A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator-induced Mouse Back Pain Model
In This Article
Summary
Methods for simple, rapid induction of a back pain model in mice are provided here using an intraligament injection of urinary plasminogen activator.
Abstract
A model of persisting lower back pain can be induced in mice with the simple methodology described herein. Step-by-step methods for simple, rapid induction of a persisting back pain model in mice are provided here using an injection of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (urokinase), a serine protease present in humans and other animals. The methodology for induction of persisting lower back pain in mice involves a simple injection of urokinase along the ligamentous insertion region of the lumbar spine. The urokinase inflammatory agent activates plasminogen to plasmin. Typically, the model can be induced within 10 min and hypersensitivity persists for at least 8 weeks.
Hypersensitivity, gait disturbance, and other standard anxiety- and depression-like measures can be tested in the persisting model. Back pain is the most prevalent type of pain. To improve awareness of back pain, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) named 2021 the "Global Year about Back Pain" and 2022 the "Global Year for Translating Pain Knowledge to Practice." One limitation of the therapeutic advancement of pain therapeutics is the lack of suitable models for testing persistent and chronic pain. The features of this model are suitable for testing potential therapeutics aimed at the reduction of back pain and its ancillary characteristics, contributing to IASP's naming 2022 as the Global Year for Translating Pain Knowledge to Practice.
Introduction
Low back pain is one of the most common causes of disability with 1 in 5 people suffering worldwide1. In spite of these efforts, few reliable animal models of back pain are popularly used in animal research in the pain field, especially in mice. Previous models have almost exclusively made use of rats for the induction of chronic back pain (CBP) such as those induced by injection of urinary plasminogen activator (uPA) into the lumbar facet joint2,3, injection of nerve growth factor (NGF) into trunk musculature4, or monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)5 or interleukin-1beta6 injection in the intravertebral disc. Of course, rats are preferred for these models mainly due to their larger size and ease of access for injection of inflammatory agents.
To be clear, mouse models of back pain do exist such as the SPARC-null mouse model of intervertebral-disc degeneration used for many years7, but these are more costly and time-consuming to establish than injection-based models. A recent mouse study established a model of lower back pain by combining NGF injection into low back muscles with vertical chronic restraint stress8. In the following protocol, we have adapted the uPA-induced CBP model from rats for mice2. Hypersensitivity is established within 1 week and persists up to 6-8 weeks. In addition, we establish that mice develop anxiety- and depression-like behaviors. Given the prevalence of back pain and the more common use of mice in molecular pain research, this durable model is readily established for use in the development of new treatment strategies for back pain relief.
Protocol
All animal procedures described are in compliance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Studies were approved by the local Institutional Care and Use Committee (IACUC #23-201364-HSC) of the University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center. All studies comply with policies under the auspices of an OLAW Assurance of Compliance (A3002-01) on the use of animals in research, as described in Part III. II. Assurances and Certifications. Animals are housed in the Animal Resources Center (ARC) housing facility maintained by the laboratory staff and Division of Laboratory and Animal Resources (DLAR) staff. The method of euthanasia (100 µL of 59 mg/mL pentobarbital injection) is rapid and reliable and allows for the dissection and collection of various tissues for further research.
1. Animals
- House adult (~3-4 weeks old) male and female BALB/c mice (20-25 g) on a reverse 12 h:12 h light:dark cycle, so their active time in the dark occurs during laboratory working hours.
NOTE: This will allow the assessment of all parameters during the animals' natural active time since rodents are naturally nocturnal animals. This reduces the contribution of alterations of the circadian clock so that animals can be tested during their active time which is now daytime. - Monitor the animals twice daily.
- Maintain the mice on normal mouse breeder chow, which is lower in soy protein content compared to standard rodent chow (known to alter hypersensitivity) if assessing drug effects on pain-related behaviors.
- Weigh the animals once a week to ensure the maintenance of healthy weight gain.
NOTE: No group differences in weight were noted throughout the 8-10-week studies, which allowed study blinding.
2. Model induction
- Perform model induction on a warm sterile flat surface fitted with a means to attach stabilization restraints to hold the mouse in place (Figure 1A). Perform the surgery with a dissection microscope on a sterilized surface.
NOTE: Use a chemical grade fume hood if anesthesia capture is not available. - Use surgical silk or even yarn with rubber bands knotted at the end of the strings hooked to the ribbed edges of the plate as restraints if using the base plate recommended in the Table of Materials.
- Place a heating pad recovery station on a surface adjacent to the surgery setup for the transfer of mice to the station immediately after injection (Figure 1B).
NOTE: Place an empty housing cage on the heating pad at least 10 min prior to injection to allow the cage to heat up to a comfortable temperature (37 °C). Place the cage half off the pad, to allow the waking mouse a preference of recovery temperatures. - Prepare the urokinase diluting it in sterile water. Alcohol clean the Hamilton syringe and rinse in sterile water. Draw up the solution in advance so the mouse is under anesthesia for as short a time as possible. Use 5 µL of 2 mg/mL urinary plasminogen activator for the model; for shams, use 5 µL of sterile saline.
- Set up the isoflurane anesthesia station at a level of 4% or less for this short procedure. Place the mouse in the induction chamber; typically, the mouse's rapid breathing rate will slow down within 1-2 min, moving from upper chest motion to the lower chest.
- Use an oxygen level of 1.5 L/min and an activated charcoal F canister or work under a biological flow or overhead evacuation hood to scrub the isoflurane to avoid exposure to the animal surgeon. If not available, perform the procedure in a chemical safety hood.
- Quickly switch the mouse and anesthetic flow to the surgical area on a 37°C warming pad, placing the mouse's nose in the nosecone to maintain the anesthetic level (Figure 1C,D). Check to be sure the mouse has no reflexive movement to toe pinch and then restrain the mouse on the base plate.
NOTE: If there is movement at all, place the mouse back into the induction chamber and repeat this. - Clean the back skin area with an alcohol swab. Adjust the LED lighting as needed to have a clear view of the anesthetized mouse's back.
NOTE: If needed, use an electric shaver to remove hair from the mouse's back so there is an unobstructed view of the ridges of the spine beneath the skin. If the experimental mice are shaved, also shave the back of the naive and sham mice for study blinding. - Inject the mouse while fully anesthetized and immobilized (no righting reflex and toe pinch withdrawal). Use two fingers to gently feel where the bottom of the mouse's ribcage meets the spine (Figure 2A). Below that point are the lumber spinal segments; aim the injection here at L2-L3.
- Place the tip of the Hamilton syringe next to the spine (Figure 2B,C). Aim the syringe at ~45° angle into the interspinous ligament immediately adjacent to the bone.
NOTE: Depending on the toughness of the mouse's skin, sometimes relying on gravity instead of active pressure and a 90° angle can work better. - Insert the tip of the needle gently but firmly into the interspinous ligament (Figure 3B,C) .
NOTE: The goal is not to breach the abdominal cavity but to inject the ligament. - Empty the contents of the needle slowly. If at any point there is liquid at the tip, the needle is not through the skin. Continue until all 5 µL have been injected.
- Hold the needle in place for ~5 s to prevent backflow from the injection. Use of blue dye in terminal or acute pilot trials is recommended.
NOTE: If done correctly, the liquid should spread into the ligament as shown (Figure 3A). - Remove the needle gently and slowly. Make sure there is no blood or discharge.
- Place the mouse into the heat recovery station with a cage top until it awakens and is mobile before returning it to the home cage.
NOTE: Assuming the procedure was performed quickly, it should not be more than a minute before the mouse awakens. - Check the mice through 1 h after surgery to ensure all normal motor function continues as a precaution.
NOTE: If done correctly, there should be no complications from this procedure. - Check the mice daily for the week following surgery, including weight assessment and injection site inspection to ensure no infection or complications have occurred. Do not use the mouse for further experimentation if there is a change in behavior, such as weight loss and lethargy.

Figure 1: Setup for urokinase CBP induction. (A) The Fine Science Tools baseplate recommended for mouse surgeries. The ribbed edges can have hooked string on them for holding the mouse in place. (B) Recovery station. An empty housing cage is recommended, half on the heating pad, half off. A clean cloth is placed on the bottom to give the mouse a comfortable resting area. (C) Anesthesia machine setup recommendation. Using a two-channel delivery system, set up one hose to the induction chamber and another to the surgery station. (D) A view of the mouse restraints. Two strings are knotted onto the ribbed edges of the base plate, then gently pulled across the mouse's neck and rear respectively. Make sure not to restrain the mouse too tightly so that it can still breathe normally. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 2: Urokinase injection induction of CBP. (A) A view of the injection site placement. As shown, feel with fingers to find the bottom of the mouse's ribcage for a reference point for L4-L5. (B) A view of the injection process, showing the angle for proper injection. (C) A 45° angle is preferable here, but adjust as needed to ensure the needle gets where it needs to. If needed, shave the injection site for better visualization. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 3: Diagram of the injection site. (A) A photograph of the location of the injection site. Ink is used here to indicate where the liquid will be entering the interspinous ligament between the L2 and L3 vertebrae. (B) A diagram showing the proper positioning of the needle and location of the injection site, shown from a side view. (C) A diagram showing a top-down view of the vertebrae, and injection sites for the interspinous ligaments. Injections will typically be on the interspinous ligaments next to the spine, but the needle can be inserted in the space between and intertransverse vertebrae as well. The use of blue dye in pilot trials is recommended as shown in (A). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Behavioral assays
- von Frey mechanical reflex response threshold testing
NOTE: Mechanical withdrawal threshold is the minimal force needed to elicit a response 50% of the time with a series of 8 von Frey monofilaments graded in diameter with ~0.2 g increases, providing log step changes in mechanical force (Table of Materials).- Test mechanical stimulation with von Frey fibers applied to the hindpaw, the innervation territory of the lumbosacral nerves. Determine the baseline paw withdrawal values before the surgery. After surgery, determine the mechanical threshold once a week during the chronic experiment.
- Move the animals from the housing room and acclimate them in the testing room for 30 min in their home cages prior to testing. From there, move the animals to restrain them individually in small clear cubicles on the screen-topped testing table for 15-20 min depending on their activity level.
NOTE: Testing can begin after mice have settled into a resting position and are not turning and moving in the chamber. Acclimation to the restraint cubicle minimizes stress-induced effects. If mice have been maintained on a reverse light cycle, testing should be done under red light conditions. - Proceed with testing using graded series of von Frey fibers as described below and in Chaplan et al.9.
- Probe the footpad in a consistent spot on each animal using the 3.61 von Frey filament which when bent elicits 0.4 g force (Table of Materials). Follow with stimulation with the 4.08 von Frey filament that elicits 1.0 g force.
NOTE: Neither of these fibers elicits responses in naïve, acclimated animals. - Apply each filament 5x at >5 s intervals perpendicular to the foot pad, being careful not to touch a fold/crevice or hair. A positive response is a foot withdrawal to three of five stimuli. Apply the next weaker filament in the series until the animal does not respond to the mechanical stimulation; at that point, use the next higher filament. If it elicits a response, use the lower filament again until four trials have been applied after the change of response to mechanical stimulation of the foot pad.
- Use the resulting response pattern to calculate the mechanical withdrawal threshold, the minimal amount of force needed to elicit a response 50% of the time, using a curve fitting algorithm9. A decrease in the force required to elicit a foot withdrawal response compared to naïve mice or the animal's own baseline indicates an increased sensitivity of the animal.
- Probe the footpad in a consistent spot on each animal using the 3.61 von Frey filament which when bent elicits 0.4 g force (Table of Materials). Follow with stimulation with the 4.08 von Frey filament that elicits 1.0 g force.
- Thermal reflex response threshold testing
NOTE: Heat and cold response thresholds are ascertained with the Hargreaves and the cold plate tests, respectively.- Hargreaves test
- Place the mice in cubicles on a glass surface that is heated with an infrared emitter from below. Record the latency to withdraw the foot as the time in seconds from the application of the infrared light (50 °C) stimulus provided by the apparatus onto the mouse's hind paw until the withdrawal from stimulation.
- Cold plate test
- Place the mice on the cold plate apparatus cooled to -9 °C. Record the latency to withdraw the foot as the time in seconds from placement of the mouse on the apparatus until the mouse begins lifting its foot.
- Alternatively, place a cold probe cooled to -9 °C underneath the mouse's hind paw while the mouse is caged on top of a wire mesh. Record the latency to withdraw as the time in seconds from placement of the apparatus under the hind paw until the mouse begins foot lifting, licking, or shaking. To avoid evoking a nociceptive response, acclimate the mouse to being touched by the probe at room temperature.
- Hargreaves test
- Cognition- and emotion-dependent behavioral assays
NOTE: Long-lasting hypersensitivity in animals produces emotional and cognition-dependent dysfunction. These are typically measured only once in week 6 after pain model induction to avoid practice effects.- Anxiety tests
NOTE: Anxiety and depression can also be reliably tested to ascertain the effectiveness of the model. It is best to wait until at least weeks 4-6 after the induction injection to allow the comorbidities to develop. Preference for the dark rather than the light chamber is a measure of nociception-related anxiety. In the zero or plus maze testing, pain model mice spend less time in the open quadrants than naïve control animals, a display of anxiety-like behavior10,11.- Light/dark place preference test: place each animal into the place preference test box with a passageway between two chambers (10 x 10 x 10 cm3). One chamber of the apparatus is brightly lit, while the opposite side remains dark. During each 10 min test, monitor the animal's location by computer to determine light and dark occupancy times and the number of transitions.
NOTE: Alternatively, mount a video camera over the test chamber and manually record the time spent in each chamber. - Elevated plus or zero mazes: place the model rodents or naïve animals on the maze and use a stopwatch to assess the time spent in the closed portions of the maze. Determine the time spent in the two walled "safe" areas and two open "unsafe" areas. Animals with pain prefer closed safe areas.
NOTE: Anxiety-like behavior can be tested in either a zero or plus maze (10 min). The zero maze is a circular track as opposed to the plus maze, which is "plus sign shaped". Both have two open and two enclosed quadrants that allow for continuous exploratory behavior. Both are raised 1 m off the ground, either a circular or plus-shaped walkway divided into four equal-sized quadrants.
- Light/dark place preference test: place each animal into the place preference test box with a passageway between two chambers (10 x 10 x 10 cm3). One chamber of the apparatus is brightly lit, while the opposite side remains dark. During each 10 min test, monitor the animal's location by computer to determine light and dark occupancy times and the number of transitions.
- Sucrose splash depression test
NOTE: The sucrose splash test is used to determine depression-like behavior. The splash test allows the measurement of the absence of normal grooming behavior as a symptom of depression resulting from chronic pain.- Score the frequency, duration, and latency of grooming for 10 min after spraying a 10-30% sucrose solution on the dorsal coat (~250 µL near the base of the tail). Have blinded observers count the number of grooming maneuvers from video tape recordings12.
NOTE: This index has been reported to be affected in rodent models of mood disorders, such as chronic mild stress, and to be corrected by chronic antidepressant treatment13.
- Score the frequency, duration, and latency of grooming for 10 min after spraying a 10-30% sucrose solution on the dorsal coat (~250 µL near the base of the tail). Have blinded observers count the number of grooming maneuvers from video tape recordings12.
- Novel object test
NOTE: Cognitive dysfunction is measurable with the novel object test.- Acclimate mice individually to a clear plastic cage with an open top (56 x 30 x 20 cm) for 1 h. Add two identical toy minifigures in opposite corners of the cage for 5 min.
- On the testing day, acclimate animals to the clear cage again for 1 h prior to placing the two identical mini-figures in the same positions of the cage for 5 min before returning them to the home cage.
- Replace one of the original figures with a distinctly different novel object, return the mice to the test cage 4 h later, and record the time spent exploring the objects.
- Calculate the reported Recognition Index (RI) as the percent time spent exploring the novel object of total object exploration time14.
- Motor function assessment
NOTE: The inkblot mobility and gait disturbance test15 assesses motor function in the back pain model.- Construct a tunnel from a paper towel tube cut lengthwise on one edge. Spread open the tunnel on a clean piece of printer paper.
- Hold the mice gently wrapped in a towel until they are calm. Place the paws on a stamp pad wet with non-toxic India ink to coat them with ink or paint the ink on the bottom of the mouse's feet using a cotton swab. Release the mice at the tunnel entrance and let them run through the tunnel, capturing them at the end.
- Score paw prints based on three parameters: stride length (the vertical distance from the back end of one print to the next), stride width (horizontal distance between prints), and toe spread (the distance between toes on the opposite sides of the paw).
NOTE: Approved treats can also be used to encourage the mouse to come through the tunnel. If paw prints are smeared or unclear, the experiment must be repeated.
- Anxiety tests
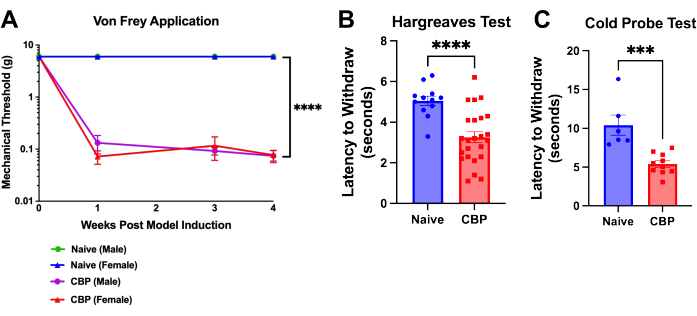
Figure 4: Mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity following CBP induction. Pain is measurable a week following model induction and persists for 8 weeks. (A) von Frey test. Mechanical threshold testing is performed with von Frey filaments applied to the footpad through a mesh top table with the up-down method as shown here over the course of 4 weeks. The naïve male threshold (green) is hidden beneath the blue line for the naïve female mice. The CBP mice (n = 4 males, 4 females) showed significantly increased mechanical sensitivity compared to the naïve controls (n = 2 males, 2 females). Two-way ANOVA (Dunnett's multiple comparisons test) was performed on these data: n = 4 per group. In post-hoc analyses, Bonferroni adjustment to all P-values for week-by-week comparisons of CBP versus Naïve yielded all 11 values < 0.0011. **** p < 0.0001. (B) Hargreaves test. The heat threshold was tested on the footpad with the Hargreaves test (50 °C). The CBP mice (n = 12 males, 12 females) showed significantly increased heat sensitivity compared to the naïve controls (n = 6 males, 6 females). Mann-Whitney two-tailed t-test was performed to test significance (p < 0.0001). (C) Cold sensitivity. The cold probe test was performed by placing mice on the cold plate apparatus cooled to -9 °C. Latency to withdraw was recorded as the time in seconds from placement of the mouse on the apparatus until the mouse begins foot lifting, licking, or shaking. In the data shown, a cold probe cooled to -9 °C was placed underneath the mouse's hind paw while the mouse is caged on top of a wire mesh. All mice were tested 1-3 weeks post injection. The CBP mice (n = 4 males, 6 females) showed significantly increased cold sensitivity compared to the naïve controls (n = 2 males, 4 females). Mann-Whitney two-tailed t-test was performed to test significance (p = 0.0002). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
Nociceptive-related behavioral testing and data analysis
Evoked measures
Hypersensitivity on the footpad develops within a day of urokinase injection. Within 1 week, the withdrawal threshold is significantly decreased and persists until euthanasia; this is shown through postsurgical week 4 (Figure 4A). Paw withdrawal latency is analyzed using the von Frey up-down method9 and the Hargreaves test. In the example plotted, mic...
Discussion
This model of chronic back pain is simple to induce, and hypersensitivity established within 1 week can last for up to (and possibly beyond) 8 weeks. This allows for accurate study of the chronic pain state as opposed to other acute models that only last for a week or two. While we show the model in mice, the uPA-induced CBP model can also be established in rats2. An advantage of the model is that the prolonged time course provokes the development of anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, which a...
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing financial interests. KNW acknowledges unpaid consultation with NeuroChronix, Bessor Pharma, and USA Elixeria BioPharm, Inc.
Acknowledgements
Grant funding was provided by NIH HEAL UG3 NS123958. The housing facilities were inspected and accredited by AAALAC. Animals were housed in the Animal Resources Center (ARC) housing facility maintained by the laboratory staff and Division of Laboratory and Animal Resources (DLAR) staff. The procedures for behavioral testing are standard methods in the field as approved by the American Pain Society and the International Association for the Study of Pain. The method of euthanasia is consistent with recommendations of the Panel on Euthanasia of the American Veterinary Medical Association.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Animals and Consumables | |||
| 70% ethanol | Local Source | ||
| BALB/c mice | Envigo | 20-25 g | |
| Cotton balls | Fisher Scientific | 19-090-702 | |
| Cotton-tipped applicators | Fisher Scientific | 19-062-616 | |
| Isoflurane inhalant anesthetic | MedVet | RXISO-250 | |
| Labeling tape | Fisher Scientific | NGFP7002 | |
| Nitrile exam gloves | Fisher Scientific | ||
| Oxygen tank | Local Source | ||
| Surgical drape, Steri-Drape Utility Sheet, Absorbent Prevention | VWR | 76246-788 | cut into 15 x 15 cm pieces |
| Tygon tubing with 3 mm inner diameter | Grainger | 22XH87 | |
| Equipment | |||
| #11 carbon steel scalpel blades | VWR | 21909-612 | |
| Anesthesia induction chamber | Summit Medical Equipment Company | AS-01-0530-LG | |
| Autoclave | Local Unit | ||
| Biology Dumont #5 forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11252-30 | |
| Glass bead sterilizer Germinator 500 | VWR | 102095-946 | |
| IITC Life Sciences Series 8 Model PE34 Hot/Cold Plate Analgesia Meter | IITC | PE34 | |
| Integra Miltex cotton & dressing pliers | Safco Dental Supply | 66-317 | |
| OPTIKA CL31 double arm LED illuminator | New York Microscope Company | OPCL-31 | |
| Plantar Test System with InfraRed Emitter, i. e. Hargreaves Apparatus | Ugo Basile | 37370-001 and 37370-002 | |
| Scalpel Handle No. 3 | VWR | 25607-947 | |
| Small animal heating pad | Valley Vet Supply | 47375 | |
| Student Vannas spring scissors, straight blade | Fine Science Tools | 91500-09 | |
| Table top animal research portable anesthesia workstation “PAM” | Patterson Scientific | AS-01-0007 | |
| Von Frey Filaments | Ugo Basile | 37450-275 |
References
- O'Sullivan, P. B., et al. Back to basics: 10 facts every person should know about back pain. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 54 (12), 698-699 (2020).
- Nauta, H. J., McIlwrath, S. L., Westlund, K. N. Punctate midline myelotomy reduces pain responses in a rat model of lumbar spine pain: evidence that the postsynaptic dorsal column pathway conveys pain from the axial spine. Cureus. 10 (3), 2371 (2018).
- Shuang, F., et al. Establishment of a rat model of lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis using intraarticular injection of urinary plasminogen activator. Scientific Reports. 5 (1), 9828 (2015).
- Reed, N. R., et al. Somatosensory behavioral alterations in a NGF-induced persistent low back pain model. Behavioural Brain Research. 418, 113617 (2022).
- Suh, H. R., Cho, H. -. Y., Han, H. C. Development of a novel model of intervertebral disc degeneration by the intradiscal application of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) in rat. The Spine Journal. 22 (1), 183-192 (2022).
- Kim, H., Hong, J. Y., Lee, J., Jeon, W. -. J., Ha, I. -. H. IL-1β promotes disc degeneration and inflammation through direct injection of intervertebral disc in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. The Spine Journal. 21 (6), 1031-1041 (2021).
- Millecamps, M., Tajerian, M., Sage, E. H., Stone, L. S. Behavioral signs of chronic back pain in the SPARC-null mouse. Spine. 36 (2), 95-102 (2011).
- La Porta, C., Tappe-Theodor, A. Differential impact of psychological and psychophysical stress on low back pain in mice. Pain. 161 (7), 1442-1458 (2020).
- Chaplan, S. R., Bach, F. W., Pogrel, J. W., Chung, J. M., Yaksh, T. L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 53 (1), 55-63 (1994).
- Takao, K., Miyakawa, T. Light/dark transition test for mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments JoVE. (1), e104 (2006).
- Deuis, J. R., Dvorakova, L. S., Vetter, I. Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 10, 284 (2017).
- David, D. J., et al. Neurogenesis-dependent and -independent effects of fluoxetine in an animal model of anxiety/depression. Neuron. 62 (4), 479-493 (2009).
- Yalcin, I., et al. A time-dependent history of mood disorders in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Biological Psychiatry. 70 (10), 946-953 (2011).
- Madathil, S. K., et al. Astrocyte-specific overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 protects hippocampal neurons and reduces behavioral deficits following traumatic brain injury in mice. PloS One. 8 (6), e67204 (2013).
- Sugimoto, H., Kawakami, K. Low-cost protocol of footprint analysis and hanging box test for mice applied the chronic restraint stress. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (143), e59027 (2019).
- Hassan, S., et al. Identifying chronic low back pain phenotypic domains and characteristics accounting for individual variation: a systematic review. Pain. , (2023).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved