A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
ערוץ יחיד הדמיה ניתוח וסידן בPodocytes של glomeruli מבודדת טרי
In This Article
Summary
Changes in the intracellular calcium levels in the podocytes are one of the most important means to control the filtration function of glomeruli. Here we explain a high-throughput approach that allows detection of real-time calcium handling and single ion channels activity in the podocytes of the freshly isolated glomeruli.
Abstract
Podocytes (renal glomerular epithelial cells) are known to regulate glomerular permeability and maintain glomerular structure; a key role for these cells in the pathogenesis of various renal diseases has been established since podocyte injury leads to proteinuria and foot process effacement. It was previously reported that various endogenous agents may cause a dramatic overload in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in podocytes, presumably leading to albuminuria, and this likely occurs via calcium-conducting ion channels. Therefore, it appeared important to study calcium handling in the podocytes both under normal conditions and in various pathological states. However, available experimental approaches have remained somewhat limited to cultured and transfected cells. Although they represent a good basic model for such studies, they are essentially extracted from the native environment of the glomerulus. Here we describe the methodology of studying podocytes as a part of the freshly isolated whole glomerulus. This preparation retains the functional potential of the podocytes, which are still attached to the capillaries; therefore, podocytes remain in the environment that conserves the major parts of the glomeruli filtration apparatus. The present manuscript elaborates on two experimental approaches that allow 1) real-time detection of calcium concentration changes with the help of ratiometric confocal fluorescence microscopy, and 2) the recording of the single ion channels activity in the podocytes of the freshly isolated glomeruli. These methodologies utilize the advantages of the native environment of the glomerulus that enable researchers to resolve acute changes in the intracellular calcium handling in response to applications of various agents, measure basal concentration of calcium within the cells (for instance, to evaluate disease progression), and assess and manipulate calcium conductance at the level of single ion channels.
Introduction
הכליות לשמור על איזון homeostatic לחומרים שונים ולהסדיר את נפח דם באופן שקובע כולל לחץ דם. הפרעות בסינון הכלייתי, הספיגה או להוביל להפרשה או מצבים פתולוגיים מלווים, החל יתר או תת לחץ דם בסופו מחלת כליות בשלב שסופו של דבר דורשת השתלת כליה. יחידת כליות הסינון (glomerulus) מורכבת משלוש שכבות - האנדותל הנימים, קרום במרתף ושכבת תא בודד של תאי אפיתל - podocytes, אשר ממלא תפקיד מרכזי בשמירה על שלמות החריץ-סרעפת והפונקציה 1. חוסר תפקוד במסנן גלומרולרי permselective גורם לאובדן שתן של מקרומולקולות, כגון חלבון. סוכנים שונים עשויים להשפיע על המבנה של podocytes ותהליכי רגלם, הקובע את שלמות מחסום סינון glomeruli.
Podocytes מעורב בתחזוקה של הגנב שפונקצית סינון eruli. זה כבר נקבע כי טיפול סידן נאותה podocyte מוביל לפציעת תא וממלא תפקיד חשוב בהתקדמות של צורות שונות של nephropathies 2,3. לכן, פיתוח של מודל המאפשר למדידה ישירה של שינויי ריכוז סידן תוך תאי יהיה אינסטרומנטלי ללימודים של פונקצית podocyte. glomeruli המבודדת שימשה בעבר במחקרים רבים, כולל מדידה של מקדם השתקפות אלבומין משנה 4 והערכה של זרמים סלולריים נפרד במדידות תיקון מהדק אלקטרו כל תא 5,6. בעבודה הנוכחית אנו מתארים את הפרוטוקול שמאפשר לחוקר למדוד תאיים שינויי ריכוז סידן בתגובה לבקשות של סוכנים תרופתיים, להעריך את הרמות בסיסיות של סידן בתוך התאים, ולהעריך את פעילות ערוצי סידן בודדת. מדידות ריכוז סידן Ratometric וelectrop תיקון מהדקhysiology שימש לקביעת שינויים בריכוז סידן תוך תאי במסגרת פעילות podocyte והערוץ, בהתאמה.
Protocol
שימוש בבעלי חיים ולרווחתם צריך לדבוק במדריך NIH לטיפול ושימוש בחי המעבדה הבא פרוטוקולים נבדקו ואושרו על ידי הוועדה המוסדית הטיפול בבעלי חיים והשימוש (IACUC).
פלאש 1. הכליות
- השתמש עכברוש 8 עד 12 בשבוע ישן זכר (הציע הוא זן ספראג Dawley, אולם זנים אחרים של גיל ומין שונים ניתן להשתמש עם שינויים מתאימים).
- להרדים את החיה על פי הנוהל מתיר פרוטוקול IACUC; לפקח עומק ההרדמה ולבדוק את בעלי החיים. התיאור מפורט של הניתוח שיבוצע ב1.3 - ניתן למצוא 1.8 בet al Ilatovskaya 7.
- לאחר הרדמה נכונה, למקם את החיה על שולחן ניתוחים בטמפרטורה מבוקרת, לעשות (עד 3 אינץ 'באורך) חתך קו האמצע של הבטן, ולחשוף את הווריד הנבוב ואב העורקים.
- הכנס מייתר סביב עורקי צליאק וmesenteric מעולה והבטןאב העורקים מעל אלה; לא לקשור.
- בוטה לנתח אב העורקים בבטן מתחת לעורקי הכליה, ומניח את שני חיבורים אותיות סביבו, אבל לא לקשור, אז מהדק את אב העורקים מעל חיבורי האותיות ולקשור את החוט התחתון.
- קטטר אב העורקים עם צינורות פוליאתילן PE50 (המצורפים למשאבת מזרק מלאה PBS) מתחת למהדק ולתקן את הקטטר עם המייתר השני; להסיר את המהדק, להפעיל את המשאבה, ולקשור את אב העורקים ועורקי mesenteric עם צליאק. במהירות לעשות חתך בעורק כליה כדי להקל את הלחץ.
- להשרות את אב העורקים עם PBS-מקורר מראש עבור 2 או 3 דקות בקצב של 6 מיליליטר / דקה.
- עצור זלוף, בלו וdecapsulate 7 הכליות, ולשים אותם על קרח בפתרון PBS. להרדים את החיה על פי פרוטוקול שאושר על ידי IACUC.
2. בידוד של glomeruli העכברוש
- הכן 30 מיליליטר של תמיסה טריות של BSA 5% בRPMI 1640.
- באמצעות סכין גילוח ומספריים,לבודד את הקליפה של שני הכליות, ולאחר מכן ברר עד הומוגנית. הליך זה כבר תואר קודם לכן 7.
- לדחוף את הרקמה טחונות בשלב הקודם דרך מסננת נירוסטה 100 רשת (ספוג מראש ב 5% BSA / פתרון RPMI) בעזרת מרית. לאסוף את הזרימה דרך בכוח הכבידה לאפשר הזרימה דרך לעבור דרך מסננת 140 רשת.
- סנן את הזרימה דרך נאסף מהרשת 140 מסננת באמצעות מסננת רשת מראש ספוג 200, לבטל את התסנין, ולשטוף את החלק העליון של המסננת עם 10 - 15 מיליליטר של פתרון BSA / RPMI מוכן לאסוף glomeruli שהמשקעת ב המסננת.
- שים את פתרון BSA / RPMI המכיל glomeruli על קרח בצינור 15 מ"ל ולתת משקעי glomeruli בחלק התחתון של הצינור עד 20 דקות. תרכיז glomeruli בחלק התחתון של הצינור יהיה לראות בבירור. הסר את הפתרון העודף, עוזב כ 2 מיליליטר בצינור.
3. ערוץ יחיד תיקון מהדק אלectrophysiology
- הכן שבבי זכוכית כיסוי 5 X 5 מ"מ על ידי ציפוי אותם עם MW 70,000 - 150,000 פולי-ʟ ליזין, ולתת יבש. השתמש כ -30 μl של פתרון מסונן סטרילי 0.01% במים לכיסוי זכוכית.
- לחמם את הפתרונות הניסיוניים לRT ולמלא את תא תיקון- clamp ופיפטה. לניטור ערוצי TRPC, להשתמש בפתרון אמבטיה, במ"מ: 126 NaCl, 1 CaCl 2, 10 HEPES, 2 MgCl 2, 10 גלוקוז, pH 7.4; פיפטה: 126 NaCl, 1.5 CaCl 2, 10 HEPES, 10 גלוקוז; pH 7.4.
- להוסיף מעכבים לפתרון פיפטה לחסום את הפעילות של ערוצי אנדוגני, שאינם רלוונטיים ללימודים (המומלצים הם: חומצת niflumic 100 מיקרומטר או DIDS (לחסום Ca 2 + Cl -activated - ערוצים), 10 מ"מ TEA (לעכב גדולות-מוליכות 2 Ca + - K התלוי + ערוץ), 10 iberiotoxin ננומטר (לחסום את Ca 2 + K + ערוצי -activated), 10 מיקרומטר nicardipine (לחסום N-סוג Ca2 + ערוצים)) ישירות לפני ניסוי תיקון מהדק.
- לערבב בעדינות הפתרון המכיל glomeruli, ולאחר מכן להחיל כ -50 μl שלו לשבבי זכוכית הכיסוי מצופה פולי-ʟ ליזין. בואו glomeruli לצרף לכ 5 דקות.
- הזז את שבבי זכוכית עם glomeruli לתא תיקון- clamp מראש מלא בפתרון האמבטיה; perfuse קאמרי בשיעור של 3 מיליליטר / דקה 1 דקות כדי להבטיח את הסרת glomeruli הפנוייה.
- לנהל ניסוי תיקון- clamp קונבנציונלי במצב 7-מצורף תא. עם טפטפת זכוכית (7-10 התנגדות פיפטה MΩ) ליצור חותם גבוהה התנגדות בין פיפטה וקרום podocyte ידי החלת שאיבה עדינה (פיפטה המצורפת לpodocyte על פני השטח של glomerulus המבודד מוצג באיור 2, ב משמאל).
- למדידות מצורפים תא, נמוך לעבור הזרמים ב 300 הרץ על ידי מסנן שמונה-מוט בסל.
- Use מבודד glomeruli בניסויי תיקון מהדק עד 4 - 6 שעות. שמור את חלק glomeruli המניות על קרח.
4. מדידות ratiometric Confocal הקרינה של ריכוז סידן תוך תאים בPodocytes
- הנח 500 μl של חלק glomeruli (שתואר על 2.5) 0.5 מיליליטר בצינור חרוטי ולהוסיף צבעי סידן פורעה אדום, בבוקר וFluo-4, בבוקר. השתמש 2 מ"מ ו 1 ריכוזי מניית מ"מ של פורעה האדום, בבוקר וFluo-4, בבוקר, בהתאמה (חנות ב -20 ° C, מומס DMSO) ולהשתמש 2.5 μl של כל צבע לμl 500 של חלק glomeruli. מייד לאחר תוספת של הצבעים לכסות את הצינור עם רדיד אלומיניום.
- מקום צינורות על שייקר מסתובב לפחות 20 דקות עד שעה 1 בRT.
הערה: ניתן להוסיף סוכנים תרופתי במהלך שלב זה. - הכן coverslips זכוכית, לכסות אותם עם פולי-ליזין ʟ ולאפשר ייבוש באמצעות סט צלחת מחומם ל -70 מעלות צלזיוס.
- ברגע שהטעינה של צבעי סידן היא completדואר, יחול של glomeruli מכילה פתרון לcoverslips המצופה פולי-ליזין 100 ʟ μl ולתת להם להיצמד למשטח לכ -5 דקות. הר coverslips המצורף glomeruli לחדר הדמיה, ותנקב עם פתרון האמבטיה (המכיל (במ"מ): 145 NaCl, 4.5 KCl, 2 MgCl 2, 10 HEPES, pH 7.35) בשיעור של 3 מיליליטר / דקה להסרת glomeruli הפנוייה והצבעים שנותרו.
- הגדר את המיקרוסקופ סריקת לייזר confocal לגל עירור 488 ננומטר ומסנני פליטה (525/25 וננומטר 650/25 לFluo-4 ופורע אדום, בהתאמה). הגדר את תוכנת הדמיה לתדר ורזולוציה רצויים.
- מצא glomeruli בbrightfield ולאחר מכן הפעל את זיהוי של אותות הקרינה. התאם את עוצמת הלייזר לכל צבע כדי למנוע הרוויה של האות. בחר את מישור המוקד עם podocytes שישירות מחוברים לזכוכית. זה ממזער את ההשפעה נגרמת על ידי התכווצות של glomerulus בתגובה לתרופהיישום. פעמיים לבדוק שglomerulus של בחירה מצורף גם לזכוכית;
- התחל הדמיה מישור המוקד של בחירה (לקחת 512 x 512 תמונות עם התדירות שנקבעה ב 4 שניות לדמיין Ca 2 + שינויים מהירים חולפים. השתמש 60x / עדשה אובייקטיבית דומה NA 1.4 או לתמונה ברזולוציה גבוהה), תחול תרופות של עניין, ולהקליט את התגובה.
- בחר מטוס מוקד רצוי (קרוב למשטח של הזכוכית ככל האפשר, כדי להבטיח הדמיה של podocytes על פני השטח של glomerulus). בדוק את עוצמת הקרינה על Fluo4 וערוצי FuraRed, ולוודא כי glomerulus נראה בbrightfield ברור.
- התחל הדמיה. לפני היישום של כל תרופות, שיא לפחות 1 דקות של הקרינה בסיס לוודא כי האות היא יציבה (אין קוצים פתאומיים או דהייה של האות).
- החל תרופות הרצויות בעזרת micropipette; להיות זהיר ולוודא את התרופה הצליחה לפזר היטב ולהגיע לglomerUlus. מערבבים את פתרון האמבטיה בעדינות אם יש צורך, לפקח על מישור המוקד הנבחר ולבדוק שזה לא זז מחוץ לפוקוס בגלל יישום הסמים.
- רשום את השינויים בעוצמת הקרינה לאותות Fluo4 וFuraRed. ודא ההקלטה היא מספיק זמן, על ידי מחכה עד האות מגיעה לרמת הרמה או מגיעה לשיא ואז חוזרת לנקודת התחלה. לבצע שינוי פתרון או תוספת של כל תרופות אחרות במידת הצורך.
- לעצור את ההקלטה, ולשמור את הקובץ בתבנית המקורית של התוכנה.
ניתוח תמונה 5. למדידות סידן
- לבצע ניתוח תמונה עם התוכנה הפתוחה ImageJ מצויד בתוסף שירות ND המאפשר יבוא תמונות בפורמט ND2 הילידים.
- לייבא את התמונה ברצף; לוודא לפצל את הערוצים ולהשתמש בגווני אפור מצב hyperstack.
- עקוב → כלים → נתיב מנהל ROI לנתח בתוכנת ImageJ לoעט חלון מנהל החזר על השקעה. בחר כמה אזורים של העניין (podocytes) באמצעות כלי בחירה סגלגלים ו" הוסף (t) "הפונקציה במנהל ההחזר על ההשקעה. כהחזר על ההשקעה האחרונה, בחר את האזור ברקע; להציל את ROIs נבחר (עוד → שמור).
- סמן את החלון המכיל את הערוץ שנבחר לניתוח. השתמש עוד → פונקצית מדידה רב במנהל את ההחזר על ההשקעה, סמן את התיבה "שורה אחת לכל פרוסה" בדיאלוג שקופץ החוצה, ולאחר מכן לחץ על אישור. התוצאות יוצגו בפורמט שניתן להגדיר בחלון התוצאות: להיכנס לתוצאות אפשרות תפריט → מדידות, בחר "Mean ערך אפור" ולחשב את ערכי עוצמה עבור כל פיקסל את ההחזר על ההשקעה, אשר יוצג ב חלון תוצאות בעמודות נפרדות לכל החזר על השקעה.
- העתק את ערכי עצמת ROI נמדדו עבור כל ערוץ (Fluo-4 ופורע אדום) לתוך תוכנת ניתוח נתונים העדיפה; ערכי עוצמת רקע לגרוע מכל DATנקודה.
- עבור כל נקודת זמן לחשב את היחס של עוצמות של Fluo-4 לערוצי פורעה אדומים. פיזור עלילה / קו שינויים של חולף Ca 2 + לכל החזר על השקעה נקודה-זמן. חישוב ממוצע ערכים / SE לglomeruli נבחרה.
הערה: טור זמן צריך להיות מוגדר על פי תדירות הדמיה נבחרה על 4.5.
6. חישובי ריכוז סידן תוך תאים באמצעות Fluo-4 פלואורסצנטי איתותים
- קח דוגמא של glomeruli ולבצע את פרוטוקול הניסוי עד שלב 4.7. לאחר ההקלטה של הקרינה הרקע להוסיף ionomycin (ריכוז סופי בתא האמבטיה צריך להיות 10 מיקרומטר) לפתרון האמבטיה, ועליית עוצמת הקרינה שיא. ברגע שמגיעה למקסימום העצמה שלה והריקבון מתחיל, להוסיף MnCl 2 (ריכוז סופי צריך להיות 5 מ"מ) כדי להרוות את הקרינה 8.
- לנתח את הנתונים שהתקבלו ב6.1. העתק את Fluo-4 ערכי עוצמת אות ROI מתקבלים לפילפרוטוקול המתואר ב5.1-5.5 על ידי תוכנת ניתוח מועדפת.
- חישוב ריכוז סידן תוך תאי (בננומטר) בpodocyte המתאים להחזר על ההשקעה באמצעות נוסחא:
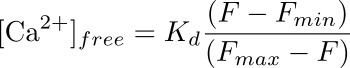
שם ד K הוא ניתוק שנקבע מראש קבוע לFluo-4 (345 ננומטר), F הוא העצמה בנקודה הזמן שאתה חישוב ריכוז סידן ל( בסיס), ודקות F ו- F מקסימום הם ערכי העצמה ב נקודת העומס מרבי סידן (לאחר יישום ionomycin) ואחרי מרווה של הקרינה (עם MnCl 2), בהתאמה (ראה איור 3).
תוצאות
כאן אנו התייחסנו לבעיה של מדידת שינויים חריפים ברמות סידן בpodocytes. איור 1 מראה ייצוג סכמטי של פרוטוקול הניסוי תוכנן על מנת לבצע הדמיה confocal הקרינה חי ברזולוציה גבוהה והקלטות פעילות ערוץ יון אחד בpodocytes של טרי glomeruli מכרסם מבודדת. בקצרה, לאחר החולדה מורדמת, צריכים ?...
Discussion
הגישה המתוארת כאן מאפשרת הניתוח של טיפול בסידן על ידי podocytes של glomeruli המכרסמים. טכניקה זו מאפשרת יישום של אלקטרופיזיולוגיה תיקון מהדק היחידה ערוץ וההדמיה confocal ratiometric הקרינה. עם זאת, ניתן להשתמש בשתי הגישות בנפרד, בכוחות עצמם. יש הפרוטוקול המוצע כמה צעדים פשוטים יחסית, ה...
Disclosures
יש המחברים אין לחשוף.
Acknowledgements
המחברים מבקשים להודות לגלן סלוקום (ספר לרפואה של ויסקונסין) וקולין א לאבין (ניקון מכשירים, Inc) לקבלת סיוע טכני מעולה עם ניסויים במיקרוסקופ. גרגורי בלס הוא הודה להגהה ביקורתית של כתב היד. מחקר זה נתמך על ידי המכון הלאומי לבריאות וHL108880 מענק איגוד סוכרת האמריקנית להעניק 1-15-BS-172 (לAS), ובן ג 'יפס מחקר המלגה מהאגודה לנפרולוגיה האמריקנית (ל- DVI).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Fluo4 AM | Life Technologies | F14217 | 500 µl in DMSO |
| FuraRed AM | Life Technologies | F-3020 | |
| Poly-ʟ-lysine | Sigma-Aldrich | P4707 | |
| Pluronic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | F-68 | solution |
| Ionomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | I3909-1ML | |
| Tube rotator | Miltenyi Biotec GmbH | 130-090-753 | Germany |
| Nikon confocal microscope (inverted) | Nikon | Nikon A1R | Laser exitation 488 nm. Emission filters 500-550 nm and 570-620 nm |
| Objective | Nikon | Plan Apo 60x/NA 1.4 Oil | |
| Cover Glass | Thermo Scientific | 6661B52 | |
| High vacuum grease | Dow Corning | Silicone Compound | |
| Software | Nikon | Nikon NIS-Elements | |
| Recording/perfusion chamber | Warner Instruments | RC-26 | |
| Patch clamp amplifier | Molecular Devices | MultiClamp 700B | |
| Data acquisition system | Molecular Devices | Digidata 1440A | Axon Digidata® System |
| Low pass filter | Warner Instruments | LPF-8 | 8 pole Bessel |
| Borosilicate glass capillaries | World Precision Instruments | 1B150F-4 | |
| Micropipette puller | Sutter Instrument Co | P-97 | Flaming/Brown type micropipette puller |
| Microforge | Narishige | MF-830 | Japan |
| Motorized micromanipulator | Sutter Instrument Co | MP-225 | |
| Inverted microscope | Nikon | Eclipse Ti | |
| Microvibration isolation table | TMC | equipped with Faraday cage | |
| Multichannel valve perfusion system | AutoMake Scientific | Valve Bank II | |
| Recording/perfusion chamber | Warner Instruments | RC-26 | |
| Software | Molecular Devices | pClamp 10.2 | |
| Nicardipine | Sigma-Aldrich | N7510 | |
| Iberiotoxin | Sigma | I5904-5UG | |
| Niflumic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | N0630 | |
| DIDS | Sigma-Aldrich | D3514-25MG | |
| TEA chloride | Tocris | T2265 | |
| RPMI 1640 | Life Technologies | 11835030 | without antibiotics |
| BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | A8327 | 30% albumin solution |
| Temperature controlled surgical table | MCW core | for rodents | |
| Steel sieves: | #100 (150 μm), 140 (106 μm) | ||
| Gilson, Inc SIEVE 3 SS FH NO200 | Fisher Sci | 50-871-316 | |
| Gilson, Inc SIEVE 3 SS FH NO270 | Fisher Sci | 50-871-318 | |
| Gilson, Inc SIEVE 3 SS FH NO400 | Fisher Sci | 50-871-320 | |
| mesh 200 | Sigma-Aldrich | s4145 | screen for CD-1 |
| Binocular microscope | Nikon | Eclipse TS100 | |
| Binocular microscope | Nikon | SMZ745 | |
| Syringe pump-based perfusion system | Harvard Apparatus | ||
| Polyethylene tubing | Sigma-Aldrich | PE50 | |
| Isofluorane anesthesia |  VetEquip, Inc. VetEquip, Inc. | 911103 | |
| Other basic reagents | Sigma-Aldrich |
References
- Machuca, E., Benoit, G., Antignac, C. Genetics of nephrotic syndrome: connecting molecular genetics to podocyte physiology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, R185-R194 (2009).
- Haraldsson, B., Nystrom, J., Deen, W. M. Properties of the glomerular barrier and mechanisms of proteinuria. Physiol. Rev. 88, 451-487 (2008).
- Patrakka, J., Tryggvason, K. New insights into the role of podocytes in proteinuria. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 5, 463-468 (2009).
- Savin, V. J., Sharma, R., Lovell, H. B., Welling, D. J. Measurement of albumin reflection coefficient with isolated rat glomeruli. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 3, 1260-1269 (1992).
- Gloy, J., et al. Angiotensin II depolarizes podocytes in the intact glomerulus of the Rat. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 2772-2781 (1997).
- Nitschke, R., et al. Angiotensin II increases the intracellular calcium activity in podocytes of the intact glomerulus. Kidney Int. 57, 41-49 (2000).
- Ilatovskaya, D., Staruschenko, A. Single-channel analysis of TRPC channels in the podocytes of freshly isolated glomeruli. Methods Mol Biol. 998, 355-369 (2013).
- Snitsarev, V. A., McNulty, T. J., Taylor, C. W. Endogenous heavy metal ions perturb fura-2 measurements of basal and hormone-evoked Ca2+ signals. Biophys. J. 71, 1048-1056 (1996).
- Fukuda, A., Fujimoto, S., Iwatsubo, S., Kawachi, H., Kitamura, K. Effects of mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II receptor blockers on proteinuria and glomerular podocyte protein expression in a model of minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Nephrology (Carlton). 15, 321-326 (2010).
- Abramowitz, J., Birnbaumer, L. Physiology and pathophysiology of canonical transient receptor potential channels). FASEB J. 23, 297-328 (2009).
- Heeringa, S. F., et al. A novel TRPC6 mutation that causes childhood FSGS. PLoS ONE. 4, e7771 (2009).
- Zhang, X., Song, Z., Guo, Y., Zhou, M. The novel role of TRPC6 in vitamin D ameliorating podocyte injury in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 399, 155-165 (2015).
- Bohrer, M. P., et al. Mechanisms of the puromycin-induced defects in the transglomerular passage of water and macromolecules. J. Clin. Invest. 60, 152-161 (1977).
- Olson, J. L., Rennke, H. G., Venkatachalam, M. A. Alterations in the charge and size selectivity barrier of the glomerular filter in aminonucleoside nephrosis in rats. Lab. Invest. 44, 271-279 (1981).
- Schiessl, I. M., Castrop, H. Angiotensin II AT2 receptor activation attenuates AT1 receptor-induced increases in the glomerular filtration of albumin: a multiphoton microscopy study. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 305, F1189-F1200 (2013).
- Ilatovskaya, D. V., Levchenko, V., Ryan, R. P., Cowley, A. W., Staruschenko, A. NSAIDs acutely inhibit TRPC channels in freshly isolated rat glomeruli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 408, 242-247 (2011).
- Peti-Peterdi, J. Calcium wave of tubuloglomerular feedback. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 291, F473-F480 (2006).
- Peti-Peterdi, J., Warnock, D. G., Bell, P. D. Angiotensin II directly stimulates ENaC activity in the cortical collecting duct via AT(1) receptors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, 1131-1135 (2002).
- Ilatovskaya, D. V., Palygin, O., Levchenko, V., Staruschenko, A. Pharmacological characterization of the P2 receptors profile in the podocytes of the freshly isolated rat glomeruli. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 305, C1050-C1059 (2013).
- Ilatovskaya, D. V., et al. Angiotensin II has acute effects on TRPC6 channels in podocytes of freshly isolated glomeruli. Kidney Int. 305, C1050-C1059 (2014).
- Schaldecker, T., et al. Inhibition of the TRPC5 ion channel protects the kidney filter. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 5298-5309 (2013).
- Roshanravan, H., Dryer, S. E. ATP acting through P2Y receptors causes activation of podocyte TRPC6 channels: role of podocin and reactive oxygen species. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 306, F1088-F1097 (2014).
- Anderson, M., Roshanravan, H., Khine, J., Dryer, S. E. Angiotensin II activation of TRPC6 channels in rat podocytes requires generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Cell. Physiol. 229, 434-442 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved