需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
集成光声、超声和血管造影断层扫描 (PAUSAT) 用于缺血性卒中的无创全脑成像
摘要
这项工作展示了使用基于多模态超声的成像平台对缺血性中风进行无创成像。该系统允许通过光声成像量化血液氧合,并通过声学血管造影在大脑中受损灌注。
摘要
这里介绍的是使用我们新开发的无创成像系统进行的实验性缺血性卒中研究,该系统集成了三种基于声学的成像技术:光声、超声和血管造影断层扫描 (PAUSAT)。结合这三种模式有助于获得脑血氧合的多光谱光声断层扫描 (PAT)、脑组织的高频超声成像和脑血灌注的声学血管造影。多模态成像平台可以研究中风后整个小鼠大脑的脑灌注和氧合变化。评估了两种常用的缺血性脑卒中模型:永久性大脑中动脉闭塞(pMCAO)模型和光血栓(PT)模型。PAUSAT用于对中风前后的相同小鼠大脑进行成像,并定量分析两种中风模型。该成像系统能够清楚地显示缺血性中风后的脑血管变化,包括与未受伤组织(对侧)相比,中风梗死区域(同侧)的血液灌注和氧合显着减少。激光散斑对比成像和三苯基氯化四唑(TTC)染色证实了结果。此外,两种卒中模型中的脑卒中梗死体积均通过TTC染色作为基本事实进行测量和验证。通过这项研究,我们已经证明PAUSAT可以成为缺血性中风无创和纵向临床前研究的有力工具。
引言
血液将氧气(通过血红蛋白)和其他重要营养素输送到我们体内的组织。当血液流经组织中断(缺血)时,可能会对组织造成严重损害,其最直接的影响是由于缺氧(缺氧)。缺血性中风是流向大脑某个区域的血流中断的结果。缺血性中风引起的脑损伤可在血管阻塞后几分钟内发生,并且通常具有使人衰弱和持久的影响1,2。评估缺血性中风后生理病理学以及识别和测试新疗法的一种非常有价值的策略是在实验室中使用小动物模型。实验室中发现的治疗方法旨在转化为临床应用并改善患者的生活。然而,动物在生物医学研究中的使用需要根据Russell和Burch的3R原则进行仔细评估:替换,减少和改进3。减少部分的目标是在不影响数据收集的情况下减少动物数量。考虑到这一点,能够通过无创成像纵向评估病变演变,在减少所需动物数量以及最大化从每只动物获得的信息方面具有很大的优势4。
光声断层扫描 (PAT) 是一种混合成像方式,将光学吸收对比与超声成像空间分辨率相结合5。PAT的成像机制如下。激发激光脉冲照射在被成像的目标上。假设目标吸收激发激光波长的光,它将温度升高。温度的快速升高导致目标的热弹性膨胀。膨胀导致超声波从目标传播出去。通过检测多个位置的超声波,可以使用波从目标传播到探测器所需的时间,通过重建算法创建图像。PAT检测深层组织区域的光吸收的能力将PAT与超声成像区分开来,超声成像可检测组织不同声阻抗的边界5。在可见光和近红外光谱中,生物体中丰富的主要高吸收生物分子是血红蛋白、脂质、黑色素和水7。中风研究中特别感兴趣的是血红蛋白。由于氧合血红蛋白和脱氧血红蛋白具有不同的光吸收光谱,PAT可以与多个激发激光波长一起使用,以确定蛋白质两种状态的相对浓度。这允许在梗死区域内外量化血红蛋白 (sO2) 的氧饱和度或血液氧合 8,9。这是缺血性卒中的重要指标,因为它可以指示缺血后受损脑组织中的氧气水平。
声波血管造影(AA)是一种对比增强超声成像方法,特别适用于体内脉管系统的形态成像10。该方法依赖于使用双晶摆动换能器(低频元件和高频元件)与注入成像对象循环系统的微气泡结合使用。换能器的低频元件用于以微气泡的谐振频率(例如2 MHz)传输,而高频元件用于接收微气泡的超谐波信号(例如,26 MHz)。当以共振频率激发时,微气泡具有很强的非线性响应,导致产生周围身体组织不产生的超谐波信号11。通过使用高频元件接收,这确保了仅检测到微气泡信号。由于微气泡仅限于血管,因此结果是血管形态的血管造影图像。AA是缺血性中风成像的有力方法,因为流经循环系统的微气泡不能流过阻塞的血管。这允许AA检测由于缺血性中风而未灌注的大脑区域,这表明梗死区域。
临床前缺血性卒中研究通常依赖于使用组织学和行为学测试来评估卒中的位置和严重程度。三苯基氯化四唑 (TTC) 染色是用于确定卒中梗死体积的常见组织学分析。但是,它只能在终点使用,因为它需要对动物实施安乐死12。行为测试可用于确定多个时间点的运动功能障碍,但它们不能提供定量的解剖学或生理学值13。生物医学成像提供了一种更定量的方法来研究缺血性中风的无创和纵向影响9,14,15。然而,现有的成像技术(如小动物磁共振成像[MRI])的成本可能很高,无法同时提供结构和功能信息,或者穿透深度有限(如大多数光学成像技术)。
在这里,我们结合了光声,超声和血管造影断层扫描(PAUSAT;参见图1中的系统 图),这允许缺血性中风16后血液灌注和氧合的互补结构和功能信息。这是评估损伤严重程度和监测恢复或对治疗反应的两个重要方面。使用这些综合成像方法可以增加每只动物获得的信息量,减少所需的动物数量,并在研究缺血性中风的潜在治疗方法方面提供更多信息。
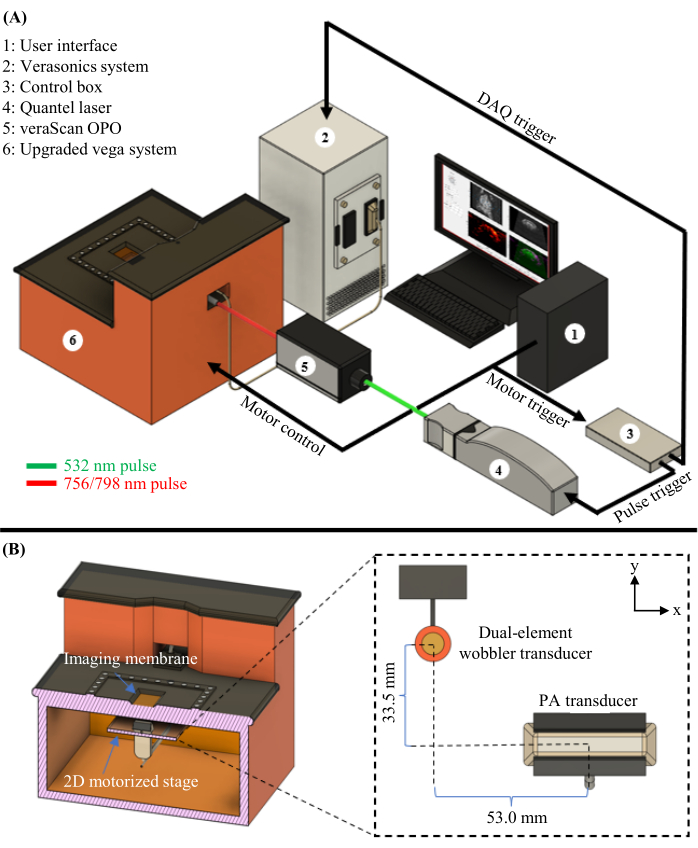
图1:PAUSAT图。 (A)PAUSAT系统的完整原理图,包括用于PAT的激光器和OPO。 (B)PAUSAT系统的内部视图,包括两个超声换能器。双晶摆动探头用于B型超声和AA,线性阵列探头用于PAT。两个传感器都安装在同一个2D电动载物台上,允许扫描以生成体积数据。这一数字已从16修改而来。请点击此处查看此图的大图。
研究方案
所有动物程序均由杜克大学医学中心动物护理和使用委员会批准,并按照美国公共卫生署的《实验动物人道护理和使用政策》进行。雄性和雌性C57BL / 6J小鼠(见 材料表)用于这些研究。每个中风模型组至少对三只动物进行成像。有关此协议中遵循的工作流程,请参见 图 2 。
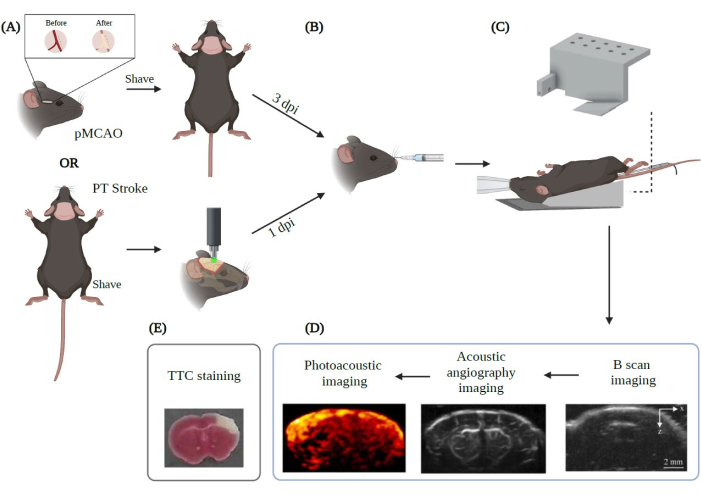
图2:应用于中风的PAUSAT成像实验程序摘要。 用 Biorender.com 创建。该图显示了从(A)两种主要卒中模型(pMCAO和PT中风)开始的成像程序的工作流程。(B)在将动物定位在PAUSAT膜上之前,必须进行微泡的眶后注射。(C)在此设置中,需要提供连续麻醉的面罩和保持动物体温稳定的加热垫。动物的身体放在加热垫上,而头部放在系统的膜上。(D)图中还显示了图像采集的顺序。(E)进行TTC染色以验证我们在本研究中的结果。DPI:受伤后几天。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
1.诱导中风小鼠模型
- 永久性大脑中动脉闭塞术 (pMCAO) 伴颈总动脉 (CCA) 结扎术。
注意:简而言之,对右侧CCA进行永久性结扎术,并对右大脑中动脉(MCA)进行后部电灼术17。该手术限制了大脑右皮层的脑血流,导致缺血性中风18。- 使用5.0%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中的吸入混合物在诱导室中诱导麻醉,直到意识丧失(被认为是踏板反射的丧失)。
- 使用20 G导管(材料表)对动物进行插管并将其连接到自动呼吸机。根据动物的体重设置流速,并使用1.5%-2.0%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中保持动物麻醉。
- 使用加热灯和连接到温度控制器设备的直肠探头,将动物的体温保持在 37 °C。
- 在老鼠的眼睛上滴一滴润滑眼膏。
- 将动物置于仰卧位,并使用理发器去除颈部区域的毛发。
- 首先使用含有聚维酮碘的棉签清洁皮肤区域,然后使用含有70%乙醇的无菌垫。执行此操作三次。
- 通过轻轻捏住动物的后爪来验证麻醉深度和无疼痛。
- 在颈部中线做一个0.8厘米的矢状切口,露出右CCA。
- 通过将 4-0 丝线解离成构成主线的较细线来准备 CCA 结扎的缝合线。使用其中一个子线程的 1.5 厘米长度永久连接 CCA。
注意:拧紧结后,通过在与结的距离处切割延伸部分 1-2 毫米来去除多余的螺纹。 - 在闭合伤口之前涂抹一滴布比卡因。
- 使用中断的4-0丝手术缝合线关闭切口,并在表面上涂抹三重抗生素软膏以防止感染。
- 移动鼠标以露出动物身体的右侧。
-
使用理发器去除耳朵和眼部区域之间的头发。
-
使用含有聚维酮碘的棉签对手术区域进行消毒,然后用含有70%乙醇的无菌垫进行消毒。重复此步骤三次。
-
放置无菌窗帘以固定手术区域。然后,在动物的右眼和耳朵之间做一个0.5厘米的切口,露出颅骨和颞肌之间的关节。
- 使用烧灼环,烧灼肌肉以将其与颅骨分离并暴露MCA区域。
- 使用电钻钻 0.2 mm2 窗口以暴露 MCA,并在 MCA 上使用电灼术以阻塞血流。
注意:80%功率强度的单个脉冲足以烧灼MCA。 - 使用连接到27G针头的1mL注射器,在手术部位滴一滴布比卡因(材料表)。
- 使用中断的6-0透明单丝缝合线关闭皮肤切口,并在表面上涂抹三重抗生素软膏以防止感染。
- 完成手术后,将动物转移到温度受控(32°C)的孵化器中,让动物恢复。
- 2小时后,将动物转移到其家笼中,并 随意提供食物和水。
- 光血栓性卒中(PT 卒中)
注意:简而言之,PT中风是通过照亮大脑血管内的孟加拉玫瑰来进行的。孟加拉玫瑰腹膜内给药,一旦它很好地分布在全身(5分钟),它就会被绿色冷光照亮,激活孟加拉玫瑰产生活性氧(ROS)。这些ROS破坏内皮细胞膜,在整个照明区域内产生血栓,并导致局部脑血流中断19。- 使用5.0%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中的吸入混合物在诱导室中诱导麻醉,直到意识丧失(被认为是踏板反射的丧失)。
- 将动物置于立体定位框架下,使用面罩和1.5%-2.0%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中保持动物麻醉。
- 使用热水循环加热器和直肠探头将动物保持在37°C以测量动物的体温。
- 在老鼠的眼睛上滴一滴润滑眼膏。
- 使用理发器剃掉动物的头部。
- 清洁剃光的头皮区域三次,首先使用含有聚维酮碘的棉签,然后使用含有70%乙醇的无菌垫。
- 通过轻轻捏住动物的后爪来验证没有疼痛。
- 用手术刀在头皮中线做一个1.4厘米的矢状切口,露出头骨。
- 使用锋利的铅笔,在距前膛向右侧 1.5 毫米处做一个标记。
- 在 1.5 毫米标记的中心放置一个直径为 2.5 毫米的圆形针孔。
注意:可以使用双面黑色胶带制作包含圆形针孔的正方形,并使用上述尺寸的单孔冲孔工具在中心开一个直径为 2.5 毫米的开口。 - 将绿色冷光放在圆形针孔上,将灯与针孔之间的间隙保持在最小。
- 用铝箔覆盖该区域,以免光线扩散。
- 一旦设置准备就绪,腹膜内注射10mg / kg孟加拉玫瑰(10mg / mL在1x磷酸盐缓冲盐水[PBS]中)并等待5分钟。
- 5分钟后,打开冷光源(强度:4.25)并保持曝光15分钟。
- 接下来,关闭冷光并通过肉眼(该区域预计比周围区域更白)或使用外部设备测量脑血流量(例如,通过使用激光斑点对比成像(材料表;见步骤5.1))验证中风。
- 使用连接到27G针头的1mL注射器,在手术部位滴一滴布比卡因(材料表)。
- 使用中断的6-0透明单丝缝合线关闭皮肤切口,并在表面上涂抹三重抗生素软膏以防止感染。
- 完成手术后,将动物转移到温度受控(32°C)的孵化器中,让动物恢复。
- 2小时后,将动物转移到其家笼中,并 随意提供食物和水。
2. 准备用于成像的PAUSAT项目
- 打开 532 nm 激光并将其打开 15 分钟以预热。
- 为麻醉动物准备成像平台。
- 将定制的斜坡(图2C)连接到成像膜旁边的手动可调载物台(材料表)上。
- 将呼吸管连接到定制斜坡的鼠标牙架连接起来,并将加热垫固定在斜坡表面上。
- 激光预热后,使用近红外检测器卡(材料表)检查激光路径和耦合到光纤束中是否对齐良好,方法是将卡放在光纤束输入的前面并确保激光进入光纤束。
注意: 根据需要调整任何激光路径反射镜,以确保激光输入与光纤束输入居中。
3. 为PAUSAT准备动物
注意:PAUSAT在PT中风手术后1天或pMCAO手术后3天进行。准备PAUSAT成像(步骤2)大约需要20分钟,应在准备动物进行PAUSAT之前立即完成。
- 使用5%异氟醚与30%O 2/70%N2混合的吸入混合物在诱导室中诱导麻醉,直到意识丧失(识别为踏板反射的丧失)。
- 将动物转移到带有牙齿支架和面罩的加热平台上,并将麻醉保持在30%O 2/70%N 2中的1.5%-2.0%异氟醚。
- 使用连接到温度控制器装置的加热灯和直肠探头将动物的体温保持在 37 °C。
- 使用电动剃须刀修剪动物头顶上的毛发。包括从眼睛附近到耳朵后面的区域。
- 通过涂抹商业脱毛膏剃掉动物头顶的毛发,以完全去除剩余的短毛。留在皮肤上 5-6 分钟,然后用棉签蘸水擦拭,以帮助完全去除乳霜。重复直到皮肤没有毛发。
注意:对于手术后1天的成像,可以在开始手术前执行这些步骤;在PT卒中后1天,可以省略它们。当手术后几天进行PAUSAT图像采集时,迫切需要执行此步骤。 - 一旦动物和系统准备好进行成像,在将动物转移到系统平台之前,使用 27 G 针在轨道上以储备浓度(材料表)逆轨道注入 100 μL 微泡溶液。
注意:一旦气泡在血液中循环,成像的时间有限,而不会显着丢失信号(~10分钟)。 - 在鼠标的眼睛上滴一滴护目化妆水。
注意:在进行眶后注射之前,不建议使用眼睛润滑剂,以避免异物进入动物的血液。因此,脱毛霜的应用必须缓慢而小心地进行,以避免离眼睛太近(但足以暴露预期中风的感兴趣区域)。用事先蘸水的棉签去除护发霜,防止护发霜滴落,从而损害眼睛。
4. PAUSAT成像
注意:这样做是为了对中风后大脑的对侧和异侧区域进行成像
- 将鼠标转移到集成的PAUSAT(材料表)图像平台,将鼠标置于自定义斜坡上的仰卧位置(图2C)。
- 在成像窗口表面填充足够的蒸馏水以进行声耦合。
注意:建议使用3D打印机进行可选的坡道打印,以防止动物的身体在图像采集过程中弄湿并提高动物的舒适度。它还有助于保持稳定的体温。此外,斜坡可以连接到手动载物台(材料表),以调整双晶摆动探头相对于鼠标头的焦深。自定义斜坡设计文件可应要求提供给作者。 - 将鼠标头固定在牙架中,并确保适当的麻醉和气流。
- 使用加热灯和连接到温度控制器设备的直肠探头,将动物的体温保持在 37 °C。
- 打开成像应用程序(材料表)并导航到B模式超声。
- 使用实时超声波窗口手动将鼠标头调整到所需位置。
- 使用实时超声窗口调整载物台的高度,使换能器的焦深(19 mm)大约在要成像区域的中间。
- B型超声成像
- 调整B模式下超声传输频率的值(对于这些研究,使用16 MHz)。
- 在映像应用程序中输入保存目录信息。
- 使用浮动框选择所需的区域进行大脑的B模式扫描。
- 按 获取静态 按钮。
- 图像采集完成后,在应用程序中检查扫描结果,以确保所需区域已成像。
注意:避免B模式成像采集中不必要的延迟,以确保血液中有足够高浓度的微气泡保留给AA。
- AA 成像
- 返回 图像采集。
- 在成像应用程序中更改为 声学血管造影 模式(材料表)。
- 输入所需的扫描协议参数(其中最重要的是帧间距和每个位置的帧数,对于这些研究,分别设置为 0.2 mm 和 10)。
- 按 获取静态 按钮。
注意:AA 采集比 B 型超声需要更长的时间。 - 扫描完成后,在图像分析下检查扫描结果,以确保 图像 质量符合预期。
注意:对于AA模式,可以通过在大脑内的不同焦深重复第二次扫描,然后通过适当的后处理重新组合图像来获得更具代表性的全脑体积(见 图3)。
- 光声断层扫描成像
- 打开光学参量振荡器 (OPO) 应用程序(材料表)并将其设置为 756 nm。
注意:OPO很容易脱离校准,因此在实验之前,请确保使用独立的光谱仪正确校准OPO。 - 手动将线性阵列探头转换为先前确定的坐标,以确保摆动体积和线性阵列体积自动共同配准。
注意: 至关重要的是,事先使用模型网格进行共配准实验,以确定平移载物台所需的确切距离,以便将来自两个探头的结果数据以3D方式共配准。 - 打开激光应用程序并打开 532 nm 激光器。
- 使用激光功率计测量激光输出的能量并确保它是所需的能量(这些研究使用每个脉冲~10 mJ)。
- 选择所需的PAT扫描参数(0.4 mm步长、20 mm扫描长度和每个位置平均10帧)。
- 打开超声数据采集系统MATLAB程序(材料表),然后按 “运行” 按钮。
- 通过按 “开始 ”按钮获取PAT扫描。
- 扫描完成后,打开 MATLAB 保存程序。将保存名称更改为所需的文件名,然后按 “运行” 按钮。
- 将OPO波长更改为798 nm,然后重复从4.10.3到4.10.8的步骤。
注意:对于纵向研究,建议通过将动物放入孵化器中并观察几个小时(按照步骤1.1.18和1.1.19)来让动物恢复。如果需要结果验证,请在PAUSAT成像后立即继续执行第5部分。
- 打开光学参量振荡器 (OPO) 应用程序(材料表)并将其设置为 756 nm。
5. 可选:结果验证
- 激光散斑对比成像(LSCI)。
- 使用1.5%-2.0%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中麻醉动物。
- 将动物设置为立体定位框架,使用面罩和上述吸入麻醉保持动物麻醉。
- 使用热水循环加热器和直肠探头将动物保持在37°C以测量动物的体温。
- 在鼠标的眼睛上滴一滴护目化妆水。
- 通过轻轻捏住动物的后爪来验证没有疼痛。
- 使用理发器去除动物头皮上的毛发。
- 使用含有聚维酮碘的棉签对手术区域进行消毒,然后用含有70%乙醇的无菌垫进行消毒。重复此步骤三次。
- 在头皮中线上做一个1.4毫米的矢状切口,露出头骨。用镊子夹住头皮,防止它占据大脑区域进行扫描。
- 在头骨上滴几滴盐水,并将激光斑点对比系统装置(材料表)放在动物的头上。
- 在“ 文件 ”菜单下,将设备设置为 “在线”模式,该模式包含在子菜单 “工作模式”中。
- 在 “文件 ”菜单和 “保存设置 ”子菜单中选择默认图像存储文件夹。
- 在 光源 菜单中,连接引导激光(“激光开启”)和白光(“白光开启”),将成像窗口定位在正确的位置。
- 在“设置”菜单中,选择“放大设置”,手动将光标移动到 2.5,然后按“应用”和“确定”保存设置。
- 通过手动移动位于主页顶部子菜单中的焦点栏来调整焦点。
- 在“设置”菜单中,选择“伪色阈值设置”,根据需要调整阈值,然后按“应用”和“确定”保存设置。
- 在“ 光源 ”菜单中,在捕获图像之前断开引导激光(“激光关闭”)和白光(“白光关闭”)的连接。
- 通过选择主页顶部子菜单中的 “播放 ”符号来捕获图像。
- 三苯基氯化四唑 (TTC) 染色
- 使用5%异氟醚在30%O 2/70%N2中深度麻醉动物。
- 一旦动物停止呼吸,用锋利的剪刀将其斩首。
- 去除头部周围的所有皮肤和颈部区域的肌肉。
- 在颅骨的枕骨部分进行矢状切口,直到到达顶骨。
- 在血管下方的左侧和右侧进行水平切口(~5毫米)。使用直镊子去除颅骨的枕骨。
- 在颅骨的额鼻缝处切开(~5 mm)。
- 在半球之间的颅骨中线进行矢状切口(~10-15毫米),并确保它们完全分开。
- 使用#7号弯曲剪刀,从中心到两侧取出颅骨的顶骨左右骨。
- 将大脑转移到装有 5 mL 冰冷 1x PBS 的容器中,并将其放在冰上 10 分钟。
- 将大脑转移到不锈钢大脑基质(1毫米厚的切片)中。
- 使用一次性剃须刀片将大脑切成1毫米的冠状切片(材料表)。
- 将刀片放在两侧,转移到装有冰冷的 1x PBS 的容器中。
- 小心地将部分与刀片逐个分开。
- 将脑切片转移到直径70毫米的培养皿中,该培养皿含有5mL的2%TTC(材料表,3)在1x PBS中。
- 在室温(R / T)下在黑暗中孵育15分钟。
- 15分钟后,丢弃TTC,用3mL福尔马林代替,并在R / T下在黑暗中孵育至少30分钟。
- 最后,将脑切片转移到透明塑料薄膜上并扫描样品,包括扫描图像中的标尺作为未来测量的参考。
结果
大脑血管形态成像
AA通过激发循环系统中的微气泡在其共振频率下并接收微泡的超谐波响应来生成血管形态图像。通过使用连接到手动可调载物台的定制斜坡(图2C),我们可以在两个不同的焦深下以AA模式对小鼠大脑进行成像。当针对更深的区域时,更浅的区域(如大脑皮层)显示出较差的分辨率和信号强度(图3A),反之亦然(
讨论
这种方法有几个重要方面,如果操作不正确,可能会导致图像质量和定量分析显着下降。PAUSAT图像中最常见的用户错误结果是信号不足或信号强度非常低,这两种原因都可能由于各种原因而发生。其中一个原因是声耦合的问题。在成像过程中,小鼠头部周围水中的大气泡通常会阻止超声波往返换能器,从而导致系统所有三种模态的结果图像中出现阴影区域。这可以通过确保系统膜和待成像样品之?...
披露声明
作者声明对这项工作没有利益冲突。
致谢
作者要感谢SonoVol Inc.的工程团队的技术支持。这项工作部分由美国心脏协会合作科学奖(18CSA34080277)赞助,授予J. Yao和W. Yang;美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)拨款R21EB027981,R21 EB027304,RF1 NS115581(BRAIN倡议),R01 NS111039,R01 EB028143;美国国家科学基金会(NSF)职业奖2144788;陈·扎克伯格倡议拨款(2020-226178),授予J. Yao;美国国立卫生研究院向W. Yang授予R21NS127163和R01NS099590。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 20 GA catheter | BD Insyte Autoguard Winged | 381534 | For mouse intubation |
| 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride | Sigma | T8877 | Necessary for TTC-staining brain for validation |
| 532nm Laser | Quantel | Q-smart 850 | Laser used to pump the OPO for PAT |
| Automatic Ventilator Rovent Jr. | Kent Scientific | RV-JR | To keep mice under anesthesia during surgical procedure |
| Black braided silk 4-0 USP | Surgical Specialties | SP116 | Used for sutures on the neck for pMCAO surgery |
| Bupivacaine | Hospira | 0409-1159-18 | Used prior to closing wounds during surgical procedure |
| C57BL/6 Mice | Jackson Lab | #000664 | Mice used for studying ischemic stroke (2-6 month old male/female) |
| Clear suture | Ethicon | 8606 | Used for closing wound (PT stroke and pMCAO). A clear suture won't interfere with PAT |
| Cold Light LED | Schott | KL 1600 | Needed to create PT stroke |
| Disposable Razor Blade | Accutec Blades | 74-0002 | For sectioning mouse brain |
| Electric drill | JSDA | JD-700 | Used to expose MCA during pMCAO procedure |
| Electrocauterization tool | Wet-Field | Wet-Field Bipolar-RG | Stops blood flow after drilling during pMCAO procedure |
| Hair removal gel | Veet | 8282651 | Used to remove hair from mouse prior to imaging |
| High Temperature Cautery Loop Tip | BOVIE Medical Corporation | REF AA03 | Used to avoid bleeding when separating the temporal muscle from the skull |
| IR Detector Card | Thorlabs | VRC5 | Used to ensure light path is aligned |
| Laser Power Meter | Ophir | StarBright, P/N 7Z01580 | Can be used to calibrate the laser energy prior to imaging |
| Laser Speckle Imaging System | RWD Life Science Co. | RFLSI-III | Can be used to validate stroke surgery success |
| Lubricant Eye Ointment | Soothe | AB31336 | Can be used to avoid drying of the eyes |
| Manually adjustable stage | Thorlabs | L490 | Used with custom ramp for multiple focal depth AA imaging |
| Modified Vega Imaging System | Perkin Elmer | LLA00061 | System containing both B-mode/AA and PAT transducers |
| Optical Parametric Oscillator | Quantel | versaScan-L532 | Allows for tuning of excitation wavelength in a large range |
| Programmable Ultrasound System | Verasonics | Vantage 256 | Used for PAT part of system |
| Rose Bengal | Sigma | 330000 | Necessary to induce PT stroke |
| Suture | LOOK | SP116 | Used for permanent ligation of CCA |
| Temperature Contoller | Physitemp | TCAT-2 | Used to maintain stable body temperature of mice during procedures |
| VesselVue Microbubbles | Perkin Elmer | P-4007001 | Used for acoustic angiography (2.43 × 10^9 microbubbles/mL) |
参考文献
- Durukan, A., Tatlisumak, T. Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 87 (1), 179-197 (2007).
- Vander Worp, H. B., van Gijn, J. Clinical Practice. Acute ischemic stroke. The New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (6), 572-579 (2007).
- Tannenbaum, J., Bennett, B. T. Russell and Burch's 3Rs then and now: the need for clarity in definition and purpose. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 54 (2), 120-132 (2015).
- Hochrainer, K., Yang, W. Stroke proteomics: from discovery to diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Circulation Research. 130 (8), 1145-1166 (2022).
- Wang, L. V., Yao, J. A practical guide to photoacoustic tomography in the life sciences. Nature Methods. 13 (8), 627-638 (2016).
- Aldrich, J. E. Basic physics of ultrasound imaging. Critical Care Medicine. 35 (5), S131-S137 (2007).
- Jacques, S. L. Optical properties of biological tissues: a review. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 58 (11), R37-R61 (2013).
- Li, M., Tang, Y., Yao, J. Photoacoustic tomography of blood oxygenation: a mini review. Photoacoustics. 10, 65-73 (2018).
- Menozzi, L., Yang, W., Feng, W., Yao, J. Sound out the impaired perfusion: Photoacoustic imaging in preclinical ischemic stroke. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 16, 1055552 (2022).
- Gessner, R. C., Frederick, C. B., Foster, F. S., Dayton, P. A. Acoustic angiography: a new imaging modality for assessing microvasculature architecture. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging. 2013, 936593 (2013).
- Dayton, P. A., Rychak, J. J. Molecular ultrasound imaging using microbubble contrast agents. Frontiers in Bioscience. 12, 5124-5142 (2007).
- Isayama, K., Pitts, L. H., Nishimura, M. C. Evaluation of 2, 3, 5-triphenyitetrazolium chloride staining to delineate rat brain infarcts. Stroke. 22 (11), 1394-1398 (1991).
- Ruan, J., Yao, Y. Behavioral tests in rodent models of stroke. Brain Hemorrhages. 1 (4), 171-184 (2020).
- Parthasarathy, A. B., Kazmi, S. M. S., Dunn, A. K. Quantitative imaging of ischemic stroke through thinned skull in mice with Multi Exposure Speckle Imaging. Biomedical Optics Express. 1 (1), 246-259 (2010).
- Hingot, V., et al. Early ultrafast ultrasound imaging of cerebral perfusion correlates with ischemic stroke outcomes and responses to treatment in mice. Theranostics. 10 (17), 7480-7491 (2020).
- Menozzi, L., et al. Three-dimensional non-invasive brain imaging of ischemic stroke by integrated photoacoustic, ultrasound and angiographic tomography (PAUSAT). Photoacoustics. 29, 100444 (2022).
- Llovera, G., Roth, S., Plesnila, N., Veltkamp, R., Liesz, A. Modeling stroke in mice: permanent coagulation of the distal middle cerebral artery. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (89), e51729 (2014).
- Trotman-Lucas, M., Kelly, M. E., Janus, J., Fern, R., Gibson, C. L. An alternative surgical approach reduces variability following filament induction of experimental stroke in mice. Disease Models & Mechanisms. 10 (7), 931-938 (2017).
- Labat-Gest, V., Tomasi, S. Photothrombotic ischemia: a minimally invasive and reproducible photochemical cortical lesion model for mouse stroke studies. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (76), e50370 (2013).
- Matsumoto, Y., et al. Visualising peripheral arterioles and venules through high-resolution and large-area photoacoustic imaging. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 14930 (2018).
- Xu, Y., Wang, L. V., Ambartsoumian, G., Kuchment, P. Reconstructions in limited-view thermoacoustic tomography. Medical Physics. 31 (4), 724-733 (2004).
- Yal Tang, ., et al. High-fidelity deep functional photoacoustic tomography enhanced by virtual point sources. Photoacoustics. 29, 100450 (2023).
- Zheng, W., Huang, C., Zhang, H., Xia, J. Slit-based photoacoustic tomography with co-planar light illumination and acoustic detection for high-resolution vascular imaging in human using a linear transducer array. Biomedical Engineering Letters. 12 (2), 125-133 (2022).
- Wang, Y., et al. Slit-enabled linear-array photoacoustic tomography with near isotropic spatial resolution in three dimensions. Optics Letters. 41 (1), 127-130 (2016).
- Vu, T., Li, M., Humayun, H., Zhou, Y., Yao, J. A generative adversarial network for artifact removal in photoacoustic computed tomography with a linear-array transducer. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 245 (7), 597-605 (2020).
- Zhang, H., et al. Deep-E: A fully-dense neural network for improving the elevation resolution in linear-array-based photoacoustic tomography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 41 (5), 1279-1288 (2022).
- Hauptmann, A., et al. Model-based learning for accelerated, limited-view 3-D photoacoustic tomography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 37 (6), 1382-1393 (2018).
- Li, M., et al. Three-dimensional deep-tissue functional and molecular imaging by integrated photoacoustic, ultrasound, and angiographic tomography (PAUSAT). IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 41 (10), 2704-2714 (2022).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。