A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Determining Binding Affinity (KD) of Radiolabeled Antibodies to Immobilized Antigens
In This Article
Summary
Here, a method is described to determine the binding affinity (KD) of radiolabeled antibodies to immobilized antigens. KD is the equilibrium dissociation constant that can be determined from a saturation binding experiment by measuring the total, specific, and nonspecific binding of a radiolabeled antibody at various concentrations to its antigen.
Abstract
Determining binding affinity (KD) is an important aspect of the characterization of radiolabeled antibodies (rAb). Typically, binding affinity is represented by the equilibrium dissociation constant, KD, and can be calculated as the concentration of antibody at which half the antibody binding sites are occupied at equilibrium. This method can be generalized to any radiolabeled antibody or other protein and peptide scaffolds. In contrast to cell-based methods, the choice of immobilized antigens is particularly useful for validating binding affinities after long-term storage of antibodies, distinguishing binding affinities of fragment antigen-binding region (Fab) arms in bispecific antibody constructs, and determining if there is variability in antigen expression between different cell lines. This method involves immobilizing a fixed amount of antigen to specified wells on a breakable 96-well plate. Then, nonspecific binding was blocked in all wells with bovine serum albumin (BSA). Subsequently, the rAb was added in a concentration gradient to all wells. A range of concentrations was chosen to allow the rAb to reach saturation, i.e., a concentration of antibody at which all antigens are continuously bound by the rAb. In designated wells without immobilized antigen, nonspecific binding of the rAb can be determined. By subtracting nonspecific binding from total binding in the wells with immobilized antigen, specific binding of the rAb to the antigen can be determined. The KD of the rAb was calculated from the resulting saturation binding curve. As an example, binding affinity was determined using radiolabeled amivantamab, a bispecific antibody for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cytoplasmic mesenchymal-epithelial transition (cMET) proteins.
Introduction
Radiolabeled antibodies (rAb) have a variety of uses in medicine. While the majority are utilized in oncology as imaging and therapeutic agents, there are imaging applications for rheumatology-related inflammation, cardiology, and neurology1. Imaging rAbs has high sensitivity to detect lesions and has the potential to aid in patient selection for treatment2,3,4,5. They are also used for therapy because of their specificity for their respective antigens. In a strategy known as theranostics, the same rAb is used for both imaging and treatment6.
Ideally, the antibody chosen for radiolabeling is one already proven to have high binding affinity and specificity using non-radiolabeled methods. Radiolabeling of antibodies can be achieved via direct chemical modification of antibodies with a radionuclide that forms stable covalent bonds (eg. radioiodine), or indirectly via conjugation with chelators that subsequently coordinate to radiometals7,8. Direct radiolabeling such as with radioiodine specifically modifies tyrosine and histidine residues on the antibody. If these residues are important for antigen binding, then this radioconjugation would alter the binding affinity. Conversely, there are multiple established protocols for the conjugation and indirect radiolabeling of antibodies. For example, a common chelator used to bind zirconium-89 (89Zr) for PET imaging of antibodies is the p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine (DFO), which is conjugated randomly to lysine residues of the antibody9,10. If there are lysine residues at the antigen-binding region, conjugation at these sites could sterically hinder antigen binding and therefore compromise the antibody-antigen binding. Thus, the different radioconjugation methods used for indirect or direct radiolabeling of antibodies can potentially affect immunoreactivity, defined as the ability of the antibody radioconjugate to bind to its antigen7,11. Site-specific conjugation methods can circumvent this limitation, but these techniques require antibody engineering to incorporate additional cysteine residues or expertise in enzymatic reactions on carbohydrate residues12,13,14,15,16. Once an antibody is radiolabeled, it is important to test if immunoreactivity is retained as part of the characterization of the rAb. One way to measure immunoreactivity is to determine the rAb's binding affinity.
The purpose of this protocol is to describe a process for determining the binding affinity for rAbs using an established radioligand saturation assay to quantify rAb-antigen binding. The binding trend is outlined in Figure 1. The amount of antigen bound will increase as more rAb is added to a fixed amount of immobilized antigen. Once all antigen-binding sites are saturated, a plateau will be reached, and adding more rAbs will have no effect on the amount of bound antigen. In this model, the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) is the concentration of antibody that occupies half of the antigen receptors17. The KD represents how well an antibody binds to its target with a lower KD corresponding to a higher binding affinity. It was previously reported that an ideal rAb should have a KD of 1 nanomolar or less18. However, more recent rAbs have been developed with KD in the low nanomolar range, and are considered suitable for noninvasive imaging applications19,20,21,22. Another parameter that can be determined in the radioligand saturation assay of rAbs is Bmax, which corresponds to the maximum amount of antigen-binding. Bmax can be used to calculate the number of antigen molecules if needed.

Figure 1: Representative saturation binding curve. The percentage of antigen bound is plotted against increasing concentrations of antibodies added to a fixed amount of antigen. Pop-outs demonstrate binding at various points. The concentration and binding corresponding to KD and Bmax, respectively, are shown. This figure was created with BioRender.com. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
This assay is particularly important for radiolabeled bispecific antibody constructs to determine the KD for each fragment antigen-binding region (Fab) arm of the radiolabeled bispecific antibody binding with their respective antigens. This protocol can be used to determine the KD of each Fab arm separately on immobilized antigens to independently characterize whether the binding affinity of each Fab arm for its respective antigen was affected after radioconjugation. This protocol is demonstrated by the use of radiolabeled amivantamab, a bispecific antibody for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cytoplasmic mesenchymal-epithelial transition (cMET) proteins19. Radiolabeled single-arm antibodies, where one Fab arm binds to EGFR (α-EGFR) or to cMET (α-cMET) and the other Fab arm is an isotype control, were also used as examples19. This protocol is also appropriate for any radiolabeled antibody with a known antigen that can be immobilized. In this protocol, a dilution series of the rAb is added to a fixed amount of immobilized antigen in designated wells specific for each Fab arm of the rAb. The rAb is also added to wells that have only been blocked with bovine serum albumin (BSA), without antigen, to determine nonspecific binding. To determine specific binding, nonspecific binding to immobilized antigen is subtracted from the total rAb binding. The resulting saturation binding curve is then used to determine KD, as described above.
One advantage of this method is higher reproducibility when using purified antigens compared with using cell lines as the source of antigens, given that antigen expression levels could be affected during cell culture and that different cell lines have variable levels of antigen expression. In the case of radiolabeled bispecific antibodies, cell lines that only express one of the antigens without the other may not be available, which would make characterizing the binding affinity of the individual Fab arms very challenging. Notably, the key advantage of the radioligand saturation assay method over non-radiolabeled methods is the specific characterization of the binding affinity of the rAb without the contribution of the rAb's unconjugated fraction. To the best of the authors' knowledge, there are currently no purification techniques to separate the rAb from its parent unconjugated antibody. Given the relatively small size of the chelator and radionuclide, their contribution to the overall molecular weight of the rAb is insignificant in size exclusion chromatography. Thus, the product generated from any radiolabeling technique is almost always a mixture of the rAb and its parent unconjugated antibody. Characterizing binding affinity using the radiolabeled saturation assay ensures that the product being tested is solely the rAb.
Protocol
NOTE: Refer to Figure 2 for a graphical representation of the protocol.
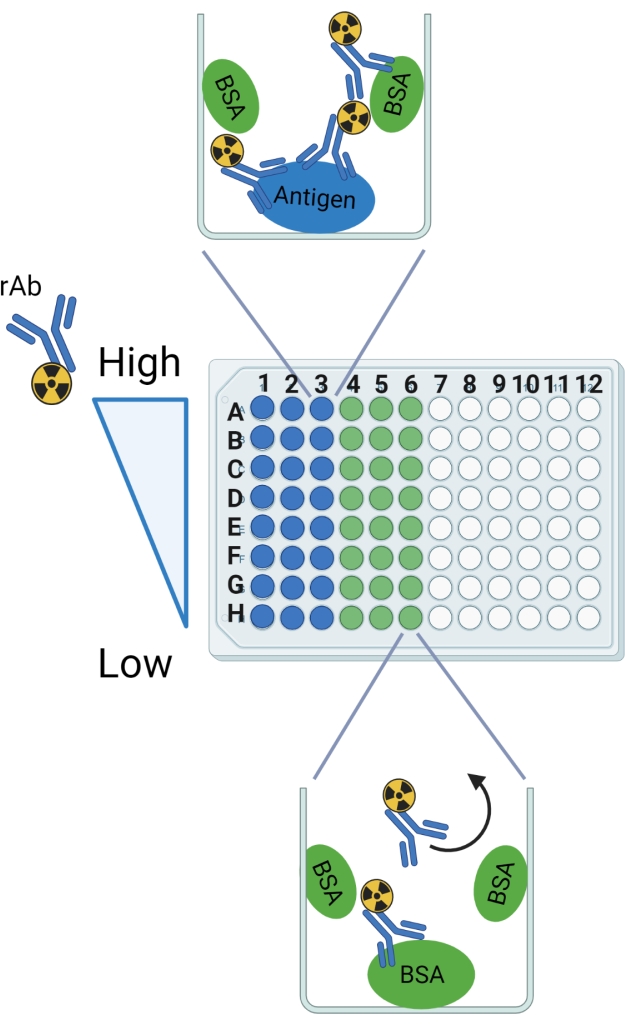
Figure 2: Schematic of the protocol. Row and column labels are indicated as a guide for setting up the breakable 96-well plate. Anticipated binding is shown in an example well for the antigen and the BSA. The curved arrow designates the rAb that is expected to be washed out of wells with BSA only. This figure was created with BioRender.com. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
1. Buffer preparation
- Prepare 50 mL of immobilization buffer (aqueous solution of 50 mM Na2CO3; pH = 9.0).
- Weigh 191 mg of NaHCO3 and 23.9 mg of Na2CO3 on weighing paper and transfer to a 50 mL conical tube. Add 40 mL of 18 MΩ water and vortex to dissolve. Adjust the pH to 9.0 if needed before bringing the total volume to 50 mL with 18 MΩ water.
- Prepare approximately 200 mL of washing buffer (phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.05% Tween-20) by adding 200 mL of PBS and then 100 µL of Tween-20 to a 250 mL bottle.
- Prepare 50 mL of binding buffer (PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20, and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)).
- Weigh 50 mg of BSA on weighing paper and transfer to a 50 mL conical tube. Add 50 mL of PBS and then 25 µL of Tween-20 to the tube. Vortex gently to mix.
- Prepare 50 mL of blocking buffer (3% BSA in PBS).
- Weigh 1.5 g of BSA on weighing paper and transfer to a 50 mL conical tube. Add 50 mL of PBS, and vortex gently to mix.
NOTE: All buffers are recommended to be stored for up to 1 week at 4 °C for best results.
- Weigh 1.5 g of BSA on weighing paper and transfer to a 50 mL conical tube. Add 50 mL of PBS, and vortex gently to mix.
2. Antigen immobilization
- Dilute the antigen in immobilization buffer to reach a concentration of 5 µg/mL.
- Add 100 µL per well of antigen to the bottom of 24 wells of a breakable 96-well, flat-bottom plate in an 8 x 3 array (columns 1-3 for rows A-H). Cover the plate with sealing tape.
NOTE: Ensure that the surface of the well-plate had been treated to maximize adsorption of mixed hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains. These pretreated plates are commercially available. - Incubate at 4 °C overnight.
- The following day, wash the plate 3x with washing buffer.
- Invert the plate briskly in the sink to dispose of the liquid and tap the plate on a pile of paper towels to remove the excess liquid.
- Using a multichannel pipette, add 300 µL per well of washing buffer to wells containing the antigen. Remove the liquid as described in 2.4.1. Repeat the washing step a total of three times.
3. Blocking of nonspecific sites with BSA
- Using a multichannel pipette, add 300 µL per well of blocking buffer to the 24 antigen-coated wells and 24 empty wells of the 96-well plate (columns 1-6 for rows A-H).
- Incubate the plate for 1 h at ambient temperature.
- Wash the plate with 300 µL per well of washing buffer a total of three times. Refer to step 2.4 for a detailed description of washing the plate.
4. Serial dilutions and addition of the rAb solution
CAUTION: The following steps involve radioactivity. Steps should only be performed by those with radiation safety training. Researchers should double glove and perform steps with adequate shielding.
- Synthesize the rAb under investigation using the method of choice. The rAbs used as an example were synthesized as described previously19.
NOTE: This protocol focuses on the characterization of a rAb once radiolabeled. - Make 8 x 3-fold serial dilutions (designated for rows A-H on the plate) of the rAb in the binding buffer.
NOTE: The concentrations of the serial dilutions will vary for each rAb. Details are discussed in the Discussion section. If the dilution factor changes, the volume needed for each dilution should be recalculated to ensure enough volume for 1) binding of the rAb in each well, 2) seeding the following dilution, and 3) aliquoting a rAb standard solution for gamma counting to measure the radioactivity of the total rAb added to each well.- Calculate the volume of stock rAb needed to make a 1.2 mL solution of the first concentration (label as A).
- Add 800 µL of binding buffer to microcentrifuge tubes labeled B, C, D, ... to H. Add 1.2 mL minus the volume calculated in step 4.2.1 of binding buffer to a microcentrifuge tube labeled A.
- Add the volume of stock rAb calculated in 4.2.1 to tube A. Vortex gently to mix and then spin down using a mini microcentrifuge to collect all liquid at the bottom of the tube.
- Add 400 µL from tube A to tube B. Vortex to mix and then spin down using a mini microcentrifuge. Repeat adding from B to C, C to D, ..., G to H.
- Add 100 µL per well of each dilution to three wells immobilized with antigen and three wells blocked with BSA only. For example, add dilution A to wells A1-A3 (antigen) and A4-A6 (BSA).
- Add 100 µL of each dilution to microcentrifuge tubes labeled A std - H std. Save these tubes as rAb standards to be assayed in the gamma counter.
- Incubate the plate for 1 h at 37 °C with gentle rocking.
5. Wash plates and assay radioactivity
- Label microcentrifuge tubes for each well (A1 to A6, B1 to B6 ... through H1-H6). Use two different colored markers to color-code samples if desired-one for wells coated with antigen and one for wells with BSA only.
- Aspirate the rAb from each well using a vacuum aspirator.
- Using a multichannel pipette, add 300 µL of washing buffer to each well. Aspirate the washing buffer. Repeat the wash a total of five times.
- Break apart the wells into the appropriate microcentrifuge tubes.
- Count the radioactivity in the tubes using a gamma counter. Count first the tubes with the antigen (H1, H2, H3 to A1, A2, A3), and then those with BSA only (H4, H5, H6 to A4, A5, A6). To minimize interference, separately count the standards for each dilution (H std to A std) at a different time.
6. Data analysis
NOTE: The supplemental files contain corresponding spreadsheet and statistical analysis templates for analyzing and plotting the data.
- In a spreadsheet, calculate the total, specific, and nonspecific binding for each sample (see the spreadsheet template attached as a supplemental file).
- Calculate "Bound Activity" as the counts per minute (CPM) of the sample (obtained from the gamma counter) divided by the CPM of the appropriate standard. Calculate "% Bound" as Bound Activity times 100.
- Calculate "Total Bound, mol/L" by multiplying "% Bound" with the concentration (mol/L) of the rAb added. Calculate "Total Bound, mol" by multiplying "Total Bound, mol/L" with the volume of rAb added in liters (0.0001 L).
- Calculate "Specific Binding, mol" by subtracting "Total Bound, mol" of the BSA dilutions from the antigen dilutions such that A1 pairs with A4, A2 with A5, A3 with A6, B1 with B4, etc.
- Calculate "Nonspecific Binding, mol" by subtracting "Specific Binding, mol" from "Total Binding, mol" for each well.
- In the statistical analysis plotting software, plot the concentration of rAb added (nmol/L) on the x-axis versus binding (mol) on the y-axis. Create separate groups to plot in triplicate total binding, specific binding, and nonspecific binding. Perform a nonlinear fit analysis by selecting the following parameters in the software used (Table of Materials; see the statistical analysis template attached as a supplemental file).
- Select New Analysis. Under XY analyses, select Nonlinear regression (curve fit). Make sure all the data is selected under Analyze which data sets? and then select Ok.
- On the Model tab, under Binding - Saturation, select One site - Specific binding. On the Confidence tab, select Identify 'ambiguous' fits. Leave all other parameters as default and select Ok.
NOTE: This will calculate the KD and Bmax for the total, specific, and nonspecific binding. The KD of the specific binding is the KD in nmol/L of the rAb bound to the antigen.
Results
This method calculates binding affinity (KD) for a rAb based on the saturation binding assay where different concentrations of rAb were added to a fixed amount of immobilized antigen. The binding curve should follow logarithmic growth where it is initially steep and then plateaus as the antigen is saturated. To ensure the determined KD is accurate, the concentrations of rAb must be high enough to reach saturation. For this assay, radiolabeled antibodies were conjugated to DFO and radiolabeled with <...
Discussion
As part of the development of rAbs, it is important to ensure a rAb binds specifically to its target with high binding affinity. Determining binding affinity can inform if the immunoreactivity of the rAb is affected by radioconjugation through the radioligand saturation assay using immobilized antigen. Determining rAb binding to BSA can be used to quantify nonspecific binding to measure specific binding to the immobilized antigen more accurately. This method tests the binding of different concentrations of rAb to generat...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank 3D Imaging for the production of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate and Dr. Sheri Moores at Janssen Pharmaceuticals for providing antibodies.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | A9647 | |
| Gamma Counter | Hidex | Hidex Automatic Gamma Counter | |
| GraphPad Prism Software | GraphPad | version 9.2; used for statistical analyses in this study | |
| Immuno Breakable MaxiSorp 96-well plates | Thermo Scientific | 473768 | |
| Microplate Sealing Tape | Corning | 4612 | |
| Microsoft Excel | Microsoft | ||
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) | Gibco | 14190144 | |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | JT Baker | 3506-01 | |
| Sodium Carbonate | Sigma-Aldrich | S7795 | |
| Tween-20 | Sigma-Aldrich | P7949 |
References
- Krecisz, P., Czarnecka, K., Krolicki, L., Mikiciuk-Olasik, E., Szymanski, P. Radiolabeled Peptides and Antibodies in Medicine. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 32 (1), 25-42 (2021).
- Dun, Y., Huang, G., Liu, J., Wei, W. ImmunoPET imaging of hematological malignancies: From preclinical promise to clinical reality. Drug Discovery Today. 27 (4), 1196-1203 (2022).
- Lohrmann, C., et al. Retooling a Blood-Based Biomarker: Phase I assessment of the high-affinity CA19-9 antibody HuMab-5B1 for immuno-pet imaging of pancreatic cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 25 (23), 7014-7023 (2019).
- Pandit-Taskar, N., et al. A phase I/II study for analytic validation of 89Zr-J591 immunoPET as a molecular imaging agent for metastatic prostate cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 21 (23), 5277-5285 (2015).
- Rousseau, C., et al. Initial clinical results of a novel immuno-PET theranostic probe in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 61 (8), 1205-1211 (2020).
- Moek, K. L., et al. Theranostics using antibodies and antibody-related therapeutics. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 58 (2), 83-90 (2017).
- Chomet, M., van Dongen, G., Vugts, D. J. State of the art in radiolabeling of antibodies with common and uncommon radiometals for preclinical and clinical immuno-PET. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 32 (7), 1315-1330 (2021).
- Kumar, K., Ghosh, A. Radiochemistry, production processes, labeling methods, and immunoPET imaging pharmaceuticals of Iodine-124. Molecules. 26 (2), 414 (2021).
- Vosjan, M. J., et al. Conjugation and radiolabeling of monoclonal antibodies with zirconium-89 for PET imaging using the bifunctional chelate p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine. Nature Protocols. 5 (4), 739-743 (2010).
- Zeglis, B. M., Lewis, J. S. The bioconjugation and radiosynthesis of 89Zr-DFO-labeled antibodies. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (96), e52521 (2015).
- Wei, W., et al. ImmunoPET: concept, design, and applications. Chemical Reviews. 120 (8), 3787-3851 (2020).
- Tavaré, R., et al. An effective immuno-PET imaging method to monitor CD8-dependent responses to immunotherapy. Cancer Research. 76 (1), 73-82 (2016).
- Tavaré, R., et al. Engineered antibody fragments for immuno-PET imaging of endogenous CD8+ T cells in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (3), 1108-1113 (2014).
- Zeglis, B. M., et al. Chemoenzymatic strategy for the synthesis of site-specifically labeled immunoconjugates for multimodal PET and optical imaging. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 25 (12), 2123-2128 (2014).
- Zeglis, B. M., et al. Enzyme-mediated methodology for the site-specific radiolabeling of antibodies based on catalyst-free click chemistry. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 24 (6), 1057-1067 (2013).
- Kristensen, L. K., et al. Site-specifically labeled 89Zr-DFO-trastuzumab improves immuno-reactivity and tumor uptake for immuno-PET in a subcutaneous HER2-positive xenograft mouse model. Theranostics. 9 (15), 4409-4420 (2019).
- Maguire, J. J., Kuc, R. E., Davenport, A. P., Davenport, A. P. . Radioligand binding assays and their analysis. in Receptor Binding Techniques. , 31-77 (2012).
- Davenport, A. P., Russell, F. D., Mather, S. J. Radioligand bindsing assays: theory and practice. Current Directions in Radiopharmaceutical Research and Development. , 169-179 (1996).
- Cavaliere, A., et al. Development of [89Zr]ZrDFO-amivantamab bispecific to EGFR and c-MET for PET imaging of triple negative breast cancer. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 48 (2), 383-394 (2021).
- Marquez, B. V., et al. Evaluation of (89)Zr-pertuzumab in breast cancer xenografts. Molecular Pharmaceutics. 11 (11), 3988-3995 (2014).
- Marquez-Nostra, B. V., et al. Preclinical PET imaging of glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B in triple negative breast cancer: feasibility of an antibody-based companion diagnostic agent. Oncotarget. 8 (61), 104303-104314 (2017).
- Ghai, A., et al. Development of [(89)Zr]DFO-elotuzumab for immunoPET imaging of CS1 in multiple myeloma. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 48 (5), 1302-1311 (2021).
- McKnight, B. N., et al. Imaging EGFR and HER3 through (89)Zr-labeled MEHD7945A (Duligotuzumab). Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 1-13 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved