Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
Synthèse de la poly (
Dans cet article
Résumé
We present a protocol to synthesize Janus microhydrogels composed entirely of the same base material, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm), with a clearly compartmentalized structure base on the phase separation of a supersaturated NIPAAm monomer solution. The synthesized Janus microhydrogels show unique properties such as anisotropic thermo-responsiveness and organophilic/hydrophilic loading capability.
Résumé
Janus microparticles are compartmentalized particles with differing molecular structures and/or functionality on each of their two sides. Because of this unique property, Janus microparticles have been recognized as a new class of materials, thereby attracting a great deal of attention from various research fields. The versatility of these microparticles has been exemplified through their uses as building blocks for self-assembly, electrically responsive actuators, emulsifiers for painting and cosmetics, and carriers for drug delivery. This study introduces a detailed protocol that explicitly describes a synthetic method for designing novel Janus microhydrogels composed of a single base material, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm). Janus microdroplets are firstly generated via a hydrodynamic focusing microfluidic device (HFMD) based on the separation of a supersaturated aqueous NIPAAm monomer solution and subsequently polymerized through exposure to UV irradiation. The resulting Janus microhydrogels were found to be entirely composed of the same base material, featured an easily identifiable compartmentalized morphology, and exhibited anisotropic thermo-responsiveness and organophilic/hydrophilic loading capability. We believe that the proposed method introduces a novel hydrogel platform with the potential for advanced synthesis of multi-functional Janus microhydrogels.
Introduction
Hydrogels are a network of hydrophilic polymer chains.1 An increasing amount of research in the field of hydrogels has promoted significant advances and revealed their similarity to biological tissues; the properties of hydrogels allow the uptake of large amounts of water while maintaining their structure. Environmentally responsive hydrogels have also been studied extensively because of their ability to swell or shrink reversibly in response to external stimuli.2 Several triggers, including temperature,3-5 pH,6,7 light,8,9 electric fields,10,11 and specific molecules, such as glucose,12,13 have been suggested to control the geometric shape of hydrogels. Among the many environmentally responsive hydrogels currently available, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm), a well-known thermo-responsive hydrogel, exhibits volume shrinkage above a low critical solution temperature (LCST) of 32 °C.14 A recent study by Sasaki et al.15 reported the intriguing liquid-liquid phase separation of supersaturated NIPAAm, which is the monomer of PNIPAAm. According to this report, supersaturated NIPAAm was dissolved with a 10-fold molar excess of H2O, and soon after, the solution separated into two liquid phases when allows to stand at a temperature above 25 °C; by contrast, dilute NIPAAm was dissolved homogeneously under the same conditions.
Microparticles made of environmentally responsive hydrogels are fascinating candidates for application in drug delivery,16,17 catalysis,18 sensing,19,20 and photonics.21 Traditional synthetic methods including emulsion polymerization, are used to produce hydrogel microparticles with polydispersity.22,23 However, certain applications require microparticles with a narrow size distribution, for example, to stabilize the pharmacokinetics of drug delivery.24 Irregularly shaped or polydisperse embolic microparticles aggregate proximally into clusters, leading to chronic inflammatory responses in embolic particles for cancer therapeutic treatment.25,26
The microfluidic approach is at the forefront of research as a means of fabricating micro-sized particles with narrow size distributions and complex shapes.27-31 The advantages of fabricating microparticles in the microfluidic device are predicated by the small characteristic length of the microfluidic device, which results in a low Reynolds number. In contrast to traditional bulk emulsification where drops are formed in parallel, microdroplets produced in microfluidic devices are generated in series and subsequently polymerized into microparticles upon exposure to UV irradiation. The fundamental principle of droplet formation using a microfluidic device is balance between the interfacial tension and the shear force of the sheath fluid acting on the core fluid.
Despite the obvious advantages of microfluidic fabrication of droplets/particles, Janus droplets/particles consisting of the same base material are rarely reported because the internal morphology of these droplets/particles is generally disturbed by the diffusion and perturbation of the core fluids. To circumvent this intrinsic limitation, two groups recently reported the preparation of the Janus microparticles by employing heat-induced phase separation of colloidal nanoparticles and UV-directed phase separation.32,33
To this end, we report a microfluidic approach to synthesize Janus microhydrogels entirely composed of a single base material and obtain a product with clearly compartmentalized morphology. Our approach is based on the primary concept of liquid-liquid phase separation of supersaturated NIPAAm monomer. The resulting Janus microhydrogels were found to possess unique properties including anisotropic thermo-responsiveness and organophilic/hydrophilic loading capability.
Protocole
1. Fabrication d'un moule maître pour la focalisation hydrodynamique dispositif microfluidique (MMPB) par photolithographie
- La conception d' un photomasque pour la MMPB (figure 1a) à l' aide de conception (CAO) assistée par ordinateur suivant le protocole du fabricant.
- Rincer une plaquette 4 'de silicium avec de l'acétone, l'alcool isopropylique (IPA), et désionisée (DI) pour enlever la poussière organique et inorganique de la plaquette.
- Nettoyer la plaquette de silicium avec plasma O 2 à 100 W de puissance pendant 5 minutes pour augmenter la force de liaison entre la plaquette et SU-8.
- Spin-couche 4 ml de la résine photosensible négative SU-8 2150, sur la tranche à 3000 tpm pendant 30 secondes pour obtenir une épaisseur de 150 um (b1 de la figure 1b).
- Placez la tranche revêtue SU-8 sur une plaque chauffante pendant 5 min à 65 ° C, régler la température à 95 ° C, puis laisser la plaquette sur la plaque chauffante pendant 30 minutes pour cuisson douce.
- Placer ledestiné photomasque au- dessus de la plaquette et exposer à une lumière UV (260 mJ cm - 2, 26 s pour 10 mW cm -2) dans un dispositif d' alignement de masque (b2 sur la figure 1b).
- Effectuer la cuisson de post-exposition sur une plaque chauffante (65 ° C pendant 5 min puis 95 ° C pendant 12 minutes).
- Développer la plaquette par immersion dans un bain de révélateur SU-8 pendant 10 min, puis le transférer dans révélateur frais pendant 5 secondes pour obtenir une surface propre.
- Rincer la plaquette pendant 20 secondes avec de l' eau déminéralisée et le sécher pendant 10 secondes avec du gaz N2 (b3 sur la figure 1b). Utilisez la plaquette fabriquée comme un moule maître pour polydiméthylsiloxane (PDMS) coulée dans la section 2.
2. Fabrication de la MMPB par PDMS Castings
- Utilisez la plaquette à motif obtenu dans la section 1 du moule maître pour PDMS coulée.
- Mélanger le pré-polymère PDMS et d'un agent de durcissement de façon homogène dans un rapport pondéral de 10: 1; par exemple, en utilisant 1 g d'agent de durcissement pour 10 g de PDMS pré Polymer.
- Verser le PDMS prépolymère dans le moule maître et dégazer pendant 1 heure dans une chambre à vide (b4 à la figure 1b).
- Placer le moule maître avec le PDMS prépolymère dans un four à 65 ° C pendant 3 h.
- Couper les PDMS durcis dans la taille d'une puce unique à l'aide d'un scalpel. Décollez délicatement la réplique PDMS durci du moule maître à la main.
- Répétez les étapes 02.02 à 02.05 pour obtenir une réplique PDMS identique.
- Poinçonner les trous d'entrée et de sortie dans l'une des répliques à l'aide d'un trou perforateur ayant un diamètre légèrement inférieur au diamètre extérieur du tube de raccordement.
- Appliquer un traitement au plasma d'air à la zone de liaison de chaque réplique en utilisant un dispositif de traitement corona. 34
Attention: Utilisez le treater corona dans une zone avec une bonne ventilation pour éviter l' accumulation de l' ozone. - Déposer 5 pl de méthanol sur les zones de plasma traité par air. aligner Finement deux PDMS identiques répliques pour fabriquer la MMPB par manipu main lation, et vérifier l' alignement au moyen d' un microscope (b5 dans la figure 1b).
Remarque: L'air du plasma traité répliques PDMS sont assez collante et difficile à manipuler. Ainsi, 5 ul de methanol est ajoutée à la surface traitée par plasma d'air pour fonctionner comme lubrifiant. - Placez la MMPB dans un four réglé à 65 ° C pendant la nuit pour renforcer le lien entre deux PDMS répliques (b6 à la figure 1b). Bond deux répliques identiques de PDMS pour augmenter la hauteur du microcanal de MMPB et évitent le colmatage des micro-gouttelettes dans le canal microfluidique au cours du fonctionnement.
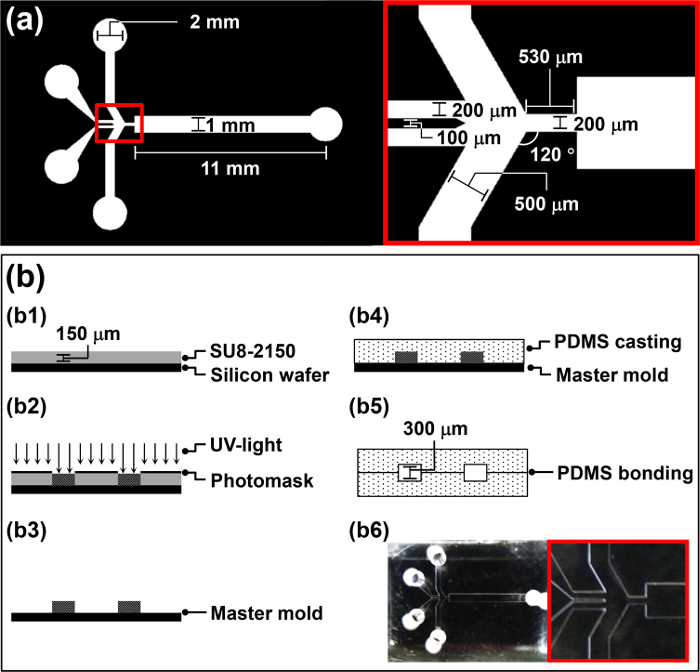
Figure 1: Vue d' ensemble de la procédure MMPB de fabrication (a) Paramètres de conception du photomasque pour la MMPB.. (B) Illustration de la procédure de fabrication pour la MMPB.ftp_upload / 52813 / 52813fig1large.jpg "target =" _ blank "> S'il vous plaît cliquer ici pour voir une version plus grande de cette figure.
3. Préparation de NIPAAm riche (N-riche), et NIPAAm pauvres (N-pauvres) Phases de séparation de phase de sursaturée NIPAAm
- Dissoudre NIPAAm monomère dans de l'eau DI à un rapport p / p de 1: 1 en utilisant un mélangeur à vortex; Par exemple, on dissout 10 g de NIPAAm dans 10 ml d'eau déminéralisée (première image de la figure 2a).
Remarque: Une fois que le monomère NIPAAm est complètement dissous à la température ambiante, la solution apparaît turbide (deuxième image de la figure 2a). Ce phénomène est le premier indice que la séparation de phase induite solubilité du monomère NIPAAm sursaturée a eu lieu avec succès. - Permettre à la solution de monomère au repos dans une position verticale à température ambiante pendant au moins 15 min. La phase supérieure est la phase N-riche, et la phase plus dense en bas est la N-pauvre phase (troisième image de la figure 2a). Les densités de thphases e N-riche et N-pauvres sont de 0,93 ± 0,01 et 0,99 ± 0,01 g cm -3, respectivement. 15
- Lorsque l'interface séparant les deux phases devient clair, extraire soigneusement 2 ml de solution de monomère à partir des phases N-riches et N-pauvres sans perturber cette interface à l'aide d'une pipette.
- Ajouter 4 mg de N, N '-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAAm) comme agent de réticulation et 4 mg de 4- (2-hydroxyéthoxy) phényl- (2-hydroxy-2-propyl) cétone comme photoinitiateur à l'extrait riche en N et N -poor solutions de monomères pour préparer les fluides noyau 1 et 2 pour la concentration en agent de réticulation faible (2 mg ml -1) échantillon (B1 et B2 sur la figure 2b).
- Répétez l'étape précédente 3.3 et ajoutez 80 mg de MBAAm et 4 mg de 4- (2-hydroxyéthoxy) phényl- (2-hydroxy-2-propyl) cétone dans chacun des extraits solution de monomère N-riche et N-pauvres pour préparer les fluides de base 1 et 2 pour la haute concentration en agent de réticulation (40 mg ml -1) échantillon (B3 et B4 à la Figure 2b).
- Dissoudre 10% en poids d'agent tensio - actif à l'huile dans une huile minérale pour préparer le fluide de gaine (b5 sur la figure 2b).
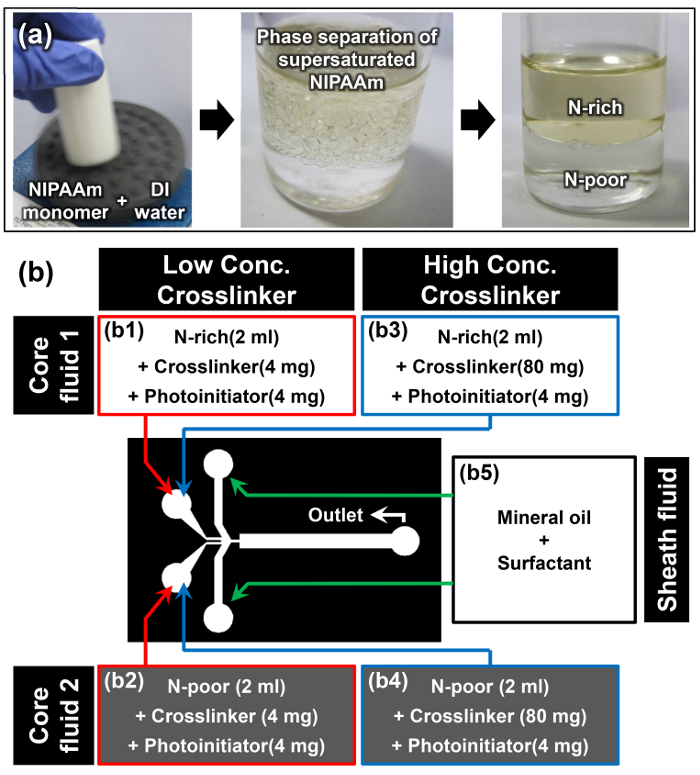
Figure 2:. Préparation du matériel pour Janus Microhydrogel Synthèse (a) Préparation de solutions de monomères N-riches et N-pauvres à travers la séparation de phase de sursaturée NIPAAm. (B) Les détails des matériaux et dispositif expérimental utilisé dans le protocole. S'il vous plaît cliquer ici pour voir une version plus grande de cette figure.
4. Synthèse de Janus Microhydrogels Utilisation de la MMPB
- Charge 2 ml de liquide de base 1 et 2 (b1, b2 b3 ou b4 in fi gure 2b) et le fluide de gaine (b5 sur la figure 2b) séparées en trois seringues de 3 ml.
- Monter les seringues dans les pompes à seringue et connecter chaque seringue à l'entrée de fluide appropriée de la MMPB en utilisant un tube (Figure (b). Utiliser un tube pour connecter la sortie de fluide de la MMPB à un réservoir de collecte.
- Définissez les pompes à seringue et laisser infuser des fluides de base 1 et 2 et fluide gaine à des taux de 2, 2, et 10 min pi -1 flux, respectivement.
- (Facultatif) Régler le débit de fluides de base 1 et 2 écoulement pour ajuster les rapports de volumes relatifs de chaque côté de la Janus microgouttelettes.
- Positionner la source de lumière UV perpendiculairement à environ 1 cm à partir du réservoir de collecte. Allumez la source de lumière UV et de suivre visuellement la production continue de microhydrogels Janus.
Attention: L' utilisation UV de protection-lunettes lors de la surveillance de la production microhydrogel. - Ramassez les microhydrogels Janus fabriqués dans un tube conique et lavez-les à l'aide de l'IAP. Ensuite, centrifuger le tube conique (780 g pendant 5 min) pour régler lamicrohydrogels.
- Répétez l'étape 4.6 plusieurs fois pour éliminer l'huile minérale entourant les microhydrogels Janus complètement.
- Répétez l'étape 4.6, mais l'utilisation d'eau DI avec un tensioactif d'eau de 0,005% (v / v) à la place de l'IPA pour enlever l'IPA restes autour des microhydrogels Janus.
- Rangez microhydrogels Janus complètement lavés dans un flacon de 10 ml contenant de l'eau DI.
5. Analyse de l'Anisotropic Thermo-réactivité de Janus Microhydrogels
- Utiliser une pipette pour placer microhydrogels Janus synthétisées à partir de la section 4 dans une plaque de 24 puits. Laisser les microhydrogels se déposer pendant 15 secondes jusqu'à ce qu'une monocouche se forme à la surface du fond du puits.
- Obtenir une image de la Janus microhydrogel à 24 ° C en utilisant un microscope optique en position verticale avec une lentille d'objectif 5X.
- Fixer un module thermo-électrique sous la plaque de puits et à contrôler la tension de ce module pour augmenter la température de la solution contenant les micro Janushydrogels à 32 ° C.
- Obtenir une image de la microhydrogel Janus à 32 ° C une fois de plus à l'aide d'un microscope optique verticale avec un objectif 5X.
- Répétez les étapes 5,2-5,4 24 fois, en prenant soin de choisir un microhydrogel Janus différent pour l'analyse statistique.
- A partir des 25 images de différents microhydrogels Janus à 24 et 32 ° C, mesurer le rayon des parties PN-riches et PN-pauvres des microhydrogels Janus en utilisant un logiciel d'analyse d'images selon les instructions du fabricant.
Résultats
La figure 3a présente un schéma du dispositif expérimental utilisé pour synthétiser microhydrogels Janus via le MMPB. Les phases riches en azote et la N-pauvres étaient précisément injectés dans la MMPB comme fluides de base 1 et 2, puis fusionnés et divisés en microgouttelettes Janus à l'orifice par le fluide d'enveloppement d'une huile minérale en raison de l'instabilité capillaire de Rayleigh. Par conséquent, microgouttelettes J...
Discussion
Deux matériaux de base non miscibles sont généralement utilisés pour synthétiser les microhydrogels Janus. Jusqu'à récemment, microhydrogels Janus composé de la même matière de base ont été rarement signalés et les microhydrogels rapportés Janus n'a pas eu une morphologie interne claire en raison de la perturbation causée par la miscibilité des matériaux constitutifs. 35, 36 Dans ce protocole, nous démontrons une méthode pour synthétiser microhydrogels Janus composées entièrement...
Déclarations de divulgation
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Remerciements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP (Nos. 2014R1A2A1A01006527 and 2011-0030075).
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silicon wafer | LG Siltron | 4", Test grade | Wafer for master mold fabrication |
| Acetone | Samchun Pure Chemical | A0097 | Cleaning silicon wafer |
| Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) | Daejung Chemicals & Metals | 5035-4404 | Cleaning silicon wafer |
| Water purification system | Merck Millipore | EMD Millipore RIOs Essential 5 | Prepering deionized water |
| O2 plasma machine | Femto Science | VITA-A | Cleaning silicon wafer |
| SU-8 2150 negative photoresist | MicroChem | Y111077 0500L1GL | Photoresist for master mold fabrication |
| Hot plate | Misung Scientific | HP330D, HP150D | Baking SU-8 |
| SU-8 developer | Microchem | Y020100 4000L1PE | Developing SU-8 |
| Mask aligner system for photolithograpy | Shinu Mst Co. | CA-6M | Photolithography |
| Sylgard 184 silicone elastomer kit | Dow Corning | 1064891 | PDMS casting |
| Laboratory Corona Treater | Electro-technic Products Inc. | Model BD-20AC | PDMS air plasma treatment |
| N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) | Sigma-Aldrich | 415324-50G | Monomer |
| N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAAm) | Sigma-Aldrich | 146072-100G | Crosslinker of NIPAAm |
| 4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl-(2-hydroxy-2-propyl)ketone, Irgacure 2959 | BASF | 55047962 | Photoinitiator of NIPAAm |
| ABIL EM 90 | Evonik Industries | 201109 | Sufactant for oil |
| Vortex mixer | Scientific Industries Inc. | Vortex-Genie 2 | Mixing |
| Tygon tubing | Saint-Gobain | I.D. 1/32", O.D. 3/32", Wall 1/32" | Connecting tube between syringes and HFMD |
| UV light source | Hamamatsu | Spot light source LC8 | Polymerization from NIPAAm to PNIPAAm |
| Syringes, NORM-JECT (3ml) | Henke-Sass Wolf GmbH | 22767 | Loading of materials |
| Syringe pump | KD Scientific | KDS model 200 | Perfusion of materials |
| Tegitol Type NP-10 | Sigma-Aldrich | NP10-500ML | Surfactant for water |
| Oil red O | Sigma-Aldrich | O0625-25G | Dye for N-rich phase |
| Oil Blue N | Sigma-Aldrich | 391557-5G | Dye for N-rich phase |
| Yellow food dye | Edentown F&B | NA | Dye for N-poor phase |
| Green food dye | Edentown F&B | NA | Dye for N-poor phase |
| Power supply | Agilent | E3649A | Power soruce for thermoelectric moduel |
| Thermoelectric module | Peltier | FALC1-12710T125 | Temparature control |
| Centrifuge machine | Labogene | 1248R | Settling down microhydrogels |
| 24-well plate | SPL Life Sciences | 32024 | Reservoir for observation |
| Optical microscope | Nikon | ECLIPSE 80i | Optical observation |
| Image analysis software | IMT i-Solution Inc. | iSolutions DT | Measurement of radius |
Références
- Hoffman, A. S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 54 (1), 3-12 (2002).
- Qiu, Y., Park, K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 53 (3), 321-339 (2001).
- Hirokawa, Y., Tanaka, T. Volume phase transition in a nonionic gel. J. Chem. Phys. 81 (12), 6379-6380 (1984).
- Bae, Y. H., Okano, T., Hsu, R., Kim, S. W. Thermo-sensitive polymers as on-off switches for drug release. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 8 (10), 481-485 (1987).
- Yoshida, R., et al. Comb-type grafted hydrogels with rapid deswelling response to temperature changes. Nature. 374 (6519), 240-242 (1995).
- Tanaka, T. Collapse of gels and the critical endpoint. Phys. Rev. Lett. 40 (12), 820-823 (1978).
- Tanaka, T., et al. Phase transitions in ionic gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 (20), 1636-1639 (1980).
- Zhao, Y. L., Stoddart, J. F. Azobenzene-based light-responsive hydrogel system. Langmuir. 25 (15), 8442-8446 (2009).
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C., Bromberg, L., Concheiro, A. Light-sensitive intelligent drug delivery systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 85 (4), 848-860 (2009).
- Tanaka, T., Nishio, I., Sun, S. T., Ueno-Nishio, S. Collapse of gels in an electric field. Science. 218 (4571), 467-469 (1982).
- Kwon, I. C., Bae, Y. H., Kim, S. W. Electrically credible polymer gel for controlled release of drugs. Nature. 354 (6351), 291-293 (1991).
- Obaidat, A. A., Park, K. Characterization of protein release through glucose-sensitive hydrogel membranes. Biomaterials. 18 (11), 801-806 (1997).
- Kataoka, K., Miyazaki, H., Bunya, M., Okano, T., Sakurai, Y. Totally synthetic polymer gels responding to external glucose concentration: their preparation and application to on-off regulation of insulin release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 (48), 12694-12695 (1998).
- Heskins, M., Guillet, J. E. Solution properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2 (8), 1441-1455 (1968).
- Sasaki, S., Okabe, S., Miyahara, Y. Thermodynamic properties of N-isopropylacrylamide in water: solubility transition, phase separation of supersaturated solution, and glass formation. J. Phys. Chem. B. 114 (46), 14995-15002 (2010).
- Bromberg, L., Alakhov, V. Effects of polyether-modified poly(acrylic acid) microgels on doxorubicin transport in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell layers. J. Controlled Release. 88 (1), 11-22 (2003).
- Coughlan, D. C., Quilty, F. P., Corrigan, O. I. Effect of drug physicochemical properties on swelling/deswelling kinetics and pulsatile drug release from thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. J. Controll. Release. 98 (1), 97-114 (2004).
- Bergbreiter, D. E., Case, B. L., Liu, Y. S., Caraway, J. W. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) soluble polymer supports in catalysis and synthesis. Macromolecules. 31 (18), 6053-6062 (1998).
- Lapeyre, V., Gosse, I., Chevreux, S., Ravaine, V. Monodispersed glucose-responsive microgels operating at physiological salinity. Biomacromolecules. 7 (12), 3356-3363 (2006).
- Hoare, T., Pelton, R. Engineering glucose swelling responses in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based microgels. Macromolecules. 40 (3), 670-678 (2007).
- Xu, S., Zhang, J., Paquet, C., Lin, Y., Kumacheva, E. From hybrid microgels to photonic crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 13 (6), 468-472 (2003).
- Clarke, J., Vincent, B. Stability of non-aqueous microgel dispersions in the presence of free polymer. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1. 77 (8), 1831-1843 (1981).
- Mears, S. J., Deng, Y., Cosgrove, T., Pelton, R. Structure of sodium dodecyl sulfate bound to a poly (NIPAM) microgel particle. Langmuir. 13 (7), 1901-1906 (1997).
- Shah, R. K., Kim, J. W., Agresti, J. J., Weitz, D. A., Chu, L. Y. Fabrication of monodisperse thermosensitive microgels and gel capsules in microfluidic devices. Soft Matter. 4 (12), 2303-2309 (2008).
- Jack, C. R., Forbes, G., Dewanjee, M. K., Brown, M. L., Earnest, F. Polyvinyl alcohol sponge for embolotherapy: particle size and morphology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 6 (4), 595-597 (1985).
- Derdeyn, C. P., Moran, C. J., Cross, D. T., Dietrich, H. H., Dacey, R. G. Polyvinyl alcohol particle size and suspension characteristics. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 16 (6), 1335-1343 (1995).
- Han, K., et al. Effect of flow rates on generation of monodisperse clay-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) embolic microspheres using hydrodynamic focusing microfluidic device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50 (6), 06-12 (2011).
- Seo, K. D., Doh, J., Kim, D. S. One-step microfluidic synthesis of Janus microhydrogels with anisotropic thermo-responsive behavior and organophilic/hydrophilic loading capability. Langmuir. 29 (49), 15137-15141 (2013).
- Seo, K. D., Kim, D. S. Microfluidic synthesis of thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate microhydrogels as chemo-embolic microspheres. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24 (8), 085001 (2014).
- Seo, K. D., Kwak, B. K., Kim, D. S., Sánchez, S. Microfluidic-assisted fabrication of flexible and location traceable organo-motor. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 14 (3), 298-304 (2015).
- Seo, K. D., Kim, D. S., Sánchez, S. Fabrication and application of complex-shaped microparticles via microfluidics. Lab Chip. , (2015).
- Shah, R. K., Kim, J. W., Weitz, D. A. Janus supraparticles by induced phase separation of nanoparticles in droplets. Adv. Mater. 21 (19), 1949-1953 (2009).
- Lone, S., et al. Microfluidic synthesis of Janus particles by UV-directed phase separation. Chem. Commun. 47 (9), 2634-2636 (2011).
- Hauber, K., Drier, T., Beebe, D. PDMS bonding by means of a portable, low-cost corona system. Lab chip. 6 (12), 1548-1549 (2006).
- Nisisako, T., Torii, T., Takahashi, T., Takizawa, Y. Synthesis of monodisperse bicolored Janus particles with electrical anisotropy using a microfluidic co-flow system. Adv. Mater. 18 (9), 1152-1156 (2006).
- Seiffert, S., Romanowsky, M. B., Weitz, D. A. Janus microgels produced from functional precursor polymers. Langmuir. 26 (18), 14842-14847 (2010).
- Peppas, N. A., Hilt, J. Z., Khademhosseini, A., Langer, R. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 18 (11), 1345-1360 (2006).
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon