需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
诱导小鼠肠道炎症由效应CD4的过继转移
摘要
Here, we present a protocol to induce colonic inflammation in mice by adoptive transfer of syngeneic CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells into T and B cell deficient recipients. Clinical and histopathological features mimic human inflammatory bowel diseases. This method allows the study of the initiation of colonic inflammation and progression of disease.
摘要
有可用于研究人炎性肠疾病(IBD),每个都有其自己的优点和缺点的发病许多不同的动物模型。我们在这里描述通过过继转移的同源脾的CD4 + CD45RB 高 T细胞的成T和B细胞缺陷型受体小鼠启动的一个实验性结肠炎模型。在CD4 + CD45RB 高 T细胞群在很大程度上是由幼稚效应细胞能够诱导的慢性肠道炎症,非常类似于人类IBD的关键环节。这种方法可以被操纵来研究疾病发作和进展的方面。此外,它可以被用来研究先天,自适应的功能,以及调节免疫细胞群,和环境暴露的作用,也就是说 ,该微生物群,在肠道炎症。在这篇文章中,我们阐述了诱导结肠炎一步一步的协议的方法。这INC吕代的成功开发实验性结肠炎的研究目的这个小鼠模型所需要的关键技术环节的视频演示。
引言
The inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis result from an incompletely defined and complex interaction between host immune responses, genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, and the enteric luminal contents1. Recent genome-wide association studies report associations between immune cell regulatory genes and IBD susceptibility2,3. Both innate and adaptive immune cell intrinsic genes are represented in these studies, indicating a central role for these cell populations in IBD pathogenesis.
There currently exist more than 50 animal models of human IBD. While no one model perfectly phenocopies human IBD, many are useful for studying various aspects of human disease, including disease onset and progression and the wound-healing response. In the method described here, intestinal inflammation is initiated with syngeneic splenic CD4+CD45RBhigh T cell adoptive transfer into T and B cell deficient recipient mice4. The CD4+CD45RBhigh T cell population contains mainly naïve T cells primed for activation that are capable of inducing chronic small bowel and colonic inflammation. This method allows the researcher to modify key experimental variables, including both innate and adaptive immune cell populations, to answer biologically relevant questions relating to disease pathogenesis. Additionally, this method provides precise initiation of disease onset and a well-characterized experimental time course. This permits the kinetic study of clinical features of disease progression in mice. Intestinal inflammation induced by this method shares many features with human IBD, including chronic large and small bowel transmural inflammation, pathogenesis driven by cytokines such as TNF and IL-12, and systemic symptoms such as wasting5. Thus, it is an ideal model system for studying the pathogenesis of human IBD.
The method here describes in detail the protocol for inducing experimental colitis by adoptive transfer of CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells into Rag1-/- mice. We discuss key technical steps, expected results, optimization, and trouble-shooting. We address the required elements for the successful development of this murine model of intestinal inflammation for research purposes.
研究方案
注:确保所有的动物协议通过并符合机构动物护理和使用委员会(IACUC)的规定和国家研究委员会的指南实验动物的护理和使用的批准。供体小鼠可以是男性或女性,但受体小鼠应该是雄性。如果女性收件人使用,供体小鼠必须是女性5。使用常规的,非无菌床上用品和非酸化水中维持菌落,因为这些可能会影响肠道菌群,并且因此,小鼠5,6的结肠炎的表型。
1.实验准备
- 用冰冷的媒体和缓冲区。保持整个实验的细胞在冰上。
- 执行使用无菌技术的实验在无菌生物危害罩。
2.分离脾T细胞的
- 安乐死捐助鼠标/鼠标在CO 2室其次是宫颈dislocatioñ。喷腹部用70%乙醇。
- 做水平切口在腹部和剥离皮肤暴露腹膜。持有腹膜远离内脏的镊子,并在左腹部腹膜切口暴露和切除脾脏。
- 放置在10ml完全培养基的脾脏在培养皿。删除和脾丢弃多余的组织。
- 使用2消毒玻片破碎,梳理出脾成单细胞悬液。通过一个70微米的过滤器过滤细胞悬浮到50ml锥形管中,并冲洗过滤用5ml完全培养基中。放置最多5脾脏在一个50ml锥形管中。
- 离心细胞,在450×g离心7分钟。浇关闭或通过真空抽吸到废物容器弃上清。
- 轻轻重悬细胞于每裂解液脾5毫升以裂解红血细胞,在室温下10分钟。加完整的媒体等体积(每脾5ml)中的管中。
- 离心细胞,在450×g离心7分钟。浇关闭或通过真空抽吸到废物容器弃上清。
- 轻轻重悬细胞于10ml标记缓冲液。
- 细胞计数台盼蓝排斥。
- 除去20微升细胞悬浮液,并加入到180微升台盼蓝到微量离心管中并充分混合。 5分钟后,添加10微升标记的细胞,以血球和在显微镜下计数非蓝色的细胞。确定存活细胞的总数。丢弃电池/台盼蓝组合。
- 离心细胞在10ml标记缓冲液中,在450×g离心7分钟。浇关闭或通过真空抽吸到废物容器弃上清。
3.富集CD4 + T细胞的
注:按照制造商的说明在本节中使用的特定产品。
- 轻轻悬浮细胞,以20×10 6个细胞/ ml,在寒冷的标签单细胞悬浮液ING缓冲。
- 添加5μl的每1×10 6个细胞的生物素化的CD4 T细胞富集的抗体。孵育细胞在冰上15分钟。
- 加入10倍体积标记缓冲液中。离心细胞,在450×g下7分钟。小心吸全部采用真空吸进废物容器上清。
- 彻底涡旋链霉亲和共轭磁性粒子。添加5μl的每1×10 6个细胞的颗粒。
- 调匀而是轻轻。保持混合物在6-12℃下进行30分钟。
- 添加标记缓冲液至20-80×10 6细胞/ ml的浓度。发送上行至1.0ml每12×75mm的圆底试管标记的细胞(称为"阳性馏分管")。
- 放置在磁铁每个正分数管6-8分钟。
- 与正馏分管仍然在磁铁,小心地从阳性馏分管与玻璃巴斯德吸管转移上清至新的无菌50ml锥形管(referred,来作为"富集级分")。这种富集的馏分含有CD4 + T细胞。要小心,不要破坏吸引到磁铁的标记细胞。
- 留在标记缓冲液的相同体积的正馏分管悬浮细胞如在步骤3.6通过上下吹打大力。将积极分数管回磁铁6-8分钟。
- 阳性馏分管仍然在磁铁,小心地从阳性馏分管与玻璃巴斯德吸管转移上清液(富集馏分,CD4 +),以无菌50ml锥形管中,从步骤3.8而不破坏附着到磁体的细胞。
- 重复步骤3.9-3.10增加获得CD4 + T细胞的产率。使用富集级分(CD4 +细胞)继续协议。
4.标签和分类 细胞7
- 离心富集的细胞在450×g离心7分钟。浇过或真空suct弃上清离子进入废物容器。
- 重悬的细胞在1ml标记缓冲液。去除细胞等分计算和台盼蓝染色,以评估细胞活力按照步骤2.9。
- 标记缓冲液的体积加至10×10 6个细胞/ ml;如果细胞是已经<10×10 6,离心机在450×g离心7分钟,弃上清通过倾倒或关闭真空抽吸到废物容器中,并标记缓冲液的添加量至10×10 6个细胞/ ml。
- 设置的各约5-10×10 5个细胞的等分试样单独对未染色,同种型染色,并且单染色的对照细胞在微量离心管中。
- 添加5微克/毫升的CD4-FITC和1微克/毫升CD45RB-PE到细胞中。加同种型对照染色和单污渍以相同的浓度到合适的离心管中的等分试样。拌匀,但轻轻地,并培育冰上避光30分钟。
- 加入10倍体积标记缓冲液的细胞和控制秒。离心机450 XG 7分钟。弃上清通过真空抽吸到废物容器。
- 在标记缓冲液悬浮体积步骤4.5。离心机450 XG 7分钟。弃上清通过真空抽吸到废物容器。
- 在标记缓冲液重悬,以10×10 6个细胞/ ml。通过70微米的过滤器进入FACS管传递细胞。置于冰上避光,直到准备流式细胞仪。
- 建立和确定的细胞分选与未染色细胞和单染控制适当的补偿。
- 排除不能存活的细胞与正向和侧向散射设门( 图1A)。成立了CD4 +和CD45RB +细胞亚型染色控制门控。门上的细胞CD4 +人口。
- 排序CD4 +细胞进入CD45RB 高 CD45RB 低的人群使用一个简单的柱状图PE染色细胞转化为管用2毫升全媒体。该CD45RB 高 人口代表的CD4 + CD45RB +细胞(CD45RB 高 )的最高40%,并且CD45RB 低人口是最低的20%的CD4 + CD45RB +细胞(CD45RB 低 ; 图1B)。
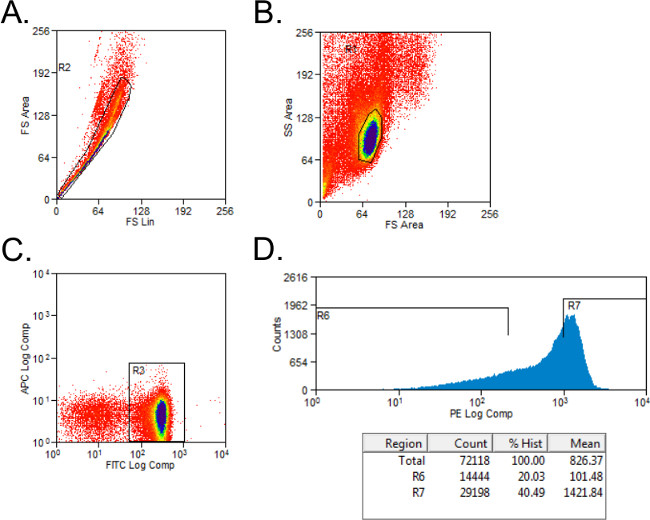
图1:在FACS分析仪曲线的CD4 + CD45RB T细胞群的代表性流(A - C)的 FITC CD4-和从通过FACS分选入供体C57BL / 6小鼠的PE CD45RB染色的脾的CD4 + CD45RB 高和CD4 +。 CD45RB 低 T细胞群。 (A)双峰事件被排除在前进散点图。 (B)的淋巴细胞进行门控,在正向和侧向散射图。 (C)CD4 + T细胞被门控,和(D)的CD4 + CD45RB + T细胞上绘制的PE与事件直方图。 CD4 + CD45RB low细胞被认为是CD45RB +细胞的最低的20%。 CD4 + CD45RB 高细胞被定义为CD45RB +细胞的最高的40%。
- 运行的FACS机器上的每个细胞群体的等分试样来评估群体的纯度。
- 离心分选的细胞在450×g离心7分钟。重悬在1ml PBS中。去除细胞等分计算和台盼蓝染色,以评估细胞活力按照步骤2.9。
5.细胞注射到收件人
- 重悬分选的细胞以4×10 6个细胞/ ml(CD45RB 高 )或2×10 6个细胞/ PBS中毫升(CD45RB 低 )。
- 每个收件人转移100微升CD45RB 高细胞对新的无菌管。添加100微升PBS每收件人该管。因此,每只动物的总注射体积是200微升,和每受体细胞的总量为4×10 5个CD4 + CD45RB 高幼稚T细胞。
- 如果实验组接受调节性T细胞的需要,每个收件人转移100微升CD45RB 高细胞对新的无菌管。加入100微升每收件人CD45RB 低细胞对相同的管中。每个动物的总注射量为200微升; CD45RB 高的比率:CD45RB low细胞是2:1。
- 注入100微升CD45RB 高或CD45RB的高 / 低 CD45RB的CD4 +细胞腹膜内成每个收件人的腹部(总200微升)的右侧和左侧。
在收件人动物6.监测病情进展
- 为了评估该受体动物的临床状况,对于以下paramete分配骨料临床得分在注射当天RS 8,此后每周,和在处死时:
- 确定通过测量重量损失浪费:0 - 没有体重减轻; 1 - 0.1-10%的损失的初始体重; 2 - 10%以上的损失初始体重( 图2A)的。

图2:炎症的临床和病理总额转移的迹象野生型CD4 + CD45RB 高 T细胞进入RAG1后出现- / -和NRDKO受体小鼠11(A)NRDKO收件人5告负的初始体重平均水平10%。周后转移,而RAG1- / -收件人未在此时显示出疾病的临床症状。每个点代表的初始体重为队列±SEM的平均百分比。 **,P <0.005。 (B)中的一些小鼠发展严重的肠道炎症,这表现在直肠脱垂的存在。这是直肠脱垂的NRDKO受体小鼠的代表图片。 (C)的眼观从冒号既RAG1 - / -和NRDKO受体小鼠增厚,缩短与从RAG1冒号- / -和NRDKO小鼠没有T细胞过继转移。从NRDKO受体小鼠冒号显示严重的炎症,增加结肠重量(数据未显示)。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
- 通过将动物干净的容器确定大便质量,直到它已通过便血:0 - 无; 1 - 大便软; 2 - 水样和/或便血。
- 确定动物的一般健康受疾病的下列迹象的存在:0 - 不弯腰驼背的姿势,毛的皮毛,或皮肤损伤; 1 - 以下目前的任何一个:弯腰驼背的姿势,毛的皮毛,或皮肤损伤。
- 确定直肠脱垂存在:0 - 缺席; 1 -本( 图2B)。
- 通过CO牺牲动物2吸入颈椎脱位时,他们已经失去了他们的出发体重20%,或期望的时间点,以先到者为准。临床疾病通常是显而易见的,在开始5周后饱食。
- 评估疾病严重程度如前所述5,7。
- 分配临床得分如在步骤6.1 8。
- 测量结肠长度和重量( 图2C)。
- 执行炎症的组织学分析5。
- 在肠组织外植体培养9确定自发细胞因子的表达,肠系膜淋巴结10,和/或血清11。
- 简单地说,对于植文化9,牺牲后删除冒号,开放纵向和干净PBS。孵育在轨道摇床设定以250rpm在完整的媒体为30分钟,在室温下冒号。
- 剁的组织切成小块并在完全培养基在37℃下放置24小时。收集上清液,并使用为每100mg组织中的细胞因子,通过ELISA定量。
- 执行的T细胞表型和/或功能10 体外表征。
结果
约10×10 6 CD4 + CD45RB 高Tg从成年C57BL / 6小鼠捐助10脾脏细胞是可靠的隔离。这个数目将根据患者的年龄的供体小鼠的应变和研究者的熟练程度而有所不同。当4×10 5只C57BL / 6的CD4 + CD45RB 高 T细胞转移到C57BL / 6 RAG1 - / -受体小鼠,疾病的临床症状出现围绕周5后饱食或更快,如果小鼠在遗传上易感更严重的疾病( 图2,3)11,12。
讨论
在这里,我们描述了一个一步一步的协议,通过过继转移CD4 + CD45RB + T细胞的免疫缺陷小鼠诱导小鼠结肠的炎症。我们使用的C57BL / 6供体脾和同系RAG1 - / -受体小鼠,尽管其它菌株( 例如 ,BALB / c小鼠,129S6 / SvEv,非肥胖糖尿病(NOD))免疫缺陷的和遗传模型( 例如 ,SCID, 的Rag2 - / - ),也可以使用4,14-16。它是公认的背景品系?...
披露声明
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
致谢
这项工作是由美国胃肠病协会(AGA)研究学者奖和克罗恩和美国(CCFA)职业发展奖(以ENS),美国国立卫生研究院NIDDK F30 DK089692(以ECS)结肠炎基金会,以及北卡罗莱纳州中心大学的胃肠生物学支持与疾病格兰特P30 DK34987(组织学核心)。在UNC流式细胞仪核心设施是由NCI中心的核心支持格兰特(P30CA016086)的UNC莱恩伯格综合癌症中心支持的一部分。我们感谢卢克B.博斯特从兽医北卡罗莱纳州立大学对他的帮助与组织病理学分析和免疫组化。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Name of Reagent/ Equipment | Company | Catalog Number | Comments/Description |
| 10x PBS | Gibco | 14200075 | |
| 12 mm x 75 mm round-bottom tube | Falcon | 352052 | |
| 15 ml conical | Corning | 430790 | |
| 26 G x 3/8 Needle | BD Biosciences | 305110 | |
| 50 ml conical | Corning | 430828 | |
| 70 μm Cell Strainer | Fisherbrand | 22363548 | |
| BD IMagnet | BD Biosciences | 552311 | |
| β-mercaptoethanol | Thermo Scientific | 35602 | |
| CD4-FITC IgG2b | eBioscience | 11-0041 | |
| CD45RB-PE IgG2a | BD Pharminogen | 553101 | |
| Complete Media | RPMI-1640, 1% Pen/Strep, 10% FBS, 0.0004% β-ME | ||
| FACS tube + strainer | BD Falcon | 352235 | |
| Glass Microscope Slides | Fisherbrand | 12550A3 | |
| Heat-inactivated FBS | Gemini | 100-106 | |
| Labeling Buffer | 1x PBS, 0.5% BSA, 2 mM EDTA | ||
| Lysis Buffer | 0.08% NH4Cl, 0.1% KHCO3, 1 mM EDTA | ||
| MoFlo XDP | Beckman Coulter | ||
| Mouse CD4 T lymphocyte Enrichment Set - DM | BD Biosciences | 558131 | |
| Mouse IgG2a-PE | BD Pharminogen | 553457 | |
| Mouse IgG2b-FITC | eBioscience | 11-4732 | |
| Pasteur pipet | Fisherbrand | 13-678-20D | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution, 100X | Corning Cellgro | 30-002-CI | |
| [header] | |||
| Petri Dish | Fisherbrand | 875713 | |
| Pure Ethanol 200 Proof | Decon Labs | 2705-HC | |
| RPMI-1640 | Gibco | 11-875-093 | |
| Syringe | BD Biosciences | 309597 | |
| Trypan blue | Corning Cellgro | 25-900-CI | |
| Wash Media | RPMI-1640, 1% Pen/Strep, 0.0004% β-ME | ||
参考文献
- Xavier, R. J., Podolsky, D. K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448 (7152), 427-434 (2007).
- Cho, J. H., Brant, S. R. Recent insights into the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 140 (6), 1704-1712 (2011).
- Jostins, L., et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 491 (7422), 119-124 (2012).
- Powrie, F., Leach, M. W., Mauze, S., Caddle, L. B., Coffman, R. L. Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C. B-17 scid mice. Int Immunol. 5 (11), 1461-1471 (1993).
- Ostanin, D. V., et al. T cell transfer model of chronic colitis: concepts, considerations, and tricks of the trade. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296 (2), 135-146 (2009).
- Ma, B. W., et al. Routine habitat change: a source of unrecognized transient alteration of intestinal microbiota in laboratory mice. PLoS One. 7 (10), e47416 (2012).
- Read, S., Powrie, F. Induction of inflammatory bowel disease in immunodeficient mice by depletion of regulatory T cells. Curr Protoc Immunol. Chapter 15 (Unit 15 13), (1999).
- Maillard, M. H., et al. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein is required for the function of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 204 (2), 381-391 (2007).
- Hegazi, R. A., et al. Carbon monoxide ameliorates chronic murine colitis through a heme oxygenase 1-dependent pathway. J Exp Med. 202 (12), 1703-1713 (2005).
- Kole, A., et al. Type I IFNs regulate effector and regulatory T cell accumulation and anti-inflammatory cytokine production during T cell-mediated colitis. J Immunol. 191 (5), 2771-2779 (2013).
- Kobayashi, T., et al. NFIL3-deficient mice develop microbiota-dependent, IL-12/23-driven spontaneous colitis. J Immunol. 192 (4), 1918-1927 (2014).
- Steinbach, E. C., et al. Innate PI3K p110delta Regulates Th1/Th17 Development and Microbiota-Dependent Colitis. J Immunol. 192 (8), 3958-3968 (2014).
- Kobayashi, T., et al. NFIL3 is a regulator of IL-12 p40 in macrophages and mucosal immunity. J Immunol. 186 (8), 4649-4655 (2011).
- Leach, M. W., Bean, A. G., Mauze, S., Coffman, R. L., Powrie, F. Inflammatory bowel disease in C.B-17 scid mice reconstituted with the CD45RBhigh subset of CD4+ T cells. Am J Pathol. 148 (5), 1503-1515 (1996).
- Powrie, F., et al. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4. T cells. Immunity. 1 (7), 553-562 (1994).
- Read, S., Malmstrom, V., Powrie, F. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 192 (2), 295-302 (2000).
- Rogers, G. B., et al. Functional divergence in gastrointestinal microbiota in physically-separated genetically identical mice. Sci Rep. 4, 5437 (2014).
- Fukata, M., et al. The myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) is required for CD4+ T cell effector function in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol. 180 (3), 1886-1894 (2008).
- Kurtz, C. C., et al. Extracellular adenosine regulates colitis through effects on lymphoid and nonlymphoid cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 307 (3), 338-346 (2014).
- Naganuma, M., et al. Cutting edge: Critical role for A2A adenosine receptors in the T cell-mediated regulation of colitis. J Immunol. 177 (5), 2765-2769 (2006).
- Ranatunga, D. C., et al. A protective role for human IL-10-expressing CD4+ T cells in colitis. J Immunol. 189 (3), 1243-1252 (2012).
- Srikrishna, G., et al. Carboxylated glycans mediate colitis through activation of NF-kappa. B. J Immunol. 175 (8), 5412-5422 (2005).
- Wang, F., et al. IFN-gamma-induced TNFR2 expression is required for TNF-dependent intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 131 (4), 1153-1163 (2006).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。