A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
A Multi-Cue Bioreactor to Evaluate the Inflammatory and Regenerative Capacity of Biomaterials under Flow and Stretch
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
The goal of this protocol is to execute a dynamic co-culture of human macrophages and myofibroblasts in tubular electrospun scaffolds to investigate material-driven tissue regeneration, using a bioreactor which enables the decoupling of shear stress and cyclic stretch.
Abstract
The use of resorbable biomaterials to induce regeneration directly in the body is an attractive strategy from a translational perspective. Such materials induce an inflammatory response upon implantation, which is the driver of subsequent resorption of the material and the regeneration of new tissue. This strategy, also known as in situ tissue engineering, is pursued to obtain cardiovascular replacements such as tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Both the inflammatory and the regenerative processes are determined by the local biomechanical cues on the scaffold (i.e., stretch and shear stress). Here, we describe in detail the use of a custom-developed bioreactor that uniquely enables the decoupling of stretch and shear stress on a tubular scaffold. This allows for the systematic and standardized evaluation of the inflammatory and regenerative capacity of tubular scaffolds under the influence of well-controlled mechanical loads, which we demonstrate on the basis of a dynamic co-culture experiment using human macrophages and myofibroblasts. The key practical steps in this approach—the construction and setting up of the bioreactor, preparation of the scaffolds and cell seeding, application and maintenance of stretch and shear flow, and sample harvesting for analysis—are discussed in detail.
Introduction
Cardiovascular tissue engineering (TE) is being pursued as an alternative treatment option to the currently used permanent cardiovascular prostheses (e.g., vascular grafts, heart valve replacements), which are suboptimal for large cohorts of patients1,2,3,4. Much sought-after applications include tissue-engineered vascular grafts (TEVGs)5,6 and heart valves (TEHVs)7,8. Most often, cardiovascular TE methodologies make use of resorbable biomaterials (either natural or synthetic) that serve as an instructive scaffold for the new tissue to be formed. The formation of new tissue can either be engineered completely in vitro, by seeding the scaffold with cells and culturing in a bioreactor prior to implantation (in vitro TE)9,10,11, or directly in situ, in which the synthetic scaffold is implanted without pre-culturing in order to induce the formation of new tissue directly in the body (in situ TE)12,13,14. For both in vitro and in situ cardiovascular TE approaches, successful functional regeneration is dominantly dependent on both the host immune response to the implanted construct and appropriate biomechanical loading.
The importance of biomechanical loading for cardiovascular TE is well-acknowledged15. In the case of cardiovascular implants, the cells that populate the scaffold are exposed to cyclic stretch and shear stresses that arise as a result of the hemodynamic environment. Numerous studies have reported the stimulatory effect of (cyclic) stretch on the formation of matrix components, such as collagen16,17,18,19, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)20, and elastin21,22, by various cell types. For example, Huang et al. demonstrated that biaxial stretch elevated the deposition and organization of collagen and elastin in in vitro TEVGs by using a vascular bioreactor23. While the emphasis typically lies on stretch as the dominant load, these studies often make use of flow-driven bioreactors in which the sample is also exposed to shear flow. Although relatively little is known about the isolated influence of shear stresses on tissue formation and inflammation in 3D, some data are available. For example, Hinderer et al. and Eoh et al. demonstrated that shear flow, in addition to a 3D scaffold microstructure, was important for the formation of mature elastin by human vascular smooth muscle cells in an in vitro model system24,25. Altogether, these findings illustrate the relevance of both cyclic stretch and shear stress for cardiovascular TE.
Another important determinant for the success or failure of TE implants is the host’s immune response to the implanted graft26. This is particularly important for material-driven in situ TE strategies, which actually rely on the acute inflammatory response to the scaffold to kickstart the subsequent processes of cellular influx and endogenous tissue formation and remodeling27. The macrophage is a critical initiator of functional tissue regeneration, which has been shown by multiple studies28,29,30. Analogous to wound healing, the regeneration of tissue is governed by paracrine signaling between macrophages and tissue-producing cells such as fibroblasts and myofibroblasts31,32,33. In addition to coordinating new tissue deposition, macrophages are involved in the active resorption of foreign scaffold material34,35. As such, the in vitro macrophage response to a biomaterial has been identified as a predictive parameter for the in vivo success of implants36,37,38.
The macrophage response to an implanted scaffold is dependent on scaffold design features such as material composition and microstructure35,39,40. In addition to scaffold properties, the macrophage response to a scaffold and their crosstalk with myofibroblasts is also impacted by hemodynamic loads. For example, cyclic stretch was shown to be an important modulator of macrophage phenotype41,42,43,44 and the secretion of cytokines43,44,45,46 in 3D electrospun scaffolds. Using a co-culture system of macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells, Battiston et al. demonstrated that the presence of macrophages led to increased levels of elastin and GAGs and that moderate levels of cyclic stretch (1.07–1.10) stimulated the deposition of collagen I and elastin47. In previous works, we have demonstrated that shear stress is an important determinant for monocyte recruitment into 3D electrospun scaffolds48,49, and that both shear stress and cyclic stretch impact the paracrine signaling between human monocytes and mesenchymal stromal cells50. Fahy et al. demonstrated that shear flow increased the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes51.
Taken together, the above evidence shows that an adequate understanding of and control over hemodynamic loads is crucial for cardiovascular TE, and that it is important to consider the inflammatory response to achieve this. Numerous bioreactors have been described previously for the in vitro52,53,54,55,56,57,58 or ex vivo59,60,61 culture of cardiovascular tissues. However, all these systems are designed to mimic the physiological hemodynamic loading conditions as much as possible. While this is highly valuable for the purpose of creating cardiovascular tissues in vitro or maintaining ex vivo cultures, such systems do not allow for systematic studies into the individual effects of individual cues. This is because the application of both cyclic stretch and shear stress in these bioreactors is driven by the same pressurized flow, which intrinsically links them. While microsystems that allow for accurate multi-cue mechanical manipulation have been described for 2D substrates62 or 3D hydrogel setups63,64, such setups do not allow for the incorporation of elastomeric 3D biomaterial scaffolds.
Here, we present the application of a tubular bioreactor system that uniquely enables the decoupling of shear stress and cyclic stretch and helps to mechanistically investigate their individual and combined effects. This system allows for testing of a broad variety of tissue engineered vascular grafts (e.g., synthetic or natural origin, different micro-architecture, various porosities). To effectively decouple the application of shear stress and stretch, the key concepts that the bioreactor uses are (1) separation of the control of shear stress and stretch using distinct pump systems and (2) stimulation of the scaffolds in an ‘inside-out’ manner with computationally driven dimensions. Flow is applied on the outside surface of the tubular scaffold through the use of a flow pump, whereas circumferential stretch of the scaffold is induced by expanding a silicone tube on which the scaffold is mounted through the use of a separate strain pump. The dimensions of the silicone tube and the glass tube that contains the construct are carefully chosen and validated using computational fluid dynamics simulations, to ensure that the shear stress on the scaffold (due to flow) and the circumferential stretch (due to tube expansion) do not significantly affect each other. This inside-out design has several practical rationales. If stretch is applied by the luminal fluid pressure (similar to physiological loading), it inherently requires the sample design to be leak-free. In addition, the pressure required to stretch the sample would be completely determined by the sample stiffness, which may vary between samples and within a sample over time, making it difficult to control the stretch. This bioreactor mounts the tissue engineered graft around a silicone tube and allows for wall shear stress (WSS) application on the outer wall of the graft and pressurizes the graft from the inside. This way, equal loading conditions between samples and within samples over time can be ensured, and moreover, the samples are allowed to be leaky, as is common for porous vascular scaffolds19. This inside-out bioreactor is specifically intended for systematic studies on the effects of shear and/or stretch, rather than the engineering of a native-like blood vessel in vitro, for which traditional vascular bioreactor setups are more suitable. See Figure 1A–B for the bioreactor design drawings, and its corresponding Table 1 for a functional description and rationale behind the main components of the bioreactor.
The use of the bioreactor is demonstrated on the basis of a series of recent studies by our group in which we investigated the individual and combined influences of shear stress and cyclic stretch on inflammation and tissue formation in resorbable electrospun scaffolds for in situ cardiovascular tissue19,43,44. To that end, we used human macrophages and myofibroblasts either in mono- or in co-culture to simulate the various phases of the in situ regenerative cascade. We have demonstrated that cytokine secretion by human macrophages is distinctly impacted by both cyclic stretch and shear stress, affecting the matrix deposition and organization by human myofibroblasts in these scaffolds, both via paracrine signaling and direct contact19,43,44. Notably, these studies revealed that in the case of combined application of shear stress and stretch, the effects on tissue formation and inflammation are either dominated by one of the two loads, or there are synergistic effects of both loads. These findings illustrate the relevance of decoupling both loads to gain a better understanding of the contribution of the mechanical environment on TE processes. This understanding can be applied to systematically optimize scaffold design parameters in relevant hemodynamic loading regimes. In addition, the mechanistic data from such well-controlled environments may serve as input for numerical models that are being developed to predict the course of in situ tissue remodeling, as recently reported for TEVGs65 or TEHVs66, to further improve predictive capacity.
Protocol
In the studies described in this protocol, primary human macrophages isolated from peripheral blood buffy coats and human myofibroblasts isolated from the saphenous vein after coronary by-pass surgery have been used44. The buffy coats were obtained from healthy, anonymized volunteers who provided written informed consent, which was approved by the Sanquin Research Institutional Medical Ethical Committee. The use of human vena saphena cells (HVSCs) was in accordance to the “Code Proper Secondary Use of Human Tissue” developed by the Federation of Medical Societies (FMWV) in the Netherlands.
1. General Preparations and Required Actions Before Setting Up the Bioreactor
NOTE: For details on the respective isolation and culturing protocols, please refer to earlier work19,43,44. All calculations in the protocol are given as examples for a co-culture experiment with monocytes and myofibroblasts, seeded in 8 hemodynamically loaded scaffolds and 2 static controls (n=10).
- Start cell isolation and cell culture. The seeding densities for the co-cultured samples of monocytes and myofibroblasts (with a seeding ratio of 2:1) are 30 × 106 monocytes/cm3 and 15 × 106 myofibroblasts/cm3, respectively.
NOTE: The electrospun material has a high porosity (>90%). To estimate the required number of cells per graft, the volume of the scaffold is calculated with the formula for volume of a hollow cylinder: π*(thickness)2*length ≈ 0.04 cm3. The total amount of cells per graft is 1.2 × 106 monocytes and 0.6 × 106 myofibroblasts. For 10 samples, at least 12 × 106 monocytes and 6 × 106 myofibroblasts are required; start with up to ~10–15% more cells to account for possible pipetting errors. - Degas the cell culture medium that will be used for experiments involving the bioreactor.
- Prepare the medium for co-cultures, which consists of RPMI-1640:aDMEM (1:1), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 0.5% L-glutamine.
- Place the medium overnight (O/N) in an incubator in a cell culture flask with filter cap to degas.
- Replace the filter cap with an air-tight cap and store at 4 °C.
- Just before use, add 0.25 mg/mL L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (vitamin C) to the medium.
NOTE: For calculations, the amount of medium required per flow culture chamber is 50 mL. Refresh the medium three times per week; 25 mL old medium is replaced by 25 mL fresh medium. For 10 samples; after seeding, a total of 500 mL fresh medium is required, and for each subsequent medium change, a total of 250 mL fresh medium is used. Always prepare medium fresh, especially, vitamin C should be added just before changing the medium.
- Prepare isotropic electrospun scaffolds (3 mm luminal diameter, 200 µm wall thickness) as described by Van Haaften et al.19 (Figure 1G–I). In brief, tubular polycaprolactone bisurea (PCL-BU) scaffolds are produced by electrospinning from 15% (w/w) chloroform-polymer solutions. The polymer solutions are electrospun at room temperature and 30% relative humidity, at a flow rate of 40 µL/min, 16 cm distance from the rotating cylindrical target (Ø 3 mm, 500 rpm), and an applied voltage of 16 kV on the electrospinning nozzle and -1 kV on the target.
NOTE: Although PCL-BU grafts were used for these experiments, a broad variety of elastomeric tissue engineered grafts can be mounted in this bioreactor (e.g., of different synthetic or natural origin, different microarchitecture, different porosities)- Remove the electrospun scaffolds from the mandrel.
- Make a small hole in the cap of a 15 mL tube to ‘hold’ the mandrel in the center and prevent it from touching the wall of the tube.
- Place the mandrel with the electrospun scaffold in the falcon tube and fill it with deionized water.
- Freeze the tubes O/N at -20 °C.
- Place the tubes at room temperature (RT) and pull out the mandrels after a few minutes, leaving the electrospun grafts in the ice.
- Let the ice thaw completely, remove the electrospun tube from the thawed water, and ‘hang’ to dry vertically for several hours. Make sure the scaffolds do not ‘collapse’ under their own weight.
- Dry scaffolds under vacuum O/N.
- Image a small sample of the electrospun grafts using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to assess their microstructure (e.g., fiber morphology, fiber diameter). The grafts in the example studies have an isotropic fiber orientation and a fiber diameter of 5 µm (Figure 1H–I).
- Remove the electrospun scaffolds from the mandrel.
- One day before starting the experiment, place the hydraulic reservoir filled with deionized water in the incubator. Close all eight connections for flow culture chambers with white Luer caps. Connect to the compressed air system and insert pressure sensor. Run the strain pump (see step 5.6) O/N to allow for small expansion of the Teflon bellow.
NOTE: Make sure all necessary materials and equipment are cleaned and/or autoclaved (see Table of Materials, Comments/Description column for which materials are allowed to be autoclaved), according to the manufacturer’s protocol or as described in steps 7.3–7.6. - Ensure sterile working conditions for the remainder of the protocol.
- Perform steps 2–5.3 (setting up the system), step 6.3 (medium change), and steps 7.1–7.2 (harvest of vascular constructs) in a sterile laminar flow cabinet.
- Place materials that are not directly needed for the subsequent steps in closed Petri dishes to keep everything as clean as possible.
- Clean or dry material surfaces regularly by soaking a paper tissue with 70% ethanol, and wipe the surfaces of the bioreactor components and the laminar flow cabinet.
2. Setting Up the Bioreactor
NOTE: Perform step 2 in a laminar flow cabinet.
- Cut the electrospun scaffolds into tubes of approximately 25 mm in length, and document them before use (e.g., photograph for the length, weigh with balance for the initial mass).
- Decontaminate the electrospun scaffolds.
- Place the electrospun scaffolds tilted in a well plate or Petri dish, with one opening facing the ultraviolet (UV) light source, to enable UV light (253.7 nm) to illuminate the inside of the scaffolds.
- Expose the electrospun scaffolds to UV light for 5 min.
- Turn all scaffolds and repeat the UV illumination for the other opening.
NOTE: After this step, only touch the electrospun scaffold when needed. Always use clean tweezers or clean gloves. - Take the glass tubes of the flow culture chambers that are stored in 70%, wash the glass tubes in ultrapure water, dry, and place in a large, closed Petri dish.
NOTE: The following steps, especially steps 2.3–2.5, are ideally performed by two experimenters.
- Mount the electrospun scaffolds onto the silicone tubing.
- Attach the 5-0 prolene suture to one end of the silicone tubing by taking the suture through one side of the tube and out of the other, leaving two opposite taut sutures spanning the cross section of the tubing. Make a small knot on both sides of the tube while compressing the tube at the locus of the knots and leave approximately 10 cm of wire on both knots. Make a third knot at the end of the two 10 cm left-over wires.
- Cut off the suture needle and all free threads that might stick out and damage the inside of the electrospun scaffold. Cut away the edges of the silicone tubing into a triangular shape to aid in pulling the silicone tubing through the electrospun scaffold.
- Dip the electrospun scaffold in 30% ethanol (this serves as extra decontamination step and aids in sliding the electrospun scaffold over the silicon tubing) and place the electrospun scaffold over the free 10 cm wire. Experimenter A stretches the silicone tubing by pulling gently on both the silicone tubing and the knot of the 10 cm suture wire, while experimenter B gently slides the electrospun scaffold over the silicone tubing using tweezers with a smooth inner tip to prevent damaging of the scaffolds.
- Slowly release the stretch on the silicone tubing, while simultaneously smoothening the electrospun scaffold with tweezers. Dip the electrospun scaffold on the silicone tubing in ultrapure water two times.
NOTE: It is possible that some wrinkling of the electrospun scaffold occurs. This wrinkling will disappear during the applied pre-stretch right before fixing the scaffolds to the pressure conduits at step 2.5.3. - Repeat steps 2.3.2 and 2.3.3 for the other electrospun scaffolds. Depending on the length of the silicone tubing, multiple electrospun scaffolds can be mounted on the same silicone tubing.
- When all electrospun scaffolds are mounted on the silicone tubing, cut the silicone tubing around the scaffolds, all to the same length (5.5 cm); at one side, close to the end of the electrospun scaffold, at the other side, leaving ~2–3 cm of free silicone tubing.
- Attach the 5-0 prolene suture to one end of the silicone tubing by taking the suture through one side of the tube and out of the other, leaving two opposite taut sutures spanning the cross section of the tubing. Make a small knot on both sides of the tube while compressing the tube at the locus of the knots and leave approximately 10 cm of wire on both knots. Make a third knot at the end of the two 10 cm left-over wires.
- Construct the bottom compartment of the flow culture chamber (Figure 1A–B).
- Take the upper part of the bottom compartment containing the flow outlet, and close the flow outlet with a male Luer plug.
- Push the pressure conduit with holes through the bottom compartment, and place a silicone O-ring around the lower end of the pressure conduit to prevent leakage. Screw the lower part of the bottom compartment to the upper part of the bottom compartment to secure the pressure conduit. Make sure that the lower engraved groove of the pressure conduit is approximately 3–5 mm above the edge of the adapter bushing of the bottom compartment; this will later ‘hold’ the tight knot of the suture wire, fixing the electrospun scaffold over the silicone tubing.
NOTE: If the pressure conduit can be easily maneuvered up and down, it indicates that the bottom compartment is not well secured. Repeat step 2.4.2 to prevent leakage in later stages (Figure 2D).
- Secure the silicone tubing with the electrospun scaffold to the pressure conduit.
- Pull the silicone tube with the electrospun scaffold over the pressure conduit.
- Make a knot with the suture wire at the lower end of the electrospun scaffold at the location of the engraved groove on the pressure conduit. Make a second knot at the opposite side to tightly secure the silicone tubing with the electrospun graft.
CAUTION: This is a critical step. Make sure that the knot exactly ‘falls’ into the engraved groove of the pressure conduit to prevent leakage of the water from the hydraulic reservoir to the flow culture chambers. If not sure, try to tighten the suture wire at several positions, above or below the expected location of the groove, to ensure that the final knots are exactly at the engraved groove (Figure 2A). - Place the scissor clamp at the upper end of the silicone tube, and stretch the silicone tubing upwards (this will directly test the first knot, if it is possible to move the silicone tubing with the electrospun scaffold over the pressure conduit, it was not tightened well enough). With the pulling force, the silicone tubing is pre-stretched. To ensure that the silicone tubing is consistent among the different samples, attach a ruler to the scissor clamp. Pull the scissor clamp upwards until the lower end of the ruler reaches the height of the lower end of the scaffold.
NOTE: It is important to keep the pre-stretch in each sample roughly the same (~5%) for two reasons: (1) if silicone tubing is pre-stretched, it will result in more homogeneous expansion along the length of the sample when pressurized; (2) the pre-stretch will impact the mechanical properties of the silicone, therefore it should be the same across all samples to ensure equal stretch conditions between the samples. - Remove wrinkles in the electrospun scaffold by gently pulling on the electrospun scaffold. Again, make two knots at both sides with a suture wire on the upper end of the scaffold at the location of the upper engraved groove on the pressure conduit.
- Release the scissor clamp, and cut away the excess of silicone tubing with a knife, leaving 20–30% of the screw thread covered with silicone tubing, to prevent leakage when the nose cone is mounted on the screw thread.
NOTE: Repeat steps 2.4 and 2.5 for all dynamic samples. - For the static control samples, secure the electrospun scaffold mounted on the silicone tubing on pressure conduits without holes. These conduits can be kept separately in a 15 mL tube until seeding (step 4) and do not need to be mounted in the flow culture chamber compartments.
- Decontaminate the partly constructed flow culture chambers with electrospun scaffold by exposing it to UV light for 10 min. Turn the flow culture chambers with electrospun scaffolds to the other side, and repeat UV light exposure for 10 min.
- Screw the nose cones on the screw thread of the pressure conduits with holes for the dynamic samples.
- Make sure the top end of the silicone tubing fits into the nose cone to prevent leakage in later stages. If there is too much silicone tubing, cut the excess of tubing away with a knife.
- Place the partly constructed flow culture chambers in a large Petri dish, and point the nose cone towards the UV light source. Apply UV illumination for 5 min.
- Complete construction of the flow culture chamber with the glass tube and top compartment of the flow culture chamber (Figure 1A–B).
- Pre-wet the electrospun scaffolds by dipping the pressure conduit with the silicone tubing and electrospun scaffold in 30% ethanol, followed by a dip in ultrapure water two times.
- Place the glass tube over the pressure conduit, and push gently in the bottom compartment and gently secure it.
- Take the top compartment containing the flow inlet, place a silicone O-ring, the flow straightener, and the adapter bushing in the correct order (Figure 1A–B), and place over the open end of the glass tube and gently secure it.
- Screw a white Luer cap on the flow inlet of the top compartment.
- Remove the male Luer plug from the flow outlet of the bottom compartment, and clean the surface around it with an ethanol-soaked paper tissue.
- Place a syringe with 10 mL of ultrapure water in the flow outlet, open the white Luer cap on the top compartment, and fill the chamber with ultrapure water. Close the white Luer cap again, remove the syringe, clean again with ethanol, and close the flow outlet with a male Luer plug.
NOTE: Repeat steps 2.6–2.8 for all flow culture chambers. - For the static controls, add 10 mL of ultrapure water to the 15 mL tubes holding the samples mounted on the pressure conduits without holes.
- Place all flow culture chambers in the incubator. Replace the ultrapure water with culture medium one day before cell seeding on the same way as described in steps 2.8.5 and 2.8.6 (make sure to collect the ‘old’ ultrapure water with an ethanol-soaked paper tissue placed directly on the flow outlet).
[The protocol can be paused here]
3. Preparations for the flow pump setup
NOTE: Perform step 3 in a laminar flow cabinet.
- Collect all pump setup materials and prepare for usage.
NOTE: Experimenters are referred to the manufacturer’s protocol for a detailed description of setting up the pump, the fluidic units, and medium tubing through the valves of the fluidic unit.- Set the pump to 200 mbar capacity.
- Screw the reservoir holders for 60 mL reservoirs to the fluidic units.
- Clean the re-usable rubber air filters with a paper tissue soaked in ethanol, make sure the air filter stays dry.
- Place the 60 mL reservoirs in the reservoir holders, and place the standard medium tubing through the valves of the fluidic unit. Connect the medium tubing with a larger inner diameter with female Luer lock couplers into an enclosed loop.
- Clamp the medium tubing with a hose clip, directly below the reservoirs.
- Fill the reservoirs with 25 mL of culture medium per 60 mL reservoir. Release the hose clip, and let the medium enter the tubing.
- Close the medium reservoirs with the rubber air filters, and place the flow pump setup in the incubator till step 4.
4. Cell Seeding Using Fibrin as a Cell Carrier
NOTE: Perform step 4 in a laminar flow cabinet.
- Prepare the fibrin gel for the cell seeding step. For details, see Mol et al.67 For the fibrin gel, the fibrinogen solution should have a final concentration of 10 mg/mL (correct for the purity of the protein stock), and the thrombin solution should have a final concentration of 10 U/mL.
- Thaw fibrinogen to RT, before weighing ~50 mg (enough for 10 samples) in a plastic container with a red lid.
- Add cell culture medium to prepare the fibrinogen solution (at a concentration of 10 mg/mL, correct for the purity of the protein stock). Mix well and filter to sterilize the fibrinogen solution with a 0.2 µm syringe filter into a sterile 15 mL tube. Keep the filtered fibrinogen solution on ice.
NOTE: Avoid preparing the fibrinogen solution too long in advance, otherwise the fibrinogen may clot spontaneously. - Thaw thrombin and make a thrombin solution (at a concentration of 10 U/mL) in cell culture medium and place on ice. Prepare 20 µL thrombin + cells solution per sample. For n=10 samples, 200 µL is needed; therefore, prepare 250 µL thrombin solution to account for possible pipetting errors.
- Collect and count the cells from the culture flasks. Mix the cells in the desired ratio and amount (1.2 × 106 monocytes and 0.6 × 106 myofibroblasts per scaffold). Make sure there are enough cells for n+1 samples to correct for pipetting errors. Centrifuge at 350 × g for 10 min at RT. Remove the supernatant.
- Make a mixture of the suspended cells and thrombin.
- For each sample, use 20 µL of the thrombin solution. For n=10 samples, add 200 µL thrombin to the cell pellet and mix. Measure the volume of the cell suspension (cells + thrombin), and calculate how to divide evenly over all 10 scaffolds (e.g., if the thrombin + cell suspension has a volume of 260 µL, each electrospun sample will receive 260 µL/10 samples = 26 µL thrombin + cell suspension).
- As the seeding of the scaffolds is performed in two steps, prepare two 1.5 mL microfuge tubes that will hold half of the cell suspension for each scaffold (in the example calculation of the previous step: prepare two tubes with 13 µL of thrombin + cell suspension). Place on ice.
NOTE: The following steps, especially step 4.4, are ideally performed by two experimenters.
- Dry the pre-wetted electrospun scaffolds with vacuum to prepare for cell seeding.
- Connect a glass Pasteur pipet to the vacuum system of the laminar flow cabinet, and place in an empty 50 mL tube for sterile temporary storage.
- Take the flow culture chambers from the incubator, remove the male Luer plug from the flow outlet, and remove the medium after opening the white Luer cap and placing an ethanol-soaked paper tissue in front of the flow outlet.
- Take off the top compartment and the glass tube, and place in a sterile Petri dish for temporary storage.
- Place the vacuum Pasteur pipet on the electrospun scaffold, and remove as much medium as possible.
CAUTION: Vacuum dry the electrospun scaffold very gently. Instead of a back-and forth linear motion over the scaffold, place the vacuum pipet at multiple locations. Clamp the vacuum tubing on top of the Pasteur’s pipet in between the fingers for better control. - Mix the fibrinogen solution in a 1:1 ratio with the thrombin + cell suspension (e.g., mix 13 µL of fibrinogen with 13 µL of thrombin + cell suspension). To make sure that the fibrin polymerizes in the scaffold and not in the microfuge tube, pipet the fibrinogen, turn the pipet wheel for the ‘extra volume’ of the thrombin + cell suspension, and pipet up and down once in the microfuge tube with cell suspension to mix.
- Directly homogeneously drip the solution over the full length of the electrospun scaffold. It is advised that Experimenter A drips the fibrin mixture, while experimenter B holds the bottom compartment with the electrospun scaffold mounted to the pressure conduit.
- After the fibrin with the cells is dripped over the electrospun scaffold, Experimenter B slowly moves the scaffold, from left to right and up and down, to further divide the cells evenly over the scaffold.
- Repeat step 4.4.5 - 4.4.7 on the other side of the electrospun scaffold.
- Mount the flow culture chamber again by carefully placing the glass tube (prevent fibrin sticking and clotting to the inner side of the glass tube), and push back the top compartment of the flow culture chamber. Directly place the seeded construct without any medium or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) in the flow culture chamber in the incubator.
- Repeat steps 4.4.1–4.4.9 for all dynamic samples. For the static samples mounted to pressure conduits without holes, seed according to steps 4.4.1–4.4.8, and place in a 15 mL tube afterwards.
- Let the fibrin polymerize for 60 min in the incubator.
[The protocol can be paused here for 30–60 min.]
- After polymerization, fill the flow culture chambers (dynamic samples) or the 15 mL tubes (static samples) with medium.
5. Coupling of the bioreactor and flow pump systems before starting experiment
NOTE: Perform steps 5.1–5.3 in a laminar flow cabinet.
- Take the tray carrying the flow culture chambers and the fluidic units with filled medium reservoirs and connected medium tubing inside the laminar flow cabinets.
- Position the flow culture chambers on the bioreactor base for the experimental groups loaded with cyclic stretch and with combined hemodynamic loads (Figure 1E).
- Tilt the flow culture chamber upside down, and fill the pressure conduit from below with ultrapure water using a syringe with thin tubing (this can be of any type, as long as it is flexible and thin, in this experiment, a 10 cm long, 0.15 mm inner diameter wire was attached to the needle).
- Place the thin tubing inside the pressure conduit, and while the pressure conduit is filled with ultrapure water by gradually pushing the water out of the syringe, pull the wire out of the pressure conduit simultaneously, to make sure that there are no air bubbles inside the pressure conduit.
- Place the flow culture chamber on one of the eight screw threads on bioreactor base. Place a silicone O-ring between the bioreactor base and the white Luer connector to prevent possible leakage, and tighten the white Luer connector from the bottom compartment.
- Repeat steps 5.2.2 and 5.2.3 for all cyclically stretched samples.
- Connect the flow culture chambers for all experimental groups, except the static control, to the flow pump system.
- Place a hose clip on the medium tubing. Remove the white Luer cap covering the flow inlet of the top compartment of the flow culture chamber. Remove the female Luer coupler of the medium tubing, and connect the medium tubing on one side with the flow inlet on the top compartment, and the other side of the medium tubing with flow outlet at the bottom compartment.
- Repeat step 5.3.1 for all flow culture chambers. At this point, the bioreactor and the flow culture chambers are filled with medium and connected to the flow systems.
- For the static control samples, place the samples vertically in a cell culture flask with filter cap by using the scissor clamp. Fill the cell culture flask with medium, and place in the incubator.
- Transfer the complete setup from the laminar flow cabinet to the incubator, and connect the fluidic units to the air pressure tubing and the electric cable.
- Start the software, and initialize the flow pumps. Start the medium flow for the samples one by one.
- Check if the valves of the fluidic unit are clicking.
- Remove the hose clamp from the medium tubing.
- Start the flow pump with 100 mbar and 10 s switching time.
- Carefully check the flow direction for possible leakage or air bubbles. Any entrapped air bubbles can be removed by turning the flow culture chamber upside down.
NOTE: Make sure that the medium levels in the medium reservoirs are balanced, to prevent suction of air into the system and air bubbles in the flow culture chambers, and to not allow the reservoirs to run dry (Figure 2C). - Repeat step 5.5 for all fluidic units one-by-one.
- Initialize the strain pump.
- Connect the pneumatic actuated pump via the air inlet on the pneumatic cylinder to the compressed air. Connect the lower air outlet with the blue tubing for air out (Figure 1F).
- Open LabVIEW software, run the LabVIEW script and compressed air pressure application system, as described by Van Kelle et al.68, enter displacement and frequency (start with low frequency of 0.2 Hz). Pause the pump when the Teflon bellow is at its lowest level.
- Place the pressure sensor in the pressure sensor inlet on the hydraulic reservoir.
- Change the pump settings to the desired settings (for 1.5 Pa, use 150 mbar, 10 s switching time).
- Start the strain pump, and apply the preferred setting (e.g., 0.5 Hz, 1.05 stretch).
6. Running Experiment for Multiple days; Monitoring of Shear and Stretch During Culture and Medium Replacement
- Calculate the WSS at the scaffold wall.
- Record the flow magnitude every other day (see the flow pump manufacturer’s manual for details). In short, observe the change in liquid levels (in mL) in the medium reservoirs in between the switching of the fluidic unit reservoir for 10 s. Conduct at least five measurements, calculate the mean value, and multiply by 6 to get the flow rate Q in mL/min.
- The flow is described by a Poiseuille flow through an annular channel. Assuming culture medium as a Newtonian fluid, calculate the WSS at the scaffold wall, r1, by Equation 1.
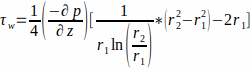 (1)
(1)
where the WSS τw at the scaffold wall (r1; here r1 = 1.7 mm), resulting from a steady state flow, is determined by the applied pressure p and the inner radius of the glass tube r2 (here r2 = 2.3 mm). The pressure gradient in the axial direction is assumed to be uniform between the flow inlet and flow outlet and is given by Equation 2 (Figure 1J).
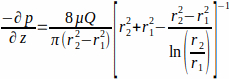 (2)
(2)
with µ the dynamic viscosity (here medium viscosity was assumed constant, µ = 0.7 × 10-3 Pa∙s at 37 °C) and Q the applied flow rate.
- Monitor the stretch applied to the scaffolds every other day.
- Place a dark background behind the flow culture chamber to increase the contrast between the scaffold and the background. Position the LED light lamps, pointing towards the scaffold, to help the visualization of the scaffold.
- Take time-lapse photographs of the scaffold at a frequency of 30 Hz for 6 s (i.e., 3 stretch cycles) with a high-speed camera.
NOTE: A lower recording frequency may suffice if the camera permits. However, the minimally required frequency was not determined. - Manually determine the minimum and maximum diameter of the scaffold from the images.
- Calculate the minimum and maximum outer diameter of the electrospun scaffold to calculate the maximum stretches according to Equation 3.
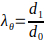 (3)
(3)
where the circumferential stretch (λθ) is given by the ratio between the outer diameter of the scaffold, d1, and its initial diameter, d0.
- Correct for medium evaporation, and refresh medium three times per week.
- Stop and decouple the cables for the flow systems and the strain pump.
- Place hose clips on the medium tubing.
- Determine how much medium evaporated based on the volume indicator marks on the medium reservoirs.
- Transfer the tray with the bioreactor and the fluidic units to the laminar flow cabinet.
- Remove the rubber air filters of the medium reservoirs; add autoclaved ultrapure water to compensate for the evaporated volume of medium. Close the medium reservoirs again, and connect to the pump again to mix the medium with the ultrapure water.
- Repeat steps 6.3.1–6.3.5. Remove the rubber air filters again, take out 25 mL of culture medium, and spin down at 300 × g for 5 min at RT.
- Collect 1.5 mL supernatant, and store at -30 °C for analysis of secretory profiles (for analysis with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)).
- Collect the desired volume of supernatant for paracrine signaling studies, by using the supernatant as conditioned medium43.
- Add 25 mL of fresh medium to the medium reservoirs.
- Place rubber air filters back on the medium reservoirs.
- Place the complete setup back in the incubator; connect all cables and air tubing to the pump and strain pump. Release the hose clips and repeat steps 5.4–5.8.
- Check if silica drying beads in the drying bottles connected to the pump are moist (white appearance), and replace with dry silica beads if required (orange appearance).
7. Ending Experiment, Sample Collection, and Equipment Cleaning and Storage
- On the last day of the experiment, correct for medium evaporation as described in steps 6.3.1–6.3.5, and harvest the samples one-by-one.
- To harvest the samples one-by-one, the flow pump and strain pump need to be paused several times. Place a hose clip on medium tubing. Temporarily stop the flow pump and the strain pump. Disconnect one flow culture chamber from the bioreactor base; replace by a white Luer cap on the bioreactor base. Take the flow culture chamber and fluidic unit to the laminar flow cabinet. Start the flow pump and strain pump again to apply the hemodynamic load to the other samples until harvesting.
- Collect medium from the medium reservoirs for paracrine cytokine production analysis via ELISA.
- Decouple flow units and harvest tubular construct. Section according to the desired cutting scheme. Parts of the construct can be stored at 4 °C (after 15 min fixation in 3.7% formaldehyde and 3 x 5 min washing in PBS) or -30 °C (after snap-freezing in liquid nitrogen) until further analysis.
- Clean the bioreactor and pump components. Additionally, the advised cleaning method per item is mentioned in the Table of Materials.
- Clean the rubber air filters with 70% ethanol. Be very careful to not moisten the inner filter!
- Collect all separate components: medium tubing, medium reservoirs, glass tubes, male Luer plugs and female Luer locks, white Luer caps, pressure conduits, nose cones, silicone O-rings, adapter bushing, flow straighteners (excluding pumps, fluidic units, rubber air filters, the bioreactor base), and rinse in running tap water.
- Place O/N in 0.1% sodium dodecylsulfate in deionized water.
NOTE: Do not use ultrapure water as the parts might rust. - Rinse with tap water and dishwashing soap.
- Immerse in deionized water, followed by 70% ethanol two times, followed by deionized water.
- Place all materials separately on paper tissues and let them dry. Use pressured air to dry tubing.
- Clean all non-autoclavable materials with a paper tissue soaked in 70% ethanol. This includes the rubber air filter (bear in mind that the air filter should stay dry) and the bioreactor base (Teflon bellow and pneumatic cylinder).
- Autoclave the components of the fluidic chamber (including the silicone O-ring), the medium tubing, the medium reservoirs (without the rubber air filter), male Luer plugs and female Luer couplers, white Luer caps, hose clips, and standard equipment (e.g., tweezers, clamping scissors)
- For convenient use during next experiments, combine the separate components for one complete fluidic chamber in an autoclavable box.
- Remove water from the hydraulic reservoir. Clean with 70% ethanol, followed by deionized water. Let it dry. Refill with deionized water and a few drops of water-bath-preserving disinfectant.
- Store the glass tubes for the flow culture chamber in 70% ethanol.
- Place the moist silica drying beads (white appearance) in the oven O/N at 120 °C to let them dry (orange appearance), and store in an air-tight flask.
Results
This bioreactor was developed to study the individual and combined effects of shear stress and cyclic stretch on vascular tissue growth and remodeling in 3D biomaterial scaffolds. The design of the bioreactor allows for culturing up to eight vascular constructs under various loading conditions (Figure 1A). The vascular constructs are positioned in a flow culture chamber (Figure 1B) in which both the circumferential stretch and WSS can be independently controlled...
Discussion
The bioreactor described herein allows for the systematic evaluation of the contributions of the individual and combined effects of shear stress and cyclic stretch on inflammation and tissue regeneration in tubular resorbable scaffolds. This approach also enables a large variety of analyses to be performed on vascular constructs, as exemplified in the representative results section. These results show the distinctive impact of the different hemodynamic loading regimes (i.e., different combinations of shear and stretch) o...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by ZonMw as part of the LSH 2Treat program (436001003) and the Dutch Kidney Foundation (14a2d507). N.A.K. acknowledges support from the European Research Council (851960). We gratefully acknowledge the Gravitation Program “Materials Driven Regeneration”, funded by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (024.003.013).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| advanced Dulbecco’s modified EagleMedium (aDMEM) | Gibco | 12491-015 | cell culture medium for fibroblasts |
| Aqua Stabil | Julabo | 8940012 | prevent microorganism growth in bioreactor-hydraulic reservoir |
| Bovine fibrinogen | Sigma | F8630 | to prepare fibrinogen gel to seed the cells on the electrospun scaffold |
| Bovine thrombin | Sigma | T4648 | to prepare fibrinogen gel to seed the cells on the electrospun scaffold |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5804 | to spin down cells and conditioned medium |
| Clamp scissor - "kelly forceps" | Almedic | P-422 | clamp the silicone tubing and apply pre-stretch to the scaffold so the scaffold can be sutured into the engraved groove (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| CO2 cell culture incubators | Sanyo | MCO-170AIC-PE | for cell culturing |
| Compressed air reservoir | Festo | CRVZS-5 | smoothing air pressure fluctuations and create time delays for pressure build-up |
| Custom Matlab script to calculate the maximum stretches | Matlab | R2017. The Mathworks, Natick, MA | calculate the minimum and maximum outer diameter of the electrospun scaffold |
| Data acquisition board | National Instruments | BNC-2090 | data processing in between amplifier system and computer |
| Ethanol | VWR | VWRK4096-9005 | to keep sterile working conditions |
| Fetal bovine calf serum (FBS) | Greiner | 758087 | cell culture medium supplement; serum-supplement |
| Flow culture chamber compartments, consisting of a pressure conduit with engraved grooves and small holes to apply pressure on silicone tubing, a screw thread, nose cone, top compartment with flow inlet and bottom compartment flow outlet, adapter bushing | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | flow culture chamber compartments (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Glass Pasteur pipet | Assistant | HE40567002 | apply vacuum on electrospun scaffold (autoclave at step 1) |
| Glass tubes of the flow culture chamber | Custon made, Equipment & Prototype Center, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | part of the flow culture chamber (clean and store in 70% ethanol, at step 1 and 7) |
| GlutaMax | Gibco | 35050061 | cell culture medium amino acid supplement, minimizes ammonia build-up |
| High speed camera | MotionScope | M-5 | to monitor the stretch during culture; time-lapse photographs of the scaffolds are captured at a frequency of 30 Hz for 6 sec (i.e. 3 stretch cycles) |
| High speed camera lens - Micro-NIKKOR 55mm f/2.8 - lens | Nikon | JAA616AB | to monitor the stretch during culture; time-lapse photographs of the scaffolds are captured at a frequency of 30 Hz for 6 sec (i.e. 3 stretch cycles) |
| Hose clip | ibidi GmbH | 10821 | block medium flow (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Hydraulic reservoir with 8 screw threads for 8 flow culture chambers | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to apply pressure to the silicone mounted constructs (clean outside with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol, rinse reservoir with 70% ethanol followed by demi water, at step 1 and 7) |
| Ibidi pump system (8x) including ibidi pump, PumpControl software, fluidic unit, perfusion set (medium tubing), air pressure tubing, drying bottles with orange silica beads | ibidi GmbH | 10902 | set up used to control the flow in the flow culture chambers. Note 1: the ibidi pumps were modified by the manufacturer to enable 200 mbar capacity. Note 2: can be replaced by pump system of other manufacturer, as long as same flow regimes can be applied. |
| Knives (no.10 sterile blades, individual foil pack) and scalpel handle (stainless steel, individually wrapped) | Swann Morton | 0301; 0933 | to cut the silicone tubing in the correct size for the scaffold and to cut the suture material |
| LabVIEW Software | National Instruments | version 2018 | to control the stretch applied to the scaffolds |
| Laminar flow biosafety cabinet with UV light | Labconco | 302310001 | to ensure sterile working conditions. The UV is used to decontaminate everything that cannot be autoclaved, or touched after autoclaving |
| Large and small petri dishes | Greiner | 664-160 | for sterile working conditions |
| L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (vitamin C) | Sigma | A8960 | cell culture medium supplement, important for collagen production |
| LED light cold source KL2500 | Zeiss | Schott AG | to aid in visualization for the time lapse of the scaffolds during monitoring of the stretch |
| Luer (female and male) locks and connectors, white luer caps | ibidi GmbH | various, see (https://ibidi.com/26-flow-accessories) | to close or connect parts of the bioreactor and the ibidi pump (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Measuring amplifier (PICAS) | PEEKEL instruments B.V. | n.a. | to amplify the signal from the pressure sensor and feedback to LabView |
| Medium reservoir (large syringes 60 mL) and reservoir holders | ibidi GmbH | 10974 | medium reservoir (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Medium tubing with 4.25 mm outer diameter and 1 mm inner diameter | Rubber BV | 1805 | to allow for a larger flow rate, the ibidi medium tubing with larger diameter is used. Note: the part of medium tubing guided through the fluidic unit valves are the same as the default ibidi medium tubing |
| Motion Studio Software | Idtvision | 2.15.00 | to make the high speed time lapse images for stretch monitoring |
| Needle (19G) | BD Microlance | 301700 | together with thin flexible tubing used to fill the hydraulic reservoir with ultrapure water without adding air bubbles |
| Needle driver | Adson | 2429218 | to handle the needle of the nylon suture through the silicone tube (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Paper tissues | Kleenex | 38044001 | for cleaning of the equipment with 70% ethanol |
| Parafilm | Sigma | P7793-1EA | quick fix if leakage occurs |
| Penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) | Lonza | DE17-602E | cell culture medium supplement; prevent bacterial contamination |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) | Sigma | P4417-100TAB | for storage and washing steps (autoclave at step 1) |
| Plastic containers (60 mL) with red screw caps | Greiner | 206202 | to prepare the fibrinogen solution |
| Pneumatic cylinder | Festo | AEVC-20-10-I-P | to actuate the Teflon bellow (clean with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol at step 1 and 7) |
| Polycaprolactone bisurea (PCL-BU) tubular scaffolds (3 mm inner diameter, 200 µm wall thickness, 20 mm length) | SyMO-Chem, Eindhoven, The Netherlands | n.a. | produced using electrospinning from 15% (w/w) chloroform (Sigma; 372978) polymer solutions. See Van Haaften et al Tissue Engineering Part C (2018) for more details |
| Pressure conduit without holes (for static control) | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to mount electrospun tubes on silicon tubing (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Pressure sensor and transducer | BD | TC-XX and P 10 EZ | the air pressure going to the pneumatic actuated pump is raised until it reaches the set pressure |
| Proportional air pressure control valve and pressure sensor | Festo | MPPES-3-1/8-2-010, 159596 | provides compressed air to the pneumatic actuated pump |
| Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (RPMI-1640) | Gibco | A1049101 | cell culture medium for monocyte/macrophage |
| Safe lock Eppendorf tubes (1.5 mL) | Eppendorf | 30120086 | multiple applications (autoclave at step 1) |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate solution 20% | Sigma | 5030 | Used to clean materials, at a concentration of 0.1%. |
| Silicone O-rings | Technirub | 1250S | to prevent leakage (autoclave at step 1, step 7) |
| Silicone tubing (2.8 mm outer diameter, 400 um wall thickness) | Rubber BV | 1805 | to mount the electrospun tubes on the pressure conduits (autoclave at step 1) |
| Sterile tube (15 mL) | Falcon | 352095 | multiple applications |
| Suture, 5-0 prolene with pre-attached taper point needle | Ethicon, Johnson&Johnson | EH7404H | Prolene suture wire 5-0 (75cm length, TF taper point needle, 1/2 circle, 13 mm needle length) |
| Syringe (24 mL) | B. Braun Melsungen AG | 2057932 | to add the ultrapure water or medium to the hydraulic reservoir or flow culture chamber |
| Syringe filter (0.2 µm) | Satorius | 17597-K | to filter the fibrinogen solution |
| T150 cell culture flask with filter cap | Nunc | 178983 | to degas culture medium |
| T75 Cell culture flask with filter cap | Nunc | 156499 | to culture static control samples |
| Teflon bellow | Custom made, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology | n.a. | to load the hydraulic reservoir (clean outside with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol at step 1 and 7) |
| Tray (stainless steel) | PolarWare | 15-248 | for easy transport of the fluidic culture chambers and the bioreactor from incubator to laminar flow cabinet and back (clean with a paper tissue with 70% ethanol before and after use) |
| Tweezers | Wironit | 4910 | sterile handling of individual parts (autoclave at step 1 and 7) |
| Ultrapure water | Stakpure | Omniapure UV 18200002 | to correct for medium evaporation, mixed with aqua stabil mixed and used as hydraulic fluid. (autoclave ultrapure water at step 1) |
| UV light | Philips | TUV 30W/G30 T8 | for decontamination of grafts and bioreactor parts before seeding |
References
- Chlupác, J., Filová, E., Bacáková, L. Blood vessel replacement: 50 years of development and tissue engineering paradigms in vascular surgery. Physiological Research. 58, 119-139 (2009).
- Huygens, S. A., et al. Bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement in elderly patients: Meta-analysis and microsimulation. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 157 (6), 2189-2197 (2019).
- Huygens, S. A., et al. Contemporary outcomes after surgical aortic valve replacement with bioprostheses and allografts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 50 (4), 605-616 (2016).
- Loh, S. A., et al. Mid- and long-term results of the treatment of infrainguinal arterial occlusive disease with precuffed expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts compared with vein grafts. Annals of Vascular Surgery. 27 (2), 208-217 (2013).
- Tara, S., et al. Vessel bioengineering. Circulation Journal. 78 (1), 12-19 (2014).
- Huang, A. H., Niklason, L. E. Engineering of arteries in vitro. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 71 (11), 2103-2118 (2014).
- Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M., Baaijens, F. P. T. Can we grow valves inside the heart? Perspective on material-based in situ heart valve tissue engineering. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. 5, 54 (2018).
- Fioretta, E. S., et al. Next-generation tissue-engineered heart valves with repair, remodelling and regeneration capacity. Nature Reviews Cardiology. , (2020).
- Kirkton, R. D., et al. Bioengineered human acellular vessels recellularize and evolve into living blood vessels after human implantation. Science Translational Medicine. 11 (485), (2019).
- Gutowski, P., et al. Arterial reconstruction with human bioengineered acellular blood vessels in patients with peripheral arterial disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery. , (2020).
- Syedain, Z., et al. Tissue engineering of acellular vascular grafts capable of somatic growth in young lambs. Nature Communications. 7 (12951), 12951 (2016).
- Sugiura, T., et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts in children with congenital heart disease: intermediate term follow-up. Seminars in Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 30 (2), 175-179 (2018).
- Kluin, J., et al. In situ heart valve tissue engineering using a bioresorbable elastomeric implant - material design to 12 months follow-up in sheep. Biomaterials. 125, 101-117 (2017).
- Fioretta, E. S., et al. Differential leaflet remodeling of bone marrow cell pre-seeded versus nonseeded bioresorbable transcatheter pulmonary valve replacements. JACC. Basic to Translational Science. 5 (1), 15-31 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., Bouten, C. V. C., Kurniawan, N. A. Vascular mechanobiology: towards control of. Cells. , 1-24 (2017).
- De Jonge, N., et al. Matrix production and organization by endothelial colony forming cells in mechanically strained engineered tissue constructs. PLoS ONE. 8 (9), 73161 (2013).
- Schmidt, J. B., Chen, K., Tranquillo, R. T. Effects of intermittent and incremental cyclic stretch on ERK signaling and collagen production in engineered tissue. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering. 9 (1), 55-64 (2016).
- Luo, J., et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts with advanced mechanical strength from human iPSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 26 (2), 251-261 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., et al. Decoupling the effect of shear stress and stretch on tissue growth and remodeling in a vascular graft. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 24 (7), 418-429 (2018).
- Gupta, V., Tseng, H., Lawrence, B. D., Jane Grande-Allen, K. Effect of cyclic mechanical strain on glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan synthesis by heart valve cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 5 (2), 531-540 (2009).
- Lin, S., Mequanint, K. Bioreactor-induced mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation and elastic fiber assembly in engineered vascular tissues. Acta Biomaterialia. 59, 200-209 (2017).
- Venkataraman, L., Bashur, C. A., Ramamurthi, A. Impact of cyclic stretch on induced elastogenesis within collagenous conduits. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 20 (9-10), 1403-1415 (2014).
- Huang, A. H., et al. Biaxial stretch improves elastic fiber maturation, collagen arrangement, and mechanical properties in engineered arteries. Tissue Engineering Part C Methods. 22 (6), 524-533 (2016).
- Hinderer, S., et al. In vitro elastogenesis: instructing human vascular smooth muscle cells to generate an elastic fiber-containing extracellular matrix scaffold. Biomedical Materials. 10 (3), 034102 (2015).
- Eoh, J. H., et al. Enhanced elastin synthesis and maturation in human vascular smooth muscle tissue derived from induced-pluripotent stem cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 52, 49-59 (2017).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Bouten, C. V. C. Tissue engineering meets immunoengineering: Prospective on personalized in situ tissue engineering strategies. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering. 6, 17-26 (2018).
- Wissing, T. B., Bonito, V., Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M. Biomaterial-driven in situ cardiovascular tissue engineering-a multi-disciplinary perspective. npj Regenerative Medicine. 2 (1), 18 (2017).
- Hibino, N., et al. A critical role for macrophages in neovessel formation and the development of stenosis in tissue-engineered vascular grafts. The FASEB Journal. 25 (12), 4253-4263 (2011).
- Godwin, J. W., Pinto, A. R., Rosenthal, N. A. Macrophages are required for adult salamander limb regeneration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (23), 9415-9420 (2013).
- Godwin, J. W., Debuque, R., Salimova, E., Rosenthal, N. A. Heart regeneration in the salamander relies on macrophage-mediated control of fibroblast activation and the extracellular landscape. npj Regenerative Medicine. 2 (1), 22 (2017).
- McBane, J. E., Cai, K., Labow, R. S., Santerre, J. P. Co-culturing monocytes with smooth muscle cells improves cell distribution within a degradable polyurethane scaffold and reduces inflammatory cytokines. Acta Biomaterialia. 8 (2), 488-501 (2012).
- Battiston, K. G., Ouyang, B., Labow, R. S., Simmons, C. A., Santerre, J. P. Monocyte/macrophage cytokine activity regulates vascular smooth muscle cell function within a degradable polyurethane scaffold. Acta Biomaterialia. 10 (3), 1146-1155 (2014).
- Ploeger, D. T., et al. Cell plasticity in wound healing: paracrine factors of M1/ M2 polarized macrophages influence the phenotypical state of dermal fibroblasts. Cell Communication and Signaling. 11 (1), 29 (2013).
- McBane, J. E., Santerre, J. P., Labow, R. S. The interaction between hydrolytic and oxidative pathways in macrophage-mediated polyurethane degradation. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A. 82 (4), 984-994 (2007).
- Wissing, T. B., et al. Macrophage-driven biomaterial degradation depends on scaffold microarchitecture. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 7, 87 (2019).
- Wolf, M. T., Vodovotz, Y., Tottey, S., Brown, B. N., Badylak, S. F. Predicting in vivo responses to biomaterials via combined in vitro and in silico analysis. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 21 (2), 148-159 (2015).
- Grotenhuis, N., Bayon, Y., Lange, J. F., Van Osch, G. J. V. M., Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y. M. A culture model to analyze the acute biomaterial-dependent reaction of human primary macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 433 (1), 115-120 (2013).
- Jannasch, M., et al. A comparative multi-parametric in vitro model identifies the power of test conditions to predict the fibrotic tendency of a biomaterial. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 1689 (2017).
- Wang, Z., et al. The effect of thick fibers and large pores of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) vascular grafts on macrophage polarization and arterial regeneration. Biomaterials. 35 (22), 5700-5710 (2014).
- McWhorter, F. Y., Davis, C. T., Liu, W. F. Physical and mechanical regulation of macrophage phenotype and function. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 72 (7), 1303-1316 (2014).
- Ballotta, V., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Strain-dependent modulation of macrophage polarization within scaffolds. Biomaterials. 35 (18), 4919-4928 (2014).
- Dziki, J. L., et al. The effect of mechanical loading upon extracellular matrix bioscaffold-mediated skeletal muscle remodeling. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 24 (1-2), 34-46 (2018).
- Wissing, T. B., et al. Hemodynamic loads distinctively impact the secretory profile of biomaterial-activated macrophages - implications for in situ vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials Science. 8 (1), 132-147 (2020).
- Van Haaften, E. E., Wissing, T. B., Kurniawan, N. A., Smits, A. I. P. M., Bouten, C. V. C. Human in vitro model mimicking material-driven vascular regeneration reveals how cyclic stretch and shear stress differentially modulate inflammation and matrix deposition. Advanced Biosystems. 4 (6), 1900249 (2020).
- Ballotta, V., Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Synergistic protein secretion by mesenchymal stromal cells seeded in 3D scaffolds and circulating leukocytes in physiological flow. Biomaterials. 35 (33), 9100-9113 (2014).
- Bonito, V., de Kort, B. J., Bouten, C. V. C., Smits, A. I. P. M. Cyclic strain affects macrophage cytokine secretion and extracellular matrix turnover in electrospun scaffolds. Tissue Engineering Part A. 25 (17-18), 1310-1325 (2019).
- Battiston, K. G., Labow, R. S., Simmons, C. A., Santerre, J. P. Immunomodulatory polymeric scaffold enhances extracellular matrix production in cell co-cultures under dynamic mechanical stimulation. Acta Biomaterialia. 24, 74-86 (2015).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. A mesofluidics-based test platform for systematic development of scaffolds for in situ cardiovascular tissue engineering. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 18 (6), 475-485 (2012).
- Smits, A. I. P. M., Ballotta, V., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. T. Shear flow affects selective monocyte recruitment into MCP-1-loaded scaffolds. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 18 (11), 2176-2188 (2014).
- Ballotta, V., Smits, A. I. P. M., Driessen-Mol, A., Bouten, C. V. C., Baaijens, F. P. T. Synergistic protein secretion by mesenchymal stromal cells seeded in 3D scaffolds and circulating leukocytes in physiological flow. Biomaterials. 35 (33), 9100-9113 (2014).
- Fahy, N., Menzel, U., Alini, M., Stoddart, M. J. Shear and dynamic compression modulates the inflammatory phenotype of human monocytes in vitro. Frontiers in Immunology. 10, 383 (2019).
- Pennings, I., et al. Layer-specific cell differentiation in bi-layered vascular grafts under flow perfusion. Biofabrication. 12 (1), 015009 (2019).
- Wang, J., et al. Ex vivo blood vessel bioreactor for analysis of the biodegradation of magnesium stent models with and without vessel wall integration. Acta Biomater. 50, 546-555 (2017).
- Huang, A. H., et al. Design and use of a novel bioreactor for regeneration of biaxially stretched tissue-engineered vessels. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 21 (8), 841-851 (2015).
- Huang, A. H., Niklason, L. E. Engineering biological-based vascular grafts using a pulsatile bioreactor. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (52), e2646 (2011).
- Bono, N., et al. A Dual-mode bioreactor system for tissue engineered vascular models. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 45 (6), 1496-1510 (2017).
- Wolf, F., et al. VascuTrainer: a mobile and disposable bioreactor system for the conditioning of tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 46 (4), 616-626 (2018).
- Ramaswamy, S., et al. A novel bioreactor for mechanobiological studies of engineered heart valve tissue formation under pulmonary arterial physiological flow conditions. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 136 (12), 121009 (2014).
- Piola, M., et al. A compact and automated ex vivo vessel culture system for the pulsatile pressure conditioning of human saphenous veins. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 10 (3), 204-215 (2016).
- Vanerio, N., Stijnen, M., de Mol, B. A. J. M., Kock, L. M. An innovative ex vivo vascular bioreactor as comprehensive tool to study the behavior of native blood vessels under physiologically relevant conditions. Journal of Engineering and Science in Medical Diagnostics and Therapy. 2 (4), (2019).
- Kural, M. H., Dai, G., Niklason, L. E., Gui, L. An ex vivo vessel injury model to study remodeling. Cell Transplantation. 27 (9), 1375-1389 (2018).
- Sinha, R., et al. A medium throughput device to study the effects of combinations of surface strains and fluid-flow shear stresses on cells. Lab on a Chip. 15 (2), 429-439 (2015).
- Beca, B. M., Sun, Y., Wong, E., Moraes, C., Simmons, C. A. Dynamic bioreactors with integrated microfabricated devices for mechanobiological screening. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 25 (10), 581-592 (2019).
- Liu, H., Usprech, J., Sun, Y., Simmons, C. A. A microfabricated platform with hydrogel arrays for 3D mechanical stimulation of cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 34, 113-124 (2016).
- Szafron, J. M., Ramachandra, A. B., Breuer, C. K., Marsden, A. L., Humphrey, J. D. Optimization of tissue-engineered vascular graft design using computational modeling. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 25 (10), 561-570 (2019).
- Emmert, M. Y., et al. Computational modeling guides tissue-engineered heart valve design for long-term in vivo performance in a translational sheep model. Science Translational Medicine. 10 (440), (2018).
- Mol, A., et al. Fibrin as a cell carrier in cardiovascular tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 26 (16), 3113-3121 (2005).
- van Kelle, M. A. J., et al. A Bioreactor to identify the driving mechanical stimuli of tissue growth and remodeling. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 23 (6), (2017).
- van den Broek, C. N., et al. Medium with blood-analog mechanical properties for cardiovascular tissue culturing. Biorheology. 45 (6), 651-661 (2008).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved