Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Fast and Sensitive Colloidal Coomassie G-250 Staining for Proteins in Polyacrylamide Gels
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This video shall popularize a colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining protocol according to Kang et al. for the detection of average 4 ng protein in gels. The staining is completed within 2 hours and without any effort. We routinely use Kang's protocol for analytical purposes in gel-based proteomics.
Streszczenie
Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) is a dye commonly used for the visualization of proteins separated by SDS-PAGE, offering a simple staining procedure and high quantitation. Furthermore, it is completely compatible with mass spectrometric protein identification. But despite these advantages, CBB is regarded to be less sensitive than silver or fluorescence stainings and therefore rarely used for the detection of proteins in analytical gel-based proteomic approaches.
Several improvements of the original Coomassie protocol1 have been made to increase the sensitivity of CBB. Two major modifications were introduced to enhance the detection of low-abundant proteins by converting the dye molecules into colloidal particles: In 1988, Neuhoff and colleagues applied 20% methanol and higher concentrations of ammonium sulfate into the CBB G-250 based staining solution2, and in 2004 Candiano et al. established Blue Silver using CBB G-250 with phosphoric acid in the presence of ammonium sulfate and methanol3. Nevertheless, all these modifications just allow a detection of approximately 10 ng protein. A widely fameless protocol for colloidal Coomassie staining was published by Kang et al. in 2002 where they modified Neuhoff's colloidal CBB staining protocol regarding the complexing substances. Instead of ammonium sulfate they used aluminum sulfate and methanol was replaced by the less toxic ethanol4. The novel aluminum-based staining in Kang's study showed superior sensitivity that detects as low as 1 ng/band (phosphorylase b) with little sensitivity variation depending on proteins.
Here, we demonstrate application of Kang's protocol for fast and sensitive colloidal Coomassie staining of proteins in analytical purposes. We will illustrate the quick and easy protocol using two-dimensional gels routinely performed in our working group.
Protokół
Part 1: Two-dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis using cup-loading
- IPG-strip rehydration and isoelectric focusing (IEF)
- Rehydrate Immobiline DryStrip gels, pH 6-11 (7 cm) in 125 μl rehydration solution [7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 4% CHAPS, 50 mM hydroxyethyldisulfide and 2% IPG Buffer pH 6-11] using Immobiline DryStrip Reswelling Tray for at least 10 hours.
- Dissolve precipitated protein sample in IEF sample buffer [7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 2% CHAPS, 2% ASB-14, 50 mM hydroxyethyldisulfide and 2% IPG Buffer pH 6-11] corresponding to 60-100 μg protein per 100 μl.
- After solubilization (at least 30 minutes at room temperature), apply protein sample via anodic cup-loading using sample cups. The volume of the cup is 100 μl (Manifold cups allow up to 150 μl).
Note: you can load larger sample amounts if you insert a low-voltage step at the beginning of the focusing protocol and refill the cups while there is still a liquid film in the cup! - Perform isoelectric focusing for 11.1 kVh in gradient mode in the Multiphor II Electrophoresis Unit.
- Equilibration and SDS-PAGE
- After IEF, the IPG strips were subjected to reduction and alkylation, each time 15 minutes on a shaker, using 1% dithiothreitol and 2.5% iodoacetamide respectively in equilibration solution [50 mM Tris-HCl/pH 8.8, 6 M urea, 30% glycerol and 2% SDS].
- Rinse the equilibrated strips with H2O and blot them onto whatman paper to remove excess equilibration buffer. Afterwards dip the strips in SDS-running buffer (1X).
- Second dimension is performed by SDS-PAGE on a vertical electrophoresis systems with a total acrylamide concentration of 12 %. The equilibrated IPG strips were placed on the top of the separating gels and fixed with hot agarose solution [0.5% agarose in running buffer containing bromophenol blue].
- Proteins were separated for 2.5 hrs, starting at 80 V for 15 minutes followed by 120 V until the dye front reaches the bottom of the gel cassette.
Part 2: Colloidal Coomassie staining with CBB G-250
1. Staining solutions
Note: for the preparation of the staining solutions, use chemicals with high quality such as analytical grade (p.a.) and water of high purity as you get from Millipore systems (Milli-Q water).
| Coomassie solution: | ad 2000 ml H2O | |
| 0.02 % (w/v) | CBB G-250 | 0,4 g |
| 5 % (w/v) | aluminum sulfate-(14-18)-hydrate | 100 g |
| 10 % (v/v) | ethanol (96%) | 200 ml |
| 2 % (v/v) | orthophosphoric acid (85 %) | 47 ml |
Note: for the preparation of the staining solution, the sequential addition of the components in the following order has to be maintained:
- first dissolve aluminum sulfate in Milli-Q water
- thereafter add ethanol, homogenize, and mix CBB G-250 to the solution
- as recently as the solution is completely dissolved, add phosphoric acid (the incorporation of the acid to the alcoholic media lets the Coomassie molecules aggregate into their colloidal state)
- finally fill up with Milli-Q water
Note: the final staining solution has a dark green-bluish appearance and is full of particles swimming around:
- Don't filtrate this solution!
- If you changed the order of preparation, you would get a more violet-bluish solution that is less sensitive.
| Destaining solution: | ad 2000 ml H2O | |
| 10 % (v/v) | ethanol (96 %) | 200 ml |
| 2 % (v/v) | orthophosphoric acid (85 %) | 47 ml |
2. Staining procedure
- After second dimension separation, carefully remove the gels from the glass plates and transfer them into a staining dish filled with Milli-Q water.
- Wash the gels three times with Milli-Q water for 10 minutes on a horizontal shaker (insufficient washing causes poor sensitivity because the remaining SDS on the gels disturbs the bounding of the dye to the protein).
- Shake the Coomassie solution before use to disperse the colloidal particles evenly.
- Incubate the gels well covered with the Coomassie solution by agitation on a shaker for 2-12 hours. This staining generates marginal background so you can observe the staining progress in between.
Note: after 10 minutes you can see first protein spots appearing, within 2 hours of incubation about 80% staining to its maximum level is completed. For nearly 100% staining, overnight incubation is recommended. In some cases, when the amount of protein to be stained is huge and the solution turns into a bright blue, a refresh of the staining solution is necessary. - After the staining procedure remove the Coomassie solution and rinse the gels twice with Milli-Q water.
Note: you can reuse the staining solution as long as particles are still remaining, otherwise discard it (keep in mind that your laboratory may have special regulations for waste disposal). - Remove sticking dye particles from the staining dish with a lint-free paper towel and destain for 10- 60 minutes.
Note: You can also wash the gels just with Milli-Q water but this we recommend only for preparative gels because there will last an irregular, weak Coomassie film on the gels that will arise during the scanning procedure. - Finally rinse the gels twice with Milli-Q water: the gels will reach their original thickness (the alcohol-acid media makes the gels shrinking) and neutralization in water additionally enhances Coomassie's color intensity.
Part 3: Representative results
If you follow the protocol described above you will get on your 2-D gel distinctive resolved and well stained dark blue protein spots. Even compared to a 2-D gel stained with silver according to Shevchenko et al.5 ,a protocol claiming good sensitivity and compatibility with mass spectrometry, we achieve equal staining results.
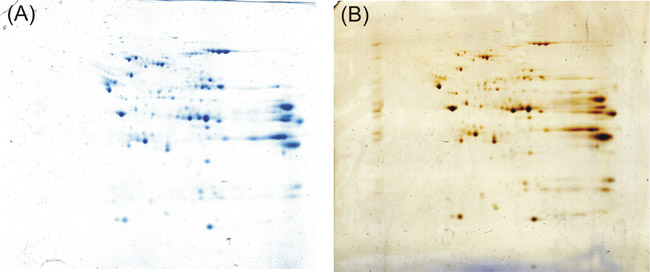
Figure 1: Final outcome of the experimentation described above. Kang's Coomassie protocol (A) performs strongly like the silver staining according to Shevchenko et al. (B) in detecting proteins after 2-D gel electrophoresis.
Part 4: Tips and tricks
- Perform some test stainings before processing your own samples. For unexplainable reasons we reported sometimes that a protein of interest could not be detected successfully even when milligrams were applied. In this case we recommend to prepare some dilution series to test sensitivity.
- If you have low in-gel detection of protein(s) in general, unsuccessful transfer from the stacking to the separating gel during SDS-PAGE will possibly be the reason. You can check for such sticky proteins by staining the complete gel including the stacking area.
- For a fast verification of your isoelectric focusing results, you can directly stain the IPG-strips without any further second dimension separation.
- Occasionally turn the gels during the staining procedure so they are stained evenly from both sides (if you keep the gels unmoved, the dye just binds to one side of the gel).
- We experienced that storage of the staining solution in a dark bottle increases its lifetime (in transparent bottles up to 4 month).
- After staining and documenting you can keep the gels in the fridge for several years (if you add acidic solution you avoid contaminations by fungi).
- Destaining of gel plugs for a tryptic digest can be accelerated by warming in a block heater.
Dyskusje
Innovative or just another Coomassie protocol?
At the moment there exist multiple protocols for staining procedures with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Most of them result from minor or major modifications of one of the most commonly used protocols by Neuhoff and colleagues2. Also Kang's protocol based on Neuhoff's formula. But is it really an alternative Coomassie staining method for proteomic research? We will picture two main issues, detection limit and usability, to evidence that it...
Ujawnienia
I have nothing to disclose.
Podziękowania
We thank Dr. Nicola Wiethölter for preparing and staining of 1-D gels.
This work was funded by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (GRK 1089/project 5 to ND and SM) and supported by a research fellowship from the Jürgen Manchot Stiftung to ND.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Immobiline DryStrip gels | GE Healthcare | 17-6001-94 | Can even be used 2 years after expire date. |
| Immobiline DryStrip Reswelling Tray | GE Healthcare | 80-6371-84 | Do not clean with organic solvents. Designed for 7-18 cm IPG-strips. |
| Immobiline DryStrip Kit | GE Healthcare | 18-1004-30 | Includes a tray, electrode holder, anode and cathode electrodes, aligner and sample cup bar and sample cups. |
| EPS 3501 XL Power Supply | GE Healthcare | 18-1130-05 | Supplies voltage up to 3500 V. |
| Multiphor II Electrophoresis Unit | GE Healthcare | 18-1018-06 | Movable electrodes enable IEF in IPG strips of all length (7-24 cm IPG strips) |
| PerfectBlue gel system Twin S | Peqlab | 45-1010-C | SDS-PAGE in 10x10 cm mini-gel format. Gel chamber includes a cooling system. |
| staining dishes with lids | VWR international | 216-3412 | Fits for mini-gels. Stackable on shaker. |
| aluminium sulfate-18-hydrate | Merck & Co., Inc. | 1.01102.5000 | We made best experience with Merck. Just available in 5 kg package. |
| orthophosphoric acid | Prolabo | 20 624.295 | Sold in glass bottles. |
Odniesienia
- Fazekas de St Groth, S., Webster, S. R. G., Datyner, A. Two new staining procedures for quantitative estimation of proteins on electrophoretic strips. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 71, 377-391 (1963).
- Neuhoff, V., Arold, N., Taube, D., Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis. 9, 255-262 (1988).
- Candiano, G., Bruschi, M., Musante, L., Santucci, L., Ghiggeri, G. M., Carnemolla, B., Orecchia, P., Zardi, L., Rigetti, P. G. Blue Silver: A very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis. 25, 1327-1333 (2004).
- Kang, D., Gho, S. G., Suh, M., Kang, C. Highly Sensitive and Fast Protein Detection with Coomassie Brilliant Blue in Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 11, 1511-1512 (2002).
- Shevchenko, A., Wilm, M., Vorm, O., Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 68, 850-858 (1996).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone