A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Using Hyperbaric Oxygen to Improve the Radiosensitivity of Human U251 Glioma Cells
In This Article
Summary
This protocol shows that hyperbaric oxygen can enhance the proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of U251 glioma cells treated with X-ray irradiation by blocking the cells in the G2/M phase. This improves the radiosensitivity of human glioma cell lines.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to explore the use of hyperbaric oxygen to enhance the radiosensitivity of human glioma cells. Sub-cultured U251 human glioma cells were randomly divided into four groups: an untreated control group, cells treated with hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) only, cells treated with X-ray irradiation (X-ray) only, and cells treated with both HBO and X-ray. Cell morphology, cell proliferation activity, cell cycle distribution, and apoptosis were observed in these groups to evaluate the role of HBO in improving the radiosensitivity of glioma cells. With the increase in X-ray doses (0 Gy, 2 Gy, 4 Gy, 6 Gy, 8 Gy), the survival fraction (SF) of glioma cells gradually decreased.
Significantly lower SF was observed for the cells treated with the HBO and X-ray together than in the X-ray group for each dose (all P < 0.05). The proliferation inhibition was significantly higher in the HBO combined with X-ray group than in the X-ray group for each dose (all P < 0.05) for the U251 cell line. The percentage of G2/M phase cells was significantly higher in the HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) group (26.70% ± 2.46%) and the HBO group (22.36% ± 0.91%) than in the control group (11.56% ± 2.01%) and X-ray (2 Gy) group (10.35% ± 2.69%) (all P < 0.05). U251 cell apoptosis was significantly higher in the HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) group than in the HBO group, the X-ray (2 Gy) group, and the control group (all P < 0.05). We conclude that HBO can enhance the proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of glioma U251 cells by blocking glioma cells in the G2/M phase and improve the radiosensitivity of U251 glioma cells.
Introduction
Glioma is a primary intracranial tumor that originates from central nervous system glial cells1. The current treatment strategy for glioma is surgery combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Postoperative radiotherapy for glioma can provide survival benefits (grade I evidence), and early postoperative radiotherapy can effectively prolong patient survival (grade II evidence)2. For higher-grade gliomas (grade III or IV), especially highly malignant and invasive glioblastoma (grade III evidence)3, postoperative radiotherapy should be performed as early as possible (<6 weeks). However, despite early intervention, glioma still has a high recurrence rate and poor prognosis after comprehensive treatment. These outcomes are mainly associated with the low radiosensitivity of glioma. Factors related to tumor radiosensitivity include the inherent radiosensitivity of tumor cells, hypoxic or non-hypoxic tumor cells, the proportion of hypoxic tumor cells, and the capacity of peritumoral tissue to repair radiation damage4.
Among these factors, hypoxic or non-hypoxic tumor cells and the proportion of hypoxic tumor cells have important effects on tumor radiosensitivity. Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) can improve tissue oxygen storage by increasing tissue oxygen tension and blood oxygen diffusion. HBO may also produce a series of beneficial biochemical, cytological, and physiological effects5. For example, HBO has a marked reparative effect on radiotherapy-induced radiation damage. Although HBO combined with radiotherapy or chemotherapy is reported to improve the clinical efficacy of radiotherapy or chemotherapy for glioma6, there is considerable debate about how HBO alone affects malignant glioma growth. Ding et al.7 and Wang et al.8 both demonstrated that HBO promotes the growth of in situ glioma in mice via mechanisms that involve the inhibition of apoptosis and the promotion of tumor angiogenesis. Under physiological conditions, HBO is reported to promote tumor angiogenesis by inducing oxidative stress9.
However, one study indicated that short-term HBO exposure promotes tumor cell proliferation, whereas prolonged HBO exposure promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation10. Therefore, further studies are needed to explore whether HBO promotes or inhibits the growth of glioma and how HBO combined with radiotherapy or chemotherapy can induce therapeutic sensitization. In particular, mechanistic details about how HBO improves the radiosensitivity of glioma are needed. To explore how HBO improves the radiosensitivity of human U251 glioma cells in this study, we used HBO combined with X-ray irradiation on glioma cell proliferation and observed the effects on cell cycle distribution and apoptosis.
Protocol
All study methods were approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital Affiliated with Lanzhou University and were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
1. Treatment of glioma cells
NOTE: The U251 glioma cell line was used in this experiment.
- U251 cell culture
- Seed U251 cells in multiple dishes with DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and culture them at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Upon reaching 50%-60% confluency, dissociate the cells using trypsin-EDTA solution (0.25%, without phenol red) and then allow them to grow to 80% confluency.
- X-ray irradiation
- Cover the culture plates or flasks with an equivalent tissue compensator of up to 1 cm thickness. Then, expose the cells to X-ray irradiation delivered from a 6 MV linear accelerator with a source-cell distance of 100 cm, adjusted by clicking the rotate button on the remote control board.
- Have a physicist measure the radiation dose and correct for attenuation. As a control, place flasks containing media in a detector before the X-ray irradiation.
- Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO)
- Disinfect the HBO chamber by turning on the ultraviolet light for 15 min and then flood it with 0.02 MPa of pure oxygen for 5 min.
- After placing the cells in plates or culture flasks in the chamber, click on the pressure regulator button on the control board outside the chamber to increase the HBO pressure in the chamber to 0.2 MPa (2.0 ATA) within 30 min of irradiation.
- Thirty minutes later, click on the pressure regulator button to decrease the HBO pressure to the previous pressure level (0.1 MPpa). Then, treat the culture bottles or plates with HBO 1x per day for 3 consecutive days.
2. U251 glioma cells in different groups
- Set a control group, X-ray (2 Gy) group, and HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) group for calculating the cell growth curves.
- Prepare single-cell suspensions from the glioma U251 cells showing the maximum growth rates (see step 1.1.2). Adjust the cell density to 1 × 106/mL by counting the cells using a hemocytometer slide. Subsequently, add 1 mL of the cell suspension to a culture bottle (cell density: 1 × 106/bottle) with three separate bottles for each group.
- Assess cell morphology at 100x magnification with a brightfield microscope to enumerate the adherent cells at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h of culture.
3. Radiosensitivity of U251 glioma cells (clone formation assay) within 30 min after HBO
- Seed the U251 single-cell suspension throughout the wells at 5 × 102 cells/mL in 6-well plates and then expose them to the indicated dose of X-ray irradiation (0 Gy, 2 Gy, 4 Gy, 6 Gy, and 8 Gy), with three parallel samples being examined for each X-ray dose.
- For the HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) group, expose the cells to X-ray irradiation within 30 min of HBO treatment. After treatment, culture the cells at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 14 days.
- After the clones are visible, remove the medium and wash the clones 2x with PBS.
- Fix the cells in 1 mL of 10% methanol for 15 min before staining with 1 mL of 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min.
- After staining, wash the cells with 6 mL of distilled water using a pipette, and then aspirate the crystal violet solution. Allow the cells to air dry.
- Count the clones with a diameter between 0.3 mm and 1.0 mm under a microscope to ensure that there are >50 cells per clone.
- Calculate the survival fraction (SF) using equation (1):
SF =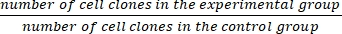 × 100% (1)
× 100% (1) - Using statistical software, generate a radiation dose-survival curve based on the single-hit multitarget (SHMT) model using equation (2):
S = 1 - (1 -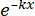 )N (2)
)N (2)
Where S = the probability of survival; k = the mean lethal dose (the dose causing a mean of one hit per cell); x = the number of hits per cell; N = the number of targets (the number of hits for cell death). - Calculate the radiobiological parameters, including the mean lethal dose (D0), quasi-threshold dose (Dq), extrapolation number (N), survival fraction at an irradiation dose of 2 Gy (SF2), sensitization enhancement ratio (D0) (SER = D0 in the control group/D0 in the experimental group), and SER (Dq) (SER = Dq in the control group/Dq in the experimental group) to evaluate the effect of HBO on the radiosensitivity of U251 glioma cells.
Where D0 = the reciprocal value of the slope of the linear portion of the survival curve (the dose reducing the survival rate by 63%)
N = the value of the intersection point formed by extrapolating the linear portion to meet the ordinate (reflecting the cellular ability to repair the radiation-caused damage)
Dq = the value of the intersection-projective point on the abscissa and the intersection formed by drawing a line through 1.0 at the ordinate and parallel to the abscissa to meet the extrapolation line.
4. Cell counting assay to assess U251 glioma cell proliferation
- Set a control group, an HBO group, and groups treated with X-ray (0 Gy, 2 Gy, 4 Gy, 6 Gy, 8 Gy) alone or combined with HBO.
- Adjust the cell density to 1 × 104 cells/mL using U251 cells in single-cell suspensions.
- Seed the cell suspensions (100 µL, density: 1 × 103/well) in 96-well plates (five wells per group). Perform the cell counting assay (see the Table of Materials), and then determine the optical density (OD) at 450 nm using a microplate reader after 48 h of culture with the reagent.
- Calculate the cell proliferation inhibition rate (IR) according to equation (3):
IR =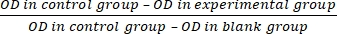 × 100% (3)
× 100% (3)
5. Detection of apoptosis of U251 glioma cells
- Set control, HBO, X-ray (2 Gy), and HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) groups.
- Remove the medium after culture and wash the cells with 1x PBS.
- Detach the cells with trypsin and then deactivate the trypsin by adding DMEM when a rounded cell morphology is observed under a microscope.
- Transfer the cells to a centrifuge tube and centrifuge for 5 min at 200 × g.
- Discard the supernatant, add 3 mL of 1x PBS to the pellet, and gently pipette to resuspend the cells.
- Centrifuge the cells again at 200 × g for 5 min. Then, aspirate the supernatant PBS and wash the cells 2x before resuspending them with gentle pipetting in 50 µL of Binding Buffer.
- Add 5 µL of annexin V-FITC to the cells at 4 °C and incubate the cells in the dark at 4 °C for 15 min before adding 400 µL of Binding Buffer. Transfer the mixture to a flow cytometry tube containing 5 µL of propidium iodide (PI) Dye Solution (10 mg/mL). Detect apoptotic cells 5 min later by flow cytometry11.
- Record red fluorescence at the 488 nm excitation wave, input them into a computer to analyze the percentage of each cell cycle in 5,000 cells, and then print the peaks of apoptotic cells.
- Collect red and green fluorescence by annexin V and PI double-labeling, input them into the computer to analyze, and then print the dot plot.
6. Detection of U251 glioma cell cycle distribution
- Wash the above-mentioned cells 2x with 1 mL of PBS before treating them with trypsin.
- When a rounded cell morphology is detected by light microscopy, add DMEM containing 10% FBS.
- Centrifuge the cells for 5 min at 200 × g at room temperature.
- Remove the supernatant and resuspend these cells in 1 mL of PBS before adding precooled 75% ethanol solution.
- Incubate the mixture for at least 4 h or overnight at −20 °C.
- Wash the cells 2x with ice-cold PBS and 180 µL of EDTA (0.1 mM, 3.7 mg of EDTA + 100 mL of PBS), 20 µL of RNase A (10 mg/mL), 35 µL of Triton X-100 (2%, 2 mL of Triton + 98 mL of FBS),and 96.5 µL of PBS. Then, add 17.5 µL of PI solution (1 mg/mL).
- Incubate the mixture at 4 °C in the dark for 10 min.
- Wash the cells in 200 µL of PBS, and then place them in a flow cytometer to assess the cell cycle distribution, as previously described12.
- Operate the flow cytometer in dual-laser, three-dimensional space, excitation mode with a 22 µm x 66 µm and 13 µm x 66 µm spot size. Use a flow room of 430 µm x 180 µm, 300-1,100 nm spectrum, ≤100 MESF detectability, and CV <2% resolution. Then, expose the cells to 488 nm excitation light and detect and measure the fluorescence signals with instrument software to determine the cell cycle distribution13.
- Determine the DNA content, and then according to the DNA content, analyze the cell cycle.
7. Statistical analysis
- Perform statistical analyses.
- Present the data as mean ± standard deviation.
- Use a Student's t-test to compare the groups, with statistical significance set as P < 0.05.
Results
Culture of U251 glioma cells
U251 glioma cells had a fusiform shape 24 h to 48 h after culture in DMEM and were adherent. These cells were used for further study (Figure 1).
Glioma cell morphology and count
The cell counts for the U251 glioma cells in the HBO combined with X-ray (2 Gy) group were significantly lower than that for the X-ray (2 Gy) group after 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h of cell culture (all P < 0....
Discussion
The glioma cell line U251 is one of the most classical human glioma cell lines and is widely used as a glioma model in many studies.
Effects of HBO on U251 glioma cell proliferation
HBO typically refers to breathing pure oxygen (100% oxygen concentration) in a sealed chamber with a pressure 1.5-3-fold higher than normal atmospheric pressure, which can increase oxygen content in microvascular plasma14. For patients with glioma, combining radiothera...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
None.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Binding Buffer | Dickinson and Company | RH10 9RR | |
| CCK-8 test kit | DOJINDO | NJ | Cell counting assay |
| CELL FIT | cell cycle analysis (DNA content) | ||
| CELLQUEST | apoptotic cell analysis | ||
| DMEM and Annexin V-FITC | Gibco BRL | ||
| flow cytometer | Dickinson | ||
| Glioma U251 and U87 cell line | Shanghai Institute of Cell Biology | ||
| hyperbaric oxygen chamber | Hongyuan Institute | ||
| medical linear accelerator | Elekta Limited Company | ||
| microplate reader | |||
| MOD FITLT formac v1.01 | cell analysis--cell cycle phase | ||
| trypsin | Hyclone Laboratories Inc |
References
- Louis, D. N., et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathologica. 131 (6), 803-820 (2016).
- Sun, M. Z., et al. Survival impact of time to initiation of chemoradiotherapy after resection of newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Journal of Neurosurgery. 122 (5), 1144-1150 (2015).
- Hegi, M. E., et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temoozolomide in glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine. 352 (10), 997-1003 (2005).
- Zhu, Y., et al. Involvement of decreased hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity and resultant G1-S cell cycle transition in radioresistance of perinecrotic tumor cells. Oncogene. 32 (16), 2058-2068 (2013).
- Kohshi, K., et al. Potential roles of hyperbaric oxygenation in the treatments of brain tumors. Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine. 40 (4), 351-362 (2013).
- Aghajan, Y., Grover, I., Gorsi, H., Tumblin, M., Crawford, J. R. Use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in pediatric neuro-oncology: a single institutional experience. Journal Neurooncology. 141 (1), 151-158 (2019).
- Ding, J. B., Chen, J. R., Xu, H. Z., Qin, Z. Y. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on the growth of intracranial glioma in rats. Chinese Medical Journal. 128 (23), 3197-3203 (2015).
- Wang, Y. G., et al. Hyperbaric oxygen promotes malignant glioma cell growth and inhibits cell apoptosis. Oncology Letters. 10 (1), 189-195 (2015).
- Milovanova, T. N., et al. Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vasculogenic stem cell growth and differentiation in vivo. Journal of Applied Physiology. 106 (2), 711-728 (2009).
- Conconi, M. T., et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on proliferative and apoptotic activities and reactive oxygen species generation in mouse fibroblast 3T3/J2 cell line. Journal of Investigative Medicine. 51 (4), 227-232 (2003).
- Vermes, I., Haanen, C., Steffiens-Nakken, H., Reutellingsperger, C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. Journal of Immunological Methods. 184 (1), 39-51 (1995).
- Cui, W., Niu, F. -. L., He, L. -. Y., W, S. -. R. Comparison of two softwares for analysing apoptosis with flow cytometry. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 24 (6), 45-47 (2001).
- Cecchini, M. J., Amiri, M., Dick, F. A. Analysis of cell cycle position in mammalian cells. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (59), e3491 (2012).
- Resanovic, I., et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on inducible nitric oxide synthase activity/expression in lymphocytes of type 1 diabetes patients: A prospective pilot study. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2019, 2328505 (2019).
- Stuhr, L. E., et al. Hyperoxia retards growth and induces apoptosis, changes in vascular density and gene expression in transplanted gliomas in nude rats. Journal of Neuro-Oncology. 85 (2), 191-202 (2007).
- Biollaz, G., et al. Site-specific anti-tumor immunity: differences in DC function, TGF-beta production and numbers of intratumoral Foxp3+ Treg. European Journal of Immunology. 39 (5), 1323-1333 (2009).
- McKenna, F. W., Ahmad, S. Fitting techniques of cell survival curves in high-dose region for use in stereotactic body radiation therapy. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 54 (6), 1593-1608 (2009).
- Malaise, E. P., Lambin, P., Joiner, M. C. Radiosensitivity of human cell lines to small doses. Are there some clinical implications. Radiation Research. 138, S25-S27 (1994).
- Björk-Eriksson, T., West, C., Karlsson, E., Mercke, C. Tumor radiosensitivity (SF2) is a prognostic factor for local control in head and neck cancers. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 46 (1), 13-19 (2000).
- Bromfield, G. P., Meng, A., Warde, P., Bristow, R. G. Cell death in irradiated prostate epithelial cells: Role of apoptotic and clonogenic cell kill. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases. 6 (1), 73-85 (2003).
- Kalns, J. E., Piepmeier, E. H. Exposure to hyperbaric oxygen induces cell cycle perturbation in prostate cancer cells. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal. 35 (2), 98-101 (1999).
- Lakka, S. S., et al. Inhibition of cathepsin B and MMP-9 gene expression in glioblastoma cell line via RNA interference reduces tumor cell invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 23 (27), 4681-4689 (2004).
- Li, S., Shi, D., Zhang, L., Yang, F., Cheng, G. Oridonin enhances the radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells by upregulating Bax and downregulating Bcl-2. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 16 (6), 4859-4864 (2018).
- Campbell, K. J., Tait, S. W. G. Targeting BCL-2 regulated apoptosis in cancer. Open Biology. 8 (5), 180002 (2018).
- Rengarajan, T., et al. D-pinitol promotes apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via induction of p53 and Bax and inhibition of Bcl-2 and NF-κB. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 15 (4), 1757-1762 (2014).
- Shinagawa, A., et al. The potent peptide antagonist to angiogenesis, C16Y and cisplatin act synergistically in the down-regulation of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and the induction of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 39 (6), 135-164 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved