A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Quantifying Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in a Tumor Spheroid Model: Application for Drug Discovery
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a method to identify compounds that modulate the ADCC mechanism, an important cancer cell-killing mechanism of antitumor antibodies. The cytotoxic effect of NK cells is measured in breast cancer cell spheroids in the presence of Trastuzumab. Image analysis identifies live and dead killer and target cells in spheroids.
Abstract
Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapy targeting tumor antigens is now a mainstay of cancer treatment. One of the clinically relevant mechanisms of action of the antibodies is antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), where the antibody binds to the cancer cells and engages the cellular component of the immune system, e.g., natural killer (NK) cells, to kill the tumor cells. The effectiveness of these therapies could be improved by identifying adjuvant compounds that increase the sensitivity of the cancer cells or the potency of the immune cells. In addition, undiscovered drug interactions in cancer patients co-medicated for previous conditions or cancer-associated symptoms may determine the success of the antibody therapy; therefore, such unwanted drug interactions need to be eliminated. With these goals in mind, we created a cancer ADCC model and describe here a simple protocol to find ADCC-modulating drugs. Since 3D models such as cancer cell spheroids are superior to 2D cultures in predicting in vivo responses of tumors to anticancer therapies, spheroid co-cultures of EGFP-expressing HER2+ JIMT-1 breast cancer cells and the NK92.CD16 cell lines were set up and induced with Trastuzumab, a monoclonal antibody clinically approved against HER2-positive breast cancer. JIMT-1 spheroids were allowed to form in cell-repellent U-bottom 96-well plates. On day 3, NK cells and Trastuzumab were added. The spheroids were then stained with Annexin V-Alexa 647 to measure apoptotic cell death, which was quantitated in the peripheral zone of the spheroids with an automated microscope. The applicability of our assay to identify ADCC-modulating molecules is demonstrated by showing that Sunitinib, a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved by the FDA against metastatic cancer, almost completely abolishes ADCC. The generation of the spheroids and image acquisition and analysis pipelines are compatible with high-throughput screening for ADCC-modulating compounds in cancer cell spheroids.
Introduction
Multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS) are widely used three-dimensional (3D) models that form due to the tendency of adherent cells to aggregate and represent an important tool for gaining mechanistic insight into cancer cell biology. They can be generated from a broad range of cell types by numerous techniques, such as liquid-based and scaffold-based 3D cultures1. Their main advantage over monolayer 2D models is that they recapitulate the main features of in vivo tumors, namely structural organization and hypoxia, by mimicking the biological behavior of tumor cells, especially the mechanisms leading to therapeutic escape and drug resistance2. Thus, since MCTS can improve the predictability of toxicity and drug sensitivity, they are widely used to study cancers in 3D and could enhance the development of effective drugs for different types of cancer3.
To study any disease, there is a critical need for relevant and convenient models. Setting up models for cancer immunology studies is challenging because the immune system consists of multiple cell types. Each cell type has several subtypes and a broad spectrum of activation states. These different immune cell types interact with cancer cells and other tumor components, ultimately influencing the outcome of the disease. 2D in vitro cell culture methods fail to recapitulate these complex cellular interactions, as they lack translatability and are unable to predict the action of a drug at the system level (e.g., in tissues)4,5. Moreover, mouse models also have severe limitations due to the fundamental differences between the human and murine immune systems. 3D culture systems can, therefore, fill the current gaps in available models, providing an alternative method and improving our understanding of cancer immunology6. Specifically, spheroid models might be used for testing immunotherapies, mainly to assess the efficiency of drug screening and therapeutic antibodies for enhancing immune cell infiltration and anti-tumoral effects against the spheroid targets7. Furthermore, the potential of MCTS composed of cells in different metabolic and proliferative states to study the interactions between stroma cells (e.g., lymphocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts) and cancer cells and for the development of new anticancer strategies has been amply demonstrated8. Hence, there is a vital need to corroborate predictive and accurate platforms in order to boost the drug-testing process, taking into account the pathophysiology of the tumor microenvironment.
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequent cancer diagnosed worldwide in women. The clinical classification of this heterogeneous disease is based on the presence of transmembrane receptors e.g., estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PR) receptors (collectively called hormone receptors, HR) along with the overexpression or amplification of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein/oncogene. Based on the immunohistochemical expression of these receptors, four subtypes are commonly recognized: luminal A (HR+/HER2-), luminal B (HR+/HER2+), HER2-positive (HR-/HER2+) and triple-negative breast cancer (HR-/HER2-). The HER2+ group constitutes 10-15% of BC cases and is characterized by high HER2 expression with absence of ER and PR, having a worse prognosis compared to luminal tumors, and requiring specific drugs directed against the HER2/neu protein9.
BC development is a multi-step process, and an early diagnosis is essential for a successful treatment of the disease10. However, despite recently emerged personalized BC treatment options (e.g., endocrine and anti-HER2 antibody therapies), BC continues to challenge oncologists. Just like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, these personalized therapies can also have severe adverse effects and patients can develop resistance to these agents, making it a long-term challenge to determine the best strategy11,12. Hence, improved understanding of the interplay between the tumor and its microenvironment is essential and expected to provide new directions for the development of novel treatments that are taking into account the specificities of the different BC subtypes13. A new wave of immunotherapies, such as antibody drug conjugates, adoptive T-cell therapies, vaccines and novel HER2-directed monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are being studied in a broad population of patients with HER2-expressing tumors14.
Trastuzumab, for example, represents an efficient treatment modality for HER2+ BC. As part of its mode of action, Trastuzumab mediates fragment crystallizable gamma receptor (FcγR)-dependent activities. FcγRs are distinguished by their affinity for the Fc fragment and the immune response they initiate. Activating FcγRIIIa (CD16A) on natural killer (NK) cells is crucial for mediating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), while triggering FcγRIIa (CD32A) and FcγRIIIa on macrophages induces antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP)15. Studies on animal models showed that mice lacking FcγRI (CD64) and FcγRIII (CD16) receptors were unable to initiate protective immune responses against tumor-specific antigens, revealing that ADCC is likely a major mechanism of action for the mAb Trastuzumab16.
Since NK cells resort to tumor cell-bound Abs for cancer cell killing by ADCC, expression of Fc receptors is critical for an efficient treatment with Trastuzumab17 (Figure 1). Moreover, their action is efficiently balanced by a stimulation of activating and inhibitory receptors, e.g., Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like (KIR) receptors18.
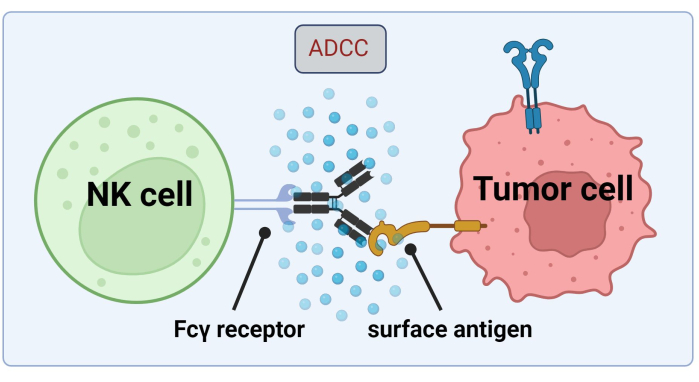
Figure 1. Mechanism of ADCC in the context of an antitumor response. The Fcγ receptor of a natural killer (NK) cell recognizes the Fc region of an antibody, which had previously bound to a surface antigen on a cancer cell. This immunological synapse leads to the degranulation of the NK cell which releases cytotoxic mediators such as granzymes and perforin. These molecules contribute to pore formation in the cell membrane and activate apoptotic pathways causing programmed cell death of the target cell (image created with Biorender.com). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Immunotherapy development for HER2+ BC represents an evolving field. In this case, one should consider interactions between various components of the immune system. Furthermore, previous publications have extensively tested combination therapies involving all types of traditional, immune or cell therapies to identify synergizing combinations19.
Several 3D models of HER2+ BC have previously been used for drug discovery. For instance, Balalaeva et al. used SKBR-3 spheroids overexpressing HER2 to assess the cytotoxicity of the HER2-targeted immunotoxin 4D5scFv-PE4020. In another study, a 3D Matrigel-based HER2+ BC culture system was established to measure cell growth in response to Trastuzumab and endocrine agents21. These studies highlight the importance of tumor spheroid models of HER2 overexpressing cancer cells in representing an effective strategy to clinically improve therapeutic responses22.
Our group previously identified Sunitinib, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, as an inhibitor of Trastuzumab-dependent ADCC in JIMT-1 HER2+ BC cells in a 2D culture assay. The study revealed that Sunitinib induces autophagy and impairs NK cells killing function, downregulating HER2 expression and enhancing surface attachment of JIMT-1 cells17.
Here we established a novel 3D, spheroid ADCC model (NK.92.CD16+Trastuzumab+JIMT-1-EGFP cancer cells) to be used for high-throughput screening applications and, in order to validate the above-mentioned findings, Sunitinib was used as a model compound. First, we generated EGFP expressing JIMT-1 cells17 and grew spheroids from these cells. ADCC was induced by NK cells together with Trastuzumab, and spheroids were kept in culture in the presence or absence of test compounds for 24 h (Figure 2). Quantification of ADCC is based on the detection of apoptotic cancer cell death (Annexin V staining) using a High-Content Analysis system.
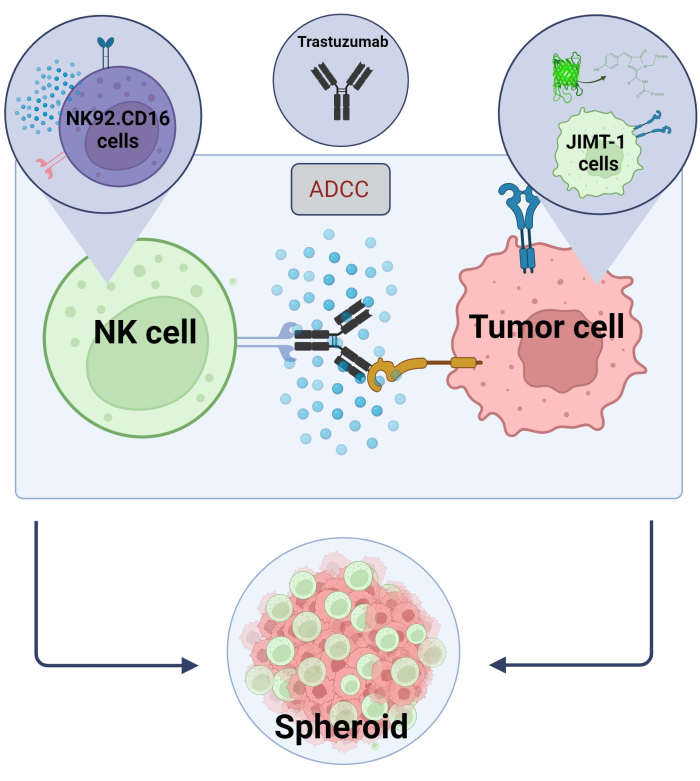
Figure 2. ADCC in a 3D spheroid co-culture system. Our experimental settings are based on a 3D spheroid system that can more accurately model the in vivo microenvironment compared to 2D models. JIMT-1 EGFP breast cancer cells were seeded on a concave cell repellent bottom to form a round-shaped cellular cluster, called spheroid. ADCC was then initiated by adding NK92.CD16 natural killer cells (E:T ratio = 20:1) and an anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody, Trastuzumab. The experimental model has proved efficient and easily applicable for the identification of ADCC modifying test compounds (image created with Biorender.com). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
We demonstrated that acquiring data in this manner can be done in real time and is statistically robust for the use in high-content screening in cancer drug discovery. Importantly, this model allows for an extended validation of a larger set of compounds, and it can be applied to several assays of interest.
Protocol
1. Setting up the JIMT-1-enhanced fluorescent protein (EGFP) spheroid model
- To form a U-shaped cell-repellent bottom, coat the 96-well plate with 0.5% agarose-PBS solution (30 µL/well). Incubate the plate at room temperature for approximately 30-45 min.
- Wash the JIMT-1-EGFP cells twice with 2 mL of sterile PBS (generation of JIMT1-EGFP cell line was reported in a previous publication17). Use T25 tissue culture flasks and JIMT-1 media (DMEM/F-12 medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 0.3 U/mL insulin (100 IU/mL, Humulin R), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin) for the cell culture.
- Add 2 mL of trypsin-EDTA to the flask and incubate it for 10 min in a CO2 incubator.
- Tap the flask to check if JIMT-1 cells detached after the incubation time.
- Use 2 mL of JIMT-1 medium to stop the digestion and collect the cell suspension into a 15 mL tube.
- Count the cells in a Bürker chamber with 0.4% trypan blue (80 µL of the dye + 20 µL of the cell suspension) and adjust the cell number to 20,000 cells/mL.
- Pipette 100 µL of the cell suspension (2000 cells/well) to each well of the 96-well plate (pre-coated with 0.5% agarose-PBS solution as indicated in 1.1).
- Allow cells to clump together during a 3-day incubation time at 37 °C in a CO2 incubator.
- Regularly check the size and shape of spheroids with an inverted microscope.
2. Coating of the HCS plate
NOTE: To prevent the attachment of JIMT-1-EGFP spheroids to the glass surface of the plate, coating the High-Content Screening (HCS) plate is crucial (otherwise high-content analysis would not be possible).
- On day 3 after induction of spheroids, coat the 96-well high-content screening plate with Pluronic-F127 (0.5% in DMSO, 50 µL/well) and incubate the plate for 45 min at room temperature.
- Aspirate the coating solution and wash the wells twice with DMEM/F-12-serum free medium (100 µL/well).
3. Transfer of spheroids to the HCS plate
- Using a 1 mL pipette, transfer the spheroids in triplicates to the glass bottom 96-well HCS plate.
4. Pre-treatment of JIMT-1 EGFP spheroids with test compounds
- Add the test compound (e.g., Sunitinib diluted in DMSO at a concentration of 40 µM) by pipetting 10 µL/well and add 10 µL of fresh JIMT-1 medium to the control (CTL) wells.
- Incubate the plate for 1 h in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C.
5. Induction of ADCC by adding the effector cells
NOTE: CD16.176V.NK92 cells (hereinafter referred to as NK cells) were cultured in α-MEM supplemented with 20% FBS, 1% MEM-NEAA, 1% Na-pyruvate, 1% glutamine, 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 100 IU/mL of IL-2.
- Collect the NK cells in the flask into a 15 mL tube. Count the cells with trypan blue (80 µL of the dye + 20 µL of the cell suspension) and adjust the cell density to 20:1 effector-to-target (E:T) ratio (40,000 NK cells/well).
- Stain the NK cells with 10 µM Cell Tracker Blue (CTB, 1 µL in 1 mL of α-MEM NK medium) and place them into a CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Centrifuge the NK cells at 150 x g for 3 min at room temperature twice to wash the excess of the dye with 1 mL of α-MEM medium.
- Resuspend the NK cell pellet in 1 mL of fresh JIMT-1 medium.
- Add the stained NK cells along with the anti-HER2 antibody (Ab) (Trastuzumab, dissolved in sterile distilled H2O) to the target JIMT-1 spheroids by pipetting 55 µL/well of CTB-stained NK cells and 55 µL/well of 10 µg/mL Ab in JIMT-1 medium (total volume of treatment added for the ADCC is 110 µL/well and the final Sunitinib concentration is 20 µM).
NOTE: For the selection of Ab concentration and E:T ratio, we relied on our previous publication17. Preliminary experiments were performed with different E:T ratios and concentrations of Trastuzumab to assess which was the most effective in inducing ADCC in spheroids (Supplementary Figure S1). - Add 110 µL/well of fresh JIMT-1 medium to control (CTL) wells.
- Incubate the plate for 24 h in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C.
NOTE: As NK92 cells are known to exert non-specific cytotoxic functions, for control use JIMT-1 cells co-incubated with both NK cells alone and with an isotype control or a F(ab')2 Ab. Here F(ab')2-Trastuzumab (TR-F(ab')2) was used as a negative CTL. TR-F(ab')2 fragment was prepared as reported by Tóth et al.19 and added in the same volume as Trastuzumab along with NK cells as described in 5.5. Concentration was adjusted to 6.6 µg/mL corresponding to an equimolar concentration with Trastuzumab23.
6. Annexin V-647 staining of spheroids
- To measure apoptotic cell death, stain the spheroids with Annexin V-Alexa Fluor 647 conjugate for 1 h in JIMT-1 medium (1:100) by pipetting 50 µL/well.
7. Imaging
NOTE: The plate is imaged at 24 h after the addition of the NK effector cells to the target cells. For imaging, a High-Content Analyzer and an image analysis software are used.
- Select the type of microplate from the list of plates using the Plate Type option. Use 96-well High-Content Screening (HCS) plate.
- Select Two Peak autofocus as the assay is carried out in plates with 10x objective with 0.3 numerical aperture (NA), using the Autofocus and Objective options, respectively. Choose confocal mode with the Opt. Mode option and apply Binning 2 using the Binning option.
- For imaging spheroids, select the appropriate channels using the Channel Selection option. To detect the EGFP-transduced JIMT-1 cells choose EGFP (integration time 200 ms, laser power 50%, stack height 2.0 µm; ex: 488 nm em: 500-550 nm), and to detect apoptotic cells use Alexa 647 (integration time 100 ms, laser power 50%, stack height 10.0 µm; ex: 640 nm em: 650-760 nm). To visualize the NK cells within the spheroids, choose the following channel: DAPI (integration time 100 ms, laser power 50%, stack height 2.0 µm; ex: 405 nm em: 435-480 nm).
- In Layout Selection option, select Z-stacks since cells in the spheroids tend to be on different focal planes of the microscope. 10 planes (with distance of 10 µm) are sufficient to cover the whole spheroid region. Set the values of the first plane and last plane at 0 µm and 90 µm, respectively.
NOTE: Before starting the measurement, sample images can be taken with the snapshot function in order to check the correct settings. - Set the number of wells and fields for imaging using the Define Layout option.
8. High-content analysis (HCA)
NOTE: Analyze the images with the Harmony software or export images for analysis using a preferred third-party software. For the analysis of ADCC efficiency, the fluorescence intensity of Annexin V 647 is measured. Target cells killed by ADCC appear in the peripheral area of the spheroids. Therefore, the Annexin V positive cells are measured in this spheroid "ring". In order to validate this method, analyses were performed with different parameters to assess which was the most reliable and producing the best results (Supplementary Figure S2). An ADCC well is shown in the video in order to demonstrate step-by-step the image analysis process.
- Identify the spheroids by the EGFP fluorescence of JIMT-1 cells using Find Texture Regions option and filter them out by size (> 25,000 µm2).
- Remove border objects by Select Population option.
- Since Annexin V positive (apoptotic) cells appear on the periphery of spheroids, measure Annexin intensity in this apoptotic 'Ring', selected by the Select Region option (outer border -90%) to determine apoptotic cell death.
- Express Annexin V intensity values as mean intensity.
Results
EGFP expressing JIMT-1 cells were generated, and spheroids were grown from these cells. Sunitinib was used as a test compound as it was previously shown to affect the course of ADCC17. Spheroids were allowed to clump for 72 h. On day 3, 10 µg/mL of Trastuzumab (or equimolar 6.6 µg/mL TR-F(ab')219) and NK cells (20:1) were added to the spheroids in the presence or the absence of 20 µM Sunitinib (1 h pre-treatment), for a total time of 24 h. JIMT...
Discussion
Despite significant improvements in treating BC over the past several decades, patients still regularly develop medication resistance or experience negative side effects24. The high morbidity and mortality linked to BC demand a continuing investigation into the underlying molecular mechanisms, just as robust screening platforms to identify new molecules actionable for therapeutic development25. These strategies require cell culture-based translational assays. 3D tumor cultu...
Disclosures
Authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Acknowledgements
LV received funding from National Research, Development and Innovation Office grants GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00010 TUMORDNS", GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00048-STAYALIVE, OTKA K132193 and K147482. This project has received funding from the HUN-REN Hungarian Research Network. CD16.176V.NK-92 cells were obtained from Dr. Kerry S. Campbell (Fox Chase Center, Philadelphia, PA, on behalf of Brink Biologics, lnc. San Diego, CA), are protected by patents worldwide, and were licensed by Nantkwest, lnc. (www.nantkwest.com). Authors are thankful to György Vereb and Árpád Szöőr for their help with the use of the NK-92 cell line and the TR-F(ab’)2, and for technical advice.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 96-well glass bottom Cell Carrier Ultra microplates | PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA | LLC 6055302 | for spheroids measurements |
| 96-well tissue culture plates | TPP | 92096 | for cell seeding |
| α-MEM medium | Sigma | M8042 | in NK medium |
| Agarose | Sigma | A9539 | for spheroids seeding |
| Annexin V-Alexa Fluo 647 conjugate | Invitrogen-ThermoFisher Scientific | A23204 | for apoptosis measurement with HCS |
| CD16.176 V.NK-92 cells | Dr. Kerry S. Campbell (the Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, PA on behalf of Brink Biologics, Inc. San Diego, CA) | ATCC CRL-2407 | for cell culture |
| Cell Tracker Blue | Invitrogen-Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | C2110 | for staining of NK cells |
| DMEM/F-12 medium | Sigma | D8437 | in JIMT1-EGFP medium |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma | D8418 | for coating HCS plate before transfering the spheroids |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Biosera | FB-1090/500 | JIMT-1-EGFP and NK medium |
| Glutamine | Gibco | 35,050–061 | in NK medium |
| GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 | GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA | for statistical analysis | |
| Harmony software | PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA | for HCA | |
| IL-2 | Proleukin, Novartis Hungária Kft., Budapest, Hungary | PHC0026 | in NK medium |
| Insulin (Humulin R) | Eli Lilly | HI0219 | JIMT-1-EGFP medium |
| JIMT-1 breast cancer cells | for cell culture | ||
| MEM Non-essential Amino Acids (MEM-NEAA) | Gibco | 11,140–050 | in NK medium |
| Na-pyruvate | Lonza | BE13-115E | in NK medium |
| Opera Phenix High-Content Analysis equipment | PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA | HH14001000 | for HCA |
| PBS (Posphate buffered saline) | Lonza | BE17-517Q | for washing the cells |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Biosera | LM-A4118 | JIMT-1-EGFP and NK medium |
| pLP-1, pLP-2, pLP-VSV-G, pWOXEGFP | Invitrogen, (Prof. József T zsér, University of Debrecen) zsér, University of Debrecen) | for JIMT-1-EGFP cell line | |
| Pluronic-F127 | Sigma | P2443 | for coating HCS plate before transfering the spheroids |
| Sunitinib malate | SigmaAldrich | PZ0012 | for treatments |
| Trastuzumab Ab (humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody) | Herzuma®, EGIS Pharmaceuticals, Budapest, Hungary | NDC-63459-303-43 | for treatments |
| Trastuzumab-F(ab')2 | Gift from Prof. György Vereb and Árpád Szö r r | Department of Biophysics and Cell Biology, University of Debrecen | for treatments |
| Trypan blue 0.4% solution | Sigma | T8154 | for cell counting |
| Trypsin-EDTA 1X in PBS | Biosera | LM-T1706 | for cells detachment |
References
- Jubelin, C., et al. Three-dimensional in vitro culture models in oncology research. Cell Biosci. 12 (1), 155 (2022).
- Mittler, F., et al. High-content monitoring of drug effects in a 3D spheroid model. Front Oncol. 7, 293 (2017).
- Badr-Eldin, S. M., Aldawsari, H. M., Kotta, S., Deb, P. K., Venugopala, K. N. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture models for efficient drug discovery: Progress so far and future prospects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 15 (8), 926 (2022).
- Brancato, V., Oliveira, J. M., Correlo, V. M., Reis, R. L., Kundu, S. C. Could 3D models of cancer enhance drug screening. Biomaterials. 232, 119744 (2020).
- Pinto, B., Henriques, A. C., Silva, P. M. A., Bousbaa, H. Three-dimensional spheroids as in vitro preclinical models for cancer research. Pharmaceutics. 12 (12), 1186 (2020).
- Fitzgerald, A. A., Li, E., Weiner, L. M. 3D culture systems for exploring cancer immunology. Cancers (Basel). 13 (1), 56 (2020).
- Zanoni, M., et al. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci Rep. 6, 19103 (2016).
- Boucherit, N., Gorvel, L., Olive, D. 3D tumor models and their use for the testing of immunotherapies. Front Immunol. 11, 603640 (2020).
- Li, Y., et al. Recent progress on immunotherapy for breast cancer: Tumor microenvironment, nanotechnology and more. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 9, 680315 (2021).
- Lo Nigro, C., et al. NK-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in solid tumors: Biological evidence and clinical perspectives. Ann Transl Med. 7 (5), 105 (2019).
- Sun, Y. S., et al. Risk factors and preventions of breast cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 13 (11), 1387-1397 (2017).
- Liu, P. H., Wei, J. C., Wang, Y. H., Yeh, M. H. Female breast cancer incidence predisposing risk factors identification using nationwide big data: A matched nested case-control study in taiwan. BMC Cancer. 22 (1), 849 (2022).
- Burguin, A., Diorio, C., Durocher, F. Breast cancer treatments: Updates and new challenges. J Pers Med. 11 (8), 808 (2021).
- Costa, R. L. B., Czerniecki, B. J. Clinical development of immunotherapies for HER2(+) breast cancer: A review of HER2-directed monoclonal antibodies and beyond. NPJ Breast Cancer. 6, 10 (2020).
- Musolino, A., et al. Role of fcgamma receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy. J Immunother Cancer. 10 (1), e003171 (2022).
- Petricevic, B., et al. Trastuzumab mediates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and phagocytosis to the same extent in both adjuvant and metastatic HER2/NEU breast cancer patients. J Transl Med. 11, 307 (2013).
- Guti, E., et al. The multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib induces resistance of HER2 positive breast cancer cells to Trastuzumab-mediated ADCC. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 71 (9), 2151-2168 (2022).
- Barok, M., et al. Trastuzumab decreases the number of circulating and disseminated tumor cells despite Trastuzumab resistance of the primary tumor. Cancer Lett. 260 (1-2), 198-208 (2008).
- Toth, G., et al. The combination of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab administered at approved doses may delay development of Trastuzumab resistance by additively enhancing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. MAbs. 8 (7), 1361-1370 (2016).
- Ehlers, F. a. I., et al. ADCC-inducing antibody Trastuzumab and selection of KIR-HLA ligand mismatched donors enhance the NK cell anti-breast cancer response. Cancers (Basel). 13 (13), 3232 (2021).
- Gangadhara, S., Smith, C., Barrett-Lee, P., Hiscox, S. 3d culture of Her2+ breast cancer cells promotes AKT to MAPK switching and a loss of therapeutic response. BMC Cancer. 16, 345 (2016).
- Balalaeva, I. V., Sokolova, E. A., Puzhikhina, A. D., Brilkina, A. A., Deyev, S. M. Spheroids of Her2-positive breast adenocarcinoma for studying anticancer immunotoxins in vitro. Acta Naturae. 9 (1), 38-43 (2017).
- Selis, F., et al. Pegylated Trastuzumab fragments acquire an increased in vivo stability but show a largely reduced affinity for the target antigen. Int J Mol Sci. 17 (4), 491 (2016).
- Johnston, R. L., et al. High content screening application for cell-type specific behaviour in heterogeneous primary breast epithelial subpopulations. Breast Cancer Res. 18 (1), 18 (2016).
- Kandaswamy, C., Silva, L. M., Alexandre, L. A., Santos, J. M. High-content analysis of breast cancer using single-cell deep transfer learning. J Biomol Screen. 21 (3), 252-259 (2016).
- Esquer, H., Zhou, Q., Abraham, A. D., Labarbera, D. V. Advanced high-content-screening applications of clonogenicity in cancer. SLAS Discov. 25 (7), 734-743 (2020).
- Pickl, M., Ries, C. H. Comparison of 3D and 2D tumor models reveals enhanced Her2 activation in 3D associated with an increased response to trastuzumab. Oncogene. 28 (3), 461-468 (2009).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved