A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Achieving Moderate Pressures in Sealed Vessels Using Dry Ice As a Solid CO2 Source
In This Article
Summary
Here we present a protocol for performing reactions in simple reaction vessels under low-to-moderate pressures of CO2. The reactions can be performed in a variety of vessels simply by administering the carbon dioxide in the form of dry ice, without the need for costly or elaborate equipment or set-ups.
Abstract
Herein is presented a general strategy to perform reactions under mild to moderate CO2 pressures with dry ice. This technique obviates the need for specialized equipment to achieve modest pressures, and can even be used to achieve higher pressures in more specialized equipment and sturdier reaction vessels. At the end of the reaction, the vials can be easily depressurized by opening at room temperature. In the present example CO2 serves as both a putative directing group as well as a way to passivate amine substrates, thereby preventing oxidation during the organometallic reaction. In addition to being easily added, the directing group is also removed under vacuum, obviating the need for extensive purification to remove the directing group. This strategy allows the facile γ-C(sp3)-H arylation of aliphatic amines and has the potential to be applied to a variety of other amine-based reactions.
Introduction
The use of gaseous compounds in chemical reactions typically requires specialized equipment and procedures1,2. At bench scale, some gases can be added directly from a tank using a high pressure regulator3. An alternative method is to condense the gas under cryogenic conditions4,5. Although useful, these strategies require the use of specialized pressure reactors with valves, which can be cost prohibitive for running numerous reactions in parallel. This can therefore greatly slow the rate at which reaction screening can proceed. As a result, chemists have found it desirable to introduce these compounds using alternative methods. Ammonia can be added to reactions using different ammonium carboxylate salts, taking advantage of the weak equilibrium between these salts and free ammonia6. Transfer hydrogenation is an important strategy for reduction reactions of olefins, carbonyl, and nitro groups that circumvents the use of flammable hydrogen gas with compounds such as ammonium formate or hydrazine as carriers of H27. Another gas of interest in this area is carbon monoxide8 – CO can be generated in situ by liberation from metal carbonyl complexes9,10, or alternatively it can be generated by decarbonylation from sources such as formates and formamides11,12,13 or chloroform14,15.
One gas which has not enjoyed significant development in this respect is carbon dioxide16. One reason for this is that many transformations that involve CO2 also require high temperatures and pressures, and thus are automatically relegated to specialized reactors17,18. Recent efforts to develop more reactive catalysts, however, have facilitated running many of these reactions under atmospheric pressures of CO219,20,21,22. We recently discovered a reaction in which carbon dioxide could be used to mediate the γ-C(sp3)–H arylation of aliphatic amines23. This strategy was expected to combine the benefits of a static directing group approach including amide24,25,26,27,28, sulfonamide29,30,31,32, thiocarbonyl33,34, or hydrazone35-based directing groups (chemical robusticity), with the ease of a transient directing group (decreased step economy)36,37,38,39.
Although the reaction could occur under atmospheric pressure of CO2, the need for a Schlenk set-up to screen reactions proved prohibitively slow. Furthermore, increasing the pressure slightly led to improved reaction yields, but could not be easily achieved using a Schlenk line. We therefore sought an alternative strategy, and subsequently identified that dry ice could be easily used as a solid source of CO2 that could be added to a variety of reaction vessels to introduce the necessary amount of carbon dioxide to achieve moderate pressures (Figure 1). Though underutilized in synthesis, a similar strategy is fairly common as a method to generate liquid CO2 for chromatography and extraction applications40,41,42,43,44. Utilizing this strategy allowed our group to rapidly screen large numbers of reactions in parallel, while the ability to access moderate CO2 pressures of between 2-20 atmospheres were critical to improving the yields of the reactions. Under these conditions, both primary (1°) and secondary (2°) amines can be arylated with electron rich and electron poor aryl halides.
Protocol
CAUTION: 1) The following protocols have been deemed safe through repeated trials. However, caution should be exercised when sealing vials, throughout the reaction, and especially when opening the reactions, as inhomogeneity in the reaction vials may lead to equipment failure. Vials should be inspected for physical defects prior to use. Vials should be placed behind some form of blast shield or hood sash immediately after sealing to prevent incidents should the vials fail. 2) Although there is little chance for asphyxiation due to the small quantities of CO2 used, reactions should be set-up as well as opened in a well-ventilated area or in a fume hood. 3) Dry ice is a cryogen and can cause serious tissue damage. Care should therefore be exercised while manipulating it to avoid frostbite, such as limiting direct contact or using cryogenic gloves. 4) Dry ice will condense water vapor, meaning that prior to use, the dry ice should be mechanically exfoliated to ensure the mass is of CO2(s) only. This can be achieved by simply rubbing the dry ice between one’s fingers, or more safely, rubbing it between one’s fingers with a protective layer such as a glove or towel.
1. Reaction in a 7.5 mL Vial (Air Not Excluded)
- Add a stir bar to a dry 7.5 mL vial.
- Add palladium acetate (6.7 mg, 0.03 mmol) to the vial.
- Add silver trifluoroacetate (99.9 mg, 0.45 mmol) to the vial.
- Add phenyl iodide (92.3 mg, 0.45 mmol) to the vial.
- Add tert-amyl amine (26.3 mg, 0.30 mmol) to the vial.
- Add acetic acid (1.0 mL) to the vial.
Note: The ratio of solution volume to vial size is important, as the immediate sublimation of CO2 upon addition of dry ice can mechanically displace solvent if too much is used relative to the size of the reaction vessel. - Add deionized water (21.7 μL, 12.1 mmol) to the vial.
- Weigh dry ice (26.3 mg, 0.60 mmol), and immediately add the dry ice to the vial, while ensuring to also immediately seal the vial with a PTFE-lined cap.
Note: The whole operation should be performed within approximately 5 seconds to prevent sublimation and escape of the small amount of CO2 added (this is slowed by the formation of frozen acetic acid around the dry ice). The amount of CO2 added will be an approximate value, and in our hands a deviation of a few mg is permissible. - Stir the sealed reaction vial for 15 minutes at room temperature.
- Transfer the reaction vessel to a pre-heated plate at 110 °C and stir for 14 hours before allowing to cool.
- Upon cooling, carefully open the vial to vent CO2.
- Remove all of the volatiles in vacuo.
Note: This operation can be performed in the vial, or the solution can be transferred to a larger round bottom flask. - Add 1.2 M HCl(aq) (6 mL) to the reaction mixture and stir open to air for 15 minutes.
- Transfer the aqueous fraction to a separatory funnel, washing with additional 1.2 M HCl (4 mL), and extract with a 1:1 diethyl ether/hexanes mixture (3 x 8 mL).
Note: This organic wash contains excess phenyl iodide and other neutral by-products, and can be disposed of. - Neutralize and make basic the aqueous solution by addition of saturated NH4OH(aq) (10 mL is a good starting point).
- Extract the aqueous layer with dichloromethane (2 x 10 mL).
- Dry the combined organic fractions over Na2SO4, then filter into a tared sample vial.
- Evaporate the solvent in vacuo, giving the product (2-Methyl-4-phenyl-butanamine) as a yellow oil.
2. Reaction in a 7.5 mL Vial (Purging Conditions – Air Excluded)
- Add a stir bar to a dry 7.5 mL vial.
- Add palladium acetate (6.7 mg, 0.03 mmol) to the vial.
- Add silver trifluoroacetate (99.9 mg, 0.45 mmol) to the vial.
- Add phenyl iodide (92.3 mg, 0.45 mmol) to the vial.
- Add tert-amyl amine (26.3 mg, 0.30 mmol) to the vial.
- Add acetic acid (1.0 mL) to the vial.
Note: The ratio of solution volume to vial size is important, as the immediate sublimation of CO2 upon addition of dry ice can mechanically displace solvent if too much is used relative to the size of the reaction vessel. - Add deionized water (21.7 μL, 12.1 mmol) to the vial.
- Tare the vial on a balance, add approximately 98 mg of dry ice, and then allow the CO2 to sublimate off until a final mass of approximately 26 mg is achieved, followed by immediately sealing the vial with a PTFE-lined cap.
Note: If desirable, this step can be performed with a greater mass of dry ice to further exclude air from the vial. It is noteworthy that this may introduce water, and thus may not be the most effective strategy for water sensitive reactions. - Stir the sealed reaction vial for 15 minutes at room temperature.
- Transfer the reaction vessel to a pre-heated plate at 110 °C and stir for 14 hours before allowing to cool.
- Upon cooling, carefully open the vial to vent CO2.
- Remove all of the volatiles in vacuo.
Note: This operation can be performed in the vial, or the solution can be transferred to a larger round bottom flask. - Add 1.2 M HCl(aq) (6 mL) to the reaction mixture, and stir open to air for 15 minutes.
- Transfer the aqueous fraction to a separatory funnel, washing with additional 1.2 M HCl (4 mL), and extract with a 1:1 diethyl ether/hexanes mixture (3 x 8 mL).
Note: This organic wash contains excess phenyl iodide and other neutral by-products, and can be disposed of. - Neutralize and make basic the aqueous solution by addition of saturated NH4OH(aq) (10 mL is a good starting point).
- Extract the aqueous layer with dichloromethane (2 x 10 mL).
- Dry the combined organic fractions over Na2SO4, then filter into a tared sample vial.
- Evaporate the solvent in vacuo, giving the product (2-Methyl-4-phenyl-butanamine) as a yellow oil.
3. Reaction in a 40 mL Vial (Air Not Excluded)
- Add a stir bar to a dry 40 mL vial.
- Add palladium acetate (33.5 mg, 0.15 mmol) to the vial.
- Add silver trifluoroacetate (499.5 mg, 2.25 mmol) to the vial.
- Add phenyl iodide (461.5 mg, 2.25 mmol) to the vial.
- Add tert-amyl amine (131.5 mg, 1.5 mmol) to the vial.
- Add acetic acid (5.0 mL) to the vial.
Note: The ratio of solution volume to vial size is important, as the immediate sublimation of CO2 upon addition of dry ice can mechanically displace solvent if too much is used relative to the size of the reaction vessel. - Add deionized water (108.5 μL, 6.02 mmol) to the vial.
- Weigh dry ice (131.5 mg, 3.0 mmol), and immediately add the dry ice to the vial, while ensuring to also immediately seal the vial with a PTFE-lined cap.
Note: The whole operation should be performed within approximately 5 seconds to prevent sublimation and escape of the small amount of CO2 added (this is slowed by the formation of frozen acetic acid around the dry ice). The amount of CO2 added will be an approximate value, and in our hands a deviation of a few mg is permissible. - Stir the sealed reaction vial for 15 minutes at room temperature.
- Transfer the reaction vessel to a pre-heated plate at 110 °C and stir for 14 hours before allowing to cool.
- Upon cooling, carefully open the vial to vent CO2.
- Remove all of the volatiles in vacuo.
Note: This operation can be performed in the vial, or the solution can be transferred to a larger round bottom flask. - Add 1.2 M HCl(aq) (30 mL) to the reaction mixture and stir open to air for 15 minutes.
- Transfer the aqueous fraction to a separatory funnel, washing with additional 1.2 M HCl (20 mL), and extract with a 1:1 diethyl ether/hexanes mixture (3 x 8 mL).
Note: This organic wash contains excess phenyl iodide and other neutral by-products, and can be disposed of. - Neutralize and make basic the aqueous solution by addition of saturated NH4OH(aq) (10 mL is a good starting point).
- Extract the aqueous layer with dichloromethane (2 x 20 mL).
- Dry the combined organic fractions over Na2SO4, then filter into a tared sample vial.
- Evaporate the solvent in vacuo, giving the product (2-Methyl-4-phenyl-butanamine) as a yellow oil.
4. Reaction in a 35 mL Pressure Tube (Air not excluded)
- Add a stir bar to a dry 35 mL pressure tube.
- Add palladium acetate (6.7 mg, 0.03 mmol) to the pressure tube.
- Add silver trifluoroacetate (132.5 mg, 0.6 mmol) to the pressure tube.
- Add phenyl iodide (183.6 mg, 0.9 mmol) to the pressure tube.
- Add 2-methyl-N-(3-methylbenzyl)butan-2-amine (57.4 mg, 0.3 mmol) to the pressure tube.
- Add acetic acid (1.0 mL) to the vial, followed by 1,1,1,3,3,3,-hexafluoroisopropanol (1.0 mL).
Note: The ratio of solution volume to vial size is important, as the immediate sublimation of CO2 upon addition of dry ice can mechanically displace solvent if too much is used relative to the size of the reaction vessel. - Add deionized water (21.7 μL, 1.2 mmol) to the pressure tube.
- Weigh dry ice (1.32 g, 30 mmol), and immediately add the dry ice to the pressure tube, while ensuring to also immediately seal the pressure tube with the appropriate Teflon screw cap.
Note: The whole operation should be performed within approximately 5 seconds to prevent sublimation and escape of the small amount of CO2 added (this is slowed by the formation of frozen acetic acid around the dry ice). The amount of CO2 added will be an approximate value, and in our hands a deviation of a few mg is permissible. - Stir the sealed reaction vessel for 15 minutes at room temperature.
- Transfer the reaction vessel to a pre-heated plate at 90 °C and stir for 24 hours before allowing to cool.
- Upon cooling, put a towel or padded glove over the cap, and carefully open the pressure tube to vent CO2.
- Remove all of the volatiles in vacuo.
Note: This operation can be performed in the pressure tube with an appropriate adaptor, or the solution can be transferred to a larger round bottom flask. - Add 1.2 M HCl(aq) (12 mL) to the reaction mixture and stir open to air for 15 minutes.
- Transfer the aqueous fraction to a separatory funnel, washing with additional 1.2 M HCl (8 mL), and extract with a 1:1 diethyl ether/hexanes mixture (3 x 8 mL).
Note: This organic wash contains excess phenyl iodide and other neutral by-products and can be disposed of. - Neutralize and make basic the aqueous solution by addition of saturated NH4OH(aq) (10 mL is a good starting point).
- Extract the aqueous layer with dichloromethane (2 x 10 mL).
- Dry the combined organic fractions over Na2SO4, then filter into a tared sample vial.
- Evaporate the solvent in vacuo, giving the product (2-Methyl-N-(3-methylbenzyl)-4-phenylbutan-2-amine) as a yellow oil.
Results
Following these protocols, it is possible to charge a reaction vial with an appropriate amount of carbon dioxide to achieve chemical reactions that require CO2 atmospheres. The pressure achieved in Step 1 is calculated to be approximately 3 atmospheres (see discussion for determination of this value), although due to partial solvation, the observed pressure is in the vicinity of 2 atmospheres at room temperature, and should be approximately 2.6 atmospheres under the reaction co...
Discussion
Using the van der Waals Equation of State, the approximate pressure of these systems can be calculated45
Eq. 1: 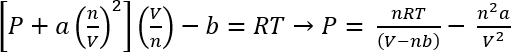
Under the conditions in Protocol 1, we can assume 26.3 mg of CO2 gives n =5.98 x 10-4 mols
Disclosures
The use of CO2 as a directing group for C-H activation of Lewis basic substrates is currently the focus of United States Provisional Patent #62/608,074.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge start-up funding from The University of Toledo, as well as funds from the American Chemical Society's Herman Frasch Foundation in partial support of this work. Mr. Thomas Kina is acknowledged for his assistance with developing a suitable pressure gauge for measuring the reaction pressures. Mr. Steve Modar is thanked for useful discussions.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 7.5 mL Sample Vial with Screw Cap (Thermoset) | Qorpak | GLC-00984 | Can be reused. |
| 40 mL Sample Vial with Screw Cap (Thermoset) | Qorpak | GLC-01039 | Can be reused. |
| Pressure Tube, #15 Thread, 7" Long, 25.4 mm O.D. | Ace Glass | 8648-06 | Can be reused. |
| Pie-Block for 2 Dram Vials | ChemGlass | CG-1991-P14 | Can be reused. |
| Pie-Block for 10 Dram Vials | ChemGlass | CG-1991-P12 | Can be reused. |
| 3.2 mm PTFE Disposable Stir Bars | Fisher | 14-513-93 | Can be reused. |
| C-MAG HS 7 Control Hotplate | IKA | 20002695 | |
| Analytical Weighing Balance | Sartorius | QUINTIX2241S | |
| Double-Ended Micro-Tapered Spatula | Fisher Scientific | 21-401-10 | |
| Hei-VAP Advantage - Hand Lift Model with G5 Dry Ice Condenser Rotary Evaporator | Heidolph | 561-01500-00 | |
| Bump Trap 14/20 Joint | ChemGlass | CG-1322-01 | |
| tert-Amyl amine | Alfa Aesar | B24639-14 | Used as received. |
| 2-Methyl-N-(3-methylbenzyl)butan-2-amine | N/A | N/A | Prepared from reductive amination of tert-amyl amine and 3-tolualdehyde in the presence of sodium borohydride in methanol. |
| Palladium Acetate | Chem-Impex International, Inc. | 4898 | Used as received. |
| Silver Trifluoroacetate | Oakwood Chemicals | 007271 | Used as received. |
| Phenyl Iodide | Oakwood Chemicals | 003461 | Used as received. |
| Acetic Acid | Fisher Chemical | A38 | Used as received. |
| 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoroisopropanol | Oakwood Chemicals | 003409 | Used as received. |
| Deionized Water | Obtained from in-house deionized water system. | ||
| Dry Ice | Carbonic Enterprises Dry Ice Inc. | Non-food grade dry ice. | |
| Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid | Fisher Chemical | A144SI | Diluted to a 1.2 M solution prior to use. |
| Diethyl Ether, Certified | Fisher Chemical | E138 | Used as received. |
| Hexanes, Certified ACS | Fisher Chemical | H292 | Used as received. |
| Saturated Ammonium Hydroxide | Fisher Chemical | A669 | Used as received. |
| Dichloromethane | Fisher Chemical | D37 | Used as received. |
| Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous | Oakwood Chemicals | 044702 | Used as received. |
| 250 mL Separatory Funnel | Prepared in-house by staff glassblower. | ||
| 100 mL Round Bottom Flask | Prepared in-house by staff glassblower. | ||
| Scientific Disposable Funnel | Caplugs | 2085136030 | |
| Borosilicate Glass Scintillation Vials, 20 mL | Fisher Scientific | 03-337-15 | |
| 5 mm O.D. Thin Walled Precision NMR Tubes | Wilmad | 666000575 | |
| Chloroform-d | Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. | DLM-7 | Used as received. |
References
- Verboom, W. Selected Examples of High-Pressure Reactions in Glass Microreactors. Chemical Engineering and Technology. 32 (11), 1695-1701 (2009).
- Schettino, V., Bini, R. Constraining Molecules at the Closest Approach: Chemistry at High Pressure. Chemical Society Reviews. 36, 869-880 (2007).
- Hemminger, O., Marteel, A., Mason, M. R., Davies, J. A., Tadd, A. R., Abraham, M. A. Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Using a Heterogeneous Rhodium Catalyst. 3. Evaluation of Solvent Effects. Green Chemistry. 4, 507-512 (2002).
- Mo, F., Dong, G. Regioselective Ketone α-Alkylation with Simple Olefins via Dual Activation. Science. 345 (6192), 68-72 (2014).
- Schultz, A. G., Kirincich, S. J., Rahm, R. Asymmetric Organic Synthesis. Preparation and Birch Reduction-Alkylation of 2-Methyl-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1-ones. Tetrahedron Letters. 36 (26), 4551-4554 (1995).
- Dong, L., Aleem, S., Fink, C. A. Microwave-Accelerated Reductive Amination Between Ketones and Ammonium Acetate. Tetrahedron Letters. 51 (39), 5210-5212 (2010).
- Wang, D., Astruc, D. The Golden Age of Transfer Hydrogenation. Chemical Reviews. 115 (13), 6621-6686 (2015).
- Morimoto, T., Kakiuchi, K. Evolution of Carbonylation Catalysis: No Need for Carbon Monoxide. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 43 (42), 5580-5588 (2004).
- Iranpoor, N., Firouzabadi, H., Motevalli, S., Talebi, M. Palladium-Free Aminocarbonylation of Aryl, Benzyl, and Styryl Iodides and Bromides by Amines Using Mo(CO)6 and Norbornadiene. Tetrahedron. 69 (1), 418-426 (2013).
- Ren, W., Yamane, M. Mo(CO)6-Mediated Carbamoylation of Aryl Halides. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 75 (24), 8410-8415 (2010).
- Wang, H., Dong, B., Wang, Y., Li, J., Shi, Y. A Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Hydroesterification of Alkenylphenols to Lactones with Phenyl Formate as CO Source. Organic Letters. 16 (1), 186-189 (2014).
- Zhang, Y., Chen, J. -. L., Chen, Z. -. B., Zhu, Y. -. M., Ji, S. -. J. Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Annulation Reactions Using Aryl Formate as a CO Source: Synthesis of 2-Substituted Indene-1,3(2H)-Dione Derivatives. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 80 (21), 10643-10650 (2015).
- Wan, Y., Alterman, M., Larhed, M., Hallberg, A. Dimethylformamide as a Carbon Monoxide Source in Fast Palladium-Catalyzed Aminocarbonylations of Aryl Bromides. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 67 (17), 6232-6235 (2002).
- Gockel, S. N., Hull, K. L. Chloroform as a Carbon Monoxide Precursor: In or Ex Situ Generation of CO for Pd-Catalyzed Aminocarbonylations. Organic Letters. 17 (13), 3236-3239 (2015).
- Zhao, H., Du, H., Yuan, X., Wang, T., Han, W. Iron-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Aryl Halides with Arylborons Using Stoichiometric Chloroform as the Carbon Monoxide Source. Green Chemistry. 18, 5782-5787 (2016).
- Chen, P., Xu, C., Yin, H., Gao, X., Qu, L. Shock Induced Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Few Layer Graphene. Carbon. , 471-476 (2017).
- Iijima, T., Yamaguchi, T. Efficient Regioselective Carboxylation of Phenol to Salicylic Acid with Supercritical CO2 in the Presence of Alumnium Bromide. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 295 (1-2), 52-56 (2008).
- Jevtovikj, I., Manzini, S., Hanauer, M., Rominger, F., Schaub, T. Investigations on the Catalytic Carboxylation of Olefins with CO2 Towards α, β-Unsaturated Carboxylic Acid Salts: Characterization of Intermediates and Ligands as well as Substrate Effects. Dalton Transactions. 44, 11083-11094 (2015).
- Juliá-Hernández, F., Moragas, T., Cornella, J., Martin, R. Remote Carboxylation of Halogenated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons with Carbon Dioxide. Nature. 545, 84-88 (2017).
- North, M., Pasquale, R. Mechanism of Cyclic Carbonate Synthesis from Epoxides and CO2. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (16), 2946-2948 (2009).
- Yeung, C. S., Dong, V. M. Beyond Aresta's Complex: Ni- and Pd-Catalyzed Organozinc Coupling to CO2. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (25), 7826-7827 (2008).
- Zhu, D. -. Y., Fang, L., Han, H., Wang, Y., Xia, J. -. B. Reductive CO2 Fixation via Tandem C-C and C-N Bond Formation: Synthesis of Spiro-Indopyrrolidines. Organic Letters. 19 (16), 4259-4262 (2017).
- Kapoor, M., Liu, D., Young, M. C. Carbon Dioxide Mediated C(sp3)–H Arylation of Amine Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , (2018).
- Zhang, Y. -. F., Zhao, H. -. W., Wang, H., Wei, J. -. B., Shi, Z. -. J. Readily Removable Directing Group Assisted Chemo- and Regioselective C(sp3)-H Activation by Palladium Catalysis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 54 (46), 13686-13690 (2015).
- He, G., Chen, G. A Practical Strategy for the Structural Diversification of Aliphatic Scaffolds Through the Palladium-Catalyzed Picolinamide-Directed Remote Functionalization of Unactivated C(sp3)-H Bonds. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 50 (22), 5192-5196 (2011).
- Nack, W. A., Wang, X., Wang, B., He, G., Cheng, G. Palladium-Catalyzed Picolinamide-Directed Iodination of Remote ortho-C-H Bonds of Arenes: Synthesis of Tetrahydroquinolines. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. 12, 1243-1249 (2016).
- Feng, P., Li, M., Ge, H. Room Temperature Palladium-Catalyzed Decarboxylative ortho-Acylation of Acetanilides with α-Oxocarboxylic Acids. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (34), 11898-11899 (2010).
- Coomber, C. E., Benhamou, L., Bučar, D. -. K., Smith, P. D., Porter, M. J., Sheppard, T. D. Silver-Free Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp3)-H Arylation of Saturated Bicyclic Amine Scaffolds. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 83 (5), 2495-2503 (2018).
- Mei, T. -. S., Wang, X., Yu, J. -. Q. Pd(II)-Catalyzed Amination of C-H Bonds Using Single-Electron or Two-Electron Oxidants. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (31), 10806-10807 (2009).
- Xie, W., Yang, J., Wang, B., Li, B. Regioselective Ortho Olefination of Aryl Sulfonamide via Rhodium-Catalyzed Direct C-H Bond Activation. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 79 (17), 8278-8287 (2014).
- Rodriguez, N., Romero-Revilla, J. A., Fernández-Ibáñez, M. &. #. 1. 9. 3. ;., Carretero, J. C. Palladium-Catalyzed N-(2-pyridyl)sulfonyl-Directed C(sp3)-H γ-Arylation of Amino Acid Derivatives. Chemical Science. 4, 175-179 (2013).
- Zheng, Y., Song, W., Zhu, Y., Wei, B., Xuan, L. Pd-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of γ-C(sp3)-H Bonds of Amines Directed by a Removable Bts-Protecting Group. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 83 (4), 2448-2454 (2018).
- Jain, P., Verma, P., Xia, G., Yu, J. -. Q. Enantioselective Amine α-Functionalization Via Palladium-Catalysed C-H Arylation of Thioamides. Nature Chemistry. 9, 140-144 (2017).
- Tran, A. T. Practical Alkoxythiocarbonyl Auxiliaries for Ir(I)-Catalyzed C-H Alkylation of Azacycles. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (35), 10530-10534 (2017).
- Huang, Z., Wang, C., Dong, G. A Hydrazone-Based exo-Directing Group Strategy for β-C-H Oxidation of Aliphatic Amines. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (17), 5299-5303 (2016).
- Xu, Y., Young, M. C., Wang, C., Magness, D. M., Dong, G. Catalytic C(sp3)-H Arylation of Free Primary Amines via an in situ Generated Exo-Directing Group. Chemie International Edition. 55 (31), 9084-9087 (2016).
- Liu, Y., Ge, H. Site-Selective C-H Arylation of Primary Aliphatic Amines Enabled by a Catalytic Transient Directing Group. Nature Chemistry. 9, 26-32 (2017).
- Wu, Y., Chen, Y. -. Q., Liu, T., Eastgate, M. D., Yu, J. -. Q. Pd-Catalyzed γ-C(sp3)-H Arylation of Free Amines Using a Transient Directing Group. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 138 (44), 14554-14557 (2016).
- Yada, A., Liao, W., Sato, Y., Murakami, M. Buttressing Salicylaldehydes: A Multipurpose Directing Group for C(sp3)-H Bond Activation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (4), 1073-1076 (2017).
- Baldwin, B. W., Kuntzleman, T. S. Liquid CO2 in Centrifuge Tubes: Separation of Chamazulene from Blue Tansy (Tanacetum annum) Oil via Extraction and Thin-Layer Chromatography. Journal of Chemical Education. 95 (4), 620-624 (2018).
- McKenzie, L. C., Thompson, J. E., Sullivan, R., Hutchison, J. E. Green Chemical Processing in the Teaching Laboratory: A Convenient Liquid CO2 Extraction of Natural Products. Green Chemistry. 6, 355-358 (2004).
- Hudson, R., Ackerman, H. M., Gallo, L. K., Gwinner, A. S., Krauss, A., Sears, J. D., Bishop, A., Esdale, K. N., Katz, J. L. CO2 Dry Cleaning: A Benign Solvent Demonstration Accessible to K-8 Audiences. Journal of Chemical Education. 94, 480-482 (2017).
- Barcena, H., Chen, P. An Anesthetic Drug Demonstration and an Introductory Antioxidant Activity Experiment with "Eugene, the Sleepy Fish.". Journal of Chemical Education. 93, 202-205 (2016).
- Bodsgard, B. R., Lien, N. R., Waulters, Q. T. Liquid CO2 Extraction and NMR Characterization of Anethole from Fennel Seed: A General Chemistry Laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education. 93, 397-400 (2016).
- Fishbane, P. M., Gasiorowicz, S. G., Thornton, S. T. . Physics for Scientists and Engineers. , (2005).
- Rumpf, B., Xia, J., Maurer, G. Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in Aqueous Solutions Containing Acetic Acid or Sodium Hydroxide in the Temperature Range from 313 to 433 K and at Total Pressures up to 10 MPa. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 37, 2012-2019 (1998).
- Luo, J., Larrosa, I. C-H Carboxylation of Aromatic Compounds Through CO2 Fixation. ChemSusChem: Chemistry & Sustainability, Energy & Materials. 10, 3317-3332 (2017).
- Manjolinho, F., Arndt, M., Gooßen, K., Gooßen, L. J. Catalytic C-H Carboxylation of Terminal Alkynes with Carbon Dioxide. ACS Catalysis. 2, 2014-2021 (2012).
- Banerjee, A., Dick., G. R., Yoshino, T., Kanan, M. W. Carbon Dioxide Utilization via Carbonate-Promoted C-H Carboxylation. Nature. 531, 215-219 (2016).
- Fei, H., Sampson, M. D., Lee, Y., Kubiak, C. P., Cohen, S. M. Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Formate Using a Mn(I) Molecular Catalyst in a Robust Metal-Organic Framework. Inorganic Chemistry. 54, 6821-6828 (2015).
- Chabolla, S. A., Yang, J. Y. For CO2 Reduction, Hydrogen-Bond Donors Do the Trick. ACS Central Science. 4, 315-317 (2018).
- Kim, D., Kley, C. S., Li, Y., Yang, P. Copper Nanoparticle Ensembles for Selective Electroreduction of CO2 to C2-C3 Products. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. , C2-C3 (2017).
- Liu, Q., Wu, L., Jackstell, R., Beller, M. Using carbon dioxide as a building block in organic synthesis. Nature Communications. 6, 5933-5945 (2015).
- Hâncu, D., Green, J., Beckman, E. J. H2O2 in CO2 Sustainable Production and Green Reactions. Accounts of Chemical Research. 35, 757-764 (2002).
- Ballivet-Tkatchenko, D., Camy, S., Condoret, J. S., Lichtofouse, E., Scwarzbauer, J., Robert, D. Carbon Dioxide, a Solvent and Synthon for Green Chemistry. Environmental Chemistry. , 541-552 (2005).
- Hyatt, J. A. Liquid and Supercritical Carbon Dioxide as Organic Solvents. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 49, 5097-5101 (1984).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved