A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
הגירה ו מהירות Phagosome נמדד המקרופאגים אדם מן המעלה הראשונה חי עם HIV-1
In This Article
Summary
We describe a method to measure the velocity of phagosomes moving towards the cell center in living cells infected with or without the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1, using spinning disk confocal fluorescence microscopy to identify fluorescent infected cells and bright field microscopy to detect phagosomes.
Abstract
Macrophages are phagocytic cells that play a major role at the crossroads between innate and specific immunity. They can be infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 and because of their resistance to its cytopathic effects they can be considered to be persistent viral reservoirs. In addition, HIV-infected macrophages exhibit defective functions that contribute to the development of opportunistic diseases.
The exact mechanism by which HIV-1 impairs the phagocytic response of macrophages was unknown. We had previously shown that the uptake of various particulate material by macrophages was inhibited when they were infected with HIV-1. This inhibition was only partial and phagosomes did form within HIV-infected macrophages. Therefore, we focused on analyzing the fate of these phagosomes. Phagosome maturation is accompanied by migration of these compartments towards the cell center, where they fuse with lysosomes, generating phagolysosomes, responsible for degradation of the ingested material. We used IgG-opsonized Sheep Red Blood Cells as a target for phagocytosis. To measure the speed of centripetal movement of phagosomes in individual HIV-infected macrophages, we used a combination of bright field and fluorescence confocal microscopy. We established a method to calculate the distance of phagosomes towards the nucleus, and then to calculate the velocity of the phagosomes. HIV-infected cells were identified thanks to a GFP-expressing virus, but the method is applicable to non-infected cells or any type of infection or treatment.
Introduction
Macrophages play a major role in the innate immune system and in homeostasis. They are professional phagocytes that internalize and eliminate pathogens and debris by a process called phagocytosis 1,2. The phagosome, the closed compartment that forms after the engulfment of particulate material, undergoes a series of fusion and fission events with endocytic compartments, leading to a degradative compartment called the phagolysosome. This compartment has an acidic pH, due to the acquisition of proton-pumping v-ATPases, contains hydrolytic enzymes and is enriched in lysosomal-associated membrane proteins (LAMPs). The maturation of phagosomes is accompanied by their migration on microtubules 3,4 towards the cell center to reach a perinuclear location where lysosomes are accumulated.
Many pathogens have been reported to hijack phagosome maturation, including bacteria with intracellular lifestyles that modify the vacuolar environment where they reside 5. The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-1 targets macrophages in addition to T cells. As macrophages are resistant to the cytopathic effects of the virus, unlike T cells, they can be considered as a reservoir for the virus. In addition, macrophages infected with HIV-1 show defective phagocytic functions and contribute to the emergence of opportunistic diseases. In particular, severe invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella disease caused by Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 has been prevalent for the last three decades in sub-Saharan African children or adults infected with HIV 6. It has been estimated that the risk of developing tuberculosis is more than 20 times greater in people living with HIV than among those without HIV infection.
For all these reasons, it is important to better define the molecular mechanisms underlying the phagocytic defects in HIV-infected macrophages. We have shown that the uptake of particulate material, opsonized particles, bacteria or fungi, was inhibited in HIV-infected macrophages 7. Given that this inhibition is partial, we then set out to analyze the fate of the internalized phagosomes in HIV infected human macrophages 8. Because phagosome maturation is tightly connected with migration to the cell center and fusion with lysosomes, a defect in phagosomal maturation can be due to modifications of the trafficking modalities in the infected cell. The method described here uses IgG-opsonized Sheep Red Blood Cells (IgG-SRBCs) as a model to target receptor-mediated phagocytosis and in particular receptors for the Fc portion of immunoglobulins (FcR). These particles are easier to image in bright field (BF) than latex beads because extracellular and intracellular SRBCs show different refraction properties 9. To measure the velocity of phagosomes moving towards the nucleus in HIV-infected macrophages, we used a fluorescent virus 10 and set up a simple manual tracking method that is described here. The method does not require advanced programming and simply uses ImageJ. It is amenable to adherent cells and any type of particle or pathogen that can be visualized with bright field microscopy or with fluorescent imaging.
Protocol
הפרוטוקול צריכה להתבצע בהתאם קפדן עם חקיקה לאומית ובינלאומית ולתקנות מקומיות. דם מתורמים בריאים כי נתנו את הסכמתם לתרום דם למטרות המחקר כבר המתקבל מרכזי עירוי דם שבה מוסדות חתמו הסכם. הגנות מיוחדות יש לנקוט בעת מדמם של בני האדם. ניסויים עם HIV-1 חייבים להתבצע ברמת בטיחות ביולוגית 3 או 2 (BSL-3 או 2) מעבדה על פי תקנות מקומיות.
1. הכנת האדם מונוציטים הנגזרות המקרופאגים (hMDMs) לפי צפיפות Gradient צנטריפוגה בחירה על ידי הדבקה
- התחל עם דם טרי מתורמים בריאים (9 מ"ל). לדלל את כל נפח של דם טרי עם בופר פוספט 1x סטרילי (PBS) ללא Ca 2 + ו Mg 2+ להשיג נפח סופי של 70 מ"ל בעדינות להוסיף את דם מדולל לשני צינורות חרוטי 50 מ"ל (35 מ"ל לכל צינור) , על גבי 15 מ"ל שלeutral, מסועף מאוד, גבוה המוני, פוליסכריד הידרופילי בתמיסה כבר בצינור אחד.
- צנטריפוגה שני צינורות דם ב 537 XG במשך 20 דקות ב 20 ° C ללא בלם. ואז לאסוף את התאים דם היקפיים mononuclear (PBMCs) הכלול טבעת תא מעונן בממשק ולהעביר אותם לתוך צינור חדש 50 מ"ל המכיל 15 מ"ל של 1x PBS ללא Ca 2 + ו Mg 2+.
- צנטריפוגה התאים ב 218 XG במשך 5 דקות ב 20 ° C ו resuspend גלולה ב 45 מ"ל של PBS 1x ללא Ca 2 + ו Mg 2+.
- צנטריפוגה התאים ב 218 XG במשך 5 דקות ב 20 מעלות צלזיוס, resuspend גלולה ב 10 מ"ל של 1x PBS ללא Ca 2 + ו Mg 2+, ולספור את התאים על ידי דילול לדילול הסופי של 1/200 ב Trypan כחול.
- צנטריפוגה התאים ב 218 XG במשך 5 דקות ב 20 ° C ו resuspend גלולה ב RPMI (מכון ממוריאל פארק Roswell) בינוני 1640 בתוספת 2 מ"מ L- גלוטמין ו 100 מיקרוגרם / מ"ל penicillin סטרפטומיצין יש 7 x 10 6 PBMCs לכל היטב 2 מ"ל של מדיום בכל טוב של צלחת גם 6.
- דגירת הצלחות ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2 על 2 hr. אחרי שעה 2 מונוציטים יהיה דבקו פלסטיק.
- כדי לאפשר מונוציטים טרי-מבודד להתמיין hMDMs, לשאוב את המדיום ולהחליף אותו עם 2 מ"ל hMDM בינוני (RPMI 1640, 10% decomplemented עוברית עגל בסרום (FCS), 2 מ"מ L- גלוטמין ו -1% פניצילין, סטרפטומיצין) בתוספת המושבה Macrophage אנושי רקומביננטי פקטור מגרה (RHM-CSF) בריכוז סופי של 10 ng / ml.
- דגירת התאים ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2 עבור 11 ימים (איור 1).
- באותו יום 11 להסיר את בינוני לשטוף 2 פעמים עם 2 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM קר לכל טוב. הבא לשטוף היטב כל 2 פעמים עם 1 מ"ל של PBS 1x קר.
- כדי לנתק hMDMs הבדיל באופן מלא, לשטוף היטב בכל פעם 1 עם 1 מ"ל של PBS 1x קר עם 2 מ"מ חומצה ethylenediaminetetraacetatic (EDTA) דגירה התאים 2 מ"ל של PBS 1x קר עם 2 מ"מ EDTA לכל טוב עבור 15-60 דקות ב 4 °.
הערה: שיטות חלופיות כדי לנתק את התאים קיימים (למשל, טריפסין או פעילויות כמו טריפסין) שעשוי לתת תוצאות טובות 11. - לאחר ניתוק (הושלמה על ידי pipetting בעדינות מעלה ומטה הבאר), לאסוף את התאים ולשים אותם בתוך שפופרת 50 מ"ל על הקרח המכיל 10 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM קר.
- צנטריפוגה התאים ב 218 XG במשך 5 דקות ב 20 מעלות צלזיוס, resuspend גלולה ב 10 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM קר, ולספור את התאים על ידי דילול 1/20 ב Trypan כחול.
- זרעי התאים ב 1 x 10 6 hMDMs לכל צלחת תחתית זכוכית כיתת מיקרוסקופיה 35 מ"מ ו דגירת הצלחות ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2 עבור 1 יום.
2. הפקה וכימות של HIV-1 מניות ויראלי
הערה: NLR4.3 HIV-1 Gag-iGFP (חלבון פלואורסצנטי ירוק) נושא מעטפה R5-טרופי, מתנה מ Schindlאה 10 משמש להדביק מאקרופאגים לראות תאים נגועים בזמן אמת.
- תוצרת מניות ויראלי על ידי transfection של תאים 293T כליה עובריים אנושיים (2 x 10 6 בצלחת מ"מ 100) עם 6 מיקרוגרם של ה- DNA proviral המתאים באמצעות מגיב transfection מסחרי.
- לכמת את ההדבקה של המניות וירוס באמצעות תאים אינדיקטור הלה TZM-bl (הנושאת את הגן SS-galactosidase בשליטת HIV-1 LTR) באמצעות דילולים סדרתי של מניות ויראלי ואחריו צבע SS-galactosidase של תאים ועוד היד נטויה של כחול תאי 12.
זיהום 3. hMDMs עם HIV-1
- מוסיפים את הנגיף על ריבוי של זיהום (משרד הפנים) 0.02-0.03 ב 1 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM כדי hMDMs (תאים מצופה ב 1.13). כדי לשלוט בארות להוסיף רק 1 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM דגירה מנות ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2 על 2 ימים (איור 1).
- באותו יום 2 לשטוף את התאים עם hMDM medium 3 פעמים ולהוסיף 1 מ"ל של מדיום hMDM טריים לכל צלחת. דגירת התאים ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2 עבור 6 ימים (איור 1).
4. Opsonization של כדוריות דם אדומות כבשים
- להכנת 7 x 10 6 SRBCs לכל צלחת, לשטוף את SRBCs שתי פעמים 100 μl של תמיסה המכילה 0.1% שור סרום אלבומין (BSA) ב 1x PBS עם צנטריפוגה ב 600 XG למשך 4 דקות.
- Resuspend את SRBCs לרחוץ 500 μl 1x PBS / BSA 0.1% עם ארנב IgG אנטי SRBCs בריכוז תת-agglutinating לכל 5 μl של SRBCs דגירה עם סיבוב ב RT במשך 30 דקות.
הערה: כדי לקבוע את הריכוז תת-agglutinating של IgG אנטי SRBCs, להכין דילולים הסידורי של IgG (ריכוז המניה ב 13.1 מ"ג / מ"ל) מ 1/50 ל -1 / 25,600 ב 20 μl בצלחת 96-היטב. להוסיף 2 x 10 6 SRBCs ב 20 μl בכל טוב ולשים את הצלחת בחדר חשוך במשך כמה שעות. הריכוז תת-agglutinating הואדילול של הבאר רק לפני הבאר עם ההתלכדות (IgG + SRBCs ויצרה רשת). - לאחר הסיבוב, בצנטריפוגה IgG-opsonized-SRBCs ב 600 XG למשך 4 דקות ולשטוף עם 100 μl של PBS 1x / BSA 0.1% עם צנטריפוגה ב 600 XG למשך 4 דקות.
- Resuspend את IgG-opsonized-SRBCs במדיום מראש חימם פנול אדום ללא RPMI בתוספת 2 מ"מ L- גלוטמין ו -1%, סטרפטומיצין פניצילין (1 מ"ל / צלחת).
5. תא חי Assay המיקרוסקופית וידאו Phagocytosis
- השתמש במערכת הדמיה confocal כגון מערכת דיסק מסתובב מצויד בתא חימום על 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם CO 2 עובר דרך בקבוק עם מים עבור humidification.
- הפעילו את תא חימום לפני הניסוי לקבל את הבמה מיקרוסקופ על 37 מעלות צלזיוס לפני תחילת assay phagocytosis. הפעל מיקרוסקופ ומחשב, ולטעון את תוכנת ההדמיה.
- מטב את הגדרות הדמיה כגון מהירות סריקה, מגניפיקטיון, רזולוציה, וכו 'יש תא אחד לפחות לכל שדה וכדי מסגרת תמונה אחת בכל דקה בין 60 עד 120 דקות.
הערה: כאן, המדגם הוא צלם מסגרת אחת בכל דקה במהלך 60 דקות עם 63X עדשה. - מניחים את צלחת הדמיה על הבמה מיקרוסקופ. התאם את המיקוד ואת המיקום למצוא רק אחת שלם מקרופאג נגוע ב- HIV-1 בתחום. השתמש בהגדרות עירור מתאימות / פליטה המבוססות על מערכת ההדמיה המשומשת חללית. כלול ערוץ שדה (BF) בהיר להתבונן phagosomes (איור 1ii). מטב את המראה של תמונות בערוץ השונות על ידי התאמת אחוז זמן אור וחשיפה המשודרת.
הערה: כאן, NLR4.3 HIV-1 Gag-iGFP היה נרגש באמצעות לייזר 491 ננומטר עם 50 msec החשיפה זמן עם 20% של לייזר (איור 1i). - מוציאים את המאפה הדמיה ולהוסיף 1 מ"ל של השעיה SRBC ב -7 x 10 6 SRBCs / ml כדי בצלחת (איור 1).
- צנטריפוגה XG ב 500 עבור2 דק 'ב RT לסנכרן phagocytosis, ולהקליט את הזמן בסוף צנטריפוגה זה ולהחזיר את הצלחת על הבמה.
- מטב את GFP המיקוד ללכוד תמונות BF בערימות-Z (לכל העובי של התא, תוך שמירת מרחק-צעד של 0.3 מיקרומטר - בדרך כלל 20 מטוסים) כל דקה במשך שעה 1 לפחות. שמור את זמן לשגות וידאו בקובץ בפורמט יליד מערכת הדמיה בשימוש.
הערה: כאן, סרטים זמן לשגות שנשמרו בתבנית המקורית, * קבצי .stk.
6. ניתוח של זמן לשגות סרטים
- עבור עריכת וידאו, לחץ על התפריט הנפתח 'יישומים' בכרטיסייה "נתונים רב מימדי לבדיקה" תוכנת עריכת וידאו.
- כדי לפתוח את הקובץ, לחץ על "קובץ מאגר בחר" ואז על "בחר Directory". ב "ערכות נתונים", סמן את הרכישה לנתח (בפורמט .nd) ולחץ על "תצוגה". הנתונים מיוצגים בטבלה עם זמן הטורד Z-תוכנית בקו.
- כדי לייצג את הזיהום בהיטל-Z (איור 2, לוחות שמאל), בחר 491 ננומטר אורך גל בתיבת "אורכי הגל" ולחץ על כרטיסיית "הקרנת Z" עם "כל המטוסים".
- כדי לנתח רצף זמן, בחר אורך גל BF בתיבת "אורכי גל" ולבחור את המטוס האופטימלי על ציר ה- Z להבחין SRBCs החיצוני (איור 2, חץ אדום), SRBCs הפנימי (איור 2, עיגול אדום) ואת הגרעין ( איור 2, כחול מעגל).
- כדי לשמור את מצרפי וידאו, לחץ על "בחירה [של X]" כרטיסייה ולאחר מכן על "טען תמונה (ים)". לבסוף, לשמור את התמונות הטעונות .tif בפורמט ולפתוח אותם באים על תוכנת ImageJ.
- השתמש תוסף "מעקב ידני" על התוכנה ImageJ כדי למדוד את המיקום של הגרעין לבין phagosomes התחלואה הנצפים בערוץ BF (איור 3).
- דאוnload התוסף "מעקב ידני" באתר האינטרנט ImageJ. ביום ImageJ, לפתוח את התוסף, רצף התמונה להיות מנותח (איור 3, שלב 1 ו -2).
- הזן את ההגדרות כגון "מרווח זמן" מייצג משך הזמן בין מסגרות סמוכות, ואת "הכיול x / y" אשר מייצג את המרחק לפיקסל (איור 3, שלב 3).
הערה: כאן, להציל את התמונה ברצף עם מרווח זמן של 1 דק 'בין כל מסגרת ו- x / y כיול של 0.205 מיקרומטר משום זום 63X ומצלמה עם פיקסל בגודל של 6.45 x 6.45 מיקרומטר 2 משמשים. - כדי להפעיל את המעקב, לחץ על "הוסף מסלול" (איור 3, שלב 4) ולחץ על מרכז SRBC במועד הראשון כאשר הוא הפנים. הפריים הבא מופיע אוטומטית.
- המשך ללחוץ על מרכז SRBC בכל המסגרות יש עמדות שונות במהלך הזמן (איור 3, שלב 6 ב תיבה אדומה).
- התחל לעקוב אחר לגרעין יש את עמדתה בכל המסגרות ידי לחיצה על במרכזו. בואו לעקוב אחר phagosomes (על ידי לחיצה על במרכזו) אחד אחרי השני בזמן (מסגרת) של ההפנמה שלהם, שונה בתפקוד של SRBCs. לנוחיותכם לראות SRBC בערוץ BF, השתמש "בהירות וחדות" החלון במהלך המעקב (איור 3, שלב 5).
- בין כל מעקב SRBC, לחץ על "הוסף מסלול" (איור 3, שלב 4) יש מסלול חדש. מספר מעקב ישונה בעמודה השנייה, "מסלול n °" של טבלת התוצאות (איור 3, שלב 6).
- שמור את הנתונים בגיליון אלקטרוני כדי להמשיך לשלב הבא של הניתוח.
- השתמש בתוכנת גיליון אלקטרוני כדי לחשב את המרחק של phagosomes המכיל SRBCs כלפי הגרעין לבין המהירות של phagosomes במהלך 5 דקות הראשונות לאחר הפנמת SRBCs (אלחוטיאיור 4).
- פתח את שולחן גיליון אלקטרוני קובץ גיליון אלקטרוני חדש. העבר לתוך קובץ חדש זה הפרמטרים הבאים בלבד, זמן, x ו- y- לתאם של הגרעין וכל SRBCs (איור 4 א).
- כדי לחשב את המרחק בין SRBCs ואת הגרעין עם רק את הקואורדינטות שלהן, לשקול את גרעין וכן SRBC במטוס XY לתאם (איור 4B).
הערה: המרחק בין שתי נקודות הוא אורך הנתיב חיבורם. במטוס, המרחק בין SRBC ואת הגרעין ניתן על ידי משפט פיתגורס.- אם ג (המרחק בין הגרעין לבין SRBC) מציין את אורך האלכסון ו A ו- B מציין את אורכי שתי הצלעות האחרות, לבטא משפט פיתגורס כפי משוואת פיתגורס:

הערה: במקביל, על orthonormal, המרחק האופקיa הוא (גרעין x -x SRBC) ואת b המרחק האנכי הוא (גרעין y -y SRBC). - לפיכך, לחשב את המרחק בין הגרעין לבין SRBC (איור 4 א, מלבן סגול) על ידי:
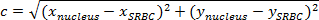
הערה: להכפיל את ערך המרחק שהושג (בפיקסלים) על ידי x / y כיול כדי לקבל את המרחק ב מיקרומטר. כאן, x / y הכיול הוא 0.205 מיקרומטר. - בכל זמן, להפחית את המרחק בין הגרעין לבין SRBC למרחק הראשוני (איור 4C).
- מגרש את המדידה נגד הזמן עבור 5 הדקות הראשונות. למרוח (איור 5 א) ליניארי מגמה אונליין לעלילה ולקבוע את השיפוע של מגמה אונליין ליניארי המייצג את מהירות phagosome כלפי הגרעין במהלך 5 הדקות הראשונות לאחר הפנמת SRBC.
- איסוף הנתונים לחישוב טעות הממוצעת וסטטיסטית שלהערכים מהירות ואת העלילה אותם בצורה הולמת באמצעות התוכנה המתאימה (איור 5).
- אם ג (המרחק בין הגרעין לבין SRBC) מציין את אורך האלכסון ו A ו- B מציין את אורכי שתי הצלעות האחרות, לבטא משפט פיתגורס כפי משוואת פיתגורס:
תוצאות
FCR בתיווך phagocytosis על ידי HIV-1-נגוע hMDMs הלא נגועים מתואר כאן על ידי שימוש SRBCs IgG-opsonized כמטרות מודל (איור 1). השלבים הקריטיים של פרוטוקול זה הם הכנת hMDMs ואת ההדבקה ב- HIV-1. ואכן, התפוקה והאיכות של מקרופאגים בדיל משתנים בין תורמים, כמו גם את שיעור ההדבקה ?...
Discussion
יש טכניקה זו יש כמה שלבים קריטיים. ראשית, הכנת hMDMs והזיהום שלהם על ידי HIV-1 הוא קריטי מאחר ואחוז הזיהום הוא תורם תלוי. ראוי לציין, החלטנו להשתמש מקרופאגים שאינם מקוטבים במבחנה לפני ההדבקה, כי מעמדה של מקרופאגים נתקלו באופן פוטנציאלי על ידי הנגיף in vivo לא התאפיינ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Jamil Jubrail for reading the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from CNRS, Inserm, Université Paris Descartes, Agence Nationale de la Recherche (2011 BSV3 025 02), Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM DEQ20130326518 including a doctoral fellowship for GLB) and Agence Nationale de Recherche sur le SIDA et les hépatites virales (ANRS, including a post-doctoral fellowship for CD) to FN. A. Dumas was supported by doctoral fellowships from Université Paris Descartes and Sidaction.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Falcon 100mm TC-Treated Cell Culture Dish | Corning | 353003 | For viral production |
| Glass Bottom Dishes 35 mm uncoated 1.5 | MatTek corporation | P35G-1.5-14-C Case | For acquisition |
| Falcon Tissue Culture Plates 6-well | Thermo Fischer Scientific | Corning. Inc. 353934 | For human monocyte-derived macrophages |
| Ficoll-Plaque PLUS | Dominique Dutscher | 17-1440-03 | a neutral, highly branched, high-mass, hydrophilic polysaccharide in solution for density centrifugation |
| DPBS, no calcium, no magnesium | Thermo Fischer Scientific | 14190-094 | Room temperature |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) 1X, liquid (High Glucose) | GIBCO, Molecular probes | 31966-021 | Conserved at 4°C ; for HEK cells culture |
| RPMI 1640 medium GLUTAMAX Supplement | Life technologies | 61870-010 | Conserved at 4°C; for hMDMs culture |
| Fœtal Calf Serum (FCS) | Eurobio | CVFSVF0001 | Conserved at -20°C ; decomplemented |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin (10,000 U/mL) | Thermo Fischer Scientific | 15140-122 | Conserved at -20°C ; for hMDMs culture |
| RPMI 1640 medium, no phenol red (10x500 ml) | Life technologies | 11835-105 | Warm in 37°C water bath before use ; for phagocytosis assay |
| FuGENE6 Transfection Reagent | Promega | E2692 | Conserved at 4°C ; for viral production |
| Sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) | Eurobio | DSGMTN00-0Q | Conserved in Alsever buffer at 4°C before use |
| Anti-sheep red blood cells IgG | MP Biomedicals | 55806 | Conserved at 4°C |
| Bovine Serum Albumin heat shock fraction, pH 7, ≥98% | Sigma | A7906 | Conserved at -20°C |
| Inverted microscope DMI600 | Leica | ||
| Confocal Spinning Disk Unit CSU-X1M1 | Yokogawa | ||
| 491 nm 50mW laser | COBOLT CALYPSO | ||
| HCX PL APO CS Objectif | Leica | Objective lens ; Magnification 100x ; Numerical aperture 1.40 ; Immersion oil | |
| CoolSnap HQ2 (FireWire) Camera | Photometrics | Pixel size 6.45 x 6.45 µm ; Definition 1392 x 1040 ; Encoding the image in 14 Bit | |
| Metamorph 7.7.5 software | Molecular Devices | For the control of the microscope | |
| GraphPad Prism software | For the statistics analysis |
References
- Flannagan, R. S., Jaumouille, V., Grinstein, S. The cell biology of phagocytosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 7, 61-98 (2012).
- Niedergang, F. . Encyclopedia of Cell Biology. 2, 751-757 (2016).
- Blocker, A., Griffiths, G., Olivo, J. C., Hyman, A. A., Severin, F. F. A role for microtubule dynamics in phagosome movement. J Cell Sci. 111 (Pt 3), 303-312 (1998).
- Blocker, A., et al. Molecular requirements for bi-directional movement of phagosomes along microtubules. J Cell Biol. 137, 113-129 (1997).
- Flannagan, R. S., Cosio, G., Grinstein, S. Antimicrobial mechanisms of phagocytes and bacterial evasion strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 7, 355-366 (2009).
- Feasey, N. A., Dougan, G., Kingsley, R. A., Heyderman, R. S., Gordon, M. A. Invasive non-typhoidal salmonella disease: an emerging and neglected tropical disease in Africa. Lancet. 379, 2489-2499 (2012).
- Mazzolini, J., et al. Inhibition of phagocytosis in HIV-1-infected macrophages relies on Nef-dependent alteration of focal delivery of recycling compartments. Blood. 115, 4226-4236 (2010).
- Dumas, A., et al. The HIV-1 protein Vpr impairs phagosome maturation by controlling microtubule-dependent trafficking. J Cell Biol. 211, 359-372 (2015).
- Greenberg, S., el Khoury, J., Kaplan, E., Silverstein, S. C. A fluorescence technique to distinguish attached from ingested erythrocytes and zymosan particles in phagocytosing macrophages. J. Immunol. Methods. 139, 115-122 (1991).
- Koppensteiner, H., Banning, C., Schneider, C., Hohenberg, H., Schindler, M. Macrophage internal HIV-1 is protected from neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 86, 2826-2836 (2012).
- Gartner, S. The macrophage and HIV: basic concepts and methodologies. Methods Mol Biol. 1087, 207-220 (2014).
- Wei, X., et al. Emergence of resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in patients receiving fusion inhibitor (T-20) monotherapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 46, 1896-1905 (2002).
- Harrison, R. E., Bucci, C., Vieira, O. V., Schroer, T. A., Grinstein, S. Phagosomes fuse with late endosomes and/or lysosomes by extension of membrane protrusions along microtubules: role of Rab7 and RILP. Mol Cell Biol. 23, 6494-6506 (2003).
- Toyohara, A., Inaba, K. Transport of phagosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Sci. 94 (Pt 1), 143-153 (1989).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved