Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Chronic Salmonella Infected Mouse Model
* Wspomniani autorzy wnieśli do projektu równy wkład.
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Establish a chronic bacterial infected mouse model with persistent Salmonella typhimurium colonization in intestine for 27 weeks.
Streszczenie
Protokół
This protocol includes three portions: bacterial culture, mouse gavage, and Salmonella detection.
1. Salmonella growth condition.
- Prepare the Salmonella Luria-Bertani broth (LB) plate, incubate at 37° C overnight.
- Pick a clone from the LB plate and put into 7 ml LB in a 12 ml tube, and shake at 37°C for about 5 hours.
- Inoculate 50 ml LB with 0.05 ml of a stationary phase culture and incubate at 37°C without shaking for about 18 hours.
- Spin overnight bacterial culture at room temperature with 6000 rpm for 10 minutes, suspend the bacteria in HBSS using ratio 100:3 (LB: HBSS). For example:
Every 50 ml LB culture will be suspended in 1.5 ml HBSS. - For the animal gavage, further dilute the bacterial culture at 1:10 ratio. For example:
Every 1.5 ml LB culture will be suspended in 15 ml HBSS.
2. Salmonella-infection model*.
- Prepare the streptomycin solution. Each mouse will be given 7.5 mg of streptomycin in 100 μl HBSS. For example, prepare total 90 mg of streptomycin in 1.2 ml HBSS for 10 mice. Always have some extra volume when preparing the streptomycin solution.
- Withdraw water and food 4 hours before oral gavage treatment.
- Gavage mice with streptomycin with 7.5 mg of streptomycin (100 μl of HBSS for control mice). Grab the skin over the mouse shoulder firmly with the thumb and middle finger, stretch the head and neck with the index finger to make the esophagus straight. Direct the ball-tip of the feeding needle along the roof of the mouth and toward the right side of the back of the pharynx, then gently pass down into the esophagus and inject the 100 μl solution. No resistance should be felt.
- At 20 hours after streptomycin treatment, withdrawn water and food again before the mice are infected with bacteria.
- Gavage each mouse with 100 μl suspension in HBSS or treated with sterile HBSS (control) by oral gavage. The gavage procedure is the same as 2.3) gavage mice with streptomycin.
*Animal experiments were performed by using specific-pathogen-free female C57BL/6 mice (Taconic, Hudson, NY) that were 6-7 weeks old as previously described1. The protocol was approved by the University of Rochester University Committee on Animal Resources (UCAR).
3. Detection of Salmonella in intestine.
- Collect mouse fecal (about 100 mg).
- Transfer fecal sample to a 1.5 micro centrifuge tube with 1ml PBS and vortex vigorously.
- Centrifuge for 10 min at 800 rpm. Transfer the supernatant into a clean microfuge tube.
- Centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 5min. Supernatant is discarded and 200 μL PBS is added to the pellets and vortexed.
- Streak the 200 μl PBS with a disposable cell spreader on a BBL CHROMagar plate to detect Salmonella. Salmonella species appear mauve (rose to purple, see Fig.1). If 200 μl yields too many colonies on the plate, use 100 μl or 50 μl for the streak.
4. Representative Results.
When the protocol is done correctly, Salmonella typhimurium colonization can be detected in the mouse intestine over 6 months. Salmonella could be detected by fecal culture over 6 months (Fig.1). As a typical out come of this model, body weigh loss and death occur within 4 weeks post infection. Dependent on the Salmonella strains used for infection, some mice may no survive over 6 months.
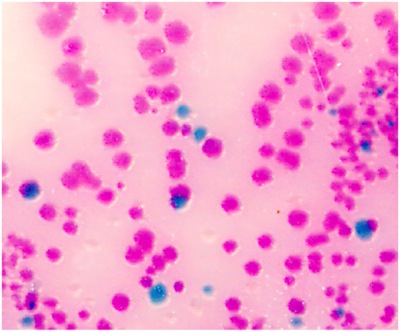
Figure 1. Intestinal Salmonella in the Salmonella species appear mauve (rose to purple) in color, due to metabolic differences in the presence of selected chromogens. Other bacteria are either inhibited or produce blue-green or colorless colonies.
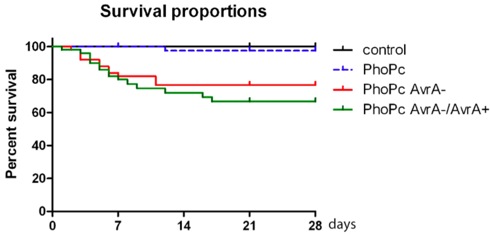
Figure 2. Survival proportions of mice infected with Salmonella mutant strain PhoPc, PhoPc AvrA-, and PhoPc AvrA-/AvrA+, PhoPc AvrA for 4 weeks (28 days).
Table 1. Body weight of mice infected with Salmonella for 4 weeks.
| 0 | 1 week | 2 weeks | 3 weeks | 4 week | |
| control | 16.78 ± 1.05 | 16.91 ± 1.28 | 18.26 ± 1.23 | 19.31 ± 1.26 | 20.26 ± 1.15 |
| PhoPc | 16.89 ± 1.03 | 17.14 ± 1.19 | 17.43 ± 1.63* | 18.68 ± 1.78 | 20.05 ± 1.11 |
| PhoPcAvrA- | 16.91 ± 1.12 | 16.96 ± 1.39 | 17.06 ± 2.14** | 18.71 ± 2.18 | 20.15 ± 1.56 |
| PhoPc AvrA-/AvrA+ | 16.94 ± 0.96 | 17.17 ± 1.02 | 17.63 ± 1.42* | 18.44 ± 2.03 | 20.09 ± 1.17 |
*compared to control group p<0.05
** compared to control group p<0.01
Table 2. Salmonella strains used in this study.
| Name | Description | Reference or source |
| Salmonella 14028s | Wild-type S. typhimurium | ATCC |
| PhoPc | Non-pathogenic complex regulator mutant | Miller et al., 1990 |
| PhoPc AvrA- | AvrA- mutation | Collier-Hyams et al., 2002 |
| PhoPcAvrA-/AvrA+ | PhoPcAvrA- with complemented plasmid encoding AvrA | Collier-Hyams et al., 2002 |
Dyskusje
To use this system, it is necessary for the researcher to learn how to gavage the animals. We detail a methodology for prepare bacterial culture and gavage the mice. We also show how to monitor the Salmonella persistence in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The critical steps in this protocol including:
- Streptomycin-pretreatment: Streptomycin-pretreatment could get rid of some commensal gut flora and make the mice susceptible to the Salmonella infection2.
- Salmonell...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
This work was supported by the NIDDK KO1 DK075386 grant and the American Cancer Society RSG-09-075-01-MBC to Jun Sun.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| HBSS | Sigma-Aldrich | ABCD1234 | |
| Luria-Bertani broth | BD Biosciences | 244610 | |
| Feeding needle | Popper & Sons, Inc. | 7920 | |
| Streptomycin | MP Biomedicals | 100556 | |
| BBL CHROMagar Salmonella | BD Biosciences | 214983 | |
| Disposable cell spreaders | Biologix Research Company | 65-1010 |
Odniesienia
- Duan, Y. beta-Catenin activity negatively regulates bacteria-induced inflammation. Lab Invest. 87 (6), 613-624 (2007).
- Barthel, M. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infection and immunity. 71 (5), 2839-2858 (2003).
- Miller, S. I., Mekalanos, J. J. Constitutive expression of the phoP regulon attenuates Salmonella virulence and survival within macrophages. Journal of bacteriology. 172 (5), 2485-2490 (1990).
- Valdez, Y. Nramp1 expression by dendritic cells modulates inflammatory responses during Salmonella Typhimurium infection. Cell Microbiol. 10 (8), 1646-1661 (2008).
- Woo, H., Okamoto, S., Guiney, D., Gunn, J. S., Fierer, J. A model of Salmonella colitis with features of diarrhea in SLC11A1 wild-type mice. PLoS ONE. 3 (2), e1603-e1603 (2008).
- Dangl, J. L. Molecular call-and-response: how Salmonella learns the gospel from its host. Trends Microbiol. 11 (6), 245-246 (2003).
- Zaharik, M. L., Vallance, B. A., Puente, J. L., Gros, P., Finlay, B. B. Host-pathogen interactions: Host resistance factor Nramp1 up-regulates the expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 virulence genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99, 15705-15710 (2002).
- Townsend, P., Morton, D. B. Laboratory Animal Care Policies and Regulations: United Kingdom. ILAR J. 37 (2), 68-74 (1995).
- Olfert, E. D., Godson, D. L. Humane endpoints for infectious disease animal models. ILAR J. 41 (2), 99-104 (2000).
- Ye, Z., Petrof, E. O., Boone, D., Claud, E. C., Sun, J. Salmonella effector AvrA regulation of colonic epithelial cell inflammation by deubiquitination. Am J Pathol. 171 (3), 882-892 (2007).
- Grassl, G. A., Valdez, Y., Bergstrom, K. S., Vallance, B. A., Finlay, B. B. Chronic enteric salmonella infection in mice leads to severe and persiste nt intestinal fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 134 (3), 768-780 (2008).
- Sukupolvi, S., Edelstein, A., Rhen, M., Normark, S. J., Pfeifer, J. D. Development of a murine model of chronic Salmonella infection. Infection and immunity. 65 (2), 838-842 (1997).
- . . Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (BMBL). , (2007).
- Wu, S., Lu, R., Zhang, Y., Sun, J. Chronic effects of a Salmonella type III secretion effector protein AvrA in vivo. PLoS ONE. , (2010).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone