Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Un enfoque visual para inducir dolicoectasia en ratones para modelar la disfunción cerebrovascular mediada por grandes vasos
En este artículo
Resumen
Demostramos la inducción química de la dilatación de grandes vasos sanguíneos en ratones como modelo para investigar la disfunción cerebrovascular, que se puede utilizar para el modelado de la demencia vascular y la enfermedad de Alzheimer. También demostramos la visualización de la vasculatura mediante la inyección de compuesto de caucho de silicona y proporcionamos una guía visual clara para medir los cambios en el tamaño de los vasos sanguíneos.
Resumen
El hematoencefálico (BBB) es un sistema crucial que regula la circulación selectiva del cerebro con la periferia, por ejemplo, permitiendo la entrada de nutrientes necesarios y la expulsión de aminoácidos o toxinas excesivas del cerebro. Para modelar cómo la BHE puede verse comprometida en enfermedades como la demencia vascular (VAD) o la enfermedad de Alzheimer (EA), los investigadores desarrollaron métodos novedosos para modelar la dilatación de los vasos. Una BHE comprometida en estos estados de enfermedad puede ser perjudicial y dar lugar a la desregulación de la BHE, lo que conduce a consecuencias adversas y patológicas que afectan a la función cerebral. Pudimos modificar una técnica existente que nos permitía inyectar directamente en la Cisterna magna (CM) para inducir la dilatación de los vasos sanguíneos utilizando elastasa y romper las uniones estrechas (TJ) de la BBB. Con este método, pudimos ver varias métricas de éxito con respecto a las técnicas anteriores, incluida la dilatación constante de los vasos sanguíneos, la reducción de la mortalidad o la mejora de la recuperación, y la mejora del agente de relleno/opacificante, un compuesto de caucho de silicona, para el etiquetado de los vasos sanguíneos para el análisis de dilatación. Este método mínimamente invasivo modificado ha tenido resultados prometedores, con un aumento del 19% al 32% en la dilatación sostenida de los vasos sanguíneos grandes en ratones de 2 semanas a 3 meses después de la inyección. Esta mejora contrasta con estudios previos, que mostraron un aumento de la dilatación solo a las 2 semanas. Los datos adicionales sugieren una expansión sostenida incluso después de 9,5 meses. Este aumento se confirmó comparando el diámetro de los vasos sanguíneos de la elastasa y el grupo inyectado en el vehículo. En general, esta técnica es valiosa para estudiar los trastornos patológicos que afectan al sistema nervioso central (SNC) utilizando modelos animales.
Introducción
Las células endoteliales microvasculares que recubren los capilares cerebrales son los principales componentes para formar la barrera hematoencefálica (BBB)1, que desempeña un papel crucial en la regulación de lo que entra o sale de la circulación cerebral con la periferia. Los nutrientes esenciales necesarios para el tejido nervioso pueden entrar en la BBB, mientras que algunos aminoácidos esenciales como el glutamato son expulsados del cerebro, ya que las altas concentraciones pueden causar un daño neuroexcitatorio permanente enel tejido cerebral. En condiciones fisiológicas normales, la BHE limita la cantidad de proteínas plasmáticas como la albúmina 3,4 y la protrombina para que no entren en el cerebro, ya que pueden tener efectos perjudiciales 5,6,7. Por último, la BHE protege al cerebro de las neurotoxinas que circulan en la periferia, como los xenobióticos procedentes de los alimentos o del medio ambiente1. En general, el daño a los tejidos cerebrales es irreversible, y el envejecimiento que se correlaciona con bajos niveles de neurogénesis8 destaca la importancia de la BHE para proteger y prevenir que cualquier factor acelere el proceso neurodegenerativo.
En la dolicoectasia (o dilatación de grandes vasos sanguíneos), se observa una disminución de la elasticidad de los vasos, lo que da lugar a que los vasos sufran cambios morfológicos, lo que los hace disfuncionales9 y conduce a una reducción del flujo sanguíneo en el cerebro. Esta reducción en el flujo sanguíneo disminuye posteriormente el suministro de oxígeno y glucosa, lo que en última instancia desencadena daños en la BHE a través de la activación de astrocitos reactivos10. Cuando la lámina de elastina interna de los vasos está dañada por la dolicoectasia11, es necesaria la estimulación repetida del factor de crecimiento endotelial vascular (VEGF) para la angiogénesis. Esto puede conducir a la formación de vasos permeables y, en última instancia, resultar en una angiogénesis patológica, caracterizada por el desarrollo de vasos defectuosos12. Durante la angiogénesis patológica, cuando los vasos sanguíneos se vuelven defectuosos, un mecanismo compensatorio parece restaurar la integridad de los vasos mediante la regulación positiva de las proteínas de unión estrecha. Sin embargo, este proceso puede alterar inadvertidamente la BHE cuando se pierde la integridad estructural de un vaso sanguíneo13. Esto puede ocurrir a través de una mayor alteración de la BHE y la promoción de la producción de placa amiloide14. Además, la fuga desde la periferia puede causar neuroinflamación15, lo que resulta en degeneración neuronal y posterior pérdida de memoria.
Estructuralmente, la protección que proporciona la BHE es a través de las uniones estrechas que impiden que los agentes xenobióticos de la sangre entren en el cerebro. Al permitir que ciertas sustancias ingresen al cerebro, la BHE lo hace principalmente a través de dos procesos principales, difusión pasiva o canales específicos (como canales iónicos y transportadores)1. En la EA, las investigaciones han demostrado que un sistema vascular disfuncional juega un papel importante en la progresión de la enfermedad12,13. La formación de placas de beta-amiloide (Aβ) y la neurodegeneración pueden ser el resultado de la descomposición de la BHE12,13 y de alteraciones en el flujo sanguíneo cerebral16. Se puede observar una reducción en el flujo sanguíneo cerebral en individuos ancianos diagnosticados con demencia vascular y EA17,18. El daño a la barrera hematoencefálica (BBB) junto con un flujo sanguíneo cerebral (CBF) disfuncional puede contribuir al aumento de la concentración de Aβ en el cerebro, acompañado de la infiltración de materiales extraños de la circulación periférica19.
Para investigar la patogénesis de enfermedades neurológicas como la EA y la demencia vascular (DV), se desarrollan modelos para replicar la enfermedad. Los modelos in vitro se utilizan ampliamente, pero carecen del entorno biológico para el modelado extensivo de enfermedades como la población de células mixtas, por lo que se requiere la importancia de los modelos in vivo. Los ratones se usan comúnmente debido a su facilidad de manipulación genética para generar propiedades similares a las humanas (por ejemplo, patología) en enfermedades. Con el progreso que se ha logrado hasta ahora, todavía existe una necesidad continua de modelos mejorados para emular fenotipos de enfermedades como la dilatación de vasos grandes y su papel en la EA. Para ello, vimos una oportunidad y modificamos una técnica que implicaba la inyección de elastasa en la Cisterna magna de ratones20,21. La elastasa es una enzima que se ha demostrado que descompone la elastina en el tejido conectivo22 y en las uniones estrechas circundantes23. La Cisterna magna fue elegida como punto de inyección debido a que se encuentra directamente sobre el círculo de Willis, el vaso sanguíneo más grande del cerebro. Al inyectar elastasa en la Cisterna magna, podemos comprometer la BHE y los vasos sanguíneos rompiendo las uniones estrechas e induciendo la dilatación de los vasos sanguíneos (círculo de Willis)24,25. La combinación de esta técnica con el uso de un modelo de patología en ratones con EA, para mejorar la comprensión de la patogénesis del componente vascular de la EA, puede proporcionar información valiosa sobre las complejas interacciones e influencias entre estas dos patologías distintas.
Estudios previos han demostrado casos en los que los pacientes muestran tanto las características patológicas de la EA como de la VaD, una condición típicamente conocida como demencia mixta26,27. Por lo tanto, la comprensión de los mecanismos interconectados entre ambas afecciones puede ofrecer una perspectiva más completa sobre la progresión y manifestación de estos trastornos neurodegenerativos, mejora nuestra comprensión de los mecanismos subyacentes y las posibles estrategias terapéuticas. Para ello, demostramos la aplicación de elastasa en un modelo murino de patología de EA (AppNL-F) para identificar cambios vasculares.
Protocolo
Para este estudio se utilizaron ratonesApp NL-F(3 meses de edad) que expresan placa amiloide humana a nivel fisiológico, aunque este sistema se puede utilizar con cualquier modelo de roedores. Todos los procedimientos con animales fueron aprobados por el Comité de Cuidado de Animales de CAMH (Protocolo # 843) y estaban de acuerdo con los estándares éticos de las directrices del Consejo Canadiense de Cuidado de Animales. Los ratones se criaron en casa y se mantuvieron en un ciclo de luz-oscuridad de 12 horas con acceso ad libitum a comida y agua.
1. Procedimiento para la inyección de Cisterna magna (CM)
- Procedimiento quirúrgico
- Colocar el ratón (APPNL-F, ambos sexos, 3 meses) en una cámara de inducción de anestesia durante 1 min.
NOTA: Enjuague la cámara con isoflurano al 5% mezclado con oxígeno al 1% durante al menos 1 min. - Después de anestesiar al ratón, retire al animal de la cámara y colóquelo sobre un paño quirúrgico nuevo y mantenga la anestesia (isoflurano, 2,5%-3%) colocando un cono nasal sobre la nariz.
NOTA: Verifique la profundidad de la anestesia pellizcando el dedo del pie para asegurarse de que no haya reflejos. - Aplique ungüento oftálmico para prevenir la sequedad. A continuación, inyectar por vía subcutánea 0,1 mL de bupivacaína (anestésico local; 1-2 mg/kg 0,125%, con una relación de dilución de 1:2) en el sitio de la incisión y Metacam (analgésico; 5 mg/kg, con una relación de dilución de 1:10). Mantenga al animal hidratado inyectando 0,5 mL de solución salina por vía subcutánea antes de realizar el procedimiento para compensar cualquier posible pérdida de sangre durante la cirugía.
- Para obtener un sitio de incisión limpio, afeite el cuello en la base del hueso occipital, limpie la superficie con PBS estéril y transfiera al sujeto al marco estereotáxico en posición prona.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que la anestesia se mantenga a través del cono estereotáxico de la nariz. - Coloque la barra nasal del marco estereotáxico en la parte superior del mouse para proporcionar estabilidad y asegurar que los dientes superiores estén sujetos.
- Coloque la cabeza del animal en un ángulo de 120° con respecto al cuerpo para elevar y distender la nuca para exponer el área quirúrgica de interés.
- Limpie el sitio quirúrgico con Betadine scrub 3x, etanol al 70% 3x y solución de betadine 1x con gasa estéril de 2 pulgadas x 2 pulgadas.
- Dobla la piel suavemente con la ayuda de unas pinzas y haz una pequeña incisión (1 cm) con unas tijeras quirúrgicas.
NOTA: Esto debe revelar la línea media de la nuca. - Pasa con cuidado el bisturí a lo largo de la línea media para cortar los músculos. Luego, con unas pinzas, separa suavemente los músculos separándolos hacia la izquierda y hacia la derecha.
NOTA: Esto debería revelar la Cisterna magna (triángulo invertido) que se encuentra debajo de la base del cráneo (Figura 1).
- Colocar el ratón (APPNL-F, ambos sexos, 3 meses) en una cámara de inducción de anestesia durante 1 min.
- Preparación de la elastasa
NOTA: El paquete de elastasa (en forma de polvo) que se ordenó contenía 250 unidades (U). La cantidad de elastasa a inyectar en cada animal es de 2,5 μL. La cantidad de elastasa que se supone que debe estar en los 2,5 μL debe ser de 15 miliunidades mU.- Primero calcule la concentración de la solución a inyectar.
Concentración = masa/volumen
= 15 mU/2,5 μL
= 6 mU/μL
Por lo tanto, la concentración que se requiere es de 6 mU/μL. - La cantidad de elastasa es de 250 u y el estudio trabaja con miliUnits, por lo que convierte las unidades a miliUnits lo que da 250000 mU.
- Después de tener una masa de 250000 mU y una concentración de 6 mU/uL, calcule el volumen (PBS) que requeriría diluir la elastasa y mantener una concentración de 6 mU/uL.
- Usando la misma fórmula anterior, reorganiza para resolver el volumen:
Volumen = masa/Conc.
= 250000 mU/ 6 mU/μL
= 41666,67 μL - Dado que es difícil pipetear 41666,67 μL, simplemente conviértalo a mililitros dividiéndolo por 1000 para obtener 41,66667 mL para obtener una solución 1x.
- Para hacer la solución más concentrada, auméntela 10x o 100x.
- Cree una solución 10x, ya que es más fácil trabajar con ella (ver más abajo).
10x solución ---------- 4,166667 mL (conc.)
- Coloque los 250 U en un tubo alícuota de 5 mL y agregue 4.167 mL de PBS estéril en el tubo alícuota para hacer la solución madre 10x.
- Pipetear 10 μL de solución madre y colocar en 100 tubos alícuotas dando 1000 μL de la solución madre de 4,167 mL. Almacene los tubos a -20 °C.
- Almacene el resto de la solución madre en tubos alícuotas a 100 μL por tubo y almacene en el congelador a -20 °C.
NOTA: Las soluciones son estables a -20 °C durante un máximo de 6 meses sin pérdidas significativas de actividad. Además, es importante tener en cuenta que la congelación y descongelación excesivas de la elastasa pueden reducir la estabilidad. Por lo tanto, para evitar que eso suceda, la solución madre se puede dividir antes de congelar de modo que solo sea necesario descongelar una muestra a la vez para la inyección. - Después de descongelar uno de los tubos alícuotas que contiene 10 μL de una solución 10x, agregue 90 μL de PBS estéril para obtener una solución 1x de 100 μL.
- Si el tubo alícuota que contiene 100 μL de una solución 10x se descongeló en su lugar, simplemente agregue 900 μL de PBS para obtener 1000 μL, que es una solución 1x. Almacene cualquiera de las soluciones a 4 °C durante 1 semana.
- Primero calcule la concentración de la solución a inyectar.
- Inyectando en la Cisterna magna
NOTA: Limpie la jeringa Hamilton antes de cargarla con elastasa cargando y aspirando con agua destilada 5 veces, luego etanol 5 veces y finalmente agua destilada 5 veces.- Cargue la jeringa Hamilton con 2,5 μL de elastasa (concentración de 15 mU) y asegúrese de que no haya burbujas de aire.
- Inserte lentamente la jeringa con el bisel hacia arriba en el centro de la Cisterna magna.
NOTA: Evite perforar los vasos sanguíneos que atraviesan la Cisterna magna. - Después de la perforación, retire el bisel. Esto facilitará la liberación de una pequeña cantidad de líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR). Use un hisopo de algodón estéril para absorber el exceso de líquido cefalorraquídeo.
- Vuelva a insertar el bisel en el sitio de punción, inyecte lentamente elastasa o vehículo durante 1 minuto en la Cisterna magna y deje la aguja en su lugar durante 1 minuto para evitar cualquier fuga de elastasa.
- Después de retirar el bisel, cierre el sitio de la incisión con una sutura quirúrgica no absorbible (#4-0 con aguja de 3/8") y apague el anestésico.
- Retire al animal del marco estereotáxico y colóquelo en una almohadilla térmica tibia a 37 ° C hasta que el sujeto se recupere.
NOTA: Se recomienda otra dosis de Metacam después de la cirugía para ayudar con el dolor durante la recuperación postquirúrgica.
2. Inyección de compuesto de caucho de silicona y recolección de tejidos
- Anestesiar al animal con una sobredosis de avertina (1 mL, 125-250 mg/kg).
NOTA: Apriete el dedo del pie para asegurarse de que cesen los reflejos. - Coloque al animal en un pañal y asegure todas las extremidades con cinta quirúrgica con la cavidad torácica hacia arriba
- Abra la cavidad torácica con pinzas y tijeras para exponer el corazón.
- Insertar una aguja roma de 23 G en el ventrículo izquierdo del corazón y perfundir con PBS infundido con heparina (100 U/mL) durante 4 min para limpiar los vasos sanguíneos utilizando una bomba de microperfusión.
- Reemplace el frasco tampón por uno que contenga un 4% de paraformaldehído (PFA) (compuesto en PBS) y perfunda durante otros 4 minutos.
- Prepare la solución de compuesto de caucho de silicona (amarillo) combinando 5 mL de compuesto con 5 mL del diluyente en un tubo de 50 mL. Mezclar bien antes de usar.
- Llene una jeringa de 10 ml con 10 ml de compuesto de caucho de silicona. Conecte la jeringa a la manguera conectada a una aguja roma de 23 g e inyecte cuidadosamente la solución manualmente en el corazón.
NOTA: Debido a la alta viscosidad del compuesto de caucho de silicona, es importante utilizar una jeringa de barril más grande o la presión será demasiado grande para empujar el émbolo. - Retire la cabeza del ratón después de la inyección y guárdela a 4 °C durante la noche, permitiendo que el compuesto de caucho de silicona se cure en los recipientes.
- Al día siguiente, retire suavemente el cráneo del ratón (preferiblemente con pinzas finas), extraiga el cerebro e incube en PFA al 4% durante la noche a temperatura ambiente (RT).
- Después de una incubación de 24 h en PFA, lavar el cerebro en PBS 3x, colocar en sacarosa al 30% y almacenar a 4 °C.
3. Análisis cuantitativo
- Para capturar imágenes de alta calidad del Círculo de Willis en todo el cerebro (Figura 3):
- Retira el cerebro de la solución de sacarosa. Seque bien el cerebro con una toalla de papel para absorber la humedad de la superficie.
- Coloque el cerebro en una cortadora de cerebros. Coloque el cortador de cerebros bajo un microscopio óptico equipado con una cámara.
- Enfoque el microscopio a una resolución clara y de alta resolución del Círculo de Willis.
- Utilice un software de análisis de imágenes con una regla de referencia de 10 cm para medir aproximadamente 1 cm y anotar el recuento de píxeles. Establezca la escala de 1 cm en función de esta medida, luego mida el grosor de la arteria basilar horizontalmente para encontrar su diámetro.
- Utilice un software de densitometría de píxeles estándar para analizar la imagen. Mida (en centímetros) cinco lecturas separadas de la arteria basilar utilizando un software de análisis de imágenes y calcule el promedio para obtener una representación precisa del diámetro de la arteria basilar.
- Utilice un análisis de varianza de 2 vías (ANOVA) para comparar el cambio promedio en el diámetro entre la elastasa y el grupo de control.
- Calcule el cambio porcentual en el diámetro usando la siguiente fórmula 21:
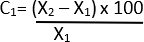
C = cambio relativo
X1 = Valor inicial (Vehículo)
X2 = Valor final (elastasa)
Considere que los valores de P inferiores a 0,05 son estadísticamente significativos. Realizar todos los análisis estadísticos utilizando un software de análisis estadístico.
- Calcule el cambio porcentual en el diámetro usando la siguiente fórmula 21:
4. Eliminación del compuesto de caucho de silicona mediante deshidratación con alcohol
NOTA: Es importante deshidratar el cerebro para ayudar a eliminar el exceso de compuesto de caucho de silicona del vaso sanguíneo, lo que puede mejorar potencialmente la calidad de la inmunotinción.
- Lave los sesos 3 veces con PBS para eliminar la sacarosa.
- Coloque el cerebro en etanol al 25%, 50%, 75%, 95% y absoluto durante 24 h en cada concentración, durante un tiempo total de 5 días.
- Después de la deshidratación del tejido, coloque el tejido en salicilato de metilo (conc. ≤100%) durante 12-24 h. El etanol y el salicilato de metilo permitirán eliminar el exceso de silicona en el tejido.
- Lave el cerebro en PBS 3 veces para eliminar los productos químicos residuales y déjelo toda la noche en una mecedora a 4 °C en PBS fresco.
- Coloque el cerebro en sacarosa y guárdelo a 4 °C antes de la sección y la inmunotinción.
5. Tinción inmunohistoquímica
- Sección de cerebros
- Antes de la inmunosección, permita que el cerebro se asiente en el fondo del tubo lleno de sacarosa.
- Congele el cerebro en la plataforma del micrótomo utilizando un compuesto de temperatura de corte óptima (OCT) rodeado de hielo seco. Corta el cerebro en secciones de 40 μm con la cuchilla del micrótomo.
- Transfiera cada sección a una placa de 96 pocillos que contenga crioprotector para evitar la congelación con un pincel de punta fina.
- Selle firmemente la placa de 96 pocillos con una envoltura de plástico. Guarde la placa sellada en un congelador a -20 °C.
- Tinción de inmunofluorescencia (usando NeuN como ejemplo)
- Coloque las secciones en un plato de 24 pocillos. Realizar tres lavados con PBS para eliminar el crioprotector.
- Para evitar la unión inespecífica, incubar durante 1 h en RT utilizando una solución bloqueante que contenga un 2% de suero de cabra, un 0,1% de Triton-X 100 y un 1% de BSA.
- Prepare todos los componentes en PBS.
NOTA: El anticuerpo primario utilizado incluyó anti-NeuN monoclonal de ratón con una dilución de 1:500. El anticuerpo secundario utilizado fue el policlonal anti-ratón 568 de cabra con una dilución 1:200. - Diluir el anti-NeuN monoclonal de ratón en la solución de bloqueo mencionada anteriormente.
- Agregue el anticuerpo diluido a cada pocillo. Incubar durante la noche a 4 °C, protegido de la luz por papel de aluminio.
- Después de la incubación primaria, lave las secciones 3 veces con PBS. Diluir el anti-ratón policlonal de cabra 568 en la misma solución de bloqueo.
- Agregue el anticuerpo diluido a cada pocillo. Incubar durante 2 h a temperatura ambiente, protegido de la luz por papel de aluminio.
- Lave las secciones 3 veces con PBS después de la incubación secundaria.
- Prepárese para el montaje transfiriendo lentamente las secciones a las guías con pinceles finos. Deje que todas las secciones se sequen.
- Aplique 125-150 μL de medio de montaje antidecoloración una vez que las secciones estén secas. Coloque con cuidado los cubreobjetos.
- Deje que los portaobjetos se sequen durante 24 horas en RT en la oscuridad, sellando los bordes con esmalte de uñas. Capture imágenes fluorescentes utilizando software de imágenes.
Resultados
Logramos localizar la Cisterna magna debajo de la región occipital del cráneo después de colocar cuidadosamente al ratón en el marco estereotáxico y diseccionar los músculos. Esta estructura anatómica, que se asemeja a un triángulo invertido y está resaltada en amarillo, está situada debajo de la base del cráneo (Figura 1). Para garantizar la precisión y evitar cualquier daño al tejido cerebral, se insertaron suavemente 1-2 mm del bisel de la jeringa Hamilton en la Cisterna magn...
Discusión
Este artículo demuestra un protocolo mejorado para la dilatación cerebrovascular, proporcionando un enfoque preciso y directo para la inyección de elastasa en la Cisterna magna de ratones. Este punto anatómico sirve como puerta de entrada directa al líquido cefalorraquídeo, ofreciendo una valiosa vía para la investigación de diferentes enfermedades neurológicas. Una de las principales ventajas de esta técnica modificada es que la inyección de una sola dosis de elastasa en la Cisterna magna de ratones fue capaz...
Divulgaciones
No hay conflicto de intereses.
Agradecimientos
Este estudio fue posible gracias a las invaluables contribuciones de Stephanie Tam, quien brindó apoyo para ayudar con las cirugías. Le expresamos nuestro más sincero agradecimiento por su ayuda. A los Institutos Nacionales de Salud (AG066162) por su apoyo a esta investigación.
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 23 G catheter | University Medstore | 2546-CABD305145 | Needed for perfusion (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Absolute ethanol | University Medstore | https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz | For removing the microfil |
| Betadine scrub | # | https://www.pittsborofeed.com/products/betadine-surgical-scrub | Sterilization |
| Betadine solution | Amazon | https://www.amazon.ca/Povidone-Iodine-10-Topical-Solution-100ml/dp/B09DTKJGHW | Sterilization |
| Bupivacaine | Provided by animal facility | N/A | Analgesic |
| Clippers | BrainTree Scientific Inc | CLP-41590 | Shave fur |
| Cotton Q-tip | University Medstore | 1962 | For surgery (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Elastase | Sigma-aldrich | E7885 | Used for the dilatation of blood vessel |
| Ethanol | University Medstore | 39752-P016-EAAN | Sterilization (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Goat anti-mouse 568 | Invitrogen | A11004 | For staining mature neurons |
| Graphpad prism 10 | Graphpad prism 10 | https://www.graphpad.com/ | Statistical analysis software |
| Hamilton syringe | Sigma-aldrich | 28614-U | Injection elastase |
| Heat pad | Amazon | https://www.amazon.ca/iPower-Temperature-Controller-Terrarium-Amphibians/dp/B08L4DBFFZ | Maintain body temperature |
| ImageJ software | Fiji Imagej software | imagej.net (USA) | Image analysis software |
| Induction chamber | Provided by animal facility | N/A | Anesthesia induction |
| Metacam | Provided by animal facility | N/A | Analgesic |
| Methyl salicylate | Sigma-aldrich | M6752 | For removing the microfil |
| Microfil | Flow Tech, Carver, Massachusetts | https://www.flowtech-inc.com/order/ | Dye (yellow) |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-NeuN | Millipore Sigma | MAB377 | For staining mature neurons |
| Olympus VS200 slide scanner and VSI software. | Olympus Life Science | https://www.olympus-lifescience.com/en/downloads/detail-iframe/?0[downloads][id]=847254104 | Imaging software |
| Paraformaldehyde | University Medstore | PAR070.1 | For protein fixation (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Perfusion pump | VWR International | https://pr.vwr.com/store/product/4787969/vwr-variable-speed-peristaltic-pumps | Needed for perfusion |
| Scalpel | University Medstore | 2580-M90-10 | For surgery (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Stereotaxic | Provided by animal facility | N/A | So secure the animal for surgery |
| Surgical scissor | University Medstore | 22751-A9-240 | For surgery (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| Surgical tape | University Medstore | https://www.amazon.ca/3M-Micropore-Tape-1530-2-Rolls/dp/B0082A9GS2 | Secure the animal on the diaper |
| Sutures | University Medstore | 2297-VS881 | For surgery (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
| X2 tweezers | University Medstore | 7731-A10-612 | For surgery (https://www.uoftmedstore.com/index.sz) |
Referencias
- Kadry, H., Noorani, B., Cucullo, L. A blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 17 (1), 69 (2020).
- Sethi, B., Kumar, V., Mahato, K., Coulter, D. W., Mahato, R. I. Recent advances in drug delivery and targeting to the brain. J Control Release. 350, 668-687 (2022).
- Vagnucci, A. H., Li, W. W. Alzheimer's disease and angiogenesis. Lancet. 361 (9357), 605-608 (2003).
- Banks, W. A., et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced blood-brain barrier disruption: roles of cyclooxygenase, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and elements of the neurovascular unit. J Neuroinflamm. 12, 223 (2015).
- Archie, S. R., Shoyaib, A. A., Cucullo, L. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in CNS disorders and putative therapeutic targets: an overview. Pharmaceutics. 13 (11), 1779 (2021).
- Jefferies, W. A., Price, K. A., Biron, K. E., Fenninger, F., Pfeifer, C. G., Dickstein, D. L. Adjusting the compass: new insights into the role of angiogenesis in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 5 (6), 64 (2013).
- Kook, S. Y., Seok-Hong, H., Moon, M., Mook-Jung, I. Disruption of blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Tissue Barriers. 1 (2), e23993 (2013).
- Kempermann, G. Activity dependency and aging in the regulation of adult neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7 (11), a018929 (2015).
- Del Brutto, V. J., Ortiz, J. G., Biller, J. Intracranial arterial dolichoectasia. Front Neurol. 8, 344 (2017).
- de la Torre, J. C., Mussivand, T. Can disturbed brain microcirculation cause Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Res. 15 (3), 146-153 (1993).
- Gutierrez, J., Sacco, R. L., Wright, C. B. Dolichoectasia-an evolving arterial disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 7 (1), 41-50 (2011).
- Desai, B. S., Schneider, J. A., Li, J. L., Carvey, P. M., Hendey, B. Evidence of angiogenic vessels in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm. 116 (5), 587-597 (2009).
- Biron, K. E., Dickstein, D. L., Gopaul, R., Jefferies, W. A. Amyloid triggers extensive cerebral angiogenesis causing blood brain barrier permeability and hypervascularity in Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 6 (8), e23789 (2011).
- Zenaro, E., Piacentino, G., Constantin, G. The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 107, 41-56 (2017).
- Brandl, S., Reindl, M. Blood-Brain barrier breakdown in neuroinflammation: current in vitro models. Int J Mol Sci. 24 (16), 12699 (2023).
- Austin, B. P., et al. Effects of hypoperfusion in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 26, 123-133 (2011).
- Jagust, W. J., Budinger, T. F., Reed, B. R. The diagnosis of dementia with single photon emission computed tomography. Arch Neurol. 44 (3), 258-262 (1987).
- Schuff, N., et al. Cerebral blood flow in ischemic vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease, measured by arterial spin-labeling magnetic resonance imaging. Alzheimers Dement. 5 (6), 454-462 (2009).
- Singh, C., Pfeifer, C. G., Jefferies, W. A. Pathogenic Angiogenic Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease. Physiologic and Pathologic Angiogenesis - Signaling Mechanisms and Targeted Therapy. , (2017).
- Dai, D., Kadirvel, R., Rezek, I., Ding, Y. H., Lingineni, R., Kallmes, D. Elastase-induced intracranial dolichoectasia model in mice. Neurosurgery. 76 (3), 337-343 (2015).
- Liu, F. X., et al. Modified protocol for establishment of intracranial arterial Dolichoectasia model by injection of elastase into cerebellomedullary cistern in mice. Front Neurol. 13, 860541 (2022).
- Lee, A. Y., Han, B., Lamm, S. D., Fierro, C. A., Han, H. Effects of elastin degradation and surrounding matrix support on artery stability. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302 (4), H873-H884 (2012).
- Li, Y., et al. The role of elastase in corneal epithelial barrier dysfunction caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 62 (9), 7 (2021).
- Temesvári, P., Ábrahám, C. S., Gellén, J., Speer, C. P., Kovács, J., Megyeri, P. Elastase given intracisternally opens blood-brain barrier in newborn piglets. Biol Neonatol. 67 (1), 59-63 (1995).
- Takata, F., et al. Elevated permeability of the blood-brain barrier in mice intratracheally administered porcine pancreatic elastase. J Pharmacol Sci. 129 (1), 78-81 (2015).
- Hanyu, H. Diagnosis and treatment of mixed dementia. Brain Nerve. 64 (9), 1047-1055 (2012).
- Chui, H. C., Ramirez-Gomez, L. Clinical and imaging features of mixed alzheimer and vascular pathologies. Alzheimers Res Ther. 7 (1), 21 (2015).
- Saito, T., et al. Single app knock-in mouse models of alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci. 17 (5), 661-663 (2014).
- Dobrin, P. B., Canfield, T. R. Elastase, collagenase, and the biaxial elastic properties of dog carotid artery. Am J Physiol. 247, H124-H131 (1984).
- Wagenseil, J. E., Ciliberto, C. H., Knutsen, R. H., Levy, M. A., Kovacs, A., Mecham, R. P. Reduced vessel elasticity alters cardiovascular structure and function in newborn mice. Circ Res. 104 (10), 1217-1224 (2009).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados