A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Clinical Factors Influencing the Radiation Dose of Circulating Immune Cells during Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a protocol to evaluate the effects of radiation therapy on immune system lymphocytes in small cell lung cancer.
Abstract
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has garnered significant attention due to its high malignancy, propensity for distant metastasis, and poor prognosis. Radiotherapy remains the cornerstone of treatment for limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC). However, outcomes with radiotherapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy remain suboptimal. Radiotherapy can induce lymphopenia by directly irradiating hematopoietic organs or destroying mature circulating lymphocytes, leading to immunosuppression and consequently diminishing therapeutic efficacy. The estimated dose of radiation to immune cells (EDRIC) model integrates factors such as hemodynamics, lymphocyte radiosensitivity, and proliferation capacity. This study employs the EDRIC model with enhancements to calculate the circulating immune cell radiation dose. By utilizing the EDRIC methodology, the study explores the correlation between EDRIC and tumor target size, average lung dose, average heart dose, clinical features, and peripheral blood lymphocytopenia during radiotherapy for LS-SCLC, aiming to inform personalized patient treatment strategies.
This study analyzed data from 64 LS-SCLC patients who met the inclusion criteria at the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University from January 2023 to January 2024, all of whom received radical thoracic conventional fractionated radiotherapy. Lymphocyte counts were recorded at the following points: before radiotherapy, at the lowest observed value during radiotherapy, at the end of radiotherapy, and one-month post-radiotherapy. Dosimetric data, including average lung, heart, and body doses, were extracted from the treatment planning system, and the circulating EDRIC was calculated using this model. The relationship between EDRIC values and therapeutic outcomes was analyzed. In LS-SCLC, the EDRIC model effectively predicts lymphocyte count reduction, correlating with planning target volume (PTV; cm3), TNM stage, and the percentage of target lesion shrinkage. Post-radiotherapy, there was a significant decrease in peripheral blood lymphocyte counts, with greater EDRIC values indicating more pronounced lymphocyte reduction.
Introduction
Lung cancer remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) comprising 13%-17% of cases1,2. SCLC is characterized by a high degree of malignancy and a propensity for early distant metastasis, often leading to late-stage diagnosis and poor prognosis. Advances in medical technology and a deeper understanding of the biological characteristics of SCLC have highlighted the potential value of radiotherapy in its treatment. Nonetheless, outcomes with radiotherapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy remain suboptimal. Identifying key factors influencing the efficacy of radiotherapy in SCLC is essential to provide a theoretical basis for individualized treatment strategies and prognosis prediction.
The immune system exhibits intricate interactions with radiation or chemotherapy, enhancing tumor cell eradication during treatment3,4. Radiation therapy, for instance, can foster immune activation via cytokine or antigen release, thereby inducing tumor regression within the radiation field (known as the abscopal effect)5. However, radiotherapy may also induce immunosuppression when treating various solid tumors, potentially compromising therapeutic efficacy. This immunosuppression may stem from myelosuppression due to direct irradiation of hematopoietic organs or the destruction of mature circulating lymphocytes, resulting in reduced lymphocytes. Studies have pinpointed specific tumor size and radiation doses to critical organs such as the heart and lungs in small cell lung cancer as crucial predictors of immunosuppression, with potential implications for patient survival6.
Lymphocytes and their precursor cells rank among the most radiation-sensitive cell types7. Susannah Yovino's8 investigation into circulating cell radiation dose (DCC) in brain glioma patients post-radiotherapy revealed that alterations in the size of the planning target volume (PTV) influence the average DCC radiation dose. The radiation dose to circulating blood cells may significantly contribute to the mechanism of induced lymphocytopenia. While irradiation of bone marrow or lymph nodes can induce lymphocytopenia, irradiation of structures devoid of lymphoid tissue or bone marrow, such as the brain, can also trigger lymphocytopenia. Jin et al.9developed the estimated dose of radiation to immune cells (EDRIC) model and dosimetry to quantify radiotherapy-induced immune system damage. This study employs the EDRIC model with enhancements from Ladbury et al.6 to calculate the circulating immune cell radiation dose.
Consequently, the EDRIC method was utilized to compute the circulating lymphocyte radiation dose and investigate its relationship with treatment efficacy and prognosis during radiotherapy for small cell lung cancer10. The correlation between EDRIC values and factors such as age, gender, Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) score, smoking history, tumor size, and tumor stage was analyzed through stratification. Furthermore, the correlation between peripheral blood lymphocytopenia and circulating lymphocyte radiation dose was compared to lay the groundwork for personalized treatment strategies and prognosis prediction.
Protocol
Following stringent adherence to this study's inclusion and exclusion criteria, informed consent for radiotherapy was obtained from each patient and their guardian. Clinical staging was conducted in accordance with the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system (8th edition). The Ethics Committee of Ningxia Medical University General Hospital (KYLL-2022-0984) granted approval for this study.
NOTE: The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) pathologically confirmed limited-stage small cell lung cancer (TNM stage II and III); (ii) initial radiotherapy treatment utilizing conformal intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) or volumetric arc intensity-modulated radiotherapy (VMAT), with a total radiation dose ranging from 50-60 Gy and a single dose of 2 Gy; (iii) pre-radiotherapy blood parameters within the normal range (WBC ≥ 4 x 109 cells/L, Hb ≥ 100 g/L, PLT ≥ 100 x 109/L), and normal function of vital organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys; (iv) availability of complete clinical data and radiotherapy records; (v) expected survival of more than 3 months; (vi) non-pregnant or lactating women. The exclusion criteria included: (i) patients with blood or immune system disorders or significant organ damage; (ii) history of prolonged oral steroid therapy; (iii) patients who did not complete planned radiotherapy; (iv) recent history of confirmed infection.
1. General clinical information
- Collect patient data.
NOTE: Data from 64 patients diagnosed with LS-SCLC, meeting the inclusion criteria and undergoing radiation therapy at the Department of Radiotherapy, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University from January 2023 to January 2024, were collected. Among them, 48 were male and 16 were female, aged from 41 to 85 years. According to the AJCC TNM staging system (8th edition), there were 9 stage II and 55 cases of stage III. All 60 patients received chemotherapy before radiotherapy, with 46 patients undergoing chemotherapy more than twice (Table 1). Radiation therapy technically includes intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy (VMAT).
2. Pretreatment preparation
- Diagnose small cell lung cancer by bronchoscopy or puncture pathology11, as shown in Figure 1.
- Exclude metastasis using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, neck, and abdomen and locate the tumor area by positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT)12, as shown in Figure 2A-C.
- Perform cardiac enzyme test, electrocardiogram, cardiac ultrasonography, pulmonary function, and thyroid function to evaluate the cardiopulmonary function and judge that there are no contraindications10.
- Fully inform patients and their families of the risks and complications related to radiotherapy and sign radiotherapy-related consents.
NOTE: Radiotherapy initiation time: for patients with large tumors, extensive metastasis of regional lymph nodes, and concomitant atelectasis, 2 courses of chemotherapy can be given first, no later than the third cycle of chemotherapy.
3. Radiotherapy
- Positioning: Keep the patient supine, with the body surface marked with mapping lines and the hands and elbows resting on the forehead. Immobilize the patient using a thermoplastic mold to ensure stability. Conduct enhanced CT scanning to provide clear visualization of the tumor and surrounding blood vessels, as shown in Figure 3A.
NOTE: Enhanced CT scaning parameters are as follows: (1) Dosage of contrast agent: 80 mL Dianbitol. (2) Injection rate: 3 mL/s. (3) Scanning time: the first phase: 30-35 s, the second phase: 70-80 s, if necessary, can be delayed 3 to 10 min. The CT simulation scan encompassed the upper skull base level, with the lower boundary extending 10 cm below the diaphragm. Image slices, 5 mm in thickness, are uploaded to the Pinnacle treatment planning system. - Target delineation: Accurately delineate the radiotherapy area for SCLC by pinnacle system in positioning CT images, as shown in Figure 3B, C.
- Gross tumor volume- primary (GTVp): Delineate the GTV using a combination of pulmonary and mediastinal window settings, adhering to RTOG criteria and referencing PET-CT, enhanced CT, and bronchoscopy findings.
- Exclude areas of atelectasis and exudates devoid of Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake from delineation. Do not wrap long burrs and pleural traction parts. Include burrs with a length of less than 5 mm in the target area.
- GTV of the metastatic lymph node (GTVnd): Delineate mediastinal metastatic lymph nodes using chest CT and PET/CT.
- Clinical target volume (CTV): Encompass the CTV GTVp with a 0.5 cm margin, incorporating anatomical trimming and cumulatively involved lymphatic drainage areas.
- Planning target volume (PTV): Derive from CTV with an additional 0.5 cm margin and anatomical trimming.
NOTE: Organs at Risk Delineation and Constraints: Spinal cord: Maximum dose (Dmax) < 40 Gy. Left lung: Volume receiving 20 Gy (V20) < 20%. Right lung: V20 < 20%. Bilateral lungs: Mean dose (Dmean) < 13 Gy. Liver: Volume receiving 30 Gy (V30) < 30%. Heart: V30 < 30%, as shown in Figure 3D-H.
- Gross tumor volume- primary (GTVp): Delineate the GTV using a combination of pulmonary and mediastinal window settings, adhering to RTOG criteria and referencing PET-CT, enhanced CT, and bronchoscopy findings.
- Develop radiotherapy planning under the computerized therapy planning system: use 6MV-X and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) to evaluate the target dose.
NOTE: PTV covered by the prescription dose line had good conformability, uniform dose distribution in the target area, no cold spot in the target area, and no hot spot in the organ at risk. Normal tissue limits were in the normal range, as shown in Figure 3I, J. - Execute the radiotherapy plan5: Perform radiotherapy using a linear accelerator and compare the cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) test with positioning CT position (once a week), double placement, once a day, 5 times a week, as shown in Figure 4A, B.
- Perform a secondary CT scan with the dose reaching 30-40 GY to evaluate the therapeutic effect. Reduce the target area if necessary until the dose reaches 50-60 GY, as shown in Figure 5A, B.
NOTE: The therapeutic response was observed during the treatment process, and symptomatic treatment was given according to the situation.
4. Evaluation method and index
- Calculate mean lung dose, mean heart dose, and overall total dose volume data according to the EDRIC method with the following formula:
EDRIC = 0.12 × MLD + 0.08 × MHD +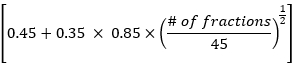 × MBD
× MBD
Where, B1% = 0.12, B2% = 0.08, B3% =0.45, and B4% = 0.35 represent the percentage of the four main blood-containing organs (lung, heart, large blood vessels, small blood vessels/capillaries) in the total blood volume in the body; MLD, MHD and MBD are the mean lung dose, mean heart dose and mean body dose, wherein MBD refers to the radiation dose per unit volume of the body. In this study, MBD is the average body dose from the thyroid cartilage level to the upper margin of the sixth thoracic vertebra, which can be statistically obtained through the treatment planning system. - Observe the changes in chest CT lesions and mediastinal lymph nodes in patients before and 1 month after radiotherapy. Evaluate treatment efficacy according to response evaluation criteria in solid tumors(RECIST), and analyze the relationship between EDRIC value and treatment efficacy.
- Count the lowest value of peripheral blood lymphocytes before and during radiotherapy and analyze its correlation with circulating lymphocyte radiation dose and therapeutic effect.
5. Statistical methods
- Perform statistical analyses using the independent sample T-test or Chi-square test to assess differences between continuous and categorical variable groups.
- Utilize the Spearman correlation coefficient to evaluate variable correlations.
NOTE: All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinical outcome
The operative time changes in chest CT lesions and mediastinal lymph nodes were observed in all patients before and 1 month after radiotherapy, with therapeutic efficacy evaluated using RECIST criteria. Among the 64 patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer, 4 cases exhibited complete response, while 57 cases showed partial response, and three patients had stable disease.
The correlation analysis between EDRIC and various clinical features revea...
Discussion
The immune system plays a pivotal role in tumor control during radiotherapy, yet radiation-induced immunotoxicity, such as lymphocytopenia, is linked to unfavorable survival outcomes13,14. SCLC is characterized by its high malignancy, often diagnosed in advanced stages with a dismal prognosis. Radiotherapy stands as the cornerstone treatment for LS-SCLC. However, its impact on the immune system is complex. The efficacy of radiotherapy alone or in combination with...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the University-level Research Project of Ningxia Medical University (XM2022017).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| CT machine | Siemens Healthcare | SOMATOM Force | |
| MRI machine | Siemens Healthcare | MAGNETOM Terra | |
| Varian Clinac_IX Medical electron linear Accelerator | Siemens Healthcare | IX |
References
- Oronsky, B., Reid, T. R., Oronsky, A., Carter, C. A. What's New in SCLC? A Review. Neoplasia. 19 (10), 842-847 (2017).
- Pike, L. R. G., et al. The impact of radiation therapy on lymphocyte count and survival in metastatic cancer patients receiving PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 103 (1), 142-151 (2019).
- Brahmer, J. R. Harnessing the immune system for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31 (8), 1021-1028 (2013).
- Takeshima, T., et al. Key role for neutrophils in radiation-induced antitumor immune responses: Potentiation with G-CSF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 113 (40), 11300-11305 (2016).
- Yoon, S. W., et al. Per-fraction positional and dosimetric performance of prone breast tangential radiotherapy on Halcyon™ linear accelerator assessed with daily rapid kilo-voltage cone beam computed tomography: a single-institution pilot study. Radiat Oncol. 15 (1), 258 (2020).
- Ladbury, C. J., Rusthoven, C. G., Camidge, D. R., Kavanagh, B. D., Nath, S. K. Impact of radiation dose to the host immune system on tumor control and survival for stage III non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 105 (2), 346-355 (2019).
- Schrek, R. Qualitative and quantitative reactions of lymphocytes to x rays. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 95, 839-848 (1961).
- Yovino, S., Kleinberg, L., Grossman, S. A., Narayanan, M., Ford, E. The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells. Cancer Invest. 31 (2), 140-144 (2013).
- Jin, J. Y., et al. A framework for modeling radiation induced lymphopenia in radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 144, 105-113 (2020).
- Jin, J. Y., et al. Higher radiation dose to the immune cells correlates with worse tumor control and overall survival in patients with stage III NSCLC: A secondary analysis of RTOG0617. Cancers (Basel). 13 (24), 6193 (2021).
- Lalić, N., et al. Invasive diagnostic procedures from bronchoscopy to surgical biopsy-optimization of non-small cell lung cancer samples for molecular testing. Medicina (Kaunas). 59 (10), 1723 (2023).
- Cerra-Franco, A., et al. Predictors of nodal and metastatic failure in early stage non-small-cell lung cancer after stereotactic body radiation therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. 20 (3), 186-193 (2019).
- Venkatesulu, B. P., Mallick, S., Lin, S. H., Krishnan, S. A systematic review of the influence of radiation-induced lymphopenia on survival outcomes in solid tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 123, 42-51 (2018).
- Upadhyay, R., et al. Risk and impact of radiation related lymphopenia in lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 157, 225-233 (2021).
- Chow, R., Simone, C. B. Radiation induced lymphopenia in head and neck cancer: The importance of rigorous statistical analysis, radiation field size, and treatment modality. Radiother Oncol. 170, 242 (2022).
- Xu, H., et al. Lymphopenia during definitive chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Association with dosimetric parameters and patient outcomes. Oncologist. 26 (3), e425-e434 (2021).
- Liu, Z., et al. Pivotal roles of tumor-draining lymph nodes in the abscopal effects from combined immunotherapy and radiotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42 (10), 971-986 (2022).
- Yovino, S., et al. The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells. Cancer Invest. 31 (2), 140-144 (2013).
- Koukourakis, M. I., Giatromanolaki, A. Lymphopenia and intratumoral lymphocytic balance in the era of cancer immuno-radiotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 159, 103226 (2021).
- Tang, C., et al. Acute phase response before treatment predicts radiation esophagitis in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 110 (3), 493-498 (2014).
- Dai, D., Tian, Q., Shui, Y., Li, J., Wei, Q. The impact of radiation induced lymphopenia in the prognosis of head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 168, 28-36 (2022).
- Damen, P. J. J., et al. The influence of severe radiation-induced lymphopenia on overall survival in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 111 (4), 936-948 (2021).
- Lin, Y. J., Kang, Y. M., Wu, Y. H., Chen, Y. W., Hu, Y. W. Lymphocytopenia and survival after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 14 (14), 1268-1275 (2023).
- Suzuki, R., et al. Prognostic significance of total lymphocyte count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 20 (2), 117-123 (2019).
- Grossman, S. A., et al. Survival in patients with severe lymphopenia following treatment with radiation and chemotherapy for newly diagnosed solid tumors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 13 (10), 1225-1231 (2015).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved