Zum Anzeigen dieser Inhalte ist ein JoVE-Abonnement erforderlich. Melden Sie sich an oder starten Sie Ihre kostenlose Testversion.
Method Article
Ein Multi-Cue-Bioreaktor zur Bewertung der entzündlichen und regenerativen Kapazität von Biomaterialien unter Strömung und Dehnung
* Diese Autoren haben gleichermaßen beigetragen
In diesem Artikel
Zusammenfassung
Das Ziel dieses Protokolls ist es, eine dynamische Kokultur von menschlichen Makrophagen und Myofibroblasten in röhrenförmigen elektrogesponnenen Gerüsten durchzuführen, um die materialgetriebene Geweberegeneration mit einem Bioreaktor zu untersuchen, der die Entkopplung von Scherspannung und zyklischer Dehnung ermöglicht.
Zusammenfassung
Die Verwendung resorbierbarer Biomaterialien zur Induktion der Regeneration direkt im Körper ist aus translationaler Sicht eine attraktive Strategie. Solche Materialien induzieren bei der Implantation eine Entzündungsreaktion, die der Treiber für die anschließende Resorption des Materials und die Regeneration von neuem Gewebe ist. Diese Strategie, auch bekannt als In-situ-Gewebe-Engineering, wird verfolgt, um kardiovaskulären Ersatz wie Gewebe-Engineering-Gefäßtransplantate zu erhalten. Sowohl der entzündungsbedingte als auch der regenerative Prozess wird durch die lokalen biomechanischen Hinweise auf dem Gerüst (d.h. Dehnungs- und Scherstress) bestimmt. Hier beschreiben wir detailliert den Einsatz eines speziell entwickelten Bioreaktors, der auf einzigartige Weise die Entkopplung von Dehnungs- und Scherspannung an einem Rohrgerüst ermöglicht. Dies ermöglicht die systematische und standardisierte Bewertung der Entzündungs- und Regenerationsfähigkeit von Rohrgerüsten unter dem Einfluss gut kontrollierter mechanischer Belastungen, die wir anhand eines dynamischen Kokulturexperiments mit menschlichen Makrophagen und Myofibroblasten demonstrieren. Die wichtigsten praktischen Schritte in diesem Ansatz – der Bau und die Einrichtung des Bioreaktors, die Vorbereitung der Gerüste und die Zellaussaat, die Anwendung und Aufrechterhaltung des Stretch- und Scherflusses sowie die Probenernte für die Analyse – werden ausführlich diskutiert.
Einleitung
Kardiovaskuläres Tissue Engineering (TE) wird als alternative Behandlungsoption zu den derzeit verwendeten permanenten Herz-Kreislauf-Prothesen (z.B. Gefäßtransplantate, Herzklappenersatz) verfolgt, die für große Kohorten von Patienten suboptimal sind1,2,3,4. Zu den gefragten Anwendungen gehören Gewebe-Engineering-Gefäßtransplantate (TEVGs)5,6 und Herzklappen (TEHVs)7,8. Meistens verwenden kardiovaskuläre TE-Methoden resorbierbare Biomaterialien (entweder natürliche oder synthetische), die als lehrreiches Gerüst für das neu zu bildende Gewebe dienen. Die Bildung von neuem Gewebe kann entweder vollständig in vitro erfolgen, indem das Gerüst mit Zellen ausgesät und vor der Implantation in einem Bioreaktor (in vitro TE)9,10,11oder direkt in situ, in dem das synthetische Gerüst ohne Vorkultivierung implantiert wird, um die Bildung von neuem Gewebe direkt im Körper (in situ TE) 12 ,13,14zu induzieren . Sowohl bei in vitro als auch bei in situ kardiovaskulären TE-Ansätzen hängt eine erfolgreiche funktionelle Regeneration sowohl von der Immunantwort des Wirts auf das implantierte Konstrukt als auch von der entsprechenden biomechanischen Belastung ab.
Die Bedeutung der biomechanischen Belastung für kardiovaskuläre TE ist anerkannt15. Bei kardiovaskulären Implantaten sind die Zellen, die das Gerüst bevölkern, zyklischen Dehnungs- und Scherspannungen ausgesetzt, die durch die hämodynamische Umgebung entstehen. Zahlreiche Studien haben die stimulierende Wirkung von (zyklischer) Dehnung auf die Bildung von Matrixkomponenten wie Kollagen16 , 17,18,19,Glykosaminoglykanen (GAGs)20und Elastin21,22, durch verschiedene Zelltypen berichtet. Zum Beispiel zeigten Huang et al., dass biaxiale Dehnung die Ablagerung und Organisation von Kollagen und Elastin in in vitro TEVGs erhöhte, indem sie einen vaskulären Bioreaktor23verwendeten. Während der Schwerpunkt typischerweise auf der Dehnung als dominanter Last liegt, verwenden diese Studien oft strömungsgetriebene Bioreaktoren, bei denen die Probe auch dem Scherfluss ausgesetzt ist. Obwohl relativ wenig über den isolierten Einfluss von Scherspannungen auf Gewebebildung und Entzündungen in 3D bekannt ist, liegen einige Daten vor. Zum Beispiel zeigten Hinderer et al. und Eoh et al., dass der Scherfluss neben einer 3D-Gerüstmikrostruktur für die Bildung von reifem Elastin durch menschliche vaskuläre glatte Muskelzellen in einem In-vitro-Modellsystem wichtig ist24,25. Insgesamt veranschaulichen diese Ergebnisse die Relevanz von zyklischer Dehnung und Scherstress für kardiovaskuläre TE.
Eine weitere wichtige Determinante für den Erfolg oder Misserfolg von TE-Implantaten ist die Immunantwort des Wirts auf das implantierte Transplantat26. Dies ist besonders wichtig für materialgetriebene In-situ-TE-Strategien, die tatsächlich auf die akute Entzündungsreaktion auf das Gerüst angewiesen sind, um die nachfolgenden Prozesse des zellulären Zustroms und der endogenen Gewebebildung und -umgestaltung anzukurbeln27. Der Makrophagen ist ein kritischer Initiator der funktionellen Geweberegeneration, was durch mehrere Studien28,29,30gezeigt wurde. Analog zur Wundheilung wird die Regeneration des Gewebes durch parakrine Signalisierung zwischen Makrophagen und gewebeproduzierenden Zellen wie Fibroblasten und Myofibroblastengesteuert 31,32,33. Neben der Koordination neuer Gewebeablagerungen sind Makrophagen an der aktiven Resorption von Fremdgerüstmaterial beteiligt34,35. Als solches wurde die In-vitro-Makrophagenreaktion auf ein Biomaterial als prädiktiver Parameter für den In-vivo-Erfolg von Implantatenidentifiziert 36,37,38.
Die Makrophagenreaktion auf ein implantiertes Gerüst hängt von Gerüstdesignmerkmalen wie Materialzusammensetzung und Mikrostrukturab 35,39,40. Neben den Gerüsteigenschaften wird auch die Makrophagenreaktion auf ein Gerüst und deren Übersprechen mit Myofibroblasten durch hämodynamische Belastungen beeinflusst. Zum Beispiel wurde gezeigt, dass zyklische Dehnung ein wichtiger Modulator des Makrophagenphänotyps41,42,43,44 und der Sekretion von Zytokinen43,44,45,46 in 3D-Elektrosponngerüsten ist. Battiston et al. zeigten unter Verwendung eines Co-Kultursystems aus Makrophagen und vaskulären glatten Muskelzellen, dass das Vorhandensein von Makrophagen zu erhöhten Elastin- und GAGsspiegeln führte und dass moderate Konzentrationen von zyklischer Dehnung (1,07-1,10) die Ablagerung von Kollagen I und Elastinstimulierten 47. In früheren Arbeiten haben wir gezeigt, dass Scherstress eine wichtige Determinante für die Rekrutierung von Monozyten in 3D-Elektrosponngerüste48,49ist und dass sowohl Scherstress als auch zyklische Dehnung die parakrine Signalübertragung zwischen menschlichen Monozyten und mesenchymalen Stromazellenbeeinflussen 50. Fahy et al. zeigten, dass der Scherfluss die Sekretion von entzündungsfördernden Zytokinen durch menschliche Monozyten erhöhte51.
Zusammengenommen zeigen die oben genannten Beweise, dass ein angemessenes Verständnis und eine angemessene Kontrolle der hämodynamischen Belastungen für die kardiovaskuläre TE von entscheidender Bedeutung sind und dass es wichtig ist, die Entzündungsreaktion zu berücksichtigen, um dies zu erreichen. Zahlreiche Bioreaktoren wurden zuvor für die in vitro 52 ,53,54,55,56,57,58 oder ex vivo59,60,61 Kultur von kardiovaskulären Geweben beschrieben. Alle diese Systeme sind jedoch so konzipiert, dass sie die physiologischen hämodynamischen Belastungsbedingungen so weit wie möglich nachahmen. Während dies für die Herstellung von Kardiovaskulärem Gewebe in vitro oder die Aufrechterhaltung von Ex-vivo-Kulturen sehr wertvoll ist, erlauben solche Systeme keine systematischen Untersuchungen der individuellen Auswirkungen einzelner Hinweise. Dies liegt daran, dass die Anwendung sowohl der zyklischen Dehnung als auch der Scherspannung in diesen Bioreaktoren durch die gleiche Druckströmung angetrieben wird, die sie untrennbar verbindet. Während Mikrosysteme, die eine genaue mechanische Manipulation mit mehreren Cues ermöglichen, für 2D-Substrate62 oder 3D-Hydrogel-Setups63,64beschrieben wurden, erlauben solche Setups nicht die Integration von elastomeren 3D-Biomaterialgerüsten.
Hier stellen wir die Anwendung eines röhrenförmigen Bioreaktorsystems vor, das auf einzigartige Weise die Entkopplung von Scherspannung und zyklischer Dehnung ermöglicht und hilft, ihre individuellen und kombinierten Wirkungen mechanistisch zu untersuchen. Dieses System ermöglicht die Prüfung einer Vielzahl von gewebezüchtigten Gefäßtransplantaten (z. B. synthetischer oder natürlicher Ursprung, unterschiedliche Mikroarchitektur, verschiedene Porositäten). Um die Anwendung von Scherspannung und Dehnung effektiv zu entkoppeln, sind die Schlüsselkonzepte, die der Bioreaktor verwendet, (1) die Trennung der Kontrolle von Scherspannung und Dehnung durch verschiedene Pumpensysteme und (2) die Stimulation der Gerüste in einer "Inside-Out" -Weise mit rechnerisch angetriebenen Abmessungen. Die Strömung wird auf der Außenfläche des Rohrgerüsts durch die Verwendung einer Strömungspumpe angewendet, während die umfangsbespannte Dehnung des Gerüsts durch Die Erweiterung eines Silikonrohrs, auf dem das Gerüst durch die Verwendung einer separaten Dehnungspumpe montiert ist, induziert wird. Die Abmessungen des Silikonrohrs und des Glasrohrs, das das Konstrukt enthält, werden sorgfältig ausgewählt und mit Hilfe von strömungsgestützten Simulationen validiert, um sicherzustellen, dass sich die Scherspannung auf dem Gerüst (aufgrund der Strömung) und die Umfangsdehnung (aufgrund der Rohrausdehnung) nicht signifikant beeinflussen. Dieses Inside-Out-Design hat mehrere praktische Gründe. Wenn die Dehnung durch den Luminalflüssigkeitsdruck (ähnlich der physiologischen Belastung) angelegt wird, muss das Probendesign von Natur aus leckagefrei sein. Darüber hinaus würde der druck, der zum Dehnen der Probe erforderlich ist, vollständig durch die Probensteifigkeit bestimmt, die zwischen den Proben und innerhalb einer Probe im Laufe der Zeit variieren kann, was es schwierig macht, die Dehnung zu kontrollieren. Dieser Bioreaktor montiert das Gewebe-Engineered Graft um einen Silikonschlauch und ermöglicht die Anwendung von Wall Shear Stress (WSS) an der Außenwand des Transplantats und druckt das Transplantat von innen. Auf diese Weise können gleiche Belastungsbedingungen zwischen Proben und innerhalb der Proben im Laufe der Zeit sichergestellt werden, und darüber hinaus dürfen die Proben undicht sein, wie es bei porösen Gefäßgerüsten üblich ist19. Dieser Inside-Out-Bioreaktor ist speziell für systematische Studien über die Auswirkungen von Scherung und / oder Dehnung gedacht, anstatt für die Entwicklung eines nativen Blutgefäßes in vitro, für das traditionelle vaskuläre Bioreaktor-Setups besser geeignet sind. Siehe Abbildung 1A–B für die Konstruktionszeichnungen des Bioreaktors und die entsprechende Tabelle 1 für eine funktionale Beschreibung und Begründung hinter den Hauptkomponenten des Bioreaktors.
Der Einsatz des Bioreaktors wird anhand einer Reihe neuerer Studien unserer Gruppe nachgewiesen, in denen wir die individuellen und kombinierten Einflüsse von Scherstress und zyklischer Dehnung auf Entzündung und Gewebebildung in resorbierbaren elektrosponnen Gerüsten für in situ kardiovaskuläres Gewebe untersucht haben19,43,44. Dazu haben wir menschliche Makrophagen und Myofibroblasten entweder in Mono- oder in Kokultur verwendet, um die verschiedenen Phasen der in situ regenerativen Kaskade zu simulieren. Wir haben gezeigt, dass die Zytokinsekretion durch menschliche Makrophagen sowohl durch zyklische Dehnung als auch durch Scherstress deutlich beeinflusst wird, was die Matrixablagerung und -organisation durch menschliche Myofibroblasten in diesen Gerüsten beeinflusst, sowohl über parakrine Signalisierung als auch durch direkten Kontakt19,43,44. Insbesondere zeigten diese Studien, dass bei kombinierter Anwendung von Scherstress und Dehnung die Auswirkungen auf Gewebebildung und Entzündung entweder von einer der beiden Lasten dominiert werden oder synergistische Effekte beider Lasten auftreten. Diese Ergebnisse verdeutlichen die Relevanz der Entkopplung beider Lasten, um den Beitrag der mechanischen Umgebung zu TE-Prozessen besser zu verstehen. Dieses Verständnis kann angewendet werden, um Gerüstkonstruktionsparameter in relevanten hämodynamischen Belastungsregimen systematisch zu optimieren. Darüber hinaus können die mechanistischen Daten aus solchen gut kontrollierten Umgebungen als Input für numerische Modelle dienen, die entwickelt werden, um den Verlauf des In-situ-Gewebeumbaus vorherzusagen, wie kürzlich für TEVGs65 oder TEHVs66berichtet, um die Vorhersagefähigkeit weiter zu verbessern.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protokoll
In den in diesem Protokoll beschriebenen Studien wurden primäre menschliche Makrophagen, die aus peripheren Blutschichten isoliert wurden, und menschliche Myofibroblasten, die nach einer koronaren Umgehungsoperation aus der Vena saphena isoliert wurden, verwendet44. Die Buffy-Mäntel wurden von gesunden, anonymisierten Freiwilligen bezogen, die eine schriftliche Einwilligung nach Aufklärung erteilten, die vom Sanquin Research Institutional Medical Ethical Committee genehmigt wurde. Die Verwendung von humanen Vena-Saphena-Zellen (HVSCs) erfolgte in Übereinstimmung mit dem "Code Proper Secondary Use of Human Tissue", der von der Federation of Medical Societies (FMWV) in den Niederlanden entwickelt wurde.
1. Allgemeine Vorbereitungen und erforderliche Maßnahmen vor der Einrichtung des Bioreaktors
HINWEIS: Einzelheiten zu den jeweiligen Isolations- und Kultivierungsprotokollen entnehmen Sie bitte den früheren Arbeiten19,43,44. Alle Berechnungen im Protokoll sind als Beispiele für ein Co-Kulturexperiment mit Monozyten und Myofibroblasten angegeben, die in 8 hämodynamisch belasteten Gerüsten und 2 statischen Kontrollen (n= 10) ausgesät sind.
- Starten Sie die Zellisolierung und Zellkultur. Die Aussaatdichten für die ko-kultivierten Proben von Monozyten und Myofibroblasten (mit einem Aussaatverhältnis von 2:1) betragen 30 ×10 6 Monozyten/cm3 bzw. 15 × 106 Myofibroblasten/cm3.
HINWEIS: Das elektrosponnte Material hat eine hohe Porosität (>90%). Um die erforderliche Anzahl von Zellen pro Transplantat zu schätzen, wird das Volumen des Gerüsts mit der Formel für das Volumen eines Hohlzylinders berechnet: π * (Dicke)2* Länge ≈ 0,04 cm3. Die Gesamtmenge der Zellen pro Transplantat beträgt 1,2 × 106 Monozyten und 0,6 × 106 Myofibroblasten. Für 10 Proben sind mindestens 12 × 106 Monozyten und 6 × 106 Myofibroblasten erforderlich; Beginnen Sie mit bis zu ~10-15% mehr Zellen, um mögliche Pipettierfehler zu berücksichtigen. - Entgasen Sie das Zellkulturmedium, das für Experimente mit dem Bioreaktor verwendet wird.
- Bereiten Sie das Medium für Co-Kulturen vor, das aus RPMI-1640:aDMEM (1:1) besteht, ergänzt mit 10% fetalem Rinderserum, 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin und 0,5% L-Glutamin.
- Legen Sie das Medium über Nacht (O/N) in einen Inkubator in einen Zellkulturkolben mit Filterkappe, um zu entgasen.
- Ersetzen Sie die Filterkappe durch eine luftdichte Kappe und lagern Sie sie bei 4 °C.
- Kurz vor Gebrauch 0,25 mg/ml L-Ascorbinsäure 2-phosphat (Vitamin C) in das Medium geben.
HINWEIS: Für Berechnungen beträgt die benötigte Mediummenge pro Durchflusskulturkammer 50 ml. Aktualisieren Sie das Medium dreimal pro Woche; 25 ml altes Medium wird durch 25 ml frisches Medium ersetzt. Für 10 Proben; Nach der Aussaat werden insgesamt 500 ml frisches Medium benötigt, und für jeden nachfolgenden Mediumwechsel werden insgesamt 250 ml frisches Medium verwendet. Bereiten Sie immer Medium frisch vor, vor allem vitamin C sollte kurz vor dem Wechsel des Mediums hinzugefügt werden.
- Isotrope elektrosponnene Gerüste (3 mm Leuchtdurchmesser, 200 μm Wandstärke) wie von Van Haaften et al.19 beschrieben (Abbildung 1G–I). Kurz gesagt, röhrenförmige Polycaprolacton-Bisurea(PCL-BU)-Gerüste werden durch Elektrospinnen aus 15% (w/w) Chloroform-Polymer-Lösungen hergestellt. Die Polymerlösungen werden bei Raumtemperatur und 30% relativer Luftfeuchtigkeit, bei einer Durchflussrate von 40 μL/min, 16 cm Abstand vom rotierenden zylindrischen Target (Ø 3 mm, 500 U/min) und einer angelegten Spannung von 16 kV an der Elektrospinndüse und -1 kV am Target elektrosponniert.
HINWEIS: Obwohl für diese Experimente PCL-BU-Transplantate verwendet wurden, kann in diesem Bioreaktor eine Vielzahl von elastomeren Gewebetransplantaten montiert werden (z. B. unterschiedlichen synthetischen oder natürlichen Ursprungs, unterschiedliche Mikroarchitektur, unterschiedliche Porositäten).- Entfernen Sie die elektrosponnenen Gerüste vom Dorn.
- Machen Sie ein kleines Loch in der Kappe eines 15-ml-Rohrs, um den Dorn in der Mitte zu "halten" und zu verhindern, dass er die Wand des Rohrs berührt.
- Legen Sie den Dorn mit dem elektrosponnierten Gerüst in das Falkenrohr und füllen Sie ihn mit entionisiertem Wasser.
- Gefrieren Sie die Röhrchen O/N bei -20 °C.
- Legen Sie die Schläuche auf Raumtemperatur (RT) und ziehen Sie die Dorne nach einigen Minuten heraus, wobei die elektrosponnen transplantierten Transplantate im Eis bleiben.
- Lassen Sie das Eis vollständig auftauen, entfernen Sie das elektrosponnierte Rohr aus dem aufgetauten Wasser und "hängen", um es mehrere Stunden lang vertikal zu trocknen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Gerüste nicht unter ihrem eigenen Gewicht "zusammenbrechen".
- Trockengerüste unter Vakuum O/N.
- Stellen Sie eine kleine Probe der elektrosponnierten Transplantate mit Rasterelektronenmikroskopie (REM) ab, um ihre Mikrostruktur (z. B. Fasermorphologie, Faserdurchmesser) zu beurteilen. Die Transplantate in den Beispielstudien haben eine isotrope Faserorientierung und einen Faserdurchmesser von 5 μm (Abbildung 1H–I).
- Entfernen Sie die elektrosponnenen Gerüste vom Dorn.
- Legen Sie einen Tag vor Beginn des Experiments das mit entionisiertem Wasser gefüllte Hydraulikreservoir in den Inkubator. Schließen Sie alle acht Anschlüsse für Strömungskulturkammern mit weißen Luer-Kappen. Schließen Sie das Druckluftsystem an und setzen Sie den Drucksensor ein. Führen Sie die Dehnungspumpe (siehe Schritt 5.6) O/N aus, um eine kleine Ausdehnung des Teflonbalgs zu ermöglichen.
HINWEIS: Stellen Sie sicher, dass alle erforderlichen Materialien und Geräte gemäß dem Protokoll des Herstellers oder wie in den Schritten 7.3–7.6 beschrieben gereinigt und/oder autoklaviert werden (siehe Materialtabelle,Kommentare/Beschreibungsspalte, für die Materialien autoklaviert werden dürfen). - Stellen Sie sterile Arbeitsbedingungen für den Rest des Protokolls sicher.
- Führen Sie die Schritte 2–5.3 (Einrichten des Systems), Schritt 6.3 (Mittelwechsel) und die Schritte 7.1–7.2 (Ernte von Gefäßkonstrukten) in einem sterilen Laminar-Flow-Schrank aus.
- Legen Sie Materialien, die nicht direkt für die nachfolgenden Schritte benötigt werden, in geschlossene Petrischalen, um alles so sauber wie möglich zu halten.
- Reinigen oder trocknen Sie Materialoberflächen regelmäßig, indem Sie ein Papiertuch mit 70% Ethanol einweichen und die Oberflächen der Bioreaktorkomponenten und des Laminar-Flow-Schranks abwischen.
2. Einrichtung des Bioreaktors
HINWEIS: Führen Sie Schritt 2 in einem Laminar-Flow-Schrank aus.
- Schneiden Sie die elektrosponnierten Gerüste in Rohre von ca. 25 mm Länge und dokumentieren Sie sie vor Gebrauch (z. B. Foto für die Länge, Wiegen mit Waage für die Anfangsmasse).
- Dekontaminieren Sie die elektrogesponnenen Gerüste.
- Legen Sie die elektrosponnierten Gerüste in eine Brunnenplatte oder Petrischale, wobei eine Öffnung der ultravioletten (UV) Lichtquelle zugewandt ist, damit UV-Licht (253,7 nm) das Innere der Gerüste beleuchten kann.
- Setzen Sie die elektrosponnenen Gerüste für 5 min UV-Licht aus.
- Drehen Sie alle Gerüste und wiederholen Sie die UV-Beleuchtung für die andere Öffnung.
HINWEIS: Berühren Sie nach diesem Schritt das elektrosponnene Gerüst nur bei Bedarf. Verwenden Sie immer eine saubere Pinzette oder saubere Handschuhe. - Nehmen Sie die Glasröhren der Strömungskulturkammern, die in 70% gelagert werden, waschen Sie die Glasröhren in Reinstwasser, trocknen Sie sie und legen Sie sie in eine große, geschlossene Petrischale.
HINWEIS: Die folgenden Schritte, insbesondere die Schritte 2.3–2.5, werden idealerweise von zwei Experimentatoren durchgeführt.
- Montieren Sie die elektrosponnenen Gerüste auf dem Silikonschlauch.
- Befestigen Sie die 5-0-Prolennaht an einem Ende des Silikonschlauchs, indem Sie die Naht durch eine Seite des Rohrs und aus der anderen herausnehmen, wobei zwei gegenüberliegende gespannte Nähte den Querschnitt des Schlauchs überspannen. Machen Sie einen kleinen Knoten auf beiden Seiten des Rohres, während Sie das Rohr an der Stelle der Knoten komprimieren und lassen Sie etwa 10 cm Draht auf beiden Knoten. Machen Sie einen dritten Knoten am Ende der beiden 10 cm restgleichen Drähte.
- Schneiden Sie die Nahtnadel und alle freien Fäden ab, die herausragen und die Innenseite des elektrogesponnenen Gerüsts beschädigen könnten. Schneiden Sie die Kanten des Silikonschlauchs in eine dreieckige Form, um den Silikonschlauch durch das elektrosponnierte Gerüst zu ziehen.
- Tauchen Sie das elektrogesponnene Gerüst in 30% Ethanol (dies dient als zusätzlicher Dekontaminationsschritt und hilft beim Schieben des elektrogesponnenen Gerüsts über den Silikonschlauch) und legen Sie das elektrogesponnene Gerüst über den freien 10 cm Draht. Experimentator A dehnt den Silikonschlauch, indem er sowohl den Silikonschlauch als auch den Knoten des 10 cm langen Nahtdrahtes sanft zieht, während Experimentator B das elektrogesponnene Gerüst mit einer Pinzette mit einer glatten Innenspitze vorsichtig über den Silikonschlauch schiebt, um eine Beschädigung der Gerüste zu verhindern.
- Lösen Sie langsam die Dehnung am Silikonschlauch und glätten Sie gleichzeitig das elektrosponnende Gerüst mit einer Pinzette. Tauchen Sie das elektrosponnende Gerüst auf dem Silikonschlauch zweimal in Reinstwasser.
HINWEIS: Es ist möglich, dass eine Faltenbildung des elektrosponnen Gerüsts auftritt. Diese Faltenbildung verschwindet während der angelegten Vordehnung, bevor die Gerüste in Schritt 2.5.3 an den Druckrohren fixiert werden. - Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 2.3.2 und 2.3.3 für die anderen elektrosponnenen Gerüste. Je nach Länge des Silikonschlauches können mehrere elektrosponnierte Gerüste auf demselben Silikonschlauch montiert werden.
- Wenn alle elektrogespannten Gerüste auf dem Silikonschlauch montiert sind, schneiden Sie den Silikonschlauch um die Gerüste herum, alle auf die gleiche Länge (5,5 cm); auf der einen Seite, nahe dem Ende des elektrosponnen gesponnenen Gerüsts, auf der anderen Seite, so dass ~ 2-3 cm freier Silikonschlauch übrig bleiben.
- Befestigen Sie die 5-0-Prolennaht an einem Ende des Silikonschlauchs, indem Sie die Naht durch eine Seite des Rohrs und aus der anderen herausnehmen, wobei zwei gegenüberliegende gespannte Nähte den Querschnitt des Schlauchs überspannen. Machen Sie einen kleinen Knoten auf beiden Seiten des Rohres, während Sie das Rohr an der Stelle der Knoten komprimieren und lassen Sie etwa 10 cm Draht auf beiden Knoten. Machen Sie einen dritten Knoten am Ende der beiden 10 cm restgleichen Drähte.
- Konstruieren Sie das untere Kompartiment der Strömungskulturkammer (Abbildung 1A–B).
- Nehmen Sie den oberen Teil des unteren Fachs, in dem sich der Durchflussauslass befindet, und schließen Sie den Durchflussauslass mit einem männlichen Luer-Stecker.
- Drücken Sie die Druckleitung mit Löchern durch das untere Fach und legen Sie einen Silikon-O-Ring um das untere Ende der Druckleitung, um ein Auslaufen zu verhindern. Schrauben Sie den unteren Teil des unteren Fachs mit dem oberen Teil des unteren Fachs, um die Druckleitung zu sichern. Stellen Sie sicher, dass sich die untere gravierte Nut der Druckleitung etwa 3–5 mm über dem Rand der Adapterbuchse des unteren Fachs befindet. Dies wird später den engen Knoten des Nahtdrahtes "halten" und das elektrogesponnene Gerüst über dem Silikonschlauch fixieren.
HINWEIS: Wenn die Druckleitung leicht nach oben und unten manövriert werden kann, zeigt dies an, dass das untere Fach nicht gut gesichert ist. Wiederholen Sie Schritt 2.4.2, um Leckagen in späteren Phasen zu vermeiden (Abbildung 2D).
- Befestigen Sie den Silikonschlauch mit dem elektrosponnierten Gerüst an der Druckleitung.
- Ziehen Sie den Silikonschlauch mit dem elektrosponnierten Gerüst über die Druckleitung.
- Machen Sie einen Knoten mit dem Nahtdraht am unteren Ende des elektrogesponnenen Gerüsts an der Stelle der gravierten Nut auf der Druckleitung. Machen Sie einen zweiten Knoten auf der gegenüberliegenden Seite, um den Silikonschlauch mit dem elektrosponnierten Transplantat fest zu sichern.
ACHTUNG: Dies ist ein kritischer Schritt. Stellen Sie sicher, dass der Knoten genau in die gravierte Nut der Druckleitung "fällt", um ein Austreten des Wassers aus dem Hydraulikbehälter in die Strömungskulturkammern zu verhindern. Wenn Sie sich nicht sicher sind, versuchen Sie, den Nahtdraht an mehreren Positionen oberhalb oder unterhalb der erwarteten Position der Nut festzuziehen, um sicherzustellen, dass sich die endgültigen Knoten genau an der gravierten Nut befinden (Abbildung 2A). - Setzen Sie die Scherenklemme am oberen Ende des Silikonschlauchs ein und strecken Sie den Silikonschlauch nach oben (dies wird den ersten Knoten direkt testen, wenn es möglich ist, den Silikonschlauch mit dem elektrosponnierten Gerüst über die Druckleitung zu bewegen, wurde er nicht gut genug angezogen). Mit der Zugkraft wird der Silikonschlauch vorgeredet. Um sicherzustellen, dass der Silikonschlauch zwischen den verschiedenen Proben konsistent ist, befestigen Sie ein Lineal an der Scherenklemme. Ziehen Sie die Scherenklemme nach oben, bis das untere Ende des Lineals die Höhe des unteren Endes des Gerüsts erreicht.
HINWEIS: Es ist wichtig, die Vordehnung in jeder Probe aus zwei Gründen ungefähr gleich zu halten (~ 5%): (1) Wenn Silikonschläuche vorgedehnt werden, führt dies zu einer homogeneren Ausdehnung entlang der Länge der Probe, wenn sie unter Druck steht; (2) Die Vordehnung wirkt sich auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften des Silikons aus, daher sollte sie in allen Proben gleich sein, um gleiche Dehnungsbedingungen zwischen den Proben zu gewährleisten. - Entfernen Sie Falten im elektrosponnenen Gerüst, indem Sie sanft am elektrosponnenen Gerüst ziehen. Machen Sie wieder zwei Knoten auf beiden Seiten mit einem Nahtdraht am oberen Ende des Gerüsts an der Stelle der oberen gravierten Nut auf der Druckleitung.
- Lösen Sie die Scherenklemme und schneiden Sie den Überschuss an Silikonschläuchen mit einem Messer weg, wobei 20-30% des Schraubgewindes mit Silikonschläuchen bedeckt bleiben, um ein Auslaufen zu vermeiden, wenn der Nasenkegel am Schraubgewinde montiert wird.
HINWEIS: Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 2.4 und 2.5 für alle dynamischen Samples. - Für die statischen Kontrollproben befestigen Sie das auf dem Silikonschlauch montierte elektrosponnenförmige Gerüst an Druckrohren ohne Löcher. Diese Leitungen können bis zur Aussaat (Schritt 4) separat in einem 15-ml-Rohr aufbewahrt werden und müssen nicht in den Strömungskulturkammerfächern montiert werden.
- Dekontaminieren Sie die teilweise konstruierten Strömungskulturkammern mit einem elektrogesponnenen Gerüst, indem Sie sie 10 min UV-Licht aussetzen. Drehen Sie die Strömungskulturkammern mit elektrogesponnenen Gerüsten auf die andere Seite und wiederholen Sie die UV-Lichteinwirkung für 10 Minuten.
- Schrauben Sie die Nasenkegel auf das Schraubgewinde der Druckleitungen mit Löchern für die dynamischen Proben.
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass das obere Ende des Silikonschlauchs in den Nasenkegel passt, um ein Auslaufen in späteren Stadien zu verhindern. Wenn zu viele Silikonschläuche vorhanden sind, schneiden Sie den Überschuss an Schläuchen mit einem Messer weg.
- Legen Sie die teilweise konstruierten Strömungskulturkammern in eine große Petrischale und richten Sie den Nasenkegel auf die UV-Lichtquelle. UV-Beleuchtung für 5 min.
- Vollständiger Aufbau der Strömungskulturkammer mit Glasrohr und oberem Fach der Strömungskulturkammer (Abbildung 1A–B).
- Befeuchten Sie die elektrosponnierten Gerüste, indem Sie die Druckleitung mit dem Silikonschlauch und dem elektrogesponnenen Gerüst in 30% Ethanol tauchen, gefolgt von einem zweimaligen Eintauchen in Reinstwasser.
- Legen Sie das Glasrohr über die Druckleitung, drücken Sie es vorsichtig in das untere Fach und befesten Sie es vorsichtig.
- Nehmen Sie das obere Fach mit dem Durchlass, legen Sie einen Silikon-O-Ring, das Strömungsglätter und die Adapterbuchse in der richtigen Reihenfolge (Abbildung 1A-B), legen Sie es über das offene Ende des Glasrohrs und befestigen Sie es vorsichtig.
- Schrauben Sie eine weiße Luer-Kappe auf den Durchflusseinlass des oberen Fachs.
- Entfernen Sie den männlichen Luer-Stecker aus dem Durchflussauslass des unteren Fachs und reinigen Sie die Oberfläche um ihn herum mit einem ethanolgetränkten Papiertuch.
- Legen Sie eine Spritze mit 10 ml Reinstwasser in den Durchflussauslass, öffnen Sie die weiße Luer-Kappe auf dem oberen Fach und füllen Sie die Kammer mit Reinstwasser. Schließen Sie die weiße Luer-Kappe erneut, entfernen Sie die Spritze, reinigen Sie sie erneut mit Ethanol und schließen Sie den Durchflussauslass mit einem männlichen Luer-Stecker.
HINWEIS: Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 2.6 bis 2.8 für alle Strömungskulturkammern. - Für die statischen Kontrollen fügen Sie 10 ml Reinstwasser in die 15-ml-Röhrchen hinzu, die die Proben ohne Löcher auf den Druckrohren halten.
- Legen Sie alle Fließkulturkammern in den Inkubator. Ersetzen Sie das Reinstwasser einen Tag vor der Zellaussaat auf die gleiche Weise wie in den Schritten 2.8.5 und 2.8.6 beschrieben durch Kulturmedium (stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie das "alte" Reinstwasser mit einem ethanolgetränkten Papiertuch sammeln, das direkt auf dem Durchflussauslass platziert wird).
[Das Protokoll kann hier pausiert werden]
3. Vorbereitungen für den Aufbau der Durchflusspumpe
HINWEIS: Führen Sie Schritt 3 in einem Laminar-Flow-Schrank aus.
- Sammeln Sie alle Pumpeneinrichtungsmaterialien und bereiten Sie sich auf den Gebrauch vor.
HINWEIS: Experimentatoren werden auf das Protokoll des Herstellers verwiesen, um eine detaillierte Beschreibung des Aufbaus der Pumpe, der fluidischen Einheiten und der mittleren Schläuche durch die Ventile der fluidischen Einheit zu erhalten.- Stellen Sie die Pumpe auf 200 mbar Kapazität ein.
- Schrauben Sie die Behälterhalter für 60 mL Behälter an die fluidischen Einheiten.
- Reinigen Sie die wiederverwendbaren Gummiluftfilter mit einem in Ethanol getränkten Papiertuch, stellen Sie sicher, dass der Luftfilter trocken bleibt.
- Legen Sie die 60-ml-Behälter in die Behälterhalter und legen Sie den Standard-Mediumschlauch durch die Ventile der Fluideinheit. Verbinden Sie den mittleren Schlauch mit einem größeren Innendurchmesser mit weiblichen Luer-Verschlusskupplungen zu einer geschlossenen Schlaufe.
- Klemmen Sie den mittleren Schlauch mit einem Schlauchclip direkt unter den Behältern.
- Füllen Sie die Reservoirs mit 25 mL Kulturmedium pro 60 mL Reservoir. Lassen Sie den Schlauchclip los und lassen Sie das Medium in den Schlauch gelangen.
- Schließen Sie die Mediumbehälter mit den Gummiluftfiltern und legen Sie die Strömungspumpe bis Schritt 4 in den Inkubator.
4. Zellaussaat mit Fibrin als Zellträger
HINWEIS: Führen Sie Schritt 4 in einem Laminar-Flow-Schrank aus.
- Bereiten Sie das Fibringel für den Zellaussaatschritt vor. Für Details siehe Mol et al.67 Für das Fibringel sollte die Fibrinogenlösung eine Endkonzentration von 10 mg / ml haben (korrekt für die Reinheit des Proteinbestands), und die Thrombinlösung sollte eine Endkonzentration von 10 U / ml haben.
- Auftauen Sie Fibrinogen auf RT, bevor Sie ~ 50 mg (genug für 10 Proben) in einem Kunststoffbehälter mit rotem Deckel wiegen.
- Fügen Sie Zellkulturmedium hinzu, um die Fibrinogenlösung herzustellen (in einer Konzentration von 10 mg / ml, korrekt für die Reinheit des Proteinbestandes). Gut mischen und filtern, um die Fibrinogenlösung mit einem 0,2 μm Spritzenfilter in ein steriles 15 ml Röhrchen zu sterilisieren. Halten Sie die gefilterte Fibrinogenlösung auf Eis.
HINWEIS: Vermeiden Sie es, die Fibrinogenlösung zu lange im Voraus vorzubereiten, da das Fibrinogen sonst spontan gerinnen kann. - Thrombin auftauen und eine Thrombinlösung (in einer Konzentration von 10 U/ml) im Zellkulturmedium herstellen und auf Eis legen. Bereiten Sie 20 μL Thrombin + Zelllösung pro Probe vor. Für n=10 Proben werden 200 μL benötigt; Bereiten Sie daher eine 250 μL-Thrombinlösung vor, um mögliche Pipettierfehler zu berücksichtigen.
- Sammeln und zählen Sie die Zellen aus den Kulturkolben. Mischen Sie die Zellen im gewünschten Verhältnis und in der gewünschten Menge (1,2 ×10 6 Monozyten und 0,6 × 106 Myofibroblasten pro Gerüst). Stellen Sie sicher, dass genügend Zellen für n+1-Proben vorhanden sind, um Pipettierfehler zu korrigieren. Zentrifuge bei 350 × g für 10 min bei RT. Entfernen Sie den Überstand.
- Machen Sie eine Mischung aus den suspendierten Zellen und Thrombin.
- Verwenden Sie für jede Probe 20 μL der Thrombinlösung. Für n=10 Proben 200 μL Thrombin in das Zellpellet geben und mischen. Messen Sie das Volumen der Zellsuspension (Zellen + Thrombin) und berechnen Sie, wie sie gleichmäßig auf alle 10 Gerüste aufgeteilt werden (z. B. wenn die Thrombin + Zellsuspension ein Volumen von 260 μL hat, erhält jede elektrospunte Probe 260 μL / 10 Proben = 26 μL Thrombin + Zellsuspension).
- Da die Aussaat der Gerüste in zwei Schritten erfolgt, bereiten Sie zwei 1,5-ml-Mikrofugenröhrchen vor, die die Hälfte der Zellsuspension für jedes Gerüst enthalten (in der Beispielberechnung des vorherigen Schritts: Zwei Röhrchen mit 13 μL Thrombin + Zellsuspension vorbereiten). Auf Eis legen.
HINWEIS: Die folgenden Schritte, insbesondere Schritt 4.4, werden idealerweise von zwei Experimentatoren durchgeführt.
- Trocknen Sie die vorbenetzten elektrosponnierten Gerüste mit Vakuum, um sich auf die Zellaussaat vorzubereiten.
- Schließen Sie eine Pasteur-Glaspipette an das Vakuumsystem des Laminar-Flow-Schranks an und legen Sie sie zur sterilen Zwischenlagerung in ein leeres 50-ml-Rohr.
- Nehmen Sie die Strömungskulturkammern aus dem Inkubator, entfernen Sie den männlichen Luer-Stecker aus dem Durchflussauslass und entfernen Sie das Medium, nachdem Sie die weiße Luer-Kappe geöffnet und ein ethanolgetränktes Papiertuch vor den Durchflussauslass gelegt haben.
- Nehmen Sie das obere Fach und den Glasschlauch ab und legen Sie es zur vorübergehenden Lagerung in eine sterile Petrischale.
- Legen Sie die Vakuum-Pasteur-Pipett auf das elektrogesponnene Gerüst und entfernen Sie so viel Medium wie möglich.
ACHTUNG: Vakuumtrocknen Sie das elektrosponnierte Gerüst sehr vorsichtig. Anstelle einer linearen Hin- und Herbewegung über das Gerüst platzieren Sie die Vakuumpipette an mehreren Stellen. Klemmen Sie den Vakuumschlauch zur besseren Kontrolle auf die Pipett des Pasteurs zwischen die Finger. - Mischen Sie die Fibrinogenlösung im Verhältnis 1:1 mit der Thrombin + Zellsuspension (z. B. mischen Sie 13 μL Fibrinogen mit 13 μL Thrombin + Zellsuspension). Um sicherzustellen, dass das Fibrin im Gerüst und nicht im Mikrofugenröhrchen polymerisiert, pipeten Sie das Fibrinogen, drehen Sie das Pipettrad für das "zusätzliche Volumen" der Thrombin + Zellsuspension und pipetieren Sie es einmal im Mikrofugenröhrchen mit Zellsuspension auf und ab.
- Tropfen Sie die Lösung direkt homogen über die gesamte Länge des elektrosponnen Gerüsts. Es wird empfohlen, dass Experimentator A die Fibrinmischung tropft, während Experimentator B das untere Fach mit dem elektrosponnierten Gerüst hält, das an der Druckleitung montiert ist.
- Nachdem das Fibrin mit den Zellen über das elektrosponnierte Gerüst getröpft wurde, bewegt Experimentator B das Gerüst langsam von links nach rechts und auf und ab, um die Zellen gleichmäßig über das Gerüst weiter zu teilen.
- Wiederholen Sie schritt 4.4.5 - 4.4.7 auf der anderen Seite des elektrosponnen gesponnenen Gerüsts.
- Montieren Sie die Strömungskulturkammer erneut, indem Sie das Glasrohr vorsichtig platzieren (verhindern Sie, dass Fibrin an der Innenseite des Glasrohrs klebt und gerinnt), und drücken Sie das obere Fach der Strömungskulturkammer zurück. Legen Sie das ausgesäte Konstrukt ohne medium oder phosphatgepufferte Kochsalzlösung (PBS) direkt in die Strömungskulturkammer im Inkubator.
- Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 4.4.1 bis 4.4.9 für alle dynamischen Beispiele. Für die statischen Proben, die an Druckrohren ohne Löcher montiert sind, gemäß den Schritten 4.4.1–4.4.8 aussäen und anschließend in ein 15-ml-Röhrchen geben.
- Lassen Sie das Fibrin 60 min im Inkubator polymerisieren.
[Das Protokoll kann hier für 30–60 Min. pausiert werden.]
- Füllen Sie nach der Polymerisation die Fließkulturkammern (dynamische Proben) oder die 15-ml-Röhrchen (statische Proben) mit Medium.
5. Kopplung der Bioreaktor- und Durchflusspumpensysteme vor Beginn des Experiments
HINWEIS: Führen Sie die Schritte 5.1 bis 5.3 in einem Laminar-Flow-Schrank aus.
- Nehmen Sie das Tablett mit den Strömungskulturkammern und den fluidischen Einheiten mit gefüllten Mediumbehältern und angeschlossenen Mediumschläuchen in den laminaren Strömungsschränken.
- Positionieren Sie die Strömungskulturkammern auf der Bioreaktorbasis für die experimentellen Gruppen, die mit zyklischer Dehnung und kombinierten hämodynamischen Lasten beladen sind (Abbildung 1E).
- Kippen Sie die Strömungskulturkammer auf den Kopf und füllen Sie die Druckleitung von unten mit Reinstwasser mit einer Spritze mit dünnem Schlauch (dies kann von jeder Art sein, solange sie flexibel und dünn ist, in diesem Experiment wurde ein 10 cm langer Draht mit einem Innendurchmesser von 0,15 mm an der Nadel befestigt).
- Legen Sie den dünnen Schlauch in die Druckleitung, und während die Druckleitung mit Reinstwasser gefüllt wird, indem Sie das Wasser allmählich aus der Spritze drücken, ziehen Sie den Draht gleichzeitig aus der Druckleitung, um sicherzustellen, dass sich keine Luftblasen in der Druckleitung befinden.
- Legen Sie die Fließkulturkammer auf eines der acht Schraubgewinde auf bioreaktorer Basis. Legen Sie einen Silikon-O-Ring zwischen die Bioreaktorbasis und den weißen Luer-Stecker, um ein mögliches Auslaufen zu verhindern, und ziehen Sie den weißen Luer-Stecker aus dem unteren Fach fest.
- Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 5.2.2 und 5.2.3 für alle zyklisch gestreckten Proben.
- Verbinden Sie die Strömungskulturkammern für alle Versuchsgruppen, mit Ausnahme der statischen Steuerung, mit dem Durchflusspumpensystem.
- Legen Sie einen Schlauchclip auf den mittleren Schlauch. Entfernen Sie die weiße Luer-Kappe, die den Durchflusseinlass des oberen Fachs der Fließkulturkammer bedeckt. Entfernen Sie die weibliche Luer-Kupplung des mittleren Schlauchs und verbinden Sie den mittleren Schlauch auf der einen Seite mit dem Strömungseinlass im oberen Fach und der anderen Seite des mittleren Schlauchs mit Durchflussauslass im unteren Fach.
- Wiederholen Sie Schritt 5.3.1 für alle Strömungskulturkammern. An dieser Stelle werden der Bioreaktor und die Strömungskulturkammern mit Medium gefüllt und mit den Strömungssystemen verbunden.
- Für die statischen Kontrollproben legen Sie die Proben mit der Scherenklemme vertikal in einen Zellkulturkolben mit Filterkappe. Füllen Sie den Zellkulturkolben mit Medium und legen Sie ihn in den Inkubator.
- Übertragen Sie das komplette Setup vom Laminar-Flow-Schrank in den Inkubator und verbinden Sie die Fluideinheiten mit dem Luftdruckschlauch und dem elektrischen Kabel.
- Starten Sie die Software und initialisieren Sie die Durchflusspumpen. Starten Sie den Mediumfluss für die Proben nacheinander.
- Überprüfen Sie, ob die Ventile der Fluideinheit klicken.
- Entfernen Sie die Schlauchklemme aus dem mittleren Schlauch.
- Starten Sie die Durchflusspumpe mit 100 mbar und 10 s Schaltzeit.
- Überprüfen Sie sorgfältig die Strömungsrichtung auf mögliche Leckagen oder Luftblasen. Eingekleinerte Luftblasen können durch Drehen der Strömungskulturkammer auf den Kopf gestellt werden.
HINWEIS: Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Mediumspegel in den Mediumbehältern ausgeglichen sind, um ein Ansaugen von Luft in das System und Luftblasen in den Strömungskulturkammern zu verhindern und die Behälter nicht austrocknen zu lassen (Abbildung 2C). - Wiederholen Sie Schritt 5.5 für alle fluidischen Einheiten nacheinander.
- Initialisieren Sie die Dehnungspumpe.
- Verbinden Sie die pneumatische Betätigungspumpe über den Lufteinlass am Pneumatikzylinder mit der Druckluft. Schließen Sie den unteren Luftauslass mit dem blauen Schlauch für den Luftaustritt an(Abbildung 1F).
- Öffnen Sie die LabVIEW-Software, führen Sie das LabVIEW-Skript und das Druckluftdruck-Anwendungssystem aus, wie von Van Kelle et al.68beschrieben, geben Sie Verschiebung und Frequenz ein (beginnen Sie mit einer niedrigen Frequenz von 0,2 Hz). Pausieren Sie die Pumpe, wenn sich der Teflonbalg auf dem niedrigsten Stand befindet.
- Platzieren Sie den Drucksensor in den Drucksensoreinlass am Hydraulikbehälter.
- Ändern Sie die Pumpeneinstellungen auf die gewünschten Einstellungen (für 1,5 Pa verwenden Sie 150 mbar, 10 s Schaltzeit).
- Starten Sie die Dehnungspumpe und wenden Sie die bevorzugte Einstellung an (z. B. 0,5 Hz, 1,05 Dehnung).
6. Ausführen des Experiments für mehrere Tage; Überwachung von Scherung und Dehnung während der Kultur und Des Mediumaustauschs
- Berechnen Sie das WSS an der Gerüstwand.
- Notieren Sie die Durchflussgröße jeden zweiten Tag (siehe Handbuch des Herstellers der Durchflusspumpe für Details). Kurz gesagt, beobachten Sie die Änderung des Flüssigkeitsstandes (in ml) in den Mediumreservoirs zwischen dem Schalten des Flüssigkeitseinheitenreservoirs für 10 s. Führen Sie mindestens fünf Messungen durch, berechnen Sie den Mittelwert und multiplizieren Sie ihn mit 6, um die Durchflussrate Q in ml/min zu erhalten.
- Die Strömung wird durch eine Poiseuille-Strömung durch einen ringförmigen Kanal beschrieben. Unter der Annahme eines Kulturmediums als Newtonsche Flüssigkeit berechnen Sie das WSS an der Gerüstwand, r1,nach Gleichung 1.
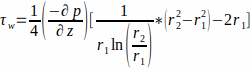 (1)
(1)
wobei das WSS τw an der Gerüstwand (r1; hier r1 = 1,7 mm), das sich aus einer stationären Strömung ergibt, durch den angelegten Druck p und den innenradius des Glasrohrs r2 (hier r2 = 2,3 mm) bestimmt wird. Der Druckgradient in axialer Richtung wird als gleichmäßig zwischen Strömungseinlass und Strömungsauslass angenommen und ist durch Gleichung 2 gegeben (Abbildung 1J).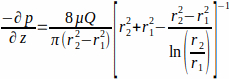 (2)
(2)
mit μ der dynamischen Viskosität (hier wurde die mittlere Viskosität konstant angenommen, μ = 0,7 × 10-3 Pa∙s bei 37 °C) und Q der angelegten Durchfluss.
- Überwachen Sie die Dehnung, die jeden zweiten Tag auf die Gerüste aufgetragen wird.
- Platzieren Sie einen dunklen Hintergrund hinter der Strömungskulturkammer, um den Kontrast zwischen dem Gerüst und dem Hintergrund zu erhöhen. Positionieren Sie die LED-Lichtlampen, die auf das Gerüst zeigen, um die Visualisierung des Gerüsts zu unterstützen.
- Machen Sie Zeitrafferfotos des Gerüsts mit einer Frequenz von 30 Hz für 6 s (dh 3 Dehnungszyklen) mit einer Hochgeschwindigkeitskamera.
HINWEIS: Eine niedrigere Aufnahmefrequenz kann ausreichen, wenn die Kamera dies zulässt. Die minimal benötigte Frequenz wurde jedoch nicht bestimmt. - Bestimmen Sie manuell den minimalen und maximalen Durchmesser des Gerüsts aus den Bildern.
- Berechnen Sie den minimalen und maximalen Außendurchmesser des elektrosponnen gesponnenen Gerüsts, um die maximalen Dehnungen gemäß Gleichung 3 zu berechnen.
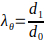 (3)
(3)
wobei die Umfangsdehnung (λθ) durch das Verhältnis zwischen dem Außendurchmesser des Gerüsts, d1, und seinem Anfangsdurchmesser d0gegeben ist.
- Korrigieren Sie die mittlere Verdunstung und erfrischen Sie das Medium dreimal pro Woche.
- Stoppen und entkoppeln Sie die Kabel für die Strömungssysteme und die Dehnungspumpe.
- Legen Sie Schlauchclips auf den mittleren Schlauch.
- Bestimmen Sie anhand der Volumenindikatormarkierungen auf den Mediumbehältern, wie viel Medium verdampft ist.
- Übertragen Sie das Tray mit dem Bioreaktor und den fluidischen Einheiten in den Laminar-Flow-Schrank.
- Entfernen Sie die Gummiluftfilter der Mediumbehälter; Fügen Sie autoklaviertes Reinstwasser hinzu, um das verdampfte Volumen des Mediums zu kompensieren. Schließen Sie die Mediumbehälter wieder und schließen Sie sie erneut an die Pumpe an, um das Medium mit dem Reinstwasser zu mischen.
- Wiederholen Sie die Schritte 6.3.1 bis 6.3.5. Entfernen Sie die Gummiluftfilter erneut, nehmen Sie 25 ml Kulturmedium heraus und drehen Sie bei 300 × g für 5 min bei RT herunter.
- 1,5 ml Überstand sammeln und bei -30 °C für die Analyse sekretorischer Profile lagern (zur Analyse mit enzymgebundenen Immunosorbent-Assay (ELISA)).
- Sammeln Sie das gewünschte Überstandsvolumen für parakrine Signalstudien, indem Sie den Überstand als konditioniertes Mediumverwenden 43.
- Fügen Sie 25 ml frisches Medium zu den mittleren Reservoirs hinzu.
- Legen Sie Gummiluftfilter wieder auf die mittleren Behälter.
- Legen Sie das komplette Setup wieder in den Inkubator; Verbinden Sie alle Kabel und Luftschläuche mit der Pumpe und Dehnungspumpe. Lassen Sie die Schlauchclips los, und wiederholen Sie die Schritte 5.4–5.8.
- Überprüfen Sie, ob Kieselsäuretrocknungsperlen in den an die Pumpe angeschlossenen Trocknungsflaschen feucht sind (weißes Aussehen), und ersetzen Sie sie bei Bedarf durch trockene Kieselsäureperlen (orangefarbenes Aussehen).
7. Beenden von Experiment, Probenentnahme und Gerätereinigung und -lagerung
- Korrigieren Sie am letzten Tag des Experiments die mittlere Verdampfung, wie in den Schritten 6.3.1–6.3.5 beschrieben, und ernten Sie die Proben nacheinander.
- Um die Proben einzeln zu entnehmen, müssen Durchflusspumpe und Dehnungspumpe mehrmals pausiert werden. Legen Sie einen Schlauchclip auf einen mittleren Schlauch. Stoppen Sie vorübergehend die Durchflusspumpe und die Dehnungspumpe. Trennen Sie eine Strömungskulturkammer von der Bioreaktorbasis; durch eine weiße Luer-Kappe auf der Bioreaktorbasis ersetzen. Bringen Sie die Strömungskulturkammer und die Fluideinheit in den Laminar-Strömungsschrank. Starten Sie die Durchflusspumpe und die Dehnungspumpe erneut, um die hämodynamische Last bis zur Ernte auf die anderen Proben aufzutragen.
- Sammeln Sie Medium aus den Mediumreservoirs für die parakrine Zytokinproduktionsanalyse über ELISA.
- Entkoppeln Sie Strömungseinheiten und ernterohrförmiges Konstrukt. Schnitt nach dem gewünschten Schnittschema. Teile des Konstrukts können bis zur weiteren Analyse bei 4 °C (nach 15 min Fixierung in 3,7% Formaldehyd und 3 x 5 min Waschen in PBS) oder -30 °C (nach Schnappgefrieren in flüssigem Stickstoff) gelagert werden.
- Reinigen Sie den Bioreaktor und die Pumpenkomponenten. Zusätzlich wird die empfohlene Reinigungsmethode pro Artikel in der Materialtabelle erwähnt.
- Reinigen Sie die Gummiluftfilter mit 70% Ethanol. Achten Sie sehr darauf, den Innenfilter nicht zu befeuchten!
- Sammeln Sie alle einzelnen Komponenten: mittlere Schläuche, mittlere Behälter, Glasröhren, männliche Luer-Stecker und weibliche Luer-Schlösser, weiße Luer-Kappen, Druckkanäle, Nasenkegel, Silikon-O-Ringe, Adapterbuchsen, Strömungsglätter (ausgenommen Pumpen, Fluideinheiten, Gummiluftfilter, die Bioreaktorbasis) und spülen Sie in fließendem Leitungswasser.
- O / N in 0,1% Natriumdodecylsulfat in deionisiertem Wasser geben.
HINWEIS: Verwenden Sie kein Reinstwasser, da die Teile rosten könnten. - Mit Leitungswasser und Spülmittel abspülen.
- Tauchen Sie in entionisiertes Wasser ein, gefolgt von zweimal 70% Ethanol, gefolgt von entionisiertem Wasser.
- Legen Sie alle Materialien separat auf Papiertaschentücher und lassen Sie sie trocknen. Verwenden Sie Druckluft, um Schläuche zu trocknen.
- Reinigen Sie alle nicht autoklavierbaren Materialien mit einem Papiertuch, das mit 70% Ethanol getränkt ist. Dazu gehören der Gummiluftfilter (beachten Sie, dass der Luftfilter trocken bleiben sollte) und die Bioreaktorbasis (Teflonbalg und Pneumatikzylinder).
- Autoklaven sie die Komponenten der Fluidkammer (einschließlich des Silikon-O-Rings), des Mediumschlauchs, der Mediumbehälter (ohne Gummiluftfilter), der männlichen Luer-Stecker und der weiblichen Luer-Kupplungen, der weißen Luer-Kappen, der Schlauchclips und der Standardausrüstung (z. B. Pinzette, Klemmschere)
- Für den bequemen Einsatz bei den nächsten Experimenten kombinieren Sie die einzelnen Komponenten zu einer vollständigen fluidischen Kammer in einer autoklavierbaren Box.
- Entfernen Sie Wasser aus dem Hydraulikbehälter. Mit 70% Ethanol reinigen, gefolgt von entionisiertem Wasser. Trocknen lassen. Nachfüllen Sie mit entionisiertem Wasser und ein paar Tropfen wasserbadkonservierendem Desinfektionsmittel.
- Lagern Sie die Glasröhren für die Strömungskulturkammer in 70% Ethanol.
- Die feuchten Kieselsäure-Trocknungsperlen (weißes Aussehen) bei 120 °C in den Ofen O/N geben, um sie trocknen zu lassen (orange Aussehen), und in einem luftdichten Kolben aufbewahren.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Ergebnisse
Dieser Bioreaktor wurde entwickelt, um die individuellen und kombinierten Auswirkungen von Scherstress und zyklischer Dehnung auf das Wachstum und den Umbau von Gefäßgewebe in 3D-Biomaterialgerüsten zu untersuchen. Das Design des Bioreaktors ermöglicht die Kultivierung von bis zu acht Gefäßkonstrukten unter verschiedenen Belastungsbedingungen (Abbildung 1A). Die Gefäßkonstrukte sind in einer Strömungskulturkammer (Abbildung 1B) positioniert, in der sowo...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Diskussion
Der hier beschriebene Bioreaktor ermöglicht die systematische Bewertung der Beiträge der einzelnen und kombinierten Wirkungen von Scherstress und zyklischer Dehnung auf Entzündungen und Geweberegeneration in röhrenförmigen resorbierbaren Gerüsten. Dieser Ansatz ermöglicht auch eine Vielzahl von Analysen an vaskulären Konstrukten, wie im Abschnitt "Repräsentative Ergebnisse" veranschaulicht. Diese Ergebnisse zeigen den unverwechselbaren Einfluss der verschiedenen hämodynamischen Belastungsregime (d.h. verschiede...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Offenlegungen
Die Autoren haben nichts preiszugeben.
Danksagungen
Diese Studie wird von ZonMw im Rahmen des LSH 2Treat-Programms (436001003) und der Dutch Kidney Foundation (14a2d507) finanziell unterstützt. N.A.K. würdigt die Unterstützung des Europäischen Forschungsrats (851960). Wir danken dem Gravitationsprogramm "Materials Driven Regeneration", das von der niederländischen Organisation für wissenschaftliche Forschung finanziert wird (024.003.013).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materialien
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| advanced Dulbecco’s modified EagleMedium (aDMEM) | Gibco | 12491-015 | cell culture medium for fibroblasts |
| Aqua Stabil | Julabo | 8940012 | prevent microorganism growth in bioreactor-hydraulic reservoir |
| Bovine fibrinogen | Sigma | F8630 | to prepare fibrinogen gel to seed the cells on the electrospun scaffold |
| Bovine thrombin | Sigma | T4648 | to prepare fibrinogen gel to seed the cells on the electrospun scaffold |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5804 | to spin down cells and conditioned medium |
| Clamp scissor - "kelly forceps" | Almedic | P-422 | clamp the silicone tubing and apply pre-stretch to the scaffold so the scaffold can be sutured into the engraved groove (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| CO2 cell culture incubators | Sanyo | MCO-170AIC-PE | for cell culturing |
| Compressed air reservoir | Festo | CRVZS-5 | smoothing air pressure fluctuations and create time delays for pressure build-up |
| Custom Matlab script to calculate the maximum stretches | Matlab | R2017. The Mathworks, Natick, MA | calculate the minimum and maximum outer diameter of the electrospun scaffold |
| Data acquisition board | National Instruments | BNC-2090 | data processing in between amplifier system and computer |
| Ethanol | VWR | VWRK4096-9005 | to keep sterile working conditions |
| Fetal bovine calf serum (FBS) | Greiner | 758087 | cell culture medium supplement; serum-supplement |
| Flow culture chamber compartments, consisting of a pressure conduit with engraved grooves and small holes to apply pressure on silicone tubing, a screw thread, nose cone, top compartment with flow inlet and bottom compartment flow outlet, adapter bushing | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | flow culture chamber compartments (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Glass Pasteur pipet | Assistant | HE40567002 | apply vacuum on electrospun scaffold (autoclave at step 1) |
| Glass tubes of the flow culture chamber | Custon made, Equipment & Prototype Center, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | part of the flow culture chamber (clean and store in 70% ethanol, at step 1 and 7) |
| GlutaMax | Gibco | 35050061 | cell culture medium amino acid supplement, minimizes ammonia build-up |
| High speed camera | MotionScope | M-5 | to monitor the stretch during culture; time-lapse photographs of the scaffolds are captured at a frequency of 30 Hz for 6 sec (i.e. 3 stretch cycles) |
| High speed camera lens - Micro-NIKKOR 55mm f/2.8 - lens | Nikon | JAA616AB | to monitor the stretch during culture; time-lapse photographs of the scaffolds are captured at a frequency of 30 Hz for 6 sec (i.e. 3 stretch cycles) |
| Hose clip | ibidi GmbH | 10821 | block medium flow (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Hydraulic reservoir with 8 screw threads for 8 flow culture chambers | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to apply pressure to the silicone mounted constructs (clean outside with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol, rinse reservoir with 70% ethanol followed by demi water, at step 1 and 7) |
| Ibidi pump system (8x) including ibidi pump, PumpControl software, fluidic unit, perfusion set (medium tubing), air pressure tubing, drying bottles with orange silica beads | ibidi GmbH | 10902 | set up used to control the flow in the flow culture chambers. Note 1: the ibidi pumps were modified by the manufacturer to enable 200 mbar capacity. Note 2: can be replaced by pump system of other manufacturer, as long as same flow regimes can be applied. |
| Knives (no.10 sterile blades, individual foil pack) and scalpel handle (stainless steel, individually wrapped) | Swann Morton | 0301; 0933 | to cut the silicone tubing in the correct size for the scaffold and to cut the suture material |
| LabVIEW Software | National Instruments | version 2018 | to control the stretch applied to the scaffolds |
| Laminar flow biosafety cabinet with UV light | Labconco | 302310001 | to ensure sterile working conditions. The UV is used to decontaminate everything that cannot be autoclaved, or touched after autoclaving |
| Large and small petri dishes | Greiner | 664-160 | for sterile working conditions |
| L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (vitamin C) | Sigma | A8960 | cell culture medium supplement, important for collagen production |
| LED light cold source KL2500 | Zeiss | Schott AG | to aid in visualization for the time lapse of the scaffolds during monitoring of the stretch |
| Luer (female and male) locks and connectors, white luer caps | ibidi GmbH | various, see (https://ibidi.com/26-flow-accessories) | to close or connect parts of the bioreactor and the ibidi pump (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Measuring amplifier (PICAS) | PEEKEL instruments B.V. | n.a. | to amplify the signal from the pressure sensor and feedback to LabView |
| Medium reservoir (large syringes 60 mL) and reservoir holders | ibidi GmbH | 10974 | medium reservoir (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Medium tubing with 4.25 mm outer diameter and 1 mm inner diameter | Rubber BV | 1805 | to allow for a larger flow rate, the ibidi medium tubing with larger diameter is used. Note: the part of medium tubing guided through the fluidic unit valves are the same as the default ibidi medium tubing |
| Motion Studio Software | Idtvision | 2.15.00 | to make the high speed time lapse images for stretch monitoring |
| Needle (19G) | BD Microlance | 301700 | together with thin flexible tubing used to fill the hydraulic reservoir with ultrapure water without adding air bubbles |
| Needle driver | Adson | 2429218 | to handle the needle of the nylon suture through the silicone tube (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Paper tissues | Kleenex | 38044001 | for cleaning of the equipment with 70% ethanol |
| Parafilm | Sigma | P7793-1EA | quick fix if leakage occurs |
| Penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) | Lonza | DE17-602E | cell culture medium supplement; prevent bacterial contamination |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) | Sigma | P4417-100TAB | for storage and washing steps (autoclave at step 1) |
| Plastic containers (60 mL) with red screw caps | Greiner | 206202 | to prepare the fibrinogen solution |
| Pneumatic cylinder | Festo | AEVC-20-10-I-P | to actuate the Teflon bellow (clean with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol at step 1 and 7) |
| Polycaprolactone bisurea (PCL-BU) tubular scaffolds (3 mm inner diameter, 200 µm wall thickness, 20 mm length) | SyMO-Chem, Eindhoven, The Netherlands | n.a. | produced using electrospinning from 15% (w/w) chloroform (Sigma; 372978) polymer solutions. See Van Haaften et al Tissue Engineering Part C (2018) for more details |
| Pressure conduit without holes (for static control) | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to mount electrospun tubes on silicon tubing (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Pressure sensor and transducer | BD | TC-XX and P 10 EZ | the air pressure going to the pneumatic actuated pump is raised until it reaches the set pressure |
| Proportional air pressure control valve and pressure sensor | Festo | MPPES-3-1/8-2-010, 159596 | provides compressed air to the pneumatic actuated pump |
| Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (RPMI-1640) | Gibco | A1049101 | cell culture medium for monocyte/macrophage |
| Safe lock Eppendorf tubes (1.5 mL) | Eppendorf | 30120086 | multiple applications (autoclave at step 1) |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate solution 20% | Sigma | 5030 | Used to clean materials, at a concentration of 0.1%. |
| Silicone O-rings | Technirub | 1250S | to prevent leakage (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Silicone tubing (2.8 mm outer diameter, 400 um wall thickness) | Rubber BV | 1805 | to mount the electrospun tubes on the pressure conduits (autoclave at step 1) |
| Sterile tube (15 mL) | Falcon | 352095 | multiple applications |
| Suture, 5-0 prolene with pre-attached taper point needle | Ethicon, Johnson&Johnson | EH7404H | Prolene suture wire 5-0 (75cm length, TF taper point needle, 1/2 circle, 13 mm needle length) |
| Syringe (24 mL) | B. Braun Melsungen AG | 2057932 | to add the ultrapure water or medium to the hydraulic reservoir or flow culture chamber |
| Syringe filter (0.2 µm) | Satorius | 17597-K | to filter the fibrinogen solution |
| T150 cell culture flask with filter cap | Nunc | 178983 | to degas culture medium |
| T75 Cell culture flask with filter cap | Nunc | 156499 | to culture static control samples |
| Teflon bellow | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to load the hydraulic reservoir (clean outside with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol at step 1 and 7) |
| Tray (stainless steel) | PolarWare | 15-248 | for easy transport of the fluidic culture chambers and the bioreactor from incubator to laminar flow cabinet and back (clean with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol before and after use) |
| Tweezers | Wironit | 4910 | sterile handling of individual parts (autoclave at step 1 and 7) |
| Ultrapure water | Stakpure | Omniapure UV 18200002 | to correct for medium evaporation, mixed with aqua stabil mixed and used as hydraulic fluid. (autoclave ultrapure water at step 1) |
| UV light | Philips | TUV 30W/G30 T8 | for decontamination of grafts and bioreactor parts before seeding |
Referenzen
- Chlupác, J., Filová, E., Bacáková, L. Blood vessel replacement: 50 years of development and tissue engineering paradigms in vascular surgery. Physiological Research. 58, Suppl 2 119-139 (2009).
- Huygens, S. A., et al. Bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement in elderly patients: Meta-analysis and microsimulation. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 157 (6), 2189-2197 (2019).
- Huygens, S. A., et al. Contemporary outcomes after surgical aortic valve replacement with bioprostheses and allografts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 50 (4), 605-616 (2016).
- Loh, S. A., et al. Mid- and long-term results of the treatment of infrainguinal arterial occlusive disease with precuffed expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts compared with vein grafts. Annals of Vascular Surgery. 27 (2), 208-217 (2013).
- Tara, S., et al. Vessel bioengineering. Circulation Journal. 78 (1), 12-19 (2014).
- Huang, A. H., Niklason, L. E. Engineering of arteries in vitro. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 71 (11), 2103-2118 (2014).
- Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M., Baaijens, F. P. T. Can we grow valves inside the heart? Perspective on material-based in situ heart valve tissue engineering. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. 5, 54(2018).
- Fioretta, E. S., et al. Next-generation tissue-engineered heart valves with repair, remodelling and regeneration capacity. Nature Reviews Cardiology. , (2020).
- Kirkton, R. D., et al. Bioengineered human acellular vessels recellularize and evolve into living blood vessels after human implantation. Science Translational Medicine. 11 (485), (2019).
- Gutowski, P., et al. Arterial reconstruction with human bioengineered acellular blood vessels in patients with peripheral arterial disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery. , (2020).
- Syedain, Z., et al. Tissue engineering of acellular vascular grafts capable of somatic growth in young lambs. Nature Communications. 7 (12951), 12951(2016).
- Sugiura, T., et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts in children with congenital heart disease: intermediate term follow-up. Seminars in Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 30 (2), 175-179 (2018).
- Kluin, J., et al. In situ heart valve tissue engineering using a bioresorbable elastomeric implant - material design to 12 months follow-up in sheep. Biomaterials. 125, 101-117 (2017).
- Fioretta, E. S., et al. Differential leaflet remodeling of bone marrow cell pre-seeded versus nonseeded bioresorbable transcatheter pulmonary valve replacements. JACC. Basic to Translational Science. 5 (1), 15-31 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., Bouten, C. V. C., Kurniawan, N. A. Vascular mechanobiology: towards control of. Cells. , 1-24 (2017).
- De Jonge, N., et al. Matrix production and organization by endothelial colony forming cells in mechanically strained engineered tissue constructs. PLoS ONE. 8 (9), 73161(2013).
- Schmidt, J. B., Chen, K., Tranquillo, R. T. Effects of intermittent and incremental cyclic stretch on ERK signaling and collagen production in engineered tissue. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering. 9 (1), 55-64 (2016).
- Luo, J., et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts with advanced mechanical strength from human iPSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 26 (2), 251-261 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., et al. Decoupling the effect of shear stress and stretch on tissue growth and remodeling in a vascular graft. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 24 (7), 418-429 (2018).
- Gupta, V., Tseng, H., Lawrence, B. D., Jane Grande-Allen, K. Effect of cyclic mechanical strain on glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan synthesis by heart valve cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 5 (2), 531-540 (2009).
- Lin, S., Mequanint, K. Bioreactor-induced mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation and elastic fiber assembly in engineered vascular tissues. Acta Biomaterialia. 59, 200-209 (2017).
- Venkataraman, L., Bashur, C. A., Ramamurthi, A. Impact of cyclic stretch on induced elastogenesis within collagenous conduits. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 20 (9-10), 1403-1415 (2014).
- Huang, A. H., et al. Biaxial stretch improves elastic fiber maturation, collagen arrangement, and mechanical properties in engineered arteries. Tissue Engineering Part C Methods. 22 (6), 524-533 (2016).
- Hinderer, S., et al. In vitro elastogenesis: instructing human vascular smooth muscle cells to generate an elastic fiber-containing extracellular matrix scaffold. Biomedical Materials. 10 (3), 034102(2015).
- Eoh, J. H., et al. Enhanced elastin synthesis and maturation in human vascular smooth muscle tissue derived from induced-pluripotent stem cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 52, 49-59 (2017).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Bouten, C. V. C. Tissue engineering meets immunoengineering: Prospective on personalized in situ tissue engineering strategies. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering. 6, 17-26 (2018).
- Wissing, T. B., Bonito, V., Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M. Biomaterial-driven in situ cardiovascular tissue engineering-a multi-disciplinary perspective. npj Regenerative Medicine. 2 (1), 18(2017).
- Hibino, N., et al. A critical role for macrophages in neovessel formation and the development of stenosis in tissue-engineered vascular grafts. The FASEB Journal. 25 (12), 4253-4263 (2011).
- Godwin, J. W., Pinto, A. R., Rosenthal, N. A. Macrophages are required for adult salamander limb regeneration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (23), 9415-9420 (2013).
- Godwin, J. W., Debuque, R., Salimova, E., Rosenthal, N. A. Heart regeneration in the salamander relies on macrophage-mediated control of fibroblast activation and the extracellular landscape. npj Regenerative Medicine. 2 (1), 22(2017).
- McBane, J. E., Cai, K., Labow, R. S., Santerre, J. P. Co-culturing monocytes with smooth muscle cells improves cell distribution within a degradable polyurethane scaffold and reduces inflammatory cytokines. Acta Biomaterialia. 8 (2), 488-501 (2012).
- Battiston, K. G., Ouyang, B., Labow, R. S., Simmons, C. A., Santerre, J. P. Monocyte/macrophage cytokine activity regulates vascular smooth muscle cell function within a degradable polyurethane scaffold. Acta Biomaterialia. 10 (3), 1146-1155 (2014).
- Ploeger, D. T., et al. Cell plasticity in wound healing: paracrine factors of M1/ M2 polarized macrophages influence the phenotypical state of dermal fibroblasts. Cell Communication and Signaling. 11 (1), 29(2013).
- McBane, J. E., Santerre, J. P., Labow, R. S. The interaction between hydrolytic and oxidative pathways in macrophage-mediated polyurethane degradation. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A. 82 (4), 984-994 (2007).
- Wissing, T. B., et al. Macrophage-driven biomaterial degradation depends on scaffold microarchitecture. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 7, 87(2019).
- Wolf, M. T., Vodovotz, Y., Tottey, S., Brown, B. N., Badylak, S. F. Predicting in vivo responses to biomaterials via combined in vitro and in silico analysis. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 21 (2), 148-159 (2015).
- Grotenhuis, N., Bayon, Y., Lange, J. F., Van Osch, G. J. V. M., Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y. M. A culture model to analyze the acute biomaterial-dependent reaction of human primary macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 433 (1), 115-120 (2013).
- Jannasch, M., et al. A comparative multi-parametric in vitro model identifies the power of test conditions to predict the fibrotic tendency of a biomaterial. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 1689(2017).
- Wang, Z., et al. The effect of thick fibers and large pores of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) vascular grafts on macrophage polarization and arterial regeneration. Biomaterials. 35 (22), 5700-5710 (2014).
- McWhorter, F. Y., Davis, C. T., Liu, W. F. Physical and mechanical regulation of macrophage phenotype and function. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 72 (7), 1303-1316 (2014).
- Ballotta, V., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Strain-dependent modulation of macrophage polarization within scaffolds. Biomaterials. 35 (18), 4919-4928 (2014).
- Dziki, J. L., et al. The effect of mechanical loading upon extracellular matrix bioscaffold-mediated skeletal muscle remodeling. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 24 (1-2), 34-46 (2018).
- Wissing, T. B., et al. Hemodynamic loads distinctively impact the secretory profile of biomaterial-activated macrophages - implications for in situ vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials Science. 8 (1), 132-147 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., Wissing, T. B., Kurniawan, N. A., Smits, A. I. P. M., Bouten, C. V. C. Human in vitro model mimicking material-driven vascular regeneration reveals how cyclic stretch and shear stress differentially modulate inflammation and matrix deposition. Advanced Biosystems. 4 (6), 1900249(2020).
- Ballotta, V., Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Synergistic protein secretion by mesenchymal stromal cells seeded in 3D scaffolds and circulating leukocytes in physiological flow. Biomaterials. 35 (33), 9100-9113 (2014).
- Bonito, V., de Kort, B. J., Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M. Cyclic strain affects macrophage cytokine secretion and extracellular matrix turnover in electrospun scaffolds. Tissue Engineering Part A. 25 (17-18), 1310-1325 (2019).
- Battiston, K. G., Labow, R. S., Simmons, C. A., Santerre, J. P. Immunomodulatory polymeric scaffold enhances extracellular matrix production in cell co-cultures under dynamic mechanical stimulation. Acta Biomaterialia. 24, 74-86 (2015).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. A mesofluidics-based test platform for systematic development of scaffolds for in situ cardiovascular tissue engineering. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 18 (6), 475-485 (2012).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Ballotta, V., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. T. Shear flow affects selective monocyte recruitment into MCP-1-loaded scaffolds. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 18 (11), 2176-2188 (2014).
- Ballotta, V., Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Synergistic protein secretion by mesenchymal stromal cells seeded in 3D scaffolds and circulating leukocytes in physiological flow. Biomaterials. 35 (33), 9100-9113 (2014).
- Fahy, N., Menzel, U., Alini, M., Stoddart, M. J. Shear and dynamic compression modulates the inflammatory phenotype of human monocytes in vitro. Frontiers in Immunology. 10, 383(2019).
- Pennings, I., et al. Layer-specific cell differentiation in bi-layered vascular grafts under flow perfusion. Biofabrication. 12 (1), 015009(2019).
- Wang, J., et al. Ex vivo blood vessel bioreactor for analysis of the biodegradation of magnesium stent models with and without vessel wall integration. Acta Biomater. 50, 546-555 (2017).
- Huang, A. H., et al. Design and use of a novel bioreactor for regeneration of biaxially stretched tissue-engineered vessels. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 21 (8), 841-851 (2015).
- Huang, A. H., Niklason, L. E. Engineering biological-based vascular grafts using a pulsatile bioreactor. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (52), e2646(2011).
- Bono, N., et al. A Dual-mode bioreactor system for tissue engineered vascular models. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 45 (6), 1496-1510 (2017).
- Wolf, F., et al. VascuTrainer: a mobile and disposable bioreactor system for the conditioning of tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 46 (4), 616-626 (2018).
- Ramaswamy, S., et al. A novel bioreactor for mechanobiological studies of engineered heart valve tissue formation under pulmonary arterial physiological flow conditions. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 136 (12), 121009(2014).
- Piola, M., et al. A compact and automated ex vivo vessel culture system for the pulsatile pressure conditioning of human saphenous veins. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 10 (3), 204-215 (2016).
- Vanerio, N., Stijnen, M., de Mol, B. A. J. M., Kock, L. M. An innovative ex vivo vascular bioreactor as comprehensive tool to study the behavior of native blood vessels under physiologically relevant conditions. Journal of Engineering and Science in Medical Diagnostics and Therapy. 2 (4), (2019).
- Kural, M. H., Dai, G., Niklason, L. E., Gui, L. An ex vivo vessel injury model to study remodeling. Cell Transplantation. 27 (9), 1375-1389 (2018).
- Sinha, R., et al. A medium throughput device to study the effects of combinations of surface strains and fluid-flow shear stresses on cells. Lab on a Chip. 15 (2), 429-439 (2015).
- Beca, B. M., Sun, Y., Wong, E., Moraes, C., Simmons, C. A. Dynamic bioreactors with integrated microfabricated devices for mechanobiological screening. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 25 (10), 581-592 (2019).
- Liu, H., Usprech, J., Sun, Y., Simmons, C. A. A microfabricated platform with hydrogel arrays for 3D mechanical stimulation of cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 34, 113-124 (2016).
- Szafron, J. M., Ramachandra, A. B., Breuer, C. K., Marsden, A. L., Humphrey, J. D. Optimization of tissue-engineered vascular graft design using computational modeling. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 25 (10), 561-570 (2019).
- Emmert, M. Y., et al. Computational modeling guides tissue-engineered heart valve design for long-term in vivo performance in a translational sheep model. Science Translational Medicine. 10 (440), (2018).
- Mol, A., et al. Fibrin as a cell carrier in cardiovascular tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 26 (16), 3113-3121 (2005).
- van Kelle, M. A. J., et al. A Bioreactor to identify the driving mechanical stimuli of tissue growth and remodeling. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 23 (6), (2017).
- van den Broek, C. N., et al. Medium with blood-analog mechanical properties for cardiovascular tissue culturing. Biorheology. 45 (6), 651-661 (2008).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Nachdrucke und Genehmigungen
Genehmigung beantragen, um den Text oder die Abbildungen dieses JoVE-Artikels zu verwenden
Genehmigung beantragenThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten