A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Functional Assessment of Intestinal Tight Junction Barrier and Ion Permeability in Native Tissue by Ussing Chamber Technique
In This Article
Summary
Intestinal epithelium confers not only nutrient absorption but protection against noxious substances. The apical-most epithelial intercellular junction, i.e., the tight junction, regulates paracellular solute and ion permeability. Here, a protocol for the preparation of mucosal sheets and assessment of the ion selectivity of tight junctions using Ussing chamber technique is described.
Abstract
The Ussing chamber technique was first invented by the Danish scientist Hans Ussing in 1951 to study the transcellular transport of sodium across frog skin. Since then, this technique has been applied to many different tissues to study the physiological parameters of transport across membranes. The Ussing chamber method is preferable to other methods because native tissue can be used, making it more applicable to what is happening in vivo. However, because native tissue is used, throughput is low, time is limited, and tissue preparation requires skill and training. These chambers have been used to study specific transporter proteins in various tissues, understand disease pathophysiology such as in Cystic Fibrosis, study drug transport and uptake, and especially contributed to the understanding of nutrient transport in the intestine. Given the whole epithelial transport process of a tissue, not only transepithelial pathways, but also paracellular pathways are important. Tight junctions are a key determinant of tissue specific paracellular permeability across the intestine. In this article, the Ussing chamber technique will be used to assess paracellular permselectivity of ions by measuring transepithelial conductance and dilution potentials.
Introduction
The Ussing chamber method was first developed by the Danish scientist Hans Ussing. Ussing first used it to measure the short-circuit current of sodium transport across frog skin after it was observed that NaCl could be transported across the skin against a steep concentration gradient1. His system consisted of the frog skin mounted between two chambers with access to either side of the skin. Each chamber contained Ringer's solution which was circulated and aerated. Two narrow agar ringer bridges situated near the skin and connected to saturated KCl-calomel electrodes measured the potential difference as read by a potentiator. A second pair of agar ringer bridges were situated at the opposite end of each chamber connected to beakers with saturated KCl saturated with AgCl to apply an electromotive force provided by a battery. A potential divider was used to adjust the voltage so that the potential difference across the skin remained zero, thus creating short-circuit conditions. A microampere meter was also connected to read the current passing through the skin (see the figure in ref.1 for original chamber design).
Over the past 70 years, this technique has been applied to many different tissues, particularly intestinal tissue, to study nutrient and ion transport. For example, the mechanism of cholera-induced diarrhea was studied by mounting rabbit ileum in these chambers, and it was found that cholera toxin-induced diarrhea is mediated by cAMP2. In addition, these chambers were also used to study the mechanism underlying glucose transport via Na+-Glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1)3. Our lab focuses on transcellular and paracellular transport in intestinal epithelial cells. Using the Ussing chamber method, peptide transport was assessed in Claudin 15 knockout mice, which have impaired paracellular sodium transport, using Ussing chambers to measure the absorption of the nonhydrolyzable dipeptide glycylsarcosine. It was found that luminal Na+ homeostasis is important for proton-coupled peptide transport4. In addition, these chambers were also used to investigate anion secretion in the murine cecum in response to submucosal activation of proteinase activated receptor 1 by the serine protease trypsin5.
Ussing chambers have also recently been used to assess the paracellular pathways in epithelial tissue. Paracellular pathways are regulated by tight junctions, which are complexes of proteins that form at the point where two or more cells meet6. The barrier function and ion selectivity (whether anions or cations are selectively able to pass through the tight junction) is determined by the presence of claudin family proteins; some of which act as barriers (claudin 3 and 7), anion pores (claudin 10a), or cation pores (claudin 2, 10b, and 15)7. Other methods have been used to assess the paracellular pathway, such as oral gavage of FITC accompanied by blood plasma FITC concentration8, or EDTA-Cr9; however, these techniques are of lower resolution and cannot assess ion selectivity or a specific section of the sections of the intestinal tract. Ussing chambers, however, can be used to assess the dilution potential of target ions, and, therefore, determine the ion selectivity of the tight junctions. For example, with NaCl, the selectivity of the tight junctions for Na+ and Cl- can be calculated by diluting one side of the membrane (usually the mucosal side) and measuring the change in transepithelial potential difference. The relative permeabilities of Na+ and Cl- can be estimated by the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation10 and the selectivity of the tight junction can be estimated using the Kimizuka-Koketsu equation11. These chambers, therefore, have the advantage of measuring the electrophysiological parameters of tissue and as a result provide more information about the passage of ions through the tight junctions than other lower resolution methods.
The Ussing chamber method is not only limited to the intestinal tract, although it is widely used in studies concerning the intestine, it has many other applications as well. For example, these chambers have been used to study Cystic Fibrosis, and specifically the chloride channel cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)12. Cystic Fibrosis is caused by a mutation in CFTR13, which results in impaired chloride secretion and fluid transport by respiratory epithelial cells, and a resulting thicker, drier mucous layer14. Study of airway epithelial CFTR has been performed with these chambers to not only understand the disease, but to discover ways to treat the disease. For example, in patients with rare mutations causing Cystic Fibrosis, analysis of patient respiratory epithelial cells has been used to test therapies such as Orkambi and an amplifier co-therapy15.
Ussing chambers have also been used to study routes of drug delivery, such as with human biopsy tissue to study drug uptake and pharmacokinetics16. Intestinal uptake is not the only route of drug delivery. These chambers have also been used to study nasal drug delivery systems17. Drug delivery studies with Ussing chambers have also been performed for the eye. In the rabbit cornea, permeability and uptake studies were conducted with Labrasol, a drug that is designed to increase the absorption of drugs across tissues18. Another study examined the effect of benzylalkonium chloride on transscleral drug delivery in the rabbit sclera19.
The Ussing chamber method is useful because native tissue can be used. As such, it is preferable over in vitro models such as Caco-2 cell lines. However, the technique requires skill and time to prepare specimens, so it is not suitable for high throughput applications. The electrophysiological properties of cell monolayers can be studied using cell culture inserts in these chambers. Recent discoveries have allowed for the culture of organoids which are mini-organs grown in culture from the harvest of epithelial or endothelial stem cells20. Organoid culture can be manipulated to be grown in a monolayer, thereby making it possible to mount organoids in an Ussing chamber21. Organoids of various epithelial and endothelial tissues can be studied, lowering the number of animals required, as organoid culture can be maintained long term. This will also increase the throughput since time consuming and laborious tissue dissection and preparation steps will not be needed. In the future, Ussing chamber studies will continue to be very useful for studying tissue transport and they will be especially important in the field of personalized medicine.
The following protocol demonstrates the application of the Ussing chamber method to assess the permselectivity and barrier function of the tight junctions in the small intestine of Claudin 15 knockout (Cldn15-/-) mice and wild type (WT) controls by measuring the dilution potential of NaCl. Tight junctions (TJ) are formed at the point where two or more cells meet in epithelial and endothelial tissue. Bicellular tight junctions (bTJ), particularly the claudin family proteins found within the bTJ, are thought to determine the barrier function and permselectivity of TJ7. Cldn15-/- mice have a mega small intestine22 and reduced nutrient uptake capability due to the loss of intestinal Na+ recycling that occurs via claudin 154,23,24. Cldn15-/- mice have impaired Na+ homeostasis, which makes them an interesting model for studying the permselectivity of the TJ. The following protocol assesses the permeability of the TJ to NaCl by measuring the dilution potential of NaCl (PNa/PCl) in the middle small intestine. Briefly, the change in membrane potential difference that occurs by diluting one side of the membrane (M side or S side, both are measured in the below protocol) can be used to calculate the permeability of Na+ (PNa) and Cl- (PCl), and the dilution potential (PNa/PCl) will show whether the tight junction has a cationic or anionic selectivity.
The experiments in this protocol were conducted using a customized Ussing chamber (Figure 1A), which consists of two halves, between which the intestinal preparation is mounted vertically, voltage clamp amplifier, electrical recorder, electrodes, salt bridges, Ringer's solution, HEPES buffer (150 mM NaCl), diluted HEPES buffer (75 mM NaCl), intestinal preparation (for details about equipment see the Table of Materials).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All animals used in these experiments were maintained in the animal care facility at the University of Shizuoka and the experiments were conducted according to the guidelines for animal research set out by the University of Shizuoka. All experiments were carried out with approval from the Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Shizuoka (Permits #205272 and #656-2303).
1. Preparation of NaCl electrodes
NOTE: The electrodes used in these experiments consist of concentrated NaCl or KCl. The KCl/calomel electrodes are purchased commercially. Before starting the experiment, ensure that all electrodes are filled to the top with concentrated NaCl or KCl solution.
- Prepare small glass jars with plastic lids (volume 20 mL).
- Drill two holes in the plastic lids, one for the NaCl salt bridge (2.5 mm diameter), and the other for silver wire (1 mm diameter; Figure 1C, NaCl electrode).
- Fill the glass jar with saturated NaCl solution (about 15 mL, until full).
- Insert silver wire (0.8 mm diameter, 7 cm long) into the jar, but ensure that the wire portion outside the jar can be connected via alligator clips (small size) to the amplifier system.
- When not in use, wrap the electrodes and ensure the holes are covered, with parafilm to prevent drying.
2. Preparation of salt bridges
NOTE: Prepare salt bridges at least a day before the experiment to provide adequate time to solidify. Salt bridges can be used repeatedly but use after 2 months is not recommended.
- NaCl salt bridges
- Prepare #7 polyethyl tubing (outer diameter 2.3 mm, inner diameter 1.3 mm), 19 G needle and lock-type syringe, 200 mL of 1 M NaCl solution, 2 g agar, sealable plastic container for salt bridge storage.
- Prepare appropriate number of salt bridges by cutting tubing to the size necessary for the Ussing chamber set up (each chamber requires two salt bridges).
- Before injection of agar, make a U shape with the tubes and place them in a beaker of warm water (to create an easy shape for setting up salt bridges).
- Make 200 mL of 1 M NaCl by dissolving 11.688 g of NaCl in 200 mL in deionized water.
- Split 1 M NaCl into 100 mL portions: Make 100 mL of 2% agar in 1 M NaCl (mix 2 g agar in NaCl, heat in microwave to dissolve).
- Using a 19 G needle and locking syringe, fill the syringe with 1 M NaCl/agar solution. Gently begin to expel solution drop by drop and while doing so insert the needle into one end of the tube and fill until the mixture comes out from the other side.
- Slowly withdraw the needle while still expressing the solution and repeat until all the required salt bridges have been made. (If the solution solidifies in the syringe or needle, briefly warm it in hot water until solution can be expressed again.)
- Check salt bridges to ensure there are no bubbles and store in remaining 1 M NaCl solution in a sealable container.
- KCl salt bridges
NOTE: Thinner tubing is used for the KCl agar bridges to avoid the increment of K+ concentration in the buffer, as the salt bridge tips can dissolve and K+ can leak into the buffer.- Prepare #3 polyethyl tubing (outer diameter 1.0 mm, inner diameter 0.5 mm), 23 G needle and lock type syringe, 200 mL of 1 M KCl solution, 2 g agar, sealable plastic container for salt bridge storage.
- Prepare appropriate number of salt bridges by cutting the tubing to the size necessary for the Ussing chamber set up (each chamber requires two salt bridges).
- Make 200 mL of 1 M KCl by dissolving 14.91 g of KCl in 200 mL of deionized water.
- Split into two 100 mL portions: Make 100 mL of 2% agar in 1 M KCl (mix 2 g agar in KCl, heat in a microwave to dissolve).
- Using a 23 G needle and locking syringe, inject tubing with 2% agar 1 M KCl mixture (ensure that the tubes are completely filled and there are no bubbles) in the same manner as with the NaCl salt bridges.
- Check salt bridges to ensure there are no bubbles and store in the remaining 1 M KCl solution in a sealable container.
3. Preparation of Ringer's solution and HEPES buffer
NOTE: Depending on the tissue mounted in the Ussing chamber, the components of Ringer's solution may differ. The recipes presented here are specific for the small and large intestine.
- Make Ringer's solution fresh on the day of the experiments as described in Table 1.
- Bubble the solution with 95% O2/5% CO2 to provide O2 to the tissue and a buffering capacity.
| Ringer's solution (small Intestine) | Ringer's solution (large intestine) |
| NaHCO3 – 21.0 mM | NaHCO3 – 21.0 mM |
| K2HPO4 – 2.4 mM | K2HPO4 – 2.4 mM |
| KH2PO4 – 0.6 mM | KH2PO4 – 0.6 mM |
| NaCl – 119.0 mM | NaCl – 119.0 mM |
| MgCl2 – 1.2 mM | MgCl2 – 1.2 mM |
| CaCl2 – 1.2 mM | CaCl2 – 1.2 mM |
| Indomethacin – 10 µM (Make 1 mM stock in 21 mM NaHCO3, add 10 mL of stock for 1 L of Ringer's solution) | Indomethacin – 10 µM (Make 1 mM stock in 21 mM NaHCO3, add 10 mL of stock for 1 L of Ringer's solution) |
| 1 mM Glutamine (0.146 g/L) | 10 mM Glucose |
Table 1: Ringer's Solution Recipe. To make Ringer's solution, mix all components together with de-ionized water. Ringer's solution is best made fresh before experiments. Keep in the refrigerator or on ice until use. Before using, gas with 95% O2/5% CO2.
- Make HEPES buffer fresh on the day of experiment as described in Table 2 by mixing ingredients in de-ionized water.
- Do not adjust to the final volume of buffer until after pH adjustment.
- Warm HEPES buffer to 37 °C and adjust the pH to 7.4 by slowly adding drops of 1 M Tris solution while stirring.
- Adjust to the final volume by adding the appropriate amount of deionized water.
| HEPES Buffer | Dilution HEPES Buffer |
| HEPES – 10 mM | HEPES – 10 mM |
| Glucose – 10 mM (Large intestine) | Glucose – 10 mM (Large intestine) |
| 1 mM Glutamine (0.146 g/L) (Small intestine) | 1 mM Glutamine (0.146 g/L) (Small intestine) |
| NaCl – 150 mM | NaCl – 75 mM + 150 mM mannitol (to adjust for osmolality differences) |
| MgCl2 – 1 mM | MgCl2 – 1 mM |
| CaCl2 – 2 mM | CaCl2 – 2 mM |
| Indomethacin – 10 µM (Make 1 mM stock in 21 mM NaHCO3, add 10 mL of stock for 1 L of Ringer's Solution) | Indomethacin – 10 µM (Make 1 mM stock in 21 mM NaHCO3, add 10 mL of stock for 1 L of Ringer's Solution) |
| Adjust to pH 7.40 (37°C) using 1 M Tris | |
Table 2: HEPES Buffer Recipe. To make HEPES buffer and dilution HEPES buffer, dissolve all ingredients in de-ionized water. Solutions must be pH adjusted with 1 M Tris solution, so do not add full volume of water (e.g., when making 1 L, dissolve all ingredients in about 800 mL of water). Then heat the solution to 37 °C, adjust the pH to 7.4 and then adjust the final volume.
4. Ussing chamber setup
NOTE: The Ussing chambers used in this protocol are custom-made continuous perfusion chambers. To assess mouse intestinal barrier function or nutrient uptake, chambers with a 4 or 5 mm diameter opening is recommended25 (Figure 1A-C).
- To reduce edge effect26 and help seal the chambers, attach 4 or 5 mm hole punched paraffin film (about 4 cm2) before setting up (Figure 1B).
- Set up in open circuit conditions for dilution potential measurement. Set in current clamp mode. Set the output as current and set current pulse to ±20 µA.
- When setting up in short circuit conditions for the measurement of short circuit current and transmucosal resistance, set in voltage clamp mode. Set the output as voltage and set voltage pulse to ±5 mV.
- Ensure 37 °C water is circulating in the water jacket.
- Fill each chamber with Ringer's solution or HEPES buffer (amount depends on the system used, the chambers used here require 5 mL for each side) and ensure there are no leaks.
- Connect salt bridges and electrodes.
- Ensure voltage is 0 and stable, pulse current to ensure that salt bridges and electrodes are properly set up.
- Allow system and Ringer's solution temperature to equilibrate for at least 20 min.
- After equilibration, correct asymmetrical voltage difference between KCl electrodes and compensate for fluid resistance by changing it to zero (check the manual for the Ussing chamber system used to determine the correct way).
5. Dissection of intestinal tissue
NOTE: All animal experimentation must be carried out within the regulations set by the country and the university.
- Before taking the intestinal tissue, prepare fresh, ice-cold Ringer's solution and bubble with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 for 15 min (step 3).
- Anesthetize mice according to guidelines governing the use of animals in research. For this experiment, mice were anesthetized with 2%-3% isoflurane administered by an anesthetizer. Check for the proper anesthesia by pinching toes and ensuring there is no pain response.
- Make an incision in the abdomen with scissors from the pelvis to the diaphragm; locate the stomach and cut the pyloric end of the stomach.
- Grip the stomach portion attached to the small intestine with forceps and gently pull the small intestine while cutting away the mesenteric attachments. Be careful not to cut or damage the intestinal tissue in any way.
- Continue dissecting the intestine all the way to the anus. For the complete removal of large intestine, cut the pelvic bones to reveal the distal portion of the large intestine and carefully remove the rest of the intestine by cutting away the attachments.
- Measure the length of the intestine and divide into desired segments. For this experiment, divide the small intestine into three segments and use the middle segment.
- Place the desired segments into ice cold, bubbled Ringer's solution; then, open each segment longitudinally by cutting along the mesenteric attachments. Trim away fat and connective tissue.
- Return the segments to the ice-cold Ringer's solution and wash thoroughly (even in the ice-cold solution, oxygenation of the luminal epithelium is important to maintain epithelial function).
6. Stripping the muscle layer and preparation of the intestinal sheet
NOTE: Removal of the serosa (muscle layer) is important for transport studies using the intestine. If the serosa remains, the intestinal tissue can be subject to random muscular contractions that will distort the electrophysiological data, and transport may be inhibited. Unstripped tissue rapidly deteriorates when mounted in Ussing chambers, since the serosa is a significant diffusion barrier for substrate and oxygen. In some special cases, it may be necessary to keep the muscle layer, so the decision is up to the researcher and the experimental design. The intestinal sheets can be prepared in two ways depending on which layer is removed (Figure 2). For this experiment, mucosa and submucosal preparations are required (Figure 2, 2nd panel).
- Prepare dissection plates (10 cm diameter) covered with silicone rubber, pins (small acupuncture needles), 5 mm punched filter paper and parafilm squares (2 cm x 2cm; may not be necessary for other systems).
- Pour fresh, ice-cold, bubbled Ringer's solution into the dissection plate (enough to cover the tissue, about 2-3 mL).
- Under a stereomicroscope, pin the ends of intestinal tissue (mucosal side down).
- Using fine forceps, bluntly dissect the muscle layer from the underlying mucosa.
- Be careful not to tear or introduce any holes into the tissue.
- Once the muscle layer is removed, cut a piece large enough for a 5 mm diameter opening. When preparing the small intestine, removal of the serosa-muscle layer should be done within 10 min, since luminal oxygenation is difficult under these conditions.
- Wet 5 mm punched filter paper square in Ringer's solution and place the intestinal tissue on it with mucosal side down, since submucosal preparations spontaneously wrap around with mucosal side outside.
- Ensure the opening is completely covered by the intestinal tissue and no wrinkles are present. Use a black board underneath the preparation to examine whether the opening is completely covered.
- Repeat this procedure for the required number of mucosal preparations (in this experiment two preparations are required: one preparation will be used to measure dilution potential, and the other will be used to measure baseline electrical parameters).
7. Mounting intestinal preparations in Ussing chambers
NOTE: Set up will depend on the type of the Ussing chamber system and recording system used.
- Suction out Ringer's solution/HEPES buffer from the Ussing chamber.
- Disassemble the Ussing chamber and lay the filter paper with the intestinal preparation mucosal side down on the mucosal side chamber and adjust so that the chamber's window aligns with the hole of the filter paper (Figure 1A, black marking around the chamber window is useful for alignment of the preparations).
- Carefully place the Serosal side chamber on to Mucosal side chamber and close tightly but be sure that the intestinal sheet has not moved during connection.
- Quickly refill both chambers with Ringer's solution or HEPES buffer, and place bubbling wands (Ringer's solution: 95% O2/5% CO2; HEPES buffer: 100% O2) at the opposite end of the chambers, away from the membrane (bubbling too close to the preparation could have an effect on the measurements).
- Reconnect salt bridges and check whether the voltage is stable and pulse current to ensure the connections are okay (Figure 1C).
- Repeat for each intestinal preparation.
- Let the system equilibrate for about 15 min. If using a recording system, let the conductance and Isc/membrane potential difference stabilize before starting the experiments.
8. Dilution potential experiment (open circuit conditions)
- Wash both sides of the chamber by suctioning the HEPES buffer and adding 5 mL of fresh pre-warmed HEPES buffer to each side.
- Turn the recording system on. Set range to 250 mV, (the system used here amplifies output voltage 10x), set marker positions, and set recording system to measure.
- Turn Ussing chamber systems to clamp mode and start measuring. Once membrane potential has stabilized (~15-20 min), the assessment can begin.
- Suction the HEPES buffer from the Mucosal side and quickly replace with 5 mL of warmed dilution HEPES buffer containing 75 mM NaCl.
- Once the membrane potential has peaked (5-10 min), remove the dilution buffer from the "Mucosal" side and replace with HEPES buffer.
- If necessary, repeat step 3 for the Serosal side, adding dilution HEPES buffer to the Serosal side.
- To ensure that the tissue is viable, add the adenylate cyclase activator Forskolin (final concentration 10 µM) to the Serosal side.
- Once the membrane potential difference has reached a peak and has started to decline, the experiment is over.
9. Measurement of transepithelial electrical conductance and baseline Isc (short-circuit conditions)
- Wash both sides of the chamber by suctioning the Ringer's solution and adding 5 mL of fresh bubbled Ringer's solution to each side.
- Turn the recording system on. Set range to 2.5 V (the system used here amplifies output voltage 10x), set marker positions, and set recording system to measure.
- Turn Ussing chamber systems to clamp mode and start measuring; once Isc and conductance have stabilized (~15-20 min), baseline measurements can be obtained.
- To ensure the tissue is viable, add the adenylate cyclase activator Forskolin (final concentration 10 µM) to the Serosal side.
- Once the membrane potential difference has reached a peak and has started to decline, the experiment is done.
10. Analyzing results
- Under open-circuit conditions, calculate transmucosal conductance from the change of voltage in response to current pulses according to Ohm's law. Determine the equivalent short circuit current (Isc) from transmucosal voltage and conductance applying Ohm's law.
- Use the dilution potential of NaCl for calculating the relative ionic selectivity (PNa/PCl) with the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation10.
- Estimate the absolute selectivity of the tight junction for each ion using the Kimizuka-Koketsu equation11.
- Calculate PNa/PCl using the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation from dilution potentials, and determine absolute permeabilities PNa and PCl from the Kimizuka-Koketsu equation as described by Yu et al.10 as follows:
![figure-protocol-19319 Nernst equation formula; chemical thermodynamics; logarithmic expression; V=RT/F ln[(α+β)/(1+αβ)].](/files/ftp_upload/62468/62468eq1.jpg)

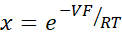

where, V: Dilution potential (mV); α: Activity ratio. The calculated activity of NaCl in the HEPES buffer divided by the calculated activity of NaCl in the dilution HEPES buffer (For this experiment it was calculated as 1.8966); e: Mathematical constant, 2.71828; GM: Transmucosal conductance (mS/cm2); F: Faraday constant (96,485.3329 C/mol); R: Gas constant (8.314 J/mol K);T: Temperature (310.15 K)
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The results shown in this paper are results that were part of larger project that has been completed (see ref.4,23,24).
Transepithelial electrical conductance of the small intestine is decreased in Cldn15-/- mice.
The baseline transmucosal conductance (under short circuit conditions) of the middle small intesti...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
In this experiment, Ussing chambers were used to measure the baseline electrical parameters and the dilution potential of NaCl in the small intestine of Cldn15-/- and WT mice. It is very important when doing Ussing chamber experiments to verify that the membrane preparation used in the experiments is viable. This is usually done by adding glucose or the adenylate cyclase activator forskolin and seeing whether there is an appropriate rise in Isc (100-300 µA/cm2 in mi...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by 17K00860 (to HH) and 19K20152 (to NI). WH would like to acknowledge the Otsuka Toshimi Scholarship Foundation for their financial support from 2018-2021.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| #3 polyethyl tubing | Hibiki | outer diameter 1.0 mm; inner diameter 0.5 mm | |
| #7 polyethyl tubing | Hibiki | outer diameter 2.3 mm; inner diameter 1.3 mm | |
| 10 mL locking syringe | Terumo | SS-10LZ | Locking syringes are necessary to prevent the needle from dislodging during filling |
| 19 g needle | Terumo | NN-1938R | Please use caution when working with needles and dispose of in sharps container |
| 23 g needle | Terumo | NN-2332R | Please use caution when working with needles and dispose of in sharps container |
| 5 mm punch | NA | NA | Use to punch holes in filter paper and parafilm |
| acupuncture needles | Seirin | NS | Used as dissection pins to pin tissue to dissection plate |
| Agar | Fujifilm Wako | 010-15815 | |
| Alligator clips | NA | NA | Connects the electrode to the amplifier |
| CaCl2 | Fujifilm Wako | 038-00445 | |
| D(-)-Mannitol | Fujifilm Wako | 133-00845 | This is used to correct for the osmolality difference in dilution HEPES buffer |
| D(+)-Glucose | Fujifilm Wako | 049-31165 | |
| Dissection kit | You will need, scissors and curved forceps | ||
| Dissection plates | We used 10 cm cell culture plates and covered with silicon rubber | ||
| DMSO | Sigma | 472301-500ML | For making forskolin stock |
| Electrical recorder | TOA Electronics | PRR-5041 | Other equivalent electrical recorders are available commercially |
| Epithelial voltage clamp amplifier | Nihon Kohden | CEZ9100 | Other equivalent amplifiers are available commerically |
| filter paper, cut into squares | NA | NA | Punched with a 5 mm punch, used to hold intestinal preparation |
| fine forceps | Fast Gene | FG-B50476 | For blunt dissection of the muscle layer |
| Forskolin | Alomone Labs | F-500 | Make 10 mM stock in DMSO, final concentration will be 10 µM |
| HEPES | Sigma | H4034-1KG | |
| Indomethacin | Sigma | I7338-5G | Make a 1 mM stock in 21 mM NaHCO3, final concentration is 10 µM |
| K2HPO4 | Fujifilm Wako | 164-04295 | |
| KCl | Fujifilm Wako | 163-03545 | |
| KCl/calomel electrode | Asch Japan Co. | SCE-100 | |
| KH2PO4 | Kanto chemical | 32379-00 | |
| L(+)-Glutamine | Fujifilm Wako | 074-00522 | |
| MgCl2 | Fujifilm Wako | 135-00165 | |
| Mixed Gas (95% O2/5% CO2) | Shizuoka Oxygen Company | Used for bubbling Ringer solution and chambers when using Ringer solution | |
| NaCl | Fujifilm Wako | 191-01665 | |
| NaCl electrode | NA | NA | Handmade electrodes which require concentrated NaCl and Silver wire |
| NaHCO3 | Fujifilm Wako | 191-01305 | |
| O2 Gas | Shizuoka Oxygen Company | Used for bubbling chambers when using HEPES buffer | |
| parafilm | Bemis | PM-996 | Used to help seal Ussing chambers |
| pH meter | DKK-TOA Corp | HM-305 | HEPES buffer needs to be adjusted to pH 7.4 at 37 °C |
| pH meter electrode | DKK-TOA Corp | GST-5311C | |
| silicone rubber | Shinetsu Chemical | KE-12 | Used to fill dissection plates |
| silver wire | Used for making NaCl electrodes | ||
| Small jars w/ plastic lids | NA | NA | Use for NaCl electrodes |
| stereomicroscope | Zeiss | Stemi 305 | A stereomicroscope allows you to see depth, so you can dissect the tissue more easily |
| Tris (Trizma base) | Sigma | T1503-1KG | Make a 1M solution to adjust pH of HEPES buffers |
| Ussing chambers | Sanki Kagaku Kougei | These chambers are custom made continuous perfusion Ussing chambers with a window diameter of 5 mm | |
| Water pump and heating system | Tokyo Rikakikai Co. Ltd. | NTT-110 |
References
- Ussing, H. H., Zerahn, K. Active transport of sodium as the source of electric current in the short-circuited isolated frog skin. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 23, 110-127 (1951).
- Field, M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. American Journal of Physiology - Legacy Content. 221, 992-997 (1971).
- Herrmann, J. R., Turner, J. R. Beyond Ussing's chambers: contemporary thoughts on integration of transepithelial transport. American Journal of Physiology - Cell Physiology. 310, 423-431 (2015).
- Ishizuka, N., et al. Luminal Na + homeostasis has an important role in intestinal peptide absorption in vivo. American Journal of Physiology - Gastorintestinal and Liver Physiology. 315, 799-809 (2018).
- Ikehara, O., et al. Subepithelial trypsin induces enteric nerve-mediated anion secretion by activating proteinase-activated receptor 1 in the mouse cecum. Journal of Physiological Sciences. 62, 211-219 (2012).
- Furuse, M. Molecular basis of the core structure of tight junctions. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2, 002907(2010).
- Tsukita, S., Tanaka, H., Tamura, A. The claudins: From tight junctions to biological systems. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 44, 141-152 (2019).
- Li, B. R., et al. In vitro and in vivo approaches to determine intestinal epithelial cell permeability. Journal of Visual Experiments: JoVE. , e57032(2018).
- Schoultz, I., Keita, ÅV. The intestinal barrier and current techniques for the assessment of gut permeability. Cells. 9, (2020).
- Yu, A. S. L., et al. Molecular basis for cation selectivity in claudin-2-based paracellular pores: Identifi cation of an electrostatic interaction site. Journal of General Physiology. 133, 111-127 (2009).
- Kimizuka, H., Koketsu, K. Ion transport through cell membrane. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 6, 290-305 (1964).
- Li, H., Sheppard, D. N., Hug, M. J. Transepithelial electrical measurements with the Ussing chamber. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis. 3, 123-126 (2004).
- Riordan, J. R., et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 245, 1066-1073 (1989).
- Smith, J. J., Karp, P. H., Welsh, M. J. Defective fluid transport by cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 93, 1307-1311 (1994).
- Molinski, S. V., et al. Orkambi and amplifier co-therapy improves function from a rare CFTR mutation in gene-edited cells and patient tissue. EMBO Molecular Medicine. 9, 1224-1243 (2017).
- Kisser, B., et al. The Ussing chamber assay to study drug metabolism and transport in the human intestine. Current Protocols in Pharmacology. 77, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1-19 (2017).
- Östh, K. The horizontal Ussing chamber method in studies of nasal drug delivery - Method Delopment and Applications Using Different Formulations. , Uppsala University. Dissertation thesis (2002).
- Guo, P., et al. Study of penetration mechanism of labrasol on rabbit cornea by Ussing chamber, RT-PCR assay, Western blot and immunohistochemistry. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 14, 329-339 (2019).
- Okabe, K., et al. Effect of Benzalkonium Chloride on transscleral drug delivery. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science. 46, 703(2005).
- Sato, T., et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett's epithelium. Gastroenterology. 141, 1762-1772 (2011).
- Kozuka, K., et al. Development and characterization of a human and mouse intestinal epithelial cell monolayer platform. Stem Cell Reports. 9, 1976-1990 (2017).
- Tamura, A., et al. Megaintestine in claudin-15-deficient mice. Gastroenterology. 134, 523-534 (2008).
- Nakayama, M., Ishizuka, N., Hempstock, W., Ikari, A., Hayashi, H. Na+-coupled nutrient cotransport induced luminal negative potential and Claudin-15 play an important role in paracellular Na+ recycling in mouse small intestine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 21, 376(2020).
- Tamura, A., et al. Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology. 140, 913-923 (2011).
- Clarke, L. L. A guide to Ussing chamber studies of mouse intestine. American Journal of Physiology - Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 296, (2009).
- Dobson, J. G., Kidder, G. W. Edge damage effect in in vitro frog skin preparations. American Journal of Physiology. 214, 719-724 (1968).
- Corman, B. Streaming potentials and diffusion potentials across rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Pflügers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 403, 156-163 (1985).
- Shen, L., Weber, C. R., Raleigh, D. R., Yu, D., Turner, J. R. Tight junction pore and leak pathways: A dynamic duo. Annual Review of Physiology. 73, 283-309 (2011).
- Frizzell, R. A., Schultz, S. G. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Journal of General Physiology. 59, 318-346 (1972).
- Otani, T., et al. Claudins and JAM-A coordinately regulate tight junction formation and epithelial polarity. Journal of Cell Biology. 218, 3372-3396 (2019).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved