Method Article
Split Retina as an Improved Flatmount Preparation for Studying Inner Nuclear Layer Neurons in Vertebrate Retina
In This Article
Summary
This work presents an alternative flatmount retina preparation in which the removal of photoreceptor cell bodies enables faster antibody diffusion and improved patch pipette access to inner retinal neurons for immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization, and electrophysiology experiments.
Abstract
Bipolar cells and horizontal cells of the vertebrate retina are the first neurons to process visual information after photons are detected by photoreceptors. They perform fundamental operations such as light adaptation, contrast sensitivity, and spatial and color opponency. A complete understanding of the precise circuitry and biochemical mechanisms that govern their behavior will advance visual neuroscience research and ophthalmological medicine. However, current preparations for examining bipolar and horizontal cells (retinal whole mounts and vertical slices) are limited in their capacity to capture the anatomy and physiology of these cells. In this work, we present a method for removing photoreceptor cell bodies from live, flatmount mouse retinas, providing enhanced access to bipolar and horizontal cells for efficient patch clamping and rapid immunolabeling. Split retinas are prepared by sandwiching an isolated mouse retina between two pieces of nitrocellulose, then gently peeling them apart. The separation splits the retina just above the outer plexiform layer to yield two pieces of nitrocellulose, one containing the photoreceptor cell bodies and another containing the remaining inner retina. Unlike vertical retina slices, the split retina preparation does not sever the dendritic processes of inner retinal neurons, allowing for recordings from bipolar and horizontal cells that integrate the contributions of gap junction-coupled networks and wide-field amacrine cells. This work demonstrates the versatility of this preparation for the study of horizontal and bipolar cells in electrophysiology, immunohistochemistry, and in situ hybridization experiments.
Introduction
The retina is a thin neural tissue located in the posterior eye where light is intercepted and processed into an electrochemical signal that can be interpreted by the brain. At the back of the retina, rod and cone photoreceptors are stimulated by light, which reduces the tonic release rate of the neurotransmitter, glutamate1. The first neurons to experience and respond to this light-induced change in glutamate concentration are the bipolar cells (BCs) and horizontal cells (HCs), whose somas reside in the outermost region of the inner nuclear layer (INL). These second-order neurons perform the first stage of signal processing in the retina and shape critical features of vision such as light adaptation, contrast sensitivity, and spatial/color opponency2. While these functions have been ascribed to BCs and HCs, the circuitry and biochemical mechanisms underlying these processes are not fully understood3. Therefore, the advancement of tools and methods for exploring BC and HC physiology is of paramount importance.
Vertical (transverse) retina sections have long proven the most practical model for studying BCs and HCs; however, certain aspects of BC and HC physiology are inaccessible to the experimenter under this model. Direct recordings from HCs or indirect measurements of their effects on BCs do not reflect the retina's endogenous connectivity since the lateral processes of these cells are severed during slicing. Whole mount retina preparations circumvent this issue by preserving these lateral processes, but the surrounding retinal layers pose a challenge for accessing these cells4. While there are abundant examples of immunostaining5,6,7,8 and patch clamp recordings9 from INL neurons in whole mount retinas, there is an opportunity to expedite and simplify the collection of these data. The inherent limitations of transverse sections and the challenges of the whole mount model thus inspired the development of this alternative flatmount retina preparation.
The following work describes a protocol for easily removing the photoreceptor layer from live, flatmount retinas to enhance access to BCs and HCs for simplified patch clamping and faster, more efficient immunolabeling. Peeling apart two pieces of nitrocellulose membrane attached to either side of an isolated retina tears the tissue through the photoreceptor axons, leaving a split retina that retains the outer plexiform layer (OPL) and all inner retinal layers. While others have described protocols for mechanically separating layers of the retina, these methods are either poorly suited to patch clamping and microscopy applications or require tedious manipulation of the tissue. Several of these methods require frozen or lyophilized tissue for layer separation, making them incompatible with electrophysiology experiments10,11,12. Others are designed for live tissue, but necessitate 5-15 sequential peels with filter paper4,11 or treatment with trypsin13 to remove the photoreceptors. The technique described here improves upon its predecessors by simplifying the photoreceptor removal procedure and expanding the repertoire of downstream applications.
Protocol
Mice were provided with water and food ad libitum and were maintained on a 12 h light/dark cycle. Mice were euthanized by exposure to isoflurane followed by cervical dislocation. All animal procedures were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines and approved by the Oregon Health and Science University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
NOTE: Eye enucleation, retina dissection, and retina splitting should be performed as quickly as possible to preserve the health of the living tissue. Aim to complete the dissection in < 4 min per eye. These three steps are to be performed sequentially. Wild-type mice: Adult (>3 months) male and female C57BL/6J mice were used for experiments. For synapse morphology, mice expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the Pcp2 promoter (Pcp2-cre/GFP)14 were used. Transgenic mice: For horizontal cell visualization with GFP during immunohistochemistry or electrophysiology experiments, a triple-transgenic mouse was used: vGATFLPo; vGlut2Cre; Ai80d. The vGATFlpo and vGluT2Cre strains are knock-in mice expressing Flpo or Cre recombinase downstream of their respective promoters. The Ai80d mouse is an intersectional reporter mouse (CatCh/EYFP) and will only express Ca2+ permeable channel rhodopsin (ChR2) in cells expressing Cre and Flpo recombinases. Thus, the triple transgenic mouse only expresses ChR2 in cells with a history of both VGAT and vGluT2 expression.
1. Materials preparation for retina dissection and retina splitting
- Prepare pieces of nitrocellulose membrane
NOTE: Detaching the split retina from the nitrocellulose membrane reduces background fluorescence in microscopy and simplifies patch clamp recording. Membrane removal can be performed before or after tissue fixation. For fixed split retinas, it is not necessary to treat the pieces of nitrocellulose membrane. For live split retinas, treat the membrane according to steps 1.1.3 - 1.1.5 to facilitate gentle detachment from the tissue.- Cut 16 pieces (or more) of nitrocellulose membrane into 5 mm x 5 mm squares. Extra can be prepared in bulk and stored for future use.
- Set aside half of the pieces of membrane for later use. These pieces will not be treated with a blocking solution.
- Incubate the remaining pieces in a detergent-free IHC blocking solution (such as 3% horse serum + 0.025% NaN3 diluted in PBS) for 10 min at room temperature, shaking gently.
CAUTION: Use appropriate PPE when handling NaN3, as it is a potent toxin. - Wash the membrane pieces thoroughly by incubation in bicarbonate-buffered Ames media for 10 min at room temperature, shaking gently.
- Completely air dry the blocked pieces of membrane (~20 min). Label and store the membrane pieces at room temperature, keeping them separate from the untreated pieces of membrane.
- Prepare Ames media
- Prepare bicarbonate-buffered Ames media and maintain the solution at room temperature under constant carbogenation (95% O2 and 5% CO2).
2. Mouse eye enucleation
- Euthanize the mouse by any available method according to institutional IACUC guidelines.
- Flip the mouse onto one side and use two fingers to gently press down around the eye socket. This will cause the eye to bulge out from the skull.
- Using curved dissection scissors, snip underneath the bulged eye to sever the optic nerve and to separate the eye from the skull.
- Scoop the eye with scissors and place it into a Petri dish filled with ice-cold Ames media.
NOTE: For downstream applications in which the tissue will be fixed after splitting, ice-cold PBS can be used instead of Ames media. - Repeat steps 2.1 - 2.4 for the remaining eye.
3. Retina dissection
- Use the custom glass transfer pipette to transfer one eye to a new Petri dish containing fresh, ice-cold Ames media.
NOTE: The wide opening of the custom transfer pipette prevents accidental squishing of the tissue, and using glass minimizes adhesion of the tissue to the walls of the pipette. However, a wide-mouth plastic transfer pipette is also acceptable if the experimenter is already proficient at using this tool. - Use forceps to stabilize the eye by pinning its extra connective tissue to the bottom of the Petri dish. Then, puncture the eye along the ora serrata line using a 25G needle to create an entry point for the Vannas scissors.
- Use Vannas scissors to cut along the ora serrata line until the cornea comes free from the rest of the eye (Supplementary Figure 1A). Remove the lens from the eyecup using forceps (Supplementary Figure 1B).
- Use the custom glass pipette to transfer the eyecup to a large volume (≥100 mL) of carbogenated Ames and repeat steps 3.1 - 3.3 with the remaining eye.
NOTE: Eyecups are placed into carbogenated Ames to maintain tissue health while the dissection is performed on the other eye. - Transfer one eyecup to a Petri dish filled with freshly carbogenated Ames.
- Using Vannas scissors, make a small snip inward from the edge of the sclera, then use two pairs of forceps to peel the sclera away from the retina (Supplementary Figure 1C). Avoid grabbing the retina with the forceps. Instead, pull apart the flaps of the sclera created by the scissor snip.
- Use the Vannas scissors to snip the optic nerve connecting the sclera and the retina (Supplementary Figure 1D), then gently pry the retina from the sclera using the scissors or forceps to isolate the retina. (Figure 1A).
NOTE: While the RPE will typically remain attached to the eyecup, no extra steps are required to remove the RPE in the event it is attached to the retina. At this point, the edges of the retina may be optionally trimmed with a scalpel to prevent curling during the flattening step (Figure 1B). - Use a scalpel to cut the retina into halves or quarters (Figure 1C), then use the custom transfer pipette to return the pieces to a large volume (≥ 100 mL) of continuously carbogenated Ames media.
NOTE: The choice of halves or quarters is subjective. Choose the best option for the desired application. - Repeat steps 3.5 - 3.8 for the remaining eye before proceeding to retina splitting.
4. Retina splitting
- Discard the Ames media from the Petri dishes and replace it with freshly carbogenated Ames.
NOTE: To maintain carbogenation throughout the remainder of the retina splitting procedure, replace the media in the Petri dish with freshly carbogenated Ames roughly every 5 min. - Using the custom transfer pipette, place a piece of retina onto a glass slide (7.5 cm x 5 cm), ganglion cell side up, then flatten it by removing the surrounding liquid with a delicate task wipe (Figure 1D). If necessary, gently pull the retinal edges with a fine tip paintbrush under a dissection microscope.
- Use forceps to lower a dry 5 mm x 5 mm piece of nitrocellulose membrane onto the retina, causing it to adhere to the ganglion cell side (Figure 1E).
NOTE: If membrane removal from live tissue is required (i.e., for electrophysiology), use a dry piece of serum-treated membrane for this step (see steps 1.1.3 - 1.1.5 for details). This reduces the strength of the adhesion to the ganglion cell layer, making it easier to remove the retina from the nitrocellulose post-split. - Flip the retina over so that the nitrocellulose is resting on the glass slide and place a dry piece of 5 mm x 5 mm membrane onto the photoreceptor side of the retina (Figure 1F).
- Touch the wetted tip of the paintbrush to the space between the two membranes and allow capillary action to suck the Ames into the sandwich (Figure 1G). This reduces the adherence of the membranes to the retina and is only necessary if the retina has been overly dried with the delicate task wipe.
NOTE: If the retina has lost its shiny appearance, it has been overly dried, and step 4.5 is necessary. - To ensure uniform adherence, apply light downward pressure to the upper membrane with a wet paintbrush (Figure 1H).
- While pinning the lower membrane to the glass with one pair of forceps, use a slow, steady motion to gently peel the upper membrane away with a second pair of forceps. This will cause the retina to split just above the OPL (Figure 1I).
- Discard the upper membrane containing the photoreceptors (Figure 1J, left). The lower membrane contains the inner retina, henceforth referred to as a split retina (Figure 1J, right).
- Immediately return the split retina to carbogenated Ames media.
NOTE: For experiments on living tissue, retinas may benefit from a 15-30 min recovery period in carbogenated Ames after splitting.
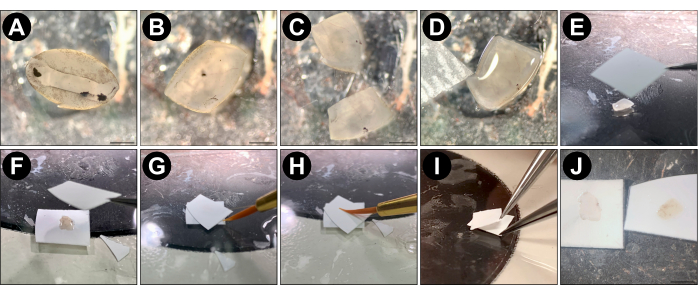
Figure 1: Split retina procedure. (A) Following enucleation and eyecup preparation in cold PBS or Ames media, isolate the mouse retina from the eyecup and replace the PBS with room temperature, carbogenated Ames media. (B) Using a scalpel, trim the edges of the retina away until there are no regions with an inward curl (optional). (C) Cut the retina into quarters or halves using a scalpel. (D) Place one piece of retina on a glass slide (ganglion cell side up) using the custom transfer pipette and remove all excess Ames using a delicate task wipe. Ensure that the semi-dry retina is lying flat on the glass before proceeding to the next step. Use an Ames-wetted paintbrush tip to gently unfold regions of the retina that are not flat. (E) Using forceps, place a pre-cut piece of dry nitrocellulose membrane (5 mm x 5 mm) onto the flattened retina. (F) Flip the piece of nitrocellulose so that the photoreceptor side of the retina is now facing up. Then place another dry piece of membrane onto the retina. (G) Touch the wet tip of the brush to the space between the two membranes and allow capillary action to suck the Ames into the sandwich. This reduces the adherence of the membranes to the retina and is only necessary if the retina was overly dried with the delicate task wipe. (H) Use a wet paintbrush tip to gently press downward onto the center of the sandwiched retina. (I) Use one pair of forceps to pin the bottom piece of membrane onto the glass slide, while using another pair of forceps to gently peel the top piece of membrane away from the bottom one. (J) The inner retina (left) remains on the bottom membrane while the photoreceptors (right) are pulled away with the top membrane. Panels (A), (B), (C), (D), and (J) were acquired using a dissection microscope; the scale bar represents approximately 1 mm; panels (E-I) were acquired with a smartphone camera without magnification. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Preparation of split retinas for immunofluorescence experiments
NOTE: The split retina will still be attached to the nitrocellulose membrane until step 5.5. Complete either step 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, or 5.4, not all four as these are for different experiments.
CAUTION: Use appropriate PPE and proceed carefully when handling paraformaldehyde (fixative).
- Preparation for flatmount immunofluorescence
- Incubate the split retina in 4% paraformaldehyde on ice for 30 min using enough solution to completely cover the retina.
- Wash the split retinas 3x in 5-10 mL of room temperature PBS. Optional pause: Split retinas may be left in PBS at 4 °C for up to 24 h.
- Preparation for immunofluorescence with vertical sections of split retina
- Incubate the split retina in 4% paraformaldehyde on ice for 30 min using enough solution to completely cover the retina.
- Wash the split retinas 3x in 5-10 mL of room temperature PBS. Optional pause: Split retinas may be left in PBS at 4 °C for up to 24 h.
- With the membrane still attached, sequentially immerse the split retina in 10%, 20%, and 30% sucrose at 4 °C for 1 h each to cryoprotect the tissue.
- Embed the cryoprotected split retinas in optimal cutting temperature (O.C.T.) compound and store them at -80 °C (up to 6 months) until cryosectioning.
- Remove the embedded split retinas from -80 °C and use a cryostat to cut sections 20 µm thick. Mount the sections onto electrostatically charged glass microscope slides, allow them to air dry, then store them at -20 °C for up to 6 months.
- Preparation for dual fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry
- Incubate the split retina in 4% paraformaldehyde on ice for 2 h using enough solution to completely cover the retina.
- Wash the split retinas 3x in 5-10 mL of room temperature PBS. Optional pause: Split retinas may be left in PBS at 4 °C for up to 24 h.
- Preparation for electrophysiology
- Prepare patch pipettes by pulling thick-walled borosilicate glass pipettes with filament using a micropipette puller. Only use pipettes with a measured resistance between 6-10 MΩ.
- Back fill the pulled pipettes with internal solution containing (in mM): 125 K-gluconate, 8 KCl, 5 HEPES, 1 MgCl2, 1 CaCl2, 0.2 EGTA, 3 ATP-Mg, and 0.5 GTP-Na.
- Removal of the split retina from the nitrocellulose membrane
- Using a hydrophobic barrier pen, prepare circular wells on a microscope slide (~1 cm in diameter) and allow them to air dry for 5-10 min.
- Place the split retinas within the prepared hydrophobic barrier pen wells and add enough PBS to completely cover them.
- Under a dissection microscope, push the bristles of a fine paintbrush under the edges of the tissue and gently lift upward. In this manner, work around the retina in a circle to lift it away from the membrane.
- Use forceps to remove the membrane from underneath the floating piece of retina.
- Carefully aspirate away the remaining PBS so that the piece of retina comes to rest on the microscope slide, ganglion cell-side down.
NOTE: The following steps are not to be performed sequentially. Choose the appropriate protocol for the desired application (i.e., immunostaining or dual fluorescence in situ hybridization [FISH] and immunohistochemistry [IHC] or electrophysiology).
6. Immunostaining
- If not yet prepared, use a hydrophobic barrier pen to create circular wells on a microscope slide (~1 cm in diameter) and allow them to air dry for 5-10 min. All incubation steps and wash steps will be performed within these pen wells.
- Incubate the split retinas or vertical split retina sections in antibody incubation solution (AIS: 3% horse serum, 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.025% NaN3 in PBS) for 30 min at room temperature.
- Incubate the split retinas or vertical split retina sections with primary antibodies diluted in AIS for 1 h at room temperature.
NOTE: Primary antibody incubation time will require optimization for different protein targets and antibodies. - Wash the tissue 3x in room temperature PBS.
- Incubate the tissue with secondary antibodies diluted in AIS for 1 h at room temperature. Wash the tissue 3x in room temperature PBS.
- If nuclear staining is desired, incubate the tissue with DAPI diluted in PBS for 30 s at room temperature. Wash the tissue 1x in room temperature PBS.
- Apply a drop of slide mounting media to each piece of tissue and mount a glass coverslip.
- Apply nail polish around the edges of coverslip to seal the sample. Store the slide at 4 °C.
7. Dual FISH and IHC
- Bake the split retinas at 40 °C for 30 min in a hybridization oven to increase adherence to the slide.
- Complete the RNAscope FISH protocol according to the manufacturer's protocol with the following exceptions and alterations:
- No antigen retrieval step is required. Use protease III with an incubation time of 18 min at room temperature.
- Perform all wash steps on the slide within the wells made by a hydrophobic barrier pen.
- Incubate the samples in primary antibody diluted (see Table of Materials) in PBS for 30 min at 40 °C in the hybridization oven. Wash the samples 3x in room temperature PBS.
- Incubate the samples in secondary antibody diluted (see Table of Materials) in PBS for 30 min at 40 °C in the hybridization oven. Wash the samples 3x in room temperature PBS.
- Incubate the samples in 1x DAPI for 30 s at room temperature. Wash the samples 1x in room temperature PBS.
- Apply a drop of anti-fade mounting media to each piece of tissue and mount a glass coverslip.
- Apply nail polish around the edges of coverslip to seal the sample. Store the slide at 4 °C.
8. Electrophysiology
- After removing the nitrocellulose membrane, transfer a split retina into the patch-clamp recording chamber and gently anchor it in place with a platinum harp.
- Throughout the experiment, continuously perfuse the split retina with Ames solution carbogenated with 95% O2 and 5% CO2. Maintain the solution between 32-34 °C.
NOTE: During the experiment, the tissue can be visualized using Dodt gradient contrast microscopy. - Under room lighting, perform whole-cell voltage-clamping to record from INL neurons.
- While recording, simulate light responses using a microcellular injection unit to apply pharmaceutical compounds, or a 470 nm LED to stimulate channelrhodopsin (ChR2).
NOTE: Light intensity can be measured using a digital optical power meter.
- While recording, simulate light responses using a microcellular injection unit to apply pharmaceutical compounds, or a 470 nm LED to stimulate channelrhodopsin (ChR2).
9. Confocal microscopy
- For confocal immunofluorescence, take images with a confocal microscope using a 40x/1.3 or 63x/1.40 oil immersion objective. Use FIJI to adjust brightness and contrast and to generate Z-projections from image stacks.
Results
Retina splitting preserves photoreceptor terminals
To confirm that retina splitting does not damage the dendrites of second order neurons in the OPL, vertical sections of split retinas were stained with antibodies against the synaptic vesicle protein synaptophysin (green), and protein kinase C alpha (PKCα; red). The intense band of synaptophysin labeling across the top of the split retina indicates that the photoreceptor synaptic terminals are retained (Figure 2). Furthermore, PKCα staining reveals normal morphology of rod bipolar cells (RBCs). No photoreceptor nuclei are visible, indicating that the retina is split between the OPL and innermost row of photoreceptor cell bodies (Figure 2).
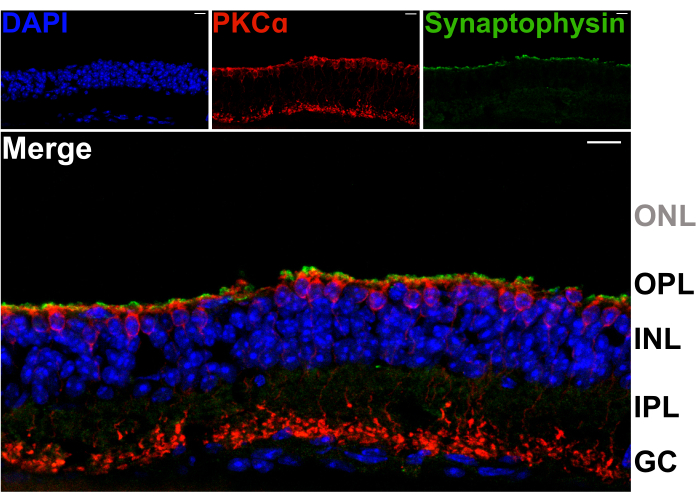
Figure 2: Split retinas retain photoreceptor terminals. Fluorescent confocal micrographs showing a vertical cross-section of a spit retina that was cryosectioned (20 µm thickness) following the splitting procedure. Each image is a maximum projection of a confocal z-stack. The section was immunolabeled with antibodies against PKCα (top center) and synaptophysin (top right) to visualize RBCs and synaptic vesicles, respectively. The merged image (bottom) shows synaptic vesicles (green), which reside in the photoreceptor terminals, just above the apical processes of the RBCs (red) in the OPL. Cell nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). No photoreceptor nuclei are visible within the ONL. Abbreviations: ONL = outer nuclear layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; GC = ganglion cells. Scale bars = 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Synapse morphology in the OPL is preserved after retina splitting
Using a mouse that expresses GFP in RBCs under the pcp2 promoter14 pre- and post-synaptic proteins in the OPL were immunolabeled to assess the integrity of this synaptic layer following a split14. Despite the shear forces occurring through the axons of the photoreceptors, splitting does not perturb the morphology of photoreceptor-BC synapses in the OPL, as normal positioning of RBC dendrites, labeled for RGS11, and photoreceptor synaptic ribbons, labeled for CtBP215 is observed (Figure 3). For each synaptic contact between rods and RBCs, RGS11 can be seen as red puncta that lie within the horseshoe shape of the synaptic ribbons (green). In a subsequent experiment, an anti-GPR179 antibody16 was used to label the post-synaptic ON-BC dendritic tips16, and an anti-PSD-95 antibody was used to label pre-synaptic rod photoreceptor terminals (Supplementary Figure 2). These results again confirm the stability of the OPL in the split retina preparation, as RBC dendrites are shown to closely associate with their pre-synaptic partner, the rod terminals.
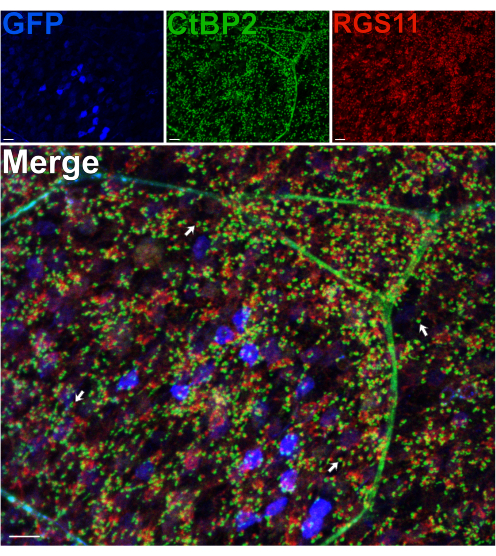
Figure 3: Synapse morphology in the OPL is preserved after retina splitting. Confocal immunofluorescence images of a split retina from a transgenic mouse expressing GFP in RBCs under the Pcp2 promoter. Levels of GFP expression (blue) vary across RBCs in the retina. Following splitting, the retina was fixed, then incubated with antibodies against CtBP2 (green) and RGS11 (red) to label photoreceptor synaptic ribbons and ON-BC dendritic tips, respectively. Each red-green pair represents a synaptic contact between a rod and an ON-BC. Scale bars = 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Retina splitting maintains RBC viability
To assess the viability of the inner-retinal neurons after a split, a membrane impermeable, near-infrared nuclear dye (MI-NIR) was used, which enables the identification of dead cells. After incubation with MI-NIR, split retinas were fixed, then labeled with anti-PKCα to identify RBCs. Confocal micrographs of the split retina reveal regional variability in cell viability across the tissue, with some regions experiencing higher rates of cell death than others. This variability may result from damage inflicted onto certain regions of the retina during the dissection, splitting, or handling procedures (Figure 4). Given that the cell bodies of RBCs reside in the outermost region of the INL, close to the site of the split, a careful evaluation of their viability was warranted. Scarce colocalization of PKCα and MI-NIR confirmed that most RBCs remain viable after retina splitting (Figure 4).
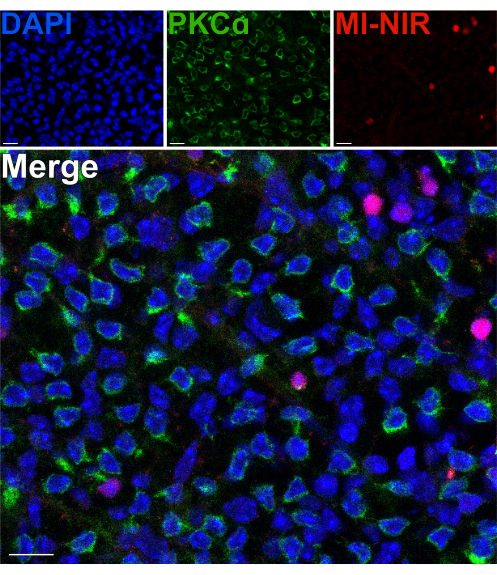
Figure 4: Rod bipolar cells are viable after retina splitting. Fluorescent confocal micrographs showing a region of a split retina in a flatmount perspective. After splitting, the live retina was incubated with MI-NIR dye (red) for 30 min at 37 °C. The retina was then fixed and immunolabeled with antibodies against PKCα to visualize RBCs. In this region of the retina, colocalization of PKCα and MI-NIR is infrequent. MI-NIR colocalizes with nuclei (blue) that do not belong to RBCs. Abbreviations: MI-NIR = membrane impermeable NIR live/dead stain. Scale bars = 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Split retinas are amenable to dual FISH and IHC
By extending the fixation time for standard IHC, split retinas can be sequentially processed by FISH and IHC to label mRNAs and proteins simultaneously17,18. Experiments confirmed that a 2 h fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde yields robust mRNA labeling while still preserving protein epitopes for antibody binding. FISH was performed on split retinas followed by IHC to visualize the expression of the GABAA receptor subunit δ (GABRD; anti-sense mRNA probes) in relation to the position of RBCs (anti-PKCα antibody) in the outer INL (Figure 5A). GABRD mRNA expression appears rare in RBCs (Figure 5A); however, the transcript is abundantly expressed by amacrine cells and ganglion cells as evidenced by the labeling pattern on transverse sections from an intact retina (Figure 5B). In the outer INL (Figure 5A), GABRD mRNA is more evenly distributed compared to the inner INL (Figure 5C) where it is concentrated in distinct cells. Antisense probes targeting other GABA receptor subunits produce distinct labeling patterns, demonstrating the specificity of the probes (data not shown).
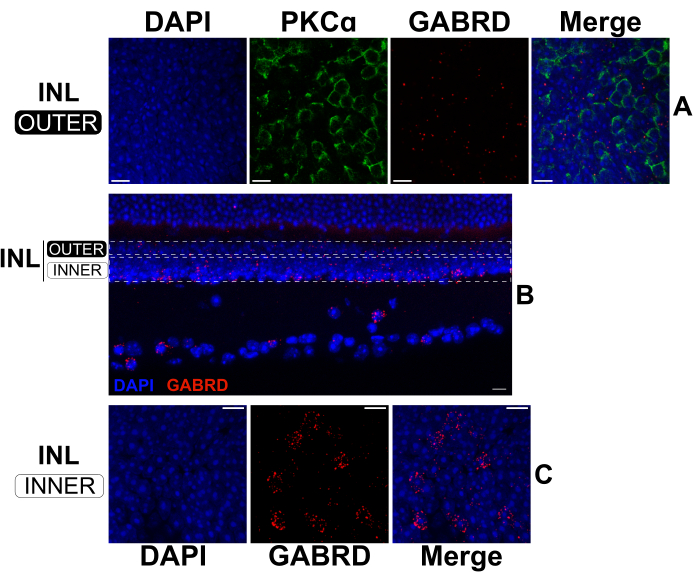
Figure 5: Dual FISH and IHC in a split retina and an intact retina. (A, C) Confocal micrographs of a flatmount split retina and (B) a vertical section from an intact retina. Images in (A) and (C) are maximum projections of optical sections in the upper and lower regions of the INL respectively. The dotted rectangles in (B) represent the approximate boundaries used to create the projections shown in (A) and (C). The split retina (A, C) was fixed for 2 h, then labeled with antisense mRNA probes against GABRD (red). Afterward, the split retina was stained with antibodies against PKCα to label RBCs (green). The PKCα channel was omitted from projections of the lower INL for clarity. The intact retina in (B) was fixed for 24 h before sectioning. Afterward, the fixed retina was labeled with antisense mRNA probes against GABRD (red). All samples were stained with DAPI (blue) for 20 s prior to coverslip mounting. Abbreviations: INL = inner nuclear layer. Scale bars= 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Split retinas are well-suited to patch-clamp electrophysiology recording from BCs and HCs
To patch a BC or HC soma in a traditional whole mount retina, the pipette must approach from either the ganglion cell side or the photoreceptor side. Both approaches require traversing several retinal layers to reach the INL, during which the pipette tip often becomes obstructed by debris. In a vibratome slice preparation, the BC and HC somas are readily accessible, but their dendritic processes may be severed, disrupting their lateral connections. In split retinas, however, the cell bodies of RBCs and HCs sit at the tissue's surface, providing greatly improved access to patch pipettes while preserving the OPL's lateral circuitry.
Figure 6 shows chemically simulated light responses recorded from BCs in a split retina. Perfused Ames medium was supplemented with L-AP4 (4 µM), a group III mGluR agonist, to simulate glutamate release from photoreceptors in darkness. The mGluR6 antagonist, CPPG (600 µM, in Ames), was puffed onto the dendrites of the patched cell (held at -60 mV) to simulate a light flash via inhibition of mGluR6. Cells responded to CPPG puffs with two types of inward currents. One type shows a transient current followed by a plateau (Figure 6A), similar to the canonical light-evoked currents recorded from RBCs in retinal slices19. The other type remains sustained throughout the puff duration (Figure 6B), resembling currents recorded from ON cone bipolar cells (ON-CBC)19.
A separate experiment was performed to target HCs, a cell type with a wide dendritic field that is often difficult to preserve in slice preparations. A mouse line expressing channel rhodopsin (ChR2) and GFP in HCs was used to facilitate easy identification under a fluorescence microscope. First, currents from HCs were recorded in response to a series of depolarization steps (-100 mV to 50 mV, step size = 15 mV) to which they responded with inward currents followed by outward currents (Figure 6C). These cells were then stimulated with a brief blue light pulse (200 ms, 470 nm) producing large, ChR2-driven inward currents in two cells (Figure 6D).
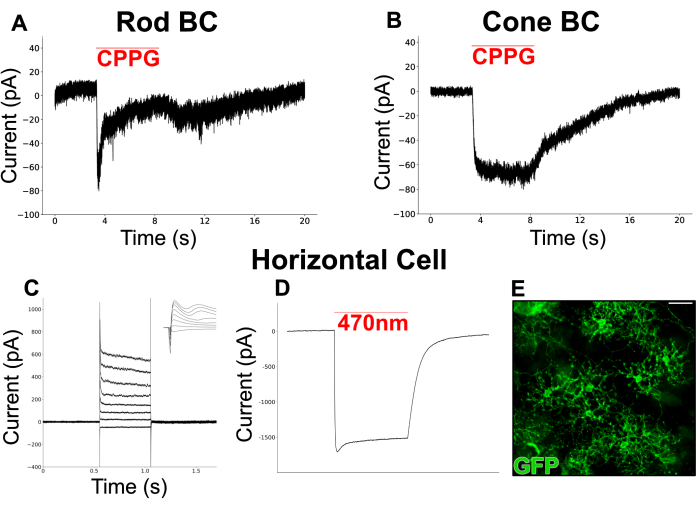
Figure 6: Patch clamp recordings from INL neurons in split retinas. (A) A putative RBC and (B) CBC were voltage-clamped at -60 mV in perfused Ames media containing L-AP4 (4 µM). Puffing CPPG (600 µM) onto the dendrites of the clamped cells invoked an inward current which was transient in the RBC but sustained in the CBC. The RBC recording in (A) is a single trace whereas the CBC recording in (B) represents the average of 3 traces. (C) A patch clamp recording from an HC in a vGATFLPo; vGlut2Cre; Ai80d mouse. The red line shows the duration of a 200 ms, 470 nm light pulse used to invoke the large, inward current through ChR2. (D) Injected current responses from an HC that was voltage clamped at -60 mV, then stepped between -70 mV and +35 mV in 15 mV intervals and returned to -60 mV. The inset shows the same traces in a 6 ms window surrounding the start of the voltage step. (E) Immunofluorescent micrograph of a flatmount split retina showing horizontal cells expressing GFP in a vGATFLPo; vGlut2Cre; Ai80d mouse. Scale bar = 20 µm. Electrophysiology data were collected at a 20 kHz sampling rate and filtered with a low-pass Bessel filter at 5 kHz. Data were then exported, and offline visualization and analysis were performed using Python 3. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Retina splitting enables rapid interrogation of INL and OPL anatomy
The retina's external limiting membrane (ELM) and ONL comprise a barrier ~90 µm thick, which impedes the diffusion of antibodies into the inner retina and creates suboptimal immunostaining conditions20,21,22. Therefore, immunolabeling targets in the OPL or INL using a conventional flatmount retina requires time-intensive staining protocols that often necessitate 48-96 h antibody incubations5,6,7,8,20,22.
Removing the photoreceptors allows for rapid antibody penetration of inner retinal neurons. As a result, labeling of inner-retina protein targets can be achieved in as little as 1 h with the use of dye-conjugated primary antibodies. Antibodies against PKCα and Calbindin-D were used to label RBCs and HCs of the INL respectively (Figure 7). Unlike traditional vertical retina sections that truncate the lateral processes of wide-field neurons, the split retina preparation enables visualization of the full dendritic arbor of wide-field cells such as HCs (Figure 6E, Figure 7).
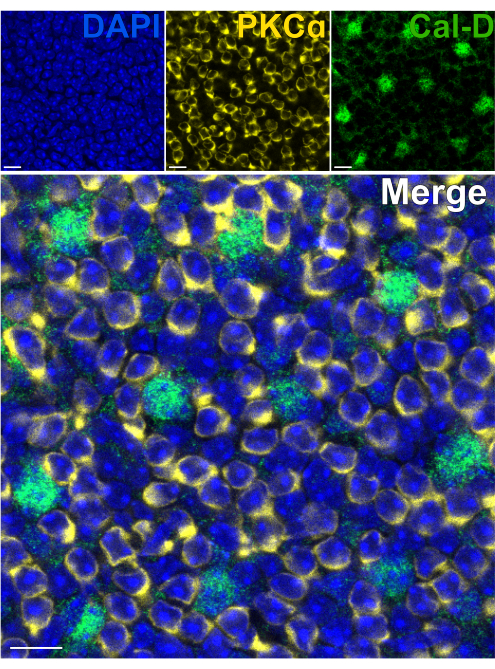
Figure 7: Rapid immunolabeling of inner retina proteins in a split retina. Confocal immunofluorescence images of a split retina from a flatmount perspective. The split retina was incubated with antibodies against PKCα (yellow) and Calbindin-D (green) for 1 h at room temperature to label ON-BCs and HCs respectively. (A) Each single channel image is an average Z-projection composed of four optical sections: DAPI, Average z10-13; Calbindin-D, Average z11-14; PKCα, Average z11-14. (B) In the merged image, the same projections are superimposed. Scale bars = 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Supplementary Figure 1: Key stages of the retina dissection. All images were taken with a smartphone camera mounted to the ocular lenses of a dissection microscope. (A) A top-down image of a mouse eye following removal of the cornea. (B) A top-down image of the mouse eyecup after the lens has been removed. (C) A small incision is made in the sclera on the mouse eyecup. Arrows indicate the two flaps of the sclera which are pulled in opposite directions by forceps to begin separating the retina from the sclera. (D) After the sclera has been partially pulled away from the retina, Vannas scissors are inserted between the sclera and the retina, and the optic nerve is severed, freeing the retina. The red dotted circle shows the optic nerve head, and the scissors demonstrate the correct cutting trajectory (insert scissors between the sclera and the retina). The isolated retina after the sclera is pried away. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary Figure 2: Characterization of pre- and post-synaptic components of the OPL in the split retina. Confocal immunofluorescence images from the OPL in a split retina. The split retina was incubated with antibodies against GPR179 and PSD95 for 1 h at room temperature to label to the dendritic tips of ON-BCs and the terminals of rod photoreceptors, respectively. The left and center images are maximum projections of several optical sections; the same projections are superimposed in the rightmost image. GPR179 puncta in the ON-BC dendritic tips are seen to associate closely with the rod photoreceptor terminals, demonstrating intact synaptic contacts within the OPL. Scale bars = 10 µm. Please click here to download this File.
Supplementary Figure 3: Troubleshooting: assessing the quality of a split retina. Fluorescent micrographs of a split retina stained with DAPI to visualize cell nuclei. Cells can be identified based on the diameter and tissue depth of the nucleus. (A) Photoreceptor nuclei are smaller, brighter, and more superficial, whereas (B) BC nuclei are larger, dimmer, and deeper. (C) A low magnification image of a region where photoreceptors were incompletely removed. The nuclei that appear in focus are from BCs, which are deeper than the photoreceptor nuclei on the edges of the image that appear out of focus. Scale bars for (A) and (B) = 20 µm. Scale bar for (C) = 50 µm. Please click here to download this File.
Discussion
After photoreceptors transduce photon absorption into neurotransmitter release, BCs and HCs are the first retinal neurons to process the visual signal23. While the importance of these neurons is well-appreciated, many of their functions are incompletely understood or unexplored altogether. Many BC and HC physiology studies would likely benefit from a flatmount retina preparation that improves access to INL neurons while preserving lateral connectivity. The development of the split retina method represents an effort to provide an easy protocol for acquiring high quality electrophysiological recordings and microscopy data from BCs and HCs in a flatmount orientation. The split retina preparation described here can be performed in about 20 min per mouse (10 min per retina) following retina isolation, without the use of specialized equipment. The method draws inspiration from existing photoreceptor removal procedures but offers significant improvements in simplicity, speed, and versatility4,10,11,12,13. Unlike previous methods for separating retinal layers, retina splitting does not require freezing, lyophilization, or repeated application of adhesives to the retina. With practice, nearly all photoreceptors can be removed in a single tear with the nitrocellulose membrane. The speed and ease of this approach allows one to minimize the time the retina spends out of carbogenated Ames, enabling high cell viability for long periods; split retinas can be maintained in carbogenated Ames media for several hours post-split. As a testament to the health of INL neurons in this preparation, a live/dead cell stain (Figure 4) and patch-clamp electrophysiology (Figure 6) confirm the viability of RBCs and HCs following a split.
The removal of the photoreceptor layer in split retinas conveys a significant advantage during immunolabeling by dramatically reducing the diffusion time for antibodies into the INL. Primary and secondary antibody labeling can be completed within 2 h, a substantial improvement to conventional flatmount staining which can take 72 h or longer depending on the target5,6,7,8,20,22. As a result, microscopy data can be acquired on the same day as tissue preparation, drastically accelerating the pace of immunofluorescence experiments. To facilitate mRNA probe annealing, FISH experiments typically recommend much longer fixation times (~24 h) than immunolabeling18. However, the experiments presented here demonstrate that a 2 h fixation still produces exceptional FISH labeling (Figure 5). Despite extending the fixation time from 30 min to 2 h, it was not necessary to perform antigen retrieval steps to obtain excellent immunolabeling, but this may vary with the antibody or antigen. The protease treatment in the FISH protocol may interfere with antibody labeling, likely due to the destruction of target epitopes. This issue was circumvented by using polyclonal antibodies that target multiple epitopes, decreasing the likelihood that epitope destruction would hinder immunolabeling. Additionally, a moderate protease treatment (ACD protease III) was used to prevent excessive epitope alteration while still providing sufficient tissue penetration.
Occasionally, the retina will instead split through the outer nuclear layer (ONL), leaving behind layers of photoreceptor somas with no INL cells visible. To prevent this, one should ensure that the retina lies completely flat on the glass, and that any residual liquid from around the retina has been removed. Pressing more firmly onto the nitrocellulose with the paintbrush may also help prevent splitting through the ONL. If the membrane becomes too wet or the retina is folded over itself, the chances of a successful split will be greatly diminished. Using DAPI to stain cell nuclei is useful for assessing the quality of the split and for determining the coverage of remaining photoreceptors. Photoreceptor nuclei are smaller, brighter, and more superficial (Supplementary Figure 3A), whereas BC nuclei are larger, dimmer, and deeper (Supplementary Figure 3B). In some cases, the plane of the tear will vary slightly across the piece of retina, resulting in patches where photoreceptors cell bodies have not been completely removed (Supplementary Figure 3C). For applications in microscopy and electrophysiology, this does not hinder the ability to collect quality data from regions where photoreceptors have been properly removed; large fields of exposed inner retina can easily be found when imaging or recording with a patch pipette. If more complete photoreceptor removal is desired, a second tear can be performed with an additional piece of nitrocellulose membrane, although 100% photoreceptor removal is not guaranteed. Caution is therefore advised when using split retinas in gene expression or proteomics studies where residual photoreceptor material could influence results. For single cell applications, this concern is unwarranted, as data from photoreceptors can be excluded from analysis.
The advantages of the split retina preparation are perhaps most salient in electrophysiological recordings of wide-field interneurons. Whereas traditional vertical slices sever the extensive processes of wide-field cells, the split retina preparation leaves the OPL and IPL intact, allowing one to capture input from wide-field cells such as HCs24, A17s25, TH ACs26, and NOS-1 ACs27 that would otherwise be overlooked in vertical slices. Therefore, interpretation of results and comparison with previous data collected from retinal slices requires careful thought. Nonetheless, in experiments using pharmacological mimics of light stimulation, these results resemble data recorded from retinal slices19. By expressing ChR2 under cell-specific promoters, one can stimulate a desired cell population while recording from BCs in the INL to investigate the desired cell's impact on the vertical information pathway. Recording directly from deeper INL neurons, such as amacrine cells, is also feasible in the split retina. While in this case the patch electrode must first travel through the more superficial INL neurons, there is considerably less tissue obstructing its path when compared to a traditional whole mount preparation.
In addition to measuring the influence of wide-field cells on other neurons, this method enables direct single-cell patch clamping from HCs, whose dendrites form an extensive gap-junction coupled network in the OPL28. Horizontal cells send critical feedback to photoreceptors which shapes the transmission of vertical information through the retina. However, since the dendritic fields of HCs are truncated in vertical slices, single cell recording data are lacking. This work presents anatomically and physiologically intact HCs from which ChR2-evoked currents are recorded in a triple transgenic mouse line (Figure 6 C-E). Outside of ChR2 stimulation, the split retina can be used to study endogenous HC currents and gap junction coupling28. While the split retina provides a convenient model for studying synaptic connectivity and neuronal activity induced by chemical application or ChR2 stimulation, the lack of photoreceptors precludes any direct exploration of natural light responses or light adaptation mechanisms.
In situ imaging in the retina has made admirable progress in recent years. However, the majority of imaging studies are limited to the ganglion cell layer in whole mount retina preparations29. The authors envision that the absence of photoreceptors in the split retina will make it an ideal model for live calcium imaging in the OPL and INL. Beyond calcium imaging, this model has great potential for use with genetically encoded biosensors such as iGluSnFR30,31, iGABASnFR32, and pHluorin33. Combined with the split retina preparation, these powerful tools may offer an efficient approach to exploring the synaptic interactions and biophysical properties of BCs and HCs that contribute to light processing in the retina.
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the following NIH grants: NIH grant R01EY031596 (to C.M.); NIH grant R01EY029985 (to C.M.); NIH grant P30EY010572 (to C.M.); NIH grant R01EY032564 (to B.S.). We thank Tammie Haley for her technical support in preparing retina sections, and Dr. Charles Allen for generously contributing the mRNA FISH probes used in this work.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| #1.5 glass coverslips | Fisherbrand | 12544E | |
| 2 pairs of Dumont #5 forceps | Ted Pella | 38125 | |
| 25 gauge needle | Becton Dickenson | 305122 | |
| 470 nm LED | THORLABS | M470L2 | |
| 5-306 curved scissors | Miltex | 5-306 | |
| 9" disposable pasteur pipetes | Fisherbrand | 13-678-20D | for constructing custom transfer pipette |
| Ai80d mouse | Jackson Laboratories | 25109 | RRID: IMSR_JAX:025109 |
| Ames Medium w/L-Glutamate | US Biological | A1372-25 | |
| amplifier control software | Molecular Devices | Clampex 10.3 software | |
| anti-calbindin D28K antibody | Invitrogen | PA-5 85669 | RRID: AB_2792808, host species = rabbit; 1:100 dilution |
| anti-CtBP2 antibody | BD Biosciences | 612044 | RRID: AB_399431, host species = mouse; 1:5000 dilution |
| anti-GPR179 antibody | NA | NA | gift from Kirill Martemyanov; Scripps Research Institute, Jupiter, FL; host species = sheep; 1:1000 dilution |
| anti-PKC alpha antibody | Sigma-Aldrich | P4334 | RRID: AB_477345, host species = rabbit; 1:5000 dilution |
| anti-PKC alpha antibody | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc8393 AF594 | RRID: AB_628142, host species = mouse; 1:1000 dilution |
| anti-PSD95 antibody | BD Transduction Laboratories | 610495 | RRID: AB_397862, host species = mouse; 1:1000 dilution |
| anti-RGS11 antibody | NA | NA | gift from Ted Wensel; Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; host species = rabbit; between 1:1000 and 1:5000 dilution |
| anti-Synaptophysin P38 antibody | Sigma | S-S5768 | RRID: AB_477523, host species = mouse; 1:1000 dilution |
| Aquamount mounting media | Epredia | 13800 | slide mounting media |
| C57BL/6J mouse | Jackson Laboratories | 000664 | RRID: IMSR_JAX:000664 |
| carbogen tank | Matheson | NA | 95% O2 and 5% CO2 |
| custom transfer pipette | custom build | NA | Instructions: use scissors to cut off the tip of a plasitc transfer pipette at the point it begins to taper. Use pliers to safely break off the last 2-3 inches of a glass pasteur pipette. Fit the narrow end of the glass pasteur pipette into the wide tip of the plastic transfer pipete. Wrap parafilm around the joint of the two pieces to enhance the seal. |
| Digitical optical power meter | THORLABS | PM100D | |
| dissection microscope | Zeiss | Stemi 2000 | |
| electrophysiology amplifier | Molecular Devices | Axopatch 200B | |
| electrophysiology microscope | Olympus | OLYMPUS, BX50WI | Dodt gradient contrast microscopy |
| Fluoromount-G | SouthernBiotech | 0100-01 | |
| HC PL APO CS2 40x/1.3 | Leica | 506358 | |
| HC PL APO CS2 63x/1.40 | Leica | 15506350 | |
| Hybridization oven | Robbins Scientific | Model 1000 | for RNAscope protocol only |
| Immedge hydrophobic barrier pen | Vector Laboratories | H-4000 | |
| isoflurane | Piramal Critical Care | 66794-017-25 | |
| Kimwipe (delicate task wipe) | Kimtech Science | 34155 | |
| Leica HC PL APO CS2 40x/1.3 oil immersion objective | Leica | 506358 | |
| Leica HC PL APO CS2 63x/1.40 oil immersion objective | Leica | 15506350 | |
| Leica TCS SP8 X confocal microscope | Leica | discontinued | |
| medium 15 mm petri dish | Corning | 25060-60 | eyes are kept here during retina dissection |
| Merit 97-275 steel scissors | Merit | 97-275 | |
| Micropipette Puller | Sutter Instrument | p-97 | |
| Mm-Gabrd-C2 mRNA probe | ACD | 459481-C2 | |
| mouse euthanasia chamber | NA | NA | custom build; glass petri dish covering a small glass jar. |
| nitrocellulose membrane filters | GE Healthcare Life Sciences; Whatman | 7184-005 | 0.45 µm pore size |
| Picospritzer | General Valve Corporation | Picospritzer II | referred to in the text as microcellular injection unit |
| plastic transfer pipets | Fisherbrand | 13-711-7M | for constructing custom transfer pipette |
| Plastic tubing | Tygon | R-603 | for connection to carbogen tank |
| platinum harp | custom build | NA | for anchoring split retinas within the electrophysiology recording chamber. |
| size 0 paint brush | generic | NA | for flattening retina during splitting. |
| SlowFade Gold antifade reagent | Molecular Probes | S36937 | referred to in the text as anti-fade mounting media |
| small 10 mm petri dish | Falcon | 353001 | eyes are placed here following enucleation |
| small glass pane (7.5 cm x 5 cm) | generic | NA | isolatd retina pieces are placed onto this for the splitting procedure |
| Superfrost plus microscope slides | Fisherbrand | 12-550-15 | electrostatically-charged glass microscope slides |
| Thick-walled borosilicate glass pipettes with filament | Sutter Instrument | BF150-86-10HP | |
| Vannas Scissors; straight | Titan Medical | TMS121 | not brand specific; any comparable scissors will work |
| vGATFLPo mouse | Jackson Laboratories | 29591 | RRID: IMSR_JAX:029591 |
| vGlut2Cre mouse | Jackson Laboratories | 28863, 016963 | RRID: IMSR_JAX:028863, RRID: IMSR_JAX:016963 |
| Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit | BioLegend | 423105 | referred to in the text as MI-NIR |
References
- Morgans, C. W. Neurotransmitter release at ribbon synapses in the retina. Immunology & Cell Biology. 78 (4), 442-446 (2000).
- Euler, T., Haverkamp, S., Schubert, T., Baden, T. Retinal bipolar cells: elementary building blocks of vision. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 15 (8), 507-519 (2014).
- Barnes, S., Grove, J. C. R., McHugh, C. F., Hirano, A. A., Brecha, N. C. Horizontal Cell Feedback to Cone Photoreceptors in Mammalian Retina: Novel Insights From the GABA-pH Hybrid Model. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 14, (2020).
- Walston, S. T., Chang, Y. C., Weiland, J. D., Chow, R. H. Method to remove photoreceptors from whole mount retina in vitro. Journal of Neurophysiology. 118 (5), 2763-2769 (2017).
- Stefanov, A., Novelli, E., Strettoi, E. Inner retinal preservation in the photoinducible I307N rhodopsin mutant mouse, a model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 528 (9), 1502-1522 (2020).
- Matsuoka, R. L., Nguyen-Ba-Charvet, K. T., Parray, A., Badea, T. C., Chédotal, A., Kolodkin, A. L. Transmembrane semaphorin signaling controls laminar stratification in the mammalian retina. Nature. 470 (7333), 259-263 (2011).
- Matsuoka, R. L., et al. Guidance-Cue Control of Horizontal Cell Morphology, Lamination, and Synapse Formation in the Mammalian Outer Retina. Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (20), 6859-6868 (2012).
- Wässle, H., Puller, C., Müller, F., Haverkamp, S. Cone Contacts, Mosaics, and Territories of Bipolar Cells in the Mouse Retina. Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (1), 106-117 (2009).
- Thoreson, W. B., Dacey, D. M. Diverse Cell Types, Circuits, and Mechanisms for Color Vision in the Vertebrate Retina. Physiological Reviews. 99 (3), 1527-1573 (2019).
- Guido, M. E., et al. A simple method to obtain retinal cell preparations highly enriched in specific cell types. Suitability for lipid metabolism studies. Brain Research Protocols. 4 (2), 147-155 (1999).
- Rose, K., Walston, S. T., Chen, J. Separation of photoreceptor cell compartments in mouse retina for protein analysis. Molecular Neurodegeneration. 12 (1), 28(2017).
- Todorova, V., et al. Retinal Layer Separation (ReLayS) method enables the molecular analysis of photoreceptor segments and cell bodies, as well as the inner retina. Scientific Reports. 12 (1), 20195(2022).
- Shiosaka, S., Kiyama, H., Tohyama, M. A simple method for the separation of retinal sublayers from the entire retina with special reference to application for cell culture. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 10 (3), 229-235 (1984).
- Ivanova, E., Hwang, G. S., Pan, Z. H. Characterization of transgenic mouse lines expressing Cre-recombinase in the retina. Neuroscience. 165 (1), 233-243 (2010).
- Sarria, I., Orlandi, C., McCall, M. A., Gregg, R. G., Martemyanov, K. A. Intermolecular Interaction between Anchoring Subunits Specify Subcellular Targeting and Function of RGS Proteins in Retina ON-Bipolar Neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience. 36 (10), 2915-2925 (2016).
- Orlandi, C., Cao, Y., Martemyanov, K. A. Orphan Receptor GPR179 Forms Macromolecular Complexes With Components of Metabotropic Signaling Cascade in Retina ON-Bipolar Neurons. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 54 (10), 7153-7161 (2013).
- Dikshit, A., Zong, H., Anderson, C., Zhang, B., Ma, X. -J. Simultaneous Visualization of RNA and Protein Expression in Tissue Using a Combined RNAscopeTM In Situ Hybridization and Immunofluorescence Protocol. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2148, Clifton, N.J. 301-312 (2020).
- Wang, F., et al. RNAscope. The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics. 14 (1), 22-29 (2012).
- Morgans, C. W., et al. TRPM1 is required for the depolarizing light response in retinal ON-bipolar cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (45), 19174-19178 (2009).
- Alessio, E., Zhang, D. Q. Immunostaining of whole-mount retinas with the CLARITY tissue clearing method. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 61 (7), 5054(2020).
- Ferguson, L. R., Dominguez, J. M., Balaiya, S., Grover, S., Chalam, K. V. Retinal Thickness Normative Data in Wild-Type Mice Using Customized Miniature SD-OCT. PLoS ONE. 8 (6), e67265(2013).
- Ivanova, E., Toychiev, A. H., Yee, C. W., Sagdullaev, B. T. Optimized Protocol for Retinal Wholemount Preparation for Imaging and Immunohistochemistry. Journal of Visualized Experiments JoVE. (82), e51018(2013).
- Kolb, H. Neurotransmitters in the Retina. Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System. , University of Utah Health Sciences Center. (1995).
- Chaya, T., et al. Versatile functional roles of horizontal cells in the retinal circuit. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 5540(2017).
- Egger, V., Diamond, J. S. A17 Amacrine Cells and Olfactory Granule Cells: Parallel Processors of Early Sensory Information. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 14, 600537(2020).
- Dacey, D. M. The dopaminergic amacrine cell. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 301 (3), 461-489 (1990).
- Park, S. J., et al. Connectomic analysis reveals an interneuron with an integral role in the retinal circuit for night vision. eLife. 9, 56077(2020).
- Janssen-Bienhold, U., et al. Connexin57 is expressed in dendro-dendritic and axo-axonal gap junctions of mouse horizontal cells and its distribution is modulated by light. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 513 (4), 363-374 (2009).
- Jain, V., et al. The functional organization of excitation and inhibition in the dendrites of mouse direction-selective ganglion cells. eLife. 9, 52949(2020).
- Marvin, J. S., et al. Stability, affinity, and chromatic variants of the glutamate sensor iGluSnFR. Nature Methods. 15 (11), 936-939 (2018).
- Strauss, S., et al. Center-surround interactions underlie bipolar cell motion sensitivity in the mouse retina. Nature Communications. 13 (1), 5574(2022).
- Marvin, J. S., et al. A genetically encoded fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of GABA. Nature Methods. 16 (8), 763-770 (2019).
- Beckwith-Cohen, B., Holzhausen, L. C., Wang, T. M., Rajappa, R., Kramer, R. H. Localizing Proton-Mediated Inhibitory Feedback at the Retinal Horizontal Cell-Cone Synapse with Genetically-Encoded pH Probes. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 39 (4), 651-662 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved