 | |
| Cacodylate buffer | EM Sciences | 11652 | |
| Carbon steel surgial blades | Swann-Morton | 0210 | size: 0.45 mm x 12 mm |
| Carbon adhesive tabs -12 mm | EM Sciences | 77825-12 | |
| Critical point dryer | Bal-Tec | CPD030 | |
| Crossbeam 540 | Zeiss | SEM system | |
| Forceps | Fine Science Tools GmbH | 91197-00 | |
| Glutaraldehyde | EM Sciences | 16220 | |
| Heparin | Sigma-Aldrich | H-3125 | |
| Ismatec Reglo ICC Digital Peristaltic pump 2-channel | Metrohm Belgium N.V | CPA-7800160 | |
| Osmium Tetroxide | EM Sciences | 19170 | |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | P6148 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Lonza | BE17-516F | |
| Platinum | Quorum | Q150T ES | PBS without Ca++ Mg++ or phenol red; sterile filtered |
| Sodium pentobarbital | Kela NV | 514 | |
| Specimen Basket Stainless Steel | EM Sciences | 70190-01 | |
| Stemi DV4 Stereo microscope | Zeiss | ||
| Surgical scissors | Fine Science Tools GmbH | 91460-11 |
References
- Vandenbroucke, R. E. A hidden epithelial barrier in the brain with a central role in regulating brain homeostasis. Implications for aging. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 13, 407-410 (2016).
- Engelhardt, B., Sorokin, L. The blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: function and dysfunction. Seminars in Immunopathology. 31 (4), 497-511 (2009).
- Engelhardt, B., Wolburg-Buchholz, K., Wolburg, H. Involvement of the choroid plexus in central nervous system inflammation. Microscopy Research and Technique. 52 (1), 112-129 (2001).
- Engelhardt, B., Vajkoczy, P., Weller, R. O. The movers and shapers in immune privilege of the CNS. Nature Immunology. 18 (2), 123-131 (2017).
- De Bock, M., et al. A new angle on blood-CNS interfaces: a role for connexins. FEBS Letters. 588 (8), 1259-1270 (2014).
- Strazielle, N., Ghersi-Egea, J. F. Physiology of blood-brain interfaces in relation to brain disposition of small compounds and macromolecules. Molecular Pharmaceutics. 10 (5), 1473-1491 (2013).
- Redzic, Z. B., Segal, M. B. The structure of the choroid plexus and the physiology of the choroid plexus epithelium. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 56 (12), 1695-1716 (2004).
- Kratzer, I., Ek, J., Stolp, H. The molecular anatomy and functions of the choroid plexus in healthy and diseased brain. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Biomembranes. 1862 (11), 183430 (2020).
- Demeestere, D., Libert, C., Vandenbroucke, R. E. Clinical implications of leukocyte infiltration at the choroid plexus in (neuro)inflammatory disorders. Drug Discovery Today. 20 (8), 928-941 (2015).
- Brkic, M., et al. Amyloid βoligomers disrupt blood-CSF barrier integrity by activating matrix metalloproteinases. Journal of Neuroscience. 35 (37), 12766-12778 (2015).
- Vandenbroucke, R. E., et al. Matrix metalloprotease 8-dependent extracellular matrix cleavage at the blood-CSF barrier contributes to lethality during systemic inflammatory diseases. Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (29), 9805-9816 (2012).
- Marques, F., et al. The choroid plexus response to a repeated peripheral inflammatory stimulus. BMC Neuroscience. 10, 135 (2009).
- Marques, F., et al. The choroid plexus in health and in disease: dialogues into and out of the brain. Neurobiology of Disease. 107, 32-40 (2017).
- Lun, M. P., Monuki, E. S., Lehtinen, M. K. Development and functions of the choroid plexus-cerebrospinal fluid system. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 16 (8), 445-457 (2015).
- Spector, R., Keep, R. F., Snodgrass, S. R., Smith, Q. R., Johanson, C. E. A balanced view of choroid plexus structure and function: Focus on adult humans. Experimental Neurology. 267, 78-86 (2015).
- Lehtinen, M. K., et al. The choroid plexus and cerebrospinal fluid: emerging roles in development, disease, and therapy. Journal of Neuroscience. 33 (45), 17553-17559 (2013).
- Balusu, S., Brkic, M., Libert, C., Vandenbroucke, R. E. The choroid plexus-cerebrospinal fluid interface in Alzheimer's disease: more than just a barrier. Neural Regeneration Research. 11 (4), 534-537 (2016).
- Demeestere, D., Libert, C., Vandenbroucke, R. E. Therapeutic implications of the choroid plexus-cerebrospinal fluid interface in neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 50, 1-13 (2015).
- Simon, M. J., Iliff, J. J. Regulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow in neurodegenerative, neurovascular and neuroinflammatory disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis of Disease. 1862 (3), 442-451 (2016).
- Serot, J. M., Zmudka, J., Jouanny, P. A possible role for CSF turnover and choroid plexus in the pathogenesis of late onset Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 30 (1), 17-26 (2012).
- Marques, F., et al. Altered iron metabolism is part of the choroid plexus response to peripheral inflammation. Endocrinology. 150 (6), 2822-2828 (2009).
- Thouvenot, E., et al. The proteomic analysis of mouse choroid plexus secretome reveals a high protein secretion capacity of choroidal epithelial cells. Proteomics. 6 (22), 5941-5952 (2006).
- Vandendriessche, C., et al. Importance of extracellular vesicle secretion at the blood-cerebrospinal fluid interface in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 9 (1), 143 (2021).
- Bowyer, J. F., et al. A visual description of the dissection of the cerebral surface vasculature and associated meninges and the choroid plexus from rat brain. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (69), e4285 (2012).
- Inoue, T., Narita, K., Nonami, Y., Nakamura, H., Takeda, S. Observation of the ciliary movement of choroid plexus epithelial cells ex vivo. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (101), e52991 (2015).
- Dani, N., et al. A cellular and spatial map of the choroid plexus across brain ventricles and ages. Cell. 184 (11), 3056-3074 (2021).
- Carloni, S., et al. Identification of a choroid plexus vascular barrier closing during intestinal inflammation. Science. 374 (6566), 439-448 (2021).
- Van Hoecke, L., et al. Involvement of the choroid plexus in the pathogenesis of Niemann-Pick disease type. C. Frontiers in Cell Neuroscience. 15, 757482 (2021).
- Shipley, F. B., et al. Tracking calcium dynamics and immune surveillance at the choroid plexus blood-cerebrospinal fluid interface. Neuron. 108 (4), 623-639 (2020).
- Guerin, C. J., Kremer, A., Borghgraef, P., Lippens, S. Targeted studies using serial block face and focused ion beam scan electron microscopy. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (150), e59480 (2019).
- JoVE. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). JoVE Science Education Database. , (2022).
- Pauwels, M., et al. Choroid plexus derived extracelular vesicles exhibit brain targeting characteristics). Biomaterials. 290, 121830 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved