A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
שחזור אמוניום מושרה Electrochemically וBioelectrochemically
In This Article
Summary
We demonstrate the extraction of ammonium from an ammonium-rich stream using an electrochemical and a bioelectrochemical system. The reactor setup, operation and data analysis are discussed.
Abstract
Streams such as urine and manure can contain high levels of ammonium, which could be recovered for reuse in agriculture or chemistry. The extraction of ammonium from an ammonium-rich stream is demonstrated using an electrochemical and a bioelectrochemical system. Both systems are controlled by a potentiostat to either fix the current (for the electrochemical cell) or fix the potential of the working electrode (for the bioelectrochemical cell). In the bioelectrochemical cell, electroactive bacteria catalyze the anodic reaction, whereas in the electrochemical cell the potentiostat applies a higher voltage to produce a current. The current and consequent restoration of the charge balance across the cell allow the transport of cations, such as ammonium, across a cation exchange membrane from the anolyte to the catholyte. The high pH of the catholyte leads to formation of ammonia, which can be stripped from the medium and captured in an acid solution, thus enabling the recovery of a valuable nutrient. The flux of ammonium across the membrane is characterized at different anolyte ammonium concentrations and currents for both the abiotic and biotic reactor systems. Both systems are compared based on current and removal efficiencies for ammonium, as well as the energy input required to drive ammonium transfer across the cation exchange membrane. Finally, a comparative analysis considering key aspects such as reliability, electrode cost, and rate is made.
This video article and protocol provide the necessary information to conduct electrochemical and bioelectrochemical ammonia recovery experiments. The reactor setup for the two cases is explained, as well as the reactor operation. We elaborate on data analysis for both reactor types and on the advantages and disadvantages of bioelectrochemical and electrochemical systems.
Introduction
שחזור של מוצרים יקרי ערך מחשיבות רווחי שפכים כמשאבים יקרי ערך נעשים נדירים וטיפול ללא התאוששות מייצג רק עלות. שפכים מכילים גם אנרגיה וחומרים מזינים שיכול להיות התאוששו, והתאוששות תזונתית יכול לעזור לסגור את ייצור הלולאה 1. שחזור של אנרגיה באמצעות עיכול אנאירובי הוא תהליך מבוסס היטב, ואילו התאוששות של חומרים מזינים היא פחות נפוצה. שחזור של חומרים מזינים מזרמי פסולת נוזליים כגון שתן וגללים נחקר באופן נרחב, למשל, באמצעות הייצור של struvite והפשטה ישירה של 2,3 אמוניה. עם זאת, הצורך בתוספת כימית הוא חסרונם של התהליכים אלה 4. כאן אנו מציגים טכניקה לשחזור של חומרים מזינים קטיוני מזרמי פסולת, כולל שני אשלגן ואמוניום. טופס קטיוני של חומרים מזינים אלו מאפשר התאוששות באמצעות קרום בררני יון במערכת אלקטרו-כימית. במקרה זה, electrochemicמערכת מורכבת מאל תא האנודה (בי החמצון מתרחש), תא קתודה (שבו ההפחתה מתרחשת) וקרום בררני יון להפריד התאים. מתח חשמלי על פני התא לייצר תזרים שוטף מהאנודה לקתודה. מתח זה יכול להיות שנוצר על ידי מקור מתח חיצוני לנהוג חמצון מים ותגובות הפחתה. לחלופין חמצון anodic, למשל, של חומרים אורגניים, ניתן היה זרז על ידי חיידקי electroactive, דורשים פחות כוח. כדי לסגור את המעגל ולשמור על איזון תשלום, מינים טעונים חייבים לנדוד בין האלקטרודות לכל אלקטרון שנוצר. תחבורת אמוניום מתא האנודה לקתודת התא על פני קרום חילופי קטיון (CEM) ולכן יכולה לפצות את השטף של אלקטרונים 4,5.
הטכניקה המוצגת כאן מסירה לא רק אמוניום מזרמי פסולת, אלא גם מאפשרת ההתאוששות שלה. חנקן אמוניה סה"כ (TAN) קיים בשיווי המשקל של שני עמוןium (NH 4 +) ואמוניה (NH 3), והוא תלוי בpH וטמפרטורה 6. NH 4 + הוא בשפע זמין בשל ריכוז גבוה TAN וליד pH הניטרלי בתא האנודה ומינים טעונים חיובי זה ולכן יכול להיות מונע על ידי נוכחי על פני CEM לתוך תא הקתודה. הנוכחי מניע את הירידה של מים על הקתודה, שמוביל לייצור של יוני הידרוקסיד וגז מימן. שיווי משקל TAN עובר לכמעט 100% NH 3 עקב הגבוה pH בתא הקתודה (> 10.0). NH 3 הוא גז שניתן להעביר בקלות באמצעות זרימת אוויר מיחידת הפשטה לעמודת הספיגה שבו הוא כלואים ומרוכז בתמיסת חומצה.
טכנולוגיה זו יש פוטנציאל להפחתת רעילות אמוניום במהלך עיכול אנאירובי של זרמי N-עשיר כמו זבל, וכך להגדיל את התאוששות האנרגיה מזרמי פסולת אלה, ובמקבילחומרים מזינים מתאוששים 4. חילוץ אלקטרוכימי וbioelectrochemical של אמוניום יכול להיות מיושם גם כטכניקה לשחזור מזין בזרמי פסולת עם תוכן TAN גבוה כגון שתן ובכך להימנע עלויות להסרת חומרים מזינים בWWTP 7.
הפרוטוקול המובא כאן יכול לשמש כבסיס לניסויים אלקטרוכימיים וbioelectrochemical רבים ושונים, כפי שאנו משתמשים כור מודולרי. ניתן לשלב סוגים שונים אלקטרודה, קרומים ועוביי מסגרת כפי שהוסבר בפרוטוקול בהמשך. המטרה העיקרית של הפרוטוקול היא לספק אמצעי להשוואה של התאוששות אמוניום אלקטרוכימיים והתאוששות אמוניום ביו-אלקטרו-כימי באמצעות תא אלקטרוליזה. המערכות מוערכות במונחים של יעילות מיצוי, קלט כוח ושחזור.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. הרכבת הכור וחיבור יחידות Stripping וקליטה
- לאסוף את כל החומר הדרוש כדי לבנות את הכור: אלקטרודות, מסגרות וגומי (ראו רשימה של חומרים). לחתוך בזהירות את כל החלקים לאותם ממדים כדי למנוע דליפות בזמן הרכבת הכור.
- לקדוח חורים בתאי הכור כדי שיתאימו לזכר למחבר זכר. לקדוח חור אחד נוסף באמצע צדו של אחד מתאי הכור כדי להתאים את האלקטרודה ההתייחסות.
- הכן מלאי של 1 MH 2 SO 4 לעמודת הספיגה. להגדיל את ריכוז זה כנדרש כדי להתאים עומסים גבוהים של אמוניה.
- ודא שהקרום הוא pretreated על פי הוראות היצרן. Pretreat פחמן הרגיש האלקטרודה על ידי שרייתו ב2 מ"מ CTAB (חומר ניקוי) במשך 3 דקות. יש לשטוף את פחמן הרגיש במי demineralized 8. האנודה היציבה לניסויים אלקטרוכימיים אינו מחייבים יחסי ציבורetreatment.
- מחסנית חלקי כור השונים על מנת בהתאם לסוג הכור. לbioreactor: endplate פרספקס, גומי, אספן נוכחי נירוסטה, גרפיט pretreated הרגיש, תא פרספקס כור, גומי, קרום חילופי קטיון, גומי, חומר spacer, אלקטרודה רשת נירוסטה, גומי, תא כור פרספקס, גומי, endplate פרספקס
- מחסנית חלקי הכור לתא אלקטרוכימי כדלקמן: endplate פרספקס, גומי, האנודה IROX דרך endplate, תא כור פרספקס, גומי, spacer, גומי, קרום חילופי קטיון, גומי, חומר spacer, אלקטרודה רשת נירוסטה, גומי, כור פרספקס תא, גומי, endplate פרספקס.
- השתמש טפלון לאטום את יציאות חיבור של הכור. מניחים את האלקטרודה ההתייחסות באותו התא כמו האלקטרודה העבודה: האנודה במקרה של תא bioelectrochemical, הקתודה או האנודה במקרה של תא אלקטרוכימי.
- השתמש אגוזים וברגים כדי לסגור את הכור. להדק ברגים בצדדים מנוגדים להשוות את הלחץ. אין להשתמש בכלים כדי לסגור את הכור כאצבע חזק מספיק כדי להבטיח כור אטום לחלוטין.
- מלא את הכור במים כדי לבדוק אם הכור הוא דליפה חינם. אם הדלפות מופיעות, בדוק אם הברגים הם הידקו מספיק או אם אחד חלקי הכור עבר בזמן הרכבת הכור. אם אין דליפות מזוהות, רוקן את המים מהכור.
- להוסיף טבעות Raschig בשני טור הרצועה וקליטה כדי למלא את העמודות באמצע הדרך.
- כייל את קצב הזרימה של כל המשאבות. חבר את משאבות הזנה ומחזור לכור ומשאבת האוויר ליחידות ההפשטה וקליטה (איור 1). למזער את אורכו של הצינור ככל האפשר.
- מלא את עמודת הספיגה עם 250 מיליליטר של 1 MH 2 SO 4, זה צריך לכסות את טבעות Raschig. ודא שזרם האוויר מתערבב החומצה גם כאשר המשאבה מופעלת. להגדיל או להחליש את עוצמת הקול של חומצה המבוסס על יכולת עיצוב עמודה ומשאבת אוויר הפשטה.

התקנת Reactor איור 1. למערכת bioelectrochemical מאפשרת חילוץ אמוניום. המערכת שהוצגה כאן פועלת במצב רציף. קווים מוצקים מייצגים זרימת נוזל, קווים מקווקווים מייצגים זרימת גז. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
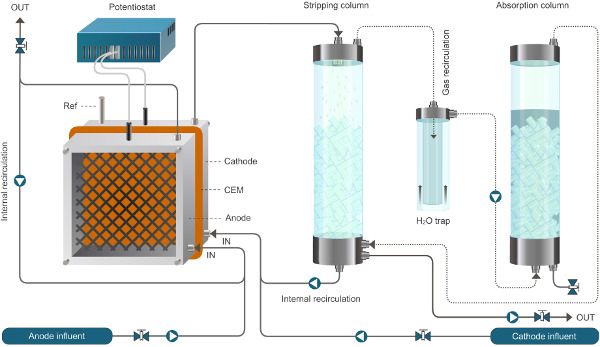
התקנת Reactor איור 2. למערכת bioelectrochemical מאפשרת חילוץ אמוניום. המערכת שהוצגה כאן פועלת במצב רציף. קווים מוצקים מייצגים זרימת נוזל, קווים מקווקווים מייצגים זרימת גז."Target =" ww.jove.com/files/ftp_upload/52405/52405fig2large.jpg _ blank "> לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
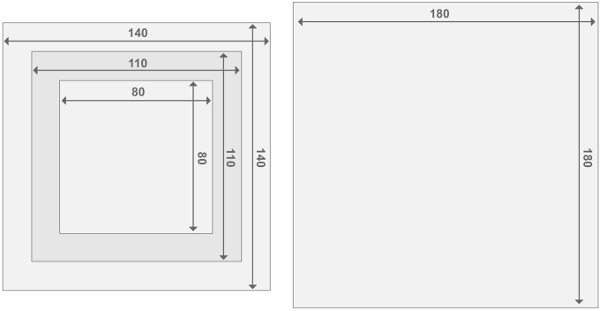
איור 3. עיצוב של מסגרות כור פרספקס. כל כור מורכב משני כורי endplate ו -2 תאי כור. כל החלקים בעובי של 2 סנטימטר. ניתן למצוא את פרטים הנוגעים לגודל של חומרים אחרים ברשימה של חומרים. לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
הפקה מונעת 2. Bioanode
- הכנת התקשורת.
- הכן anolyte לbioreactor כפי שמתואר בטבלה 1 9. להגדיל את ריכוז אמוניום במדיום לחקות זרם פסולת חנקן עשיר.
- כדי לאחסן את Mediאממ לפני שימוש, חיטוי הבינוני על מנת להבטיח את מקור פחמן לא ידולל בזיהום. הכן ויטמינים ואת עקבות אלמנטים לפי טבלת 1 ולהוסיף לאחר מעוקר וקירור הבינוני.
- רוקן הבינוני על ידי טיהור עם גז חנקן לפחות 30 דקות כדי להסיר חמצן. כדי לעשות זאת, להכניס צינורית או מחט לתוך המדיום ולהפעיל את זרם גז חנקן.
- הכן פתרון מוליך כcatholyte. במקרה זה, להשתמש 0.1 M NaCl כדי לאפשר ייצור קאוסטית.
| רכיב | הסכום | ||
| Na 2 4 HPO | 6 g / L | ||
| KH 2 PO 4 | 3 g / L | ||
| NaCl | 0.5 g / L | ||
| NH 4 Cl | 0.5 g / L | ||
| 4 MgSO · 7H 2 O | 0.1 g / L | ||
| CaCl 2 · 2H 2 O פתרון (14.6 g / L) | 1 מיליליטר | ||
| אצטט נתרן | 2 g / L (לסטארט-אפ) | ||
| יסודות קורט | 1 מיליליטר | ||
| פתרון ויטמין | 1 מיליליטר | ||
| יסודות קורט (1,000x) | g / L | ויטמינים (1,000x) | g / L |
| CoCl 2 | 0.1 | ביוטין | 0.004 |
| Na 2 Moo 4 .2H 2 O | 0.01 | חומצה פולית | 0.004 |
| H 3 BO 3 | 0.01 | hydrochloride פירידוקסין | 0.02 |
| Mg 2 Cl 2 .6H 2 O | 3 | ריבופלבין | 0.01 |
| ZnCl 2 | 0.1 | hydrochloride תיאמין | 0.01 |
| CaCl 2 .2H 2 O | 0.1 | חומצה ניקוטינית | 0.01 |
| NaCl | 1 | pantothenate DL-סידן | 0.01 |
| חומצת nitrilotriacetic | 1.5 | Vit B12 | 0.0002 |
| AlCl 3 .6H 2 O | 0.01 | חומצת -aminobenzoic p | 0.01 |
| CuCl 2 | 0.01 | חומצה ליפואית (thioctic) | 0.01 |
| FeCl 2 | 0.1 | מיו -inositol | 0.01 |
| MnCl 2 .2H 2 O | 0.5 | כולין כלוריד | 0.01 |
| התאם לpH 6.5 באמצעות KOH | niacinamide | 0.01 | |
| hydrochloride pyridoxal | 0.01 | ||
| ascorbate נתרן | 0.01 |
טבלת 1. הרכב Anolyte להפקה ביו-אמוניום האנודה מונעת.
- הרכבה של bioreactor
הערה: עבודה בתנאים סטריליים אין צורך לbioreactor זה, כבידוד תרבות מעורב משמש ותנאי כור יבחרו עבור אורגניזמים electroactive הספציפיים.- הכן את הבידוד. לbioreactor זה, להכין תערובת 30 מיליליטר של מי קולחין מbioreactors אנאירובי הפעיל כולל פרמנטור, Bioanode, digester אנאירובי ו / או שפכים גולמיים. לאסוף את התערובת במזרק.
- חבר שקית מלא בגז N 2 לבקבוק anolyte על מנת לשמור על הלחץ יציב בזמן שאינו מאפשר לחמצן כדי להיכנס. מערבבים את מקור הבידוד בהיקף של anolyte (כאן, של anolyte במשך 30 מיליליטר של מקור הבידוד 100 מיליליטר) על ידי לרוקן את המזרק עם הבידוד לבקבוק הבינוני. הקפד לקבל הנפח הדרוש כדי למלא את תא האנודה.
- באמצעות מזרק, למלא את תא האנודה וקתודה בו זמנית עם הפתרונות שלהם. חבר שקית מלא בגז N 2 לבקבוק anolyte כך שניתן יהיה להסיר את פתרון anolyte דרך יציאת דגימה ללא החדרת חמצן. סגור את נמל המדגם עם ברז בין העברות.
הערה: בצע את הצעד הזה יחד עם עמית כדי להבטיח ששני תאי הכור מלאים בו-זמנית. - כאשר שני תאי הכור מלאים, להפעיל אתמשאבת סחרור בקצב סחרור של כ 6 L / hr.
- חבר את כבל potentiostat עם שלוש אלקטרודות, באמצעות האנודה כעובד אלקטרודה. מקם את האלקטרודה ההתייחסות בתא האנודה.
- הפעל את potentiostat במצב chronoamperometry באמצעות תוכנת potentiostat. בחר פוטנציאל האנודה קבועה של -200 mV לעומת Ag / AgCl.
- פועל כור רציף להפקת אמוניום
הערה: ככל שbiofilm מפתחת, נוכחי יופק עם הצריכה אצטט. כתוצאה מדלדול אצטט, הנוכחי יהיה ירידה (ראה סעיף תוצאות, איור 3).- כדי לעבור להאכלה מתמשכת, לעבור על משאבת ההזנה להאנודה והקתודה. מהירות המשאבה תקבע את הזמן ההידראולי מגורים (HRT). כאן, להפעיל את הכור בHRT של 6 שעות.
- הפעל את משאבת האוויר של יחידת הרצועה וקליטה. Recirculate האוויר בלולאה סגורה, או להפיץ בלולאה פתוחה באמצעות אוויר הסביבה. זרימת אוויר יכולה להשפיע על תצורת יעילות ספיגה.
- רענן שלוש פעמים בינוניות בשבוע. הכן anolyte הטרי וcatholyte כפי שמתואר בצעדים 2.1.1-2.1.4.
- אחרי השלבים הבאים, לצרף שקית מלאה בגז N 2 לבקבוק ההזנה הסגור, לעצור את משאבת ההזנה, לשים מלחציים על קו influent, לעבור את הבקבוקים הישנים וחדשים, ולבסוף להסיר את מהדק ולהפעיל מחדש את המשאבה.
- בכל פעם שההזנה היא רעננה, לקחת 5 מיליליטר דגימות נוזלית של השפכים וinfluent של anolyte וcatholyte למדידת מוליכות, pH, תוכן אצטט וריכוז אמוניום.
- כאשר משנה את ההזנה, גם לקחת דגימת 3 מיליליטר של עמודת הספיגה לפקח pH ולניתוח TAN. כאשר pH גישות 4, להחליף את סופג עם פתרון חומצה טרי 1 M גופרתי כדי להבטיח את יעילות ספיגה גבוהה.
- כזרם ראשון יגדל ולאחר מכן להגיע לרמה, למדוד את האסתוכן טייט בinfluent anolyte ושפכים כדי להבטיח זה לא נגרם על ידי הגבלת פחמן: ריכוזים אצטט בשפכי anolyte מתחת ל -100 מ"ג / L מצביעים על הגבלת פחמן. להגדיל את הריכוז אצטט בהזנה במקרה ש( טבלה 2).
- אם הייצוב הנוכחי לא נגרם על ידי מגבלות אצטט, להגדיל בהדרגה את ריכוז אמוניום בהזנה, ולהמתין להתייצבות הנוכחית על מנת להעריך את יעילות שאיבה (לוח 3).
הערה: ככל שריכוז אמוניום הוא גדל, רעילות אמוניה ומוליכות גבוהות יאתגרו את biofilm וסופו של דבר הנוכחי יירד כתוצאה.
| זמן | כמות נתרן אצטט הוסיפה להזנת האנודה (ז / L) |
| יום 0 - 35 יום | 2 |
| 3 | |
| יום 37 - יום 51 | 4 |
| יום 51 - יום 61 | 5 |
ריכוז טבלה 2. של נתרן אצטט בanolyte לחילוץ אמוניום bioanode מונע.
| זמן | הסכום של NH 4 HCO 3 הוסיף להזנת האנודה (ז / L) | שלב |
| יום 0 - 16 יום | 2.26 | אני |
| יום 16 - יום 26 | 4.5 | השני |
| יום 26 - יום 33 | 9 | III |
| יום 33 - יום 40 | 14.1 | IV |
| יום 40 - יום 47 | 20 | V |
| יום 47 - יום 54 | 25.4 | VI |
| יום 54 - יום 63 | 31 | VII |
טבלה 3. ריכוז של אמוניום בanolyte לחילוץ אמוניום bioanode מונע. השלבים מצוינים בגרף צפיפות הזרם (איור 2).
3. אלקטרוכימי הפקה
- הכנת התקשורת
- הכן זרם שפכים סינטטי כanolyte לפי טבלת 4 4. להוסיף אמוניום סולפט להגיע ריכוז סופי של N / L 1, 3, או 5 גרם.
- הכן פתרון M NaCl 0.1 לcatholyte.
| רכיב | הסכום |
| Na 2 HPO 4 .2H 2 O | 1.03 g / L |
| KH 2 PO 4 | 0.58 g / L |
| 4 MgSO · 7H 2 O | 0.1 g / L |
| CaCl 2 .2H 2 O | 0.02 g / L |
| (NH 4) 2 SO 4 | בהתאם לניסוי, כדי להשיג 1/3/5 N g / ריכוז סופי L |
לוח 4. הרכב Anolyte להפקת אמוניום אלקטרוכימיים 4.
- פועל כור רציף להפקת אמוניום
- הפעל את משאבת ההזנה כדי למלא את תאי הכור. כדי לזרז את התהליך באופן זמני להגביר את קצב המשאבה.
- להפחית את מהירות המשאבה לקבלת טיפול הורמונלי של 6 שעות מהרגע שהכור מלא. הפעל את משאבת סחרור בשיעור של 6 L / hr. קח דוגמא של influent (5 מיליליטר).
הערה: מדוד את קצב הזרימה מעת לעת במהלך הניסויכדי להבטיח שזה לא ישתנה. - התחל את יחידת הרצועה וקליטה. מבצע של יחידה זו הוא זהה לbioreactor.
- הפעל את potentiostat במצב chronopotentiometry באמצעות תוכנת potentiostat. ראשון להחיל צפיפות זרם נמוכה של כ -0.5 / מ"ר לקטב את הקרום ולקבוע שטף חנקן עקב דיפוזיה לבד.
- כאשר המערכת כבר מקוטבת למשך 24 שעות, להחיל את צפיפות הזרם דרושה לניסוי. בחן את צפיפויות זרם שונות, בדרך כלל נע בין 10 '/ מ"ר עד 50' / מ"ר. לקחת דגימות של האנודה וקתודת שפכים, ועמודת הספיגה לפני הגדלת הצפיפות הנוכחית.
הערה: לאחר 3 מחזורי טיפול הורמונלי, הכור צריך להתקרב למצב יציב. - ברגע שהגיע לכור מצב יציב, תיקח לפחות 3 דגימות מעל כמובן זמן. לקחת דגימות מן האנודה וקתודת שפכים, ועמודת הספיגה (5 מיליליטר כל אחד). רשום את דגימת נפח, התאריך והשעה.
- בהתאם ליציבות של influent האנודה, לקחת דגימת influent האנודה חדשה במידת צורך. זה הכרחי כאשר נעשה שימוש בשפכים אמיתיים.
- לשנות את תנאי בדיקה, כגון צפיפות נוכחית יושמה וריכוז TAN. לאחר כל שינוי, בואו הכור לייצב לפחות 3 HRTs לפני לקיחת דגימות.
- כאשר pH של עמודת הספיגה מתקרב 4, להחליף את סופג עם פתרון חומצה גופרתית טרי 1 M.
ניתוח 4. לדוגמא
- למדוד את רמת החומציות ומוליכות של הדגימות באותו היום כמו דגימה כדי להפחית אי דיוקים עקב אובדן של אמוניה תנודתי. למדוד pH ומוליכות באמצעות בדיקות pH ומוליכות מכוילות כראוי.
- אם המדגם אינו נמדד באופן מיידי, דגימות חנות לניתוח TAN (שני הכורים) וניתוח של חומצות שומן (bioreactor) בשעה 4 ° C. דגימות מסנן משפכי האנודה bioreactor וinfluent דרך 0.45 מיקרומטר מסננים מחדשלעבור ביומסה ולעזור לשמר את חומצות שומן. למלא את כל צינורות המדגם לשפה על מנת למזער NH 3 הפסד.
- למדוד חנקן כTAN בשיטת הזיקוק בקיטור הסטנדרטי או כל שיטה אחרת למדידה אמינה TAN 10.
- למדוד חומצות שומן כיצטטו בכל דרך אמינה, כגון כרומטוגרפיה יון או גז כרומטוגרפיה 11.
5. ניתוח נתונים וחישובים
- לייצא את קובץ נתוני potentiostat מהתוכנה ולייבא אותו לתוכנת גיליונות אלקטרוניים. חישוב ממוצע לשעה למשתנים אלקטרוכימיים כדי להקטין את מספר נקודות הנתונים ולהחליק את הקימורים כאשר זממו.
- לאסוף את כל הנתונים שנמדדו (pH, אמוניום, VFA) בקובץ נתונים אחד לחישובים. החישובים נדונים בסעיף התוצאות.
- לחשב את ההפקה הנוכחית על ידי bioreactor. זה מיוצג בצורה הטובה ביותר צפיפות זרם, המחושב כדלקמן (1 משוואה,12):
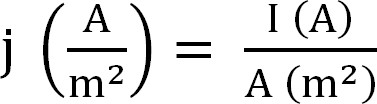 משוואת 1
משוואת 1
עם j כצפיפות זרם, אני נוכחי המוחלט, ושטח פנים מוקרנים של האלקטרודה. בתוכנה מסוימת ניתן לי זה מחושב באופן אוטומטי על-ידי הזנת שטח האנודה לפני תחילת הניסוי. - לחשב את הפרמטרים הקשורים לחילוץ אמוניום
- חשב את שטף החנקן. לנרמל שטף חנקן (N / מ"ר / ד ז) לאזור משטח הקרום אז בא לידי ביטוי כצפיפות זרם (אני N). השתמש בערך זה כדי לחשב את הספירה (משוואת 2, 3, ו -4):
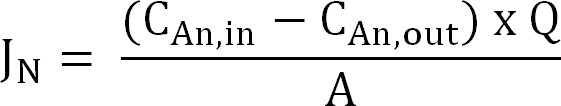 משוואה 2
משוואה 2
כאשר C, ב( N g / L) ו- C, החוצה (N g / L) הם הריכוזים שנמדדו אמוניום נכנסים ויוצא תא האנודה,בהתאמה. Q (L / ד) הוא קצב זרימת האנודה ו( מ '2) הוא שטח הממברנה (שווה להאנודה מוקרנת ושטח פן קתודה). - להציג את שטף החנקן כצפיפות זרם (אני N, A / מ"ר):
 משוואה 3
משוואה 3
שבו z NH4 + (-) הוא אחראי על NH 4 +, F הקבוע פאראדיי (96485 C / mol) וM המשקל המולקולרי של חנקן (14 g / mol). - לחשב את היעילות הנוכחית (CE,%) כ:
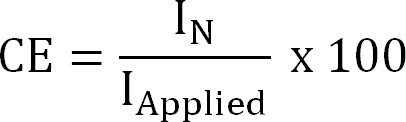 משוואה 4
משוואה 4
איפה אני יישומית ('/ מ"ר) הוא (החילוץ אלקטרוכימיים) הותקן, או שצפיפות זרם (חילוץ bioelectrochemical) נמדדה. - חשב את שטף החנקן התיאורטי. לחשב את החנקן התיאורטי המרביהשטף (J N, מקס, N / מ"ר / ד ז) לניתן להחיל אזור הנוכחי וקרום פני השטח (משוואה 5) כ:
 משוואה 5
משוואה 5 - לחשב את יעילות סילוק חנקן (RE,%). עיין באחוז אמוניום שהוסר מanolyte כיעילות ההסרה. לחשב מinfluent האנודה וריכוזי שפכי TAN (משוואה 6).
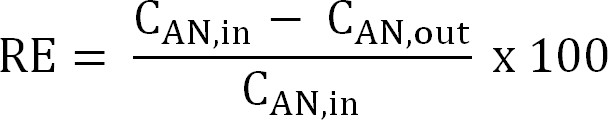 משוואה 6
משוואה 6 - לחשב את יעילות סילוק חנקן התיאורטית המרבית (RE מקסימום,%) לinfluent ניתנה עומס TAN ולהחיל נוכחית (משוואה 7):
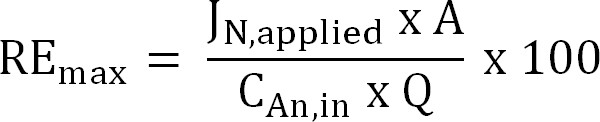 משוואה 7
משוואה 7
שבו J N, מ 'N מיושם (ז -2 ד - 1) הוא צפיפות הזרם מיושמת לידי ביטוי כחנקן שטף.
- חשב את שטף החנקן. לנרמל שטף חנקן (N / מ"ר / ד ז) לאזור משטח הקרום אז בא לידי ביטוי כצפיפות זרם (אני N). השתמש בערך זה כדי לחשב את הספירה (משוואת 2, 3, ו -4):
- לחשב גז נוזלי יחס / כ( משוואה 8):
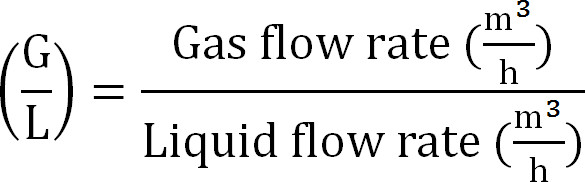 משוואה 8
משוואה 8 - לחשב את הקיבולת המרבית של עמודת הספיגה. לחשב את עומס N התיאורטי המרבי לעמודת הספיגה מהשטף המרבי התיאורטי חנקן J nmax, ריכוז TAN בinfluent (mol / L), הזמן של t פעולה, את פני שטח קרום, והנפח של V הסופג ( משוואה 9):
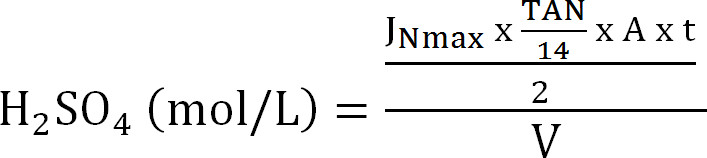 משוואה 9
משוואה 9 - לחשב את יעילות הפשטת SE (%) (משוואת 10):
 60; משוואה 10
60; משוואה 10 - לחשב את השקעת האנרגיה להפקת אמוניום דרך הממברנה חילופי קטיון (E N, הביע כואט / קילוגרם N) (11 משוואה):
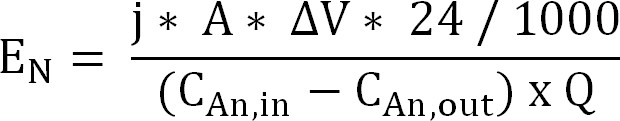 משוואה 11
משוואה 11
עם ΔV הפרש הפוטנציאלים נמדד בין האנודה וקתודה. במקרה של bioreactor, ΔV חושב כממוצע לתקופה הדגימה, לכור אלקטרוכימיים הממוצע לכל הטווח נלקח.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
תוצאות
Chronoamperometry נובע מbioreactor
תוצאות chronoamperometry, המחושב על פי משוואת 1, להראות גרף אופייני לכור רציף (איור 4). בתחילת הניסוי, האנודה והקתודה הופעלו במצב סחרור. זה מאפשר biofilm לפתח ותחילת הייצור הנוכחי. לאחר 5 ימים של מבצע, הצפ?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
כתב יד זה מספק את הכלים הדרושים כדי להקים bioelectrochemical ותא אלקטרוכימי להתאוששות אמוניום. החישובים שהוצגו בסעיף התוצאות מספקים פרמטרים להערכה של ביצועי המערכת. המערכות הביולוגיות ואלקטרוכימיים דומות בהתקנה ובתפקוד. ההבדל העיקרי בין שתי המערכות הוא הבחירה של נוכחי קבו?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the BOF grant for SG from Ghent University. AL is supported by the Rutgers University NSF Fuels-IGERT. SA is supported by the European Union Framework Programme 7 project “ProEthanol 2G.” SA and KR are supported by Ghent University Multidisciplinary Research Partnership (MRP)—Biotechnology for a sustainable economy (01 MRA 510W). JD is supported by an IOF Advanced grant (F2012/IOF-Advanced/094). KR is supported by by the ERC Starter Grant “Electrotalk”. The authors thank Tim Lacoere for designing the TOC art figure, Robin Declerck for building the strip and absorption columns and Kun Guo for providing the inoculum source.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Carbon Felt 3.18 mm Thick | Alfa Aesar | ALFA43199 | Used as bioanode, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Ti electrode coated with Ir MMO | Magneto Special Anodes (The Netherlands) | Used as stable anode for electrochemical tests | |
| Stainless steel mesh | Solana (Belgium) | RVS 554/64: material AISI 316L, mesh width: 564 micron, wire thickness: 140 micron, mesh number: 36,6 | Used as cathode, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Stainless steel plate | Solana (Belgium) | inox 304 sheet, thickness: 0.5 mm | Used as current collector for the bioanode |
| Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode | Bio-Logic (France) | A-012167 RE-1B | |
| Potentiostat (VSP Multipotentiostat) | Bio-Logic (France) | ||
| EC Lab | Bio-Logic (France) | software for performing electrochemistry measurements | |
| Cation Exchange Membrane | Membranes International (USA) | Ultrex CMI-7000 | Pretreated according to the manufacturers' instructions |
| Turbulence Promotor mesh | ElectroCell Europe A/S (Tarm, Denmark) | EPC20432-PP-2 | spacer material, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Connectors | Serto | 1,281,161,120 | Other sizes possible, dependant on tubing type and size of holes in frames |
| Strip and absorption column | In house design | ||
| Tubing | Masterflex | HV-06404-16 | |
| Gas bag | Keika Ventures | Kynar gas bag with Roberts valve | |
| Rashig Rings | Glasatelier Saillart (Belgium) | Raschig rings 4 x 4 mm | Put inside the strip and absorption column to improve the air/liquid contact. Available with many suppliers |
| Rubber sheet | Cut to fit on the perspex frames | ||
| Perspex reactor frames | Vlaeminck, Beernem | In-house design, see tab "reactor frames" in this file |
References
- Verstraete, W., Van de Caveye, P., Diamantis, V. Maximum use of resources present in domestic "used water". Bioresource Technology. 100 (23), 5537-5545 (2009).
- Lei, X., Sugiura, N., Feng, C., Maekawa, T. Pretreatment of anaerobic digestion effluent with ammonia stripping and biogas purification. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 145 (3), 391-397 (2007).
- Siegrist, H. Nitrogen removal from digester supernatant-comparison of chemical and biological methods. Water Science and Technology. 34 (1), 399-406 (1996).
- Desloover, J., Abate Woldeyohannis, A., Verstraete, W., Boon, N., Rabaey, K. Electrochemical Resource Recovery from Digestate to Prevent Ammonia Toxicity during Anaerobic Digestion. Environmental Science & Technology. 46 (21), 12209-12216 (2012).
- Kim, J. R., Zuo, Y., Regan, J. M., Logan, B. E. Analysis of ammonia loss mechanisms in microbial fuel cells treating animal wastewater. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 99 (5), 1120-1127 (2008).
- Emerson, K., Russo, R. C., Lund, R. E., Thurston, R. V. Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. Journal of the Fisheries Board of Canada. 32 (12), 2379-2383 (1975).
- Kuntke, P., Sleutels, T. H. J. A., Saakes, M., Buisman, C. J. N. Hydrogen production and ammonium recovery from urine by a Microbial Electrolysis Cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 39 (10), 4771-4778 (2014).
- Guo, K., et al. Surfactant treatment of carbon felt enhances anodic microbial electrocatalysis in bioelectrochemical systems. Electrochemistry Communications. 39, 1-4 (2014).
- Guo, K., Chen, X., Freguia, S., Donose, B. C. Spontaneous modification of carbon surface with neutral red from its diazonium salts for bioelectrochemical systems. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 47, 184-189 (2013).
- Standard Methods For The Examination Of Water And Wastewater. Rice, E. W., Greenberg, A. E., Clesceri, L. S., Eaton, A. D. , American Public Health Association. (1992).
- Andersen, S. J., et al. Electrolytic Membrane Extraction Enables Production of Fine Chemicals from Biorefinery Sidestreams. Environmental Science & Technology. 48 (12), 7135-7142 (2014).
- Harnisch, F., Rabaey, K. The Diversity of Techniques to Study Electrochemically Active Biofilms Highlights the Need for Standardization. Chemsuschem. 5 (6), 1027-1038 (2012).
- Clauwaert, P., et al. Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: the road to applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 79 (6), 901-913 (2008).
- Atkins, P., De Paula, J. Elements of Physical Chemistry. , Oxford University Press. Oxford, UK. (2012).
- Aelterman, P., Freguia, S., Keller, J., Verstraete, W., Rabaey, K. The anode potential regulates bacterial activity in microbial fuel cells. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 78 (3), 409-418 (2008).
- Kuntke, P., et al. Ammonium recovery and energy production from urine by a microbial fuel cell. Water Research. 46 (8), 2627-2636 (2012).
- Liu, H., Cheng, S., Logan, B. E. Power Generation in Fed-Batch Microbial Fuel Cells as a Function of Ionic Strength. Temperature, and Reactor Configuration. Environmental Science & Technology. 39 (14), 5488-5493 (2005).
- Gimkiewicz, C., Harnisch, F. Waste Water Derived Electroactive Microbial Biofilms: Growth, Maintenance, and Basic Characterization. JoVE. (82), e50800(2013).
- Ping, Q., Cohen, B., Dosoretz, C., He, Z. Long-term investigation of fouling of cation and anion exchange membranes in microbial desalination cells. Desalination. 325, 48-55 (2013).
- Guerin, T., Mondido, M., McClenn, B., Peasley, B. Application of resazurin for estimating abundance of contaminant-degrading micro-organisms. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 32 (5), 340-345 (2001).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved