Bu içeriği görüntülemek için JoVE aboneliği gereklidir. Oturum açın veya ücretsiz deneme sürümünü başlatın.
Method Article
Bitki Doku Organik Asit belirlememize Kılcal Elektroforez kullanma: Bir Test Case incelenmesi
Bu Makalede
Özet
Bu makalede, algılama ve serbest Kılcal bölge elektroforezi ile bitki maddesinden organik asitlerin ölçümü için bir yöntem sunulur. Kahve tohumları organik asit seviyesi üzerinde ikincil bir fermantasyon etkilerini belirleyen bu yöntemin olası bir uygulama, bir örneği temin edilmiştir.
Özet
Karboksilik asitler, bir ya da daha çok terminal karboksil (COOH) veya fonksiyonel gruplar içeren organik asitlerdir. Kısa zincirli karboksilik asitler (merkezler, yerelde, üç ila altı karbon atomu içeren karboksilik asitler) gibi malat ve sitrat gibi, hücresel solunum fonksiyonu ve hücre sağlık göstergesi olarak hizmet birçok biyolojik sistemler, düzgün işlemesi için kritiktir. gıdalar, organik asit içeriği, ekşi veya "asit" terimi tat ile artan SCCA düzeyleri ile tat üzerinde önemli bir etkiye sahip olabilir. Bu nedenle, organik asit, düzeylerinin hızlı analizi için yöntemler yiyecek ve içecek sanayii için özel bir öneme sahiptir. Ancak ne yazık ki, SCCA ölçümü için kullanılan en yöntemler pahalı kromatografik ve / veya kütle spektrometrik analizi ve ardından tehlikeli tepkin maddeler ile örneklerin türetme gerektiren zaman alıcı protokolleri bağlıdır. Bu yöntem org tespiti ve ölçülmesi için alternatif bir yöntem detaylarıBitki materyali ve serbest Kılcal bölge elektroforezi (CZE) ile gıda örnekleri arasında organik asitler, bazen sadece kapiler elektroforez (CE) olarak adlandırılır. CZE algılama düşük limiti (0.005 mg / ml) ile merkezler, yerelde ölçmek için bir düşük maliyetli yöntem sağlar. Bu makalede bitki örneklerinden merkezler, yerelde çıkarılmasını ve miktarının ayrıntıları. Resim yöntemi kahve çekirdeklerinden merkezler, yerelde ölçümü odaklanırken, Resim yöntem birden fazla bitki bazlı gıda maddeleri uygulanabilir.
Giriş
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds containing one or more terminal carboxyl functional groups, each attached to an R-group containing one or more carbons (R-C[O]OH). Short chain, low molecular weight carboxylic acids (short chain carboxylic acids, SCCAs) containing between one and six carbons, are essential components of cellular respiration, and function in several biochemical pathways necessary for cell growth and development. SCCAs play critical roles in cellular metabolism1, cell signaling2, and organismal responses to the environment (such as antibiosis3). Because of this, SCCAs can serve as useful indicators of disruptions to cellular metabolism, plant stress responses4,5, and fruit quality6,7. To date, SCCAs have been quantified primarily through chromatographic techniques such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). While these methods, are capable of achieving very low limits of detection, they can be expensive, require the derivatization of target SCCAs using caustic and/or toxic reagents, and include lengthy separation runs on the GC or HPLC. Because of this, interest in the use of free zonal capillary electrophoresis (CZE), which does not require sample derivatization, to quantify organic acids has steadily increased8.
Free zonal capillary electrophoresis (CZE) is a chromatographic separation methodology that, due to its high number of theoretical plates, speed, and relative ease-of-use, is increasingly replacing both GC-MS and high-pressure liquid chromatography as an analytical method for the quantification (particularly for quality control purposes) of anions, cations, amino acids, carbohydrates, and short chain carboxylic acids (SCCAs)8,9,10. CZE-based separation of small molecules, including SCCAs, is based two primary principles: the electrophoretic movement of charged ions in an electrical field established across the buffer filling the capillary; and the electro-osmotic movement of the entire buffer system from one end of the capillary to the other, generally towards the negative electrode. In this system, small molecules move towards the negative electrode at varying speeds, with the speed of each molecule determined by the ratio of the net charge of the molecule to the molecular mass. As the movement of each individual molecule in this system is dependent on the charge state of the molecule and the overall rate of electro-osmotic flow (which is itself based on the ion content of the buffer used to fill the capillary), the buffer pH and ionic composition heavily impact the degree to which molecules can be efficiently separated using CZE. Because of this, SCCAs, with their relatively high charge-to-mass ratios, are ideal targets for CZE-based separation. Metabolites separated using CZE can be detected using a variety of methods, including UV absorbance, spectral absorbance (which is generally performed using a photo-diode array [PDA]), and/or mass spectroscopy (CE-MS or CE-MS/MS)8. The diversity of separation and detection methods provided by CZE makes it an extremely flexible and adaptable technique. Because of this, CZE has been increasingly applied as a standard method of analysis in the areas of food safety and quality11,12, pharmaceutical research13, and environmental monitoring13,14.
Capillary electrophoresis has been used to detect and quantify short chain carboxylic acids for nearly two decades13. The resolving power (particularly for small, charged molecules), short run time, and low per sample cost of CZE analyses make CZE an ideal technique for the separation and quantification of SCCAs13. This method presents a protocol to utilize CZE to measure the concentration of organic acids from plant tissues. Example data was generated through the successful implementation of this protocol to measure the change in organic acid levels in coffee seeds following a secondary fermentation treatment. The protocol details the critical steps and common errors of CZE-based separation of SCCAs, and discusses the means by which this protocol can be successfully applied to quantify SCCAs in additional plant tissues.
Protokol
1. Numune Hazırlama
- kısa zincirli karboksilik asit (SCCA) çıkarılması için örnekleri birleştirin. işlendikten sonra kalacak yeterli örnek sağlamak için her seferinde kahve tohum 1.0 g hazırlayın.
- Numuneler önce öğütme işlemi donmuş olsaydı, donma / çözülme hasarı ve örnek oksidasyonunu önlemek için işlem boyunca dondurulmuş doku tutun. taşlama için gerekli yalnızca dondurucu veya sıfırın depolama numuneyi çıkarın.
- taşlama örnek sıvı azot içinde flaş dondurma, taze numuneleri hemen önce. Bir harç sıvı nitrojen ile önceden doldurulmuş yerleştirerek örnek işleme, flaş dondurma örnekleri en aza indirmek için.
- hemen nesil veya flash -20 ° C'de sıvı nitrojen ve mağaza dondurma veya analize kadar -80 ºC aşağıdaki sıvı örnekleri analiz edin. Analizden önce, depolama donmuş örnekleri kaldırmak ve çözülme için izin verir. Sıvı numuneler için işleme (3.5) adıma geçin.
- beğenme Wearsıvı azot ile çalışmaya başlamadan önce (koruyucu gözlük, eldiven ve laboratuvar önlüğü dahil) zemelerle kişisel koruyucu donanımlar.
- Seramik bir havan ve havan tokmağı kullanılarak sıvı azot içinde bir ince toz halinde homojen (yani, düzgün parçacık boyutu) için üç öğütmek doku örnekleri alındı.
Not: homojen bir partikül boyutu yakalayan SCCA ekstraksiyon etkinliğini maksimize etmek için önemlidir.- harç önceden soğuk ve numunenin eklenmesinden önce sıvı nitrojen ile tokmak. Örnek ilave olarak sıvı azot, küçük hacimde doldurulmuş harç tutun.
- Bir kepçe kullanarak, numuneyi tamamen batırmak için harç yeterli sıvı azot ekleyin.
- sıvı azot, yaprak ve kavrulmuş kahve gibi kolayca zemin örnekleri, ekleme ve dairesel taşlama hareket kullanarak ezmek. sıvı azot seviyesi sadece zar zor örnekleri kapsayan noktaya düşmüştür zaman örnekleri eziyet başlayın.
- örnekleri, böyle bir öğütmek için zor eklesıvı azot çiğ kahve çekirdekleri, s ve onları taşlama önce 10-30 sn (ya da sıvı azot şiddetle kaynar durana kadar) için dondurmak için izin. dikey kırma hareketi kullanarak küçük parçalara doku kırmak ve daha sonra tam doku dairesel taşlama hareket kullanarak taşlama.
- Numuneler üç kez toplam zemin böylece, adım iki kez daha 1.3.2-1.3.4 tekrarlayın. Tipik olarak, öğütme birbirini izleyen üç mermi un benzeri kıvamda bir toz örnekleri azaltacaktır.
- un benzeri bir kıvam elde değilse, adımları tekrarlayın 1.3.2-1.3.4 örnekler eşit küçük tanecik boyutuna sahip bir toz indirgenmiş kadar (ekstraksiyon verimi parçacık boyutu ile ters orantılıdır).
- cam şişeler veya 1.5 ml mikrosantrifüj tüplerine toz aktarın. hemen öğütme sonra aşağı işleme başlatmak (önerilir), veya örnekleri kadar -80 ° C'de mağaza örnekleri çıkarılması için hazırız.
- Numuneler önce depolanması gerekiyorsaAnaliz, 500 mg alikotları (ya da 500 ul sıvı numuneler için hacimde) ve depolama için birden fazla tüpler arasında bölünmüş içine örnek bölün. bu örnek bileşimini değiştirmek ve olumsuz gelecek numune ölçümleri etkileyebilir olarak, tekrarlanan donma / çözülme döngüsü örnekleri maruz kaçının.
2. Organik Asit Standart Hazırlama
- ilgi merkezler, yerelde otantik standartlar birleştirin. Bu SCCA konsantrasyonları belirlenmesinde kullanım için dış ve iç standart çözümler oluşturmak için kullanılır. Çay numuneleri iç standart olarak ilgi ve adipik asit asitler sitrik, malik, asetik, laktik asit, için.
- Seçilen iç standart numune doğal olarak bulunan ve numune profilinde diğer zirveleri ile standart olmadığını co-elute olmadığından emin olun.
- ilgi her SCCA için standart eğrileri çalıştırın ve inst çalışan için bölüm 4 (her SCCA için doğrusal tepki aralığı belirlemek bkzructions). numunesinde ölçülebilir her SCCA için standart eğriler çalıştırmak için emin olun.
Not: Standart eğriler tampon ya da numune GEÇMİŞİ tahlil edilmesi ya çalıştırılabilir. İkinci durumda ( "standart ekleme"), her standart eğri noktası pik alanı değerleri numunenin arka uzaklıkta çıkarılmasıyla belirlenir. - Ön etiket SCCA asit adı, konsantrasyon ve tahlil tarihi ile gerekli tüm tüpler ve cam.
- Standart hazırlanması sırasında doğruluğunu sağlamak için, bir ölçülü balona kullanılarak bilinen bir konsantrasyonu (10 mg / ml) her bir standart için stok çözelti hazırlayın.
- stok çözeltisi için arzu edilen konsantrasyonu sağlamak için, aşırı saf su (18.2) katı SCCA standartları (sitrik asit ve malik asit) içinde çözülür.
- 10 ml'lik bir volumetrik bir şişeye, standart 100 mg eklenerek 10 mg / ml stok çözelti oluşturur. d ultra saf su ile 10 mi hattına ölçülü balona Dolguasit issolve.
- çözeltisi içine adipik asit gibi SCCA standart zor çözülür sürücü şişeler ısı yavaşça asit standart daha düşük bir konsantrasyonda oluşturma veya.
- İstenilen konsantrasyona ulaşmak için, aşırı saf su içinde sıvı faz asit standartları (asetik asit ve laktik asit) seyreltin.
- ultra saf su, 5 ml bir balon jojeye önceden doldurur. şişeye (satıcı tarafından sağlanan asit yoğunluk kullanılarak hesaplanmıştır), 10 mg / ml çözelti hazırlamak için yeterli asit ilave ve daha sonra 10 ml çözeltinin son hacmi getirmek için yeterli su ilave edilir.
- stok çözeltisi için arzu edilen konsantrasyonu sağlamak için, aşırı saf su (18.2) katı SCCA standartları (sitrik asit ve malik asit) içinde çözülür.
- kap kaplı bir politetrafloroetilen (PTFE), temiz bir 15 ml'lik bir cam tüpe her bir stok çözeltisini, plastik parafın film ile kapatın. Stok çözeltileri 1 hafta boyunca 4 ° C'de kapalı tüplerde saklanabilir.
- stok solüsyonları HAZIRLIK sonra buzdolabında olması halinde SCCA standartları kullanmadan önce çözümün dışına çöktürülmüş değil emin oluntirme. Sürücü hafif ısıtma ile çözelti haline geri çöker.
- SCCA çıkarma çözeltisi hazırlayın. örneklerde tarama için yeterli bir konsantrasyonda (0.05 mg / ml) iç standart içerir. Tüm örnekler ayıklamak için yeterli bir çözüm hazırlayın.
- ultra saf su içinde 0.05 mg / ml dahili standart stok çözelti seyreltilerek SCCA ekstraksiyon çözeltisi 50 ml hazırlayın. su 49.75 mi, iç standart stok solüsyonu (10 mg / ml) 250 ul ekleyin.
- Ekstre seyreltildi gerekirse nihai konsantrasyon ölçümü sınırları içinde kaldığı, böylece, ekstre çözeltisi içinde iç standart konsantrasyonunu ayarlamak (bir tespit veren ama doymuş aşırı zirve aşağıda 5.2.2 bakınız olan) seyreltildikten sonra CE sistemi (0.05 mg / ml).
- (Her bir deney serisi için, yani,) ekstraksiyon her bir seri için taze bir ekstraksiyon çözeltisi hazırlayın.
- standart eğri örnekleri hazırlamaken az 5 puan asgari kullanılarak ilgi merkezler, yerelde (Uygun bir dizi seyreltisi). Kullanılan standart eğri konsantrasyonları belirli bir SCCA için doğrusal tepki aralığında olması gerekir, ve örnekler beklenen SCCA konsantrasyonlarını yayılma.
- örneklerde, iç standart miktarını belirlemek için bir standart eğri Çözeltilerin seçilen iç standart içerir. iç standart tepe tanımlanması ve hesaplama ekstraksiyon verimi (bölüm 6) yardımcı olmak için kullanılır.
- Yukarıda belirlenen konsantrasyonda, her SCCA seyreltilir (0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08 mg / ml; yukarıdaki 2.4.2 bakınız), aşırı saf su ile yeni bir mikrosantrifüj tüplerinde (her konsantrasyon / standart eğri noktası için bir tane). Her bir standart eğri konsantrasyonu noktası için solüsyonun 1 ml hazırlayın. Her konsantrasyon noktası dört asit standartları ve doğru konsantrasyonda iç standart içerdiğinden emin olun.
- Her set için yeni standart eğri noktaları hazırlayınNumunelerin kapiller elektroforez sistemi üzerinde çalışmak üzere. hedef dokularda (bölüm 3) den merkezler, yerelde çıkarılması aşağıdaki oluşacak olan analize kadar 4 ° C'de standart eğri SCCA örnekleri tutun.
3. Organik asit ekstraksiyon
- Her bir numune için en az bir boru hazırlamak ön etiket örneği tüpler ekstre edilmesi.
- Numuneler depolama ayıklanmasını çıkarın ve ekstraksiyon için malzeme dışarı ağırlığında iken buz koyun.
- SCCA çıkarılması için örnek 100 mg tartılır.
- Her numune ağırlığında sonra, temiz bir 1.5 ml mikrosantrifüj tüp doku aktarın. Değişkenliği azaltmak mümkün hedef kütlesine yakın numunenin bir miktarını ölçün.
- tespit merkezler, yerelde miktarları örnek kütlesi kullanılarak normalize edileceği gibi (aşağıdaki 6.5.2 bakınız), ölçülen her numune kütlesinin takip edin.
- Bütün numuneler Tartıldıktan sonra (wate ekstraksiyon çözeltisi 1 ml ekleyinr + Örnek tüplerin her adım 2.4 iç standart karışımı). (Bu durumda, 100 ± 5 mg doku başına 1 ml), doku kütlesi ekstraksiyon boyunca aynı ekstraksiyon çözeltisinin oranı tutun. 10 saniye boyunca girdap tarafından iyice karıştırın.
- Numuneler 1 saat boyunca oda sıcaklığında bekletin. Bu bir saat boyunca, adım 3.4 gibi her tüpü her 15 dakika karıştırın.
- ekstraksiyon 1 saat sonra, numuneler son bir kez karıştırmak ve bir mikrosantrfuj örnek tüpleri aktarın. 4 ° C'de santrifüj örnekleri, 10 dakika boyunca 10,000 x g'de bir katı madde (hücre duvarları, ayrı ayrı parçacıklı madde gibi) çökeltildi.
- sıvı örnekleri işlerken, iç standardın uygun konsantrasyonunu eklemek kısaca ve santrifüj karıştırın. Santrifüj işleminden sonra, katı örneklerinden ekstresi için aynı sıvı örnekleri davranın.
- onlar tespit kiti çalışan tampon pH aralığı ile uyumlu olduğunu teyit etmek için numunelerin pH kontrol (adım 4.6) ya da emp olma sistemi tamponloyed. örnek hacimleri, genellikle oldukça küçük olduğundan, pH kağıdı ile izlenebilir.
- şırınga monte disk filtreler (3.8) kullanarak örnekleri filtrelemek için hazırlayın.
NOT: Her filtre doğru süpernatant aktarmadan önce bir şırıngaya takılı olduğundan sağlayarak örnek kaybını önleyin. Her numune (standart eğri numuneleri dahil) analiz edilecek bir disk filtresi ile donatılmış bir şırınga hazırlayın. - Numunelerin santrifüj ve şırınga filtresi hazırlanmasından sonra 0.2 um'lik bir şırınga filtresi ile donatılmış bir 3 ml şırınga her numune süpernatant aktarın. Her bir örnek için yeni bir filtre ve şırınga kullanın. önce CE sistemi üzerinde çalışan standart eğri örnekleri ve tampon kontrolleri dahil olmak üzere tüm örnekler, Filtre.
- Temiz bir mikrosantrifüj tüpü içine doğrudan örnek filtre. Filtreleme işleminden sonra, tüp içeren süzüntü kapatın ve şırınga / filtre cihazı atın.
- Hemen süzüldü örnekleri yerSCCA tespiti için CE sistemine; gece boyunca 4 ° C'de veya mağaza örnekleri. Numuneler gecede saklanması ise, gaz değişimi ve örnek buharlaşmasını önlemek için plastik parafin film ile tüpler mühür.
- Numuneler filtreleme bir gün sonra daha uzun saklanabilir gerekiyorsa, -20 ° C'de sıvı azot veya donma flaş dondurma özler. Çözündükten sonra, ancak, gerektiğinde her bir numune (adım 3.6 gibi) bir çökelti oluşumu ve filtre için incelenir emin olun.
4. SCCA Algılama Run Kurma
- programlama ve kontrol yazılımı özel ayrıntılar için CE kullanım kılavuzuna başvurun.
- SCCA tespiti için kılcal elektroforez (CE) örnek şişeleri hazırlayın. Emin olun şişeler düzgün etiketli, temiz ve arızasız vardır.
- Yıkayın ve kullanmadan önce CE flakon kapaklarını kurutun.
- ultra saf su içinde daldırarak ve onları bir gece ıslanmasına imkan sağlayarak kapaklar yıkayın. kapaklar iliklerine sonra, emmek atınçözüm ing ve ultra saf su ile iki kez daha kapaklarını yıkayın.
- Aktarım havsız dokusu ile kaplı temiz bir kurutma yüzeyine kapakları durulanır ve kurumaya onlara izin. Emin olun kapaklar basınç arızaları önlemek için kullanmadan önce tamamen kuru.
- Şişenin boyun içine örnek sıçramasına yanlışlıkla önlemek için dikkatli olmak, her CE şişesine numune 1 ml aktarın. Transferden sonra, her flakon üzerine CE kapağı yerleştirin.
- bir seyreltme gerekli ise, kahve, tohum örnekleri 1:10 veya 1 seyreltin: 100 doğrudan CE şişede ultra saf su ile. 1'den büyük dilüsyonları için: 100, pipet hatalarını önlemek için bir ara seyreltme oluşturun.
- CE şişelere adım 2.5 standart eğri çözümleri (1.0 mi) aktararak, her standart eğri noktası için bir şişe hazırlanır. transferi sonrası her tüp kap.
- peletler T90 mi ultra saf su ihtiva eden bir beher NaOH 0.04 g ekleme ve izin vererek, sodyum hidroksit (NaOH) içindeki bir 0.1 M çözelti hazırlayıno çözülür. 100 ml'lik bir volümetrik şişeye, 0.1 M NaOH solüsyonu aktarın ve 100 ml toplam hacim getirmek.
- Temiz CE şişe ve kapağın 0.1 M NaOH çözeltisi 1 ml.
- Numunelerin her parti için CE tampon şişeleri hazırlayın CE sistemi üzerinde çalışmak üzere. Ayırma kitleri kullanılabilir veya özel tamponlar 13 kullanılabilir.
- tampon çözeltisi ve kapak başlangıç 1 ml 1 flakon hazırlayın.
- 1 ml tampon çözelti ve kap çalışan her üç şişeleri hazırlayın. örnekler ve standart eğri noktalarının her parti önce çalışan tampon değiştirin veya 35 örneklerinin sonra, hangisi önce gerçekleşirse.
- ultra saf su, 1 ml üç ek şişeler doldurulur ve her bir flakon kapağı.
- kapaklı 1 boş "atık" flakon hazırlayın.
- Adım 4.8 açıklanan şişeleri hazırladıktan sonra, kapiller elektroforez sys tampon tepsisine (adım 4.8.2-5 itibaren) tamponlar ve su içeren flakon yanı sıra atık şişeleri yüktem, üreticinin talimatlarına 15 başına. Dikkatle otomatik örnekleyici programlama için her şişeye konumunu not edin.
- Standart eğri noktalarını içeren şişeleri yükleyin ve üreticinin talimatlarına açıklandığı gibi örnekleri içeren şişeler, giriş numune tepsiye tahlil edilecek. Otomatik numune programlama için her şişeye konumuna dikkat edin (adımları aşağıda 4.11.1 bakınız).
- Klima ve örnek ayırma yöntemleri (bunlar için programlar sırasıyla Tablo 1 ve 2'de verilmiştir) hazırlayın ve enstrüman kullanma kılavuzu doğrultusunda örnek bir sekans dosyası yazmak. Tablo 2'de ayrıntılı ayırma yöntemi kullanın: 0.2 dakika boyunca başlatıcı (20 psi) ile sütun yıkayın; (12 dakika boyunca 20 kV, 0.09 dakika boyunca, ayrı numuneler kolonuna örnekleri (0.5 psi) enjekte, 0.5 dakika boyunca hızlandırıcı (20 psi) ile yıkayın 0.5 dakika süreyle NaOH (20 psi) ile yıkayın ve son olarak su ile yıkayın 20 psi) 0,5 dakika karıştırıldı.
- usiCE kontrol yazılımı ng (yani, iş listesi; numuneler analiz edilecek sırayı ayrıntılı bir liste dosyası ve yöntem her numune ayırmak için kullanılacak) numune çalışan dizisini yazmak "dizisi" tablo arabirimini kullanarak. tablo üzerinde her satır, bir örnek çalışma karşılık ve tek bir veri dosyası üretecektir.
- dizisi dosyasını yazarken, numuneler numune tepsisine doğru pozisyonda kullanılarak tanımlanır emin olun. Her bir veri dosyası, önceki dosyaların üzerine yazmasını yazılımları önlemek için benzersiz bir ada sahip olduğundan emin olun. Örnek ayırma yöntemini içeren dizi çalıştırmak öncesinde ayrı bir dizi olarak bir program CE kılcal klima çalışır.
- SCCA örneklerinin ardından standart eğri çözümler çalıştırmak örnek dizisi, başlar ve standart eğri çözümleri ikinci çalışma ile sona erer. Bu örnek analizleri sırasında oluşan herhangi bir sinyal kaybı derecesi hesaplama sağlayacaktır.

Tablo 1: Kılcal yoluyla kısa zincirli karboksilik asit ayrılması için kılcal hazırlamak için kullanılan şartlandırma yöntemi programı elektroforez.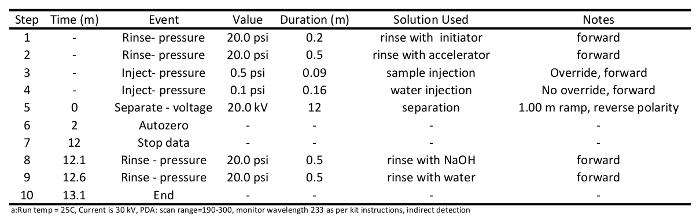
Tablo 2: kılcal bir elektroforez ile kısa zincirli karboksilik asitler, analiz için kullanılan ayırma yöntemi programı.5. SCCA Algılama Run İcra ve Veri Toplama
- kılcal klima çalışır başlatın. Sütun örnek ayrılması için hazır olmadan önce kılcal iki ya da üç kez şart bekliyoruz. Sütun Tertibatı Tablo 1 'de tarif edildiği gibi gerçekleştirilmelidir. Kısaca, 1 dakika için 0.1 M NaOH (20 psi) ile sütun durulama suyu (20 psi) için durulayın1 dakika, 10 dakika, 30 kV, 0.5 dakika, ayrı hızlandırıcı hızlandırıcı (20 psi) ile çalkalanmıştır 0.5 dakika için başlatıcı (20 psi) ile yıkayın 0.5 dakika boyunca 0.1 M NaOH (20 psi) ile sütun durulama ve son olarak da 0.5 dakika boyunca su (20 psi) ile sütun yıkayın.
- Her numune dizisi çalıştırmak öncesinde kılcal hale getirin. ayırma gerilimini tutarak uygun klima ulaşmak çalışma boyunca sürekli ve fotodiyot dizisi iz üzerinde düz bir taban çizgisi izlemektedir.
- Klima sonra, (yani, üzerine tıklayarak) yazılımında "kontrol" menüsünü açarak ve seçerek örnek ayrımı başlatmak "run dizisi." Doğru ayrılmasını sağlamak için fotodiyot dizisi (PDA) iz izleyin.
- Bireysel asit zirveleri ilk iz gözlemlemek ve düz bir dayanak vardır ve temiz (bazal çözünürlük) çözüldü emin olun. Aşırı yüklü örnekleri uzun tepe kuyrukları ya da pik kuyruklanmasını gösterecek ve (Şekil 1) seyreltilmiş gerekecektir.

Şekil 1:. PDA karşılaştırılması yüklenmiş bir örneği vurgulayarak izleri analit konsantrasyonu arttıkça, bireysel zirve geometri asimetrik olmaya başlayabilir. (A) 0.05 mg / ml 'de, asetik asit, iyi tanımlanmış, iki taraflı, simetrik tepe sunulur. Asetik asit konsantrasyonu arttıkça, (b) 0.07 mg / ml ve (c) 0.10 mg / ml bir zirve kuyruk formları (oklar) görülmektedir. Bu zirve atık numunesi aşırı iyi bir göstergesidir. Bu rakamın büyük halini görmek için lütfen buraya tıklayınız.- dizi çalışmasının bitiminde, veri dosyaları CE analiz yazılımı teker teker açıp doruklarına entegre.
- Örnek doruklarına entegre edin.
- İlk dosyasını açın(Tablo 1 'de tarif edildiği üzere voltaj ve kolon akışı dolayısıyla yönü tersine çevrilir) çalıştırmak ilk 3 dakika hariç tutmak için, otomatik entegrasyon adımları ayarlayın. Aynı menüde, iz arka plan gürültü asit doruklarına ayıran, seçicilik bir orta yüksek düzeyde sağlamak için 50 birim minimum pik genişliği ve 100 adet (veya üreticinin varsayılan ayarlarına) pik alanına zirve seçim kriterleri ayarlayın.
- El ile uygun zirve entegrasyonunu sağlamak için her PDA iz zirve sınırları ve taban kontrol edin. Yanış entegre zirveler (yani, otomatik yazılım tarafından iki ayrı zirveleri olarak entegre edilmiştir biraz asimetrik SSCA tepe) el ile yeniden entegre edilmesi gerekecektir.
- Örnek doruklarına entegre edin.
- entegrasyon sonra, yüzde alanı raporunu görüntülemek, daha sonra gelin ve yüzde alanı raporu kopyalamak ve ayrı bir e-tabloya yapıştırın. Tam çalışma zirve yapılandırma raporlama oluşturmak için her bir örnek için tekrarlayıntek bir pik temsil eden her satırda t (ayırma iyi çalışıp çalışmadığını yani. Her zirve tek bir bileşik içermelidir).
6. Veri Analizi
- (5.4) inşa tablo kullanarak analiz için veri hazırlayın. iç standart olmak üzere, standart eğri noktalarının her biri için asit standartları etiketleyerek analizi başlayın.
- Bu örnekteki iç standardın alıkonma zamanında numunenin her tepe için bir tutma süresine bölünerek her bir tepe noktasının için bir tutma indisine hesaplayın. Her numunenin ilgi doruklarına tanımlamak için ortaya çıkan tutma endeksine göre belirlenen verileri sıralamak.
- her bir ilgi asit zirve noktasının tanımlanmasından sonra, dış standart bir eğri noktalarını kullanarak her asit için öngörülen standart eğrilerini oluşturmak.
- Xa konsantrasyonu SCCA standartlarının her bir konsantrasyonu için pik alanının belirlenmesi ve işaretlenmesiyle her SCCA standardı için standart (konsantrasyon) eğrisi oluşturmaky-ekseni üzerinde pik alanı vs taksiler. Her SCCA standart eğri için lineer regresyon arsa ve eğimi denklemini define (y = mx + b).
- Sayımsal en doğru şekilde, standart eğrinin lineer aralığında gerçekleştirilir doğrusal regresyon R2 değerleri 0.90 veya daha yüksek olduğundan emin olun.
- pik alanı ve (yukarıda 6.3.2 hesaplanan), standart eğrinin lineer regresyon çizgisinin eğimi denklem kullanılarak bir örnekte, belirli bir SCCA için asit konsantrasyonu hesaplanır. Kısaca, bu asit standart eğri için regresyon çizgisinin eğimi tarafından belirli bir asit için gözlenen en yüksek alan bölün.
- iç standart (adım 6.5) kullanılarak işlenmesi sırasında numune kaybı için adım 6.4 hesaplanan ham konsantrasyon değerleri düzeltin.
- iç standart kullanılarak her numune için düzeltme faktörünü hesaplamak.
- Internal standart gerçek konsantrasyonunu bölün (yani, knoörnek dahili standart (gözlenen değer) deneyin başlangıcında ilave wn miktarı, yani, iç standart için bir standart eğri eğimi aşağıdaki denklem kullanılarak hesaplanmıştır tutar). Bu düzeltme faktörü ile numunedeki her SCCA ham konsantrasyon değerleri çarpın.
- numune kütlesinin herhangi bir varyasyonu için düzeltmek için çıkarımı için kullanılan, örneğin kütlesinde SCCA konsantrasyonu düzeltilmiş iç standart bölün. Bu hesaplama, örnek kütlesine (mg SCCA başına mg bu örnekte kahve) daha sonra belirli bir çalışma için uygun bir birim (mg / mg mg / g dönüştürülebilir, g / g, vb her analit miktardadır ).
- SCCA konsantrasyonları hesaplandıktan sonra ([sıvı numuneler için] ya [katı veya sıvı numuneler için] kütle veya hacim normalize), deneysel tasarım ve ilgi soru taleplerine göre istatistiksel analiz için bu değerleri kullanın.
- usiCE kontrol yazılımı ng (yani, iş listesi; numuneler analiz edilecek sırayı ayrıntılı bir liste dosyası ve yöntem her numune ayırmak için kullanılacak) numune çalışan dizisini yazmak "dizisi" tablo arabirimini kullanarak. tablo üzerinde her satır, bir örnek çalışma karşılık ve tek bir veri dosyası üretecektir.
Sonuçlar
Bu protokol başarıyla yeşil kahve tohumlarının SCCA içeriğine tohum tedavilerin etkilerini ölçmek için kullanılmıştır. Bu deneyde, altı tedavi edildi: Leuconostoc doymuş bir mikrobiyal süspansiyonu su içinde GCP674 mikropların (1), bir sulu süspansiyon, büyüme ortamı içinde streyn GCP674 pseudomesenteroides (2), asetik asit ve laktik asit (0.15 ve 0.4 arasında bir sulu çözelti mg /), sırasıyla mL (3), bir harcanan M1 büyüme ortamı işleme...
Tartışmalar
herhangi bir analitik tekniği ile olduğu gibi, önemli ölçüde üretilen verilerin kalitesini ve güvenilirliğini etkileyebilir birçok kritik faktör vardır. İlk olarak, donma / erime devirine minimum verimli örnekleri işlemek için önemlidir. Tekrarlanan donma ve çözülme işleme veya analiz öncesi numunenin kimyasal bileşimi bozabilir. İkincisi, sürekli ve eşit tüm örneklerde bu protokolün adımlarını uygulamak için kritik öneme sahiptir. tutarsız numune hazırlama ve işleme kaynaklanan tekn...
Açıklamalar
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Teşekkürler
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of this project by The J.M. Smucker company.
Malzemeler
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Ceramic Moarter and Pestle | Coorstek | 60310 | |
| Beckman Coulter P/ACE MDQ CE system | Beckman Coulter | Various | |
| Glass sample vials | Fisher Inc. | 033917D | |
| 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes | Fisher Inc. | 02-681-5 | |
| LC/MS grade water | Fisher Inc. | W6-1 | Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ.cm) is also acceptable |
| 15 ml glass tube/ Teflon lined cap | Fisher Inc. | 14-93331A | |
| Parafilm M | Fisher Inc. | 13-374-12 | |
| CElixirOA detection Kit pH 5.4 | MicroSolv | 06100-5.4 | |
| BD Safety-Lok syringes | Fisher Inc. | 14-829-32 | |
| 17 mm Target Syringe filter, PTFE | Fisher Inc. | 3377154 | |
| 32 Karat, V. 8.0 control software | Beckman Coulter | 285512 | |
| capillary electrophoresis (CE) sample vials | Beckman Coulter | 144980 | |
| caps for CE vials | Beckman Coulter | 144648 | |
| Liquid Nitrogen | N/A | N/A | Liquid nitrogen is available from most facilities services |
Referanslar
- Araújo, W. L., Nunes-Nesi, A., Nikoloski, Z., Sweetlove, L. J., Fernie, A. R. Metabolic Control and Regulation of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in Photosynthetic and Heterotrophic Plant Tissues: TCA Control and Regulation in Plant Tissues. Plant Cell Environ. 35 (1), 1-21 (2012).
- Finkemeier, I., Konig, A. C., et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Role of Carboxylic Acids in Metabolite Signaling in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Physiol. 162 (1), 239-253 (2013).
- Doyle, M. P., Buchanan, R. . Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers. , (2013).
- Tůma, P., Samcová, E., Štulìk, K. Determination of the Spectrum of Low Molecular Mass Organic Acids in Urine by Capillary Electrophoresis with Contactless Conductivity and Ultraviolet Photometric Detection-An Efficient Tool for Monitoring of Inborn Metabolic Disorders. Anal Chim Acta. 685 (1), 84-90 (2011).
- López-Bucio, J., Nieto-Jacobo, M. F., Ramı́rez-Rodrı́guez, V., Herrera-Estrella, L. Organic Acid Metabolism in Plants: From Adaptive Physiology to Transgenic Varieties for Cultivation in Extreme Soils. Plant Sci. 160 (1), 1-13 (2000).
- Cebolla-Cornejo, J., Valcárcel, M., Herrero-Martìnez, J. M., Rosellò, S., Nuez, F. High Efficiency Joint CZE Determination of Sugars and Acids in Vegetables and Fruits: CE and CEC. Electrophoresis. 33 (15), 2416-2423 (2012).
- Rosello, S., Galiana-Balaguer, L., Herrero-Martinez, J. M., Maquieira, A., Nuez, F. Simultaneous Quantification of the Main Organic Acids and Carbohydrates Involved in Tomato Flavour Using Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. J Sci Food Agr. 82 (10), 1101-1106 (2002).
- Wasielewska, M., Banel, A., Zygmunt, B. Capillary Electrophoresis in Determination of Low Molecular Mass Organic Acids. Int J Environ Sci Dev. 5 (4), 417-425 (2014).
- Galli, V., Garcìa, A., Saavedra, L., Barbas, C. Capillary Electrophoresis for Short-Chain Organic Acids and Inorganic Anions in Different Samples. Electrophoresis. 24 (1213), 1951-1981 (2003).
- Klampfl, C. W. Determination of Organic Acids by CE and CEC Methods. Electrophoresis. 28 (19), 3362-3378 (2007).
- Kenney, B. F. Determination of Organic Acids in Food Samples by Capillary Electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 546, 423-430 (1991).
- Galli, V., Barbas, C. Capillary Electrophoresis for the Analysis of Short-Chain Organic Acids in Coffee. J Chromatogr A. 1032 (1-2), 299-304 (2004).
- Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Capillary Electrophoresis: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 384 (2008).
- Nollet, L. . Chromatographic analysis of the environment 3rd ed. , (2006).
- . . ElixerOA Organic Acids/Anions Operating and Instruction Manual, MicroSolv Technology Corperation. , (2001).
- Dahlen, J., Hagberg, J., Karlsson, S. Analysis of low molecular weight organic acids in water with capillary zone electrophoresis employing indirect photometric detection. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 366 (5), 488-493 (2000).
- Ibanez, A. B., Bauer, S. Analytical method for the determination of organic acids in dilute acid pretreated biomass hydrolysate by liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectroscopy. Biotech. For Biofuels. 7 (145), (2014).
Yeniden Basımlar ve İzinler
Bu JoVE makalesinin metnini veya resimlerini yeniden kullanma izni talebi
Izin talebiThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır