A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Setup for the Quantitative Assessment of Motion and Muscle Activity During a Virtual Modified Box and Block Test
In This Article
Summary
The protocol described here aims to enhance the quantitative evaluation of upper limb deficits, with the goal of developing additional technology for remote assessment both in the clinic and at home. Virtual reality and biosensor technologies are combined with standard clinical techniques to provide insights into the functioning of the neuromuscular system.
Abstract
The ability to move allows us to interact with the world. When this ability is impaired, it can significantly reduce one's quality of life and independence and may lead to complications. The importance of remote patient evaluation and rehabilitation has recently grown due to limited access to in-person services. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic unexpectedly resulted in strict regulations, reducing access to non-emergent healthcare services. Additionally, remote care offers an opportunity to address healthcare disparities in rural, underserved, and low-income areas where access to services remains limited.
Improving accessibility through remote care options would limit the number of hospital or specialist visits and render routine care more affordable. Finally, the use of readily available commercial consumer electronics for at-home care can enhance patient outcomes due to improved quantitative observation of symptoms, treatment efficacy, and therapy dosage. While remote care is a promising means to address these issues, there is a crucial need to quantitatively characterize motor impairment for such applications. The following protocol seeks to address this knowledge gap to enable clinicians and researchers to obtain high-resolution data on complex movement and underlying muscle activity. The ultimate goal is to develop a protocol for remote administration of functional clinical tests.
Here, participants were instructed to perform a medically-inspired Box and Block task (BBT), which is frequently used to assess hand function. This task requires subjects to transport standardized cubes between two compartments separated by a barrier. We implemented a modified BBT in virtual reality to demonstrate the potential of developing remote assessment protocols. Muscle activation was captured for each subject using surface electromyography. This protocol allowed for the acquisition of high-quality data to better characterize movement impairment in a detailed and quantitative manner. Ultimately, these data have the potential to be used to develop protocols for virtual rehabilitation and remote patient monitoring.
Introduction
Movement is how we interact with the world. While everyday activities such as picking up a glass of water or walking to work may seem simple, even these movements rely on complex signaling between the central nervous system, muscles, and limbs1. As such, personal independence and quality of life are highly correlated to the level of an individual's limb function2,3. Neurological damage, as in spinal cord injury (SCI) or peripheral nerve injury, can result in permanent motor deficits, thereby diminishing one's ability to execute even simple activities of daily living4,5. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, over 100 million people in the United States experience motor deficits, with stroke as one of the leading causes6,7,8. Due to the nature of these injuries, patients often require prolonged care in which quantitative motor assessment and remote treatment may be beneficial.
Current practices for treating movement disorders often require both initial and ongoing clinical assessment of function through observation by trained experts such as physical or occupational therapists. Standard validated clinical tests often require trained professionals to administer them, with specific time constraints and subjective scoring of predefined movements or functional tasks. However, even in healthy individuals, identical movements can be accomplished with varying combinations of joint angles. This concept is termed musculoskeletal redundancy.
Functional clinical tests often do not account for the individual redundancy underlying inter-subject variability. For clinicians and researchers alike, distinguishing between normal variability caused by redundancy and pathological changes in movement remains a challenge. Standardized clinical assessments performed by well-trained raters utilize low-resolution scoring systems to reduce inter-rater variability and improve test validity. However, this introduces ceiling effects, thus lowering the sensitivity and predictive validity for subjects who may have mild movement deficits9,10. Furthermore, these clinical tests cannot differentiate if deficits are caused by passive body mechanics or active muscle coordination, which may be of importance during initial diagnosis and when designing a patient-specific rehabilitation plan. Randomized clinical trials have revealed inconsistent efficacy of treatment plans formulated based on evidence provided by these clinical tests11,12,13. Several studies have emphasized the need for quantitative, user-friendly clinical metrics that may be used to guide the design of future interventions14,15.
In previous studies, we demonstrated the implementation of automated movement assessment using readily available consumer motion capture devices in post-stroke arm impairment, as well as the evaluation of shoulder function after chest surgery in breast cancer patients16,17. Additionally, we have shown that using active joint moments to estimate muscle moments of specific active movements is a more sensitive measure of motor deficits after stroke compared to joint angles18. Motion capture and surface electromyography (EMG) may therefore be of critical importance in the assessment of patients who are diagnosed as asymptomatic by standard clinical tests, but who may still be experiencing movement difficulties, fatigue, or pain. This paper describes a system that may enable detailed and quantitative characterization of movement during standard clinical tests for the future development of methods for at-home evaluation and rehabilitation in movement-impaired patient populations.
Virtual reality (VR) can be used to construct an immersive user experience while modeling everyday tasks. Typically, VR systems track the hand movements of the user to allow for simulated interactions with the virtual environment. The protocol we describe here uses consumer VR products for motion capture to quantify the assessment of motor deficits, similar to other studies demonstrating the use of off-the-shelf video game controllers in quantitative evaluation of impairment after stroke or shoulder surgery16,17. In addition, EMG is a non-invasive measure of the neural activity underlying muscular contraction19. As such, EMG may be used to indirectly evaluate the quality of the neural control of movement and provide a detailed assessment of motor function. Muscle and nerve damage may be detected by EMG, and disorders such as muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy are commonly monitored using this technique20,21. Furthermore, EMG may be used to track changes in muscle strength or spasticity, which may not be evident in kinematic assessments22,23, as well as fatigue and muscle coactivation. Metrics such as these are critical in considering rehabilitation progress23,24,25.
The experimental paradigm described here seeks to leverage a combination of VR and EMG to address the limitations of traditional clinical assessment tools. Here, participants were asked to perform a modified Box and Block task (BBT)26 using real objects and in VR. The standard BBT is a clinical tool used in the general assessment of gross upper extremity function, in which subjects are asked to move as many 2.5 cm blocks as possible from one compartment, over a partition, to an adjoining compartment within one minute. While often used to reliably assess deficits in patients with stroke or other neuromuscular conditions (e.g., upper extremity paresis, spastic hemiplegia), normative data have also been reported for healthy children and adults, ages 6-8926. A virtual movement assessment is used to simulate functional aspects of the validated clinical test performed in real life. VR is used here to decrease required hardware while allowing for the provision of standardized instructions and programmed, automated scoring. As such, constant supervision by trained professionals would no longer be necessary.
The BBT in this study has been simplified to focus on capturing the reaching and grasping of one block at a time that appears in the same location. This maximized the reproducibility of the movements and minimized the inter-subject variability in recorded data. Lastly, virtual reality headsets can be purchased for as little as $300 and have the potential to house multiple assessments. Once programmed, this would significantly decrease the cost associated with typical professional evaluation and allow for increased accessibility of these standard, validated clinical tests in both clinical and remote/at-home settings.
Protocol
Experimental procedures were approved by the West Virginia University Institutional Review Board (IRB), protocol # 1311129283, and adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Risks from this protocol are minor but it is necessary to explain all procedures and potential risks to participants and written, informed consent was acquired with documentation approved by the institutional ethical review board.
1. System characteristics and design
NOTE: The setup for this protocol consists of the following elements: (1) EMG sensors and base, (2) EMG data acquisition (DAQ) software, (3) a motion capture system, and (4) a VR headset with corresponding software. These components are visualized in Figure 1.
- Setup of the system components
- Connect the EMG system.
- Plug in the EMG base station to power.
- Connect the EMG base station to a dedicated computer (Figure 1C) containing the DAQ scripts.
NOTE: Example scripts can be found at: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/7se5lih4noxj584/AACqFDZytpDm-L8jAULFwfTHa?dl=0. Some commercial products may come with licensed DAQ software, which may also be used.
- Connect the motion capture system.
- Connect a second dedicated computer (Figure 1A) to a network router.
- Connect the network router to a motion capture server.
- Connect the motion capture server to a computer monitor for visualization.
- Connect the cameras to the motion capture server.
- Connect the VR system.
- Connect the VR headset to a third dedicated computer with the corresponding DAQ scripts (Figure 1B).
NOTE: Example scripts can be found at: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/7se5lih4noxj584/AACqFDZytpDm-L8jAULFwfTHa?dl=0 - Load the VR gaming environment containing the intended tasks to the computer linked to the VR headset (Figure 1B).
- Connect the VR headset to a third dedicated computer with the corresponding DAQ scripts (Figure 1B).
- Prepare the area where the subject will complete the task.
- Use an arm-less, sturdy chair to ensure that there is no interference with the subject's normal reaching.
- For the safety and accuracy of the data collected, confirm that the testing area is clear of all obstacles.
- Synchronize the systems.
- Use a custom software function to synchronize systems in time to a one-time server.
- Alternatively, use one computer or a preferred message manager.
- Connect the EMG system.
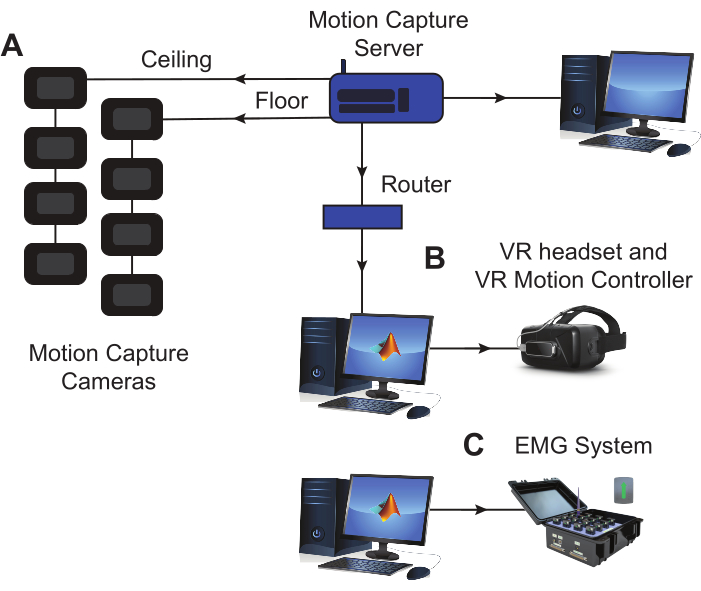
Figure 1: Experimental equipment setup. (A) The marker motion capture cameras are positioned on the floor and in the ceiling around the experimental space, establishing an optimal space for tracking motion. A dedicated computer is used to run the motion capture software and save the data. (B) The headset used to display the modified BBT in VR is connected to a dedicated computer where the virtual assessment and task data are saved. (C) The EMG base is connected to a dedicated computer where muscle activity data is recorded and saved during the task execution. EMG sensors and LED markers for motion capture are both placed on the subject's arm during the session (see Figure 2). Abbreviations: VR = virtual reality; EMG = electromyography. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Experimental procedures
NOTE: a visual representation of the experimental flow described in this protocol is shown in Figure 2.
- Setup EMG
- To determine EMG sensor placement for best signal quality, palpate the muscle belly while the participant contracts the relevant muscle27. See Table 1 for the muscle selection used in this protocol.
- Using an alcohol wipe, carefully clean each electrode and the intended sensor placement site on the subject's arm.
NOTE: Thorough cleaning of both the EMG sensors and the subject's skin will ensure a low electrode-to-skin impedance. This ensures that recorded EMG data has a high signal-to-noise ratio. Excess hair at the sensor placement site may cause low-quality data even if properly cleaned. In this case, it may be necessary to shave the hair. - After preparing the EMG electrodes and the subject's skin, place the EMG sensors on the subject, ensuring good contact between the electrodes and skin. Bipolar electrodes should be positioned so that the sensors are parallel to the direction of the muscle fibers.
- Setup motion capture system
NOTE: This may not be necessary if only a VR headset is being used to track hand movements for kinematics.- Calibrate the motion tracking cameras using the manufacturer's instructions. Move the calibration wand throughout the experimental space to calibrate the motion tracking cameras and set the 3D axis of the space.
NOTE: The marker motion capture system used in this protocol includes a calibration wand with LED markers. - Place the LED motion capture markers on the bony landmarks of the subject's upper extremity and trunk that are needed to construct the desired biomechanical models.
- Use the provided motion capture software to ensure that all markers are recognized and tracked by the motion capture cameras. Instruct the subject to perform several practice movements while study personnel visually monitor marker data in real time.
- Calibrate the motion tracking cameras using the manufacturer's instructions. Move the calibration wand throughout the experimental space to calibrate the motion tracking cameras and set the 3D axis of the space.
- Setup VR skill assessment task
- Position a chair in the center of the motion capture experimental space. Use a chair that is similar to that used for the traditional, real-world test.
- Calibrate the VR headset in the chair where the subject will perform the assessment task. Once calibrated, instruct the subject to sit in the chair and place the VR headset on their head.
- While the subject is seated, measure the distance between the subject's shoulder and the ground, as well as the length of the subject's arm. Use these distances to set the location where the table and assessment task will spawn in VR.
- In the VR task control script, input the subject's measurements and program the desired number of block spawn repetitions.
NOTE: In this Modified BBT, individual blocks will spawn one at a time to increase reproducibility.
- Instruct the subject to perform the modified BBT assessment in VR.
- Provide a brief explanation of the task to the subject.
- The virtual block will spawn on the left or right side, as determined by the experimenter.
- Explain to the subject that they will need to pick up the virtual block, transport it over the partition, and place it onto the target in the opposing compartment (Figure 2).
NOTE: In the virtual modified BBT used here, the block will automatically disappear and re-spawn at the starting position as many times as determined by the experimenter.
- Start collecting EMG data.
- Start collecting motion capture data.
- Start the VR skill assessment task.
- Let the task run for the preset number of repetitions before automatically ending.
- Save the EMG and kinematic data for post-hoc analysis.
- Determine a clinically relevant score for the Modified BBT post-hoc as the number of blocks successfully carried over the barrier or repetitions of the task in 60 s.
- Provide a brief explanation of the task to the subject.
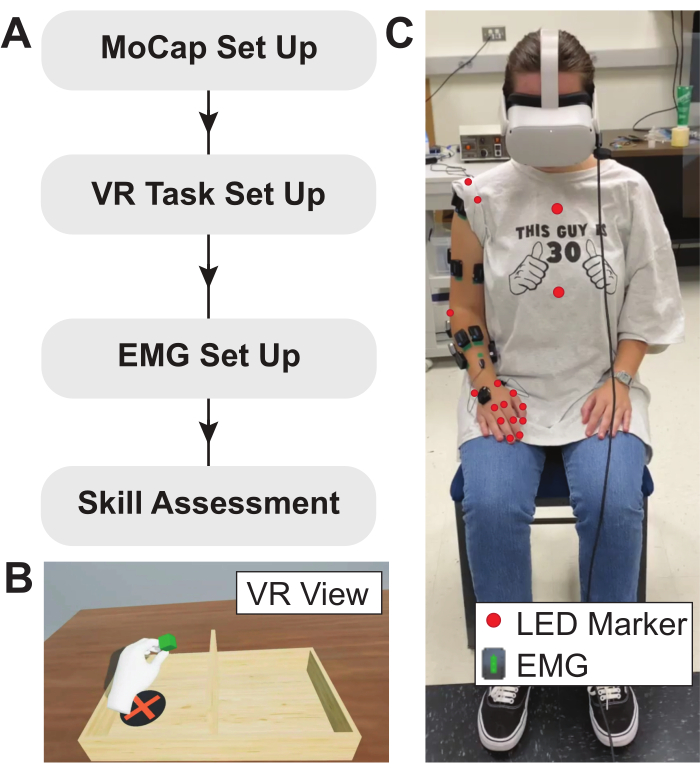
Figure 2: Experimental protocol, VR task, and subject setup. (A) Flow diagram describing the experimental protocol used here. (B) Example view of modified BBT implemented in VR environment. Anatomical measurements are used to calibrate the VR task, ensuring that the virtual table spawns at the correct relative location. (C) Placement of LED motion capture markers and EMG sensors on the subject. EMG sensors are placed on the muscles of interest and LED motion capture markers are positioned over bony landmarks. Abbreviations: VR = virtual reality; EMG = electromyography; LED = light-emitting diode. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
EMG, kinematic, and force data obtained from subjects using this protocol can be used to characterize movements across repetitions of the same task, as well as during different tasks. Data shown here represent results from healthy control participants to demonstrate the feasibility of this setup. Representative EMG profiles recorded from a healthy subject performing the modified BBT in VR are shown in Figure 3. High muscle activation of the anterior deltoid (DELT_A) can be seen, suggesting t...
Discussion
EMG system
The hardware of the EMG system consists of 15 EMG sensors used to obtain muscle activation data. A commercially available Application Programming Interface (API) was used to generate custom EMG recording software. The VR system hardware consists of a virtual reality headset used to display the immersive VR environment and a cable to link the headset to the dedicated computer where the virtual assessment task is stored. The software consists of 3D computer graphics software to create and ...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs through the Restoring Warfighters with Neuromusculoskeletal Injuries Research Program (RESTORE) under Award No. W81XWH-21-1-0138. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions, and recommendations are those of the authors and are not necessarily endorsed by the Department of Defense.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Armless Chair | N/A | A chair for subjects to sit in should be armless so that their arms are not interfered with. | |
| Computer | Dell Technologies | Three computers were used to accompany the data acquisition equipment. | |
| Leap Motion Controller | Ultraleap | Optical hand tracking module that captures the hand and finger movement. The controller has two 640 x 240-pixel near-infrared cameras (120 Hz), which are capable of tracking movement up to 60 cm from the device and in a 140 x 120° field of view. This device was attached to the VR headset or secured above the head during movement. | |
| MATLAB | MathWorks, Inc. | Programming platform used to develop custom data acquisition software | |
| Oculus Quest 2 | Meta | Immersive virtual reality headset equipped with hand tracking ability through 4 infrared build-in cameras (72-120 Hz). Can be substituted with other similar devices (ex. HTC Vive, HP Reverb, Playstation VR). | |
| Oculus Quest 2 Link cable | Meta | Used to connect the headset to the computer where the VR game was stored | |
| PhaseSpace Motion Capture | PhaseSpace, Inc. | Markered motion capture system, consisting of a server, cameras with 60° field of view, red light emitting diode (LED) as markers, and a calibration object | |
| Trigno Wireless System | Delsys, Inc. | By Delsys Inc., includes EMG, accelerometer, force sensors, a base station, and collection software. The Trigno-MATLAB Application Programming Interface (API) was used to develop custom recording software. | |
| UnReal Engine 4 | Epic Games | Software used to create and run the modified Box and Block Task in VR |
References
- Rosenbaum, D. A. . Human motor control. , (2010).
- Kalsi-Ryan, S., Curt, A., Fehlings, M., Verrier, M. Assessment of the hand in tetraplegia using the Graded Redefined Assessment of Strength, Sensibility and Prehension (GRASSP): impairment versus function. Topics in Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 14 (4), 34-46 (2009).
- Kalsi-Ryan, S., et al. The Graded Redefined Assessment of Strength Sensibility and Prehension: reliability and validity. Journal of Neurotrauma. 29 (5), 905-914 (2012).
- Menorca, R. M. G., Fussell, T. S., Elfar, J. C. Nerve physiology. Hand Clinics. 29 (3), 317-330 (2013).
- Spinal cord injury. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/spinal-cord-injury (2023)
- Peripheral neuropathy. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/fact-sheets/peripheral-neuropathy-fact-sheet (2023)
- Statistics: Get informed about Parkinson's disease with these key numbers. Parkinson's Foundation Available from: https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/statistics (2023)
- Virani, S. S., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 143 (8), e254 (2021).
- Hsieh, Y., et al. Responsiveness and validity of three outcome measures of motor function after stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 40 (4), 1386-1391 (2009).
- Van Der Lee, H., Beckerman, H., Lankhorst, G. J., Bouter, L. M. The responsiveness of the action research arm test and the Fugl-Meyer assessment scale in chronic stroke patients. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 33 (3), 110-113 (2001).
- Duncan, P., et al. Randomized clinical trial of therapeutic exercise in subacute stroke. Stroke. 34 (9), 2173-2180 (2003).
- Saposnik, G., et al. Efficacy and safety of non-immersive virtual reality exercising in stroke rehabilitation (EVREST): a randomised, multicentre, single-blind, controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology. 15 (10), 1019-1027 (2016).
- Wolf, S. L., et al. The EXCITE stroke trial: Comparing early and delayed constraint-induced movement therapy. Stroke. 41 (10), 2309-2315 (2010).
- Krakauer, J. W., Carmichael, S. T. . Broken movement: the neurobiology of motor recovery after stroke. , (2017).
- Pollock, A., et al. Interventions for improving upper limb function after stroke. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (11), (2014).
- Olesh, E. V., Yakovenko, S., Gritsenko, V. Automated assessment of upper extremity movement impairment due to stroke. PLoS ONE. 9 (8), e104487 (2014).
- Gritsenko, V., et al. Feasibility of using low-cost motion capture for automated screening of shoulder motion limitation after breast cancer surgery. PLOS ONE. 10 (6), e0128809 (2015).
- Thomas, A. B., Olesh, E. V., Adcock, A., Gritsenko, V. Muscle torques and joint accelerations provide more sensitive measures of poststroke movement deficits than joint angles. Journal of Neurophysiology. 126 (2), 591-606 (2021).
- De Luca, C. Electromyography. Encyclopedia of Medical Devices and Instrumentation. , (2006).
- Lin, C. -. J., Guo, L. -. Y., Su, F. -. C., Chou, Y. -. L., Cherng, R. -. J. Common abnormal kinetic patterns of the knee in gait in spastic diplegia of cerebral palsy. Gait & Posture. 11 (3), 224-232 (2000).
- Lin, J., Shah, D., McCracken, C., Verma, S. Quantitative EMG in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (P6.328). Neurology. 86, (2016).
- EMG test for neuromuscular disease. Brigham and Women's Hospital Available from: https://www.brighamandwomens.org/medical-resources/emg-test (2023)
- Kuthe, C. D., Uddanwadiker, R. V., Ramteke, A. A. Surface electromyography based method for computing muscle strength and fatigue of biceps brachii muscle and its clinical implementation. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. 12, 34-43 (2018).
- Holtermann, A., Grönlund, C., Karlsson, J. S., Roeleveld, K. Motor unit synchronization during fatigue: Described with a novel sEMG method based on large motor unit samples. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 19 (2), 232-241 (2009).
- Kim, H., Lee, J., Kim, J. Electromyography-signal-based muscle fatigue assessment for knee rehabilitation monitoring systems. Biomedical Engineering Letters. 8 (4), 345-353 (2018).
- Mathiowetz, V., Volland, G., Kashman, N., Weber, K. Adult norms for the box and block test of manual dexterity. American Journal of Occupational Therapy. 39 (6), 386-391 (1985).
- Hermens, H. J., Freriks, B., Disselhorst-Klug, C., Rau, G. Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 10 (5), 361-374 (2000).
- Yough, M. Advancing medical technology for motor impairment rehabilitation: Tools, protocols, and devices. Graduate Theses, Dissertations, and Problem Reports. , (2023).
- Velliste, M., Perel, S., Spalding, M. C., Whitford, A. S., Schwartz, A. B. Cortical control of a prosthetic arm for self-feeding. Nature. 453 (7198), 1098-1101 (2008).
- Talkington, W. J., Pollard, B. S., Olesh, E. V., Gritsenko, V. Multifunctional setup for studying human motor control using transcranial magnetic stimulation, electromyography, motion capture, and virtual reality. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (103), e52906 (2015).
- Murillo, C., et al. High-density electromyography provides new insights into the flexion relaxation phenomenon in individuals with low back pain. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 15938 (2019).
- Péter, A., et al. Comparing surface and fine-wire electromyography activity of lower leg muscles at different walking speeds. Frontiers in Physiology. 10, 1283 (2019).
- Isenstein, E. L., et al. Rapid assessment of hand reaching using virtual reality and application in cerebellar stroke. PLOS ONE. 17 (9), e0275220 (2022).
- Varela-Aldás, J., Buele, J., López, I., Palacios-Navarro, G. Influence of hand tracking in immersive virtual reality for memory assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 20 (5), 4609 (2023).
- Robertson, D., et al. Human kinetics. Research methods in biomechanics. , (2004).
- Dunne, J. J., Uchida, T. K., Besier, T. F., Delp, S. L., Seth, A. A marker registration method to improve joint angles computed by constrained inverse kinematics. PLOS ONE. 16 (5), e0252425 (2021).
- Delp, S. L., et al. OpenSim: Open-source software to create and analyze dynamic simulations of movement. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 54 (11), 1940-1950 (2007).
- Naceri, A., Gultekin, Y. B., Moscatelli, A., Ernst, M. O. Role of tactile noise in the control of digit normal force. Frontiers in Psychology. 12, 612558 (2021).
- Wottawa, C. R., et al. The role of tactile feedback in grip force during laparoscopic training tasks. Surgical Endoscopy. 27 (4), 1111-1118 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved