A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Development of a Selective Aortic Arch Perfusion System in a Porcine Model of Exsanguination Cardiac Arrest
In This Article
Summary
The goal of this protocol is to demonstrate a porcine exsanguination cardiac arrest model and a specifically built selective aortic arch perfusion circuit for translational research.
Abstract
Hemorrhage constitutes the majority of potentially preventable deaths from trauma. There is growing interest in endovascular resuscitation techniques such as selective aortic arch perfusion (SAAP) for patients in cardiac arrest. This involves active perfusion of the coronary circulation via a thoracic aortic balloon catheter and is approaching clinical application. However, the technique is complex and requires refinement in animal models before human use can be considered. This paper describes a large animal model of exsanguination cardiac arrest treated with a bespoke SAAP system.
Swine were anesthetized, instrumented and a splenectomy was performed before a controlled, logarithmic exsanguination was initiated. Animals were heparinized and the shed blood collected in a reservoir. Once cardiac arrest was observed, the blood was pumped through an extra-corporeal circuit into an oxygenator and then delivered through a 10 Fr balloon catheter placed in the thoracic aorta.
This resulted in the return of a spontaneous circulation (ROSC) as demonstrated by ECG and aortic root pressure waveform. This model and accompanying SAAP system allow for standardized and reproducible recovery from exsanguination cardiac arrest.
Introduction
Hemorrhage accounts for the majority of potentially preventable trauma deaths1. In the terminal stages of exsanguination, coronary perfusion is reduced, leading to cardiac arrest and death. Current strategies – intravenous transfusion and cardiac massage – are ineffective as they do not address the failure of coronary perfusion.
SAAP is a catheter-based resuscitation technique that aims to address this problem by the infusion of oxygenated resuscitation fluid and drugs directly to proximal aorta, perfusing the coronary and cerebral circulation. Limited swine studies have demonstrated promising outcomes in restoring cardiac activity following ventricular fibrillation and hemorrhagic cardiac arrest2,3,4. However, SAAP research is ongoing and the technique remains in the pre-clinical phases.
There are several technical challenges with SAAP. It is critical that a certain volume of perfusate be delivered via the catheter at a precise infusion rate, and currently there is no commercially available, FDA approved catheter for use in SAAP. The technique requires a specific circuit which is capable of efficiently storing, oxygenating and delivering perfusate during SAAP. The aim of this study is to present a traumatic pulseless electrical activity (PEA) cardiac arrest animal model and custom built, reliable SAAP system for use in exploring this tool in exsanguination animal research.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
This study was conducted at the Medical School Teaching Facility (MSTF, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, USA), which is accredited by the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. The study protocol was approved by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
1. Animal selection and housing
- Use adult male swine (Sus Scrofa) weighing 60-80 kg.
- Following arrival to the animal facility, house the animals one per cage but with ability to interact with animals in the neighboring cages.
- House the animals for a minimum of 48 hours to assure acclimatization. Allow the animals free access to water and feed them a standard diet until the night before the experiment when the animals should be fasted to minimize the risk of aspiration during intubation.
- Monitor the animals regularly to confirm that they are in good health.
2. Sedation and induction of general anesthesia
- Sedate the animal while it is still in its housing area by intramuscular injection of Telazol (4-5 mg/kg)/xylazine (1.8-2.2 mg/kg) caudal to the ear or in the gluteus muscle.
- Transport the animal from the housing area to the operating room and place it in dorsal recumbency on the operating table.
- Place a pulse oximetry probe on the animal’s ear, place a face mask on the animal’s snout and give Isoflurane in 100% O2, until the mandible is relaxed, to induce anesthesia.
- Place an endotracheal (ET) tube using a laryngoscope. This should be achieved by holding the jaws open, pulling out the tongue, identifying the epiglottis, passing the tip of the laryngoscope into the oropharynx and displacing the epiglottis from the soft palate. Advance the ET tube through the vocal folds 6-10 cm and then rotate it in a curve down position relative to the top of the animal’s head.
- Inflate the ET cuff with air with 10 cm3, secure the ET tube to the animal’s snout using gauze ties and auscultate the animal’s chest to confirm correct placement of the tube.
- Connect the ET tube to a mechanical ventilator via a heat and moisture exchanger.
- Confirm appropriate mechanical ventilator settings to deliver an inspired O2 fraction of 30%, with a tidal volume of 7-10 mL per kg of body mass, a respiratory rate of 10-15 breaths/min, aiming for an end tidal CO2 tension of 38-42 mmHg.
- To maintain anesthesia, use 1.5-3% isoflurane. Regularly asses the animal’s respiratory parameters.
3. Surgery
- Surgical site sterilization and preparation
- Remove the hair overlying the site for the laparotomy incision and percutaneous access sites using an electric hair clipper.
- Scrub all incision sites and percutaneous puncture sites with betadine and allow to dry.
- Place sterile drapes around the operative sites to preserve the sterile surgical fields and prevent contamination. Secure these in place with staples.
- Retract the front and back hooves with slight flexion and restrain in place with rope or tape.
- Place the ECG adhesive electrodes on the right forelimb, left forelimb, right hindlimb and left hindlimb and over the xiphoid. Attach the correct ECG leads to the adhesive electrodes.
- Laparotomy
- Use electrocautery to make a 20 cm midline abdominal incision.
- Use electrocautery to dissect through the subcutaneous tissue and linea alba. Enter the peritoneal cavity under direct vision using scissors.
- Splenectomy
- Remove the spleen to prevent autotransfusion in response to exsanguination.
- Deliver the spleen into the midline wound, clamp the hilum vessels with two hemostats and transect between the hemostats. Ligating the transected ends with 0 silk ties.
- Identify the deeper lying short gastric vessels, place two hemostats, transect the vessels between the hemostats and ligate the ends with 0 silk ties.
- Carefully inspect the ligated vessels to ensure hemostasis. Ligate any bleeding vessels.
- Examine the spleen in situ to make sure it is dissected free and remove it.
- Cystostomy
- Deliver the bladder through the laparotomy wound.
- Grasp the ventral part of the bladder between two DeBakey clamps and make a 1 cm incision using scissors.
- Pass a suction catheter into the opening and remove the urine from the bladder.
- Place a 14 Fr urinary catheter into the bladder. Inflate the catheter balloon with 10 mL of saline.
- Place a purse string suture using a 3.0 nylon suture to secure the catheter in the bladder to prevent urine spillage.
- Connect the catheter to a collection bag.
- Close the laparotomy wound with a running stitch using a 3’0 nylon suture.
4. Instrumentation
NOTE: See Table 1 for key steps in connecting the SAAP circuit.
- Percutaneous vascular access
- Right and left internal jugular vein cannulation (Figure 1)
- Using ultrasound (US) guidance, visualize the internal jugular vein; it is usually located about 2-3 cm deep to the skin in the jugular furrow.
- Puncture the skin with an 18 G needle placed at a 45° angle to the skin and introduce it into the venous lumen under US vision. Pass an 0.035” Seldinger guidewire through the needle.
- Remove the needle, taking care to leave the guidewire in the venous lumen.
- Make a 5 mm skin incision adjacent to the wire, and thread a 7 Fr sheath with a dilator into the vein over the guidewire.
- Remove the guidewire and the introducer, leaving the sheath in position. Secure the sheath in place by suturing it to the skin with 1.0 silk sutures.
- Repeat the above steps to cannulate the contralateral Internal jugular vein.
NOTE: One of the jugular vein sheaths is used for right atrial pressure monitoring, the other one can be used for drug delivery depending on the study protocol. Alternatively, external jugular veins can be used for cannulation.
- Carotid Artery Cannulation (Figure 1)
- Locate the carotid artery just lateral to the trachea using US guidance.
- Puncture the skin with an 18 G needle placed at a 45° angle to skin and introduce it into the arterial lumen under US vision, pass an 0.035” Seldinger guidewire through the needle.
- Remove the needle, taking care to leave the guidewire in the arterial lumen.
- Make a 5 mm skin incision adjacent to the wire, and thread a 7 Fr sheath with a dilator into the artery over the guidewire.
- Remove the guidewire and the introducer, leaving the sheath in position. Secure the sheath in place by suturing it to the skin with 1.0 silk sutures.
- Right and left femoral artery cannulation
- Locate the right femoral artery in the femoral canal using US guidance.
- Puncture the skin with an 18 G needle at a 45° angle to skin and introduce it into the arterial lumen under US vision. Pass an 0.035” Seldinger guidewire through the needle.
- Remove the needle, taking care to leave the guidewire in the arterial lumen.
- Make a 10 mm skin incision adjacent to the wire.
- Thread a 14 Fr sheath with a dilator into the artery over the guidewire.
- Remove the guidewire and the introducer, leaving the sheath in position. Secure the sheath in place by suturing it to the skin with 1.0 silk sutures.
- For the left femoral arterial access, locate the left femoral artery in the femoral canal using US.
- Puncture the skin with an 18 G needle at a 45° angle and introduce it into the arterial lumen under US vision. Pass a 90 cm 0.035” Seldinger guidewire through the needle.
- Remove the needle, taking care to leave the guidewire in the arterial lumen.
- Make a 10 mm skin incision adjacent to the wire.
- Thread an 18 cm long, 15 Fr ECMO cannula into the artery over the guidewire.
- Remove the guidewire along with the dilator and clamp the distal end of the cannula to prevent the back bleeding.
- Femoral vein cannulation
- Locate the femoral vein in the femoral canal using US guidance.
- Puncture the skin with an 18 G needle at a 45° angle and introduce it into the venous lumen under US vision, pass an 0.035” Seldinger guidewire through the needle.
- Remove the needle, taking care to leave the guidewire in the venous lumen.
- Make a 5 mm skin incision adjacent to the wire, and thread a 9 Fr central venous catheter with an introducer into the vein over the guidewire.
- Remove the guidewire and the introducer, leaving the catheter in position. Secure the line in place by suturing it to the skin with 1.0 silk sutures.
- Right and left internal jugular vein cannulation (Figure 1)
- Percutaneous vascular monitoring (Figure 1)
- Aortic Root Pressure
- Using fluoroscopy introduce a micromanometer catheter into the 7 Fr sheath in the right carotid artery.
- Confirm the catheter tip is in the aortic arch by visualizing the aortic pressure waveform presented on the data collection screen.
- Right atrial pressure
- Using fluoroscopy introduce a previously calibrated micromanometer catheter into the 7 Fr sheath in the right internal jugular vein.
- Confirm the catheter tip placement in right atrium by observing the pressure waveform presented on the data collection screen.
- Aortic Root Pressure
5. Exsanguination
- Preparing the setup
- Inject 15,000 IU of unfractionated heparin via the sidearm of the IJV sheath.
- Load the exsanguination tubing into the roller of the peristaltic pump used for the exsanguination.
- Connect one end of the tubing to the circuit reservoir using standard IV tubing.
- Connect the other end of the exsanguination pump tubing using a straight coupler and a 2-inch segment of ¼” ID tubing to the end of the 15 Fr ECMO cannula in the femoral artery.
- Remove the clamp from the 15 Fr Cannula.
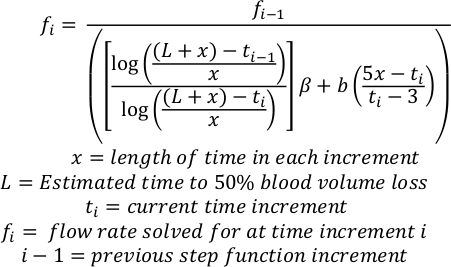
- Calculate logarithmic exsanguination rate intervals using the formula5. Interval length and exsanguination rate depend on the study protocol.
- Set the desired pump rate according to the protocol using the programmable specific pump computer software -PUMPTERM.
- Connect the computer the programmable pump using a standard Ethernet port. Once the controlled pump is programmed with updated initial flow rate displayed on the digital display, it can be disconnected from the computer.
- Pump controlled exsanguination
- Begin the exsanguination by pressing the START/ STOP button on the pump.
- Continue the exsanguination as per protocol until PEA is demonstrated by loss of aortic pressure (SBP <10 mmHg) with loss of pulsatility in the aortic root pressure waveform accompanied by sinus ECG rhythm.
- Stop the exsanguination by manually pressing the START/ STOP button on the pump.
6. SAAP
- SAAP circuit preparation
- Construct the circuit tubing using barbed Y and straight connectors and 3/8” ID tubing to incorporate a reperfusion limb, main perfusion limb, SAAP perfusion limb and a peripheral perfusion limb (Figure 2). Secure the connections with cable ties.
- Connect the proximal tubing to the blood reservoir.
- Connect the tubing to the centrifugal pump.
- Connect the tubing to the oxygenator.
- Connect the oxygenator to the source of oxygen using a standard oxygen tubing by inserting it into the oxygen infusion port on the oxygenator.
- Load the main perfusion limb of the circuit into the peristaltic pump head.
- Deliver the oxygen at 6 L/min by rotating the dial on the oxygen cylinder.
- Add 15,000 IU of unfractionated heparin into the circuit reservoir.
- Confirm that the perfusion limb of the circuit is clamped, and the reperfusion limb is open as the shed blood is pumped into the blood reservoir during exsanguination. Activate the centrifugal pump in the SAAP circuit by pressing the START/ STOP button and set the flow at any rate. This will allow blood to circulate preventing coagulation.
- Mark the balloon insertion length by placing it externally against anatomical landmarks. Aim for the balloon to sit in the proximal thoracic aorta.
- Flush the SAAP catheter and confirm it has a 3-way stopcock attached to the catheter hub.
- Confirm that the balloon is fully deflated and confirm the catheter has a 2-way stopcock at the balloon port.
- Prefill a 60 mL syringe with a solution of 0.1 mg of epinephrine (in 1 mL), 10 mL of contrast and 49 mL of saline. This solution is the aortic valve (AV) closure bolus which will be injected immediately prior to SAAP perfusion to prevent retrograde filling of the left ventricle.
- Prefill another syringe with 15 mL of saline/contrast solution (1:1). This will be used to inflate the catheter balloon.
- Set the peristaltic pump in the SAAP circuit to deliver the perfusate (oxygenated blood) at a rate of 10 mL/kg of the animal’s body weight by manually programming the pump using the “up” and “down” buttons on the pump dial.
- SAAP delivery
- Insert the SAAP catheter into the 14 Fr sheath in the femoral artery to a previously determined length, attach the syringe prefilled with 15 mL of saline contrast solution to the balloon port (Figure 2) and inject the volume of the syringe to inflate the balloon.
- Confirm the balloon placement with fluoroscopy.
- Connect the SAAP perfusion limb to the SAAP catheter and the peripheral perfusion limb to the venous catheter (Figure 3).
- Close the reperfusion limb of the SAAP circuit by applying the clamp to it and open the perfusion limb by taking the clamp off it (Figure 2).
- Attach the previously prefilled 60mL syringe with AV closure bolus to the side port of the three way stopcock at the arterial lumen of the SAAP catheter (Figure 3) and quickly manually inject the entire volume of the syringe, followed by closing off the side port to the syringe.
- Immediately open the end port of the arterial port stopcock.
- Start the Peristaltic pump in the SAAP circuit by pressing the RUN/STOP button.
- After sixty seconds stop the peristaltic pump by pressing the RUN/STOP button.
- Deflate the SAAP balloon by aspirating the entire volume from the the SAAP balloon port.
- Close off the flow to the catheter with stop stopcock at the arterial lumen of the catheter.
- Assess the SBP and ECG rhythm.
NOTE: If after 2 minutes from starting SAAP SBP < 90 mmHg, up to 7 boluses of 200 mL of heparinized shed blood or pre-purchased citrated whole blood can be infused via the SAAP to maintain SBP >90 mmHg.- If stored blood is used for SAAP, co- infusion with calcium gluconate is necessary to prevent citrate calcium binding in the myocardium. Inject calcium gluconate immediately before SAAP perfusion using a syringe attached to the side port of the 3- way stopcock connected to the SAAP Catheter. Use 1 gram of calcium gluconate per packed RBC unit and 3 grams per whole blood unit5.
- If the animal develops ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, attempt defibrillation by placing paddles over the sternum and the apex and, following personnel clearance form contact with the animal.
- Continue ventilation, immediately prior to delivering shocks disconnect the pressure transducers from the signal conditioning units- reconnect these immediately after delivering the shock.
- Deliver a shock using a biphasic defibrillator starting at 150 J, reassess the rhythm for up to one-minute following this. If ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation are present deliver up to two more shocks at 200 J following one minute of rhythm assessment after each shock.
NOTE: The defibrillation algorithm used here is for a biphasic defibrillator, monophasic defibrillators will usually require less energy. If other cardiac rhythms are identified- Atrial Fibrillation, PEA etc. defibrillation should not be attempted, and the animal should be treated according to specific study protocol.
7. Peripheral perfusion
NOTE: Following successful SAAP resuscitation depending on the study protocol, further volume replacement can be continued peripherally using the SAAP circuit.
- Clamp the SAAP perfusion limb of the main perfusion limb.
- Confirm that the peripheral perfusion limb of the SAAP circuit is connected to the sidearm of the catheter in the femoral vein and the stopcocks and tubing are open.
- Assure appropriate resuscitation fluid and volume is in the SAAP reservoir.
- Assure that the recirculation limb of the SAAP circuit is clamped.
- Infuse the fluid according to protocol needs by setting the appropriate flow settings on the peristaltic pump.
8. Euthanasia
- At the end of the experiment, euthanize the animal by injecting >2 mmol/kg of potassium chloride into a central vein and wait for 1 minute of asystole.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Aortic root blood pressure was 83/58 mmHg at baseline and gradually decreased to 0-10 mmHg during the exsanguination. Following onset of pulseless electrical activity (PEA), SAAP was performed, during which, the systolic blood pressure rapidly increased to 120 mmHg for the duration of SAAP (Figure 4). Following cessation of SAAP and aortic balloon deflation BSP dropped to about 60 mmHg however it gradually increased again during the post- SAAP period to baseline levels with a couple of spike...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Adequate perfusate oxygenation is a critical capability of SAAP12. We use a filter that is integrated with a reservoir. The filter is connected to an oxygen cylinder via standard oxygen tubing. The oxygen flow is delivered to the oxygenator at 6 L/min. The centrifugal pump incorporated in the circuit propels the blood, which is filtered through the oxygenator. Adequate oxygenation can be confirmed by performing a blood gas analysis of a sample from the perfusion limb of the circuit. A blood gas sa...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
JJ Morrison is a clinical advisory board member of Prytime Medical Inc. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The views expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the official policy of the Department of Army/Navy/Air Force, Department of Defense, or U.S. Government.
Funding for this study was received by University of Maryland, School of Medicine.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 3/8” ID tubing | Saint-Gobain | E-3603 | This tubing is used throughout the circuit. |
| 1/4" Tubing | Tygon | E-3603 | 2" segment for a connector between Exsanguination tubing and ECMO cannula |
| 2-way stopcocks | Harvard Apparatus | 72-2650 | standard stopcock |
| 3-way | Harvard Apparatus | 72-2658 | Standard stopcock |
| Barbed Connectors | Harvard Apparatus | 72-1587 | Y connectors |
| Barbed Connectors | Harvard Apparatus | 72-1575 | Straight connectors |
| Blood Reservoir | LivaNova | 50715 | This is sold together with the oxygenator |
| Cable ties | Commercial Electric | GT-200ST | Standard cable ties. |
| Centrifugal pump BVP-Z | ISMATEC | ISM 446 | Centrifugal Pump used for recirculation of blood |
| Controlled Peristaltic Dispensing Pump | New Era Pump Systems | NE-9000B | Peristaltic pump for Exsanguination |
| ECMO Cannula | Medtronic | 96570-015 | Exsanguination cannula |
| Gas tubing | AirLife | 1302 | Standard oxygen tubing |
| Oxygen source | AirGas | OX USP300 | Standard oxygen tank with flowmeter |
| Oxygenator | LivaNova | 50715 | This is sold together with the reservoir |
| Peristaltic pump 1 MCP | ISMATEC | ISM 405 | SAAP peristaltic pump |
| SAAP catheter | n/a | n/a | Proprietary catheter designed by Dr. Manning |
| Venous catheter | Teleflex | CDC-29903-1A | 9 French single lumen catheter |
References
- Kauvar, D. S., Lefering, R., Wade, C. E. Impact of Hemorrhage on Trauma Outcome: An Overview of Epidemiology, Clinical Presentations, and Therapeutic Considerations. Journal of Trauma-Injury Infection. 60 (6), 3-11 (2006).
- Manning, J. E., et al. Selective aortic arch perfusion using serial infusions of perflubron emulsion. Academic Emergency Medicine. 4 (9), 883-890 (1997).
- Manning, J. E., et al. Selective aortic arch perfusion during cardiac arrest: a new resuscitation technique. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 21 (9), 1058-1065 (1992).
- Manning, J. E., et al. Selective aortic arch perfusion during cardiac arrest: enhanced resuscitation using oxygenated perflubron emulsion, with and without aortic arch epinephrine. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 29 (5), 580-587 (1997).
- Madurska, M. J., et al. The Cardiac Physiology Underpinning Exsanguination Cardiac Arrest. Shock. , (2020).
- Manning, J. E., et al. Selective aortic arch perfusion with hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier-201 for resuscitation from exsanguinating cardiac arrest in swine. Critical Care Medicine. 29 (11), 2067-2074 (2001).
- Madurska, M. J., Sachse, K. A., Jansen, J. O., Rasmussen, T. E., Morrison, J. J. Fibrinolysis in trauma: a review. European Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery. 44 (1), 35-44 (2018).
- Ontaneda, A., Annich, G. M. Novel Surfaces in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Circuits. Frontiers of Medicine (Lausanne). 5, 321(2018).
- Barnard, E. B. G., et al. A comparison of Selective Aortic Arch Perfusion and Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta for the management of hemorrhage-induced traumatic cardiac arrest: A translational model in large swine. PLoS Medicine. 14 (7), 1002349(2017).
- Hoops, H. E., et al. Selective aortic arch perfusion with fresh whole blood or HBOC-201 reverses hemorrhage-induced traumatic cardiac arrest in a lethal model of noncompressible torso hemorrhage. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 87 (2), 263-273 (2019).
- Manning, J. E., Ross, J. D., McCurdy, S. L., True, N. A. Aortic Hemostasis and Resuscitation: Preliminary Experiments Using Selective Aortic Arch Perfusion With Oxygenated Blood and Intra-aortic Calcium Coadministration in a Model of Hemorrhage-induced Traumatic Cardiac Arrest. Academic Emergency Medicine. 23 (2), 208-212 (2016).
- Frankel, D. A. Z., et al. Physiologic response to hemorrhagic shock depends on rate and means of hemorrhage. Journal of Surgical Research. 143 (2), 276-280 (2007).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved