Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Multi-parameter Measurement of the Permeability Transition Pore Opening in Isolated Mouse Heart Mitochondria
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
A spectrofluorometric protocol for the measurement of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening in isolated mouse heart mitochondria is presented here. The assay involves the simultaneous measurement of mitochondria Ca2+ handling, mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial volume. The procedure for obtaining high-quality and functional heart mitochondria is also described.
Streszczenie
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mtPTP) is a non specific channel that forms in the inner mitochondrial membrane to transport solutes with a molecular mass smaller than 1.5 kDa. Although the definitive molecular identity of the pore is still under debate, proteins such as cyclophilin D, VDAC and ANT contribute to mtPTP formation. While the involvement of mtPTP opening in cell death is well established1, accumulating evidence indicates that the mtPTP serves a physiologic role during mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis2, bioenergetics and redox signaling 3.
mtPTP opening is triggered by matrix Ca2+ but its activity can be modulated by several other factors such as oxidative stress, adenine nucleotide depletion, high concentrations of Pi, mitochondrial membrane depolarization or uncoupling, and long chain fatty acids4. In vitro, mtPTP opening can be achieved by increasing Ca2+ concentration inside the mitochondrial matrix through exogenous additions of Ca2+ (calcium retention capacity). When Ca2+ levels inside mitochondria reach a certain threshold, the mtPTP opens and facilitates Ca2+ release, dissipation of the proton motive force, membrane potential collapse and an increase in mitochondrial matrix volume (swelling) that ultimately leads to the rupture of the outer mitochondrial membrane and irreversible loss of organelle function.
Here we describe a fluorometric assay that allows for a comprehensive characterization of mtPTP opening in isolated mouse heart mitochondria. The assay involves the simultaneous measurement of 3 mitochondrial parameters that are altered when mtPTP opening occurs: mitochondrial Ca2+ handling (uptake and release, as measured by Ca2+ concentration in the assay medium), mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitochondrial volume. The dyes employed for Ca2+ measurement in the assay medium and mitochondrial membrane potential are Fura FF, a membrane impermeant, ratiometric indicator which undergoes a shift in the excitation wavelength in the presence of Ca2+, and JC-1, a cationic, ratiometric indicator which forms green monomers or red aggregates at low and high membrane potential, respectively. Changes in mitochondrial volume are measured by recording light scattering by the mitochondrial suspension. Since high-quality, functional mitochondria are required for the mtPTP opening assay, we also describe the steps necessary to obtain intact, highly coupled and functional isolated heart mitochondria.
Protokół
1. Isolation of Mitochondria from Mouse Heart
- To isolate heart mitochondria, anesthetize and sacrifice mice according to the procedures approved by your local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Note: All steps of the mitochondria isolation protocol must be performed on ice. Use ice cold buffers and pre-chilled Petri dishes, Falcon tubes and Eppendorf tubes. The volumes given in the protocol are for a sample containing 2 mouse hearts.
- Remove hearts, place them in cold Mitochondria Isolation Buffer (300 mM sucrose, 10 mM Na-HEPES, 200 μM EDTA, pH 7.4) and rinse off blood.
Note: For optimal results, the pH of mitochondrial buffers should be adjusted with KOH and Acetic Acid.
- Place hearts on a cold Petri dish, remove fat and atria, and mince finely using a blade until obtaining a homogeneous product.
- Transfer minced hearts to a 50 ml Falcon tube, add 10 ml of Mitochondria Isolation Buffer with 0.1 mg/ml trypsin and allow the sample to digest on ice for 10 min.
Note: Trypsin during the isolation procedure increases the yield of isolated mitochondria and should be kept constant between mitochondrial preparations. We recommend testing mitochondrial functions on preparations isolated is the absence of trypsin to ensure that the enzyme does not interfere with functionality.
- Add 10 ml of Mitochondria Isolation Buffer with 0.1% fatty acid free BSA and 5 mg trypsin inhibitor (soybean) and mix by inverting the tube several times to neutralize the trypsin.
Note: Mitochondria Isolation Buffer can be prepared in advance and can be stored at -20 °C. Check pH upon thawing. Trypsin, trypsin inhibitor or BSA must be added to the Mitochondria Isolation Buffer on the day of the experiment.
- Recover the digested tissue by low-to-medium speed centrifugation for 1 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend tissue in 8 ml Mitochondria Isolation Buffer with 0.1% fatty acid free BSA and homogenize using a motorized Dounce homogenizer with a Teflon pestle (4-6 passes at 1,200-14,00 rpm). Keep the sample on ice while homogenizing.
- Transfer homogenate into a 15 ml Falcon tube and centrifuge at 800xg for 10 min at 4 °C to pellet nuclei and tissue debris.
- Recover the supernatant containing the mitochondria into Eppendorf tubes and centrifuge at 8,000 x g for 15 min, at 4 °C.
- Remove carefully the top white layer and wash the remaining darker pellet containing the mitochondria in 1 ml Mitochondria Isolation Buffer.
- Centrifuge at 8000xg for 15 min at 4 °C. Discard supernatant and resuspend mitochondria pellet in 150 μl Mitochondrial Isolation Buffer. Keep mitochondria on ice for further assays.
Note: For best results during functional assays, use mitochondria within 4 hr of isolation.
- Quantify mitochondrial protein using the Bradford assay.
2. Quality Control of Isolated Mitochondria
2.1. Measurement of respiratory control ratio (RCR)
- Calibrate the Oxytherm oxygen electrode with air-saturated water to establish the maximum oxygen line. When a stable level of oxygen is obtained add 100 μl of a freshly prepared 10 mM sodium hydrosulfite solution to establish the zero oxygen line. Perform measurements at 30 °C.
- Add 2 ml Mitochondria Respiration Buffer (125 mM KCl, 20 mM HEPES, 3 mM MgCl2, 400 μM EGTA, 300 μM DTT, 5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.2) with 1 μM rotenone to the Oxytherm chamber, seal the chamber and start recording.
- When oxygen signal is stable, add 250 μg mitochondria and record basal respiration for 1 min. The respiration at this point should be very low as mitochondria are respiring on endogenous substrates (State 1 respiration).
- Add 5 mM succinate and record signal for 1 min. Oxygen consumption should increase during State 2 respiration.
- Induce State 3 respiration by adding 150 μM ADP. At this point oxygen consumption should increase due to ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation. Record signal until respiration slows, indicating ADP consumption and transition to State 4 respiration. Record State 4 respiration for at least 1 min.
- Add 1 μM CCCP and record signal for 1 min. Uncoupled respiration should be maximal.
Note: The effect of CCCP on mitochondrial respiration is dose dependent: high concentrations of CCCP can inhibit oxygen consumption and should therefore be carefully titrated.
- Calculate the respiratory control ratio (RCR) by dividing oxygen consumption rate during State 3 respiration by the oxygen consumption rate during State 4 respiration. A target RCR should be ≥ 4.
2.2. Assessment of mitochondrial membrane integrity (cytochrome c test)
- Thoroughly wash the Oxytherm chamber with 70% ethanol and water and repeat steps 2.1.2 -2.1.4.
- Add 1 mM ADP and record oxygen consumption for 1 min.
- Add 10 μM cytochrome c. Since cytochrome c is impermeable to intact mitochondrial membranes, an increase in respiration indicates broken or damaged mitochondrial membranes.
3. Measurement of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Opening
- Setup the spectrofluorometer for the multi-parameter measurement of mtPTP opening. Using the FelixGx program, create a new hardware configuration (Quanta master steady state) comprising the light source, excitation monochromator, sample compartment and two detectors positioned at 90 ° and 270 ° with respect to the excitation monochromator (Figure 4). To achieve maximal time resolution, both emission monochromators (90 ° and 270 °) must be disabled and the emission filters at 90 ° and 270 ° in the sample compartment enabled in the hardware configuration menu. This step will remove the motor control of the emission wavelengths and fix each monochromator at a particular wavelength. If the emission monochromators are not disabled, each detector will cycle between both wavelengths and duplicate measurements will be recorded.
- Create a new acquisition protocol using the Multi Dye type and enter the following dyes:
- Fura (high Ca++): excitation 340 nm, emission 525 nm (detector 1)
- Fura (low Ca++): excitation 380 nm, emission 525 nm (detector 1)
- JC1 (aggregate): excitation 543 nm, emission 595 nm (detector 2)
- JC1 (monomer): excitation 498 nm, emission 525 nm (detector 1)
- Swelling: excitation 525 nm, emission 525 nm (detector 1)
- Set the excitation and emission slits to 1 nm and the temperature to 37 °C.
- To obtain the ratiometric signal for Fura and JC-1, generate two derived traces: Fura (high Ca++)/Fura (low Ca++) and JC1 (aggregate)/JC1 (monomer).
- Manually adjust the emission wavelength of detectors 1 and 2 to 525 nm and 595 nm, respectively.
- Mix 1 ml Mitochondria Assay Buffer (120 mM KCl, 10 mM NaCl, 1 mM KH2PO4, 20 mM HEPES-Tris, pH 7.2) with 1 μM rotenone, 5 mM succinate and 800 nM Fura FF in a disposable 4-sided methacrylate cuvette. Add 250 μg mitochondria and place sample in the sample compartment. Make sure that the magnetic stirrer is turned on.
- Start recording. After 1 min, pause the acquisition, add 500 nM JC-1 and then restart the acquisition. The JC-1 ratio signal should increase, indicating dye uptake by active mitochondria. Continue recording until JC-1 signal has reached a plateau (usually within 5 min).
- Add 20 μM CaCl2. An instantaneous increase in Fura FF ratio signal should be observed by the increased Ca2+ presence in the assay buffer, followed by a gradual decrease due to mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. The JC-1 ratio signal should exhibit a brief transient decrease indicative of slight mitochondrial membrane depolarization.
- Wait until Fura FF ratio signal returns to basal level prior to addition of another CaCl2 pulse (1-1.5 min). Continue pulsing at fixed intervals until mitochondria cannot accumulate Ca2+ and begin releasing Ca2+ into the assay buffer. mtPTP opening is visualized by a concurrent increase in the Fura FF ratio signal due to Ca2+ release, a decrease in the JC-1 signal ratio due to membrane potential collapse, and a decrease in light scattering due to mitochondrial swelling (Figure 5).
- Following mtPTP activation, verify the specificity of Fura FF, JC-1 and swelling signals respectively with 1 mM EGTA, 1 μM CCCP and 5 μg/ml alamethicin.
- To verify specificity of mtPTP opening, repeat steps 3.6 - 3.9 in the presence of 1 μM of the cyclophilin D inhibitor cyclosporine A (cyclophilin D is a component of the mtPTP). In the presence of cyclosporine A, opening of the mtPTP requires significantly more CaCl2 pulses than control samples (Figure 6).
4. Representative Results
Figure 2 shows a typical respiratory control of isolated mouse heart mitochondria. State 3 respiration is achieved by addition of ADP to mitochondria respiring on succinate, and is characterized by significantly increased oxygen consumption with respect to the substrate alone. Depletion of added ADP initiates State 4 respiration, during which oxygen consumption slows and is comparable to rates attained prior to ADP addition. RCR is obtained by dividing the oxygen consumption rate for State 3 respiration by that of State 4 respiration. The cytochrome c test is used to assay the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane: when cytochrome c is added to mitochondria respiring on succinate and ADP, no further increase in respiration is observed, indicating an intact outer mitochondrial membranes (Figure 3).
A representative image for the mtPTP opening in isolated heart mitochondria is shown in Figure 4. In this case mtPTP opening was triggered by the addition of 4 CaCl2 pulses (20 μM each) at 1.5 min intervals. mtPTP opening is apparent by the near simultaneous release of mitochondrial Ca2+ (increase in Fura FF ratio signal), collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential (decrease in JC-1 ratio signal) and increased mitochondrial volume (decrease in the swelling signal). When cyclosporine A is added, which binds to the cyclophilin D component of mtPTP, mtPTP opening requires 7 pulses of CaCl2 instead of 4 (Figure 5).
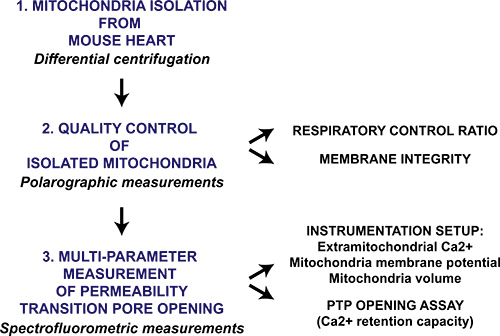
Figure 1. Flow chart of the multi-parameter mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening protocol for isolated heart mitochondria. Heart is harvested from mice and mitochondria are isolated through differential centrifugation. The mitochondrial preparation is then qualitatively evaluated by polarographic measurement of the respiratory control ratio and mitochondrial membrane intactness in the presence of cytochrome c. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening in isolated mitochondria is triggered by sequential CaCl2 additions and is measured with a spectrofluorometer by monitoring Ca2+ release from mitochondria, membrane potential collapse and swelling of the mitochondrial matrix.
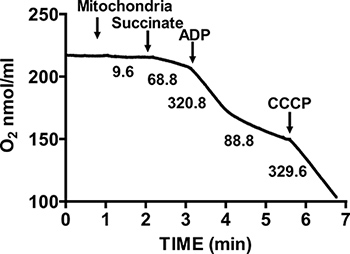
Figure 2. Measurement of respiratory control ratio (RCR) of isolated heart mitochondria. Oxygen consumption by isolated heart mitochondria is measured during State 3 respiration in the presence of succinate and ADP, and during State 4 respiration after ADP consumption. The response of isolated mitochondria to uncouplers is measured by the addition of CCCP. Numbers on the graph are the rates of oxygen consumption by isolated mitochondria in nmol/min/mg protein.
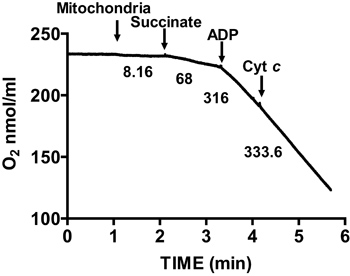
Figure 3. Measurement of membrane integrity of isolated heart mitochondria. Mitochondrial membrane integrity is determined by measuring oxygen consumption in isolated mitochondria in the presence of succinate and ADP and after the addition of cytochrome c. Numbers on the graph are the rates of oxygen consumption by isolated mitochondria in nmol/min/mg protein.
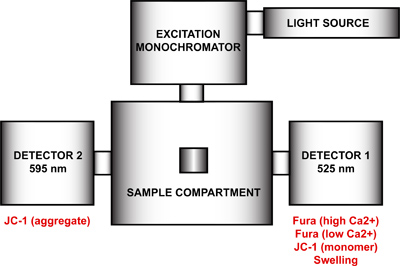
Figure 4. Spectrofluorometer hardware configuration for the multi-parameter measurement of mtPTP opening. The hardware configuration of the spectrofluorometer includes a light source, an excitation monochromator, a sample compartment and two detectors with fixed emission wavelengths at 525 nm and 595 nm. Detector 1 is used for the signal detection of Fura FF high and low Ca2+, JC-1 monomer, and the swelling signal. Detector 2 measures the JC-1 aggregate signal.
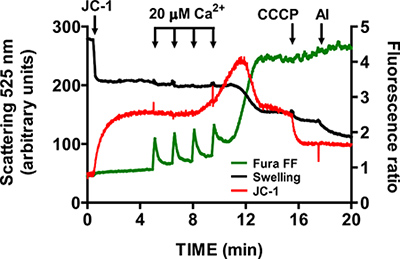
Figure 5. Multi-parameter measurement of mtPTP opening in isolated heart mitochondria. mtPTP opening was triggered by sequential additions of 20 μM CaCl2 and was characterized by Ca2+ release from mitochondria, mitochondrial membrane potential collapse and increased mitochondrial matrix volume (swelling). Extramitochondrial Ca2+ and membrane potential were measured with the ratiometric indicators Fura FF (green trace) and JC-1 (red trace). Swelling of mitochondria was measured by recording light scattering at 525 nm (black trace). Specificity of JC-1 and swelling signals was tested with 1 μM CCCP and 5 μg/ml alamethicin (a microbial toxin).
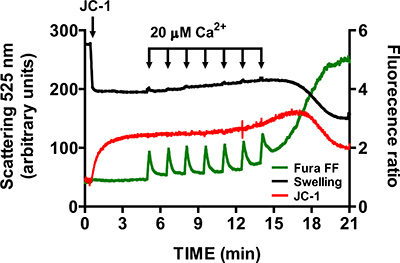
Figure 6. Multi-parameter measurement of mtPTP opening in isolated heart mitochondria in the presence of cyclosporine A. Cyclosporine A (1 μM) increases the number of CaCl2 pulses required to open mtPTP in isolated heart mitochondria.
Dyskusje
The protocol presented here describes the necessary experimental steps to assess permeability transition pore opening in isolated heart mitochondria (Figure 1 and Figure 4): the procedure for isolating mouse heart mitochondria, the respiratory controls that ensure their integrity and functionality, the mitochondrial parameters monitored during mtPTP opening and the dyes employed for their measurement, the setting up of the spectrofluorometric instrumentation, and the characterization of ...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
This work was supported by HL094536 (B.J.H.).
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Trypsin | Sigma-Aldrich | T3030 | |
| Trypsin inhibitor (soybean) | Sigma-Aldrich | T9128 | |
| Sodium hydrosulfite | Sigma-Aldrich | 71699 | |
| Rotenone | Sigma-Aldrich | R8875 | |
| Cytochrome c | Sigma-Aldrich | C7752 | |
| Alamethicin | Sigma-Aldrich | A4665 | |
| CCCP | Sigma-Aldrich | C2759 | |
| Cyclosporin A | Calbiochem | 239835 | |
| Fura FF | Invitrogen | F14180 | |
| JC-1 | Invitrogen | T3168 | |
| Tissue grinder Potter-Elvehjem with Teflon pestle 15 ml | Wheaton Industries | ||
| Overhead stirrer | Wheaton Industries | 903475 | |
| Oxytherm (temperature controlled oxygen electrode) | Hansatech Instruments | ||
| QuantaMaster 80 dual emission spectrofluorometer | Photon Technology International, Inc. |
Odniesienia
- Kroemer, G., Galluzzi, L., Brenner, C. Mitochondrial Membrane Permeabilization in Cell Death. Physiol. Rev. 87, 99-163 (2007).
- Elrod, J., Wong, R., Mishra, S., Vagnozzi, R. J., Sakthievel, B., Goonasekera, S. A., Karch, J., Gabel, S., Farber, J., Force, T., Brown, J. H., Murphy, E., Molkentin, J. D. Cyclophilin D controls mitochondrial pore-dependent Ca2+ exchange, metabolic flexibility, and propensity for heart failure in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 120, 3680-3687 (2010).
- Hom, J. R., Quintanilla, R. A., Hoffman, D. L., de Mesy Bentley, K. L., Molkentin, J. D., Sheu, S. S., Porter, G. A. The permeability transition pore controls cardiac mitochondrial maturation and myocyte. 21, 469-478 (2011).
- Halestrap, A. P. What is the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 46, 821-831 (2009).
- Wei, A. C., Liu, T., Cortassa, S., Winslow, R. L., O'Rourke, B. Mitochondrial Ca2+ influx and efflux rates in guinea pig cardiac mitochondria: low and high affinity effects of cyclosporine A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1813, 1373-1381 (2011).
- Saks, V. A., Kuznetsov, A. V., Kupriyanov, V. V., Miceli, M. V., Jacobus, W. E. Creatine kinase of rat heart mitochondria. The demonstration of functional coupling to oxidative phosphorylation in an inner membrane-matrix preparation. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 7757-7764 (1985).
- Boehm, E. A., Jones, B. E., Radda, G. K., Veech, R. L., Clarke, K. Increased uncoupling proteins and decreased efficiency in palmitate-perfused hyperthyroid rat heart. AJP - Heart. 280, 977-983 (2001).
- Fontaine, E., Eriksson, O., Ichas, F., Bernardi, P. Regulation of the Permeability Transition Pore in Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12662-12668 (1998).
- Berman, S. B., Watkins, S. C., Hastings, T. G. Quantitative biochemical and ultrastructural comparison of mitochondrial permeability transition in isolated brain and liver mitochondria: evidence for reduced sensitivity of brain mitochondria. Exp. Neurol. 164, 415-425 (2000).
- Panov, A., Dikalov, S., Shalbuyeva, N., Hemendinger, R., Greenamyre, J. T., Rosenfeld, J. Species- and tissue-specific relationships between mitochondrial permeability transition and generation of ROS in brain and liver mitochondria of rats and mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 292, 708-718 (2007).
- Frezza, C., Cipolat, S., Scorrano, L. Organelle isolation: functional mitochondria from mouse liver, muscle and cultured filroblasts. Nature Protocols. 2, 287-295 (2007).
- Pallotti, F., Lenaz, G. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from animal cells and tissue culture lines. Methods Cell Biol. 80, 3-44 (2007).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone