このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
坐骨神経痛に対するフー皮下ニードリングの有効性:慢性狭窄損傷ラットモデルにおける行動的および電気生理学的変化
* これらの著者は同等に貢献しました
要約
ラットの坐骨神経痛を誘発するために、慢性狭窄損傷モデルでFuの皮下ニードリングを使用するためのプロトコルを提示します。
要約
フーの皮下ニードリング(FSN)は、伝統的な中国医学から発明された鍼治療技術であり、痛みを和らげるために世界中で使用されています。しかし、作用機序はまだ完全には解明されていません。FSN治療中、FSN針は揺れ動きで皮下組織に挿入され、長時間保持されます。しかし、研究者にとって、動物モデル(ラットなど)でFSNを操作しながら姿勢を維持することには課題があります。不快な治療は、FSN針に対する恐怖や抵抗感につながり、怪我のリスクを高め、研究データに影響を与えることさえあります。麻酔も研究結果に影響を与える可能性があります。したがって、動物に対するFSN療法では、介入中の傷害を最小限に抑える戦略が必要です。この研究では、Sprague-Dawleyラットの慢性狭窄損傷モデルを使用して、神経因性疼痛を誘発します。このモデルは、末梢神経の外科的狭窄によってヒトに観察される神経損傷によって引き起こされる痛みを再現し、神経圧迫症候群や末梢神経障害などの状態で見られる圧迫または閉じ込めを模倣しています。FSN針を動物の体の皮下層に簡単に挿入するための、針の挿入と方向、針の保持、揺れ動きなど、適切な操作を紹介します。ラットの不快感を最小限に抑えることで、ラットが緊張して筋肉が収縮し、針の挿入を妨げ、研究効率が向上します。
概要
神経損傷によって引き起こされる痛みとして定義される神経因性疼痛は、世界人口の6.9%〜10%が罹患していると推定されており、報告されている生涯有病率は49%〜70%です1,2。また、管理が最も難しい疼痛症候群の1つと考えられています。神経因性疼痛を管理するための薬理学的使用は、非ステロイド性抗炎症薬やオピオイドなどの一般的に処方される鎮痛薬がこの種の痛みを和らげる効果をほとんど示していないため、限られた成功しか得られていません3,4。したがって、新しい治療オプション、特に非薬理学的治療を探求する必要性が高まっています。鍼治療は、非薬理学的介入として、体性感覚系に鎮痛効果を及ぼすことにより、神経障害性疼痛を緩和する可能性がある。臨床研究と前臨床試験の両方で、鍼治療は重大な副作用なしに神経因性疼痛の症状を和らげるのに効果的であることが示されています5,6,7。しかし、神経因性疼痛の疼痛緩和のための鍼治療の中心的なメカニズムは、さらに調査されるべきものです。
近年、フーの皮下ニードリング(FSN)は、疼痛関連の神経疾患の治療に人気を博しています8。FSNは伝統的な中国の鍼治療に由来し、1996年に伝統的な中国の医師Zhonghua Fuによって最初に説明されました9,10。FSNは伝統的な鍼治療に由来しますが、経絡ベースの鍼治療、陰と陽の原則、経穴の概念とは技術と理論が大きく異なります。FSNは、筋膜性疼痛に効果的に対処するために、神経生理学的および解剖学的アプローチをより重視しています11。FSN療法は、筋肉と密接に関連する結合組織を標的とし、特に筋肉の引き締まった筋肉(TM)の治療に焦点を当てて、さまざまな痛みを伴う筋肉障害に対処するために臨床診療に適用されます12。疼痛緩和の補完療法として、FSNは、迅速な疼痛管理と軟部組織のけいれんの大幅な改善に加えて、軟部組織の損傷の治療に有効であるという臨床的証拠もあります13,14。FSN療法には、症状に関連する根本的な筋膜トリガーポイント(MTrP)に対処するために調整された特定の技術が含まれます。FSNの針の挿入位置は、これらのトリガーポイントの位置に基づいて慎重に選択され、患部を正確にターゲットにすることができます。施術中、FSN針を皮下層に挿入し、治療効果を最適化するために意図的に停止させます。次に、組織を刺激し、治療反応を促進するために針の穏やかな振動運動を含む、揺れ運動として知られる独特の技術が採用される10。MTrPの発症は、慢性的な筋肉過負荷、過度の運動、不適切な運動姿勢、筋肉の萎縮、変性などの要因が筋肉組織の虚血や低酸素症の発症に寄与する可能性があると説明するエネルギー危機理論に関連しています。筋肉組織内のこの酸素とエネルギーの欠乏は、MTrPの形成に重要な役割を果たすと考えられています15,16。以前の動物実験では、ラットの慢性疼痛に対するFSN治療がTMのミトコンドリアの形態学的構造と機能をある程度改善することを発見しており、損傷した神経と筋肉の回復を促進するFSN療法の可能性が検証されています17。
坐骨神経痛は神経因性疼痛に分類されています18。神経障害性疼痛の原因は、運動終板と筋肉の外側の線維層の間のどこかにあり、微小血管系と細胞レベルの神経伝達物質が関与していると考えられています。神経損傷が起こると、筋肉の神経支配の喪失と神経支配された神経細胞のアポトーシスが起こり19、罹患した手足の痛みに関連する歩行につながります。さらに、神経の慢性的な圧迫や刺激は、神経機能の方法にさまざまな変化をもたらす可能性があり、坐骨神経痛の症状をさらに悪化させる可能性があります20。しかし、神経系は複雑なため、in vitroで再現することが困難であるため、このような研究には動物モデルを使用する必要があります。神経因性疼痛障害の調査では、坐骨神経結紮術、離断術、圧迫術など、直接的な末梢神経損傷のさまざまな方法を含むモデル生物が一般的に採用されています21,22。Sprague-Dawleyラットの慢性狭窄損傷(CCI)モデルは、神経因性疼痛を誘発するために使用されています。このモデルは、末梢神経の外科的狭窄によってヒトに観察される神経損傷によって引き起こされる痛みを再現し、神経圧迫症候群や末梢神経障害などの状態で見られる圧迫または閉じ込めを模倣しています。
本研究では、慢性狭窄障害および神経障害性疼痛を有するラットを対象に、FSN療法と低周波電気療法(経皮的電気神経刺激装置、TENS)の鎮痛効果を評価した。麻酔は神経インパルスを遅らせたり遮断したりし、シナプス伝達とニューロン機能に影響を与えるため23、すべてのニードリング手順と揺れ動きの下で動物に麻酔をかけることはできません。したがって、ラットの不快感を軽減するために適切な針技術が必要です。ラットCCIモデルを確立するための手順、麻酔なしでの揺れ運動を組み合わせたFSNによるラットの治療方法、実行可能な動物行動パターンテスト、および電気生理学的調査について詳細に説明します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
2022年10月、台湾の彰化市にあるChang Bing Show Chwan Memorial Hospital(111031)のInstitutional Animal Care and Use Committee(IACUC)によって、動物を対象とするすべての処置が承認されました(図1)。
1.動物の調製
- 48匹の雄のSprague-Dawley(SD)ラット(年齢:8-10週、体重:250-300 g)を購入します。
- ハツネズミを24±2°Cの換気ケージに個別に入れ、12時間の暗明サイクル。
- ラットに標準的なペレット飼料とすぐに使用できる滅菌飲料水を与え、柔らかい寝具を提供します。
2.動物のグループ化
- 48匹のSDラットを6つのグループ(グループあたりn = 8)にランダムに分割します:偽群、CCI群、CCI + FSN群、CCI + TENS群、FSN単独群、およびTENS単独群 Chanらが実施した以前の研究24。
注:6つのグループの詳細:(1)偽グループ:手術も治療もなし。(2)CCIグループ:無治療の手術に備える。(3)CCI + FSN治療グループ:CCIモデリングが成功した後のFSN治療。(4)CCI + TENS治療グループ:CCIモデリングが成功した後のTENS治療。(5)FSN治療単独グループ:手術なしのFSN治療のみ。(6)TENS治療単独群:手術を伴わないTENS治療のみ。
3. CCIラットモデルの確立
注:ラットのCCI手術モデルは、1988年に実施されたBennettとXieに従って修正されました25。
- オペレーターがサージカルマスク、使い捨て手術キャップ、滅菌手袋を着用していることを確認してください。
- 手術台の表面を70%エタノールで消毒します。器具(ハサミ、鉗子、リトラクターなど)、ガーゼ、ホッチキス、綿棒をオートクレーブ滅菌で滅菌します。
注:無菌技術は、外科的処置全体を通して使用されます。 - 標準的な皮膚の準備(シェービング)後にラットに4%イソフルランで麻酔をかけ、2%イソフルランで維持します(図2A)。
- 後足をつまんだ後の反応の欠如を観察し、処置全体を通して麻酔ラットを監視することにより、麻酔の適切な深さを確認します。
- 乾燥を防ぐために、十分な量の獣医用眼軟膏を目に塗ります。.
- ラットを手術台の上でうつ伏せの姿勢に置き、右後ろ足の側面の毛を剃った後、ポビドンヨード溶液と75%エタノールで皮膚を3回消毒します。手術中は体温サポートを提供し、手術部位を覆うために滅菌ドレープを使用します。
- 大腿骨から3〜4mm下の皮膚を約20〜50mm平行に切開します。
- 大殿筋と大腿二頭筋の位置の特定を優先します。外科用ハサミを使用して皮下脂肪と表在性筋膜を層ごとに分離し、周囲の結合組織を切断して筋肉を露出させます(図2B)。
注意: 皮下脂肪層と表在性筋膜層を区別するには、質感と色を観察します。皮下脂肪層は、黄色がかったまたは白っぽい外観で、柔らかくしなやかに見えるはずです。表在性筋膜は、皮下脂肪の真下にある薄い線維層です。やさしく触診するか、鈍器で探り、皮下脂肪が表在性筋膜に比べて圧力に対する抵抗力が高いことに注意して、層を区別します。
- 鈍いはさみを使用して、表在性大臀筋と大腿二頭筋の間の結合組織を切断します。
- 坐骨神経を露出させるために、リトラクターを使用してこれら2つの筋肉の間のギャップを広げます(図2C)。
注:ラットの坐骨神経を視覚的に識別するには、大腿部に焦点を合わせます。大腿部の中点を見つけて、坐骨神経を視覚化します。典型的には、神経は大腿部の後方に沿って走り、股関節領域から始まり、膝に向かって伸びる。 - 神経の形態を変えることなく、坐骨神経をマイクロニードルで良い光源を通して摘み取ります。3-0クロミック腸結紮を使用して坐骨神経を2回結紮し、2つの縫合糸の間に結紮点を約1mm離して配置します。
- 各結紮糸の緩いループから始めて、結紮糸の端をループの近くでつかみ、ループがぴったりと収まるまで締めて、結紮糸が神経に沿って滑らないようにします。結紮中に四肢のわずかなけいれんが観察されたら中止します(図2D)。
- 坐骨神経を露出させるために、リトラクターを使用してこれら2つの筋肉の間のギャップを広げます(図2C)。
- 筋肉と皮膚を4-0の縫合線で層ごとに閉じます。最後に、創傷をヨウ素で消毒します(図2E)。
- 麻酔中のラットのバイタルサインを注意深く監視し、ラットが目を覚ますまで個々の回復ケージに入れてからケージに戻します。意識不明の動物の窒息を防ぐために、ケージに平らな紙の寝具を並べます。術後四肢の短いけいれんは、手術が成功したことを示します(図2F)。
- 疼痛過敏症検査をCCI(ベースライン)の前に数回実施し、CCI後のさまざまな時点で実施します。
- モデル構築後 1、3、5、および 7 日目に自発的な痛みと行動の変化を観察します。
注意: 右後肢の歩行と姿勢、および手足の舐めたり噛んだりする様子を観察します。- 神経因性疼痛の存在を特定して、モデルの確立が成功したかどうかを判断し、失敗したラットを除外します。
注:下肢歩行の脱力感、軽度の外反で固定された右肢のつま先、頻繁なぶら下がっている、着地を躊躇するなどの兆候を観察して、モデルの成功を評価します。ネズミが左後肢で体重を支え、右後肢を上げて腹部に近づけて立っているのを観察します。
- 神経因性疼痛の存在を特定して、モデルの確立が成功したかどうかを判断し、失敗したラットを除外します。
4. FSN操作の管理
- FSN治療群(CCI + FSNおよびFSN単独群を含む)のラットを、患肢を横方向に露出させたげっ歯類拘束具に固定します。手順全体を通してサーマルサポートを提供します。両群ともFSN使い捨て針で治療した(図3A)。
- 麻酔なしで、ラットの後肢をしっかりと伸ばすまで徐々にゆっくりと伸ばします(図3B)。
注:ラットの頭は、動物を落ち着かせて安定させるために外科用ドレープで覆われています。脚を伸ばしすぎてラットに怪我をさせないでください。ラットの反応を注意深く観察して、苦痛や不快感の兆候がないか確認します。ラットに痛みや不快感の兆候が見られる場合は、延長を中止し、休憩してから再試行してください。 - FSN針の保護シースを取り外します。
- FSN針の先端を、腰と後部にある大殿筋にほぼ近いTM(MTrPのある筋肉)に向かって挿入します。
- FSN針を平らに置き、約15°の角度で皮膚に入ります。
- 皮膚から皮下腔に慎重かつ迅速に押し込み、完全に挿入されるまでラットにストレスを与えないようにします。針が十分に挿入され、ソフトチューブが皮膚の下に完全に埋まるようにします。
- 前方に押し出すときは、針先を少し上げて、皮膚の膨らみが針先に沿って移動するかどうかを確認します(図3C)。
- 人差し指、中指、薬指を一直線に揃えながら、親指を支点としてFSNの針先を滑らかに柔らかく扇ぐように揺れ動きます。
- FSN針を中指と親指で挟み、対面で持ち、人差し指と薬指で前後に交互に動かします。
- 周波数を毎分100ストロークに設定し、約1分間操作を実行します(図3D)。
- 操作が完了したら、FSN針をすばやく引き抜きます。
注:操作は、合計4つのセッション(CCIモデルが作成されてから1日目、3日目、5日目、および7日目)で2日ごとに実行されました。使い捨てのFSN針は一度使用する必要があります。繰り返し使用すると、針が鈍くなり、ラットの痛みが増します。
5.TENS操作の管理
- TENS治療群(CCI + TENSおよびTENS単独群を含む)のラットを、患肢を横方向に露出させたげっ歯類拘束具に固定します。手順全体を通してサーマルサポートを提供します。処理する前に、毛皮が剃られていることを確認してください。
注:電極は45 mm(長さ)×5 mm(幅)に切断されました(図4A)。 - TENS の場所として Zusanli ポイント (ST36) と Sanyinjiaoポイント (SP6) を選択します。これは、神経因性疼痛を治療するための理論に基づいています26,27。
- 膝のすぐ下の脛骨と腓骨の間の脛骨の前結節から約5mm横のZusanliポイント(ST36)を見つけます28。
- 内側くるぶし28の近位3mmの脛骨の後縁にあるSanyinjiaoポイント(SP6)を見つけます。
注:これら2つの経穴は両方とも、StuxとPomeranzによって説明されているように、および動物の鍼治療アトラス28,29(図4B)に記載されている手動検査によって特定されます。
- 低周波電気刺激(2Hz連続正弦波、3mA)を10分間、TENS装置を用いて神経の周りの脚に電極を装着し、照射します。ラットの頭の頭を外科用ドレープで覆い、落ち着いて安定させます。
メモ: この手順は、合計 4 つのセッション(CCI モデル作成後 1、3、5、および 7 日目)で 2 日ごとに実行されます。
6. 動物行動試験による生理学的測定
注:坐骨神経機能指数(SFI)30 は、神経損傷の病理学と潜在的な治療を研究する研究者によって広く使用されている指標であり、負傷したラットの罹患後足の形状を反対側の足の形状と比較し、反対側の足と比較することによって決定されます。
- 透明なプレキシガラスとチルトミラーを使用してネズミの歩行路を設計し、歩行中のネズミの足跡と体の向きをキャプチャします。
注:通路は、長さ10 cm、幅50 cm、高さ15 cmのプラットフォームで、下部に白い紙の裏地があります(図5A)。 - ラットを箱に優しく自由に入れ、記録する前に少なくとも5分間、新しい環境に順応させます。
注:姿勢の筋肉の緊張への影響を避けるために、動物への不必要なストレスを最小限に抑えるために特別な注意が払われています。 - ネズミの足を赤いインクに浸し、ネズミが歩道に沿って歩くのを許し、裏紙に痕跡を残します。各テストで少なくとも2秒間の連続歩行を記録します。ラットを一方向に少なくとも3回歩かせます(図5B)。
注意: 速乾性、無毒、水溶性の赤インクを両後ろ足に塗布して、後肢の足跡をはっきりと見えるようにします。 - 実験の最後に、歩道ストリップを乾燥させてパラメータを測定します。定規で足跡を測り、0.5mm単位で丸めます。
注:各ラットの3つの明確な足跡をいくつかの足跡から選択し、3つの異なるパラメータを測定しました。SFIの要因には、プリント長(PL)、トウスプレッド(TS)、および中間トウスプレッド(ITS)が含まれます。
SFI値は、次の式31を使用して計算されます。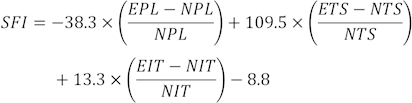
(EPL、実験的な印刷長さ;NPL、通常の印刷長。ETS、実験的なつま先の広がり。NTS、正常なつま先の広がり。EIT、実験的な中間つま先の広がり;NIT、中間つま先スプレッド。
SFI = 0 および -100 は、正常で完全な機能障害を示します。足の指を引きずるネズミには、任意に-100の値が割り当てられました。正常な神経機能の場合、SFIは0前後で振動し、-100前後のSFIは完全な機能障害を表します32。
7. 電気生理学的測定による神経生理学的評価33
注:筋電図検査は、この研究の電気生理学的活動を記録するために使用されました。複合筋活動電位(CMAP)は、神経から供給される標的筋の筋線維の活性化によって引き起こされます。CMAPの振幅と遅延が調査されます。CMAPの振幅は、ベースラインから負のピークまで測定されます。CMAPの潜伏時間は、刺激の印加から刺激部位と記録部位の間の距離に影響される複合活動電位の発現までの時間を測定することによって決定される。電気生理学は、ラットの末梢神経機能の客観的な評価を提供します。
- ゾレチル50(40 mg / kg、ip)を投与してラットに麻酔をかけます。.標準的なプロトコル(シェービング)に従って皮膚を準備します。
- 使い捨ての粘着面電極(外径20mm)を所定の場所に設置します。記録電極を腓腹筋の外側および背側表面に固定します(図6A)。
- 右坐骨神経近位部に電気刺激(強度1.2mA)を印加する。腓腹筋の複合筋活動電位(CMAP)を記録します(図6B)。
注意: 電極を挿入するときは、筋肉組織を避けるために注意してください。 - 各ラットについて、3回繰り返し測定した効果を記録します。
注:CMAPは、各グループの平均±SDとして表されます。信号は増幅器によって増幅され、フィルタリングされました(0.3-3 kHz)。積分後(時定数=0.05秒)、元の信号と積分された信号の両方が入力されます。元の信号と積算された信号は、PowerLabシステムでデジタル化され、コンピュータのハードディスクに保存されます。 - 電気生理学の手順が完了したら、ラットを別のケージに移動し、胸骨の横臥姿勢を維持するのに十分な意識を取り戻すまで監視します。ラットが麻酔薬から完全に回復したら、元のケージに戻します。
8. 統計:
- 反復測定分散分析(ANOVA)を使用して、グループ間のSFIとCMAPの差を評価します。
- 実験条件を知らないアシスタントがデータを定量化します。データを平均±標準偏差として表します。
- 必要に応じて、スチューデントの両側対応のある t 検定と対応のない t 検定を使用してデータを比較します。p < 0.05 として統計的有意性を確立します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
SFIの足跡と決定
CCI単独、CCI+FSN、およびCCI+TENSグループにおけるSFIの発現を調べました(図7)。CCI手術の7日目にFSNおよびTENS治療を4回行った後、CCI+FSN群のSFI(-15.85 ± 3.46)およびCCI+TENS(-29.58 ± 9.19)群のSFIは、CCI単独群(-87.40±14.22)と比較して有意に改善した。改善は、CCI+TENS群と比較して、CCI+FSN群で有意でした(図7A)。
?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
この研究では、ラットCCIモデルの神経因性疼痛に対するFSN治療の効果を観察します。この研究は、FSNまたはTENS治療後の治療効果を評価するためのSFIおよび電気生理学的検査のプロトコルを提示します。さらに、非侵襲的な行動テストと生理学的測定を使用して、損傷した神経の機能回復を評価する方法を示します。その結果、CCI誘発性坐骨神経痛後のFSN治療は、TENS治療よりもすべての予後?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
著者らは、競合する利益相反は存在しないことを宣言します。
謝辞
この研究は、台湾の彰化にあるChang Bing Show Chwan記念病院の動物センターからの助成金によって支援されました。著者らは、この研究プロジェクト全体を通して貴重な支援と支援をしてくれたShow Chwan Memorial Hospital IRCAD TAIWANに感謝します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Forceps | World Precision Instruments | 14098 | |
| Fu’s subcutaneous needling | Nanjing Paifu Medical Science and Technology Co. | FSN needles are designed for single use. The FSN needle is made up of three parts: a solid steel needle core (bottom), a soft casing pipe (middle), and a protecting sheath (top). | |
| Medelec Synergy electromyography | Oxford Instrument Medical Ltd. | 034W003 | Electromyogram (EMG) are used to help in the diagnosis and management of disorders such as neuropathies. Contains a portable two-channel electromyography/nerve conduction velocity system. |
| Normal saline (0.9%) 20 mL | Taiwan Biotech Co.,Ltd. | 4711916010323 | Lot: 1TKB2022 |
| POLYSORB 4-0 VIOLET 30" CV-25 | UNITED STATES SURGICAL, A DIVISION OF TYCO HEALTHC | GL-181 | |
| Retractor | COOPERSURGICAL, INC.(USA) | 3311-8G | |
| Rompun | Elanco Animal Health Korea Co. Ltd. | 27668 | |
| SCISSORS CVD 90MM | BBRUAN | XG-LBB-BC101R | |
| Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation | Well-Life Healthcare Co. | Model Number 2205A | Digital unit which offers TENS. Supplied complete with patient leads, self-adhesive electrodes, 3 AAA batteries and instructions in a soft carry bag. Interval ON time 1–30 s. Interval OFF time 1–30 s. |
| Zoletil | VIRRBAC | 8V8HA |
参考文献
- van Hecke, O., Austin, S. K., Khan, R. A., Smith, B. H., Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 155 (4), 654-662 (2014).
- Younes, M., et al. Prevalence and risk factors of disk-related sciatica in an urban population in Tunisia. Joint Bone Spine. 73 (5), 538-542 (2006).
- Woolf, C. J., Mannion, R. J. Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 353 (9168), 1959-1964 (1999).
- Baron, R., et al. Neuropathic low back pain in clinical practice. European Journal of Pain. 20 (6), 861-873 (2016).
- Ma, X., et al. Potential mechanisms of acupuncture for neuropathic pain based on somatosensory system. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 16, 940343(2022).
- Jang, J. H., et al. Acupuncture alleviates chronic pain and comorbid conditions in a mouse model of neuropathic pain: the involvement of DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex. Pain. 162 (2), 514-530 (2021).
- He, K., et al. Effects of acupuncture on neuropathic pain induced by spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence Based Complement and Alternative Medicine. 2022, 6297484(2022).
- Fu, Z., Lu, D. Fu's Subcutaneous Needling: A Novel Therapeutic Proposal. Acupuncture - Resolving Old Controversies and Pointing New Pathways. IntechOpen. , (2019).
- Fu, Z. H. The Foundation of Fu's Subcutaneous Needling. , People's Medical Publishing House, Co, Ltd. China. (2016).
- Fu, Z. H., Chou, L. W. Fu's Subcutaneous Needling, Trigger Point Dry Needling: An Evidence and Clinical-Based Approach. 2nd Edition. , Elsevier Health Sciences. Chapter 16 255-274 (2018).
- Fu, Z., Shepher, R. Fu's Subcutaneous Needling, a Modern Style of Ancient Acupuncture? Acupuncture in Modern Medicine. IntechOpen. , (2013).
- Chiu, P. E., et al. Efficacy of Fu's subcutaneous needling in treating soft tissue pain of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 11 (23), 7184(2022).
- Huang, C. H., Lin, C. Y., Sun, M. F., Fu, Z., Chou, L. W. Efficacy of Fu's Subcutaneous Needling on Myofascial Trigger Points for Lateral Epicondylalgia: A randomized control trial. Evidence Based Complement and Alternative Medicine. 2022, 5951327(2022).
- Huang, C. H. Rapid improvement in neck disability, mobility, and sleep quality with chronic neck pain treated by Fu's subcutaneous needling: A randomized control study. Pain Research and Management. 2022, 7592873(2022).
- Chou, L. W., Hsieh, Y. L., Kuan, T. S., Hong, C. Z. Needling therapy for myofascial pain: recommended technique with multiple rapid needle insertion. Biomedicine (Taipei). 4 (2), 13(2014).
- Ye, L., et al. Depression of mitochondrial function in the rat skeletal muscle model of myofascial pain syndrome is through down-regulation of the AMPK-PGC-1α-SIRT3 axis. Journal of Pain Research. 13, 1747-1756 (2020).
- Li, Y., et al. Effects of Fu's subcutaneous needling on mitochondrial structure and function in rats with sciatica. Molecular Pain. 18, 17448069221108717(2022).
- Perreault, T., Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C., Cummings, M., Gendron, B. C. Needling interventions for sciatica: Choosing methods based on neuropathic pain mechanisms-A scoping review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 10 (10), 2189(2021).
- Weller, J. L., Comeau, D., Otis, J. A. D. Myofascial pain. Seminars in Neurology. 38 (6), 640-643 (2018).
- Grøvle, L., et al. The bothersomeness of sciatica: patients' self-report of paresthesia, weakness and leg pain. European Spine Journal. 19 (2), 263-269 (2010).
- Jaggi, A. S., Jain, V., Singh, N. Animal models of neuropathic pain. Fundament Clinical Pharmacology. 25 (1), 1-28 (2011).
- Burma, N. E., Leduc-Pessah, H., Fan, C. Y., Trang, T. Animal models of chronic pain: Advances and challenges for clinical translation. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 95 (6), 1242-1256 (2017).
- McCann, M. E., Soriano, S. G. Does general anesthesia affect neurodevelopment in infants and children. British Medical Journal. 367, 6459(2019).
- Chan, K. Y., et al. Ameliorative potential of hot compress on sciatic nerve pain in chronic constriction injury-induced rat model. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience. 14, 859278(2022).
- Bennett, G. J., Xie, Y. K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 33 (1), 87-107 (1988).
- Somers, D. L., Clemente, F. R. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the management of neuropathic pain: The effects of frequency and electrode position on prevention of allodynia in a rat model of complex regional pain syndrome type II. Physical Therapy. 86 (5), 698-709 (2006).
- Xing, G., Liu, F., Wan, Y., Yao, L., Han, J. Electroacupuncture of 2 Hz induces long-term depression of synaptic transmission in the spinal dorsal horn in rats with neuropathic pain. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 35 (5), 453-457 (2003).
- Schone, A. M. Veterinary Acupuncture: Ancient Art to Modern Medicine. , American Veterinary Publication. (1999).
- Stux, G., Pomeranz, B. Acupuncture: Textbook and Atlas. , Springer-Verlag. Berlin. (1987).
- de Medinaceli, L., Freed, W. J., Wyatt, R. J. An index of the functional condition of rat sciatic nerve based on measurements made from walking tracks. Experimental Neurology. 77 (3), 634-643 (1982).
- Bain, J. R., Mackinnon, S. E., Hunter, D. A. Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 83 (1), 129-138 (1989).
- Kanaya, F., Firrell, J. C., Breidenbach, W. C. Sciatic function index, nerve conduction tests, muscle contraction, and axon morphometry as indicators of regeneration. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 98 (7), 1264-1271 (1996).
- Wild, B. M., et al. In vivo electrophysiological measurement of the rat ulnar nerve with axonal excitability testing. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (132), e56102(2018).
- Wong, J. Y., Rapson, L. M. Acupuncture in the management of pain of musculoskeletal and neurologic origin. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 10 (3), 531-545 (1999).
- Qin, Z., Liu, X., Yao, Q., Zhai, Y., Liu, Z. Acupuncture for treating sciatica: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open. 5 (4), 007498(2015).
- Zhi, M. J., et al. Application of the chronic constriction injury of the partial sciatic nerve model to assess acupuncture analgesia. Journal of Pain Research. 10, 2271-2280 (2017).
- Fu, Z. H., Xu, J. G. A brief introduction to Fu's subcutaneous needling. Pain Clinic. 17, 343-348 (2005).
- Peng, J., et al. The effect of Fu's subcutaneous needling combined with reperfusion approach on surface electromyography signals in patients with cervical spondylosis and neck pain: A clinical trial protocol. Biomed Research International. 2022, 1761434(2022).
- Fu, Z. H., Wang, J. H., Sun, J. H., Chen, X. Y., Xu, J. G. Fu's subcutaneous needling: possible clinical evidence of the subcutaneous connective tissue in acupuncture. Journal Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 13 (1), 47-51 (2007).
- Harrison, T. M., Churgin, S. M. Acupuncture and traditional Chinese veterinary medicine in zoological and exotic animal medicine: A review and introduction of methods. Veterinary Science. 9 (2), 74(2022).
- Gollub, R. L., Hui, K. K., Stefano, G. B. Acupuncture: pain management coupled to immune stimulation. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 20 (9), 769-777 (1999).
- Simons, D. G., Travell, J., Simons, L. E. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual. 2nd ed. , Williams and Wilkins. Baltimore, MD. (1999).
- Gerwin, R. D., Dommerholt, J., Shah, J. P. An expansion of Simons' integrated hypothesis of trigger point formation. Current Pain and Headache Reports. 8 (6), 468-475 (2004).
- Hong, C. Z., Simons, D. G. Pathophysiologic and electrophysiologic mechanisms of myofascial trigger points. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 79 (7), 863-872 (1998).
- Fu, Z., et al. Remote subcutaneous needling to suppress the irritability of myofascial trigger spots: an experimental study in rabbits. Evidence Based Complement and Alternative Medicine. 2012, 353916(2012).
- Hsieh, Y. L., Yang, C. C., Liu, S. Y., Chou, L. W., Hong, C. Z. Remote dose-dependent effects of dry needling at distant myofascial trigger spots of rabbit skeletal muscles on reduction of substance P levels of proximal muscle and spinal cords. Biomed Research International. 2014, 982121(2014).
- Ma, K., et al. Peripheral nerve adjustment for postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, controlled clinical study. Pain Medicine. 14 (12), 1944-1953 (2013).
- Gao, Y., Sun, J., Fu, Z., Chiu, P. E., Chou, L. W. Treatment of postsurgical trigeminal neuralgia with Fu's subcutaneous needling therapy resulted in prompt complete relief: Two case reports. Medicine. 102 (9), e33126(2023).
- Lucas, L. R., Wang, C. J., McCall, T. J., McEwen, B. S. Effects of immobilization stress on neurochemical markers in the motivational system of the male rat. Brain Research. 1155, 108-115 (2007).
- Yang, C. H., et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on response to immobilization stress. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 72 (4), 847-855 (2002).
- Adams, S., Pacharinsak, C. Mouse anesthesia and analgesia. Current Protocols in Mouse Biology. 5 (1), 51-63 (2015).
- Cantwell, S. L. Traditional Chinese veterinary medicine: the mechanism and management of acupuncture for chronic pain. Topics in Companion Animal Medicine. 25 (1), 53-58 (2010).
- Liebano, R. E., Rakel, B., Vance, C. G. T., Walsh, D. M., Sluka, K. A. An investigation of the development of analgesic tolerance to TENS in humans. Pain. 152 (2), 335-342 (2011).
- Khalil, Z., Merhi, M. Effects of aging on neurogenic vasodilator responses evoked by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: relevance to wound healing. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 55 (6), B257-B263 (2000).
- Sato, K. L., Sanada, L. S., Silva, M. D. D., Okubo, R., Sluka, K. A. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, acupuncture, and spinal cord stimulation on neuropathic, inflammatory and, non-inflammatory pain in rat models. The Korean Journal of Pain. 33 (2), 121-130 (2020).
- Maeda, Y., Lisi, T. L., Vance, C. G., Sluka, K. A. Release of GABA and activation of GABA(A) in the spinal cord mediates the effects of TENS in rats. Brain Research. 1136 (1), 43-50 (2007).
- Degrugillier, L., et al. A new model of chronic peripheral nerve compression for basic research and pharmaceutical drug testing. Regenerative Medicine. 16 (10), 931-947 (2021).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved