A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Analyzing the Interaction of Fluorescent-Labeled Proteins with Artificial Phospholipid Microvesicles using Quantitative Flow Cytometry
In This Article
Summary
Here, we describe a set of methods for characterizing the interaction of proteins with membranes of cells or microvesicles.
Abstract
In the human body, most of the major physiologic reactions involved in the immune response and blood coagulation proceed on the membranes of cells. An important first step in any membrane-dependent reaction is binding of protein on the phospholipid membrane. An approach to studying protein interaction with lipid membranes has been developed using fluorescently labeled proteins and flow cytometry. This method allows the study of protein-membrane interactions using live cells and natural or artificial phospholipid vesicles. The advantage of this method is the simplicity and availability of reagents and equipment. In this method, proteins are labeled using fluorescent dyes. However, both self-made and commercially available, fluorescently labeled proteins can be used. After conjugation with a fluorescent dye, the proteins are incubated with a source of the phospholipid membrane (microvesicles or cells), and the samples are analyzed by flow cytometry. The obtained data can be used to calculate the kinetic constants and equilibrium Kd. In addition, it is possible to estimate the approximate number of protein binding sites on the phospholipid membrane using special calibration beads.
Introduction
Biomembranes separate the inner contents of animal cells and extracellular space. Note that membranes also surround microvesicles formed during the cell's life cycle and organelles. The cell membrane is predominantly composed of lipids and proteins. Membrane proteins perform signaling, structural, transport, and adhesive functions. However, the lipid bilayer is also essential for the interrelation of the animal cell with the extracellular space. This paper proposes a method for studying the peripheral interaction of external proteins with the lipid membrane.
The most striking example of reactions occurring on the outer membrane layer of an animal cell is the blood coagulation reaction. An important feature of blood coagulation is that all the main reactions proceed on the phospholipid membranes of cells and microvesicles arising from these cells and not in the plasma1,2,3. Membrane-dependent reactions include the process of starting coagulation (on the cell membranes of the subendothelium, inflamed endothelium, or activated immune cells, with the participation of a tissue factor), all reactions of the main cascade-activation of factors IX, X, prothrombin; activation of factor XI by thrombin (on the membranes of activated platelets, erythrocytes, lipoproteins, and microvesicles); reactions of the protein C pathway; inactivation of coagulation enzymes (on the membranes of endothelial cells with the participation of thrombomodulin cofactors, endothelial protein C receptor, heparan sulfate); and contact pathway reactions (on membranes of platelets and some microvesicles with the participation of unknown cofactors). Thus, it is impossible to investigate blood coagulation without studying the interaction of various plasma proteins with the membrane of blood cells.
This paper describes a flow-cytometry-based method for characterizing the interaction of proteins with lipid membranes of cells or microvesicles. This approach was initially proposed to study the interaction of blood plasma with platelets and artificial phospholipid vesicles. Moreover, most of the studied proteins interact directly with negatively charged membrane phospholipids, particularly with phosphatidylserine4,5. Additionally, there are proteins whose interaction with the membrane is mediated by special receptors6.
An important ability of flow cytometry is discriminating between free and bound ligands without additional separation. This feature of cytometry allows the study of ligand equilibrium binding at the endpoint and helps perform continuous kinetic measurements. The technique is unsophisticated and does not require complex sample preparation. Flow cytometry is actively used to quantitatively study the dynamics of interaction between fluorescent peptides, receptors, and G-proteins in intact and detergent-permeable neutrophils7. This approach is also applicable for exploring protein-DNA interactions and the kinetics of endonuclease activity in real time8. Over time, this method was used to quantitatively study high-affinity protein-protein interactions with purified lipid vesicles9, or, more generally, with membrane proteins expressed in a highly efficient Sf9 cell expression system10. Quantitative methods have also been described for characterizing protein-liposome interactions using flow cytometry for transmembrane proteins11.
This technique uses self-made calibration beads to avoid using commercially available beads7. The calibration beads used previously7 were intended to work with fluorescein, which substantively restricted the assortment of accessible fluorescent ligands on the proteins. In addition, this paper offers a new way to acquire and analyze kinetic data for reasonable time resolution. Although this method is described for artificial phospholipid vesicles, there are no obvious limitations for its adaptability to cells, natural vesicles, or artificial phospholipid vesicles with a different lipid composition. The method described herein allows the estimation of the parameters of interaction (kon, koff) and equilibrium (Kd) and facilitates quantitative characterization of the number of protein binding sites on the membrane. Note that this technique provides an approximate estimate of the number of binding sites. The advantages of the method are its relative simplicity, accessibility, and adaptability to native cells and natural and artificial microvesicles.
Protocol
1. Fluorescent protein labeling
- Material preparation
- Prepare 1 M Sodium bicarbonate buffer, pH 9.0, store it at 4 °C, and use it within one week.
- Prepare 1.5 M hydroxylamine hydrochloride buffer, pH 8.5, immediately before use.
- Prepare a 10 mg/mL solution of fluorescent dye (see the Table of Materials) in dimethylsulfoxide.
NOTE: This solution can be stored for a month at -20 °C in the dark. - Prepare solutions of purified antibodies or other proteins at 1-10 mg/mL.
NOTE: Avoid buffers containing ammonium ions or primary amines. Replace the buffers containing Tris or glycerol with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) by dialysis. Neither sodium azide (≤3 mM) nor thimerosal (≤1 mM) will significantly affect the conjugation reaction. - Incubate the gel filtration medium (see the Table of Materials) for protein purification in PBS overnight at room temperature or for 2 h at 60 °C. Apply the gel filtration medium onto spin columns with 0.2 µm membranes.
- Calculate the amount of reactive dye to be used for each reaction according to the concentration of protein to be labeled by using Eq (1).
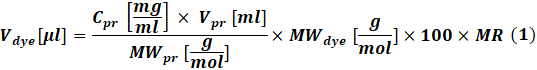
Where Vdye is the volume of the dye stock solution; Cpr, Vpr and MWpr is the concentration, volume and molar weight of the protein; MWdye is the dye molar weight; 100 is a unit conversion factor; MR is the molar ratio of dye to protein in the reaction mixture.
NOTE: The following MRs are recommended for IgG labeling reactions: MR = 40 if the antibody is at 1-3 mg/mL or MR = 30 if the antibody is at 4-10 mg/mL. For coagulation factors, MR = 5 is usually used. - Conjugation reaction
- In a reaction tube, mix the protein solution with a 10x lower volume of 1 M bicarbonate solution.
- Add the required amount of fluorescent dye (see step 1.2) with continuous stirring.
- Incubate the reaction mixture at room temperature for approximately 1 h, protected from light and with continuous stirring.
- For each 200 µL of protein solution, add 5 µL of 1.5 M hydroxylamine hydrochloride.
- Incubate the reaction mixture at room temperature for approximately 30 min, protected from light and with continuous stirring.
- Prepare the spin column.
- Add 500 µL of gel filtration medium for protein purification to a column. Centrifuge the column for 3 min at 1,000 × g.
- Discard the buffer from the collection tube. If the column is not full, add more gel filtration medium, and centrifuge the column for 3 min at 1,000 × g. Repeat this step until the column is full.
- Purification
- Centrifuge the reaction mixture (from step 1.3.5) for 5 min at 17,000 × g and remove the precipitate.
- Transfer the supernatant to the spin column with gel filtration medium. Allow the solution to absorb into the gel bed.
- Use an empty collection tube for the spin column and centrifuge it for 5 min at 1,000 × g. After centrifugation, collect the labeled protein from the collection tube.
- Determination of the degree of labeling
- Correct for the contribution of the dye to the absorbance at A280 by measuring the absorbance of free dye at 280 nm (A280) and the λmax for the dye (Amax) (see Eq (2)).
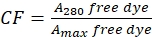 (2)
(2) - Measure the absorbance of the protein-dye conjugate at 280 nm (A280) and the λmax for the dye (Amax) and calculate the protein concetration using Eq (3).
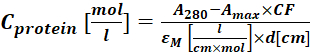 (3)
(3)
Where εM is the molar extinction coefficient of the protein at 280 nm; d is the optical path length during the measurement of the absorbance; CF is the contribution of the dye to the absorbance at A280 (step 1.6.1). - Calculate the degree of labeling (DOL) using Eq (4).
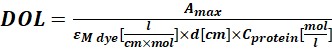 (4)
(4)
Where εM dye is the molar extinction coefficient of the dye at λmax nm; d is the optical path length during the measurement of the absorbance; Cprotein is the concentration of the protein (step 1.6.2).
- Correct for the contribution of the dye to the absorbance at A280 by measuring the absorbance of free dye at 280 nm (A280) and the λmax for the dye (Amax) (see Eq (2)).
2. Preparation of phospholipid vesicles
- Preparation and storage of the lipid mixture
- Combine the lipids in the appropriate ratio (phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine at a ratio of 20 mol% to 80 mol%).
- Dry the lipid mixture after lyophilization or evaporation and store it under an inert atmosphere in glass ampules.
- Lipid film production
- Open the ampule, and resuspend the lipid mixture in a small amount (~100 µL) of chloroform.
NOTE: Do not use too much chloroform as it does not evaporate completely. - Add DiIC16(3) in ethanol at 0.2 mol%. Transfer the lipid mixture to a round bottom flask. Spread the mixture thinly over the sides of the flask by rotating it. Dry the lipid mix for 30 min under an argon stream.
- Open the ampule, and resuspend the lipid mixture in a small amount (~100 µL) of chloroform.
- Hydration of the lipid mixture
- Add a suitably warm (~55 °C) aqueous buffer (HEPES 20 mM, NaCl 140 mM, pH 7.4) in a volume corresponding to the expected lipid concentration to the flask with the lipid film. Incubate the mixture with vortexing at 55 °С for 30 min for complete hydration.
- Placing the sample tube in a freezer or warm thermostat to make the lipid suspension undergo 3-5 freeze-thaw cycles.
- Formation of lipid vesicles by extrusion
- Prepare the extruder according to the manufacturer's instructions. Warm up all the extruder components to the phase transition temperature of the lipid mixture.
- Fill one of the extruder syringes with the hydrated lipid mixture. Wait for 5-10 min for the temperature of the lipid suspension to equilibrate with the temperature of the extruder.
- Extrude the lipid mixture through the membrane at least 10 times. For the final extrusion, place the lipid suspension in the alternate syringe and look for a change in appearance from a slightly nebulous to a clear solution.
- Store the resulting mixture of lipid vesicles at 4 °C, preferably in an inert atmosphere of argon or nitrogen, for 3-4 days. Do not freeze.
3. Isolation of platelets from whole blood
- Collect whole blood from healthy donors in tubes containing 3.2% sodium citrate.
- Add prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) (1 µM) and apyrase (0.1 U/mL) to the blood, followed by centrifugation at room temperature at 100 × g for 8 min.
- After centrifugation, take the platelet-rich plasma and add sodium citrate solution (106 mM, pH 5.5) to a plasma/citrate ratio of 3:1. Centrifuge the plasma at room temperature at 400 × g for 5 min.
- Remove the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet in 300 µL of Tyrode's buffer without BSA (20 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.4 mM NaH2PO4, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM glucose, pH 7.4). Purify the platelets from plasma proteins by gel chromatography on the gel filtration medium for platelet purification (see the Table of Materials).
4. Detection of protein - lipid interaction by flow cytometry
- Kinetic binding experiments
- Dilute phospholipid vesicles (from step 2.4.4) in Tyrode's buffer (20 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.4 mM NaH2PO4, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM glucose, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.4) to a concentration of 1 µM and total volume of 250 µL.
- Mix fluorescent-labeled coagulation factor X (fX-fd) from step 1 at a concentration of 500 nM with the phospholipid vesicles from step 4.1.1 in a 1:1 ratio (final vesicle concentration 0.5 µM, fX-fd concentration is 250 nM of fX) to a total volume of 500 µL.
- Immediately inject the 500 µL of the mixed suspension (~20 min for analysis with a low flowing rate) into the flow cytometer. Use a low flow rate and ensure that the threshold for channel FL2 (exсitation 488 nm, emission filter 585/42 nm) is as value 200. Measure the mean fluorescence in channel FL4 (exсitation 633 nm, emission filter 660/20) for the fluorescence dye from the Table of Materials.
NOTE: Choose a cytometer without an autosampler. This will speed up the process of injection of the sample into the measuring cell. - When saturation of binding is achieved (no significant increase in fluorescence within 5 min), rapidly dilute the sample 20-fold with Tyrode's buffer, and monitor the dissociation until baseline fluorescence is reached (complete dissociation) or until a plateau is reached (no significant decrease in fluorescence within 5 min).
NOTE: As a control, add 10 µM EDTA and monitor complete dissociation for 5 min.
- Equilibrium binding experiments
NOTE: Use the kinetic curve of binding to determine the time to reach saturation; the time for saturation for fX-fd and artificial vesicles is 20 min.- Incubate artificial phospholipid vesicles (5 µM) for the binding assay with different concentrations of fX-fd (from 0 to 1,000 nM) in Tyrode's buffer for 20 min.
- Dilute each sample from step 4.2.1 by 20x to a final volume of 200 µL with Tyrode's buffer. Immediately analyze the diluted sample by flow cytometry within 30 s. Use settings from step 4.1.3.
NOTE: As a control for nonspecific binding, use similar samples with EDTA (10 µM) and incubate them for 5 min.
5. Analysis of flow cytometry data
- Export experiments in FSC format from cytometry data acquisition software to cytometer software for data analysis (see the Table of Materials). Choose File | Export | FCS files. Open FSC files in cytometer software for data analysis by selecting the files on the computer and dragging them to the workspace of the program.
- For gating of the microvesicles, identify the region of microvesicles by the fluorescence of the lipophilic dye DiIC16(3). Use menu commands or plot button in the worksheet to create dot plot SSC from FL2 (dye DilC16(3)) in log coordinates. Choose the Rectangular Gate button to draw a gating region so that events from a sample without vesicles are not included in this region (Figure 1B,C).
- Analyze the kinetic experiments.
- Create a dot-plot using the coordinates of fluorescence (FL4) over time for the region of the vesicles (double-click in the region of vesicles in step 5.2)
- Export the data on the change in fluorescence over time in csv format. Choose Sample | Right-click | Export | Choose FL4 and Time in Parameters | Select directory for saving | Select CSV format | Export.
- Open the CSV file in any statistical software (see the Table of Materials). Calculate a simple moving average of fluorescence and time for every 1,000 events.
- Approximate a graph of the dependence of the simple moving average fluorescence on time under the assumption of exponential dependence (Analysis > Fitting >Nonlinear Curve Fit) and use this to calculate the kinetic association constant using Eq (5).
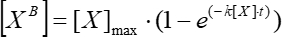 (5)
(5)
Where [XB] is the bound factor concentration at each moment of time (user-defined units) according to the simple moving average from step 5.3.3; [X] is the added factor concentration; [X]max is the maximum bound factor concentration; k is the association constant; t is the time. - Repeat the same set of actions (5.3.1-5.3.4) to calculate the kinetic dissociation constant using Eq (6).
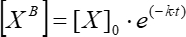 (6)
(6)
Where [XB] is the bound factor concentration at each moment of time; [X]0 is the bound factor concentration at the initial moment of time; k is the dissociation constant; t is the time.
- Equilibrium binding assay
- Determine the average fluorescence of fX-fd in the region of the vesicles for each selected concentration of fX-fd.
- Approximate the dependence of the bound factor fluorescence from the concentration of the added factor in the assumption of simple single-site binding. Calculate the average binding parameters using Eq (7) from three independent repeats at a minimum.
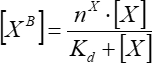 (7)
(7)
Where [XB] is the bound factor concentration; [X] is the added factor concentration; nx is the apparent number of binding sites per vesicle; Kd is the apparent dissociation constant.
6. Converting fluorescence intensity to the mean number of binding sites
- Prepare calibrated beads.
- Incubate gel-filtered platelets (see step 3.3) with A23187 (10 µM) in the presence of CaCl2 (2.5 mM) for 10 min at room temperature.
- Add to the activated platelets the various concentrations of fX-fd (0 to 1,000 nM). Add 2% v/v formaldehyde and incubate for 1 h. Stop the reaction by incubating the platelets with 3 M glycine and 5% BSA for 30 min at room temperature.
- Purify the mixture from the unreacted dye. Centrifuge the platelets for 5 min at 400 × g, remove the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet in Tyrode's buffer (containing 0.5% BSA).
NOTE: Repeat step 6.1.3 three times.
- Measure the fluorescence level of the calibration beads in each sample first using a spectrofluorometer (for fluorescent dye from the Table of Materials, excitation 633 nm, emission 670 nm) and then using the flow cytometer (in channel FL4: excitation 633 nm, emission filter 660/20). Using a cell counter, determine the number of beads in each sample.
- Convert the fluorescence intensity of each respective bead sample to the concentration of soluble fluorescent dye using a spectrofluorometer. Recalculate the fluorescent dye concentration for the number of fluorophore molecules using Eq (8).
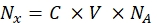 (8)
(8)
Where Nx is the number of fluorophore molecules; C is the fluorescent dye concentration; NA is Avogadro constant; NA = 6.02214076×1023 mol -1. - Create a dependence graph of the average fluorescence of the beads in a flow cytometer (step 6.2) on the number of fluorophore molecules (see step 6.3) for each sample using any statistical software (see the Table of Materials). Approximate this dependence by line proportionality (Analysis | Fitting | Fit linear). From the approximation in Eq (9), calculate the conversion factor of the mean fluorescence to binding sites.
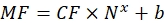 (9)
(9)
Where MF is the mean fluorescence of beads by flow cytometry; Nx is the number of fluorophore molecules per bead; CF represents the conversion factor of the mean fluorescence to binding sites. CF and b are obtained from the results of fitting the graph by linear proportionality. - Calculate the apparent number of binding sites per vesicle of interest using Eq (10).
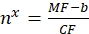 (10)
(10)
Where nx is the apparent number of binding sites per vesicle of interest; MF is the mean fluorescence of the vesicles of interest by flow cytometry; CF and b are conversion factors from the Eq (8).
Results
The flow cytometry method described herein is used to characterize the binding of plasma coagulation proteins to activated platelets. In addition, phospholipid vesicles PS:PC 20:80 were applied as a model system. This paper mainly focuses on artificial phospholipid vesicles as an example. The parameters of the cytometer, in particular, the photomultiplier tube (PMT) voltage and the compensation must be selected for each specific device, the object of study (cells, artificial or natural microvesicles), and the dyes used. ...
Discussion
The proposed method can be adapted for a rough characterization of the interaction of proteins with phospholipid membranes from various sources and compositions. The quantitative flow cytometry described here concedes to surface plasmon resonance (SPR) in several parameters. In particular, it has a lower sensitivity and time resolution and requires fluorescent labeling of proteins. Fluorescent labeling can lead to a change in conformation and loss of activity for many proteins and therefore requires careful control. Howe...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors were supported by a Russian Science Foundation grant 20-74-00133.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| A23187 | Sigma Aldrich | C7522-10MG | |
| Alexa Fluor 647 NHS Ester (Succinimidyl Ester) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A37573 | fluorescent dye |
| Apyrase from potatoes | Sigma Aldrich | A2230 | |
| BD FACSCantoII | BD Bioscience | ||
| bovine serum albumin | VWR Life Science AMRESCO | Am-O332-0.1 | |
| Calcium chloride, anhydrous, powder, ≥97% | Sigma Aldrich | C4901-100G | |
| Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrometer | Agilent | ||
| D-(+)-Glucose | Sigma Aldrich | G7528-1KG | |
| DiIC16(3) (1,1'-Dihexadecyl-3,3,3',3'-Tetramethylindocarbocyanine Perchlorate) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D384 | |
| DMSO | Sigma Aldrich | D8418 | |
| EDTA disodium salt | VWR Life Science AMRESCO | Am-O105B-0.1 | |
| FACSDiva | BD Bioscience | cytometry data acquisition software | |
| FlowJo | Tree Star | cytometer software for data analysis | |
| HEPES | Sigma Aldrich | H4034-500G | |
| Human Factor X | Enzyme research | HFX 1010 | |
| Hydroxylamine hydrochloride | Panreac | 141914.1209 | |
| L-α-phosphatidylcholine (Brain, Porcine) | Avanti Polar Lipids | 840053P | |
| L-α-phosphatidylserine (Brain, Porcine) (sodium salt) | Avanti Polar Lipids | 840032P | |
| Magnesium chloride | Sigma Aldrich | M8266-100G | |
| Mini-Extruder | Avanti Polar Lipids | 610020-1EA | |
| OriginPro 8 SR4 v8.0951 | OriginLab Corporation | Statistical software | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) Tablets, Biotechnology Grade | VWR Life Science AMRESCO | 97062-732 | |
| Potassium chloride | Sigma Aldrich | P9541-500G | |
| Prostaglandin E1 | Cayman Chemical | 13010 | |
| Sephadex G25 | GE Healthcare | GE17-0033-01 | gel filtration medium for protein purification |
| Sepharose CL-2B | Sigma Aldrich | CL2B300-500ML | gel filtration medium for platelet purification |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Corning | 61-065-RO | |
| Sodium chloride | Sigma Aldrich | S3014-500G | |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Sigma Aldrich | S3139-250G | |
| Spin collumns with membrane 0.2 µm | Sartorius | VS0171 | |
| Trisodium citrate dihydrate | Sigma Aldrich | S1804-1KG |
References
- Hoffman, M., Monroe, D. M. A cell-based model of hemostasis. Thrombosis and haemostasis. 85 (6), 958-965 (2001).
- Roberts, H. R., Hoffman, M., Monroe, D. M. A cell-based model of thrombin generation. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 32, 32-38 (2006).
- Panteleev, M. A., Dashkevich, N. M., Ataullakhanov, F. I. Hemostasis and thrombosis beyond biochemistry: roles of geometry, flow and diffusion. Thrombosis Research. 136 (4), 699-711 (2015).
- Podoplelova, N. A., et al. Hysteresis-like binding of coagulation factors X/Xa to procoagulant activated platelets and phospholipids results from multistep association and membrane-dependent multimerization. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1858 (6), 1216-1227 (2016).
- Panteleev, M. A., Ananyeva, N. M., Greco, N. J., Ataullakhanov, F. I., Saenko, E. L. Two subpopulations of thrombin-activated platelets differ in their binding of the components of the intrinsic factor X-activating complex. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 3 (11), 2545-2553 (2005).
- Kotova, Y., et al. Binding of coagulation factor XIII zymogen to activated platelet subpopulations: roles of integrin αIIbβ3 and fibrinogen. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 119 (6), 906-915 (2019).
- Fay, S. P., Posner, R. G., Swann, W. N., Sklar, L. A. Real-time analysis of the assembly of ligand, receptor, and G protein by quantitative fluorescence flow cytometry. Biochemistry. 30 (20), 5066-5075 (2002).
- Nolan, J. P., Shen, B., Park, M. S., Sklar, L. A. Kinetic analysis of human flap endonuclease-1 by flow cytometry. Biochemistry. 35 (36), 11668-11676 (1996).
- Sarvazyan, N. A., Lim, W. K., Neubig, R. R. Fluorescence analysis of receptor−G protein interactions in cell membranes. Biochemistry. 41 (42), 12858-12867 (2002).
- Sarvazyan, N. A., Neubig, R. R. Analysis of molecular assemblies by flow cytometry: determinants of Gi1 and by binding. Advances in Optical Biophysics. 3256, 122-131 (1998).
- De Franceschi, N., et al. ProLIF - Quantitative integrin protein-protein interactions and synergistic membrane effects on proteoliposomes. Journal of Cell Science. 132 (4), (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved