A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation of Primary Patient-specific Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells and Semiquantitative Real-time Contraction Measurements In Vitro
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This paper describes an explant culture-based method for the isolation and culturing of primary, patient-specific human aortic smooth muscle cells and dermal fibroblasts. Furthermore, a novel method is presented for measuring cell contraction and subsequent analysis, which can be used to study patient-specific differences in these cells.
Abstract
Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) are the predominant cell type in the aortic media. Their contractile machinery is important for the transmission of force in the aorta and regulates vasoconstriction and vasodilation. Mutations in genes encoding for the SMC contractile apparatus proteins are associated with aortic diseases, such as thoracic aortic aneurysms. Measuring SMC contraction in vitro is challenging, especially in a high-throughput manner, which is essential for screening patient material. Currently available methods are not suitable for this purpose. This paper presents a novel method based on electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS). First, an explant protocol is described to isolate patient-specific human primary SMCs from aortic biopsies and patient-specific human primary dermal fibroblasts for the study of aortic aneurysms. Next, a detailed description of a new contraction method is given to measure the contractile response of these cells, including the subsequent analysis and suggestion for comparing different groups. This method can be used to study the contraction of adherent cells in the context of translational (cardiovascular) studies and patient and drug screening studies.
Introduction
Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) are the predominant cell type in the aortic medial layer, the thickest layer of the aorta. Within the wall, they are radially oriented and are involved in, among other functions, vasoconstriction and vasodilation1. The SMC contractile machinery is involved in the transmission of force in the aorta through the functional link with the extracellular matrix2. Mutations in genes encoding for the proteins of the SMC contractile apparatus, such as smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (MYH11) and smooth muscle actin (ACTA2), have been related to cases of familial thoracic aortic aneurysms, underscoring the relevance of SMC contraction in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of the aorta1,2. Furthermore, mutations in the TGFβ signaling pathway are also associated with aortic aneurysms, and their effects in aortic aneurysm pathophysiology can also be studied in skin fibroblasts3.
High-throughput measurement of SMC contraction in vitro is challenging. As SMC contractility cannot be measured in vivo in humans, in vitro assays on human cells present a feasible alternative. Moreover, abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) development in animal models is either chemically induced by, for example, elastase perfusion, or caused by a specific mutation. Therefore, animal data are not comparable to AAA development in humans, which mostly has a multifactorial cause, such as smoking, age, and/or atherosclerosis. In vitro SMC contractility has so far been mainly measured by traction force microscopy4,5, quantification of Fura-2 fluorescence intracellular calcium fluxes6, and collagen wrinkling assays7. While traction force microscopy provides invaluable numeric insight into the forces generated by a single cell, it is not suitable for high-throughput screening due to the complex mathematical data processing and the analysis of one cell at a time, meaning that it is very time-consuming to measure a representative number of cells per donor. Fura-2 dye and collagen wrinkling assays allow the superficial determination of contraction and do not give a precise numerical output, making them less suitable for discriminating patient-specific differences. Impaired SMC contraction in cells derived from the aorta of abdominal aortic aneurysm patients was demonstrated for the first time by optimizing a novel method for measuring SMC contraction in vitro8. This was done by repurposing the electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) method. ECIS is a real-time, medium-throughput assay for the quantification of adherent cell behavior and contraction9,10,11 such as SMC growth and behavior in wound-healing and migration assays12,13,14. The exact method is described in the protocol section. In this optimized way, the ECIS can also be used to study fibroblast contraction due to their similar size and morphology.
The aim of this paper is to provide a stepwise description of the method for measuring SMC contraction in vitro using ECIS8 and comparing the contraction between control and patient SMCs. First, the isolation and culturing of primary SMCs from control and patient aortic biopsies is explained, which can be used for contraction measurement. Second, contraction measurements and analysis, alongside the verification of SMC marker expression, are described. Furthermore, this paper describes the method for the isolation of patient-specific dermal fibroblasts whose contraction can be measured using the same methodology. These cells can be used for patient-specific studies focused on aortic aneurysm or other cardiovascular pathologies15 or prognostic studies using a transdifferentiation protocol that allows contraction measurement prior to aneurysm surgery16.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
NOTE: Aortic biopsies were obtained during open aneurysm repair in Amsterdam University Medical Centers, VU University Medical center, Amsterdam, Zaans Medisch Centrum, Zaandam and Dijklander hospital, Hoorn, the Netherlands. Control aortic tissue was obtained from the piece of the aorta attached to the renal artery harvested for kidney transplants. Only patients above the age of 18 were included, and all patients gave their informed consent to participate in the study. All material was collected in accordance with the regulations of the WMA Declaration of Helsinki and institutional guidelines of the Medical Ethical Committee of the VU Medical Center. All the experiments and experimental protocols were performed in accordance with institutional guidelines and approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of the VU Medical Center. For complete information about the control and patient cell lines used, refer to 8.
1. Isolating primary human SMCs from aortic biopsies
NOTE: Perform the following steps under a sterile tissue culture laminar flow hood. Wear gloves and use standard aseptic techniques when handling human blood and human tissue samples. SMCs are cultured in 231 Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Basal Medium supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and Smooth Muscle Growth Supplement referred to as SMC medium.
- Sterilize two pairs of surgical forceps and a scalpel by immersing them in 70% ethanol and subsequently wiping them dry.
- Pipette 2 mL of SMC medium in a Petri dish in which the tissue dissection will be performed.
- Pipette 2.5 mL of SMC medium into two T25 flasks. Swirl the flasks around so that the small volume of medium covers the whole surface.
- Transport the harvested human aortic wall biopsy from the operating room to the laboratory on ice in a sterile plastic tube with cold, sterile tissue transfer solution (see the Table of Materials) or 0.9% NaCl.
- Open the tube with the tissue inside the tissue culture hood. Take the biopsy out of the tube using the sterilized forceps and place it in the Petri dish (Figure 1A).
- Visually inspect the biopsy to identify the three aortic layers, the tunica intima (inner), media (middle), and adventitia (outer layer). Look for the presence of atherosclerotic plaques on the intima side and slimy connective tissue on the adventitial side (Figure 1B) to distinguish the layers.
- To isolate SMCs from the media, remove the other two layers. Place the tissue with the intima plaque side up first (Figure 1B). Remove the solid plaque by pulling it away from the tissue with forceps while pushing the tissue down with the other pair of forceps. Remove subsequent layers of plaque until the pink, uniform medial layer is visible.
- Flip the tissue (Figure 1C). Repeat the same procedure, as in step 1.7, by pulling off the adventitial layer (Figure 1D). Be sure to remove all visible parts in as many attempts as needed, as this layer will not detach from the media easily.
NOTE: It is essential that the intimal and adventitial layers be removed properly to obtain as clean an SMC population as possible. - Once the medial layer is isolated, cut the tissue into cubes of approximately 1 mm x 1 mm x 1 mm. Press the media down with forceps and cut the tissue in one direction using the scalpel. Do not cut back and forth; make clean, unidirectional cuts to minimize damage. Try to make as many cubes as possible, given the size of the biopsy (Figure 1E).
- Place the tissue pieces in the upper quarter of the T25 flask using the forceps. Place 10-20 cubes per flask if the amount of material allows it (Figure 1F).
NOTE: Use smooth forceps to minimize adhesion of the tissue to the ribs of the forceps and easily detach the tissue into the flask. - Incubate the tissue cubes in the T25 flasks for approximately 10 days at 5% CO2 at 37 °C in an incubator.
NOTE: First cell outgrowth is expected around that time. The cells that initially migrate might look smaller than normal SMCs. - Once cell growth is observed, add 2.5 mL of medium to the flask, making sure not to pipette it onto the tissue pieces to prevent them from detaching.
- After approximately 5 more days, when clusters of cells are observed around the tissue pieces, change the culture medium. If tissue pieces detach, remove them as they will not reattach.
- Once the cells are 80-90% confluent, transfer them to a T75 flask and continue culturing in this format.
NOTE: A 1:2 or 1:3 split ratio is recommended. Freeze a backup of the cells at an early passage. The cells generally maintain their properties until passage 10; later passages should not be used for experiments.
2. Isolating primary dermal fibroblasts from skin biopsies
NOTE: Perform the following steps under a sterile tissue culture laminar flow hood. Wear gloves and use standard aseptic techniques when handling human blood and human tissue samples. Fibroblasts are cultured in Basal Medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin, referred to as fibroblast medium.
- Sterilize two pairs of surgical forceps and a scalpel by dipping them in 70 % ethanol and subsequently wiping them dry.
- Pipette 2 mL of fibroblast medium in a Petri dish in which the tissue dissection will be performed.
- Pipette 2.5 mL of fibroblast medium into two T25 flasks. Swirl the flasks around so that the small volume of medium covers the whole surface.
- Transport the harvested skin biopsy from the operating room to the laboratory on ice in cold, sterile tissue transfer solution (see the Table of Materials) or 0.9% NaCl in a sterile plastic tube.
- Open the tube with the tissue inside the tissue culture hood. Take the biopsy out of the tube using the sterilized forceps and place it in the Petri dish (Figure 2A).
- Visually inspect the biopsy to identify the three skin layers, the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat. Look for a recognizable skin surface, sometimes with visible hair, to identify the epidermis. On the opposite side, look for the subcutaneous fat, which is often yellow and slimy. Identify the layer between the epidermis and the subcutaneous fat as the dermis-the source of viable fibroblasts (Figure 2B).
- To isolate fibroblasts from the dermis, remove the other two layers and place the tissue on its side so that all three layers are visible.
NOTE: Unlike the aortic tissue, skin layers cannot be pulled apart from each other; hence, they must be cut. The tissue is also more rubbery, making it more difficult to cut. Use a sharp scalpel. - Hold the tissue down with forceps. Cut in parallel to the border between the epidermis and dermis. Cut away the whole epidermis. Try to cut in one clean line and do not move back and forth to avoid tissue damage.
- Flip the tissue. Repeat the same procedure as in step 2.8; this time, cut within the dermis parallel to the border with the subcutaneous fat.
- Once the dermis is isolated, cut the tissue into cubes approximately 1 x 1 x 1 mm3. Press the tissue down with forceps and cut the tissue in one direction using the scalpel. Do not cut back and forth; make clean, unidirectional cuts to minimize damage. Try to make as many cubes as possible, given the size of the biopsy (Figure 2C).
- Place the tissue pieces in the upper quarter of the T25 flask using the forceps. Place 10-20 cubes per flask if the amount of material allows it (Figure 2D).
NOTE: Use smooth forceps to minimize the adhesion of the tissue to the ribs of the forceps and easily detach the tissue into the flask. - Incubate the tissue cubes in the T25 flasks for approximately 10 days at 5% CO2 at 37 °C in an incubator.
NOTE: First cell outgrowth is expected around then. The cells that initially migrate might look smaller than normal fibroblasts. - Once cell growth is observed, add 2.5 mL of medium to the flask, making sure not to pipette it onto the tissue pieces to prevent them from detaching.
- After approximately 5 more days, when clusters of cells can be observed around the tissue pieces, change the culture medium. If tissue pieces detach, remove them as they will not reattach.
- Once the cells are 80-90% confluent, transfer them to a T75 flask and continue culturing in this format.
NOTE: A 1:2 or 1:3 split ratio is recommended. Freeze a backup of the cells at an early passage. The cells generally maintain their properties until passage 10; later passages should not be used for experiments.
3. Measuring contraction (example SMCs)
- Prepare a 96w10e ECIS array (see Figure 3A for a representative image of the array with magnified electrodes and cells seeded on the electrodes).
NOTE: Perform the following steps under a sterile tissue culture laminar flow hood.- Coat a sterile 96w10e array with 200 µL of 10 mM L-cysteine per well for 30 min at room temperature.
- Wash the plate twice with sterile water. Let the plate dry overnight in the tissue culture hood with the lid slightly open.
NOTE: Coating the plate with L-cysteine is only necessary when using the plate for the first time. - The next day, UV-sterilize plate and lid for 30 min. Turn the lid upwards so that the inside is sterilized. Once the plate is sterilized, do not open the plate outside the flow hood.
- Seeding cells on the ECIS array
- Prewarm 1% sterile gelatin solution in the water bath for 30 min.
NOTE: The solution is stored in the fridge and might solidify, making it difficult to pipette. - Subsequently, coat the wells with 100 µL of the 1 % gelatin solution per well and incubate the plate at 37 °C for at least 1 h.
- Aspirate the gelatin from the wells.
- Count the cells using an automated cell counter and seed the SMCs in triplicate at a seeding density of 30,000 cells/well in 200 µL of SMC medium.
- Place the plate with the SMCs into the ECIS 96-well holder in the cell culture incubator. Double-click on the ECIS Applied Biophysics software to open the program and press the Setup button.
- Check if all the electrodes have contact with the holder (green; red if no connection) in the left lower panel labeled Well Configuration. If the electrodes are not properly connected, adjust the plate in the holder before starting the measurement.
- Select the plate type (96-well array) in the same panel by clicking Array type.
- In the right upper panel Data Collection Setup, click on single frequency and change the impedance value to 4000 Hz and the interval to 8 s.
- Click the Start button to start measurements. Wait for a new panel to open, where the ECIS file can be saved.
- Allow the cells to attach and establish a monolayer for 48 h.
NOTE: The attachment and spreading of cells on the electrodes generate a baseline resistance value (Figure 3B).
- Prewarm 1% sterile gelatin solution in the water bath for 30 min.
- Stimulation of cells to induce contraction
- Induce SMC contraction by stimulating the cells with 10 µg/mL of the calcium ionophore, ionomycin.
NOTE: Ionomycin will induce the influx of extracellular Ca2+, activating the contractile cascade; see Figure 4A for representative images of non-stimulated and stimulated contracted cells. - Dilute 1 mg of ionomycin powder in 100 µL of dimethylsulfoxide to make a stock solution of 10 mg/mL, and store 10 µL aliquots at -20 °C. Before use, dilute the ionomycin solution 1:10 in SMC medium to prepare the working solution to be added to the cells.
- Perform the cell stimulation while the array is still in the array holder inside the cell culture incubator and the electrodes are attached to the system.
- To stimulate the cells, remove the lid and place it on a sterile surface inside the incubator. Prepare two pipettes, set at 2 µL and 150 µL.
- Before starting the stimulation, press Mark in the software and place a comment.
NOTE: This will make it easier to find the exact timing of the stimulation when analyzing the data. - Pipette 2 µL of the ionomycin working solution into each well as quickly as possible. Once all the cells have been stimulated, mix the medium in the wells using the second pipette.
NOTE: Due to the rapid effects, it is not necessary to change tips between different cell lines and conditions. Work quickly while stimulating and mixing because the ionomycin has an acute effect. When stimulating a full plate, stimulate a maximum of 3 columns at once. After every stimulation, wait at least 30 min until the next stimulation to let the cells recover from the temperature and CO2 change caused by the opening of the incubator door. - Directly after the stimulation is done, press Mark again to add a comment that the stimulation is done.
- Finishing the stimulation experiment
- Record the impedance values for approximately 5 min after the ionomycin stimulation. Finish the recording by pressing Finish.
- Reuse the ECIS arrays up to three times: wash the wells twice with sterile water, and incubate the plate at 37 °C for 2-3 h with trypsin or a similar reagent. Repeat steps 3.1.2 and 3.1.3.
- Induce SMC contraction by stimulating the cells with 10 µg/mL of the calcium ionophore, ionomycin.
- Exporting the data
- To export the data, click File | Export data | To Excel (Selected). Select a folder to save the file.
- Click Separate when the program asks to combine or separate sheets.
- Analyzing the contractile output
- To calculate the contractile response, use the following equation (1), where C indicates contraction (expressed in % of change compared to baseline), prestimulation (PrS) indicates the resistance value (expressed in Ω) just before ionomycin stimulation and post-stimulation (PoS) indicates the resistance (expressed in Ω) 2 min after finishing the stimulation.
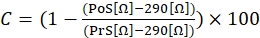 (1)
(1)
NOTE: As shown in equation (1), the impedance value of a well filled with culture medium without any attached cells (value of 290 Ω) is subtracted from all the results in the final calculation. It is recommended to measure contractile responses in triplicate in each experiment and perform three independent experiments with the same cell line to account for any inter- and intra-experimental variation. - Once the three independent experiments have been performed, group the data together by calculating the average of the three measurements, including the standard deviation (SD).
- To calculate the contractile response, use the following equation (1), where C indicates contraction (expressed in % of change compared to baseline), prestimulation (PrS) indicates the resistance value (expressed in Ω) just before ionomycin stimulation and post-stimulation (PoS) indicates the resistance (expressed in Ω) 2 min after finishing the stimulation.
- Comparing different groups
- To define the range of normal contraction and investigate subsequent specific research questions, use the control group to define "normal contraction" and compare it to the contractile response of patients or treatment groups.
- Calculate the mean and SD of the whole control group, i.e., of the end values for all cell lines, as described in step 3.5.2.
- Use the range of the mean ± 2SD to identify cells in the other group that fall outside this range, indicating that they have an altered contractile response.
NOTE: The mechanism behind the altered contractile response is subject to specific research questions and is cell- and condition-dependent and will not be discussed in this protocol.
4. Detecting the presence of SMC specific markers
- RNA isolation
- Seed the same patient-specific cell lines used for the contraction measurements in 6-well plates, one well per cell line. Count the cells using an automated cell counter and seed the cells at a seeding density of 200,000 cells/well in SMC medium and allow them to attach overnight.
- Wash the cells once with sterile PBS.
- Lyse the cells and isolate the cells according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- cDNA synthesis
- Perform cDNA synthesis in 20 µL of a reverse transcription reaction mixture. Dilute the concentrations of total isolated RNA according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- qPCR
- Measure the gene expression of SMC marker genes, e.g., ACTA2, CNN1, SMTN, and TAGLN to confirm that the isolated cells are indeed SMCs and detect SMC markers. Check for correlation of the results with the contractile output.
- Use at least two housekeeping genes to normalize the data, e.g., YWHAZ and TBP.
NOTE: The qPCR run and analysis can be performed using different PCR machines and compatible software, depending on what is available and optimized in the laboratory. See Supplemental Table S1 for primer sequences.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
To test the reproducibility of this method, the method was first validated using control SMCs only. To determine interexperimental measurement reproducibility, two independent measurements of all included control and patient cell lines were plotted as a Bland-Altman plot (Figure 3B). The plot demonstrated that this method does not show variability outside the confidence interval, except for one outlier cell line. Furthermore, these results demonstrated that two wells seeded within the same e...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
This paper presents a method to measure SMC contraction in vitro, based on the changes in impedance and surface occupation. First, the isolation, culturing, and expansion of patient-specific primary human SMCs and skin fibroblasts is described, followed by how to use them for contraction measurements.
A limitation of the study is related to obtaining the cells through an explant protocol. The cells that proliferate from the biopsy might have different properties than the original tis...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge Tara van Merrienboer, Albert van Wijk, Jolanda van der Velden, Jan D. Blankensteijn, Lan Tran, Peter L. Hordijk, the PAREL-AAA team, and all vascular surgeons of the Amsterdam UMC, Zaans Medisch Centrum, and Dijklander hospital for providing materials and support for this study. This study is funded by the Dutch Heart Foundation, Dekkerbeurs senior clinical scientist award, project no. 2019T065.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 96-well Array | Applied Biophysics | 96W10idf PET | Array used to measure contraction in the ECIS setup |
| Custodiol | Dr. Franz Höhler Chemie GmbH | RVG 12801 | Solution used to transfer tissue in from surgery room to laboratorium |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 472301 | Solution used to dilute ionomycin |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Gibco | 26140079 | Addition to cell culture medium |
| Ham's F-10 Nutrient Mix | Gibco | 11550043 | Medium used to culture skin fibroblasts |
| Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Basal Medium (formerly ''Medium 231'') | Gibco | M231500 | Medium used to culture smooth muscle cells |
| Invitrogen countess II | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AMQAX1000 | Automated cell counter |
| Ionomycin calcium salt from Streptomyces conglobatus | Sigma-Aldrich | I0634-1MG | Compound used for contraction stimulation |
| NaCl 0.9% | Fresenius Kabi | B230561 | Solution used to transfer tissue in from surgery room to laboratorium |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140122 | Antibiotics used for cell culture medium |
| Phospathe buffered saline | Gibco | 10010023 | Used to wash cells |
| Quick-RNA Miniprep Kit | Zymo Research | R1055 | Kit used for RNA isolation |
| Smooth Muscle Growth Supplement (SMGS) | Gibco | S00725 | Supplement which is added to smooth muscle cell culture medium |
| SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11754250 | Kit used for cDNA synthesis |
| SYBR Green PCR Master Mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 4309155 | Reagent for qPCR |
| Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 15400-054 | Used to trypsinize cells |
| ZTheta | Applied Biophysics | ZTheta | ECIS instrument used for contraction measurements |
References
- Milewicz, D. M., et al. Genetic basis of thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections: focus on smooth muscle cell contractile dysfunction. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 9, 283-302 (2008).
- Milewicz, D. M., et al. Altered smooth muscle cell force generation as a driver of thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 37 (1), 26-34 (2017).
- Groeneveld, M. E., et al. Betaglycan (TGFBR3) up-regulation correlates with increased TGF-β signaling in Marfan patient fibroblasts in vitro. Cardiovascular Pathology. 32, 44-49 (2018).
- Chen, J., Li, H., SundarRaj, N., Wang, J. H. C. Alpha-smooth muscle actin expression enhances cell traction force. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton. 64 (4), 248-257 (2007).
- Peyton, S. R., Putnam, A. J. Extracellular matrix rigidity governs smooth muscle cell motility in a biphasic fashion. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 204 (1), 198-209 (2005).
- Williams, D. A., Fogarty, K. E., Tsien, R. Y., Fay, F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 318 (6046), 558-561 (1985).
- Wu, D., et al. NLRP3 (nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3)-caspase-1 inflammasome degrades contractile proteins: implications for aortic biomechanical dysfunction and aneurysm and dissection formation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 37 (4), 694-706 (2017).
- Bogunovic, N., et al. Impaired smooth muscle cell contractility as a novel concept of abdominal aortic aneurysm pathophysiology. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 1-14 (2019).
- Hurst, V., Goldberg, P. L., Minnear, F. L., Heimark, R. L., Vincent, P. A. Rearrangement of adherens junctions by transforming growth factor-β1: role of contraction. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 276 (4), 582-595 (1999).
- Hu, N., et al. Comparison between ECIS and LAPS for establishing a cardiomyocyte-based biosensor. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 185, 238-244 (2013).
- Peters, M. F., Lamore, S. D., Guo, L., Scott, C. W., Kolaja, K. L. Human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in cellular impedance assays: bringing cardiotoxicity screening to the front line. Cardiovascular Toxicology. 15 (2), 127-139 (2015).
- Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Kone, B. C., Allen, J. C., Kahn, A. M. Insulin-stimulated cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration by inhibiting Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Circulation. 107 (11), 1539-1544 (2003).
- Halterman, J. A., Kwon, H. M., Zargham, R., Bortz, P. D. S., Wamhoff, B. R. Nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 31 (10), 2287-2296 (2011).
- Bass, H. M., Beard, R. S., Cha, B. J., Yuan, S. Y., Nelson, P. R. Thrombomodulin induces a quiescent phenotype and inhibits migration in vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Annals of Vascular Surgery. 30, 149-156 (2016).
- Burger, J., et al. Molecular phenotyping and functional assessment of smooth muscle like-cells with pathogenic variants in aneurysm genes ACTA2, MYH11, SMAD3 and FBN1. Human Molecular Genetics. , (2021).
- Yeung, K. K., et al. Transdifferentiation of human dermal fibroblasts to smooth muscle-like cells to study the effect of MYH11 and ACTA2 mutations in aortic aneurysms. Human Mutation. 38 (4), 439-450 (2017).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved