A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation of Valvular Endothelial Cells
In This Article
Summary
We provide a method for isolating and culturing pure populations of heart valve endothelial cells (VEC). VEC can be isolated from either side of the cusp or leaflet and immediately following, underlying interstitial cell (VIC) isolation is straightforward.
Abstract
Heart valves are solely responsible for maintaining unidirectional blood flow through the cardiovascular system. These thin, fibrous tissues are subjected to significant mechanical stresses as they open and close several billion times over a lifespan. The incredible endurance of these tissues is due to the resident valvular endothelial (VEC) and interstitial cells (VIC) that constantly repair and remodel in response to local mechanical and biological signals. Only recently have we begun to understand the unique behaviors of these cells, for which in vitro experimentation has played a key role. Particularly challenging is the isolation and culture of VEC. Special care must be used from the moment the tissue is removed from the host through final plating. Here we present protocols for direct isolation, side specific isolation, culture, and verification of pure populations of VEC. We use enzymatic digestion followed by a gentle swab scraping technique to dislodge only surface cells. These cells are then collected into a tube and centrifuged into a pellet. The pellet is then resuspended and plated into culture flasks pre-coated with collagen I matrix. VEC phenotype is confirmed by contact inhibited growth and the expression of endothelial specific markers such as PECAM1 (CD31), Von Willebrand Factor (vWF), and negative expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). The functional characteristics of VEC are associated with high levels of acetylated LDL. Unlike vascular endothelial cells, VEC have the unique capacity to transform into mesenchyme, which normally occurs during embryonic valve formation1. This can also occur during significantly prolonged post confluent in vitro culture, so care should be made to passage at or near confluence. After VEC isolation, pure populations of VIC can then be easily acquired.
Protocol
1. Preparation
- Autoclave in a covered instrument tray the following items:
- Serrated tissue forceps - For handling the leaflet tissue
- Tissue scissors (8 cm) - For trimming leaflet tissue and cusps
- Cotton Swabs - For isolating the endothelial layer from the leaflet or cusp
- Make sterile collagenase solution
- Add 4.0 grams of powdered DMEM to 250 mL of 18 MΩ water.
- Add 1.11 grams of sodium bicarbonate.
- Add (600 U/mL) 180,000 units of collagenase.
- Add 1% (3mL) Penicillin/Streptomycin.
- Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.2.
- Bring the solution up to 270 mL.
- Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 μm filter.
- Add 10% (30mL) of sterile fetal bovine serum.
- Make sterile endothelial cell medium
- Add 6.7 grams of powdered DMEM to 400 mL of 18 MΩ water.
- Add 1.85 grams of sodium bicarbonate.
- Add (50 U/mL) 25,000 units of heparin.
- Add 1% (5mL) Penicillin/Streptomycin.
- Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.2.
- Bring the solution up to 450 mL.
- Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 μm filter.
- Add 10% (50mL) of sterile fetal bovine serum.
- Make sterile interstitial cell medium
- Add 13.37 grams of powdered DMEM to 800 mL of 18 MΩ water.
- Add 3.7 grams of sodium bicarbonate.
- Add 1% (10mL) Penicillin/Streptomycin.
- Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.2.
- Bring the solution up to 900 mL.
- Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 μm filter.
- Add 10% (100mL) of sterile bovine serum.
2. Isolation of Heart Valve Leaflets
- Excise the aortic root immediately and aseptically from the heart after sacrifice.
- Thoroughly rinse the aortic root of blood with cold sterile DPBS. It is imperative to remove all blood components as soon as possible to limit VEC death and bacterial contamination. Antibiotics and antimycotics are not advised at this stage since they are potentially harmful to the VEC.
- Isolate valve leaflets (3 per valve) directly from the root and place in a sterile 15 mL conical tube filled with 12 mL cold DPBS. Shake several times to remove debris and refill with fresh DPBS.
- Transport back to the lab on ice.
- Upon arrival at the laboratory, place the container with the tissue under the sterile hood.
3. Isolation of Endothelial Layer
- Fill a sterile 35mm dish with 3mL of cold collagenase solution per valve (3 leaflets).
- Place all three leaflets from the 15 mL tube into the dish filled with the collagenase solution.
- Incubate the tissue for 5-10 minutes at 37°C.
- Gently remove the endothelial layer by rotating a dry sterile swab onto the surface of the leaflet. The direction of rotation and amount of shear applied is critical for the purity of your sample. The rotation of the swab should be in an opposite direction to linear motion of your hand creating a controlled shear. This shear is what lifts the endothelial cells from the tissue. The amount of force applied should be enough to feel the resistance of the tissue but, not penetrate the basement membrane.
- Occasionally, dab the swab within the collagenase solution to dislodge cells from the tip fibers. After swabbing is complete, the texture of the endothelial layer should feel slightly smoother than before.
- Collect the cell suspension/collagenase and transfer to a new sterile 15mL tube.
- Centrifuge the tubes at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes to pellet any isolated cells and aspirate supernatant. If isolating interstitial cells as well, perform that protocol while these cells are being centrifuged.
- Add 3 mL of endothelial porcine medium to the 15 mL tubes, centrifuge a second time, and aspirate media. This second centrifugation helps filter some of the unwanted material such as tip fibers.
- Re-suspend the centrifuged endothelial cells in 5 mL of endothelial porcine medium and plate the cells in a pre-coated T-25 flask with collagen (use 1 flask per centrifuge tube).
- Let the cells grow at least 2-3 days before changing the endothelial medium. This helps the cells recover and divide since the isolation process is fairly harsh and the cell yield may be low. It is critical to passage cells near confluence since contact inhibition could lead to cell transformation.
4. Preparation of 60 mm Culture Dish for Side Specific Isolation
- Line the 60 mm glass petri dishes with aluminum foil (2 glass dishes per leaflet). The aluminum foil helps to remove the paraffin, so that the glass petri dish can be reused for other isolations.
- Place paraffin beads within the dishes, about half full, and cover for autoclaving.
- Once the autoclaving is complete and paraffin is melted, move the dish ensemble to a cool flat surface. As the paraffin cools, it will harden and create a layer that will support needle punctures.
- After 30 minutes, the sterilized dish can then be used as an isolation chamber to immobilize the leaflet tissue.
5. Isolation of Side Specific Endothelial Layer
- Remove the leaflets from the 15mL tubes and place on prepared 60mm culture dish for side specific isolation.
- Manipulate the leaflet so that the ventricularis side is face down on the paraffin surface leaving the fibrosa side exposed. Pin the edges of the leaflet to expose the endothelial layer.
- Place a few drops of cold collagenase on each (upwards-facing) endothelial surface and incubate the tissue for 5-10 minutes at 37°C.
- As before, gently remove the endothelial layer by rotating a dry sterile swab onto the surface of the leaflet. The direction of rotation and amount of shear applied is critical for the purity of your sample. The rotation of the swab should be in an opposite direction to linear motion of your hand creating a controlled shear. This shear is what lifts the endothelial cells from the tissue and nothing else. The amount of force applied should be enough to feel the resistance of the tissue but, does not penetrate within the tissue.
- Occasionally, dab the swab within the collagenase solution to dislodge cells from the tip fibers. After swabbing is complete, the texture of the endothelial layer should feel slightly smoother than before.
- Collect the cell suspension/collagenase and transfer to a new sterile 15mL tube. Indicate side specificity on label (leaflets from the same valve can be pooled together).
- Transfer the leaflets to a new culture dish so that the ventricularis side is now exposed and repeat steps (5.3-5.6).
- Once all cell suspension/collagenase is collected, centrifuge the tubes at 1000 rpm for 5minutes to pellet any isolated cells and aspirate supernatant. If isolating interstitial cells as well, perform that protocol while these cells are being centrifuged.
- Add 3 mL of endothelial porcine medium to the tubes, centrifuge a second time, and aspirate media. This second centrifugation helps filter some of the unwanted material such as tip fibers.
- Re-suspend the centrifuged endothelial cells in 5 mL of endothelial porcine medium and plate the cells in a pre-coated T-25 flask with collage (use 1 flask per centrifuge tube).
- Let the cells grow at least 2-3 days before changing the endothelial medium. This helps the cells recover and divide since the isolation process is fairly harsh. If you notice the yield to be very low, consider moving to a smaller flask or well plate since cell-cell adhesion promotes cell growth. Remember to passage near confluence since contact inhibition could lead to cell transformation.
6. Isolation of Interstitial Cells
- Fill a sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube with 10 mL of collagenase solution per valve (3 leaflets).
- After swabbing the leaflets of endothelial cells, immediately place them in the appropriate 15mL tube with the collagenase solution.
- Incubate for approximately 12 to 18 hours (agitate gently if desired).
- Mix the degraded tissue gently with a serological pipette until cell suspension/collagenase becomes homogenized. This homogenization helps break up the tissue and release the interstitial cells.
- Centrifuge the digested tissue for 5 minutes at 1000 rpm and aspirate the supernatant.
- Add 5 mL interstitial porcine medium to the 15mL tubes, centrifuge a second time, and aspirate supernate.
- Re-suspend the centrifuged endothelial cells in 5 mL of interstitial porcine medium and plate the cells in a T-75 flask (use 1 flask per centrifuge tube).
- Let the cells grow at least 1-2 days before changing the interstitial cell medium. There will be much more tissue debris than with the endothelial cells but, that is expected. The cells should also grow to confluence faster than the endothelial cells because of the cell yield and their nature.
7. Representative Images
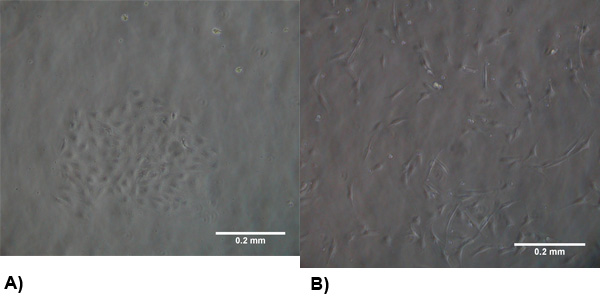
Figure 1. The morphology of isolated cells at 2-3 days post isolation. (A) VEC exhibit a typical endothelial morphology and form clusters to promote growth . (B) VIC morphology is similar to myofibroblasts which are generally spindle shaped and spread evenly throughout the flask.
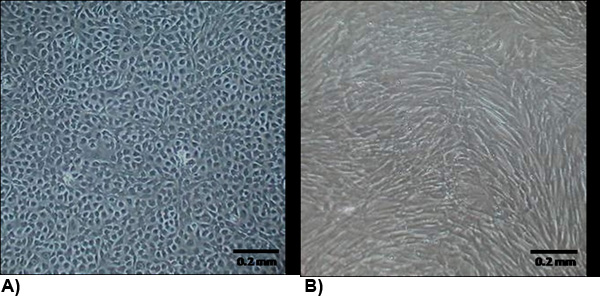
Figure 2. The morphology of isolated cells at confluency. (A) VEC exhibit a typical endothelial morphology which are generally cobblestone and growth contact inhibited. (B) VIC morphology is similar to myofibroblasts which are generally spindle shaped and not growth contact inhibited.
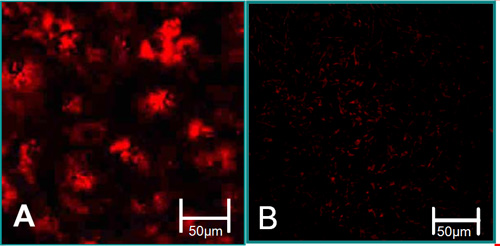
Figure 3. The function characteristics of isolated cells6. (A) VEC are associated with high levels of acetylated LDL uptake (red). (B) VIC are associated with low levels of acetylated LDL uptake.
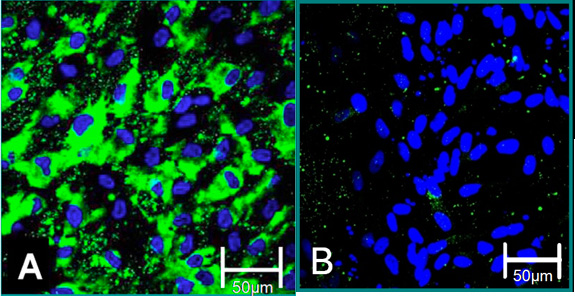
Figure 4. Cellular markers of isolated cells 6. (A) VEC phenotype is contributed to positive staining for Von Willebrand Factor (green), blue (nuclei). (B) VIC phenotype is contributed to negative staining for Von Willebrand Factor.
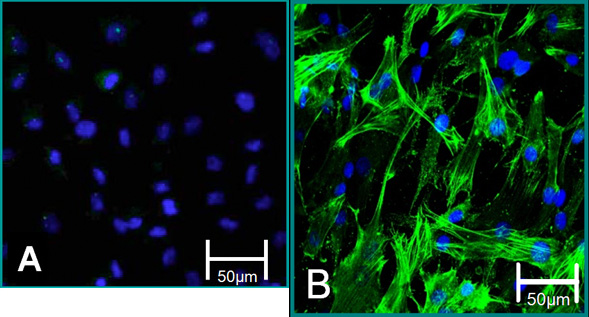
Figure 5. Cellular markers of isolated cells. (A) VEC phenotype is contributed to negative staining for alpha SMA (green), blue (nuclei). (B) VIC phenotype is contributed to positive staining for alpha SMA.
| Dissociation Agent | Dissociation Technique | Cell Collection | Cell Quantity | Cell Purity | Contamination |
| EDTA (3mM) without CaCl2 | 5, 20, 60 min. before CaCl2 addition | 20, 60, 120 min. before collection | - | +/- | +++ |
| EDTA (6mM) without CaCl2 | 5, 20, 60 min. before CaCl2 addition | 20, 60, 120 min. before collection | +/- | + | +++ |
| Trypsin-EDTA (0.5 g/L) | 5, 10, 15 min. before deactivation | Medium collected immediately | + | + | ++ |
| Collagenase II (300 U/ mL) | 5, 10, 15 min. before deactivation | Medium collected immediately | -, +, ++ | -, ++, + | + |
| Collagenase II (600 U/ mL) | 5, 10, 15 min. before deactivation | Medium collected immediately | +, ++, + ++ | ++, ++, - | - |
Table 1. Results of preliminary valvular endothelial cell isolation protocols.
Discussion
An understanding of valvular biology has been impaired by technical difficulties isolating and culturing pure populations of valvular endothelial cells. Typical isolation techniques involve enzymatic digestion of the underlying basal matrix or chemical dissociation of endothelial adhesive bonds2,3. Preliminary isolation experiments were qualitatively assessed by varying dissociation agents and incubation periods. The results of these experiments showed that EDTA (or Trypsin-EDTA) incubation for up to 60 min...
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the NSF CAREER award, the Hartwell Foundation, and the American Heart Association (#0830384N).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium | Mediatech, Inc. | 50-103-PB | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | 26140 | |
| Penicillin Streptomycin | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | 15140-122 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | 25200 | |
| Heparin Sodium Salt | Sigma-Aldrich | H4784-1G | |
| Collagenase Type 2 | Worthington Biochemical | LS004176 | |
| DPBS | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | 21300-058 | |
| Rat Tail Collagen | BD Biosciences | 354236 | |
| Critical Swabs | VWR international | 89031-270 | |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Sigma-Aldrich | 55761 | |
| T25 Flasks | BD Biosciences | 353018 | |
| T75 Flasks | BD Biosciences | 353136 | |
| 24 Well Plate | Falcon BD | 353047 | |
| 60x15 mm Dishes | VWR international | 25384-092 | |
| 60x15 Glass Dishes | VWR international | 89000-310 | |
| Paraffin Embedding Wax | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 19304-01 | |
| Precision Glide Needles | BD Biosciences | 305165 | |
| 500 mL Nalgene Filters | VWR international | 73520-985 | |
| 1L Nalgene Filters | VWR international | 73520-986 | |
| Tissue Forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11023-15 | |
| FSC Tweezers #5 | Fine Science Tools | 11295-00 |
References
- Thompson, R. P., Fitzharris, T. P. Morphogenesis of the truncus arteriosus of the chick embryo heart: the formation and migration of mesenchymal tissue. Am J Anat. 154, 545-556 (1979).
- Johnson, C. M., Fass, D. N. Porcine cardiac valvular endothelial cells in culture: A relative deficiency of fibronectin synthesis in vitro. Lab Invest. 49 (5), 589-598 (1983).
- Manduteanu, I., Popov, D., Radu, A., Simionescu, M. Calf cardiac valvular endothelial cells in culture: production of glycosaminoglycans, prostacyclin and fibronectin. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 20 (2), 103-118 (1988).
- Cheunyg, W. Techniques for isolating and purifying porcine aortic valve endothelial cells. JHVD. 17 (6), 674-681 (2008).
- Paranya, G., Vineberg, S., Dvorin, E., Kaushal, S., Roth, S. J., Rabkin, E., Schoen, F. J., Bischoff, J. Aortic valve endothelial cells undergo transforming growth factor-beta-mediated and non-transforming growth factor-beta-mediated transdifferentiation in vitro. Am J Pathol. 159 (4), 1335-1343 (2001).
- Butcher, J. T., Penrod, A., Garcia, A. J. M., Nerem, R. M. Unique morphology and focal adhesion development of valvular endothelial cells in static and fluid flow environments. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Bio. 24 (1), 1429-1434 (2004).
- Simmons, C. A., Grant, G. R., Manduchi, E., Davies, P. F. Spatial heterogeneity of endothelial phenotypes correlates with side-specific vulnerability to calcification in normal porcine aortic valves. Circ Res. 96, 792-799 (2005).
- Butcher, J. T., Tressel, S., Johnson, T., Turner, D., Sorescu, G., Jo, H., Nerem, R. M. Transcriptional Profiles of Valvular and Vascular Endothelial Cells Reveal Phenotypic Differences: Influence of Shear Stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26, 69-69 (2006).
- Parachuri, S., Yang, J. H., Aikawa, E., Melero-Martin, J. M., Khan, Z. A., Loukogeorgakis, S., Schoen, F. J., Bischoff, J. Human Pulmonary Valve Progenitor Cells Exhibit Endothelial/Mesenchymal Plasticity in Response to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A and Transforming Growth Factor-β2. Circ Res. 99 (8), 861-869 (2006).
- Shi, Q. Evidence for circulating bone marrow-derived endothelial cells. Blood. 92, 362-367 (1998).
- Rehman, J., Li, J., Orschell, C. M., March, K. L. Peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells are derived from monocyte/macrophages and secrete angiogenic growth factors. Circulation. 107, 1164-1169 (2003).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved