このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
電気化学的およびBioelectrochemically誘起アンモニウム回復
要約
We demonstrate the extraction of ammonium from an ammonium-rich stream using an electrochemical and a bioelectrochemical system. The reactor setup, operation and data analysis are discussed.
要約
Streams such as urine and manure can contain high levels of ammonium, which could be recovered for reuse in agriculture or chemistry. The extraction of ammonium from an ammonium-rich stream is demonstrated using an electrochemical and a bioelectrochemical system. Both systems are controlled by a potentiostat to either fix the current (for the electrochemical cell) or fix the potential of the working electrode (for the bioelectrochemical cell). In the bioelectrochemical cell, electroactive bacteria catalyze the anodic reaction, whereas in the electrochemical cell the potentiostat applies a higher voltage to produce a current. The current and consequent restoration of the charge balance across the cell allow the transport of cations, such as ammonium, across a cation exchange membrane from the anolyte to the catholyte. The high pH of the catholyte leads to formation of ammonia, which can be stripped from the medium and captured in an acid solution, thus enabling the recovery of a valuable nutrient. The flux of ammonium across the membrane is characterized at different anolyte ammonium concentrations and currents for both the abiotic and biotic reactor systems. Both systems are compared based on current and removal efficiencies for ammonium, as well as the energy input required to drive ammonium transfer across the cation exchange membrane. Finally, a comparative analysis considering key aspects such as reliability, electrode cost, and rate is made.
This video article and protocol provide the necessary information to conduct electrochemical and bioelectrochemical ammonia recovery experiments. The reactor setup for the two cases is explained, as well as the reactor operation. We elaborate on data analysis for both reactor types and on the advantages and disadvantages of bioelectrochemical and electrochemical systems.
概要
排水·ゲインの重要性から価値ある製品の回収貴重な資源が回復せずに乏しいと治療になるとだけコストを表しています。廃水を回収することができる両方のエネルギーと栄養素を含み、栄養回復が生産ループ1を閉じるのを助けることができる。栄養素の回復はあまり一般的ではないながら、嫌気性消化によるエネルギーの回収は、十分に確立されたプロセスである。尿や肥料などの液体廃棄物の流れからの栄養分の回復が広くスツルバイトアンモニア2,3の直接のストリッピングの生産を通して、 例えば 、検討されている。しかしながら、化学添加の必要性は、これらのプロセス4の欠点がある。ここでは、カリウム及びアンモニウムの両方を含む廃棄物の流れからのカチオン性栄養素の回収のための手法を提示する。これらの栄養素のカチオン形態は、電気化学システムにおけるイオン選択性膜を使用して回収を可能にする。この場合、electrochemicらのシステムは(酸化が起こる)陽極室から成る、(還元が起こる)陰極室と区画を分離するためのイオン選択膜。電圧は、アノードからカソードへの電流の流れを生成するために、セルの両端に印加される。この電圧は、水の酸化還元反応を駆動するために外部電源によって生成することができる。代替的に、陽極酸化は、 例えば 、有機物の、より少ない電力を必要とする、電気細菌によって触媒され得る。回路を閉じて、電荷バランスを維持するために、荷電種は、生成された各電子のための電極の間に移行する必要があります。陽イオン交換膜(CEM)全体の陰極室に陽極室からアンモニウム輸送は、このように電子が4,5のフラックスを補償することができる。
ここで紹介するテクニックだけでなく、廃棄物の流れからアンモニアを削除するだけでなく、そのリカバリを可能にします。総アンモニア態窒素(TAN)は、両方のアモンの平衡状態で存在するイウム(NH 4 +)およびアンモニア(NH 3)、そしてpHおよび温度6に依存する。 NH 4 +は、陽極室に高いTAN濃度にし、pHが中性付近に豊富に入手可能であり、この正に帯電した種は、従って、陰極室にCEM横切る電流で駆動することができる。電流は、水酸化物イオンおよび水素ガスの産生をもたらす、カソードにおける水の還元を駆動する。 TAN平衡に起因陰極室(> 10.0)で高いpHにほぼ100%のNH 3に移行する。 NH 3を簡単には、酸溶液中で捕捉され、集中して吸収塔に、ストリッピングユニットからの空気の循環を介して転送することができるガスである。
この技術は、肥料のようなNに富むストリームの嫌気性消化中にアンモニウム毒性を減少させる可能性があり、従って、これらの廃棄物の流れからのエネルギー回収を増加させると同時に、一方回復栄養素4。廃棄物に栄養回復技術は、尿、それによってWWTP 7における栄養素を除去するためのコストを回避するような高TAN含量ストリームとして電気化学的およびアンモニウムの生物電気化学抽出を適用することもできる。
我々はモジュール式反応器を用いるようにここに提示プロトコルは、多くの異なる化学的及び生物電気化学実験のための基礎として役立つことができる。以下のプロトコールで説明したように異なる電極タイプ、膜およびフレームの厚さを組み合わせることができる。プロトコルの主な目的は、電解セルを用いた電気化学アンモニウム回収、バイオ電気化学アンモニウム回復を比較するための手段を提供することである。システムは、抽出効率、電力入力および再現性の観点から評価される。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
1.原子炉のアセンブルとストリップと吸収装置を接続
- (材料のリストを参照)、電極、フレームやゴム:原子炉を構築するために必要なすべての材料を収集します。慎重に原子炉の組み立てながら、漏れを避けるために、同じ寸法のすべての部分をカットします。
- オスコネクタにオスに合うように、原子炉の区画に穴を開けます。参照電極に合わせて、反応器区画の一方の側の中央に一つの追加の穴をドリル。
- 吸収塔のために1 MH 2 SO 4の株式を準備します。アンモニアのより高い負荷に対応するために、必要に応じて、この濃度を増加させます。
- 膜は、製造元の指示に従って前処理されていることを確認します。炭素を前処理3分間2mMのCTAB(洗剤)でそれを浸すことにより、電極を感じた。脱塩水8と感じた炭素をすすぐ。 PRを必要としない電気化学的な実験のための安定したアノードetreatment。
- 反応器の種類に応じた順序で、異なる反応器部品を積み重ねる。パースペックス終板、ゴム、ステンレス鋼の集電体、前処理されたグラファイトフェルト、パースペックス反応器コンパートメント、ゴム、陽イオン交換膜、ゴム、スペーサ材料、ステンレス鋼メッシュ電極、ゴム、パースペックスリアクターコンパートメント、ゴム、パースペックスエンドプレート:バイオリアクターのための
- パースペックス終板、ゴム、終板を介してのIrOxアノード、パースペックスリアクトルコンパートメント、ゴム、スペーサー、ゴム、陽イオン交換膜、ゴム、スペーサ材料、ステンレス鋼メッシュ電極、ゴム、パースペックスリアクターを以下のように電気化学セルのための反応器部品を積み重ねるコンパートメント、ゴム、パースペックスエンドプレート。
- 反応装置の接続ポートを密封するために、テフロン(登録商標)を使用する。電気化学セルの場合、生物電気化学セルの場合には、アノード、カソードまたはアノード:作用電極と同一の区画内に基準電極を配置する。
- ナットを使用して、ボルトは、反応器を閉じます。圧力を均等にする両側のボルトを締めます。指締めが完全に密封された原子炉を確保するのに十分であるように原子炉を閉じるためのツールを使用しないでください。
- 原子炉は、漏れのないかどうかをテストするために水で原子炉を埋める。漏れが表示されている場合はボルトが十分に締められている場合には、確認したり、原子炉を組み立てながら、原子炉部品の一つは、移動した場合。漏れが検出されない場合、反応器から水を空にする。
- 途中で列を埋めるためにストリップと吸収塔の両方にラシヒリングを追加します。
- すべてのポンプの流量を校正。反応器とストリッピングと吸収ユニットへの空気ポンプ( 図1)への供給および再循環ポンプを接続します。できるだけ多くのチューブの長さを最小化します。
- 1 MH 2 SO 4 250mlで吸収塔を埋めるには、ラシヒリングをカバーする必要があります。ポンプをオンにすると、空気の流れがよく酸を混合することを確認してください。増やすか、ストリッピング塔の設計および空気ポンプ容量に基づく酸の量を減少させる。

アンモニウム抽出を可能にする生物電気化学システム図1.原子炉のセットアップが。ここで紹介するシステムは、連続モードで動作します。実線は液体の流れを表し、点線はガスの流れを表している。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
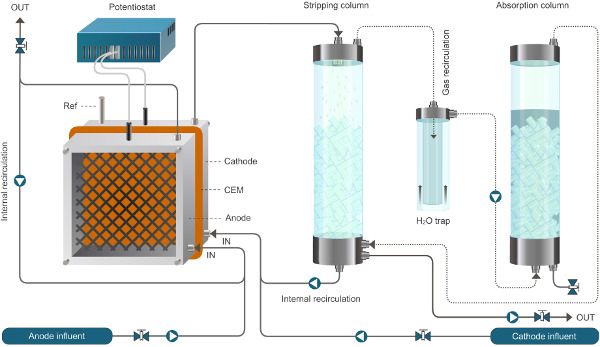
アンモニウム抽出を可能にする生物電気化学システム図2.原子炉のセットアップが。ここで紹介するシステムは、連続モードで動作します。実線は液体の流れを表し、点線はガスの流れを表している。ww.jove.com/files/ftp_upload/52405/52405fig2large.jpg「ターゲット= "_空白">この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
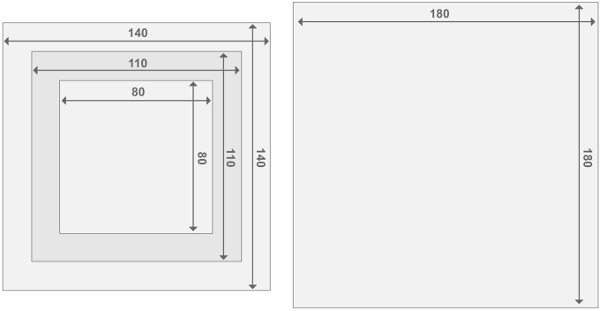
パースペックスリアクターフレームの図3の設計は 、 各反応器は、2つのエンドプレートリアクタ2の反応器の区画で構成されている。すべての部品は、2cmの厚さを有する。他の材料のサイズに関する詳細は、材料のリストに記載されています。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
2.バイオアノード駆動型の抽出
- メディアの準備。
- 表1〜9で説明したように、バイオリアクターのための陽極液を準備します。窒素リッチ廃棄物の流れを模倣する培地中でアンモニウム濃度を増やします。
- MEDIを保存するにはUM使用前に、炭素源は汚染を通して枯渇されていないことを確認するためにメディアをオートクレーブ。 表1によれば、ビタミンおよび微量要素を準備し、オートクレーブ培地を冷却した後に追加。
- 酸素を除去するために、少なくとも30分間、窒素ガスでパージすることによって培地をフラッシュする。これを行うには、培地中にチューブまたは針を挿入し、窒素ガス流をオンにします。
- 陰極液の導電性溶液を調製する。この場合、苛性製造を可能にするために0.1 M NaClを使用。
| コンポーネント | 額 | ||
| のNa 2 HPO 4 | 6グラム/ L | ||
| KH 2 PO 4 | が3g / L | ||
| NaClを | 0.5g / Lの | ||
| NH 4 Clを | 0.5g / Lの | ||
| 硫酸マグネシウム4·7H 2 O | は0.1g / L | ||
| のCaCl 2·2H 2 O溶液(14.6グラム/ L) | 1ミリリットル | ||
| 酢酸ナトリウム | (起動用)を2g / L | ||
| 微量元素 | 1ミリリットル | ||
| ビタミン溶液 | 1ミリリットル | ||
| 微量元素(1,000倍) | グラム/ L | ビタミン(1,000倍) | グラム/ L |
| のCoCl 2 | 0.1 | ビオチン | 0.004 |
| のNa 2のMoO 4·2H 2 O | 0.01 | 葉酸 | 0。004 |
| H 3 BO 3 | 0.01 | 塩酸ピリドキシン | 0.02 |
| のMg 2のCl 2·6H 2 O | 3 | リボフラビン | 0.01 |
| のZnCl 2 | 0.1 | チアミン塩酸塩 | 0.01 |
| のCaCl 2·2H 2 O | 0.1 | ニコチン酸 | 0.01 |
| NaClを | 1 | DL-パントテン酸カルシウム | 0.01 |
| ニトリロ三酢酸 | 1.5 | ビタミンB12 | 0.0002 |
| のAlCl 3·6H 2 O | 0.01 | P -aminobenzoic酸 | 0.01 |
| のCuCl 2 | 0.01 | リポ(チオクト酸) | 0.01 |
| のFeCl 2 | 0.1 | ミオ -イノシトール | 0.01 |
| のMnCl 2·2H 2 O | 0.5 | 塩化コリン | 0.01 |
| KOHを用いてpHを6.5に調整し | ナイアシンアミド | 0.01 | |
| ピリドキサール塩酸塩 | 0.01 | ||
| アスコルビン酸ナトリウム | 0.01 |
バイオアノードドリブンアンモニウム抽出表1陽極液組成物。
- バイオリアクターの接種
注:混合培養接種材料が使用され、反応器条件は、特定の電気活性有機体のために選択されますように、無菌状態での作業は、このバイオリアクターには必要ありません。- 接種材料を準備します。このバイオリアクターは、発酵槽を含むアクティブ嫌気性バイオリアクターからの流出物を30mlの混合物を調製、バイオアノード、嫌気性消化および/または生の廃水。注射器内の混合物を収集します。
- 酸素が 入ることを可能にしないが、安定した圧力を維持するために、陽極液ボトルにN 2を充填ガスバッグを接続します。培地ボトルに接種材料と注射器を空にすることによって(ここでは、接種源の30ミリリットルのための陽極液の100ミリリットル)陽極液の体積の接種源を混ぜる。アノード室を埋めるために必要な音量を得るようにしてください。
- シリンジを用いて、それらのそれぞれの溶液と同時に、アノードとカソード区画を埋める。陽極液が酸素を導入することなく、サンプリングポートを介して除去することができるように、陽極液ボトルにN 2を充填したガスバッグを接続する。転送間のタップでサンプルポートを閉じます。
注:両方の原子炉区画は同時に充填されることを保証するために同僚と一緒に、この手順を実行します。 - 両方の原子炉区画は満たされると、オンにし約6 L / hrの再循環速度で再循環ポンプ。
- 作用電極として陽極を使用して、3電極をポテンショスタットケーブルを接続します。アノード室での参照電極を配置します。
- ポテンショスタットソフトウェアを使用してクロノアンモードでポテンショスタットに切り替えます。 -200 mVのAg / AgClに対しての固定アノード電位を選択します。
- アンモニウム抽出のための連続反応を実行する
注:バイオフィルムが発達するように、電流は、酢酸の消費に生成される。酢酸枯渇の結果として、電流が(結果セクション、 図3を参照)低下する。- 連続供給に変更するには、アノードとカソードのための供給ポンプのスイッチを入れる。ポンプ速度は、油圧滞留時間(HRT)を決定する。ここでは、6時間のHRTで反応器を操作する。
- ストリップと吸収ユニットのエアーポンプのスイッチを入れる。閉ループ内の空気を循環させる、または中を循環する周囲空気を用いてオープンループ。エアフロー構成は、吸収効率に影響を与えることができる。
- 週中3回更新します。手順で説明するように、新鮮な陽極液と陰極液を準備し2.1.1-2.1.4。
- これらのステップの後、古いものと新しいボトルを切り替えて、最終的にクランプを削除し、ポンプを再起動して、流入ラインにクランプを置く、供給ポンプを停止し、閉じられたフィードボトルにN 2を充填ガス袋を添付します。
- フィードが更新されるたびに、5ミリリットルの導電率、pHは、酢酸塩含有量とアンモニア濃度の測定のための陽極と陰極液の廃液と流入の液体試料を取る。
- フィードを変更する場合、また、pHを監視し、TAN分析のために、吸収塔3mlのサンプルを取る。 pHが4に近づくと、高い吸収効率を確保するために、新鮮な1Mの硫酸溶液と吸収剤を交換する。
- 電流が第1の増加した後、プラトーに達するように、エースを測定これを確実に陽極液の流入と流出液中のテイトコンテンツは、炭素制約によるものではない:100 mg / Lの下の陽極液流出物中の酢酸濃度は、炭素制限を示している。その場合( 表2)でフィード中の酢酸濃度を高める。
- 電流安定化酢酸の制限に起因していない場合は、徐々にフィード中のアンモニア濃度を増加させ、抽出効率( 表3)を評価するために、電流が安定するのを待つ。
NOTE:アンモニウム濃度が増加すると、アンモニア毒性と高い導電性がバイオフィルムに挑戦すると、電流が最終的に結果として低下する。
| 時間 | 酢酸ナトリウムの量は、アノード供給量(g / L)に添加し |
| 0日 - 35日 | 2 |
| 35日 - デイ37 | 3 |
| デイ37 - デイ51 | 4 |
| デイ51 - 61日 | 5 |
バイオアノード従動アンモニウム抽出のための陽極液中の酢酸ナトリウムの表2濃度。
| 時間 | NH 4 HCO 3の量は、アノード供給量(g / L)に添加し | 相 |
| 0日 - 16日目 | 2.26 | 私 |
| 16日目 - 26日目 | 4.5 | 二 |
| デイ26 - 33日目 | 9 | 三 |
| デイ33 - 40日 | 14.1 | 4 |
| デイ40 - デイ47 | 20 | V |
| デイ47 - 54日 | 25.4 | 六 |
| デイ54 - 63日 | 31 | 七 |
バイオアノード従動アンモニウム抽出のための陽極液中のアンモニアの濃度を表3。相を、電流密度のグラフ( 図2)に示されている。
3.電気化学抽出
- メディアの準備
- 表4 4に記載の陽極液として合成廃水ストリームを準備する1,3、または5gのN / Lの最終濃度に達するように硫酸アンモニウムを追加する。
- 陰極液のため、0.1M NaCl溶液を準備します。
| コンポーネント | 額 |
| のNa 2 HPO 4·2H 2 O | 1.03グラム/ L |
| KH 2 PO 4 | 0.58グラム/ L |
| 硫酸マグネシウム4·7H 2 O | は0.1g / L |
| のCaCl 2·2H 2 O | 0.02グラム/ L |
| (NH 4)2 SO 4 | 1/3/5グラムのN / Lの最終濃度を得るために、実験に応じて |
電気化学アンモニウム抽出4表4.陽極液組成物。
- アンモニウム抽出のための連続反応を実行する
- 原子炉区画を埋めるために供給ポンプのスイッチをオンにします。処理を高速化するには、一時的にポンプ速度を増加させる。
- 反応器がいっぱいになると6時間のHRTを得るために、ポンプ速度を減らします。 6 L / hrの速度で再循環ポンプのスイッチをオンにします。流入(5ミリリットル)のサンプルを取る。
注:実験を通して定期的に流量を測定確実にするためには、変化しない。 - ストリップと吸収ユニットを開始します。このユニットの動作は、バイオリアクターの場合と同じです。
- ポテンショスタットソフトウェアを使用してクロノモードでポテンショスタットに切り替えます。第一の膜を分極し、一人で拡散による窒素フラックスを決定するために、約0.5 A / m 2の低電流密度を適用します。
- システムは24時間に偏光された場合、実験に必要な電流密度を適用する。通常10 A / m 2でから50 A / m 2の範囲の、異なる電流密度をテストします。電流密度を増加させる前に、アノードとカソード流出物のサンプルを、吸収塔を取る。
注:3 HRTサイクルの後、反応器は定常状態に近づく必要があります。 - 反応器は定常状態に達した後、時間経過にわたって、少なくとも3つのサンプルを取る。アノードとカソード流出物からサンプルを取り、吸収カラム(各5ml)。サンプリングボリューム、日付と時刻を書き留めます。
- 必要に応じて、アノード流入の安定性に応じて、新しいアノード流入サンプルを取る。実際の廃水を用いた場合、これが必要である。
- このような印加電流密度およびTAN濃度などの試験条件を変更する。それぞれの変更後、反応器は、サンプルを採取する前に、少なくとも3高精度タイマ安定化してみましょう。
- 吸収塔のpHが4に近づくと、新鮮な1Mの硫酸溶液と吸収剤を交換する。
4.サンプルの分析
- 揮発性のアンモニアの損失による不正確さを減らすために、サンプリングと同じ日のpH、サンプルの導電率を測定します。適切に校正され、pHと導電率プローブを用いてpHと導電率を測定します。
- 試料はすぐに測定されない場合は、TAN分析(両方の反応器)と4℃での脂肪酸分析(バイオリアクター)に対するストアサンプル。再ためのバイオリアクターアノード流出物及び流入から0.45μmのフィルターを通してフィルター試料バイオマスを移動し、脂肪酸を維持するに役立つ。 NH 3の損失を最小限にするためにリムのすべての試料管を埋める。
- 標準的な水蒸気蒸留法やTAN 10を測定するための任意の他の確実な方法によりTANとして窒素を測定する。
- そのようなイオンクロマトグラフィーやガスクロマトグラフィー11などの任意の信頼性の高い方法によって、酢酸などの脂肪酸を、測定します。
5.データ解析と計算
- ソフトウェアからのポテンショスタットデータファイルをエクスポートし、スプレッドシートプログラムにインポート。電気化学的な変数は、データ点の数を減少させ、それをプロットする際に、曲線を平滑化するための時間当たりの平均を計算する。
- 計算のための一つのデータファイル内のすべての測定データ(pHは、アンモニウム、VFA)を収集します。計算は、結果セクションで説明します。
- バイオリアクターによる現在の生産を計算します。これは最高の、式1(次のように計算される電流密度として表され12):
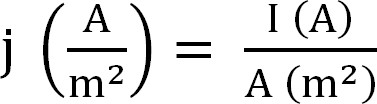 式1
式1
電流密度、I絶対電流、電極の投影面積としてjを持つ。一部のソフトウェアでは、これは、実験開始前に、アノード表面積を入力することにより自動的に計算させることが可能である。 - アンモニウム抽出に関連するパラメータを算出する
- 窒素フラックスを計算します。その後、電流密度(I N)として表さ膜表面積を窒素フラックス(グラムN / m 2の/ d)を正規化する。 CE(式2、3、および4)を計算するためにこの値を使用します。
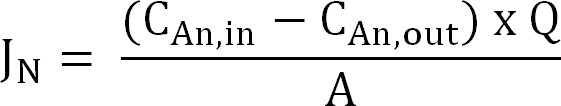 式2
式2
(グラムN / L) で C 項、およびC Anは、アウト (グラムN / L)は、陽極室及び出てくる測定アンモニウム濃度がどこそれぞれ。 Q(L / d)は、アノード流量で、A(m 2)が (投影されたアノードおよびカソードの表面積に等しい)膜表面積である。 - 電流密度(I N、A /広)などの窒素フラックスを現在:
 式3
式3
ここで、z NH4 +( - )は、NH 4 +、Fはファラデー定数(96485 C / mol)をM窒素の分子量(14グラム/モル)の電荷である。 - 電流効率(CE、%)などを計算します。
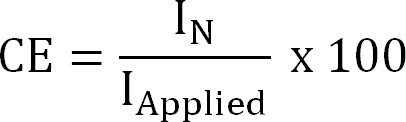 式4
式4
私応用 (A /㎡)を適用(電気化学的抽出)または測定(生物電気化学抽出)現在の密度である。 - 理論上の窒素フラックスを計算します。理論上の最大窒素を計算します所与のフラックス(J N、マックス 、グラムN / m 2の/ d)は、現在、膜表面積(式5)を適用。
 式5
式5 - 窒素除去効率(RE、%)を計算します。除去効率として陽極液から除去するアンモニアの割合を参照してください。アノード流入、流出TAN濃度(式6)から算出してください。
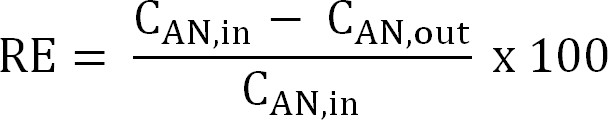 式6
式6 - 与えられた流入TAN負荷に対して理論上の最大窒素除去効率(RE MAX、%)を計算し、(式7)現在の適用:
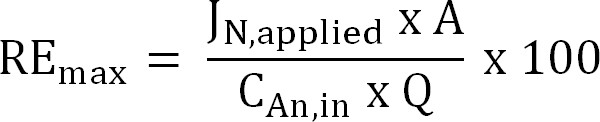 式7
式7
ここでJ N、適用 (グラム数N m -で2 D - 1)窒素フラックスとして表現印加電流密度である。
- 窒素フラックスを計算します。その後、電流密度(I N)として表さ膜表面積を窒素フラックス(グラムN / m 2の/ d)を正規化する。 CE(式2、3、および4)を計算するためにこの値を使用します。
- (式8)のようなガス/液体の比率を計算する。
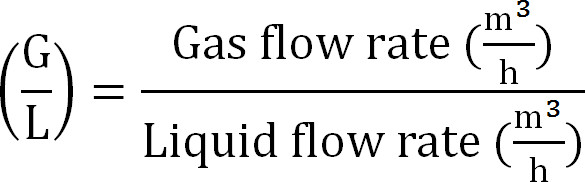 式8
式8 - 吸収塔の最大容量を計算します。 (理論上の最大窒素フラックスJ Nmaxに 、流入におけるTAN濃度(モル/ L)と、操作トン、膜表面積Aの時間、吸収Vの容積から吸収カラムに最大理論Nの負荷を計算する式9):
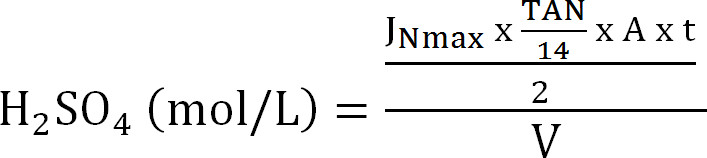 式9
式9 - スト効率SE(%)(式10)を計算します。
 60;式10
60;式10 - 陽イオン交換膜を介しアンモニウム抽出のためのエネルギー入力を算出する(式11)(E Nは 、キロワット時/キログラムNとして表される)。
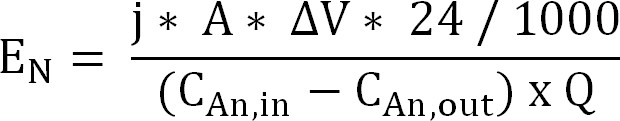 式11
式11
アノードとカソードとの間のΔVを測定電位差。バイオリアクターの場合、ΔVは、実行全体の平均が取られた電気化学反応器のために、サンプリング期間の平均として算出した。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
バイオリアクターからのクロノアンペロメトリーの結果
クロノアンペロメトリーの結果は、式(1)に従って算出( 図4)連続反応のための典型的なグラフを示している。実験の開始時に、アノード及びカソードは、再循環モードで操作した。これは開発するバイオフィルムと、現在の生産の開始を可能にする。操作の5日後に、電流密度は、現?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
この原稿は、アンモニウム回復のための生物電気化学および電気化学セルを設定するために必要なツールを提供します。結果のセクションで提示計算は、システムの性能を評価するためのパラメータを提供する。生物学的および電気化学システムは、セットアップおよび機能において類似している。二つのシステムの主な違いは、生物電気化学セットアップのための固定アノード電位に対し?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
The authors have nothing to disclose.
謝辞
This work was supported by the BOF grant for SG from Ghent University. AL is supported by the Rutgers University NSF Fuels-IGERT. SA is supported by the European Union Framework Programme 7 project “ProEthanol 2G.” SA and KR are supported by Ghent University Multidisciplinary Research Partnership (MRP)—Biotechnology for a sustainable economy (01 MRA 510W). JD is supported by an IOF Advanced grant (F2012/IOF-Advanced/094). KR is supported by by the ERC Starter Grant “Electrotalk”. The authors thank Tim Lacoere for designing the TOC art figure, Robin Declerck for building the strip and absorption columns and Kun Guo for providing the inoculum source.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Carbon Felt 3.18 mm Thick | Alfa Aesar | ALFA43199 | Used as bioanode, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Ti electrode coated with Ir MMO | Magneto Special Anodes (The Netherlands) | Used as stable anode for electrochemical tests | |
| Stainless steel mesh | Solana (Belgium) | RVS 554/64: material AISI 316L, mesh width: 564 micron, wire thickness: 140 micron, mesh number: 36,6 | Used as cathode, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Stainless steel plate | Solana (Belgium) | inox 304 sheet, thickness: 0.5 mm | Used as current collector for the bioanode |
| Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode | Bio-Logic (France) | A-012167 RE-1B | |
| Potentiostat (VSP Multipotentiostat) | Bio-Logic (France) | ||
| EC Lab | Bio-Logic (France) | software for performing electrochemistry measurements | |
| Cation Exchange Membrane | Membranes International (USA) | Ultrex CMI-7000 | Pretreated according to the manufacturers' instructions |
| Turbulence Promotor mesh | ElectroCell Europe A/S (Tarm, Denmark) | EPC20432-PP-2 | spacer material, 110 mm x 110 mm |
| Connectors | Serto | 1,281,161,120 | Other sizes possible, dependant on tubing type and size of holes in frames |
| Strip and absorption column | In house design | ||
| Tubing | Masterflex | HV-06404-16 | |
| Gas bag | Keika Ventures | Kynar gas bag with Roberts valve | |
| Rashig Rings | Glasatelier Saillart (Belgium) | Raschig rings 4 x 4 mm | Put inside the strip and absorption column to improve the air/liquid contact. Available with many suppliers |
| Rubber sheet | Cut to fit on the perspex frames | ||
| Perspex reactor frames | Vlaeminck, Beernem | In-house design, see tab "reactor frames" in this file |
参考文献
- Verstraete, W., Van de Caveye, P., Diamantis, V. Maximum use of resources present in domestic "used water". Bioresource Technology. 100 (23), 5537-5545 (2009).
- Lei, X., Sugiura, N., Feng, C., Maekawa, T. Pretreatment of anaerobic digestion effluent with ammonia stripping and biogas purification. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 145 (3), 391-397 (2007).
- Siegrist, H. Nitrogen removal from digester supernatant-comparison of chemical and biological methods. Water Science and Technology. 34 (1), 399-406 (1996).
- Desloover, J., Abate Woldeyohannis, A., Verstraete, W., Boon, N., Rabaey, K. Electrochemical Resource Recovery from Digestate to Prevent Ammonia Toxicity during Anaerobic Digestion. Environmental Science & Technology. 46 (21), 12209-12216 (2012).
- Kim, J. R., Zuo, Y., Regan, J. M., Logan, B. E. Analysis of ammonia loss mechanisms in microbial fuel cells treating animal wastewater. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 99 (5), 1120-1127 (2008).
- Emerson, K., Russo, R. C., Lund, R. E., Thurston, R. V. Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. Journal of the Fisheries Board of Canada. 32 (12), 2379-2383 (1975).
- Kuntke, P., Sleutels, T. H. J. A., Saakes, M., Buisman, C. J. N. Hydrogen production and ammonium recovery from urine by a Microbial Electrolysis Cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 39 (10), 4771-4778 (2014).
- Guo, K., et al. Surfactant treatment of carbon felt enhances anodic microbial electrocatalysis in bioelectrochemical systems. Electrochemistry Communications. 39, 1-4 (2014).
- Guo, K., Chen, X., Freguia, S., Donose, B. C. Spontaneous modification of carbon surface with neutral red from its diazonium salts for bioelectrochemical systems. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 47, 184-189 (2013).
- Standard Methods For The Examination Of Water And Wastewater. Rice, E. W., Greenberg, A. E., Clesceri, L. S., Eaton, A. D. , American Public Health Association. (1992).
- Andersen, S. J., et al. Electrolytic Membrane Extraction Enables Production of Fine Chemicals from Biorefinery Sidestreams. Environmental Science & Technology. 48 (12), 7135-7142 (2014).
- Harnisch, F., Rabaey, K. The Diversity of Techniques to Study Electrochemically Active Biofilms Highlights the Need for Standardization. Chemsuschem. 5 (6), 1027-1038 (2012).
- Clauwaert, P., et al. Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: the road to applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 79 (6), 901-913 (2008).
- Atkins, P., De Paula, J. Elements of Physical Chemistry. , Oxford University Press. Oxford, UK. (2012).
- Aelterman, P., Freguia, S., Keller, J., Verstraete, W., Rabaey, K. The anode potential regulates bacterial activity in microbial fuel cells. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 78 (3), 409-418 (2008).
- Kuntke, P., et al. Ammonium recovery and energy production from urine by a microbial fuel cell. Water Research. 46 (8), 2627-2636 (2012).
- Liu, H., Cheng, S., Logan, B. E. Power Generation in Fed-Batch Microbial Fuel Cells as a Function of Ionic Strength. Temperature, and Reactor Configuration. Environmental Science & Technology. 39 (14), 5488-5493 (2005).
- Gimkiewicz, C., Harnisch, F. Waste Water Derived Electroactive Microbial Biofilms: Growth, Maintenance, and Basic Characterization. JoVE. (82), e50800(2013).
- Ping, Q., Cohen, B., Dosoretz, C., He, Z. Long-term investigation of fouling of cation and anion exchange membranes in microbial desalination cells. Desalination. 325, 48-55 (2013).
- Guerin, T., Mondido, M., McClenn, B., Peasley, B. Application of resazurin for estimating abundance of contaminant-degrading micro-organisms. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 32 (5), 340-345 (2001).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved