JoVE 비디오를 활용하시려면 도서관을 통한 기관 구독이 필요합니다. 전체 비디오를 보시려면 로그인하거나 무료 트라이얼을 시작하세요.
Method Article
식물 조직에서 유기산을 정량화하는 모세관 전기 영동을 사용하여 : 테스트 케이스 검사
요약
이 문서에서는 검색 및 무료 띠 모세관 전기 영동을 이용하여 식물 재료에서 유기산 정량하는 방법을 제시한다. 커피 종자 유기산 농도에서 발효 차의 효과를 결정하는 이러한 방법의 잠재적 인 애플리케이션의 일례가 제공된다.
초록
카르 복실 산, 하나 이상의 단말 카르복실기 (COOH) 작용기를 함유하는 유기산이다. 짧은 체인 카르 복실 산 (SCCAs, 3 ~ 6 탄소를 포함하는 카르 복실 산) 등의 말 산염과 구연산 등이, 그들은 세포 호흡에서 기능과 세포 건강의 지표 역할을 할 수있는 많은 생물 시스템의 적절한 기능에 중요하다. 식품에서의 유기산 함유량은 신 또는 "산"맛 결과 증가 SCCA 수준의 맛에 큰 영향을 가질 수있다. 이 때문에 유기산 농도의 신속한 분석을위한 방법은 음식 및 음료 산업에서 특히 중요하다. 그러나, 불행히도 SCCA 정량 방법에 사용 가장 비싼 크로마토 그래피 및 / 또는 질량 분광 분석을 하였다 위험한 시약과 시료의 유도체를 요구하는 시간 소모적 인 프로토콜에 의존한다. 이 방법은 조직의 검출과 정량을위한 다른 방법의 자세한 사항식물 재료 및 무료 띠 모세관 전기 영동 (CZE)를 이용하여 음식 샘플로부터 anic 산은 때때로 단순히 모세관 전기 영동 (CE) 라 함. CZE 검출의 하한 (0.005 ㎎ / ㎖)로 SCCAs을 측정하기위한 비용 효율적인 방법을 제공한다. 이 문서에서는 식물 샘플에서 SCCAs의 추출 및 정량을 자세히 설명합니다. 제공된 방법은 커피 콩 SCCAs 측정에 초점을 맞추고 있지만, 제공되는 방법은 여러 식물성 식품 재료에 적용될 수있다.
서문
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds containing one or more terminal carboxyl functional groups, each attached to an R-group containing one or more carbons (R-C[O]OH). Short chain, low molecular weight carboxylic acids (short chain carboxylic acids, SCCAs) containing between one and six carbons, are essential components of cellular respiration, and function in several biochemical pathways necessary for cell growth and development. SCCAs play critical roles in cellular metabolism1, cell signaling2, and organismal responses to the environment (such as antibiosis3). Because of this, SCCAs can serve as useful indicators of disruptions to cellular metabolism, plant stress responses4,5, and fruit quality6,7. To date, SCCAs have been quantified primarily through chromatographic techniques such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). While these methods, are capable of achieving very low limits of detection, they can be expensive, require the derivatization of target SCCAs using caustic and/or toxic reagents, and include lengthy separation runs on the GC or HPLC. Because of this, interest in the use of free zonal capillary electrophoresis (CZE), which does not require sample derivatization, to quantify organic acids has steadily increased8.
Free zonal capillary electrophoresis (CZE) is a chromatographic separation methodology that, due to its high number of theoretical plates, speed, and relative ease-of-use, is increasingly replacing both GC-MS and high-pressure liquid chromatography as an analytical method for the quantification (particularly for quality control purposes) of anions, cations, amino acids, carbohydrates, and short chain carboxylic acids (SCCAs)8,9,10. CZE-based separation of small molecules, including SCCAs, is based two primary principles: the electrophoretic movement of charged ions in an electrical field established across the buffer filling the capillary; and the electro-osmotic movement of the entire buffer system from one end of the capillary to the other, generally towards the negative electrode. In this system, small molecules move towards the negative electrode at varying speeds, with the speed of each molecule determined by the ratio of the net charge of the molecule to the molecular mass. As the movement of each individual molecule in this system is dependent on the charge state of the molecule and the overall rate of electro-osmotic flow (which is itself based on the ion content of the buffer used to fill the capillary), the buffer pH and ionic composition heavily impact the degree to which molecules can be efficiently separated using CZE. Because of this, SCCAs, with their relatively high charge-to-mass ratios, are ideal targets for CZE-based separation. Metabolites separated using CZE can be detected using a variety of methods, including UV absorbance, spectral absorbance (which is generally performed using a photo-diode array [PDA]), and/or mass spectroscopy (CE-MS or CE-MS/MS)8. The diversity of separation and detection methods provided by CZE makes it an extremely flexible and adaptable technique. Because of this, CZE has been increasingly applied as a standard method of analysis in the areas of food safety and quality11,12, pharmaceutical research13, and environmental monitoring13,14.
Capillary electrophoresis has been used to detect and quantify short chain carboxylic acids for nearly two decades13. The resolving power (particularly for small, charged molecules), short run time, and low per sample cost of CZE analyses make CZE an ideal technique for the separation and quantification of SCCAs13. This method presents a protocol to utilize CZE to measure the concentration of organic acids from plant tissues. Example data was generated through the successful implementation of this protocol to measure the change in organic acid levels in coffee seeds following a secondary fermentation treatment. The protocol details the critical steps and common errors of CZE-based separation of SCCAs, and discusses the means by which this protocol can be successfully applied to quantify SCCAs in additional plant tissues.
프로토콜
1. 샘플 준비
- 짧은 체인 카르 복실 산 (SCCA) 추출을위한 샘플을 조립합니다. 처리 후 남아 충분한 샘플을 보장하기 위해 한 번에 커피 씨앗의 1.0 g을 준비합니다.
- 샘플 전에 연삭 가공에 고정 된 경우, 동결 / 해동의 손상 및 샘플 산화를 방지하는 처리를 통하여 냉동 조직을 유지한다. 연삭에 필요한 전용으로 냉동 또는 영하의 기억에서 샘플을 제거합니다.
- 분쇄 시료에 액체 질소에 플래시 동결 신선한 샘플은 직전. 박격포 액체 질소로 미리 충전에 배치하여 시료 처리, 플래시 동결 샘플을 최소화합니다.
- 즉시 생성, 또는 플래시 -20 ºC에서 액체 질소와 상점에서 동결 또는 분석 할 때까지 -80 ºC 다음 액체 샘플을 분석 할 수 있습니다. 이전 분석, 저장에서 냉동 샘플을 제거하고 해동 할 수 있습니다. 액체 샘플은 처리를 위해 (3.5) 단계로 진행합니다.
- 아프로을 착용액체 질소로 작업하기 전에 (안전 안경, 장갑, 및 실험실 코트 포함) 절한 개인 보호 장비.
- 세라믹 박격포와 유 봉을 사용하여 액체 질소에 균일하게 미세 분말 (즉, 균일 한 입자 크기)에 트리플 갈기 조직 샘플.
주 : 균일 한 입자 크기를 성취하는 것이 SCCA 추출 효율을 극대화하기 위해 필수적이다.- 모르타르를 사전 진정 및 샘플을 추가하기 전에 액체 질소와 유 봉. 샘플이 추가로 액체 질소의 작은 볼륨 가득 박격포를 유지합니다.
- 국자를 사용하여 완전히 샘플을 잠수함에 박격포에 충분한 액체 질소를 추가합니다.
- 액체 질소에, 같은 나뭇잎이나 볶은 커피 쉽게 접지 샘플을 추가하고 원형 연삭 모션을 사용하여 분쇄. 액체 질소 수준이 겨우 샘플을 커버하는 포인트 감소 할 때 샘플을 갈기 시작한다.
- 샘플 등을 갈기 위해 하드 추가액체 질소에 원시 커피 씨앗을, S와이를 분쇄하기 전에 10 ~ 30 초 (또는 액체 질소가 적극적으로 끓는 멈출 때까지)에 대한 고정 할 수 있습니다. 수직 분쇄 모션을 사용하여 작은 조각으로 조직을 파괴하고 전체 조직 원형 연삭 모션을 사용하여 연삭.
- 샘플을 세 번 총을 접지되도록, 단계를 두 번 더 1.3.2-1.3.4 반복합니다. 일반적으로 연마의 3 개의 연속 라운드는 밀가루와 같은 일관성 분말 샘플을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 밀가루와 같은 농도가 달성되지 않은 경우, 단계를 반복 1.3.2-1.3.4 시료를 균일하게 작은 입자 크기의 분말로 감소 될 때까지 (추출 효율은 입자 크기에 반비례한다).
- 유리 병 또는 1.5 ml의 마이크로 원심 튜브에 분말을 전송합니다. 즉시 분쇄 후 다운 스트림 처리를 시작합니다 (권장) 또는 샘플까지 -80 ºC에서 저장 샘플 추출을위한 준비가되어 있습니다.
- 샘플을하기 전에 저장해야하는 경우분석, 500 밀리그램 씩 (또는 500 ㎕의 액체 시료 분취) 및 저장을위한 다수의 튜브들 사이에서 분할에 샘플을 분할합니다. 이 샘플 구성을 변경하고 부정적인 미래의 샘플 측정에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로, 반복되는 동결 / 해동 사이클에 샘플을 실시하지 마십시오.
2. 유기산 표준 준비
- 관심있는 SCCAs에 대한 확실한 기준을 조립합니다. 이러한 SCCA 농도를 결정하는 데 사용하기위한 외부 및 내부 표준 용액을 만드는 데 사용된다. 커피 샘플은 내부 표준으로서 관심과 아 디프 산의 산으로서 시트르산, 말산, 아세트산, 젖산 등의 경우.
- 선택된 내부 표준 샘플에서 자연적으로 발견, 샘플 프로필에 다른 봉우리와 표준이되지 않습니다 공동 용출되지 않았는지 확인합니다.
- 관심의 각 SCCA 표준 곡선을 실행하고 이달를 실행 부 (4) (각 SCCA에 대한 선형 응답 범위를 결정 참조ructions). 샘플에서 측정 할 각 SCCA에 대한 표준 곡선을 실행해야합니다.
주 : 표준 곡선 버퍼 또는 샘플의 배경 분석 될 하나에서 실행될 수있다. 두번째 경우 ( "표준 첨가")에서, 각각의 표준 곡선 점의 피크 면적 값은 샘플의 배경을 얻어 감산함으로써 결정된다. - 사전에 라벨 SCCA 산 이름, 농도 및 분석의 날짜와 필요한 모든 튜브와 유리.
- 표준 준비하는 동안 정확성을 보장하기 위해 부피 플라스크를 사용하여 알려진 농도 (10 ㎎ / ㎖) 각 표준에 대한 재고 솔루션을 준비합니다.
- 원액에 바람직한 농도를 달성하기 위하여 초순수 (18.2 MΩ) 고체 SCCA 규격 (시트르산 및 말산)을 녹인다.
- 10 ml의 부피 플라스크에 표준 100 mg을 추가하여 10 ㎎ / ㎖ 원액을 만듭니다. D 초순수로 10 ㎖ 라인에 메스 플라스크 채우기산을 issolve.
- 솔루션으로, 아 디프 산처럼, SCCA 표준을 어려운이-용해 운전 플라스크를 가열 부드럽게 산 표준의 낮은 농도를 만들거나.
- 원하는 농도를 달성하기 위하여, 초순수에 액상 산 규격 (아세트산 및 락트산)을 희석.
- 초순수 5 ml의 부피 플라스크에 사전 입력합니다. 플라스크 (벤더에 의해 제공되는 산성 농도를 이용하여 계산)를 10 ㎎ / ㎖ 용액을 제조하기에 충분한 산을 추가 한 다음 10 ㎖의 상기 용액의 최종 부피를 가지고 충분한 물을 첨가 하였다.
- 원액에 바람직한 농도를 달성하기 위하여 초순수 (18.2 MΩ) 고체 SCCA 규격 (시트르산 및 말산)을 녹인다.
- 모자 안감 폴리 테트라 플루오로 에틸렌 (PTFE)으로, 깨끗한 15 ML의 유리관에 각각의 원액을 전송, 플라스틱 파라핀 필름 밀봉. 스톡 용액을 1 주일 동안 4 ºC 밀봉 튜브에 저장 될 수있다.
- 재고 솔루션을 위해 준비 할 후 냉장 된 경우 SCCA 표준을 사용하기 전에 용액을 침전하지 않았는지 확인ATION. 드라이브는 부드러운 가열을 통해 용액에 다시 침전.
- SCCA 추출 솔루션을 준비합니다. 샘플에서 검출을위한 충분한 농도 (0.05 ㎎ / ㎖)의 내부 표준을 포함합니다. 모든 샘플을 추출 할 수있는 충분한 솔루션을 준비합니다.
- 초순수에 0.05 ㎎ / ㎖의 내부 표준 원액을 희석함으로써 SCCA 추출 용액 50 ㎖를 준비한다. 물 49.75 ml의 내부 표준 원액 (10 ㎎ / ㎖)의 250 μl를 추가합니다.
- 추출액을 희석 할 필요가 있다면, 최종 농도는 정량 한계 내에 있도록, 추출 용액에 내부 표준 물질의 농도를 조절 (검출을 제공하지만, 포화 과도 피크는 아래 5.2.2 참조하지 않음)의를 희석 후 CE 장치 (0.05 ㎎ / ㎖).
- (각 실험 시리즈 즉,) 추출의 각 시리즈에 대한 신선한 추출 용액을 준비합니다.
- 표준 곡선 샘플을 준비적어도 5 점 최소하여 관심 SCCAs위한 (적절한 희석액 시리즈). 사용되는 표준 곡선 농도는 주어진 SCCA 대한 선형 반응 범위에있을 필요가 있고, 샘플에서 예상 SCCA 농도 걸쳐 것이다.
- 시료에 내부 표준 정량화 할 수 있도록 표준 곡선 솔루션에서 선택된 내부 표준을 포함합니다. 내부 표준 피크 식별 및 계산 추출 효율 (6 장)을 돕기 위해 사용된다.
- 상기 결정된 농도로 각각 SCCA 희석 (0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08 ㎎ / ㎖, 상술 2.4.2 참조), 초순수를 사용하는 새로운 마이크로 원심 튜브 (각 농도 / 표준 곡선 지점에 대한 것). 각 표준 곡선 농도 포인트 용액 1 ㎖를 준비한다. 각각의 농도 포인트가 네 산 표준과 정확한 농도 내부 표준이 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다.
- 각 세트에 대한 새로운 표준 곡선 점을 준비샘플의 모세관 전기 영동 시스템에서 실행된다. 표적 조직 (섹션 3)에서 SCCAs의 추출 다음 발생하는 분석까지 4 ºC에서 표준 곡선 SCCA 샘플을 누릅니다.
3. 유기산 추출
- 각 샘플에 대해 적어도 하나의 튜브를 준비하는 사전 라벨 샘플 튜브를 추출한다.
- 샘플 저장소에서 추출 할 제거하고 추출 물질을 계량하는 동안 얼음에 배치합니다.
- SCCA 추출을위한 시료 100 mg의를 달아.
- 각각의 샘플을 계량 한 후, 깨끗한 1.5 ML의 microcentrifuge 관에 조직을 전송합니다. 변동성을 감소시킬뿐만 대상 질량에 가까운 샘플의 양을 측정한다.
- 검출 SCCAs의 양이 샘플 질량을 사용하여 정규화하는 바와 같이 (아래 6.5.2 참조), 측정 된 각 시료의 질량을 추적합니다.
- 모든 샘플을 칭량 한 후합니다 (식 수용 추출 용액 1 ㎖를 추가R + 샘플 튜브의 각 단계 2.4에서 내부 표준 혼합물). (이 경우에는 100 ± 5 mg의 조직을 1 ㎖) 조직 덩어리 전체에 걸쳐 동일한 추출하는 추출 용액의 비율을 유지한다. 10 초 동안 소용돌이에 의해 잘 섞는다.
- 샘플을 실온에서 1 시간 동안 방치시키고. 이 시간 동안, 단계 3.4에서 각 관마다 15 분을 섞는다.
- 추출의 1 시간 후, 샘플을 한 마지막 시간을 혼합하고 마이크로 원심에 샘플 튜브를 전송합니다. 4 ℃에서 원심 분리 된 샘플은 10 분 동안 10,000 × g으로는 고체 물질 (세포벽, 미립자 등)을 석출한다.
- 액체 샘플을 처리 할 때, 내부 표준 물질의 적절한 농도를 추가 간단히 원심 분리기를 섞는다. 원심 분리 후, 고체 시료의 추출 동일 액체 샘플을 취급합니다.
- 그들이 검출 키트 주행 완충액의 pH 범위와 호환 확인하는 샘플의 pH를 체크한다 (단계 4.6) 또는 EMP되는 시스템 버퍼loyed. 샘플의 부피는 일반적으로 매우 작은으로 pH를 용지를 사용하여 모니터링 할 수있다.
- 주사기에 장착 된 디스크 필터 (3.8)를 사용하여 샘플을 필터링 할 준비합니다.
참고 : 각 필터가 제대로 뜨는을 전송하기 전에 주사기에 연결되어 있는지 확인하여 샘플 손실을 방지합니다. 각 시료 (표준 곡선 샘플 포함)를 분석하기 위해 디스크 필터를 장착 한 주사기를 준비합니다. - 샘플을 원심 분리하고 시린지 필터를 제조 한 후, 0.2 ㎛의 주사기 필터를 구비 한 3 ㎖ 주사기로 각 샘플의 상등액을 전송. 각 샘플에 대한 새 필터 주사기를 사용합니다. 이전 CE 시스템에서 실행에 표준 곡선 샘플 및 버퍼 컨트롤을 포함한 모든 샘플을 필터링합니다.
- 깨끗한 microcentrifuge 관에 직접 샘플을 필터링합니다. 필터링 한 후, 튜브를 포함하는 여과 액을 닫고 주사기 / 필터 장치를 폐기합니다.
- 즉시 필터링 된 샘플을 배치SCCA 검출 용 CE 시스템으로; 밤새 4 ° C에서 저장하거나 샘플. 시료를 하룻밤 동안 저장되는 경우, 가스 교환 및 샘플의 증발을 방지하기 위해 플라스틱 파라핀 필름 튜브를 밀봉.
- 샘플을 필터링 한 후 하루보다 더 오래 저장해야하는 경우, -20 ºC에서 액체 질소 또는 동결 플래시 동결 추출물. 해동 후, 그러나, 필요한 경우 각 샘플 (단계 3.6에서와 같이) 침전물 형성과 필터에 대한 조사되어 있는지 확인합니다.
4. SCCA 탐지 실행 설정
- programming- 및 제어 소프트웨어 관련 자세한 내용은 CE 사용자 설명서를 참조하십시오.
- SCCA 검출을위한 모세관 전기 영동 (CE) 샘플 유리 병을 준비합니다. 확인 병이 제대로 표시된 깨끗하고 결함이있다.
- 세척하고 사용하기 전에 CE 튜브의 캡을 건조.
- 초순수에서 그들을 잠수하고 하룻밤 담가 할 수 있도록하여 캡을 씻으십시오. 뚜껑을 몸을 담근 후, 흡수 폐기솔루션을 보내고 및 초순수로 두 번 더 뚜껑을 씻어.
- 전송 보풀이없는 조직이 줄 지어 깨끗하고 건조 표면에 모자를 세척하고 자연 건조로 할 수 있습니다. 확인 캡은 압력 장애를 피하기 위해 사용하기 전에 완전히 건조합니다.
- 유리 병의 목에 샘플을 튀는 실수에주의하면서 각 CE 유리 병에 시료 1 ㎖를 전송합니다. 전송 후, 각 유리 병에 CE 캡을 배치합니다.
- 희석이 필요하다면, 커피 종자 샘플 1:10 희석 1 : 100을 직접 CE 바이알에 초순수를 사용. 1보다 큰 희석의 경우 : 100, 피펫 오류를 방지하기 위해 중간 희석을 만들 수 있습니다.
- CE 유리 병에 단계 2.5에서 표준 곡선 솔루션 (1.0 ml)에 전송하여 각각의 표준 곡선 점에 대한 하나의 유리 병을 준비합니다. 전송 후 각 튜브 캡.
- 펠릿의 t를 90 mL의 초순수를 넣은 비커에 0.04 g의 NaOH를 첨가시킴으로써 수산화 나트륨 (NaOH) 0.1 M 용액을 준비오 용해. 100㎖의 메스 플라스크에 0.1 M NaOH 용액을 전송하고 100 ml의 총 부피를 가져온다.
- 깨끗한 CE 유리 병 및 캡 0.1 M NaOH 용액 1ml를 추가합니다.
- 샘플의 각 배치에 대한 CE 버퍼 튜브를 준비는 CE 시스템에서 실행합니다. 분리 키트를 사용할 수 있습니다 또는 사용자 정의 버퍼 (13)를 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 완충 용액 캡을 시작하는 1 ml의 1 병을 준비합니다.
- 1 ml의 완충 용액 캡을 실행하는 각각의 세 튜브를 준비합니다. 샘플 및 표준 곡선 점의 각 배치하기 전에 실행 버퍼를 교체하거나 (35) 샘플 후, 둘 중 먼저 발생합니다.
- 초순수의 1 ml의 세 가지 추가 튜브를 작성하고 각각의 유리 병 캡.
- 모자 1 빈 "폐기물"유리 병을 준비합니다.
- 단계 4.8에 기재된 튜브를 제조 한 후, 모세관 전기 영동 (SYS)의 버퍼 트레이 (단계 4.8.2-5)에서 버퍼 및 물을 함유하는 튜브뿐만 아니라 폐 튜브로드TEM, 제조 업체의 지침 (15)에 따라. 조심스럽게 자동 샘플러 프로그래밍을위한 각 유리 병의 위치를 확인합니다.
- 표준 곡선의 포인트를 포함하는 튜브를 넣고 제조자의 지침에 따라 샘플을 함유하는 튜브는 입구 샘플 트레이로 분석한다. 자동 샘플러 프로그래밍을위한 각 유리 병의 위치를 참고 (단계 아래 4.11.1 참조).
- 에어컨 및 시료 분리 방법 (이들을위한 프로그램이 각각 표 1 및 2에 제공된다)를 준비하고, 악기 조작 지시에 따라, 샘플 시퀀스 파일 물품. 표 2에 설명 된 분리 방법을 사용하여 0.2 분 개시 (20 PSI)에 열을 씻어; (12 분 20 kV의에서 0.09 분에 대해 별도의 샘플을 컬럼 상에 샘플 (0.5 PSI)을 주입, 0.5 분 가속기 (20 psi) 이상 씻어 0.5 분의 NaOH (20 PSI)로 세척하고, 마지막으로 물로 씻어 20 PSI) 0.5 분.
- USI세륨 제어 소프트웨어 겨 (즉, 작업리스트를 상기 샘플 분석 될 순서를 상세히리스트 파일 및 방법은 각각의 샘플을 분리하는 데 사용되어야한다) 샘플 실행 시퀀스 쓰기 "시퀀스"스프레드 시트 인터페이스를 사용. 스프레드 시트의 각 행은 샘플 실행에 대응하고 하나의 데이터 파일을 생성한다.
- 시퀀스 파일을 기록 할 때, 샘플을 샘플링 트레이의 정확한 위치를 사용하여 식별되어 있는지 확인합니다. 각 데이터 파일이 이전 파일을 덮어에서 소프트웨어를 방지하기 위해 고유 한 이름을 가지고 있는지 확인하십시오. 시료 분리 방법을 포함하는 시퀀스를 실행하기 전에 별도의 시퀀스로서 프로그램 CE 모세관 컨디셔닝 실행.
- SCCA 샘플 뒤에 검량선 용액 실행 샘플 시퀀스를 시작하고, 표준 곡선 솔루션 번째 실행으로 끝난다. 이 샘플을 분석하는 동안 발생하는 신호 손실의 정도의 계산을 허용한다.

표 1 : 모세관을 통해 단쇄 카르 복실 산의 분리를위한 캐 필러 리를 제조하는데 사용 냉방 방법 프로그램은 전기 영동.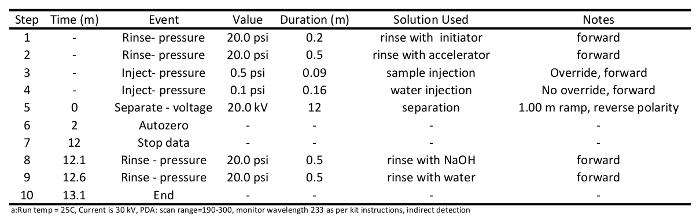
표 2는 모세관 전기 영동을 통해 단쇄 카르 복실 산을 분석하는 데 사용되는 분리 방법 프로그램.5. SCCA 감지 실행 실행 및 데이터 수집
- 모세관 에어컨 실행을 시작합니다. 열이 샘플 분리를위한 준비가되기 전에 모세에게 두 세 번 컨디셔닝 것으로 예상된다. 열 조절은 표 1에 설명 된대로 수행해야합니다. 요약하면, 1 분 동안 0.1 M의 NaOH (20 PSI)에 열을 씻어 물 (20 PSI)에 대한 씻어1 분, 10 분, 30 kV의 0.5 분, 별도의 가속기 가속기 (20 PSI)로 세정 0.5 분 동안 개시 (20 PSI), 씻어 0.5 분 동안 0.1 M의 NaOH (20 PSI)에 열을 씻어, 그리고 마지막으로 0.5 분 동안 물 (20 PSI)에 열을 씻어.
- 각각의 샘플 시퀀스를 실행하기 전에 모세를 조정. 분리 전압을 유지하여 적절한 조화를 달성하면 실행에 걸쳐 일정 및 포토 다이오드 어레이 추적에 평면 기준을 준수합니다.
- 조절 한 후, (즉, 클릭) 소프트웨어의 "관리"메뉴를 열고 선택하여 샘플 분리를 시작합니다 "실행 순서를." 적절한 분리를 보장하기 위해, 포토 다이오드 어레이 (PDA) 트레이스를 모니터한다.
- 개별 산 피크를 첫 번째 추적을 준수하고 평평한 기준을 가지고 깨끗하게 (기본 해상도) 해결되었는지 확인합니다. 오버로드 샘플은 긴 피크 꼬리, 또는 피크 테일링이 표시됩니다, (그림 1)로 희석해야합니다.

그림 1. PDA의 비교는 오버 샘플을 강조 트레이스 분석 물질 농도가 증가함에 따라, 각각의 피크 형상은 비대칭되기 시작할 수있다. (a) 0.05 ㎎ / ㎖에서 아세트산 잘 정의 된, 좌우 대칭의 피크를 나타낸다. 초산의 농도가 증가로서 (b) 0.07 mL의 밀리그램 / 및 (c) 0.10 ㎎ / ㎖, 피크 꼬리 형태 (화살표). 이 피크 테일링이 샘플이 과부하있는 좋은 지표이다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.- 시퀀스 실행의 결말에서, 데이터 파일 께 CE 분석 소프트웨어에 한번에 하나씩 열고 피크를 통합하고있다.
- 샘플 피크를 통합 할 수 있습니다.
- 첫 번째 파일을 엽니 다및 (표 1에 기재된 바와 같이, 전압 및 열 흐름의 방향 때문에, 반전) 런의 제 3 분을 제외하는 자동 통합 단계를 설정한다. 같은 메뉴에서 추적에서 배경 잡음에서 산 피크를 분리, 선택의 적당히 높은 수준을 제공하기 위해 50 단위의 최소 피크 폭 100 단위 (또는 제조업체의 기본 설정)의 피크 면적에 최고 선택 기준을 설정합니다.
- 수동으로 적절한 피크 통합을 보장하기 위해 각 PDA 추적을위한 최대의 경계와 기준을 확인합니다. 잘못 통합 피크 (즉, 자동화 된 소프트웨어에 의해 두 개의 봉우리로 통합되어 약간 비대칭 SSCA 피크)를 수동으로 다시 통합해야합니다.
- 샘플 피크를 통합 할 수 있습니다.
- 통합 후 %의 영역 보고서를 보려면, 다음 강조 표시하고 퍼센트의 영역 보고서를 복사하여 별도의 스프레드 시트에 붙여 넣습니다. 전체 실행 피크 REPOR를 구성하는 각 샘플에 대해 반복하나의 피크를 나타내는 각 행과 t은 (분리가 잘 작동하는지, 즉., 각각의 피크가 하나의 화합물을 포함한다).
6. 데이터 분석
- (5.4)에 지어진 스프레드 시트를 사용하여 분석을 위해 데이터를 준비합니다. 내부 표준을 포함하여 표준 곡선 지점마다 산 기준 라벨에 의한 분석을 시작한다.
- 그 시료 중의 내부 표준 물질의 머무름 시간함으로써 샘플에서 각각의 피크에 대한 보유 시간을 분할하여 각 피크에 대한 보유 지수를 계산한다. 각 샘플에 대한 관심의 피크를 식별 할 얻어진 보존 지수에 의해 설정 데이터를 정렬.
- 관심있는 각각의 산에 대한 피크를 식별 한 후, 외부 표준 곡선 점을 이용하여 각각의 산에 대한 표준 곡선을 구성.
- XA에 농도를 SCCA 기준의 각 농도에 대한 피크 면적을 결정하고, 각 플로팅 SCCA 규격 표준 (농도) 곡선을 생성Y 축에 대한 피크 면적 대 XIS. 각 SCCA 표준 곡선의 선형 회귀를 플롯 및 경사 식을 정의 (MX = Y + b).
- 정량화가 가장 정확하게 표준 곡선의 선형 범위에서 수행되는 선형 회귀의 R 2 값이 0.90 이상이 있는지 확인합니다.
- 피크 면적과 (상기 6.3.2 계산) 표준 곡선의 선형 회귀 직선에 대한 경사의 방정식을 사용하여 샘플에서 주어진 SCCA위한 산 농도를 계산한다. 요약하면, 그 산의 표준 곡선에 대한 회귀 직선의 기울기에 의해 소정의 산을위한 관찰 된 피크 면적을 분할.
- 내부 표준 (단계 6.5)를 사용하여 처리하는 동안 샘플 손실에 대해 단계 6.4에서 계산 된 원료 농도 값을 수정합니다.
- 내부 표준을 사용하여 각 샘플에 대한 보정 계수를 계산한다.
- 내부 표준의 실제 농도를 나누고 (즉, KNO시료 중의 내부 표준 (관측 된 값) 실험의 시작 부분에 추가 WN 량 즉, 내부 표준에 대한 표준 곡선의 기울기의 방정식을 사용하여 계산 된 양). 이 보정 계수를 각 시료에 SCCA의 원료 농도 값을 곱한다.
- 샘플 질량의 모든 변동을 보정하는 추출에 사용되는 시료의 질량 SCCA 농도 보정 된 내부 표준 나눈다. 이 계산은 시료의 질량 (㎎을 SCCA 당 밀리그램이 예에서 인스턴트 커피)를 소정의 연구에 적절한 단위 (밀리그램 / ㎎, 밀리그램 / g으로 변환 할 수, g / g 등의 당 분석 물의 양을 수득 ).
- SCCA 농도를 계산 한 후 ([액체 샘플]을 어느 [고체 또는 액체 시료 질량 또는 부피에 정규화), 실험 설계 및 관심의 질문의 요구에 따라 통계 분석을 위해이 값을 사용합니다.
- USI세륨 제어 소프트웨어 겨 (즉, 작업리스트를 상기 샘플 분석 될 순서를 상세히리스트 파일 및 방법은 각각의 샘플을 분리하는 데 사용되어야한다) 샘플 실행 시퀀스 쓰기 "시퀀스"스프레드 시트 인터페이스를 사용. 스프레드 시트의 각 행은 샘플 실행에 대응하고 하나의 데이터 파일을 생성한다.
결과
이 프로토콜은 성공적 녹색 커피 씨의 SCCA 내용에 시드 처리의 효과를 측정하기 위해 이용되고있다. 이 실험에서, 여섯 치료 하였다 : 로이코 노 스톡 포화 미생물 현탁액 물 GCP674 미생물 (1) 수성 현탁액 성장 배지에서 균주 GCP674을 pseudomesenteroides (2), 아세트산 및 락트산 (0.15 및 0.4의 수용액 밀리그램 /) 각각 ㎖ (3)와, 소요 M1 성장 배지 처리 (4), DH 2 O ?...
토론
임의의 분석 기법으로 크게 발생되는 데이터의 품질과 신뢰성에 영향을 미칠 수있는 여러 가지 중요한 요소가있다. 첫째, 냉동 / 해동 사이클을 최소화하여, 샘플을 효율적으로 처리하는 것이 중요하다. 반복 된 동결 융해 처리 또는 분석 전에 샘플의 화학 성분을 손상시킬 수있다. 둘째, 일관되고 균일 모든 샘플이 프로토콜의 단계를 적용하는 것이 중요하다. 일관성 샘플 준비 및 처리 기술에서 ...
공개
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
감사의 말
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of this project by The J.M. Smucker company.
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Ceramic Moarter and Pestle | Coorstek | 60310 | |
| Beckman Coulter P/ACE MDQ CE system | Beckman Coulter | Various | |
| Glass sample vials | Fisher Inc. | 033917D | |
| 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes | Fisher Inc. | 02-681-5 | |
| LC/MS grade water | Fisher Inc. | W6-1 | Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ.cm) is also acceptable |
| 15 ml glass tube/ Teflon lined cap | Fisher Inc. | 14-93331A | |
| Parafilm M | Fisher Inc. | 13-374-12 | |
| CElixirOA detection Kit pH 5.4 | MicroSolv | 06100-5.4 | |
| BD Safety-Lok syringes | Fisher Inc. | 14-829-32 | |
| 17 mm Target Syringe filter, PTFE | Fisher Inc. | 3377154 | |
| 32 Karat, V. 8.0 control software | Beckman Coulter | 285512 | |
| capillary electrophoresis (CE) sample vials | Beckman Coulter | 144980 | |
| caps for CE vials | Beckman Coulter | 144648 | |
| Liquid Nitrogen | N/A | N/A | Liquid nitrogen is available from most facilities services |
참고문헌
- Araújo, W. L., Nunes-Nesi, A., Nikoloski, Z., Sweetlove, L. J., Fernie, A. R. Metabolic Control and Regulation of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in Photosynthetic and Heterotrophic Plant Tissues: TCA Control and Regulation in Plant Tissues. Plant Cell Environ. 35 (1), 1-21 (2012).
- Finkemeier, I., Konig, A. C., et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Role of Carboxylic Acids in Metabolite Signaling in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Physiol. 162 (1), 239-253 (2013).
- Doyle, M. P., Buchanan, R. . Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers. , (2013).
- Tůma, P., Samcová, E., Štulìk, K. Determination of the Spectrum of Low Molecular Mass Organic Acids in Urine by Capillary Electrophoresis with Contactless Conductivity and Ultraviolet Photometric Detection-An Efficient Tool for Monitoring of Inborn Metabolic Disorders. Anal Chim Acta. 685 (1), 84-90 (2011).
- López-Bucio, J., Nieto-Jacobo, M. F., Ramı́rez-Rodrı́guez, V., Herrera-Estrella, L. Organic Acid Metabolism in Plants: From Adaptive Physiology to Transgenic Varieties for Cultivation in Extreme Soils. Plant Sci. 160 (1), 1-13 (2000).
- Cebolla-Cornejo, J., Valcárcel, M., Herrero-Martìnez, J. M., Rosellò, S., Nuez, F. High Efficiency Joint CZE Determination of Sugars and Acids in Vegetables and Fruits: CE and CEC. Electrophoresis. 33 (15), 2416-2423 (2012).
- Rosello, S., Galiana-Balaguer, L., Herrero-Martinez, J. M., Maquieira, A., Nuez, F. Simultaneous Quantification of the Main Organic Acids and Carbohydrates Involved in Tomato Flavour Using Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. J Sci Food Agr. 82 (10), 1101-1106 (2002).
- Wasielewska, M., Banel, A., Zygmunt, B. Capillary Electrophoresis in Determination of Low Molecular Mass Organic Acids. Int J Environ Sci Dev. 5 (4), 417-425 (2014).
- Galli, V., Garcìa, A., Saavedra, L., Barbas, C. Capillary Electrophoresis for Short-Chain Organic Acids and Inorganic Anions in Different Samples. Electrophoresis. 24 (1213), 1951-1981 (2003).
- Klampfl, C. W. Determination of Organic Acids by CE and CEC Methods. Electrophoresis. 28 (19), 3362-3378 (2007).
- Kenney, B. F. Determination of Organic Acids in Food Samples by Capillary Electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 546, 423-430 (1991).
- Galli, V., Barbas, C. Capillary Electrophoresis for the Analysis of Short-Chain Organic Acids in Coffee. J Chromatogr A. 1032 (1-2), 299-304 (2004).
- Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Capillary Electrophoresis: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 384 (2008).
- Nollet, L. . Chromatographic analysis of the environment 3rd ed. , (2006).
- . . ElixerOA Organic Acids/Anions Operating and Instruction Manual, MicroSolv Technology Corperation. , (2001).
- Dahlen, J., Hagberg, J., Karlsson, S. Analysis of low molecular weight organic acids in water with capillary zone electrophoresis employing indirect photometric detection. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 366 (5), 488-493 (2000).
- Ibanez, A. B., Bauer, S. Analytical method for the determination of organic acids in dilute acid pretreated biomass hydrolysate by liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectroscopy. Biotech. For Biofuels. 7 (145), (2014).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기더 많은 기사 탐색
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유