Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
A Neonatal BALB/c Mouse Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
* Wspomniani autorzy wnieśli do projektu równy wkład.
W tym Artykule
Erratum Notice
Podsumowanie
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most severe gastrointestinal (GI) disease that often occurs in premature infants, especially very low birth weight infants, with high mortality and unclear pathogenesis. The cause of NEC may be related to inflammatory immune regulatory system abnormalities. An NEC animal model is an indispensable tool for NEC disease immune research. NEC animal models usually use C57BL/6J neonatal mice; BALB/c neonatal mice are rarely used. Related studies have shown that when mice are infected, Th2 cell differentiation is predominant in BALB/c mice compared to C57BL/6J mice. Studies have suggested that the occurrence and development of NEC are associated with an increase in T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and are generally accompanied by infection. Therefore, this study used neonatal BALB/c mice to induce an NEC model with similar clinical characteristics and intestinal pathological changes as those observed in children with NEC. Further study is warranted to determine whether this animal model could be used to study Th2 cell responses in NEC.
Streszczenie
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most severe gastrointestinal (GI) disease that often occurs in premature infants, especially very low birth weight infants, with high mortality and unclear pathogenesis. The cause of NEC may be related to inflammatory immune regulatory system abnormalities. An NEC animal model is an indispensable tool for NEC disease immune research. NEC animal models usually use C57BL/6J neonatal mice; BALB/c neonatal mice are rarely used. Related studies have shown that when mice are infected, Th2 cell differentiation is predominant in BALB/c mice compared to C57BL/6J mice. Studies have suggested that the occurrence and development of NEC are associated with an increase in T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and are generally accompanied by infection. Therefore, this study used neonatal BALB/c mice to induce an NEC model with similar clinical characteristics and intestinal pathological changes as those observed in children with NEC. Further study is warranted to determine whether this animal model could be used to study Th2 cell responses in NEC.
Wprowadzenie
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), the most severe gastrointestinal (GI) disease, occurs in most premature infants (>90%), especially those with very low birth weight (VLBW)1. In VLBW infants, the incidence of the disease ranges from 10% to 12%, and the mortality of children diagnosed with NEC is between 20% and 30%2,3. The cause of NEC may be related to mucosal injuries, invasion by pathogenic bacteria, and intestinal feeding, which can lead to inflammatory responses and the induction of intestinal injuries in susceptible hosts3. The pathogenesis of NEC is unclear. Relevant research shows that the affected infant's immune response is abnormal, and genetic susceptibility, microvascular tension, and intestinal bacterial changes may play important roles in the disease3.
The NEC animal model is an indispensable tool for research on the pathogenesis of NEC. The animal species used for NEC models are pigs, rats, and mice. However, due to the long gestation period, growth cycles, and high costs, in recent years, pigs have not been the first choice for NEC models and have been replaced with rats or mice4. As there are differences in the immune background of different mouse strains5, different studies need to use different strains of mice to establish NEC animal models. BALB/c mice have an important feature; when they are infected or cope with external damage, the polarization of TH2 cells during infection in mice is significantly stronger than that in other strains of mice6,7,8. T helper cells play a crucial role in the occurrence and progression of NEC, especially the development of TH2 cells3,9,10,11. Therefore, this study used BALB/c mice to establish the NEC model, which might be helpful for NEC disease research on T cells.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protokół
This research was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center (NO. 174A01) and the Animal Ethical Committee of the Guangzhou Forevergen Biosciences Laboratory Animal Center (IACUC-G160100). All animals were bred in the same room in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) environment, and experiments were carried out in a conventional environment. The mice used for breeding were 7-8 weeks old; the mice for inducing NEC (n = 72) were separated from the dam on Day 4, and the dams(n=14) were kept in the original cage and nursed the control (Cont.) group mice(n=24).
1. Preparation of reagents and devices
- Prepare the milk substitute for the BALB/c mice in the corresponding ratio (premature baby milk powder: goat milk powder = 2:1).
NOTE: The final nutritional compositions of formula milk12 are shown in Table 1. - LPS solution (2.5 mg/mL)
- Dissolve a total of 10 mg of LPS powder in 4 mL of sterilized double-distilled water, mix well, and store in a refrigerator at -20 °C after aliquoting.
NOTE: The LPS solution is stored in the dark at 2-8 °C for immediate use or at -20 °C for long-term storage.
- Dissolve a total of 10 mg of LPS powder in 4 mL of sterilized double-distilled water, mix well, and store in a refrigerator at -20 °C after aliquoting.
2. Induce necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal BALB/c mice
- Feed the neonatal mice.
- Keep the neonatal mice in the same cage with the dam, nursed by the dam on Days 0-4.
- On the night of Day 4 (when the neonatal mice weigh 2.5-3 g), separate the neonatal mice in the NEC group from the dam to induce NEC, keep them in an animal incubator, and feed them with formula. However, the Cont. group is allowed to stay with and be fed by the dam.
NOTE: Neonatal mice that are separated from the dam must be raised in an incubator because of their weak body temperature regulation.
- Prepare the gavage tube by soaking it in 75% alcohol containers for 1-2 min and wash them twice in clean, double-distilled water.
NOTE: To avoid cross-contamination among the mice, the above process must be performed after feeding each mouse. - Induce the NEC model.
- Take the neonatal mice from the dam on Day 4 and fast them for one night.
- Gavage the mice with LPS (20-30 µL at a time) and feed them with formula on Day 5 (40-50 µL at a time).
- From Day 5 onwards, subject the mice to a hypoxia-reoxygenation-cold-shock cycle twice a day for 5 days. Place the mice in a hypoxia device at 5% O2 for 90 s and reoxygenate them for 3 min; repeat this process five times. Next, place the mice in a 4 °C environment for 15 min and then transfer them to an incubator. See Figure 1A,B for the induction process.
NOTE: A cycle of hypoxia-reoxygenation-cold stimulation was performed once in the morning and once in the afternoon. A mixture of 5% O2 with 95% N2 was prepared in the container, and the concentration was measured with an oxygen detector.
- Closely observe all the mice, weigh them every day, record the survival of the mice during the induction period, and record the stool characteristics (with or without sticky stools/bloody stools).
NOTE: The established NEC model lasts for 5 days. - On Day 10 or earlier, when the mice show NEC symptoms (ileus, hematochezia, diarrhea)13, euthanize the mice by inhalation anesthesia with isoflurane, then immediately collect the intestinal tissue. Do not collect tissues from the mice that died spontaneously.
NOTE: In this study, the end-point of mouse euthenasia was adapted when the mouse displayed hematochezia and cyanosis of the whole body.
3. Gavage the mouse
- Fix the mouse head, holding the gastric tube in the right hand. Insert the gastric tube from the left corner of the mouth of the mouse.
NOTE: The head was fixed with the index finger on the mouse's head and gently pressed backward and downwards to prevent the mouse from bending forwards during the operation and affecting the insertion of the gastric tube. - Slowly move the tube to the center of the mouth. After inserting the tube approximately 2-3 cm, push 40-50 µL of formula or 20-30 µL of LPS into the digestive tract. See Figure 2A,B for the gavage.
NOTE: Under normal circumstances, the gastric tube is inserted into the digestive tract smoothly. If the mouse has a strong vomiting reflex, the gastric tube has been inserted into the trachea by mistake. The gastric tube must be pulled out gently and the mouse allowed to rest for a while before attempting gavage again. In addition, the gavage procedure is used to induce the model of NEC prior to euthanasia of mice.
4. Collect fresh intestinal tissue specimens for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining
- Immerse the fresh ileum tissue from the mouse in 10% formalin for 24 h.
- Embed the tissues in paraffin and slice them into 4 µm sections.
- Deparaffinize the sections in xylene and rehydrate them successively in absolute ethanol, 95% ethanol, 80% ethanol, 70% ethanol, and distilled water, soaking for 5 min in each step. Stain the sections with hematoxylin solution for 5 min and differentiate them in 1% hydrochloric acid in 75% alcohol for 5 s. Finally, stain them with eosin solution for 1 min.
NOTE: After staining with hematoxylin solution, it must be differentiated with 1% hydrochloric acid in ethanol to remove excessively bound hematoxylin solution and cytoplasmic hematoxylin dye. The concentration of 1% hydrochloric acid is suitable for intestinal tissue. - Examine the histopathology of the intestinal tissue at 40x magnification.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Wyniki
The BALB/c mouse NEC model was induced by formula feeding, LPS feeding, hypoxia, and cold stimulation. During the induction period, the mice were observed for intestinal pathology, stool characteristics, body weight changes, and daily survival. Representative images of the small intestine during NEC induction; the numbers in the picture represent the intestinal pathology score from 0 (normal epithelium) to 4 (the most severe) (Figure 3A). The intestinal pathology score was significantly high...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Dyskusje
NEC is the most common gastrointestinal system emergency for neonates, with a high incidence and mortality, especially in premature infants1,2,3. However, its pathogenesis is still unclear. It is currently believed that mucosal damage, pathogen invasion, and enteral feeding are high-risk factors for NEC3. To date, the animals used for the NEC model are mainly pigs, rats, and mice. Most studies have used n...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Ujawnienia
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Podziękowania
The authors thank the Clinical Biological Resource Bank of Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center for providing the clinical sample and Guangzhou Forevergen Biosciences Laboratory Animal Center for providing mice. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 81770510 (R.Z.).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Absolute ethanol | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., LTD. | 100092683 | |
| Goat Milk powder | Petag | 71795558417 | |
| HE dye solution | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., LTD. | G1003 | |
| Isoflurane | RWD, Shenzhen Reward Life Technology Co., LTD. | R510 | |
| LPS | Sigma-Adrich | L2880 | |
| Medical oxygen | various | various | |
| Microscope | NIKON | NIKON imaging system (DS-Ri2) | |
| Neutral resin | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., LTD. | 10004160 | |
| Paraffin | various | various | |
| Premature baby milk powder | Abbott | 57430 | |
| Xylene | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., LTD. | 10023418 | |
| 1% Hydrochloric acid | various | various | |
| 10% Formalin | LEAGENE | DF0110 |
Odniesienia
- Horbar, J. D., et al. Mortality and neonatal morbidity among infants 501 to 1500 grams from 2000 to 2009. Pediatrics. 129 (6), 1019-1026 (2012).
- Stoll, B. J., et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 126 (3), 443-456 (2010).
- Neu, J., Walker, W. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (3), 255-264 (2011).
- Sangild, P. T., et al. Invited Review: The preterm pig as a model in pediatric gastroenterology. Journal of Animal Science. 91 (10), 4713-4729 (2013).
- Cancro, M. P., Sigal, N. H., Klinman, N. R. Differential expression of an equivalent clonotype among BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 147 (1), 1-12 (1978).
- Kuroda, E., Yamashita, U. Mechanisms of enhanced macrophage-mediated prostaglandin E2 production and its suppressive role in Th1 activation in Th2-dominant BALB/c mice. Journal of Immunology. 170 (2), 757-764 (2003).
- Fornefett, J., et al. Comparative analysis of clinics, pathologies and immune responses in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice infected with Streptobacillus moniliformis. Microbes and Infection. 20 (2), 101-110 (2018).
- Rosas, L. E., et al. Genetic background influences immune responses and disease outcome of cutaneous L. mexicana infection in mice. International Immunology. 17 (10), 1347-1357 (2005).
- Sproat, T., Payne, R. P., Embleton, N. D., Berrington, J., Hambleton, S. T cells in preterm infants and the influence of milk diet. Frontiers in Immunology. 11, 1035(2020).
- Nanthakumar, N., et al. The mechanism of excessive intestinal inflammation in necrotizing enterocolitis: an immature innate immune response. PLoS One. 6 (3), 17776(2011).
- Afrazi, A., et al. New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis: Toll-like receptors and beyond. Pediatric Research. 69 (3), 183-188 (2011).
- Auestad, N., Korsak, R. A., Bergstrom, J. D., Edmond, J. Milk-substitutes comparable to rat's milk; their preparation, composition and impact on development and metabolism in the artificially reared rat. British Journal of Nutrition. 61 (3), 495-518 (1989).
- Liu, Y., et al. Lactoferrin-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell therapy attenuates pathologic inflammatory conditions in newborn mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 129 (10), 4261-4275 (2019).
- MohanKumar, K., et al. A murine neonatal model of necrotizing enterocolitis caused by anemia and red blood cell transfusions. Nature Communications. 10 (1), 3494(2019).
- He, Y. M., et al. Transitory presence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in neonates is critical for control of inflammation. Nature Medicine. 24 (2), 224-231 (2018).
- Cho, S. X., et al. Characterization of the pathoimmunology of necrotizing enterocolitis reveals novel therapeutic opportunities. Nature Communications. 11 (1), 5794(2020).
- Halpern, M. D., et al. Decreased development of necrotizing enterocolitis in IL-18-deficient mice. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 294 (1), 20-26 (2007).
- Wu, N., et al. MAP3K2-regulated intestinal stromal cells define a distinct stem cell niche. Nature. 592 (7855), 606-610 (2021).
- Nino, D. F., Sodhi, C. P., Hackam, D. J. Necrotizing enterocolitis: new insights into pathogenesis and mechanisms. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 13 (10), 590-600 (2016).
- Chuang, S. L., et al. Cow's milk protein-specific T-helper type I/II cytokine responses in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatric Allergy & Immunology. 20 (1), 45-52 (2009).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: A Neonatal BALB/c Mouse Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Posted by JoVE Editors on 3/07/2022. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: A Neonatal BALB/c Mouse Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. The Representative Results section was updated.
Figure 1 was updated from:

Figure 1: Induction of the BALB/c NEC model process. (A) The mice in the NEC group were separated from the dam at birth until they were 4 days old (on Day 4) and fasted that night. The NEC model was induced from Day 5 onwards after birth and lasted for 5 days. Intestinal tissue specimens were collected on Day 10 or earlier. The mice in the Cont. group were housed with and nursed by the dam. (B) The sequence of operations for each day after inducing the NEC model. Abbreviations: Cont. = control; NEC = necrotizing enterocolitis; LPS = lipopolysaccharide. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
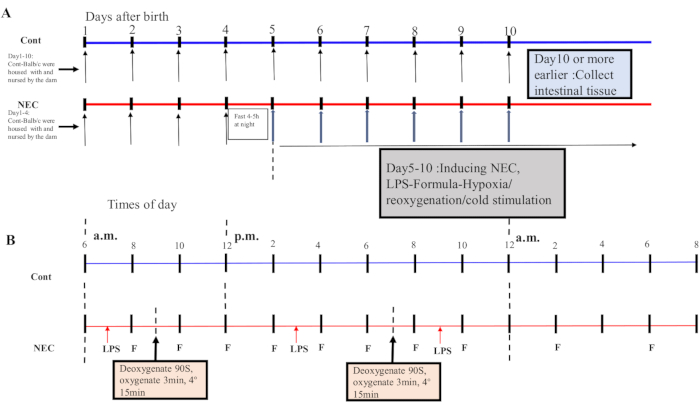
Figure 1: Induction of the BALB/c NEC model process. (A) The mice in the NEC group were separated from the dam at birth until they were 4 days old (on Day 4) and fasted that night. The NEC model was induced from Day 5 onwards after birth and lasted for 5 days. Intestinal tissue specimens were collected on Day 10 or earlier. The mice in the Cont. group were housed with and nursed by the dam. (B) The sequence of operations for each day after inducing the NEC model. Abbreviations: Cont. = control; NEC = necrotizing enterocolitis; LPS = lipopolysaccharide. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone