A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Tailoring In Vivo Cytotoxicity Assays to Study Immunodominance in Tumor-specific CD8+ T Cell Responses
In This Article
Summary
We describe here a flow cytometry-based in vivo killing assay that enables examination of immunodominance in cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses to a model tumor antigen. We provide examples of how this elegant assay may be employed for mechanistic studies and for drug efficacy testing.
Abstract
Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-based in vivo cytotoxicity assays enable sensitive and accurate quantitation of CD8+ cytolytic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses elicited against tumor- and pathogen-derived peptides. They offer several advantages over traditional killing assays. First, they permit the monitoring of CTL-mediated cytotoxicity within architecturally intact secondary lymphoid organs, typically in the spleen. Second, they allow for mechanistic studies during the priming, effector and recall phases of CTL responses. Third, they provide useful platforms for vaccine/drug efficacy testing in a truly in vivo setting. Here, we provide an optimized protocol for the examination of concomitant CTL responses against more than one peptide epitope of a model tumor antigen (Ag), namely, simian virus 40 (SV40)-encoded large T Ag (T Ag). Like most other clinically relevant tumor proteins, T Ag harbors many potentially immunogenic peptides. However, only four such peptides induce detectable CTL responses in C57BL/6 mice. These responses are consistently arranged in a hierarchical order based on their magnitude, which forms the basis for TCD8 “immunodominance” in this powerful system. Accordingly, the bulk of the T Ag-specific TCD8 response is focused against a single immunodominant epitope while the other three epitopes are recognized and responded to only weakly. Immunodominance compromises the breadth of antitumor TCD8 responses and is, as such, considered by many as an impediment to successful vaccination against cancer. Therefore, it is important to understand the cellular and molecular factors and mechanisms that dictate or shape TCD8 immunodominance. The protocol we describe here is tailored to the investigation of this phenomenon in the T Ag immunization model, but can be readily modified and extended to similar studies in other tumor models. We provide examples of how the impact of experimental immunotherapeutic interventions can be measured using in vivo cytotoxicity assays.
Introduction
Conventional CD8+ T cells (TCD8) play important parts in anticancer immune surveillance. They primarily function in the capacity of cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that recognize tumor-specific or -associated peptide antigens (Ags) displayed within the closed cleft of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. Fully armed CTLs utilize their cytotoxic arsenal to destroy malignant cells. Anticancer TCD8 can be detected in the circulation or even inside primary and metastatic masses of many cancer patients and tumor-bearing animals. However, they are often anergic or exhausted and fail to eradicate cancer. Therefore, many immunotherapeutic modalities are designed to increase anticancer TCD8 frequencies and to restore and boost their functions.
Tumor proteins harbor many peptides, some of which can be immunogenic and potentially immunoprotective. However, quantifiable TCD8 responses are elicited with varying magnitudes against few peptides only. This creates an “immunodominance hierarchy” among TCD8 clones1. Accordingly, immunodominant (ID) TCD8 occupy prominent hierarchical ranks, which is commonly judged by their abundance. In contrast, TCD8 cells whose T cell receptor (TCR) is specific for subdominant (SD) epitopes occur in lower frequencies. We and others have identified some of the factors that dictate or shape immunodominance in TCD8 responses. These include, among others, the mode of Ag presentation to naïve TCD8 (i.e., direct presentation, cross-presentation, cross-dressing)2,3,4, the type of Ag-presenting cells (APCs) participating in TCD8 activation5, the abundance and stability of protein Ags6,7 and the efficiency and kinetics of their degradation by proteasomes7,8, the relative selectivity of transporter associated with Ag processing (TAP) for peptides9, the affinity of liberated peptides for MHC I molecules9,10, the presence, precursor frequencies and TCR diversity of cognate TCD8 in T cell pools11,12,13, cross-competition among T cells for access to APCs14,15, and the fratricidal capacity of TCD8 clones16. In addition, TCD8 immunodominance is subjected to immunoregulatory mechanisms mediated by several suppressor cell types such as naturally occurring regulatory T (nTreg) cells17, the cell surface co-inhibitory molecule programmed death-1 (PD-1)16, and certain intracellular enzymes such as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)18 and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)19. It is important to note, however, that the above factors do not always fully account for immunodominance.
Apart from the basic biology of TCD8 immunodominance, the examination of this intriguing phenomenon has important implications in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. First, an ID status does not necessarily confer upon a given TCD8 clone the ability to prevent tumor initiation or progression20. Whether and how ID and SD TCD8 contribute to antitumor immunity may be dependent upon the type and the extent of malignancy and the experimental system employed. Second, it is thought that ID TCD8 clones may be ‘too visible’ to the immune system and consequently more prone to central and/or peripheral tolerance mechanisms16,21. Third, heterogeneic tumors may contain neoplastic cells that avoid detection by many, if not most, CTLs by displaying only a narrow spectrum of peptide:MHC complexes. Under these circumstances, TCD8 responses of insufficient breadth are likely to afford such tumor cells a survival advantage, thus potentiating their outgrowth22. It is for the above reasons that many view immunodominance as a hurdle to successful TCD8-based vaccination and therapies against cancer.
Inoculation of C57BL/6 mice with simian virus 40 (SV40)-transformed cells that express large tumor Ag (T Ag) provides a powerful preclinical system to study TCD8 immunodominance. This model offers several benefits. First, the peptide epitopes of this clinically relevant oncoprotein are well-characterized in this mouse strain23 (Table 1). Second, T Ag epitopes, which are called sites I, II/III, IV, and V, trigger TCD8 responses that are consistently arranged in the following hierarchical order: site IV >> site I ≥ site II/III >> site V. Accordingly, site IV-specific TCD8 mount the most robust response to T Ag. In contrast, sites I and II/III are subdominant, and site V-specific TCD8 are least abundant and usually only detectable in the absence of responsiveness to other epitopes23,24. Third, the T Ag+ tumor cell line utilized in the protocol described herein, namely C57SV fibrosarcoma cells, and those used in our previous investigations16,17,18,19,25,26, are transformed with subgenomic SV40 fragments25. Therefore, they are unable to assemble and release SV40 virions that could potentially infect host APCs. In addition, C57SV cells are devoid of classic costimulatory molecules such as CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2), and CD137 ligand (4-1BBL)16. The above attributes make these lines ideal for examination of in vivo TCD8 activation via cross-priming. Cross-priming is a major pathway in inducing TCD8 responses, especially those launched against tumor cells of non-hematopoietic origin that fail to directly prime naïve T cells25.
Antitumor TCD8 frequencies and/or functions can be monitored by MHC I tetramer staining, intracellular staining for effector cytokines (e.g., interferon [IFN]-γ) or lytic molecules (e.g., perforin), enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) assays and ex vivo cytotoxicity assays. Since their inception in the 1990s27,28, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-based in vivo killing assays have enabled evaluation of cytotoxic responses mediated by antiviral CTLs29,30,31, antitumor CTLs16,32, natural killer (NK) cells33, glycolipid-reactive invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells34, and preexisting and de novo donor-specific alloantibodies26. Therefore, their applications can be of interest to a wide readership, including but not limited to investigators working in the areas of tumor immunology and immunotherapy, anti-pathogen immunity, and preventative and therapeutic vaccine design.
To assess cell-mediated cytotoxicity in typical scenarios, two populations of naïve splenocytes that display either an irrelevant Ag or a cognate Ag(s) are labeled with two different doses of CFSE, mixed in equal numbers and injected into naïve (control) or killer cell-harboring mice. The presence/absence of each target population is then examined by flow cytometry.
We have optimized and employed in vivo killing assays in our studies on immunodominance in both antiviral and antitumor TCD8 responses12,16,17. Here, we provide a detailed protocol for the simultaneous assessment of ID and SD TCD8 responses to T Ag epitopes, which can be readily adopted for similar investigations in other experimental systems. We also provide representative results demonstrating that nTreg cell depletion and PD-1 blockade can selectively enhance ID TCD8- and SD TCD8-induced cytotoxicity, respectively. At the end, we will discuss multiple advantages of in vivo killing assays as well as some of their inherent limitations.
Protocol
The experiments described here follow animal use protocols approved by institutional entities and adhered to established national guidelines.
1. Inoculation of C57BL/6 Mice with T Ag-expressing Tumor Cells
- Grow the SV40-transformed fibrosarcoma cell line C57SV (or a similar T Ag+ adherent cell line) in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 4.5 g/L D-glucose and L-glutamine (1x) and supplemented with 1 mM sodium pyruvate and 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) in tissue culture-treated flasks at 37 °C in humidified atmosphere containing 10% CO2.
- Once the cells become fully confluent or slightly overconfluent, gently remove and discard the medium and rinse the monolayer with pre-warmed sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
NOTE: Maximal T Ag expression is achieved when T Ag+ cells reach 100% confluency. - Inside a biological safety cabinet, add pre-warmed trypsin-EDTA (0.25%) to cover the monolayer at room temperature until the cells are dislodged in patches. Tap the sides of the culture flask(s) several times to release the remaining adherent cells.
NOTE: If necessary and to expedite the trypsinization process, transfer the flask(s) into a 37 °C incubator. Dislodged cells will quickly adopt a rounded shape under a light microscope. This step should last approximately 5 min. - Add 5 mL of DMEM medium and dissociate clumps to prepare a single-cell suspension by pipetting the content of each flask up and down.
- Transfer the cell suspension through a cell strainer with 70-µm pores into a tube.
- Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant. Resuspend pelleted cells in 10 mL of sterile cold PBS.
- Repeat steps 1.6 and 1.7 twice.
- Count cells using a hemocytometer. Prepare a uniform suspension containing 4 x 107 cells/mL sterile PBS.
- Inject 500 µL of the above suspension intraperitoneally (i.p.) into each adult (6-12-week-old) male or female C57BL/6 mouse.
2. Treatment Regimens
- Treatment Regimen to Examine the Contribution of nTreg Cells to TCD8 Immunodominance
- Four days before in vivo priming of C57BL/6 mice with C57SV cells (step 1.10), inject each animal once i.p. with 0.5 mg of a low-endotoxin, azide-free anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (clone PC-61.5.3), which depletes nTreg cells, or with a rat IgG1 isotype control (e.g., clone KLH/G1-2-2, clone HRPN, or clone TNP6A7).
- Treatment Regimen to Test the In Vivo Significance of PD-1-PD-L1(2) Interactions in Shaping TCD8 Immunodominance
NOTE: The engagement of PD-1 by PD-L1 often, but not always, mediates the co-inhibition and/or exhaustion of Ag-specific TCD8. Therefore, treatment with anti-PD-1 can be performed in parallel with administration of anti-PD-L1 and anti-PD-L2 mAbs to reveal the exact intercellular interaction involved in a biological phenomenon.
3. Preparation of Target Splenocytes
- Euthanize sex-matched naïve C57BL/6 mice (6-12 weeks of age) that will serve as splenocyte donors by cervical dislocation.
- Position each mouse with its abdomen facing up inside a biological safety cabinet. Spray the skin with 70% (v/v) EtOH. Using sterile forceps and scissors, lift the skin and make a small ventral midline incision. Then, cut the skin in a cross-like fashion to expose the peritoneum.
- Using forceps, pull up the peritoneum in a tent-like fashion without snatching any of the internal organs. Cut the peritoneum open to expose the peritoneal cavity and gently remove the spleen.
- Place the spleen(s) inside a 15 mL Dounce tissue grinder containing 5 mL of sterile PBS. Apply manual pressure using the grinder’s glass plunger until the splenic tissue dissipates into a red homogenous cell suspension.
NOTE: Depending on the number of recipient animals per experimental group, several donor mouse spleens may be needed for target cell preparation. Up to 3 spleens can be homogenized together inside a 15 mL grinder. - Transfer the homogenate into a 15 mL tube. Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant. Resuspend pelleted cells in 4 mL of ammonium-chloride-potassium (ACK) lysing buffer for 4 min to eliminate erythrocytes.
NOTE: This is a time-sensitive step. Overexposing splenocytes to ACK lysing buffer will increase their fragility and render them susceptible to non-specific cell death. - To each tube, add 8 mL of RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS, L-alanyl-L-glutamine, 0.1 mM minimum essential media (MEM) nonessential amino acids, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 mM HEPES, and 1x penicillin/streptomycin, which will hereafter be referred to as complete RPMI medium (Table of Materials).
- Transfer the content through 70 µm pores of a cell strainer into a new 15 mL tube.
- Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant. Resuspend pelleted cells in 12 mL of complete RPMI.
- Split the splenocyte suspension into 3 equal portions (4 mL each) in 3 separate tubes.
4. Coating Target Splenocytes with Irrelevant and Cognate Peptides
- Label the tubes according to the peptides that will be used to pulse target splenocytes. Control splenocytes will be pulsed with an irrelevant peptide, and each population of cognate target splenocytes will be pulsed with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the T Ag-derived immunodominant epitope (site IV) or a subdominant T Ag epitope (site I or site II/III) (Table 1).
NOTE: The choice of irrelevant peptides depends on the experimental set-up and the mouse strain used in each investigation. The authors often use gB498-505 (an H-2Kb-restricted immunodominant peptide epitope of herpes simplex virus [HSV]-1) and/or GP33-41 (an H-2Db-restricted immunodominant peptide epitope of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus ([LCMV]) in C57BL/6 mice (Table 1). These peptides are optimal choices because: (i) they are derived from pathogens not previously encountered in the mouse model described here; (ii) similar to T Ag-derived peptides, gB498-505 and GP33-41 are restricted by and binds to H-2b molecules. In ‘three-peak’ in vivo killing assays, each of the two peaks that correspond to cognate target cells may represent splenocytes pulsed with an immunodominant or subdominant peptide. The choice of each peptide set varies according to the objectives of each experiment. See Figure 1 and Figure 2 as examples of such variation. For the remainder of this protocol, T Ag-derived sites I and IV will represent subdominant and immunodominant peptides, respectively. - Pulse the content of each labeled tube with 1 µM of the respective peptide for 1 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Use a separate cell strainer (with 70-μm pores) for each tube to remove clumps and debris if necessary.
- Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend pelleted cells in 12 mL of sterile cold PBS and repeat step 4.4 once more.
NOTE: It is important to remove as much FBS as possible because FBS can bind CFSE in the next step.
5. Labeling target splenocytes with CFSE
- Resuspend peptide-pulsed splenocytes in 4 mL of sterile PBS.
- Add CFSE at 0.025 μM, 0.25 μM, and 2 μM into the tubes containing irrelevant peptide-, site I-, and site IV-pulsed splenocytes, respectively.
NOTE: To achieve uniform CFSE labeling, hold each tube at a 45° angle before adding CFSE to the side slightly above the cell suspension followed immediately by gentle vortexing. This will ensure the appearance of smooth histograms at the end. Batch-to-batch and age-dependent variations in CFSE intensities are not uncommon. Therefore, one may need to experiment with differential CFSE doses before deciding on optimal concentrations to be used.
CAUTION: CFSE is toxic at concentrations that are higher than 5 μM. - Place the tubes inside a 37 °C incubator for 15 min and invert them once every 5 min.
- Add 3 mL of heat-inactivated FBS to each tube to stop the CFSE reaction. Top up the content with sterile PBS.
- Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend pelleted cells in 12 mL of sterile PBS and repeat step 5.5.
6. Examination of Adequate/Equal CFSE Labeling of Target Splenocyte Populations
- Resuspend pelleted cells in 3 mL of PBS.
- Vortex the tubes gently. Transfer 10 μL, each, of CFSElow, CFSEintermediate (int), and CFSEhigh cell suspensions into a 5 mL round-bottom polystyrene fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) tube containing 200 μL OF PBS.
- Interrogate cells using a flow cytometer equipped with a 488 nm laser. Draw a lymphocyte gate based on forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) properties of the cells before acquiring 5000 events falling within the lymphocyte gate in the FL-1 channel.
- Within the ‘parent’ CFSE+ population, draw additional histogram gates to identify CFSElow, CFSEint, and CFSEhigh subpopulations.
- Confirm equal or near-equal event numbers within the three gates. If necessary, adjust cell numbers in the ‘source’ tubes (step 6.1) before mixing and injecting target splenocytes into naïve and primed mice in section 7.
7. Injection of CFSE-labelled Target Cells into Naïve and T-Ag-primed Recipients
- Gently vortex the source tubes. Transfer the three CFSE-labeled cell suspensions in equal ratios into a new tube.
- Top up the content with sterile PBS.
- Spin down the tube at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Resuspend pelleted cells with sterile PBS.
- Count cells in trypan blue by a hemocytometer to ensure cellular viability of at least 95%.
- Adjust the volume in order to inject 1 x 107 mixed target cells/200 μL PBS intravenously (i.v.), via tail vein, into each recipient C57BL/6 mouse.
NOTE: Store the cells on ice in between injections. Gently mix target cells prior to each injection. Record the exact time of injection for each mouse, which will determine when the animal will need to be euthanized. It is important to keep the duration of in vivo cytotoxicity consistent among all animals in the same experiment.
8. Data Acquisition
- Two or four hours after the injection of CFSE-labeled target cells, euthanize the recipient mice by cervical dislocation.
NOTE: The duration of in vivo cytotoxicity can vary depending on the experimental system employed, the immunogenicity of target Ags, the anticipated abundance of peptide antigen-specific TCD8 in the spleen, and the robustness of their lytic function among other factors. - Remove and process each spleen separately as in steps 3.2−3.9.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pelleted cells in 3 mL of PBS.
NOTE: Take extra care to handle the splenic tissue and cell preparations at 4 °C or on ice before cytofluorimetric analyses. This is to prevent continued cytotoxicity ex vivo. - Transfer approximately 1 x 107 cells from each processed spleen into a clean FACS tube.
- Interrogate cells immediately using a flow cytometer equipped with a 488-nm laser. Draw a lymphocyte gate based on FSC and SSC properties of the cells.
- Identify CFSE- recipient’s splenocytes and CFSE+ transferred target cells. Draw additional gates accommodating distinct CFSElow, CFSEint, and CFSEhigh target cell populations.
- Acquire a total of 2000 CFSElow events in the FL-1 channel.
9. Data Analysis
- Calculate the specific lysis of each cognate target cell population using the following formula:
% Specific cytotoxicity =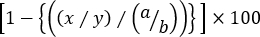
where x = CFSEint/high event number in T Ag-primed mouse, y = CFSElow event number in T Ag-primed mouse, a = CFSEint/high event number in naïve mouse, and b = CFSElow event number in naive mouse.
NOTE: In ‘three-peak’ cytotoxicity assays in which the specific lysis of more than one cognate target population is evaluated, it is not appropriate to use target cell frequencies. This is simply because the frequency of a cognate target cell population is influenced not only by the percentage of the irrelevant controls but also by that of the other cognate target splenocytes. Therefore, event numbers within each gate should be used in the above formula to accurately calculate the lysis of each cognate target cell population (either CFSEint or CFSEhigh cells) against CFSElow controls.
Results
The goal of the experiment whose results are depicted in Figure 1 was to determine whether the presence and functions of nTreg cells shape or alter the immunodominance hierarchy of T Ag-specific TCD8. C57BL/6 mice were injected i.p. with PBS or with 0.5 mg of an anti-CD25 mAb (clone PC-61.5.3 [PC61]) four days before they received 2 x 107 C57SV tumor cells i.p. In separate experiments, a rat IgG1 isotype control was used in lieu of PBS. Successful nTreg cell depletion b...
Discussion
CFSE-based in vivo cytotoxicity assays offer several advantages over traditional killing assays such as radioactive chromium (51Cr) release and colorimetric lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assays. First, they permit the monitoring of CTL function within an architecturally intact secondary lymphoid organ.
Second, the specific killing of target cells in in vivo cytotoxicity assays reflects the absolute number of Ag-specific TCD8, which is usually, but not always, a func...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) grants MOP-130465 and PJT-156295 to SMMH. JC is partially supported by a Queen Elizabeth II Graduate Scholarship in Science and Technology from the Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities. CEM was a recipient of an Alexander Graham Bell Canada Graduate Scholarship (doctoral) from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (1X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25200-056 | |
| ACK Lysing Buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A1049201 | |
| Anti-mouse CD25 (clone PC-61.5.3) | Bio X Cell | BE0012 | |
| Anti-mouse PD-1 (clone RMP1-14) | Bio X Cell | BE0146 | |
| CFSE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | C34554 | |
| DMEM (1X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11965-092 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Wisent Bioproducts | 080-150 | Heat-inactivate prior to use |
| GlutaMAX (100X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 35050-061 | |
| HEPES (1M) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15630080 | 10 mM final concentration |
| MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution (100X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11140-050 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | P0781 | Stock is 100X |
| Rat IgG1 (clone KLH/G1-2-2) | SouthernBiotech | 0116-01 | Isotype control |
| Rat IgG1 (clone HRPN) | Bio X Cell | BE0088 | Isotype control |
| Rat IgG1 (clone TNP6A7) | Bio X Cell | BP0290 | Isotype control |
| Rat IgG2a (clone 2A3) | Bio X Cell | BP0089 | Isotype control |
| RPMI 1640 (1X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11875-093 | |
| Sodium Pyruvate (100 mM) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11360-070 | 1 mM final concentration |
References
- Yewdell, J. W., Bennink, J. R. Immunodominance in major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T lymphocyte responses. Annual Review of Immunology. 17, 51-88 (1999).
- Chen, W., et al. Reversal in the immunodominance hierarchy in secondary CD8+ T cell responses to influenza A virus: roles for cross-presentation and lysis-independent immunodomination. The Journal of Immunology. 173 (8), 5021-5027 (2004).
- Otahal, P., et al. Inefficient cross-presentation limits the CD8+ T cell response to a subdominant tumor antigen epitope. The Journal of Immunology. 175 (2), 700-712 (2005).
- Lauron, E. J., et al. Cross-priming induces immunodomination in the presence of viral MHC class I inhibition. PLoS Pathogens. 14 (2), e1006883 (2018).
- Crowe, S. R., et al. Differential antigen presentation regulates the changing patterns of CD8+ T cell immunodominance in primary and secondary influenza virus infections. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 198 (3), 399-410 (2003).
- Probst, H. C., et al. Immunodominance of an antiviral cytotoxic T cell response is shaped by the kinetics of viral protein expression. The Journal of Immunology. 171 (10), 5415-5422 (2003).
- Gileadi, U., et al. Generation of an immunodominant CTL epitope is affected by proteasome subunit composition and stability of the antigenic protein. The Journal of Immunology. 163 (11), 6045-6052 (1999).
- Zanker, D., Waithman, J., Yewdell, J. W., Chen, W. Mixed proteasomes function to increase viral peptide diversity and broaden antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. The Journal of Immunology. 191 (1), 52-59 (2013).
- Deng, Y., Yewdell, J. W., Eisenlohr, L. C., Bennink, J. R. MHC affinity, peptide liberation, T cell repertoire, and immunodominance all contribute to the paucity of MHC class I-restricted peptides recognized by antiviral CTL. The Journal of Immunology. 158 (4), 1507-1515 (1997).
- Chen, W., Khilko, S., Fecondo, J., Margulies, D. H., McCluskey, J. Determinant selection of major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted antigenic peptides is explained by class I-peptide affinity and is strongly influenced by nondominant anchor residues. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 180 (4), 1471-1483 (1994).
- Kotturi, M. F., et al. Naive precursor frequencies and MHC binding rather than the degree of epitope diversity shape CD8+ T cell immunodominance. The Journal of Immunology. 181 (3), 2124-2133 (2008).
- Haeryfar, S. M., et al. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase establishes and broadens antiviral CD8+ T cell immunodominance hierarchies. The Journal of Immunology. 181 (1), 649-659 (2008).
- Leon-Ponte, M., Kasprzyski, T., Mannik, L. A., Haeryfar, S. M. Altered immunodominance hierarchies of influenza A virus-specific H-2(b)-restricted CD8+ T cells in the absence of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Immunological Investigations. 37 (7), 714-725 (2008).
- Kedl, R. M., et al. T cells compete for access to antigen-bearing antigen-presenting cells. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 192 (8), 1105-1113 (2000).
- Kastenmuller, W., et al. Cross-competition of CD8+ T cells shapes the immunodominance hierarchy during boost vaccination. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 204 (9), 2187-2198 (2007).
- Memarnejadian, A., et al. PD-1 Blockade Promotes Epitope Spreading in Anticancer CD8(+) T Cell Responses by Preventing Fratricidal Death of Subdominant Clones To Relieve Immunodomination. The Journal of Immunology. 199 (9), 3348-3359 (2017).
- Haeryfar, S. M., DiPaolo, R. J., Tscharke, D. C., Bennink, J. R., Yewdell, J. W. Regulatory T cells suppress CD8+ T cell responses induced by direct priming and cross-priming and moderate immunodominance disparities. The Journal of Immunology. 174 (6), 3344-3351 (2005).
- Rytelewski, M., et al. Suppression of immunodominant antitumor and antiviral CD8+ T cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. PLoS One. 9 (2), e90439 (2014).
- Maleki Vareki, S., et al. Differential regulation of simultaneous antitumor and alloreactive CD8(+) T-cell responses in the same host by rapamycin. American Journal of Transplantation. 12 (1), 233-239 (2012).
- Irvine, K., Bennink, J. Factors influencing immunodominance hierarchies in TCD8+ -mediated antiviral responses. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology. 2 (1), 135-147 (2006).
- Grossmann, M. E., Davila, T., Celis, T. Avoiding tolerance against prostatic antigens with subdominant peptide epitopes. Journal of Immunotherapy. 24 (3), 237-241 (2001).
- Schreiber, H., Wu, T. H., Nachman, J., Kast, W. M. Immunodominance and tumor escape. Seminars in Cancer Biology. 12 (1), 25-31 (2002).
- Mylin, L. M., et al. Quantitation of CD8(+) T-lymphocyte responses to multiple epitopes from simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen in C57BL/6 mice immunized with SV40, SV40 T-antigen-transformed cells, or vaccinia virus recombinants expressing full-length T antigen or epitope minigenes. Journal of Virology. 74 (15), 6922-6934 (2000).
- Fu, T. M., et al. An endoplasmic reticulum-targeting signal sequence enhances the immunogenicity of an immunorecessive simian virus 40 large T antigen cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope. Journal of Virology. 72 (2), 1469-1481 (1998).
- Chen, W., et al. Cross-priming of CD8+ T cells by viral and tumor antigens is a robust phenomenon. European Journal of Immunology. 34 (1), 194-199 (2004).
- Memarnejadian, A., Meilleur, C. E., Mazzuca, D. M., Welch, I. D., Haeryfar, S. M. Quantification of Alloantibody-Mediated Cytotoxicity In Vivo. Transplantation. 100 (5), 1041-1051 (2016).
- Aichele, P., et al. Peptide antigen treatment of naive and virus-immune mice: antigen-specific tolerance versus immunopathology. Immunity. 6 (5), 519-529 (1997).
- Oehen, S., Brduscha-Riem, K. Differentiation of naive CTL to effector and memory CTL: correlation of effector function with phenotype and cell division. The Journal of Immunology. 161 (10), 5338-5346 (1998).
- Coles, R. M., Mueller, S. N., Heath, W. R., Carbone, F. R., Brooks, A. G. Progression of armed CTL from draining lymph node to spleen shortly after localized infection with herpes simplex virus 1. The Journal of Immunology. 168 (2), 834-838 (2002).
- Barber, D. L., Wherry, E. J., Ahmed, R. Cutting edge: rapid in vivo killing by memory CD8 T cells. The Journal of Immunology. 171 (1), 27-31 (2003).
- Meilleur, C. E., et al. Bacterial superantigens expand and activate, rather than delete or incapacitate, preexisting antigen-specific memory CD8+ T cells. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. , (2018).
- Goldszmid, R. S., et al. Dendritic cells charged with apoptotic tumor cells induce long-lived protective CD4+ and CD8+ T cell immunity against B16 melanoma. The Journal of Immunology. 171 (11), 5940-5947 (2003).
- Oberg, L., et al. Loss or mismatch of MHC class I is sufficient to trigger NK cell-mediated rejection of resting lymphocytes in vivo - role of KARAP/DAP12-dependent and -independent pathways. European Journal of Immunology. 34 (6), 1646-1653 (2004).
- Wingender, G., Krebs, P., Beutler, B., Kronenberg, M. Antigen-specific cytotoxicity by invariant NKT cells in vivo is CD95/CD178-dependent and is correlated with antigenic potency. The Journal of Immunology. 185 (5), 2721-2729 (2010).
- Brinster, R. L., et al. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 37 (2), 367-379 (1984).
- Tatum, A. M., et al. CD8+ T cells targeting a single immunodominant epitope are sufficient for elimination of established SV40 T antigen-induced brain tumors. The Journal of Immunology. 181 (6), 4406-4417 (2008).
- Schell, T. D., Tevethia, S. S. Control of advanced choroid plexus tumors in SV40 T antigen transgenic mice following priming of donor CD8(+) T lymphocytes by the endogenous tumor antigen. The Journal of Immunology. 167 (12), 6947-6956 (2001).
- Greenberg, N. M., et al. Prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (8), 3439-3443 (1995).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved