JoVE 비디오를 활용하시려면 도서관을 통한 기관 구독이 필요합니다. 전체 비디오를 보시려면 로그인하거나 무료 트라이얼을 시작하세요.
Method Article
세포 분열 및 확장의 운동 학적 분석 : 성장과 샘플링 발달 영역의 세포 기초의 정량화
요약
Quantifying cell division and expansion is of crucial importance to the understanding of whole-plant growth. Here, we present a protocol to calculate cellular parameters determining maize leaf growth rates and highlight the use of these data for investigating molecular growth regulatory mechanisms by directing developmental stage-specific sampling strategies.
초록
Growth analyses are often used in plant science to investigate contrasting genotypes and the effect of environmental conditions. The cellular aspect of these analyses is of crucial importance, because growth is driven by cell division and cell elongation. Kinematic analysis represents a methodology to quantify these two processes. Moreover, this technique is easy to use in non-specialized laboratories. Here, we present a protocol for performing a kinematic analysis in monocotyledonous maize (Zea mays) leaves. Two aspects are presented: (1) the quantification of cell division and expansion parameters, and (2) the determination of the location of the developmental zones. This could serve as a basis for sampling design and/or could be useful for data interpretation of biochemical and molecular measurements with high spatial resolution in the leaf growth zone. The growth zone of maize leaves is harvested during steady-state growth. Individual leaves are used for meristem length determination using a DAPI stain and cell-length profiles using DIC microscopy. The protocol is suited for emerged monocotyledonous leaves harvested during steady-state growth, with growth zones spanning at least several centimeters. To improve the understanding of plant growth regulation, data on growth and molecular studies must be combined. Therefore, an important advantage of kinematic analysis is the possibility to correlate changes at the molecular level to well-defined stages of cellular development. Furthermore, it allows for a more focused sampling of specified developmental stages, which is useful in case of limited budget or time.
서문
성장 분석은 일반적으로 환경 적 요인에 대한 유전자형 결정 성장의 차이 및 / 또는 표현형의 반응을 설명하기 위해 식물 과학자들에 의해 사용되는 도구 세트에 따라 달라집니다. 그들은 성장의 기본 메커니즘을 탐구하는 크기와 무게 전체 식물의 측정 또는 장기 성장 속도의 계산을 포함한다. 장기 성장은 세포 수준에서 세포 분열과 팽창에 의해 결정된다. 따라서, 분석 성장이 두 프로세스의 정량화를 포함하는 전체 장기 성장 1의 차이를 이해하는 열쇠이다. 따라서, 비 전문 실험실에서 사용하는 것이 상대적으로 쉽다 세포 성장 파라미터를 결정하는 적절한 방법을 위해 중요하다.
운동 학적 분석은 이미 장기 성장 모델이 개발을위한 강력한 프레임 워크를 제공하는 방식으로 설정되어있다. 이 기술은 선형 시스템에 최적화 된,이러한 애기 장대의 뿌리와 잎 외떡잎로서뿐만 아니라, 쌍떡잎 식물 잎 3 비 - 선형 시스템에 대한. 오늘날,이 방법은 점점 방법 유전 호르몬 발달을 연구하는 데 사용되는, 환경 적 인자, 세포 분열 및 다양한 기관에서 팽창 (표 1)에 영향을 준다. 제한이 식물 재료의보다 많은 양을 필요로 기술 (예, 대사 산물에 대한 장기의 크기와 공간적인 조직에 의해 부과 될 수 있지만, 또한, 또한, 그들의 기본적인 생화학 적 분자, 및 생리적 규정 (표 2)에 세포 과정을 연결하는 프레임 워크를 제공한다 측정 프로테오믹스 등).
예컨대 옥수수 (ZEA 메이스) 잎과 같은 외떡잎 잎 순차적 성숙에 도달하는 분열 조직 및 연신 존을 통과하는 세포가 선단을 향해 판의베이스를 이동하는 선형 시스템을 나타내는존. 이는 성장 (4)의 공간 패턴의 정량적 연구 이상적인 모델 시스템 만든다. 또한, 옥수수 잎 (몇 cm (5)에 걸친 분열과 신장 영역) 큰 성장 영역이 다른 조직 수준의 연구에 대한 가능성을 제공합니다. 이 분자 기술, 생리 학적 측정 및 세포 생물학 접근 (표 2)의 범위를 통해 운동 학적 분석에 의해 정량화 세포 분열 및 확장을 제어 (추정) 규제 메커니즘의 조사를 할 수 있습니다.
여기서는 단자엽 나뭇잎의 운동 학적 분석을 수행하기위한 프로토콜을 제공한다. 첫째, 우리는 리프 축의 위치와 얼마나 학적 매개 변수를 계산하는 함수로서 세포 분열과 세포 신장 둘의 적절한 분석을 수행하는 방법을 설명한다. 둘째, 우리는 또한이가 샘플링 디자인의 기초로 사용할 수있는 방법을 보여줍니다. 여기서 우리는 두 가지 사례를 토론 고해상도 샘플링을D는 각각 향상된 데이터 해석 및 시간 / 비용의 절감을 가능하게 샘플링을 집중했다.
운동의 표 1. 개요 세포 분열 및 다양한 기관에서 확장 정량화하는 방법을 분석한다.
| 오르간 | 참고 |
| 외떡잎 잎 | 16, 20, 21, 22 |
| 루트 팁 | 2, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 |
| 쌍떡잎 식물 잎 | 21, 30, 31 |
| 혀끝의 분열 조직을 촬영 | (32) |
운동의 표 1. 개요 세포 분열 및 다양한 기관에서 확장 정량화하는 방법을 분석한다.
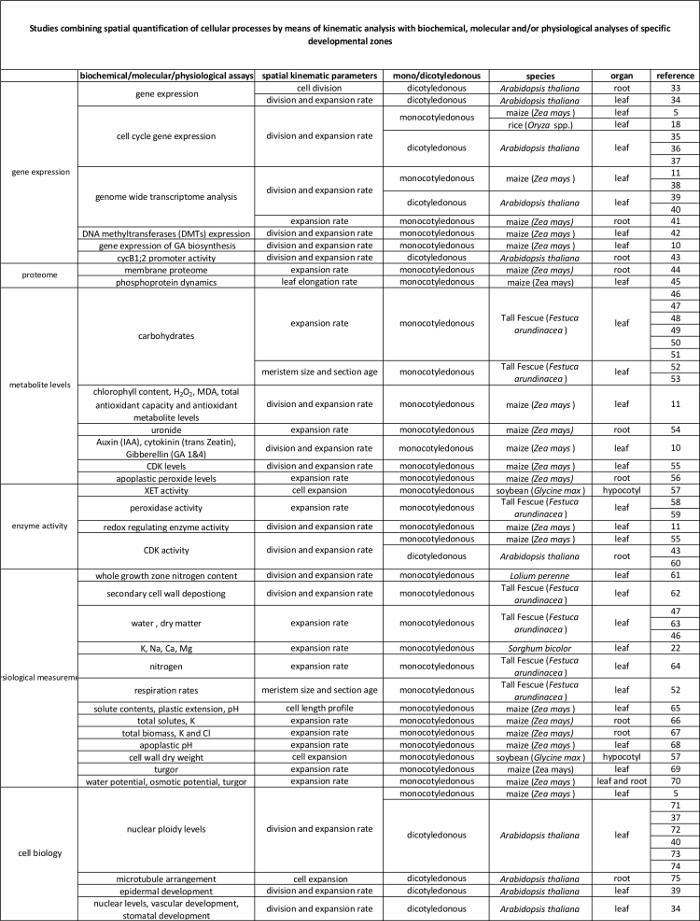
분자 수준에서 자신의 규제기구 학적 분석에 의해 정량 세포 과정과 표 2에 연결합니다. 다양한 종 및 기관에서 생화학 및 분자 분석 결과에 세포 프로세스의 정량화를 연결하는 다양한 연구에 대한 참조. 크 실로 글루칸 endotransglucosylase (XET), 말론 디 알데히드 (MDA), 사이클린 의존 키나제 (CDK). 이 테이블의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
프로토콜
참고 : 운동 학적 분석을 위해 다음 프로토콜은 정상 상태 성장하는 동안 잎에만 유효합니다. 이것은 몇 일 (6)의 기간 동안 안정한 잎의 신장 속도와 셀 길이와 리프 팽창 공간 패턴을 의미한다.
1. 식물 성장과 잎 신장 속도의 측정 (LER)
- 정상 상태의 성장에 잎과 관심의 발달 단계를 선택합니다.
참고 : 동일한 축의 연속 잎 유사한 공간 패턴을 의미 정상 성장 및 반복적 성장의 차이가있다. 묘목 성장의 초기 단계 동안, 연속 된 잎은 일반적으로 성장 영역 (7)의 크기를 증가시키는 것이 점점 더 빠른 증가로 인해. 약간 높은 위치 리프 유사한 성장 패턴 (8)이있을 수 있지만,이 연구중인 치료제에 의해 영향을받을 수있는 과도 단계이다. 라인과 TR을 비교하는 것이 중요 그것은 다른 시간에 개발 될지라도, 엄격하게 동일한 위치에서 리프 eatments. 비록 일정한 신장 속도로 성장 속도 프로파일은 반드시 상이한 발달 단계에서 동일하지 않다. 따라서, 일반적으로 출현 후 일수에 의해 정의 된 동일한 발달 단계 8에서 잎을 분석하는 것이 중요하다. - 성장 룸에서 통제 된 조건 하에서 각각의 치료 및 유전자형 적어도 15 식물을 성장, 외떡잎에 잎 성장의 전체 운동 학적 분석을 수행합니다.
- 잎이 완전히 (그림 1I) 확장 될 때까지 관심의 잎 (주변 잎의 가마에서 출현)가 나타납니다 당시 통치자 매일 잎의 길이를 측정하기 시작합니다. 리프 길이 판의 선단에 오물 레벨까지의 길이를 의미한다. 이 성장을 변경할 수 있으므로, 휴식 또는 잎이 손상되지 않도록주의하십시오.
1 다시 "SRC ="/ 파일 / ftp_upload / 54887 / 54887fig1.jpg "/>
그림 1 :. 옥수수 잎의 운동 학적 분석의 도식 개요는 관심의 잎은 잎 신장 비율 (LER)를 계산하는 세 가지 일 연속 통치자로 측정된다. 그 후, 리프 수확되고 세 cm 세그먼트는 분열 크기의 결정에 사용된다. 이것은 DAPI 염색 후 가장 말단 유사 분열의 그림을베이스까지의 길이를 측정하여 수행됩니다. 증식 유사 분열 수치와 (B) 조형 유사 분열 수치의 (A) 예. 중간 정맥의 다른 쪽 판베이스에서 제 십일cm은 셀 길이를 측정 한 10 상자 cm 세그먼트를 절단하는 데 사용된다. 이러한 측정은 성숙한 세포의 길이 (L 메트) 및 분열 (패 DIV)를 떠나는 셀의 길이를 결정하는 역할을 셀 길이 프로파일을 생성하기위한 기초를 제공한다. 그만큼 패 DIV 및 L 메르가 분열 조직 (N 메르) 세포의 수를 계산하는데 사용되지만 m> LER 및 L 매트는 전지 생산 속도 (P)을 계산하기 위해 사용된다. 차례로, P 및 N 메르 세포주기의 기간 (T의 c)의 역수이다 평균 셀 분할 률 (D)을 계산하는 데 사용된다. 동일 컬러의 화살표는이 화살표 다음의 파라미터를 계산하는데 사용되는 매개 변수를 나타낸다. 스케일 바는 40 μm의 =. 로마 숫자는 프로토콜에 설명 된 특정 실험 절차를 참조하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
2. 수확
- 관심의 발달 단계에서 (예를 들어, 출현 후 셋째 날), 적어도 다섯 대표 쪽을 선택배치에서 lants이되는 운동 학적 분석을 수행합니다. 마지막 잎의 길이를 결정하는 단계 130에서 설명한 바와 같이 식물의 나머지를 계속 측정.
- 식물의 위 지상 부분을 잘라. 뿌리에 최대한 가깝게 잘라 그대로 (그림 1II을)를 분열 부분을 유지합니다.
- 외부 잎에서 시작, 부드럽게 하나씩 줄이기 모든 관심의 잎까지 잎 제거합니다. 필요한 경우, 잎을 분리 기지에서 몇 가지 추가 밀리미터를 제거합니다. 또한 관심 (그림 1iii)의 잎으로 둘러싸인 정점 작은 잎을 제거 할 수 있습니다.
- 중간 정맥의 일측에 상기베이스부터 3 CM 구간을 잘라, 3 가득 1.5 mL를 시험관에 보관 : 1 (V : V) 무수 에탄올 : 아세트산 용액 (주의 : 장갑을 착용)에서 몇 달에 24 시간까지 4 ° C를 (그림 1iv). 이 세그먼트는 나중에 분열의 길이를 결정하는 데 사용된다.
- 로부터정맥의 다른 측면은,베이스에서 11cm 세그먼트를 잘라 (그림 1 V) 및 안료 (그림 1 VI)를 제거하기 위해 적어도 6 시간 동안 4 ° C에서 무수 에탄올로 가득 15 ML 튜브에 넣습니다.
주 : 나중에, (설명을 참조) 셀 길이 프로파일을 결정하는 첫 번째 10cm를 사용한다. - 적어도 24 시간 (그림 1vi) 4 ° C에서 청소의 또 다른 라운드의 무수 에탄올을 갱신.
- 마지막으로, 순수 젖산과 무수 에탄올을 대체 (주의 : 장갑을 착용) 청소 및 저장을 위해 4 ° C에서 24 시간 동안 또는 추가 사용 (그림 1vi)까지.
3. 분열 조직 길이 측정
- 50 mM 염화나트륨 (NaCl을), 5 mM의 에틸렌 디아민 테트라 아세트산이 포함 된 세척 버퍼 준비 (EDTA 단계;주의 : 장갑을 착용) 및 10 mM 트리스 (히드 록시 메틸) 아미노 메탄 - 염산 (트리스 - 염산, pH가 7).
- 2.4 절 등등에서 3cm 세그먼트를 타고20 분 (그림 1vii)에 대한 버퍼를 AK.
- 대기하는 동안, 얼음 및 진한에서 유지 한 μg의 / ㎖ 4 ', 6-diamidino -2- 페닐 인돌 (DAPI) 염색 액을 조제 린스 버퍼를 사용한다.
- DAPI 염색 용액에 2-5 분 동안 분열 조직 세그먼트를 배치하여 핵을 염색. 얼음과 어둠 (그림 1vii)에서 작업 할 수 있습니다.
- 빠르게 현미경 유리에 세그먼트를 장착하고 커버 유리를 덮어 형광 신호를 확인합니다. 표피 세포가있는 동안 기본 세포 층이 안, 형광을 표시해야합니다.
- 염색이 충분하지 않은 경우 일부 여분 분간 DAPI 염색 용액에 다시 넣어 세그먼트.
- , 염색을 중지 커버 유리와 현미경 슬라이드와 커버에 버퍼를 세척 한 방울의 세그먼트를 장착합니다.
- 1,000 epiderm의 시각화를 허용하는 20X의 배율로 UV 형광 장착 된 현미경을 사용하여알 세포를 한 번에. 세그먼트에 걸쳐 스크롤 증식 유사 분열 수치 (중기, anaphase (핵분열 말기), telophase 및 세포질 분열)을 찾아,하지만 개발 기공 (그림 1viii)의 조형 세포 분열을 피하기 9. 가장 말단 유사 분열 그림이있는 위치를 정의합니다.
- 잎의베이스와 가장 후방 표피 유사 분열 지수 사이의 거리를 측정함으로써 분열의 길이를 결정한다. 이미지 프레임의 전체 길이를 측정하는 이미지 분석 소프트웨어 (예 ImageJ에)를 사용한다.
- (가장 먼 유사 분열의 그림을 판베이스)에서 전체 분열 길이를 커버 프레임 수를 세어 전체 분열 길이 (도 1ix)을 획득 한 프레임의 길이만큼이 값을 곱한다.
4. 셀 길이 프로필
- 젖산 (단계 2.5)에 저장되어있는 세그먼트를 가지고 벤치에 조심스럽게 놓습니다. 세그먼트 재치를 잘라1cm 각 (그림 1 배)의 10 세그먼트 하는 메스.
- 젖산의 작은 방울의 현미경 슬라이드에 연속 잎 세그먼트를 탑재합니다. 지속적으로 향축 또는 배축면이 위로를 직면해야합니다. 원칙적으로, 특정 측면에 대한 선호가 없습니다.
- 리프베이스부터 세그먼트를 분석하는 미분 간섭 대비 (DIC) 광학계를 구비 한 현미경을 사용한다. 일관 동일한 세포 유형을 선택하기 위해 이미지 분석 소프트웨어와 기공 파일로 직접 인접하는 파일의 적어도 20 복제 표피 세포의 길이를 측정한다.
- 세그먼트 (세그먼트 충분할 당 4 위치)의 각각을 따라 등 간격 위치에서이 작업을 수행하고, 잎 (그림 1xi)에 걸쳐 각 측정에 해당하는 위치를 기록해야합니다.
- 로컬 평활 다항식 P를 사용하여 리프 축을 따라 각 mm의 평균 셀 길이를 결정rocedure,에 R-스크립트 (; 보충 파일 1 그림 1xii)에서 구현.
주 : R-스크립트 매끄럽게 증가하는 일련의 데이터를 제공한다. 필요한 스무딩 양은 단지 로컬 잡음을 제거하지만, 전체적인 곡선에 영향을 미치지 않아야 이상적 다소 임의적이며. 한 실험에서 모든 샘플에 대한 평활화의 동일한 금액을 사용하십시오. - 식물 사이의 각각의 위치에서의 셀 길이를 평균 판 축을 따라 셀 길이 프로파일을 생성하기 위해 표준 오차를 계산한다.
운동 학적 매개 변수 5. 계산 (보조 파일 2 참조)
- (단계 130에서와 같이 예를 들면 24 시간) 두 개의 연속 시점 사이 리프 길이의 변화를 고려하여 시간 간격을 분할함으로써 LER을 계산한다.
- 세포가 성숙한 CE의 95 %에 도달 여기서베이스로부터 먼 위치에 대응하는 성장 영역 (L의 GZ)의 길이를 계산평활 셀 길이 프로필에 게요 길이.
- 그 위치 (도 2) 다음의 모든 셀의 길이의 평균의 평활 셀 길이 프로필 95 %의 각 위치에 가라.
- 각 위치에서 계산 된 95 % 셀 길이의 셀 평활화 길이 (단계 4.4)을 비교한다. (, 보완 데이터 2도 2 참조) 잎의 기부에서 시작하여, 성장 영역은 실제 셀 길이는 다음의 셀의 길이의 95 %를 동일 위치에서 종료한다.
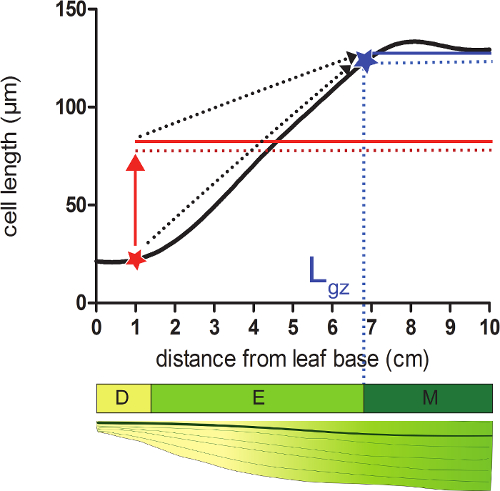
그림 2. 성장 영역의 종료를 결정하는 분열 조직은 : 적색 별표 표시된 위치에서는, 실제의 셀 크기보다 작은 95 %가이 위치에 따라 모든 셀의 평균 셀 크기 (빨간색 점선) (적색 고체 인 선). 성장 영역 (L의 GZ의 끝, AB로 표시95 %이 위치 (청색 선 다음 모든 셀의 평균 셀 크기의 (점선 파란색 라인)) 실제 셀 크기를 동일 곳 루 스타)에 위치해 있습니다. 분할 영역 (D), 신장 영역 (E), 성숙 영역 (M). 점선 화살표는 로컬 크기와 잎의 끝 부분에 기초 위치에서 이동하는 잎의 선단부의 평균 크기의 95 % 사이의 융합을 나타냅니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
- 성장 영역 (L의 GZ) 및 분열 크기의 길이 차이 등의 연신 존 (L EL)의 길이를 계산한다 (L 메르을, 3 단계에서).
- 성숙한 영역의 평균 셀 길이와 성숙 세포의 길이 (L 매트)를 계산한다.
- 를 얻을 리터 매트에 의해 LER 나눈다셀 생산 률 (P).
- N 및 N의 GZ 메르 차이로 연신 존 (N EL) 세포의 수를 계산한다. 분열 조직 (N 메르) 세포의 수는 분열에 대응 한 간격으로 위치한 셀의 누적 개수와 동일. 성장 영역 (N의 GZ) 세포의 수는 증가 영역에 대응 한 간격으로 위치한 셀의 누적 개수와 동일.
- P의 / N의 메르로서 평균 셀 분할 률 (D)을 계산한다. 세포주기 기간 (T의 C)는 LN (2) / D 같다.
- P가 N EL 나누어 연신 존 (T EL)의 시간을 계산한다. 분할 영역에서 시간은 로그 2 (N 메르) * T의 C 같습니다. 분열 조직을 떠나 세포의 길이 (L의 사업부)분열 조직 끝의 평활 셀 길이 프로필에서 셀 길이 같다.
- LN (L 매트) -ln (리터 사업부)] / T 엘 : 평균 다음 공식을 사용하여 세포의 확장 속도 (R 엘)을 계산합니다.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
결과
여기, 우리는 그들의 잎 성장의 관점에서 가뭄 스트레스 조건 (가뭄, 34 % SWC)를 실시 잘 급수 설비 (제어, 54 % 토양 수분 함량, (SWC))과 식물 사이의 비교를 나타낸다. 모든 식물은 ° C를 하루 / 밤, 300-400 μEm -2 초 -1 광합성 활성 방사선 (PAR). 가뭄 조건 25 ° C / 18을, 통제 된 조건 (16 시간 일 / 8 시간 밤에서 성장 챔버에서 성장했다 올바른 SWC에 도달 한 후, 추가?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
토론
옥수수 잎 전체 학적 분석 판 성장의 셀룰러 기반의 판정이 가능하고 효율적인 샘플링 전략의 디자인을 허용한다. 프로토콜은 비교적 간단하지만, 몇 가지주의 사항은 다음 중요한 단계 추천 : (1)은 분열 조직의 길이 결정 (3 단계) 때문에, 분열 조직에 손상을주지 않고 젊은, 동봉 된 잎 (2.3 단계) 분리하는 것이 중요합니다 전체가 필요합니다 분열 조직은 존재합니다. 연습은 사전에 필요할 수 있?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
공개
저자는 더 경쟁 재정적 이해 관계가 없음을 선언합니다.
감사의 말
이 작품은 VA에 앤트워프 대학에서 박사 친교에 의해 지원되었다; KS에 플랑드르 과학 재단 (FWO, 11ZI916N)에서 박사 교제; FWO (G0D0514N)에서 프로젝트 보조금; 공동의 연구 활동 (GOA) 연구 보조금, 앤트워프 대학의 연구위원회에서 "잎 형태 형성의 시스템 생물학 접근"; 그리고 Interuniversity 매력 폴란드 (IUAP VII / 29, MARS), 모든 비디오에 기여 GTSB 한 Asard, Bulelani L. Sizani과 하마다 AbdElgawad에 벨기에 연방 과학 정책 사무실 (BELSPO)에서 "옥수수와 애기 장대 뿌리와 성장을 쏴" .
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Pots | Any | Any | We use pots with the following measures, but can be different depending on the treatment/study: bottom diameter: 11 cm, opening diameter: 15 cm, height: 12 cm. We grow one maize plant per pot. |
| Planting substrate | Any | Any | We use potting medium (Jiffy, The Netherlands), but other substrates can be used, depending on treatment/study. |
| Ruler | Any | Any | An extension ruler that covers at least 1.5 meters is needed to measure the final leaf length of the plants. |
| Seeds | Any | NA | Seeds can be ordered from a breeder. |
| Scalpel | Any | Any | The scalpel is used during leaf harvesting to detach the leaf of interest from its surrounding leaves and right after harvesting to cut a proper sample for cell length and meristem length measurements. |
| 15 mL falcon tubes | Any | Any | The 15 mL falcon tubes are used for storing samples used for cell length measurements during sample clearing with absolute ethanol and lactic acid. |
| Eppendorf tubes | Any | Any | The eppendorf tubes are used for storing samples used for meristem length measurements in ethanol:acetic acid 3:1 (v:v) solution. |
| Gloves | Any | Any | Latex gloves, which protect against corrosive reagents. |
| Acetic acid | Any | Any | CAUTION: Corrosive to metals, category 1 Skin corrosion, categories 1A,1B,1C Serious eye damage, category 1; Flammable liquids, categories 1,2,3 |
| Absolute ethanol | Any | Any | CAUTION: Hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (permeator), of ingestion |
| Lactic acid >98% | Any | Any | CAUTION: Corrosive to metals, category 1 Skin corrosion, categories 1A,1B,1C Serious eye damage, category 1 |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Any | Any | |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) | Any | Any | CAUTION: Acute toxicity (oral, dermal, inhalation), category 4 Skin irritation, category 2 Eye irritation, category 2 Skin sensitisation, category 1 Specific Target Organ Toxicity – Single exposure, category 3 |
| Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride (Tris-HCl) | Any | Any | This material can be an irritant, contact with eyes and skin should be avoided. Inhalation of dust may be irritating to the respiratory tract. |
| 4′,6-Diamidine-2′-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) | Any | Any | Cell permeable fluorescent minor groove-binding probe for DNA. Causes skin irritation. May cause an allergic skin reaction. May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Ice | Any | NA | The DAPI solution has to be kept on ice. |
| Fluorescent microscope | AxioScope A1, Axiocam ICm1 from Zeiss or other | Any fluorescent microscope can be used for determining meristem length. | |
| Microscopic slide | Any | Any | |
| Cover glass | Any | Any | |
| Tweezers | Any | Any | Tweezers are needed for unfolding the rolled maize leaf right after harvesting in order to cut a proper sample for cell length and meristem length measurements. |
| Image-analysis software | Axiovision (Release 4.8) from Zeiss | NA | The software can be downloaded at: http://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/en_de/downloads/axiovision.html. Other softwares such as ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/) could be used as well. |
| Microscope equipped with DIC | AxioScope A1, Axiocam ICm1 from Zeiss or other | Any microscope, equipped with differential interference contrast (DIC) can be used to measure cell lengths. | |
| R statistical analysis software | R Foundation for Statistical Computing | NA | Open source; Could be downloaded at https://www.r-project.org/ |
| R script | NA | NA | We use the kernel smoothing function locpoly of the Kern Smooth package (Wand MP, Jones MC. Kernel Smoothing: Chapman & Hall/CRC (1995)). The script is available for Mac and Windows upon inquiry with the corresponding author. |
참고문헌
- Fiorani, F., Beemster, G. T. S. Quantitative analyses of cell division in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 60, 963-979 (2006).
- Silk, W. K., Erickson, R. O. Kinematics of Plant-Growth. J. Theor. Biol. 76, 481-501 (1979).
- Rymen, B., Coppens, F., Dhondt, S., Fiorani, F., Beemster, G. T. S. Kinematic Analysis of Cell Division and Expansion. Plant Developmental Biology. Hennig, L., Köhler, C. , Chapter 14 (2010).
- Avramova, V., Sprangers, K., Beemster, G. T. S. The Maize Leaf: Another Perspective on Growth Regulation. Trends Plant Sci. 20, 787-797 (2015).
- Rymen, B., et al. Cold nights impair leaf growth and cell cycle progression in maize through transcriptional changes of cell cycle genes. Plant Physiol. 143, 1429-1438 (2007).
- Muller, B., Reymond, M., Tardieu, F. The elongation rate at the base of a maize leaf shows an invariant pattern during both the steady-state elongation and the establishment of the elongation zone. J. Exp. Bot. 52, 1259-1268 (2001).
- Beemster, G. T. S., Masle, J., Williamson, R. E., Farquhar, G. D. Effects of soil resistance to root penetration on leaf expansion in wheat (Triticum aestivum L): Kinematic analysis of leaf elongation. J. Exp. Bot. 47, 1663-1678 (1996).
- Bernstein, N., Silk, W. K., Lauchli, A. Growth and Development of Sorghum Leaves under Conditions of Nacl Stress - Spatial and Temporal Aspects of Leaf Growth-Inhibition. Planta. 191, 433-439 (1993).
- Sylvester, A. W., Smith, L. G. Cell Biology of Maize Leaf Development. Handbook of maize: It's Biology. Bennetzen, J. L., Hake, S. C. , Springer. NY. (2009).
- Nelissen, H., et al. A Local Maximum in Gibberellin Levels Regulates Maize Leaf Growth by Spatial Control of Cell Division. Curr. Biol. 22, 1183-1187 (2012).
- Avramova, V., et al. Drought Induces Distinct Growth Response, Protection, and Recovery Mechanisms in the Maize Leaf Growth Zone. Plant Physiol. 169, 1382-1396 (2015).
- Picaud, J. C., et al. Total malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations as a marker of lipid peroxidation in all-in-one parenteral nutrition admixtures (APA) used in newborn infants. Pediatr. Res. 53, 406(2003).
- Basu, P., Pal, A., Lynch, J. P., Brown, K. M. A novel image-analysis technique for kinematic study of growth and curvature. Plant Physiol. 145, 305-316 (2007).
- Vander Weele, C. M., et al. A new algorithm for computational image analysis of deformable motion at high spatial and temporal resolution applied to root growth. Roughly uniform elongation in the meristem and also, after an abrupt acceleration, in the elongation zone. Plant Physiol. 132, 1138-1148 (2003).
- Nelissen, H., Rymen, B., Coppens, F., Dhondt, S., Fiorani, F., Beemster, G. T. S. Plant Organogenesis. DeSmet, I. , Chapter 17 (2013).
- Ben-Haj-Salah, H., Tardieu, F. Temperature Affects Expansion Rate of Maize Leaves without Change in Spatial-Distribution of Cell Length - Analysis of the Coordination between Cell-Division and Cell Expansion. Plant Physiol. 109, 861-870 (1995).
- Fiorani, F., Beemster, G. T. S., Bultynck, L., Lambers, H. Can meristematic activity determine variation in leaf size and elongation rate among four Poa species? A kinematic study. Plant Physiol. 124, 845-855 (2000).
- Pettko-Szandtner, A., et al. Core cell cycle regulatory genes in rice and their expression profiles across the growth zone of the leaf. J. Plant Res. 128, 953-974 (2015).
- Poorter, H., Remkes, C. Leaf-Area Ratio and Net Assimilation Rate of 24 Wild-Species Differing in Relative Growth-Rate. Oecologia. 83, 553-559 (1990).
- Macadam, J. W., Volenec, J. J., Nelson, C. J. Effects of Nitrogen on Mesophyll Cell-Division and Epidermal-Cell Elongation in Tall Fescue Leaf Blades. Plant Physiol. 89, 549-556 (1989).
- Tardieu, F., Granier, C. Quantitative analysis of cell division in leaves: methods, developmental patterns and effects of environmental conditions. Plant Mol. Biol. 43, 555-567 (2000).
- Bernstein, N., Silk, W. K., Lauchli, A. Growth and Development of Sorghum Leaves under Conditions of Nacl Stress - Possible Role of Some Mineral Elements in Growth-Inhibition. Planta. 196, 699-705 (1995).
- Erickson, R. O., Sax, K. B. Rates of Cell-Division and Cell Elongation in the Growth of the Primary Root of Zea-Mays. P. Am. Philos. Soc. 100, 499-514 (1956).
- Beemster, G. T. S., Baskin, T. I. Analysis of cell division and elongation underlying the developmental acceleration of root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 116, 1515-1526 (1998).
- Goodwin, R. H., Stepka, W. Growth and differentiation in the root tip of Phleum pratense. Am. J. Bot. 32, 36-46 (1945).
- Hejnowicz, Z. Growth and Cell Division in the Apical Meristem of Wheat Roots. Physiologia Plantarum. 12, 124-138 (1959).
- Gandar, P. W. Growth in Root Apices .1. The Kinematic Description of Growth. Bot. Gaz. 144, 1-10 (1983).
- Baskin, T. I., Cork, A., Williamson, R. E., Gorst, J. R. Stunted-Plant-1, a Gene Required for Expansion in Rapidly Elongating but Not in Dividing Cells and Mediating Root-Growth Responses to Applied Cytokinin. Plant Physiol. 107, 233-243 (1995).
- Sacks, M. M., Silk, W. K., Burman, P. Effect of water stress on cortical cell division rates within the apical meristem of primary roots of maize. Plant Physiol. 114, 519-527 (1997).
- Granier, C., Tardieu, F. Spatial and temporal analyses of expansion and cell cycle in sunflower leaves - A common pattern of development for all zones of a leaf and different leaves of a plant. Plant Physiol. 116, 991-1001 (1998).
- De Veylder, L., et al. Functional analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 13, 1653-1667 (2001).
- Kwiatkowska, D. Surface growth at the reproductive shoot apex of Arabidopsis thaliana pin-formed 1 and wild type. J. Exp. Bot. 55, 1021-1032 (2004).
- Kutschmar, A., et al. PSK-alpha promotes root growth in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 181, 820-831 (2009).
- Vanneste, S., et al. Plant CYCA2s are G2/M regulators that are transcriptionally repressed during differentiation. Embo J. 30, 3430-3441 (2011).
- Eloy, N. B., et al. Functional Analysis of the anaphase-Promoting Complex Subunit 10. Plant J. 68, 553-563 (2011).
- Eloy, N. B., et al. SAMBA, a plant-specific anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome regulator is involved in early development and A-type cyclin stabilization. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109, 13853-13858 (2012).
- Dhondt, S., et al. SHORT-ROOT and SCARECROW Regulate Leaf Growth in Arabidopsis by Stimulating S-Phase Progression of the Cell Cycle. Plant Physiol. 154, 1183-1195 (2010).
- Baute, J., et al. Correlation analysis of the transcriptome of growing leaves with mature leaf parameters in a maize RIL population. Genome Biol. 16, (2015).
- Andriankaja, M., et al. Exit from Proliferation during Leaf Development in Arabidopsis thaliana: A Not-So-Gradual Process. Dev. Cell. 22, 64-78 (2012).
- Beemster, G. T. S., et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression profiles associated with cell cycle transitions in growing organs of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 138, 734-743 (2005).
- Spollen, W. G., et al. Spatial distribution of transcript changes in the maize primary root elongation zone at low water potential. Bmc Plant Biol. 8, (2008).
- Candaele, J., et al. Differential Methylation during Maize Leaf Growth Targets Developmentally Regulated Genes. Plant Physiol. 164, 1350-1364 (2014).
- West, G., Inze, D., Beemster, G. T. S. Cell cycle modulation in the response of the primary root of Arabidopsis to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 135, 1050-1058 (2004).
- Zhang, Z., Voothuluru, P., Yamaguchi, M., Sharp, R. E., Peck, S. C. Developmental distribution of the plasma membrane-enriched proteome in the maize primary root growth zone. Front. Plant Sci. 4, (2013).
- Bonhomme, L., Valot, B., Tardieu, F., Zivy, M. Phosphoproteome Dynamics Upon Changes in Plant Water Status Reveal Early Events Associated With Rapid Growth Adjustment in Maize Leaves. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 11, 957-972 (2012).
- Schnyder, H., Nelson, C. J. Growth-Rates and Assimilate Partitioning in the Elongation Zone of Tall Fescue Leaf Blades at High and Low Irradiance. Plant Physiol. 90, 1201-1206 (1989).
- Schnyder, H., Nelson, C. J., Spollen, W. G. Diurnal Growth of Tall Fescue Leaf Blades .2. Dry-Matter Partitioning and Carbohydrate-Metabolism in the Elongation Zone and Adjacent Expanded Tissue. Plant Physiol. 86, 1077-1083 (1988).
- Schnyder, H., Nelson, C. J. Growth-Rates and Carbohydrate Fluxes within the Elongation Zone of Tall Fescue Leaf Blades. Plant Physiol. 85, 548-553 (1987).
- Vassey, T. L., Shnyder, H. S., Spollen, W. G., Nelson, C. J. Cellular Characterisation and Fructan Profiles in Expanding Tall Fescue. Curr. T. Pl. B. 4, 227-229 (1985).
- Allard, G., Nelson, C. J. Photosynthate Partitioning in Basal Zones of Tall Fescue Leaf Blades. Plant Physiol. 95, 663-668 (1991).
- Spollen, W. G., Nelson, C. J. Response of Fructan to Water-Deficit in Growing Leaves of Tall Fescue. Plant Physiol. 106, 329-336 (1994).
- Volenec, J. J., Nelson, C. J. Carbohydrate-Metabolism in Leaf Meristems of Tall Fescue .1. Relationship to Genetically Altered Leaf Elongation Rates. Plant Physiol. 74, 590-594 (1984).
- Volenec, J. J., Nelson, C. J. Carbohydrate-Metabolism in Leaf Meristems of Tall Fescue .2. Relationship to Leaf Elongation Rates Modified by Nitrogen-Fertilization. Plant Physiol. 74, 595-600 (1984).
- Silk, W. K., Walker, R. C., Labavitch, J. Uronide Deposition Rates in the Primary Root of Zea-Mays. Plant Physiol. 74, 721-726 (1984).
- Granier, C., Inze, D., Tardieu, F. Spatial distribution of cell division rate can be deduced from that of p34(cdc2) kinase activity in maize leaves grown at contrasting temperatures and soil water conditions. Plant Physiol. 124, 1393-1402 (2000).
- Voothuluru, P., Sharp, R. E. Apoplastic hydrogen peroxide in the growth zone of the maize primary root under water stress.1. Increased levels are specific to the apical region of growth maintenance. J. Exp. Bot. 64, 1223-1233 (2012).
- Wu, Y. J., Jeong, B. R., Fry, S. C., Boyer, J. S. Change in XET activities, cell wall extensibility and hypocotyl elongation of soybean seedlings at low water potential. Planta. 220, 593-601 (2005).
- Macadam, J. W., Nelson, C. J., Sharp, R. E. Peroxidase-Activity in the Leaf Elongation Zone of Tall Fescue .1. Spatial-Distribution of Ionically Bound Peroxidase-Activity in Genotypes Differing in Length of the Elongation Zone. Plant Physiol. 99, 872-878 (1992).
- Macadam, J. W., Sharp, R. E., Nelson, C. J. Peroxidase-Activity in the Leaf Elongation Zone of Tall Fescue .2. Spatial-Distribution of Apoplastic Peroxidase-Activity in Genotypes Differing in Length of the Elongation Zone. Plant Physiol. 99, 879-885 (1992).
- Beemster, G. T. S., De Vusser, K., De Tavernier, E., De Bock, K., Inze, D. Variation in growth rate between Arabidopsis ecotypes is correlated with cell division and A-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Plant Physiol. 129, 854-864 (2002).
- Kavanova, M., Lattanzi, F. A., Schnyder, H. Nitrogen deficiency inhibits leaf blade growth in Lolium perenne by increasing cell cycle duration and decreasing mitotic and post-mitotic growth rates. Plant Cell Environ. 31, 727-737 (2008).
- Macadam, J. W., Nelson, C. J. Secondary cell wall deposition causes radial growth of fibre cells in the maturation zone of elongating tall fescue leaf blades. Ann. Bot-London. 89, 89-96 (2002).
- Schnyder, H., Nelson, C. J. Diurnal Growth of Tall Fescue Leaf Blades .1. Spatial-Distribution of Growth, Deposition of Water, and Assimilate Import in the Elongation Zone. Plant Physiol. 86, 1070-1076 (1988).
- Gastal, F., Nelson, C. J. Nitrogen Use within the Growing Leaf Blade of Tall Fescue. Plant Physiol. 105, 191-197 (1994).
- Vanvolkenburgh, E., Boyer, J. S. Inhibitory Effects of Water Deficit on Maize Leaf Elongation. Plant Physiol. 77, 190-194 (1985).
- Silk, W. K., Hsiao, T. C., Diedenhofen, U., Matson, C. Spatial Distributions of Potassium, Solutes, and Their Deposition Rates in the Growth Zone of the Primary Corn Root. Plant Physiol. 82, 853-858 (1986).
- Meiri, A., Silk, W. K., Lauchli, A. Growth and Deposition of Inorganic Nutrient Elements in Developing Leaves of Zea-Mays L. Plant Physiol. 99, 972-978 (1992).
- Neves-Piestun, B. G., Bernstein, N. Salinity-induced inhibition of leaf elongation in maize is not mediated by changes in cell wall acidification capacity. Plant Physiol. 125, 1419-1428 (2001).
- Bouchabke, O., Tardieu, F., Simonneau, T. Leaf growth and turgor in growing cells of maize (Zea mays L.) respond to evaporative demand under moderate irrigation but not in water-saturated soil. Plant Cell Environ. 29, 1138-1148 (2006).
- Westgate, M. E., Boyer, J. S. Transpiration-Induced and Growth-Induced Water Potentials in Maize. Plant Physiol. 74, 882-889 (1984).
- Horiguchi, G., Gonzalez, N., Beemster, G. T. S., Inze, D., Tsukaya, H. Impact of segmental chromosomal duplications on leaf size in the grandifolia-D mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 60, 122-133 (2009).
- Fleury, D., et al. The Arabidopsis thaliana homolog of yeast BRE1 has a function in cell cycle regulation during early leaf and root growth. Plant Cell. 19, 417-432 (2007).
- Vlieghe, K., et al. The DP-E2F-like gene DEL1 controls the endocycle in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 15, 59-63 (2005).
- Boudolf, V., et al. The plant-specific cyclin-dependent kinase CDKB1;1 and transcription factor E2Fa-DPa control the balance of mitotically dividing and endoreduplicating cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 16, 2683-2692 (2004).
- Baskin, T. I., Beemster, G. T. S., Judy-March, J. E., Marga, F. Disorganization of cortical microtubules stimulates tangential expansion and reduces the uniformity of cellulose microfibril alignment among cells in the root of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 135, 2279-2290 (2004).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기더 많은 기사 탐색
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유