A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Extraction and Visualization of Protein Aggregates after Treatment of Escherichia coli with a Proteotoxic Stressor
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes the extraction and visualization of aggregated and soluble proteins from Escherichia coli after treatment with a proteotoxic antimicrobial. Following this procedure allows a qualitative comparison of protein aggregate formation in vivo in different bacterial strains and/or between treatments.
Abstract
The exposure of living organisms to environmental and cellular stresses often causes disruptions in protein homeostasis and can result in protein aggregation. The accumulation of protein aggregates in bacterial cells can lead to significant alterations in the cellular phenotypic behavior, including a reduction in growth rates, stress resistance, and virulence. Several experimental procedures exist for the examination of these stressor-mediated phenotypes. This paper describes an optimized assay for the extraction and visualization of aggregated and soluble proteins from different Escherichia coli strains after treatment with a silver-ruthenium-containing antimicrobial. This compound is known to generate reactive oxygen species and causes widespread protein aggregation.
The method combines a centrifugation-based separation of protein aggregates and soluble proteins from treated and untreated cells with subsequent separation and visualization by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Coomassie staining. This approach is simple, fast, and allows a qualitative comparison of protein aggregate formation in different E. coli strains. The methodology has a wide range of applications, including the possibility to investigate the impact of other proteotoxic antimicrobials on in vivo protein aggregation in a wide range of bacteria. Moreover, the protocol can be used to identify genes that contribute to increased resistance to proteotoxic substances. Gel bands can be used for the subsequent identification of proteins that are particularly prone to aggregation.
Introduction
Bacteria are inevitably exposed to a myriad of environmental stresses, including low pH (e.g., in the mammalian stomach)1,2, reactive oxygen and chlorine species (ROS/RCS) (e.g., during oxidative burst in phagocytes)3,4,5, elevated temperatures (e.g., in hot springs or during heat-shock)6,7, and several potent antimicrobials (e.g., AGXX used in this protocol)8. Proteins are particularly vulnerable to any of these stressors, and exposure can provoke protein un-/misfolding that then seeds aggregation. All organisms employ protective systems that allow them to cope with protein misfolding9. However, severe stress can overwhelm the protein quality control machinery and disrupt the secondary and/or tertiary structure of proteins, which ultimately inactivates proteins. As a consequence, protein aggregates can severely impair critical cellular functions required for bacterial growth and survival, stress resistance, and virulence10. Therefore, research focusing on protein aggregation and its consequences in bacteria is a relevant topic due to its potential impact on infectious disease control.
Heat-induced protein unfolding and aggregation are often reversible7. In contrast, other proteotoxic stresses, such as oxidative stress, can cause irreversible protein modifications through the oxidation of specific amino acid side chains resulting in protein un-/misfolding and, eventually, protein aggregation4. Stress-induced formation of insoluble protein aggregates has been extensively studied in the context of molecular chaperones and their protective functions in yeast and bacteria11,12,13. Several protocols have been published that utilize a variety of biochemical techniques for the isolation and analysis of insoluble protein aggregates14,15,16,17. The existing protocols have mainly been used to study bacterial protein aggregation upon heat-shock and/or identification of molecular chaperones. While these protocols have certainly been an advancement to the field, there are some major inconveniences in the experimental procedures because they require (i) a large bacterial culture volume of up to 10 L14,17, (ii) complicated physical disruption processes, including the use of cell disruptors, French press, and/or sonication14,15,17, or (iii) time-consuming repeated washing and incubation steps15,16,17.
This paper describes a modified protocol that aims to address the limitations of the previous approaches and allows the analysis of the amount of protein aggregates formed in two different Escherichia coli strains after treatment with a proteotoxic antimicrobial surface coating. The coating is composed of metal-silver (Ag) and ruthenium (Ru)-conditioned with ascorbic acid, and its antimicrobial activity is achieved by the generation of reactive oxygen species8,18. Herein is a detailed description of the preparation of the bacterial culture after treatment with the antimicrobial compound and a comparison of protein aggregation status upon exposure of two E. coli strains with distinct susceptibility profiles to increasing concentration of the antimicrobial. The described method is inexpensive, fast, and reproducible and can be used to study protein aggregation in the presence of other proteotoxic compounds. In addition, the protocol can be modified to analyze the impact that specific gene deletions have on protein aggregation in a variety of different bacteria.
Protocol
1. Stress treatment of E. coli strains MG1655 and CFT073
- Inoculate 5 mL of lysogeny broth (LB) medium with a single colony of commensal E. coli strain MG1655 and uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) strain CFT073, respectively, and incubate for 14-16 h (overnight) at 37 °C and 300 rpm.
NOTE: Escherichia coli CFT073 is a human pathogen. Handling of CFT073 must be performed with appropriate biosafety measures in a Biosafety Level-2 certified lab. - Dilute each strain into a 500 mL flask containing 70 mL of 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS)-glucose (MOPS-g) (Table 1) medium to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) value of 0.1. Incubate at 37 °C and 300 rpm until mid-log phase is reached (OD600 = 0.5-0.55).
- Transfer 20 mL of each culture into three prewarmed 125 mL flasks and incubate at 37 °C and 300 rpm for 2 min.
NOTE: As timely processing of the samples is required, handle no more than 6 cultures at a time. - Prepare an antimicrobial compound solution in MOPS-g medium at a concentration of 2 mg/mL. Add the antimicrobial to each culture to reach the indicated concentrations. For the untreated control, add the required volume of MOPS-g medium.
NOTE: Vortex the 2 mg/mL antimicrobial solution to allow an even distribution of the compound particles and avoid sedimentation. - Incubate the cultures for 45 min at 37 °C and 300 rpm.
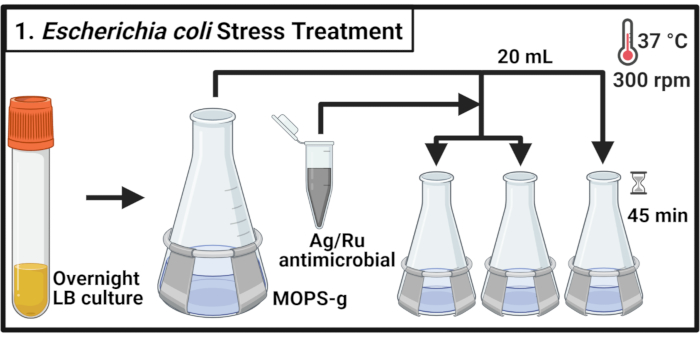
Figure 1: Escherichia coli stress treatment. Bacterial cultures are grown in MOPS-g and treated with the indicated concentrations of the silver-ruthenium-containing antimicrobial when the mid-log phase is reached. Abbreviations: LB = lysogeny broth; Ag-Ru = silver-ruthenium; MOPS-g = 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS)-glucose. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Collecting bacterial cell samples
- After 45 min of stress treatment, determine the OD600 of each culture. For each sample, harvest cells equivalent to 4 mL of OD600 = 1 in 15 mL centrifuge tubes by centrifugation for 15 min at 3,000 × g and 4 °C.
- Completely remove the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellets in 50 µL of ice-cold lysis buffer (Table 1). Incubate the samples for 30 min on ice.
NOTE: This lysis step degrades the peptidoglycan layer. Always use freshly prepared lysis buffer. - Transfer the samples into 1.7 mL microcentrifuge tubes. Freeze at -80 °C until further use.
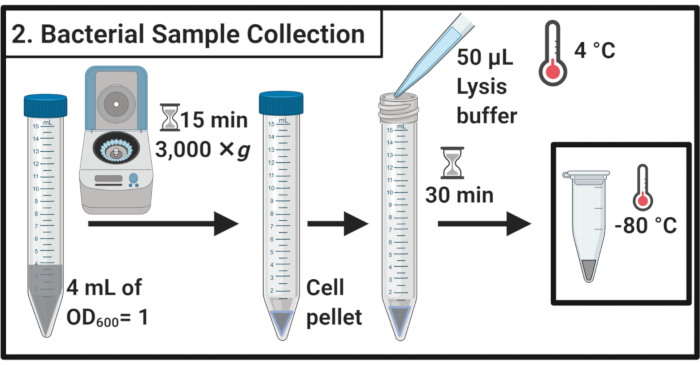
Figure 2: Bacterial sample collection. Cell samples are harvested by centrifugation and resuspended in lysis buffer followed by storage at -80 °C. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Extracting the insoluble protein aggregates
- Thaw samples on ice.
NOTE: The freeze-thaw cycle contributes to cell lysis. - Add 360 µL of ice-cold buffer A (Table 1) and mix gently by pipetting.
NOTE: The osmotic shock will also contribute to cell lysis. - Transfer the sample to a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing ~200 µL of 0.5 mm glass beads. Incubate for 30 min at 8 °C in a thermomixer with shaking at 1,400 rpm.
NOTE: This step results in the physical disruption of the cell. A protease inhibitor can be used to minimize protein degradation. The disruption can be performed at 4 °C. Note that the use of glass beads has been reported to induce aggregation of a small subset of proteins in yeast19. - Incubate for 5 min on ice without shaking to settle the glass beads. Transfer 200 µL of the cell lysate into 1.7 mL microcentrifuge tubes.
NOTE: Avoid the transfer of the glass beads. - Centrifuge at 16,000 × g and 4 °C for 20 min. Collect the supernatant, which contains soluble proteins, and proceed to section 4.
- Resuspend the pellet in 200 µL of ice-cold buffer A (Table 1) using the pipette. Centrifuge at 16,000 × g and 4 °C for 20 min. Carefully remove the supernatant altogether.
- Add 200 µL of ice-cold buffer B (see Table 1 and the Table of Materials) and carefully resuspend the pellet by pipetting.
NOTE: The non-ionic detergent solubilizes membrane protein. - Repeat the centrifugation at 16,000 × g and 4 °C for 20 min. Carefully remove the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in 200 µL of cold buffer A (Table 1) by pipetting. Centrifuge at 16,000 × g and 4 °C for 20 min. Completely remove the supernatant.
- Resuspend the pellet in 100 µL of 1x reducing SDS sample buffer (Table 1) and boil for 5 min at 95 °C in a thermomixer.
- Store the sample at -20 °C to proceed later or immediately load on an SDS polyacrylamide gel for separation.
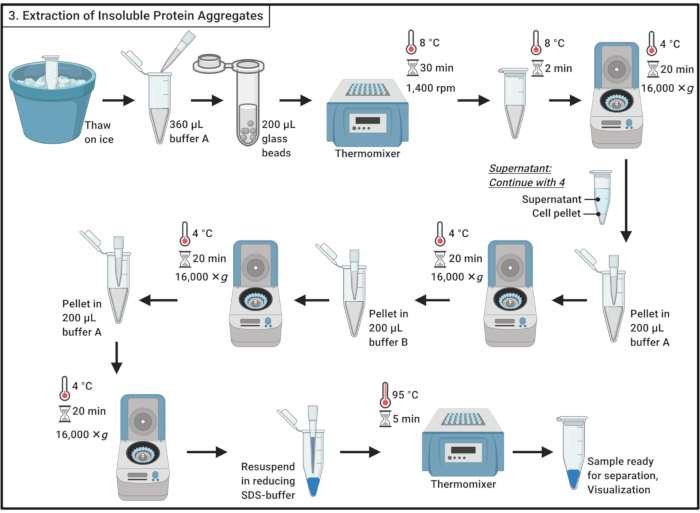
Figure 3: Extraction of insoluble protein aggregates. The extraction of protein aggregates involves a series of steps including cell disruption, the separation of protein aggregates from soluble proteins, the solubilization of membrane proteins, and washing. Abbreviation: SDS = sodium dodecyl sulfate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Soluble protein sample preparation
- Mix 1 volume of 100% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) with 4 volumes of soluble protein sample from step 3.6.
NOTE: Handling of TCA requires a fume hood and personal protective equipment and an approved waste disposal procedure. - Incubate for 10 min at 4 °C to allow for protein precipitation.
NOTE: White precipitate will appear very soon. - Centrifuge to precipitate at 21,000 × g and 4 °C for 5 min and remove the supernatant. Wash the pellet with 200 µL of ice-cold acetone to remove cellular debris. Centrifuge at 21,000 × g and 4 °C for 5 min and remove the supernatant. Repeat these actions in step 4.3 a total of three times.
- Place the microcentrifuge tubes with open lids in a thermomixer at 37 °C to remove the remaining acetone from the pellet.
NOTE: Incubation of more than 5 min may reduce the solubility of the protein pellet. - Add 100 µL of 1x reducing SDS buffer (Table 1) and completely dissolve the pellet. Boil the sample for 5 min at 95 °C.
- Store sample at -20 °C to proceed later or immediately load on an SDS polyacrylamide gel for separation.
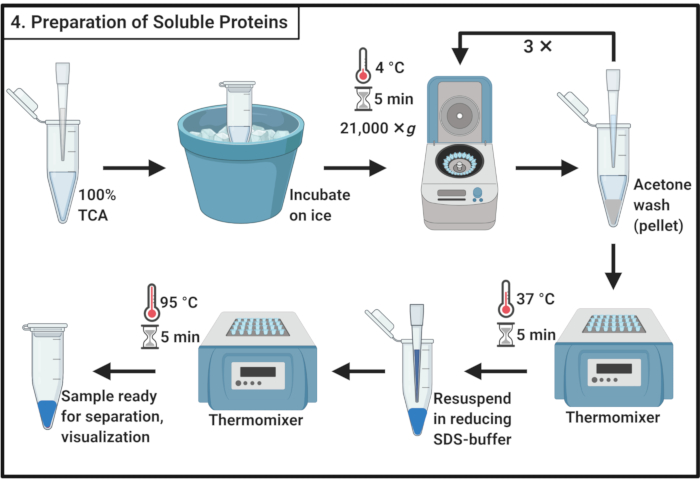
Figure 4: Preparation of soluble proteins. The preparation of soluble protein involves a precipitation step with trichloroacetic acid and repeated washing with ice-cold acetone. Abbreviations: TCA = trichloroacetic acid; SDS = sodium dodecyl sulfate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Separation and visualization of extracted protein aggregates using SDS-PAGE
- Prepare a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel.
- For two separating gels, pipette 5.1 mL of double-distilled water (ddH2O), 3.75 mL of Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 7.5 mL of 20% (w/v) SDS, 6 mL of 30% acrylamide/bisacrylamide (29:1) solution, 75 mL of 10% w/v ammonium persulfate, and 10 mL of tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) into a 15 mL centrifuge tube and mix gently without introducing air bubbles. Pour the gel using a 1 mL pipet within the glass plates, leaving the upper 2 cm free of the mixture. Add 70% ethanol on the top of the separating gel and allow an even interface between the two layers.
- After polymerization of the separating gel, prepare the stacking gel by pipetting 1.535 mL of ddH2O, 625 mL of Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 12.5 mL of 20% (w/v) SDS, 335 mL of 30% acrylamide/bisacrylamide (29:1) solution, 12.5 mL of 10% w/v ammonium persulfate, and 2.5 mL of TEMED. Remove the ethanol from the separating gels and add the stacking gel solution. Insert a comb with the desired number of pockets without introducing air bubbles. Allow polymerization for 20-30 min.
- Load 4 µL of each sample and protein ladder into separate wells and run the gel(s) in Tris-Glycine running buffer (Table 1) at 144 V for 45 min at room temperature.
NOTE: Stop the gel when the bromophenol band is about to migrate out of the gel. - Stain the gel(s) in a prewarmed Fairbanks solution A (Table 1) for 30 min on a rocker.
- Decolor the gel(s) in a prewarmed Fairbanks solution D (Table 1) until the desired background (e.g., overnight) on a rocker.
Figure 5: Protein separation and visualization. The samples are separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie staining. Abbreviation: SDS-PAGE = sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
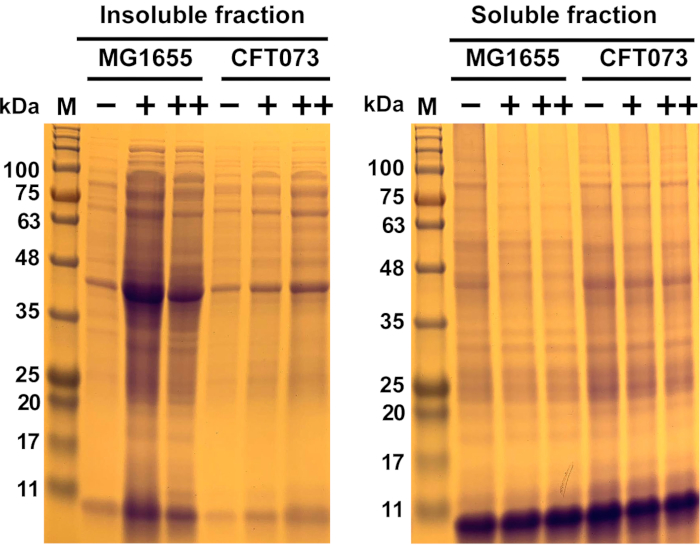
Figure 6: Representative results of antimicrobial-induced protein aggregation in commensal Escherichia coli strain MG1655 and UPEC strain CFT073. E. coli strains MG1655 and CFT073 were grown at 37 °C and 300 rpm to OD600= 0.5-0.55 in MOPS-g media before they were treated with the indicated concentrations (-, 0 mg/mL; +, ...
Discussion
This protocol describes an optimized methodology for the analysis of protein aggregate formation after treatment of different E. coli strains with a proteotoxic antimicrobial. The protocol allows the simultaneous extraction of insoluble and soluble protein fractions from treated and untreated E. coli cells. Compared to existing protocols for protein aggregate isolation from cells14,15,16,
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Illinois State University School of Biological Sciences startup funds, Illinois State University New Faculty Initiative Grant, and the NIAID grant R15AI164585 (to J.-U. D.). G.M.A. was supported by the Illinois State University Undergraduate Research Support Program (to G.M.A.). K. P. H. was supported by a RISE fellowship provided by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD). The authors thank Dr. Uwe Landau and Dr. Carsten Meyer from Largentech Vertriebs GmbH for providing the AGXX powder. Figures 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, and Figure 5 were generated with Biorender.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Chemicals/Reagents | |||
| Acetone | Fisher Scientific | 67-64-1 | |
| 30% Acrylamide/Bisacrylamide solution 29:1 | Bio-Rad | 1610156 | |
| Ammonium persulfate | Millipore Sigma | A3678-100G | |
| Benzonase nuclease | Sigma | E1014-5KU | |
| Bluestain 2 Protein ladder, 5-245 kDa | GoldBio | P008-500 | |
| β-mercaptoethanol | Millipore Sigma | M6250-100ML | |
| Bromophenol blue | GoldBio | B-092-25 | |
| Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 | MP Biomedicals LLC | 821616 | |
| D-Glucose | Millipore Sigma | G8270-1KG | |
| D-Sucrose | Acros Organics | 57-50-1 | |
| Ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) | Sigma-Aldrich | SLBT9686 | |
| Glacial Acetic acid | Millipore Sigma | ARK2183-1L | |
| Glycerol, 99% | Sigma-Aldrich | G5516-1L | |
| Glycine | GoldBio | G-630-1 | |
| Hydrochloric acid, ACS reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | 320331-2.5L | |
| Isopropanol (2-Propanol) | Sigma | 402893-2.5L | |
| LB broth (Miller) | Millipore Sigma | L3522-1KG | |
| LB broth with agar (Miller) | Millipore Sigma | L2897-1KG | |
| Lysozyme | GoldBio | L-040-25 | |
| 10x MOPS Buffer | Teknova | M2101 | |
| Nonidet P-40 | Thomas Scientific | 9036-19-5 | |
| Potassium phosphate, dibasic | Sigma-Aldrich | P3786-1KG | |
| Potassium phosphate, monobasic | Acros Organics | 7778-77-0 | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | Sigma-Aldrich | L3771-500G | |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) | Millipore Sigma | T9281-50ML | |
| Thiamine | Sigma-Aldrich | T4625-100G | |
| 100% Trichloroacetic acid | Millipore Sigma | T6399-100G | |
| Tris base | GoldBio | T-400-1 | |
| Material/Equipment | |||
| Centrifuge tubes (15 mL) | Alkali Scientific | JABG-1019 | |
| Erlenmeyer flask (125 mL) | Carolina | 726686 | |
| Erlenmeyer flask (500 mL) | Carolina | 726694 | |
| Freezer: -80 °C | Fisher Scientific | ||
| Glass beads (0.5 mm) | BioSpec Products | 1107-9105 | |
| Microcentrifuge | Hermle | Z216MK | |
| Microcentriguge tubes (1.7 mL) | VWR International | 87003-294 | |
| Microcentriguge tubes (2.0 mL) | Axygen Maxiclear Microtubes | MCT-200-C | |
| Plastic cuvettes | Fischer Scientific | 14-377-012 | |
| Power supply | ThermoFisher Scientific | EC105 | |
| Rocker | Alkali Scientific | RS7235 | |
| Shaking incubator (37 °C) | Benchmark Scientific | ||
| Small glass plate | Bio-Rad | 1653311 | |
| Spacer plates (1 mm) | Bio-Rad | 1653308 | |
| Spectrophotometer | Thermoscientific | 3339053 | |
| Tabletop centrifuge for 15 mL centrifuge tubes | Beckman-Coulter | ||
| Vertical gel electrophoresis chamber | Bio-Rad | 1658004 | |
| Vortexer | Fisher Vortex Genie 2 | 12-812 | |
| Thermomixer | Benchmark Scientific | H5000-HC | |
| 10 well comb | Bio-Rad | 1653359 |
References
- Dahl, J. -. U., et al. HdeB functions as an acid-protective chaperone in bacteria. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 290 (1), 65-75 (2015).
- Foit, L., George, J. S., Zhang, B. W., Brooks, C. L., Bardwell, J. C. A. Chaperone activation by unfolding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (14), 1254-1262 (2013).
- Sultana, S., Foti, A., Dahl, J. -. U. Bacterial defense systems against the neutrophilic oxidant hypochlorous acid. Infection and Immunity. 88 (7), 00964 (2020).
- Dahl, J. -. U., Gray, M. J., Jakob, U. Protein quality control under oxidative stress conditions. Journal of Molecular Biology. 427 (7), 1549-1563 (2015).
- Groitl, B., Dahl, J. -. U., Schroeder, J. W., Jakob, U. Pseudomonas aeruginosa defense systems against microbicidal oxidants. Molecular Microbiology. 106 (3), 335-350 (2017).
- Casadevall, A. Thermal restriction as an antimicrobial function of fever. PLoS Pathogens. 12 (5), 1005577 (2016).
- Richter, K., Haslbeck, M., Buchner, J. The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Molecular Cell. 40 (2), 253-266 (2010).
- Van Loi, V., Busche, T., Preuß, T., Kalinowski, J., Bernhardt, J. The AGXX ® antimicrobial coating causes a thiol-specific oxidative stress response and protein S-bacillithiolation in Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9, 3037 (2018).
- Anfinsen, C. B., Scheraga, H. A. Experimental and theoretical aspects of protein folding. Advances in Protein Chemistry. 29, 205-300 (1975).
- Schramm, F. D., Schroeder, K., Jonas, K. Protein aggregation in bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews. 44 (1), 54-72 (2020).
- Tomoyasu, T., Mogk, A., Langen, H., Goloubinoff, P., Bukau, B. Genetic dissection of the roles of chaperones and proteases in protein folding and degradation in the Escherichia coli cytosol. Molecular Microbiology. 40 (2), 397-413 (2001).
- Gray, M. J., et al. Polyphosphate is a primordial chaperone. Molecular Cell. 53 (5), 689-699 (2014).
- Weids, A. J., Ibstedt, S., Tamás, M. J., Grant, C. M. Distinct stress conditions result in aggregation of proteins with similar properties. Scientific Reports. 6, 24554 (2016).
- Mogk, A., et al. Identification of thermolabile Escherichia coli proteins: prevention and reversion of aggregation by DnaK and ClpB. EMBO Journal. 18 (24), 6934-6949 (1999).
- Fay, A., Glickman, M. S. An essential nonredundant role for mycobacterial DnaK in native protein folding. PLoS Genetics. 10 (7), 1004516 (2014).
- Schramm, F. D., Heinrich, K., Thüring, M., Bernhardt, J., Jonas, K. An essential regulatory function of the DnaK chaperone dictates the decision between proliferation and maintenance in Caulobacter crescentus. PLoS Genetics. 13 (12), 1007148 (2017).
- Maisonneuve, E., Fraysse, L., Moinier, D., Dukan, S. Existence of abnormal protein aggregates in healthy Escherichia coli cells. Journal of Bacteriology. 190 (3), 887-893 (2008).
- Heiss, A., Freisinger, B., Held-Föhn, E. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver-ruthenium coated hollow microparticles. Biointerphases. 12 (5), (2017).
- Papnayotou, I., Sun, B., Roth, A. F., Davis, N. G. Protein aggregation induced during glass bead lysis of yeast. Yeast. 27 (10), 801-816 (2010).
- Chuang, S. E., Blattner, F. R. Characterization of twenty-six new heat shock genes of Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology. 175 (16), 5242-5252 (1993).
- Imlay, J. A. The molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences of oxidative stress: Lessons from a model bacterium. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 11 (7), 443-454 (2013).
- Mühlhofer, M., et al. The heat shock response in yeast maintains protein homeostasis by chaperoning and replenishing proteins. Cell Reports. 29 (13), 4593-4607 (2019).
- Chandrangsu, P., Rensing, C., Helmann, J. D. Metal homeostasis and resistance in bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 15, 338-350 (2017).
- Stevens, M., et al. HSP60/10 chaperonin systems are inhibited by a variety of approved drugs, natural products, and known bioactive molecules. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 29 (9), 1106-1112 (2019).
- Schramm, F. D., Schroeder, K., Alvelid, J., Testa, I., Jonas, K. Growth-driven displacement of protein aggregates along the cell length ensures partitioning to both daughter cells in Caulobacter crescentus. Molecular Microbiology. 111 (6), 1430-1448 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved