A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Step-by-Step Stapedotomy through Transcanal Exclusive Endoscopic Approach
In This Article
Summary
The aim of this article is to provide a step-by-step method for endoscopic stapes surgery from operating room setting and patient positioning to post-operative care. This work would represent a guide for any otologic surgeon who is willing to treat otosclerosis with endoscopic transcanal technique.
Abstract
In recent years there has been an increasing trend in the use of the endoscope to treat a variety of middle ear pathologies, including otosclerosis. Several studies comparing traditional microscopic and endoscopic stapes surgery have reported similar hearing results and an overall low rate of complications. The endoscope has unraveled its full potential in demanding settings of stapes surgery, such as unfavorable anatomy of the oval window niche or revision cases. Reduced manipulation of the chorda tympani and low rate of post-operative dysgeusia are further benefits to mention for endoscopic stapes surgery.
Being a one-handed technique, management of bleeding, positioning, and crimping of the prosthesis may be challenging for novice endoscopic surgeons, so some training in endoscopic ear surgery is recommended before performing endoscopic stapedotomy. The problem of sharing the surgical field between the endoscope and the operating instruments could be easily overcome if proper instruments positioning is understood. One-handed bleeding control in the narrow space of the ear canal may represent an issue during the elevation of the tympano-meatal flap, possibly discouraging the surgeon since the preliminary steps of surgery. Following appropriate technique to raise the flap and the collaboration with the anesthesiology team in keeping the blood pressure low guarantee an adequate bleeding control in most cases.
The aim of this article is to describe the entire surgical procedure of a transcanal exclusive endoscopic stapedotomy, from operating room set up and patient positioning to post-operative care. A step-by-step description of the surgical maneuvers with technical hints is reported, to guide the surgeon across the procedure and allow any ear surgeon to perform stapes surgery endoscopically.
Introduction
The use of the endoscope in ear surgery has gradually increased since its first application in the 1990s, to treat a variety of middle ear pathologies, including otosclerosis1. As compared to the microscope, the endoscope guarantees a wide field of exposure, high magnification and resolution images, reduced bone removal and a significantly improved quality of life after surgery2,3,4.
The use of one hand has been mentioned as a limitation of the endoscopic technique, especially in functional procedures such as the stapes surgery5,6. However, a growing number of papers have shown that endoscopic stapes surgery (EStS) is feasible, safe, and has favorable outcomes, similar to the traditional stapedotomy7,8. Moreover, the endoscope has unraveled its full potential especially in patients with unfavorable anatomy or in revision cases, representing a valuable tool to support the surgeon in these demanding settings9,10. Limited manipulation of the chorda tympani and low rate of post-operative dysgeusia are further benefits of this technique11.
EStS could be challenging for surgeons who do not have much experience in the use of the endoscope. The problem of sharing the surgical field between the endoscope and the operating instruments could be easily overcome if proper instruments handling is understood. One-handed bleeding control in the narrow space of the external auditory canal (EAC) and the tympanic cavity could be frustrating for a novice surgeon12,13. Moreover, it is important to properly position the patient and set up the operating room in order to guarantee a comfortable setting for the surgeon across the entire operation.
The aim of this article is to show the surgical procedure of a transcanal exclusive endoscopic stapedotomy, from operating room set up and patient positioning to post-operative care. A step-by-step description of the procedure is reported, to allow any ear surgeon to understand and possibly reproduce such intervention.
We report the case of a 56-year-old female who underwent right transcanal EStS for bilateral otosclerosis. The patient reported slowly progressing and bilateral hearing loss (HL), without vertigo or tinnitus. While the right otoscopy was normal, the audiometric test demonstrated a right moderate mixed HL, with a mean preoperative bone conduction-pure tone average (BC-PTA) of 24 dB, a mean preoperative air-conduction pure tone average (AC-PTA) of 71 dB, and a mean preoperative air-bone gap (ABG) of 47 dB. The tympanogram was bilateral type A and stapedial reflexes were absent. No CT scan was deemed necessary as preoperative assessment.
Protocol
This research has been conducted in accordance with ethical principles, including the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki (2002) and the institutional human research ethics committee's guidelines (Comitato Etico dell'Area Vasta Emilia Nord). The local ethical committee does not perform a formal ethical assessment for case reports.
1. Preparation of the patient
- After oro-tracheal intubation and general anesthesia, position the patient supine with the head tilted toward the opposite side of the affected ear, and the chin slightly hyperextended. Pull down the same-side shoulder as much as possible, to create a wide angle between the head and the shoulder allowing easier access to the ear.
- Using a 5 mL syringe with G25 0.50 x 42 mm needle, inject around 1-2 mL of local anesthetic diluted with a vasoconstrictor agent (e.g., 2% mepivacaine and epinephrine 1:200,000) in the four main points of the EAC skin (posterior wall, superior and inferior angle, retrotragal region).
2. Preparation of the sterile surgical site
- Use an iodopovidone-soaked gauze to sterilize the whole external ear, to create an aseptic field.
- Ensure that iodopovidone enters the EAC and reaches the tympanic membrane.
3. Preparation of the operating room and surgical instruments
- Place the endoscopic tower or a high-resolution monitor when available, in front of the surgeon, at his/her eye level, at adequate distance to keep a comfortable position of the head and neck during the surgery.
- Connect a 3 mm diameter, 14 cm length, 0° rigid endoscope to the high-definition digital camera and xenon light source. Keep the light source at 50% intensity to prevent heat damage to the inner ear.
- Perform white balance by pushing the central button on the camera head and adjust the focus by turning its gray wheel before starting the surgery.
- Prepare a quality de-misting (anti-fog) solution to clean the endoscope tip. Dip a cotton pad in this solution and place it close to the external ear.
NOTE: The standard otological instruments set for stapes surgery is prepared on the instrument table, as shown in Figure 1.
4. Surgical steps
NOTE: Hold the endoscope with the non-dominant hand, leaning it against the posterior wall of the EAC, and the surgical instruments with the dominant one. Surgical instruments, if any, should be introduced in the EAC before the endoscope and moved toward the middle ear under endoscopic vision, to prevent accidental damage to the external and middle ear structures. It is advisable to keep any working instrument above the endoscope and stabilize its movement keeping the fourth and fifth fingers on the patient's head (Figure 2).
- Under direct endoscopic vision, perform anesthesia by slowly injecting another 1-2 mL of local anesthetic diluted with a vasoconstrictor agent (e.g., 2% mepivacaine and epinephrine 1:200,000) in the subperiosteal plane of the posterior wall of the EAC.
- Use scissors to cut hair of the most lateral part of the EAC, to avoid contaminating the tip of the endoscope at each in and out passage of the canal.
- Use the monopolar (molecular resonance hook) with 15 W power to delineate the tympano-meatal flap (TMF) incision from 5 to 12 o'clock, about 8 to 10 mm far from the annulus (modified Rosen incision).
- Use the round knife to perform the actual skin incision following the previously marked line and raise the TMF with the help of epinephrine-soaked cottonoids.
- Once the annulus is identified as a white thickening of the tympanic membrane, continue the dissection under it. Detach the pars flaccida from the short process of the malleus with Hartmann forceps, keeping the pars tensa adherent to the umbus.
NOTE: During this step, identify the chorda tympani as a whitish string emerging from the chordal eminence, and leave it untouched. - Remove the posterior wall of the EAC and the scutum through the curette to achieve a good exposure of the oval window region. In some cases, even if the oval window region is fully exposed, some curettage is necessary to create a favorable working area on the stapes. Displace the chorda tympani medially with a hook to further expose the footplate.
NOTE: Take some time to inspect the middle ear anatomy to check the important anatomical landmarks, such as the facial nerve, which could be dehiscent and/or prolapsed onto the footplate, as in the present case. - Check the ossicular chain by gently pushing the stapes and the malleus with a hook, and confirm stapes fixation.
- Use the microdrill with a 0.6 mm diamond burr to perform posterior crurotomy. Then, create a hole in the mid or posterior portion of the footplate.
- Cut the stapedial tendon with Bellucci scissors. Then, disarticulate the incus from the stapes with the help of a hook and remove the stapes superstructure.
NOTE: Avoid using suction on the hole to prevent perilymphatic fluid removal and minimize post-operative vertigo or inner ear damage. - Use the Fisch hook to regularize the footplate hole and check its adequate calibration, as well as to remove possible small bone fragments from the vestibule.
- Insert the stapes prosthesis (0.6 mm x 4.75 mm - total length 5.75 mm platinum/polytetrafluoroethylene prosthesis) into the EAC using the suction tube.
- Gently position it into the footplate hole with the hook. Crimp the prosthesis hook after anchoring it to the long process of the incus.
- Check the proper movement of the prosthesis, by gently pushing on the handle of the malleus.
- Replace the TMF and pack the EAC with resorbable hemostatic pledgets.
5. Ear dressing
- Cover the auricle with an adhesive plaster. No compression is needed.
6. Post operative care
- Allow the patient to drink, eat, and stand up at least 8 h post-operatively, if no nausea or vomiting occurred.
- The following day assess the facial nerve function, using the House-Brackman scale14 and the presence of spontaneous nystagmus with Frenzel googgles. Perform bone conduction pure tone audiometry to exclude sensorineural HL15.
NOTE: A two week-follow up visit is planned to remove residual pledgets of hemostatic material and check the healing process. Complete audiometric evaluation and otoendoscopy are usually performed between 1 to 2 months post-operatively.
Results
The patient had a normal post-operative course, without facial palsy or vertigo. The 6-month post-operative hearing test16 is shown in Figure 3. The otoendoscopy showed regular healing of the tympanic membrane. The patient denied any taste impairment.
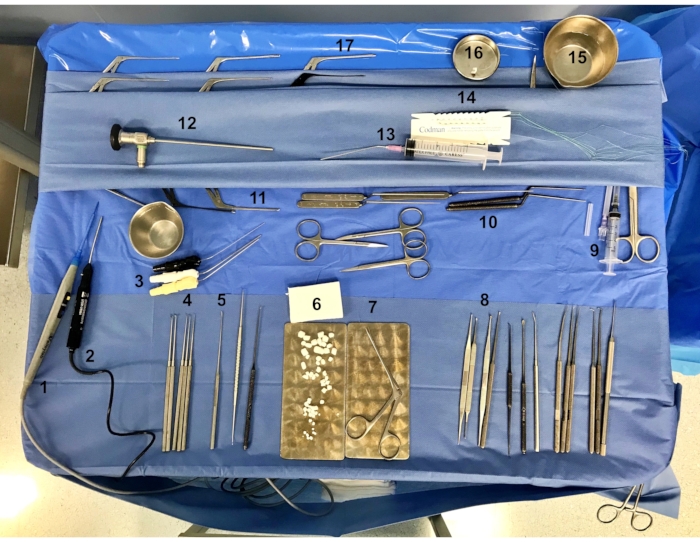
Figure 1: Standard otologi...
Discussion
A protocol for totally EStS is herein proposed, to guide any otologic surgeon in performing stapes surgery endoscopically.
The first surgical step (elevation of the TMF) could be the bloodiest phase of the whole procedure, and it represents a challenge for the surgeon in relation to one-hand bleeding control13. Moreover, in otosclerosis cases, the tympanic membrane is intact; so maximal care should be paid not to damage it. As reported in our protocol, some technical hi...
Disclosures
All the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
None.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Antifog solution | GOLFF | ||
| Aspirator system (40L/min power) | EXTRUDAN SURGERY APS | 4m long, dimeter ch25 | |
| Cold light source with cable | STORZ | ||
| Consumables: - Iodopovidone solution - Epinephrine - Sterile water to rinse - Spongostan (adsorbable hemostatic sponge) | ETHICON INC. | ||
| Cotton pads | FARMAC ZABBAN | 10x10cm | |
| Cottonoid pledgets | CODMAN | 10 surgical patties | |
| Endoscope | STORZ | 3mm diameter, 15cm length, 0° | |
| Local anesthetic with vasoconstrictor in sterile and non-sterile syringe | GALENICA SENESE | 10 vials x 5ml | |
| Otologic set instruments | STORZ | round knife, hook, curette, Bellucci scissors and Hartmann forceps, suction tubes | |
| Skeeter Drill | MEDTRONIC | 0.6 mm diamond burr | |
| Stapes prosthesis | SPIGGLE & THEIS | 0.6x4.75mm | |
| Surgical scrub set for otologic patients | EURONDA | ||
| Surgical scrub set for operating surgeon | EURONDA | ||
| Surgical scrub set for nurse | EURONDA | ||
| Vesalius molecular resonance electrosurgical unit | TELEA ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING | ||
| Video equipment: 4K Camera - HD screen - Video processor (Image 1S system) | STORZ |
References
- Manna, S., Kaul, V. F., Gray, M. L., Wanna, G. B. Endoscopic versus microscopic middle ear surgery: A meta-analysis of outcomes following tympanoplasty and stapes surgery. Otology & Neurotology. 40 (8), 983-993 (2019).
- Das, A., Mitra, S., Ghosh, D., Sengupta, A. Endoscopic stapedotomy: Overcoming limitations of operating microscope. Ear, Nose & Throat Journal. 100 (2), 103-109 (2021).
- Marchioni, D., et al. Complications in endoscopic ear surgery. Otology & Neurotology. 39 (8), 1012-1017 (2018).
- Lucidi, D., et al. Disease-specific quality of life and psychological distress after endoscopic tympanoplasty. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 279 (1), 191-198 (2021).
- Lucidi, D., et al. Does microscopic experience influence learning curve in endoscopic ear surgery? A multicentric study. Auris, Nasus, Larynx. 48 (1), 50-56 (2020).
- Kozin, E. D., et al. Systematic review of outcomes following observational and operative endoscopic middle ear surgery. The Laryngoscope. 125 (5), 1205-1214 (2015).
- Lucidi, D., Molinari, G., Reale, M., Alicandri-Ciufelli, M., Presutti, L. Functional results and learning curve of endoscopic stapes surgery: A 10-year experience. The Laryngoscope. 131 (4), 885-891 (2020).
- Fang, L., Xu, J., Wang, W., Huang, Y. Would endoscopic surgery be the gold standard for stapes surgery in the future? A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 278 (4), 925-932 (2021).
- Fernandez, I. J., et al. The role of endoscopic stapes surgery in difficult oval window niche anatomy. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 276 (7), 1897-1905 (2019).
- Fernandez, I. J., Villari, D., Botti, C., Presutti, L. Endoscopic revision stapes surgery: surgical findings and outcomes. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 276 (3), 703-710 (2019).
- Molinari, G., et al. Taste impairment after endoscopic stapes surgery: do anatomic variability of chorda tympani and surgical technique matter. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. , (2021).
- Alicandri-Ciufelli, M., et al. Rating surgical field quality in endoscopic ear surgery: proposal and validation of the Modena Bleeding Score. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 276 (2), 383-388 (2019).
- Anschuetz, L., et al. Management of bleeding in exclusive endoscopic ear surgery: Pilot clinical experience. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. 157 (4), 700-706 (2017).
- House, J. W., Brackmann, D. E. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. 93 (2), 146-147 (1985).
- Marchioni, D., et al. Complications in endoscopic ear surgery. Otology & Neurotology. 39 (8), 1012-1017 (2018).
- Campbell, K. C. The basic audiologic assessment. Essential Audiology for Physicians. , (1998).
- Alicandri-Ciufelli, M., et al. Epinephrine use in endoscopic ear surgery: Quantitative safety assessment. ORL. 82 (1), 1-7 (2020).
- Anschuetz, L., et al. Discovering middle ear anatomy by transcanal endoscopic ear surgery: A dissection manual. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (131), e56390 (2018).
- Altamami, N. M., et al. Is one of these two techniques: CO2 laser versus microdrill assisted stapedotomy results in better post-operative hearing outcome. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 276 (7), 1907-1913 (2019).
- Alicandri-Ciufelli, M., et al. Acquisition of surgical skills for endoscopic ear and lateral skull base surgery: A staged training programme. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica. 38 (2), 151-159 (2018).
- Anschuetz, L., et al. An ovine model for exclusive endoscopic ear surgery. JAMA Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery. 143 (3), 247-252 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved