A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Polymerase Chain Reaction and Dot-Blot Hybridization for Leptospira Detection in Water Samples
In This Article
Summary
In this study, a dot-blot application was designed to detect Leptospira from the three main clades in water samples. This method allows for the identification of minimal DNA quantities specifically targeted by a digoxigenin-labeled probe, easily detected by an anti-digoxigenin antibody. This approach is a valuable and satisfactory tool for screening purposes.
Abstract
The dot-blot is a simple, fast, sensitive, and versatile technique that enables the identification of minimal quantities of DNA specifically targeted by probe hybridization in the presence of carrier DNA. It is based on the transfer of a known amount of DNA onto an inert solid support, such as a nylon membrane, utilizing the dot-blot apparatus and without electrophoretic separation. Nylon membranes have the advantage of high nucleic acid binding capacity (400 µg/cm2), high strength, and are positively or neutrally charged. The probe used is a highly specific ssDNA fragment of 18 to 20 bases long labeled with digoxigenin (DIG). The probe will conjugate with the Leptospira DNA. Once the probe has hybridized with the target DNA, it is detected by an anti-digoxigenin antibody, allowing its easy detection through its emissions revealed in an X-ray film. The dots with an emission will correspond to the DNA fragments of interest. This method employs the non-isotopic labeling of the probe, which may have a very long half-life. The drawback of this standard immuno-label is a lower sensitivity than isotopic probes. Nevertheless, it is mitigated by coupling polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and dot-blot assays. This approach enables the enrichment of the target sequence and its detection. Additionally, it may be used as a quantitative application when compared against a serial dilution of a well-known standard. A dot-blot application to detect Leptospira from the three main clades in water samples is presented here. This methodology can be applied to large amounts of water once they have been concentrated by centrifugation to provide evidence of the presence of Leptospiral DNA. This is a valuable and satisfactory tool for general screening purposes, and may be used for other non-culturable bacteria that may be present in water, enhancing the comprehension of the ecosystem.
Introduction
Leptospirosis in humans mainly originates from environmental sources1,2. The presence of Leptospira in lakes, rivers, and streams is an indicator of leptospirosis transmission among wildlife, and domestic and production animals that may eventually come into contact with these bodies of water1,3,4. Furthermore, Leptospira has been identified in non-natural sources, including sewage, stagnant and tap water5,6.
Leptospira is a worldwide distributed bacteria7,8, and the role of the environment in its preservation and transmission has been well recognized. Leptospira can survive in drinking water under variable pH and minerals9, and in natural bodies of water1. It can also survive for long periods in distilled water10, and under constant pH (7.8), it may survive up to 152 days11. Moreover, Leptospira may interact in bacterial consortiums to survive harsh conditions12,13. It may be part of biofilms in freshwater with Azospirillum and Sphingomonas and is even capable of growing and enduring temperatures exceeding 49 °C14,15. It can also multiply in waterlogged soil and remain viable for up to 379 days16, preserving its ability to cause the disease for as long as a year17,18. However, little is known about the ecology within water bodies and how it is distributed within them.
Since its discovery, the study of the genus Leptospira was based on serological tests. It was not until the current century that molecular techniques became more prevalent in the study of this spirochaete. The dot-blot has been scarcely used for its identification using (1) an isotopic probe based on the 16S rRNA and on an inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR)19,20, (2) as a nanogold based immunoassay for human leptospirosis applied to urine21, or (3) as an antibody-based assay for bovine urine samples22. The technique fell in disuse because it was originally based on isotopic probes. However, it is a well-known technique that, coupled with PCR, yields enhanced results, and it is considered safe due to the use of non-isotopic probes. PCR plays a crucial role in the enrichment of the Leptospira DNA by amplifying a specific DNA fragment that may be found in trace amounts in a sample. During each PCR cycle, the amount of the targeted DNA fragment is doubled in the reaction. At the end of the reaction, the amplicon has been multiplied by a factor of more than a million23. The product amplified by PCR, often not visible in agarose electrophoresis, becomes visible through specific hybridization with a DIG-labeled probe in the dot-blot24,25,26.
The dot-blot technique is simple, robust, and suitable for numerous samples, making it accessible to laboratories with limited resources. It has been employed in a variety of bacteria studies, including (1) oral bacteria27, (2) other sample types such as food and feces28, and (3) the identification of unculturable bacteria29, often in agreement with other molecular techniques. Among the advantages offered by the dot-blot technique are: (1) The membrane has a high binding capacity, capable of binding over 200 μg/cm2 of nucleic acids and up to 400 μg/cm2; (2) Dot-blot results can be visually interpreted without requiring special equipment, and (3) they can be conveniently stored for years at room temperature (RT).
The genus Leptospira has been classified into pathogenic, intermediate, and saprophytic clades30,31. The distinction among these clades can be achieved based on specific genes such as lipL41, lipL32, and the 16S rRNA. LipL32 is present in the pathogenic clades and exhibits high sensitivity in various serological and molecular tools, whereas it is absent in saprophyte species21. The housekeeping gene lipL41 is known for its stable expression and used in molecular techniques32, while the 16S rRNA gene is utilized for their classification.
This methodology can be applied to large volumes of water once they have been concentrated by centrifugation. It allows the assessment of various points and depths within a water body to detect the presence of leptospiral DNA and the clade to which it belongs. This tool is valuable for both ecological and general screening purposes and can also be employed to detect other non-culturable bacteria that may be present in water.
Additionally, PCR and dot-blot assays are technically and economically affordable to a wide range of laboratories, even those lacking sophisticated or expensive equipment. This study aims to apply the digoxigenin-based dot-blot for the identification of the three Leptospira clades in water samples collected from natural bodies of water.
Bacterial strains
Twelve Leptospira serovars (Autumnalis, Bataviae, Bratislava, Canicola, Celledoni, Grippothyphosa, Hardjoprajitno, Icterohaemorrhagiae, Pomona, Pyrogenes, Tarassovi, and Wolffi) were included in this study. These serovars are part of the collection at the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and Zootechnics, National Autonomous University of Mexico, and they are currently used in the microagglutination test (MAT).
All Leptospira serovars were cultured in EMJH, and their DNA was extracted using a commercial DNA extraction kit (see Table of Materials). A genomic DNA mix of the twelve serovars was used as a positive control for the Leptospira pathogenic clade. As a positive control of the Leptospira intermediate clade, genomic DNA from Leptospira fainei serovar Hurstbridge strain BUT6 was included, and as a positive control for the Leptospira saprophyte clade, genomic DNA of Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain Patoc I, was also included.
Negative controls consisted of an empty plasmid, DNA from non-related bacteria (Ureaplasma urealyticum, Staphylococcus aureus, Brucella abortus, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella boydii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Escherichia coli), and PCR-grade water, which served as non-template control.
Water samples
Twelve trial grab samples were collected using a stratified-haphazard sampling method from the Cuemanco Biological and Aquaculture Research Center (CIBAC) (19° 16' 54" N 99° 6' 11" W). These samples were obtained at three depths: superficial, 10, and 30 cm (Figure 1A, B). The water collection procedures did not impact any endangered or protected species. Each sample was collected in a sterile 15 mL microcentrifuge tube. To collect the sample, each tube was gently submerged in the water, filled at the selected depth, and then sealed. The samples were maintained at 22 °C and promptly transported to the laboratory for processing.
Each sample was concentrated by centrifugation in sterile 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes at 8000 x g for 20 min at room temperature. This step was repeated until all the samples were concentrated into one tube, which was then used for DNA extraction (Figure 1C).
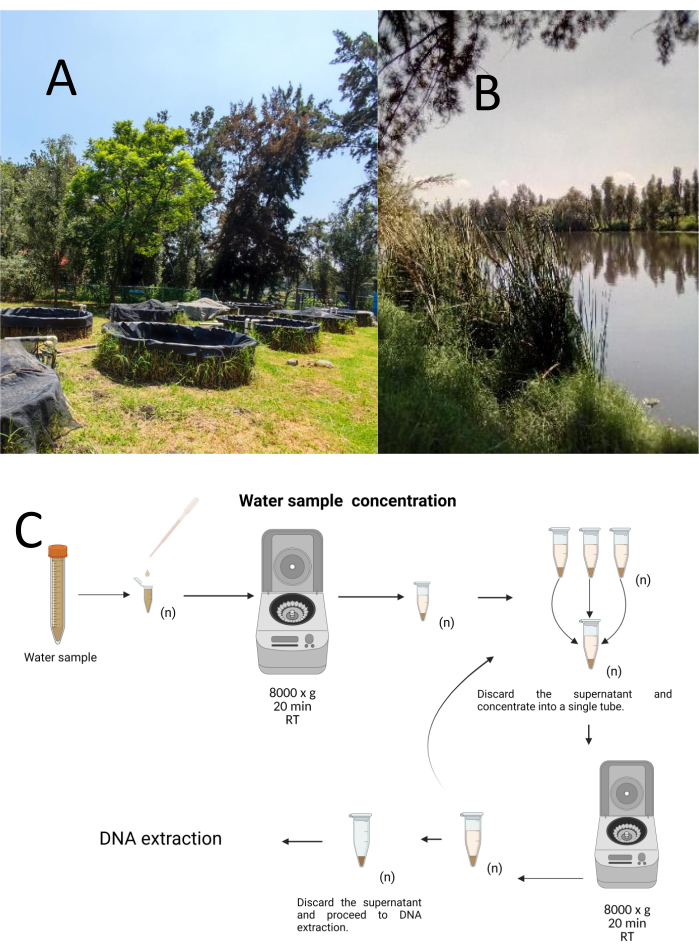
Figure 1: Concentration of water samples by centrifugation. (A) Water sampling ponds, and (B) Natural streams. (C) Centrifugation-based water sample processing in repeated steps as many times as needed (n). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
DNA extraction
Total DNA was isolated using a commercial Genomic DNA kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (see Table of Materials). DNA extractions were eluted in 20 µL of elution buffer, and DNA concentration was determined by a UV Spectrophotometer at 260-280 nm, and stored at 4 °C until use.
PCR amplification
The PCR targets were the 16S rRNA, lipL41, and lipL32 genes, which identify DNA from the genus Leptospira and allow the distinction among the three clades: pathogenic, saprophytic, and intermediate. Both primers and probe designs were based on the previous works by Ahmed et al., Azali et al., Bourhy et al., Weiss et al., and Branger et al.33,34,35,36,37. The sequence of each probe, primer, and amplified fragment are described in Table 1, and their alignment with reference sequences are provided in Supplementary File 1, Supplementary File 2, Supplementary File 3, Supplementary File 4, and Supplementary File 5. The PCR reagents and thermocycling conditions are described in the protocol section.
Amplification products were visualized by electrophoretic separation on a 1% agarose gel in TAE (40 mM Tris base, 20 mM Acetic acid, and 1 mM EDTA; pH 8.3), at 60 V for 45 min with ethidium-bromide detection, as shown in Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic DNA obtained from each serovar was used with concentrations ranging from 6 x 106 to 1 x 104 genomic equivalent copies (GEq) in each PCR reaction, based on the genome size of L. interrogans (4, 691, 184 bp)38 for pathogenic Leptospira, the genome size of L. biflexa (3, 956, 088 bp)39 for saprophytic Leptospira, and the genome size of L. fainei serovar Hurstbridge strain BUT6 (4, 267, 324 bp) with accession number AKWZ00000000.2.
The sensitivity of the probes was assessed with DNA from each pathogenic serovar, L. biflexa serovar Patoc strain Patoc I, and L. fainei serovar Hurstbridge strain BUT6 in each experiment. To assess the specificity of the PCR and dot-blot hybridization assay, DNA from non-related bacteria was included.
Table 1: PCR primers and probes to amplify products for identifying the pathogenic, saprophyte, and intermediate clades of Leptospira. Please click here to download this Table.
Dot-blot hybridization assay
The technique is called dot-blot because the holes in which the DNA sample is placed have a dot shape, and when they are sucked to be fixed in place by vacuum suction, they acquire this shape. This technique was developed by Kafatos et al.40. The technique allows the semi-quantification of Leptospira in each PCR-positive sample. The protocol consists of a denaturation with NaOH 0.4 M at room temperature, samples with Leptospira DNA from 30 ng to 0.05 ng, corresponding to 6 x 106 to 1 x 104 leptospires, are blotted onto a nylon membrane with a 96-well dot-blot apparatus. After immobilization, the DNA is bound to the membrane by exposure to 120 mJ UV light. Each DNA probe is conjugated with digoxigenin-11 dUTP by a terminal transferase catalysis step at the 3' end (Digoxigenin is a plant steroid obtained from Digitalis purpurea, used as a reporter41). Following the stringent hybridization of the labeled DNA probe (50 pmol) at the specific temperature onto the target DNA, the DNA hybrids are visualized by the chemiluminescence reaction with the anti-digoxigenin alkaline phosphatase antibody covalently conjugated with its substrate CSPD. The luminescence is captured by exposure to an X-ray film (Figure 2).
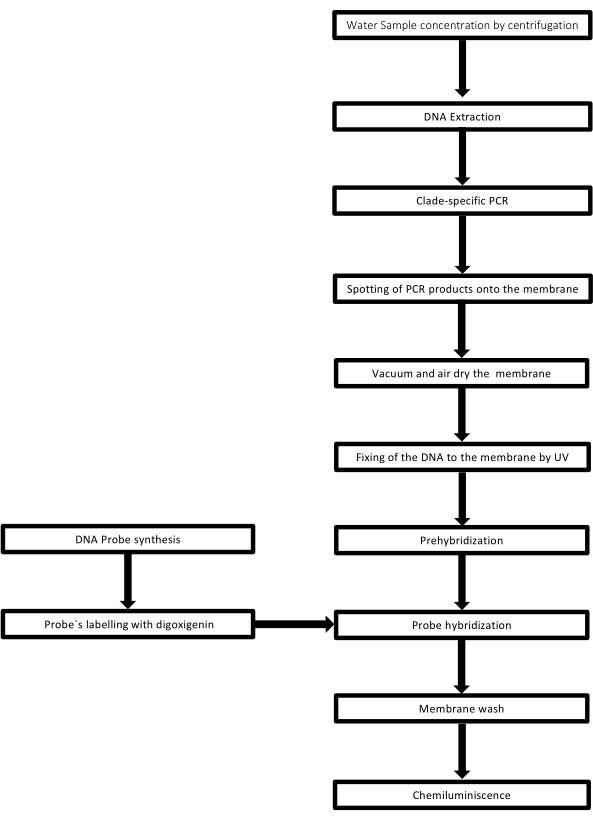
Figure 2: Steps of the procedure for the PCR-dot-blot assay. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
1. Sample preparation
- Concentrate each water sample in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes by centrifugation at 8,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C. Repeat this step, as many times as required, to concentrate the sample into a volume of 250 µL.
- Use the DNA extraction kit according to the manufacturer´s instructions (see Table of Materials).
- Perform the specific PCR according to the dot-blot probe that will be used (Table 1).
- Perform the amplifications in PCR tubes with the final volume of 25 µL containing 1 X buffer, 2.5 units of Taq polymerase, 1 µM of each primer, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2, and 100 ng of target DNA from each water sample or reference genomic-DNA.
- Program the PCR reaction in a thermocycler according to the thermocycling conditions (Table 2).
- Store the reactions at 4 °C until use.
- Place 10 µL of each PCR product to be blotted in a separate well of a 96-well plate.
- Add 40 µL of TE to each well and mix by pipetting.
NOTE: The 96-well plate can be sealed and stored at 4 °C overnight. Follow the instructions provided in Supplementary File 6 to prepare buffers and solutions for the protocol. Figure 3 depicts the steps of sample preparation.
Table 2: PCR thermocycling conditions for the 16S, lipL41, and lipL32 genes. Please click here to download this Table.
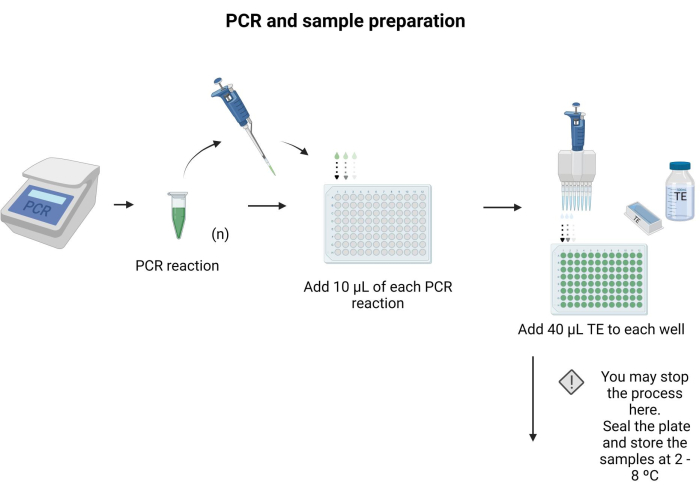
Figure 3: PCR and sample preparation. Applying the specific PCR protocol, the PCR product was transferred to a microtiter plate, and 40 µL of TE was added to each well. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Assembling the dot-blot apparatus
NOTE: The assembling of the dot-blot apparatus is shown in Figure 4. During the procedure, wear gloves to handle the alkali solutions and protect the nylon membrane from contamination.
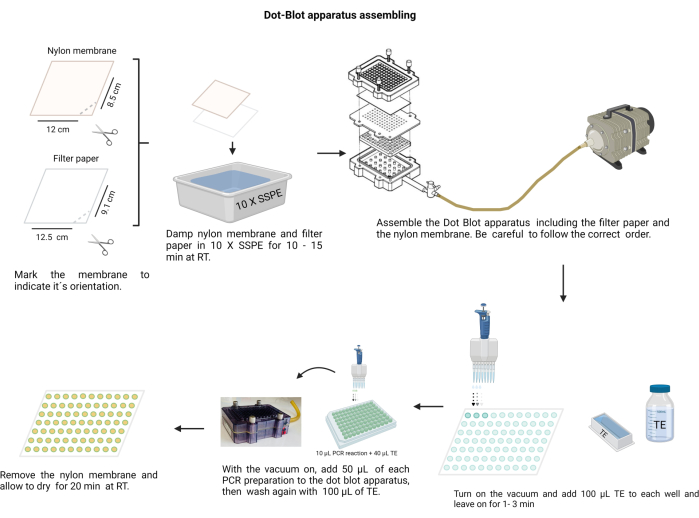
Figure 4: Dot-blot apparatus assembling. The filter paper and the nylon membrane (previously moistened in 10 X SSPE) must be arranged in the correct order. The assembly must be secured with the screws tightly before applying the vacuum. Each well needs to be washed with TE, and the PCR products are loaded into their respective wells. After transferring the PCR product through the membrane, each well is washed again with TE and allowed to dry. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Cut the nylon membrane (see Table of Materials) and filter paper into sheets of size 12 x 8.5 cm.
- Mark the membrane with a permanent marker.
- Make a notch with scissors at one edge to indicate the right orientation. Use the mark to remember the sample order.
- Moisten the membrane and filter paper with 10 X Saline-sodium phosphate-EDTA buffer (SSPE; 3 M NaCl, 0.2 M NaH2PO4, and 0.02 M EDTA, pH 7.4) (Supplementary File 6). Handle the membrane with a clean, blunt-ended tweezer.
- Assemble the dot-blot chamber; first, the filter paper, followed by the membrane over the plastic seal. Secure the cover with the screws in a crosswise manner.
- Connect the chamber to the vacuum, place 100 µL of TE in each well, hold the vacuum for 1 min, and then stop it.
- Switch on the vacuum at low speed and load 50 µL of each sample into the corresponding well on the membrane of the dot-blot apparatus (following the pre-decided membrane distribution).
NOTE: Homogenize each sample in the hemagglutination 96 well plate prior to placing it in the dot-blot chamber. - Allow the vacuum to dry the membrane. If necessary, hit the chamber gently to release the bubbles in the sample.
- Wash each well by placing 100 µL of TE into it with a continuous vacuum and allowing it to dry.
NOTE: After completing the transfer, it is crucial to first switch off the pump and detach it. Failure to do so may result in reflux entering the apparatus. DNA does not need a denaturation step if a positively charged nylon membrane is used, but if using other inert support, a pre-denaturation step and alkali-based denaturation may be needed41.
3. DNA denaturation and fixation
NOTE: Figure 5 illustrates the DNA membrane fixation procedure.
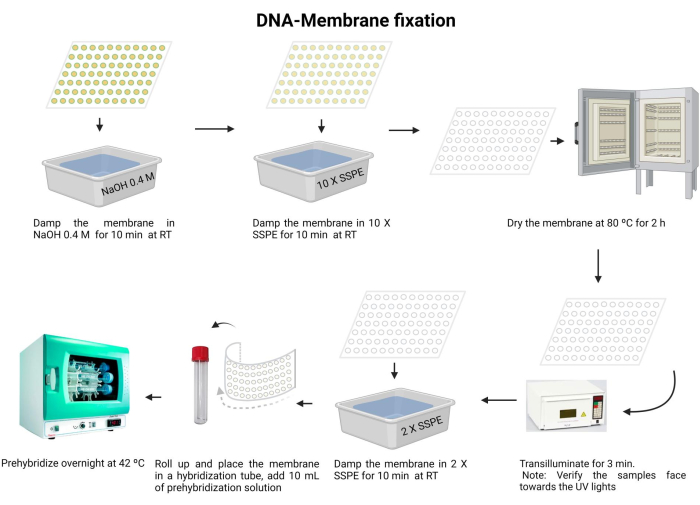
Figure 5: DNA-membrane fixation procedure. The DNA is denatured in an alkaline solution. Next, it is neutralized with 10 X SSPE, and the membrane is dried. Next, the membrane is transilluminated. The membrane is rehydrated with 2 X SSPE and pre-hybridized overnight. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Incubate the membrane with 0.4 M NaOH for 10 min at room temperature.
- Equilibrate the membrane with 10 X SSPE for 10 min at room temperature.
- Dry the membrane at 80 °C for 2 h.
- Transilluminate with 120 mJ UV light for 3 min. Ensure that the samples are oriented face down towards the UV light source. If using a UV-crosslinker, confirm that the samples are facing upward and repeat this step twice.
NOTE: The membrane must be completely dry before UV crosslinking. DNA will be immobilized by a covalent bond to the nylon membrane. Each cross-linking takes about 18'' to 1' with an optimal UV irradiation dose, for most hybridization experiments, of approximately 0.6-0.8 kJ/m2.
Exposure to UV irradiation is harmful to the eyes and skin. Wear appropriate protective equipment and avoid exposure to bare skin. - Wash the membrane with 2 X SSPE for 10 min.
- Carefully fold the membrane and insert it into the hybridization tube (use a 15 mL microcentrifuge tube).
- Add 10 mL of the pre-hybridization solution (Supplementary File 6) to the tube and incubate at 42 °C overnight. Ensure that the tube has been properly sealed to prevent any leakage.
4. Hybridization
- Remove 5 mL of the pre-hybridization solution from the hybridization tube. To use the 5 mL for a second time, keep it in another tube and store it at -4 °C.
- Add 15 µL of the labeled probe (Table 1) to the hybridization tube. Rinse the tip into the solution to ensure that the labeled probe was thoroughly instilled into the dilution.
NOTE: The DNA probe's binding is not as strong as the antigen-antibody binding. Therefore, changes in the concentration of the probe or DNA in the sample can influence the intensity of the emitted fluorescence. DNA probes are stoichiometric, meaning that the number of probe molecules bound to DNA is equivalent to the number of DNA molecules present in the solution. Figure 6 depicts the probe hybridization. - Incubate at 42 °C overnight.
- Perform DNA probe DIG labeling. Follow the instructions specified in Table 3 to mix the reagents, then incubate the mixture at 37 °C for 1 h. Next, add 80 µL of distilled water and store the tailed probe at 4 °C.
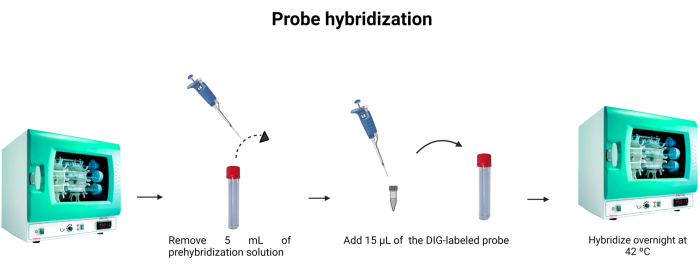
Figure 6: Probe hybridization. The volume of the hybridization buffer is adjusted, and the digoxigenin-labeled probe is incorporated to allow the probe's hybridization overnight. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Table 3: Reagents for the probes labeling with digoxigenin (DIG). Please click here to download this Table.
5. Chemiluminescence (anti-DIG tagging)
- Wash the membrane twice with 2 X SSPE/0.1% SDS at room temperature for 10 min.
- Incubate the membrane with 5 X SSPE/0.1% SDS at the probe's annealing temperature for 15 min.
NOTE: In this step, use a container with a lid to maintain the temperature as long as possible. Ensure uniform and constant temperature across the membrane. The approximate volume in each wash is 100 mL of the solution indicated. - Wash the membrane once with Buffer 1 (Supplementary File 6) at room temperature for 5 min.
- Wash the membrane once with Buffer 2 (Supplementary File 6) at room temperature for 30 min.
- Wash the membrane with Buffer 2 and add the anti-digoxigenin antibody (15 µL) (see Table of Materials), then incubate for 45 min (the incubation time may vary from 30-60 min). This secondary antibody tags the probe for detection.
NOTE: The membrane may be stored in Buffer 2 with the anti-digoxigenin antibody overnight at 4-8 °C. Anti-DIG tagging of the chemiluminescence process is depicted in Figure 7.
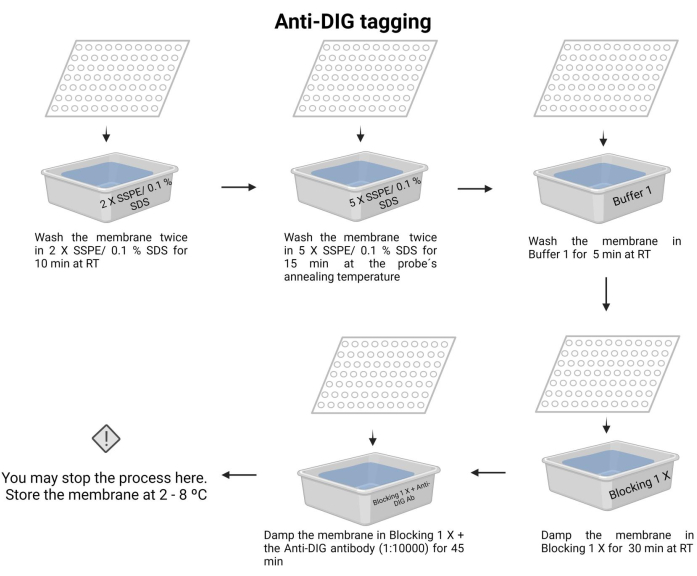
Figure 7: Anti-DIG tagging of the chemiluminescence process. The unbonded nucleic acids are removed with buffer solutions. The probe is aligned with the target DNA, and the excess is removed. The membrane is blocked with the blocking 1 X buffer, and the anti-DIG antibody is added (1:10000). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
6. Chemiluminescence (substrate application)
- Wash the membrane twice in Buffer 1 at room temperature for 15 min.
- Wash once in Buffer 3 (see Supplementary file 6) at room temperature for 5 min, allowing the membrane to drain most of the buffer, leaving it almost dry.
- Add CSPD ready to use (Disodium 3-(4-methoxyspiro {1,2-dioxetane-3,2′-(5′-chloro) tricyclo [3.3.1.13,7] decan}-4-yl) phenyl phosphate, see Table of Materials), and let stay for 5 min, (with damped fingers homogenize the CSPD from one side to the other).
- Place the membrane in a transparent plastic bag (12.5 x 9 cm) that fits the membrane dimension. Carefully remove air bubbles, evenly distribute the CSPD, and heat-seal the bag.
- Incubate the membrane in a water bath at 37 °C for 15 min (it can be up to 30 min), and ensure that the membrane with samples is placed downwards so that it is well submerged. Ensure that the temperature remains constant and well distributed over the membrane.
- Dry the plastic bag and fix it with scotch tape on an already-used radiographic film. This will allow easy handling during the exposure procedure.
NOTE: Figure 8 shows the substrate application of the chemiluminescence process.

Figure 8: Substrate application of the chemiluminescence process. The free antibody is removed, and the substrate CSPD (1:250) is added to the membrane. The reaction is activated by incubation at 37 °C and the membrane is arranged to record the chemiluminescence in an X-ray film. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
7. Chemiluminescence (detection)
- Perform the exposure procedure. In the darkroom, prepare the developer and fixer solutions (see Table of Materials) in the respective trays.
- In the dark, carefully place the fixed membrane facing a new radiographic film and insert it into a radiographic cassette (see Table of Materials).
- Register the time of exposure. The time of exposure may vary from 1 min to 30 min or more. Start with 5 min and adjust the time accordingly.
- Damp the X-ray film in developer solution for 1-3 min and rinse gently with tap water (15-45 s).
- Damp the X-ray film in fixer solution for 1-3 min and rinse gently with tap water (45 s).
- Allow the X-ray film to air dry and document the assay in a visible white lightbox.
NOTE: Avoid shaking the membrane during the X-ray exposure time. The detection process is depicted in Figure 9. - Proceed to the result interpretation. In the exposed X-ray film, the dots with emission can be visually located and correspond to the DNA fragments with the probe's hybridization. The intensity of the emitted signal depends on the luminescence and the duration of the exposure.
NOTE: Membranes can be stored dried between filter paper for several months at room temperature.
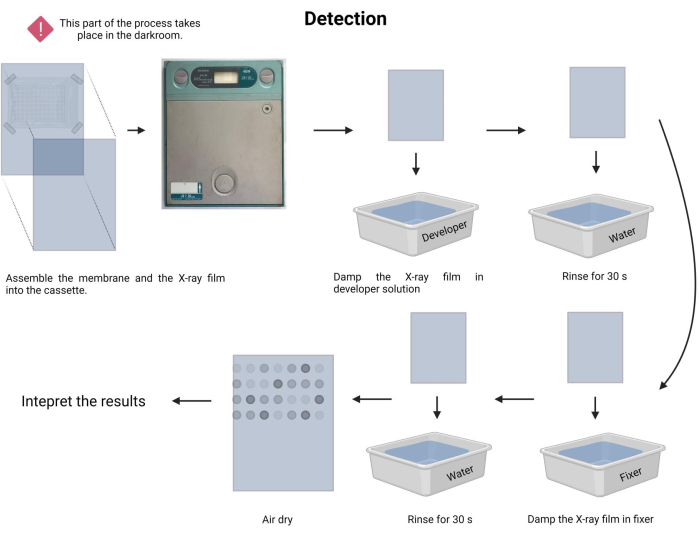
Figure 9: Detection of the chemiluminescence process. Under dark conditions, the membrane is exposed to an X-ray film inside an X-ray cassette. Next, it was allowed to stand during the exposition time, and then the X-ray film was developed and fixed. Finally, it was air dried and interpreted. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
8. Membrane de-hybridization procedure
- Wash the membrane twice for 10 min with distilled water.
- Wash the membrane for 20 min with 0.4 M NaOH at 53 °C (twice).
- Wash twice the membrane for 10 min with 2 X SSPE.
- Allow the membrane to dry at room temperature.
- Keep the membrane and return to step 3.5 of the protocol.
NOTE: The membrane may be stored in the pre-hybridization buffer overnight at 4-8 °C. The next day, restart with an incubation at 42 °C for 1 h, allowing the pre-hybridization buffer to reach the temperature. Then, proceed to step 3.5 of the protocol.
Results
To assess the effectiveness of the technique, genomic DNA from pure cultures of each Leptospira serovar was used, along with the clade-specific probe. Membranes were prepared with 100 ng of genomic DNA per PCR reaction for each serovar, followed by eight genomic DNA of non-related bacteria and variable concentrations of genomic DNA of the ad hoc Leptospira serovars. Each assay included positive, negative, and non-template control. These non-related genomic DNA did not show an affinity for the dot-blot p...
Discussion
The critical steps of the dot-blot technique include (1) DNA immobilization, (2) blocking of the free binding sites on the membrane with non-homologous DNA, (3) the complementarity between the probe and the target fragment under annealing conditions, (4) removal of the unhybridized probe, and (5) the detection of the reporter molecule41.
The PCR-Dot-blot has certain limitations, such as the technique does not provide information about the size of the hybridized fragment...
Disclosures
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the Leptospira collection of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and Zootechnics, National Autonomous University of Mexico. We are grateful for the generous donation of the reference Leptospira strains; Leptospira fainei serovar Hurstbridge strain BUT6 and Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain Patoc I to Dr. Alejandro de la Peña Moctezuma. We thank Dr. José Antonio Ocampo Cervantes, the CIBAC Coordinator, and the personnel for their logistical support. EDT was under the Terminal Project program for undergraduate students of the Metropolitan Autonomous University-Campus Cuajimalpa. We acknowledge the Biorender.com software for the creation of figures 1, and 3 to 9.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| REAGENTS | |||
| Purelink DNA extraction kit | Invitrogen | K182002 | |
| Gotaq Flexi DNA Polimerase (End-Point PCR Taq polymerase kit) | Promega | M3001 | |
| Whatman filter paper, grade 1, | Merk | WHA1001325 | |
| Nylon Membranes, positively charged Roll 30cm x 3 m | Roche | 11417240001 | |
| Anti-Digoxigenin-AP, Fab fragments Sheep Polyclonal Primary-antibody | Roche | 11093274910 | |
| Medium Base EMJH | Difco | S1368JAA | |
| Leptospira Enrichment EMJH | Difco | BD 279510 | |
| Blocking Reagent | Roche | 11096176001 | |
| CSPD ready to use Disodium 3-(4-methoxyspiro {1,2-dioxetane-3,2′-(5′-chloro) tricyclo [3.3.1.13,7] decan}8-4-yl) phenyl phosphate | Merk | 11755633001 | |
| Deoxyribonucleic acid from herring sperm | Sigma Aldrich | D3159 | |
| Developer Carestream | Carestream Health Inc | GBX5158621 | |
| Digoxigenin-11-ddUTP | Roche | 11363905910 | |
| EDTA, Disodium Salt (Dihydrate) | Promega | H5032 | |
| Ficoll 400 | Sigma Aldrich | F8016 | |
| Fixer Carestream | Carestream Health Inc | GBX 5158605 | |
| Lauryl sulfate Sodium Salt (Sodium dodecyl sulfate; SDS) C12H2504SNa | Sigma Aldrich | L5750 | |
| N- Lauroylsarcosine sodium salt CH3(CH2)10CON(CH3) CH2COONa | Sigma Aldrich | L-9150 | It is an anionic surfactant |
| Polivinylpyrrolidone (PVP-40) | Sigma Aldrich | PVP40 | |
| Polyethylene glycol Sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20) | Sigma Aldrich | 9005-64-5 | |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | Sigma Aldrich | 7647-14-5 | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | Sigma Aldrich | 151-21-3 | |
| Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Sigma Aldrich | 1310-73-2 | |
| Sodium phosphate dibasic (NaH2PO4) | Sigma-Aldrich | 7558-79-4 | |
| Terminal transferase, recombinant | Roche | 3289869103 | |
| Tris hydrochloride (Tris HCl) | Sigma-Aldrich | 1185-53-1 | |
| SSPE 20X | Sigma-Aldrich | S2015-1L | It can be Home-made following Supplementary File 6 |
| Primers | Sigma-Aldrich | On demand | Follow table 1 |
| Probes | Sigma-Aldrich | On demand | Follow table 1 |
| Equipment | |||
| Nanodrop™ One Spectrophotometer | Thermo-Scientific | ND-ONE-W | |
| Refrigerated microcentrifuge Sigma 1-14K, suitable for centrifugation of 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes at 14,000 rpm | Sigma-Aldrich | 1-14K | |
| Disinfected adjustable pipettes, range 2-20 µl, 20-200 µl | Gilson | SKU:F167360 | |
| Disposable 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes (autoclaved) | Axygen | MCT-150-SP | |
| Disposable 600 µl microcentrifuge tubes (autoclaved) | Axygen | 3208 | |
| Disposable Pipette tips 1-10 µl | Axygen | T-300 | |
| Disposable Pipette tips 1-200 µl | Axygen | TR-222-Y | |
| Dot-Blot apparatus Bio-Dot | BIORAD | 1706545 | |
| Portable Hergom Suction | Hergom | 7E-A | |
| Scientific Light Box (Visible-light PH90-115V) | Hoefer | PH90-115V | |
| UV Crosslinker | Hoefer | UVC-500 | |
| Thermo Hybaid PCR Express Thermocycler | Hybaid | HBPX110 | |
| Radiographic cassette with IP Plate14 X 17 | Fuji |
References
- Bierque, E., Thibeaux, R., Girault, D., Soupé-Gilbert, M. E., Goarant, C. A systematic review of Leptospira in water and soil environments. PLOS One. 15 (1), e0227055 (2020).
- Haake, D. A., Levett, P. N. Leptospirosis in humans. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. 387, 65-97 (2015).
- Tripathy, D. N., Hanson, L. E. Leptospires from water sources at Dixon Springs Agricultural Center. Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 9 (3), 209-212 (1973).
- Smith, D. J., Self, H. R. Observations on the survival of Leptospira australis A in soil and water. The Journal of Hygiene. 53 (4), 436-444 (1955).
- Karpagam, K. B., Ganesh, B. Leptospirosis: a neglected tropical zoonotic infection of public health importance-an updated review. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology. 39 (5), 835-846 (2020).
- Casanovas-Massana, A., et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of pathogenic Leptospira in surface waters from the urban slum environment. Water Research. 130, 176-184 (2018).
- Costa, F., et al. Global morbidity and mortality of Leptospirosis: A systematic review. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 9 (9), e0003898 (2015).
- Mwachui, M. A., Crump, L., Hartskeerl, R., Zinsstag, J., Hattendorf, J. Environmental and behavioural determinants of Leptospirosis transmission: A systematic review. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 9 (9), e0003843 (2015).
- Andre-Fontaine, G., Aviat, F., Thorin, C. Waterborne Leptospirosis: Survival and preservation of the virulence of pathogenic Leptospira spp. in fresh water. Current Microbiology. 71 (1), 136-142 (2015).
- Trueba, G., Zapata, S., Madrid, K., Cullen, P., Haake, D. Cell aggregation: A mechanism of pathogenic Leptospira to survive in freshwater. International Microbiology: the Official Journal of the Spanish Society for Microbiology. 7 (1), 35-40 (2004).
- Smith, C. E., Turner, L. H. The effect of pH on the survival of leptospires in water. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 24 (1), 35-43 (1961).
- Barragan, V. A., et al. Interactions of Leptospira with environmental bacteria from surface water. Current Microbiology. 62 (6), 1802-1806 (2011).
- Abdoelrachman, R. Comparative investigations into the influence of the presence of bacteria on the life of pathogenic and apathogenic leptospirae. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 13 (1), 21-32 (1947).
- Singh, R., et al. Microbial diversity of biofilms in dental unit water systems. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 69 (6), 3412-3420 (2003).
- Kumar, K. V., Lall, C., Raj, R. V., Vedhagiri, K., Vijayachari, P. Coexistence and survival of pathogenic leptospires by formation of biofilm with Azospirillum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 91 (6), 051 (2015).
- Yanagihara, Y., et al. Leptospira Is an environmental bacterium that grows in waterlogged soil. Microbiology Spectrum. 10 (2), 0215721 (2022).
- Gillespie, R. W., Ryno, J. Epidemiology of leptospirosis. American Journal of Public Health and Nation’s Health. 53 (6), 950-955 (1963).
- Bierque, E., et al. Leptospira interrogans retains direct virulence after long starvation in water. Current Microbiology. 77 (10), 3035-3043 (2020).
- Zhang, Y., Dai, B. Marking and detection of DNA of leptospires in the dot-blot and situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled probes. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences. 23 (4), 353-435 (1992).
- Mérien, F., Amouriaux, P., Perolat, P., Baranton, G., Saint Girons, I. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of Leptospira spp. in clinical samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 30 (9), 2219-2224 (1992).
- Veerapandian, R., et al. Silver enhanced nano-gold dot-blot immunoassay for leptospirosis. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 156, 20-22 (2019).
- Junpen, S., et al. Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based dot-blot ELISA for detection of Leptospira spp in bovine urine samples. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 66 (5), 762-766 (2005).
- Ishmael, F. T., Stellato, C. Principles and applications of polymerase chain reaction: basic science for the practicing physician. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology: Official Publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. 101 (4), 437-443 (2008).
- Boerner, B., Weigelt, W., Buhk, H. J., Castrucci, G., Ludwig, H. A sensitive and specific PCR/Southern blot assay for detection of bovine herpesvirus 4 in calves infected experimentally. Journal of Virological Methods. 83 (1-2), 169-180 (1999).
- Curry, E., Pratt, S. L., Kelley, D. E., Lapin, D. R., Gibbons, J. R. Use of a Combined duplex PCR/Dot-blot assay for more sensitive genetic characterization. Biochemistry Insights. 1, 35-39 (2008).
- Pilatti, M. M., Ferreira, S. d. e. A., de Melo, M. N., de Andrade, A. S. Comparison of PCR methods for diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis in conjunctival swab samples. Research in Veterinary Science. 87 (2), 255-257 (2009).
- Conrads, G., et al. PCR reaction and dot-blot hybridization to monitor the distribution of oral pathogens within plaque samples of periodontally healthy individuals. Journal of Periodontology. 67 (10), 994-1003 (1996).
- Langa, S., et al. Differentiation of Enterococcus faecium from Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus strains by PCR and dot-blot hybridisation. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 88 (2-3), 197-200 (2003).
- Francesca, C., Lucilla, I., Marco, F., Giuseppe, C., Marisa, M. Identification of the unculturable bacteria Candidatus arthromitus in the intestinal content of trouts using dot-blot and Southern blot techniques. Veterinary Microbiology. 156 (3-4), 389-394 (2012).
- Arent, Z., Pardyak, L., Dubniewicz, K., Plachno, B. J., Kotula-Balak, M. Leptospira taxonomy: then and now. Medycyna Weterynaryjna. 78 (10), 489-496 (2022).
- Thibeaux, R., et al. Biodiversity of environmental Leptospira: Improving identification and revisiting the diagnosis. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9, 816 (2018).
- Carrillo-Casas, E. M., Hernández-Castro, R., Suárez-Güemes, F., de la Peña-Moctezuma, A. Selection of the internal control gene for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assays in temperature treated Leptospira. Current Microbiology. 56 (6), 539-546 (2008).
- Azali, M. A., Yean Yean, C., Harun, A., Aminuddin Baki A, N. N., Ismail, N. Molecular characterization of Leptospira spp. in environmental samples from North-Eastern Malaysia revealed a pathogenic strain, Leptospira alstonii. Journal of Tropical Medicine. 2016, 2060241 (2016).
- Ahmed, N., et al. Multilocus sequence typing method for identification and genotypic classification of pathogenic Leptospira species. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials. 5, 28 (2006).
- Bourhy, P., Collet, L., Brisse, S., Picardeau, M. Leptospira mayottensis sp. nov., a pathogenic species of the genus Leptospira isolated from humans. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 64, 4061-4067 (2014).
- Weiss, S., et al. An extended Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) scheme for rapid direct typing of Leptospira from clinical samples. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 10 (9), e0004996 (2016).
- Branger, C., et al. Polymerase chain reaction assay specific for pathogenic Leptospira based on the gene hap1 encoding the hemolysis-associated protein-1. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 243 (2), 437-445 (2005).
- Ren, S. X., et al. Unique physiological and pathogenic features of Leptospira interrogans revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature. 422 (6934), 888-893 (2003).
- Picardeau, M., et al. Genome sequence of the saprophyte Leptospira biflexa provides insights into the evolution of Leptospira and the pathogenesis of leptospirosis. PLOS One. 3 (2), e1607 (2008).
- Kafatos, F. C., Jones, C. W., Efstratiadis, A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Research. 7 (6), 1541-1552 (1979).
- Bhat, A. I., Rao, G. P. Dot-blot hybridization technique. Characterization of Plant Viruses. , 303-321 (2020).
- Yadav, J. P., Batra, K., Singh, Y., Singh, M. Comparative evaluation of indirect-ELISA and Dot-blot assay for serodetection of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae antibodies in poultry. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 189, 106317 (2021).
- Malinen, E., Kassinen, A., Rinttilä, T., Palva, A. Comparison of real-time PCR with SYBR Green I or 5'-nuclease assays and dot-blot hybridization with rDNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes in quantification of selected faecal bacteria. Microbiology. 149, 269-277 (2003).
- Wyss, C., et al. Treponema lecithinolyticum sp. nov., a small saccharolytic spirochaete with phospholipase A and C activities associated with periodontal diseases. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 49, 1329-1339 (1999).
- Shah, J. S., I, D. C., Ward, S., Harris, N. S., Ramasamy, R. Development of a sensitive PCR-dot-blot assay to supplement serological tests for diagnosing Lyme disease. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology. 37 (4), 701-709 (2018).
- Niu, C., Wang, S., Lu, C. Development and evaluation of a dot-blot assay for rapid determination of invasion-associated gene ibeA directly in fresh bacteria cultures of E. coli. Folia microbiologica. 57 (6), 557-561 (2012).
- Wetherall, B. L., McDonald, P. J., Johnson, A. M. Detection of Campylobacter pylori DNA by hybridization with non-radioactive probes in comparison with a 32P-labeled probe. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 26 (4), 257-263 (1988).
- Kolk, A. H., et al. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical samples by using polymerase chain reaction and a nonradioactive detection system. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 30 (10), 2567-2575 (1992).
- Scherer, L. C., et al. PCR colorimetric dot-blot assay and clinical pretest probability for diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in smear-negative patients. BMC Public Health. 7, 356 (2007).
- Armbruster, D. A., Pry, T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. The Clinical Biochemist Reviews. 29, S49-S52 (2008).
- Zhang, Y., Dai, B. Detection of Leptospira by dot-blot hybridization with photobiotin- and 32P-labeled DNA. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences = Huaxi like daxue xuebao. 23 (2), 130-132 (1992).
- Terpstra, W. J., Schoone, G. J., ter Schegget, J. Detection of leptospiral DNA by nucleic acid hybridization with 32P- and biotin-labeled probes. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 22 (1), 23-28 (1986).
- Shukla, J., Tuteja, U., Batra, H. V. DNA probes for identification of leptospires and disease diagnosis. The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 35 (2), 346-352 (2004).
- Jiang, N., Jin, B., Dai, B., Zhang, Y. Identification of pathogenic and nonpathogenic leptospires by recombinant probes. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences = Huaxi like daxue xuebao. 26 (1), 1-5 (1995).
- Fach, P., Trap, D., Guillou, J. P. Biotinylated probes to detect Leptospira interrogans on dot-blot hybridization or by in situ hybridization. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 12 (5), 171-176 (1991).
- Huang, N., Dai, B. Assay of genomic DNA homology among strains of different virulent leptospira by DNA hybridization. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences = Huaxi like daxue xuebao. 23 (2), 122-125 (1992).
- Dong, X., Dai, B., Chai, J. Homology study of leptospires by molecular hybridization. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences = Huaxi like daxue xuebao. 23 (1), 1-4 (1992).
- Komminoth, P. Digoxigenin as an alternative probe labeling for in situ hybridization. Diagnostic Molecular Pathology: The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, part B. 1 (2), 142-150 (1992).
- Saengjaruk, P., et al. Diagnosis of human leptospirosis by monoclonal antibody-based antigen detection in urine. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 40 (2), 480-489 (2002).
- Okuda, M., et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of canine Leptospira antibodies using recombinant OmpL1 protein. The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 67 (3), 249-254 (2005).
- Suwimonteerabutr, J., et al. Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based dot-blot ELISA for detection of Leptospira spp in bovine urine samples. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 66 (5), 762-766 (2005).
- Kanagavel, M., et al. Peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies of Leptospiral LigA for acute diagnosis of leptospirosis. Scientific reports. 7 (1), 3250 (2017).
- Levett, P. N. Leptospirosis. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 14 (2), 296-326 (2001).
- Monahan, A. M., Callanan, J. J., Nally, J. E. Proteomic analysis of Leptospira interrogans shed in urine of chronically infected hosts. Infection and Immunity. 76 (11), 4952-4958 (2008).
- Rojas, P., et al. Detection and quantification of leptospires in urine of dogs: a maintenance host for the zoonotic disease leptospirosis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology. 29 (10), 1305-1309 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved