Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Cell Trafficking: A Method of Cell Radiolabeling
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Presented here is a protocol to radiolabel cells with a positron emission tomography (PET) radioisotope, 89Zr (t1/2 78.4 h), using a ready-to-use radiolabeling synthon, [89Zr]Zr-p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine ([89Zr]Zr-DBN). Radiolabeling cells with [89Zr]Zr-DBN allows noninvasive tracking and imaging of administered radiolabeled cells in the body with PET for up to 7 days post-administration.
Streszczenie
Stem cell and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are emerging as promising therapeutics for organ regeneration and as immunotherapy for various cancers. Despite significant progress having been made in these areas, there is still more to be learned to better understand the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the administered therapeutic cells in the living system. For noninvasive, in vivo tracking of cells with positron emission tomography (PET), a novel [89Zr]Zr-p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine ([89Zr]Zr-DBN)-mediated cell radiolabeling method has been developed utilizing 89Zr (t1/2 78.4 h). The present protocol describes a [89Zr]Zr-DBN-mediated, ready-to-use, radiolabeling synthon for direct radiolabeling of variety of cells, including mesenchymal stem cells, lineage-guided cardiopoietic stem cells, liver regenerating hepatocytes, white blood cells, melanoma cells, and dendritic cells. The developed methodology enables noninvasive PET imaging of cell trafficking for up to 7 days post-administration without affecting the nature or the function of the radiolabeled cells. Additionally, this protocol describes a stepwise method for the radiosynthesis of [89Zr]Zr-DBN, biocompatible formulation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN, preparation of cells for radiolabeling, and finally the radiolabeling of cells with [89Zr]Zr-DBN, including all the intricate details needed for the successful radiolabeling of cells.
Wprowadzenie
Stem cell and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are gaining popularity and are under active investigation for the treatment of various diseases, such as myocardial failure1,2, retinal degeneration2, macular degeneration2, diabetes2, myocardial infarction3,4,5, and cancers6,7,8,9,10. Among the two plausible approaches of stem cell therapies, stem cells can either be directly engrafted on the disease site to cause a therapeutic response, or cause changes in the microenvironment of the disease site without adhering to the disease site to initiate an indirect therapeutic response. An indirect therapeutic response could cause changes in the microenvironment of the disease site by releasing factors that would repair or treat the disease5. These approaches of stem cell therapies could be evaluated by noninvasive imaging of radiolabeled stem cells. Noninvasive imaging could correlate the uptake of the radiolabeled cells on the disease site with a therapeutic response to decipher the direct versus indirect therapeutic response.
Additionally, immune cell-based therapies are being developed to treat various cancers using CAR T-cell6,7,8,9,10and dendritic cell immunotherapy11,12. Mechanistically, in CAR T-cell immunotherapy6,7,8,9,10, T-cells are engineered to express an epitope that binds to a specific antigen on tumors that needs to be treated. These engineered CAR T-cells, upon administration, bind to the specific antigen present on the tumor cells through an epitope-antigen interaction. After binding, the bound CAR T-cells undergo activation and then proliferate and release cytokines, which signals the immune system of the host to attack the tumor expressing the specific antigen. In contrast, in the case of dendritic cell therapies11,12, dendritic cells are engineered to present a specific cancer antigen on their surface. These engineered dendritic cells, when administered, home to the lymph nodes and bind to the T-cells in the lymph nodes. The T-cells, upon binding to the specific cancer antigens on the administered dendritic cells, undergo activation/proliferation and initiate an immune response of the host against the tumor expressing that specific antigen. Hence, the assessment of trafficking of administered CAR T-cells to a tumor site9,10 and homing of dendritic cells to the lymph nodes11,12 is possible by imaging radiolabeled CAR T-cells and dendritic cells to determine the efficacy of immunotherapy. Furthermore, noninvasive cell trafficking can help to better understand the therapeutic potential, clarify the direct versus indirect therapeutic response, and predict and monitor the therapeutic response of both stem cell and immune cell-based therapies.
Different imaging modalities for cell trafficking have been explored3,4,9,10,12, including optical imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and positron emission tomography (PET). Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages. Among these, PET is the most promising modality due to its quantitative nature and high sensitivity, which are essential for the reliable quantification of cells in imaging-based cell trafficking3,4,9,10.
The positron-emitting radioisotope 89Zr, with a half-life of 78.4 h, is suitable for cell labeling. It allows PET imaging of cell trafficking for over 1 week and is readily produced by widely available, low-energy medical cyclotrons13,14,15,16,17. Additionally, an appropriately functionalized, p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine (DFO-Bn-NCS) chelator is commercially available for the synthesis of a 89Zr-labeled, ready-to-use, cell labeling synthon, [89Zr]Zr-p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine, also known as [89Zr]Zr-DBN18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25. The principle of [89Zr]Zr-DBN-mediated cell labeling is based on a reaction between primary amines of cell membrane proteins and the isothiocyanate (NCS) moiety of [89Zr]Zr-DBN to produce a stable covalent thiourea bond.
[89Zr]Zr-DBN-based cell labeling and imaging have been published to track a variety of different cells, including stem cells18,23,25, dendritic cells18, cardiopoietic stem cells19, decidual stromal cells20, bone marrow-derived macrophages20, peripheral blood mononuclear cells20, Jurkat/CAR T-cells21, hepatocytes22,24, and white blood cells25. The following protocol provides step-by-step methods of preparation and cell radiolabeling with [89Zr]Zr-DBN and describes changes that may be required in the radiolabeling protocol for a specific cell type. For greater clarity, the method of cell radiolabeling presented here is divided into four sections. The first section deals with the preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN by chelating 89Zr with DFO-Bn-NCS. The second section describes the preparation of a biocompatible formulation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN that can be readily used for cell radiolabeling. The third section covers the steps needed for the preconditioning of cells for radiolabeling. The preconditioning of cells involves washing the cells with protein-free phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and HEPES buffered Hanks balanced salt solution (H-HBSS) to remove external proteins, which might interfere or compete with the reaction of [89Zr]Zr-DBN with primary amines present on the cell surface proteins during radiolabeling. The final section provides steps involved in the actual radiolabeling of the cells and quality control analysis.
Protokół
Dendritic cells and melanoma cells were obtained commercially18. Hepatocytes were isolated from the liver of pigs following laparoscopic partial hepatectomy22,24. Stem cells were isolated from bone marrow aspirates18,19,26. The adipose tissue-derived stem cells were obtained from the Human Cellular Therapy Laboratory, Mayo Clinic Rochester23. Human white blood cells were isolated from the collected blood received from the Division of Transfusion Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester25. Various cells used for radiolabeling were obtained and used in compliance with guidelines recommended by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Mayo Clinic Stem Cell Research Oversight Subcommittee, Division of Transfusion Medicine Research Committee, Institutional Biosafety Committee, and by the Radiation Safety Committee.
1. Preparation of [ 89Zr ]Zr-p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine ([ 89Zr ]Zr-DBN)
Timing: ~160-220 min
NOTE: For the preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN, isolate 89Zr in the form of [89Zr]Zr-hydrogen phosphate ([89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2) or [89Zr]Zr-chloride ([89Zr]ZrCl4), as mentioned in step 1.1.
- Isolate 89Zr from parent 89Y using an established hydroxamate resin-based purification method13,17. In brief, first prepare a column with ~100 mg of hydroxamate resin, then activate the hydroxamate resin by washing the column with 8.0 mL of pure anhydrous acetonitrile, followed by a flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air. Then, wash the column with 15 mL of deionized water, followed by another flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air, and then pass 2.0 mL of 0.50 N HCl (trace metal basis grade) followed by an additional flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air. Next, load the solution containing both 89Zr and 89Y to the hydroxamate resin slowly, and wash the unbound 89Y from the hydroxamate resin with 20 mL of 2.0 N HCl, followed by 10 mL of deionized water and a flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air.
NOTE: After the flush with air, the elution of 89Zr can be performed as shown below.- For eluting 89Zr in the form of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, first add 0.50 mL of 1.2 M K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer (pH 3.5) to the column from step 1.1 and allow it to sit on the column for 30 min to promote the release of 89Zr as a [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 from the resin. Then, elute the 89Zr from the column with an additional 1.50 mL of 1.2 M K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer (pH 3.5). After the elution of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, follow steps 1.2, 1.2.1, and 1.2.2 for the preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN using [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, as shown in Figure 1.
- For obtaining 89Zr as [89Zr]ZrCl4, first elute 89Zr as [89Zr]Zr-oxalate.
- For eluting 89Zr in the form of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate, add 0.50 mL of 1.0 M oxalic acid to the column from step 1.1 and allow it to sit on the column for 1 min to promote the release of 89Zr as a [89Zr]-oxalate from the resin. Then, elute the 89Zr from the column with an additional 2.50 mL of 1.0 M oxalic acid (total of 3.0 mL)17.
- To convert [89Zr]Zr-oxalate into [89Zr]ZrCl4 using an anion exchange column, as described by Larenkov et al.14, first activate the column by washing with 6.0 mL acetonitrile, followed by a flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air. Then, wash the column with 10.0 mL of saline, followed by another flush of 5.0-6.0 mL of air. Finally, pass 10.0 mL of deionized water, followed by a flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air.
- Load the 3.0 mL solution containing [89Zr]Zr-oxalate onto the activated anion exchange column slowly, followed by a flush of 5.0-6.0 mL of air. Then, wash the 89Zr-loaded column with 50.0 mL of deionized water to remove unbound oxalate ion, followed by a flush with 5.0-6.0 mL of air.
- For eluting 89Zr in the form of [89Zr]ZrCl4, add 0.10 mL of 1.0 N HCl to the column, allow it to sit on the column for 1.0 min to promote the release of 89Zr as [89Zr]ZrCl4 from the resin, and elute the 89Zr from the column with an additional 0.40 mL of 1.0 N HCl (total of 0.5 mL). Dry the eluted [89Zr]ZrCl4 in a V-shaped vial by placing it in a heating block at 65 °C under a steady flow of nitrogen gas for 10-30 min. After drying down, reconstitute the dried [89Zr]ZrCl4 in water and follow steps 1.3 and 1.3.1 for the preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN using [89Zr]ZrCl4, as shown in Figure 1.
- Take ~120 µL of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, formulated in 1.2 M K2HPO4/KH2PO4 (pH 3.5) (10-25 MBq) from step 1.1.1, and neutralize the solution to achieve pH 7.5-8.0 with ~100 µL of 1.0 M HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5) and ~65 µL of 1.0 M K2CO3.
- To obtain the appropriate amount of DFO-Bn-NCS for steps 1.2.2 or 1.3.1 for different 89Zr formulations with a varied apparent specific activity of 89Zr, perform a set of chelation reactions using a fixed volume of a neutralized formulation of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4 with a range of DFO-Bn-NCS (7.5-15 µg). In the case of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, incubate the chelation reaction at 37 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 60 min. Whereas, in the case of [89Zr]ZrCl4, incubate the chelation reaction at 25 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 30 min. Discard the chelation reaction that shows precipitate during or at the end of incubation. At the end of incubation, perform radioactive thin layer chromatography (rad-TLC) with 100 mM diethylenetriamine pentaacetate (DTPA), pH 7.0, as a mobile phase to estimate the chelation efficiency of DFO-Bn-NCS for each chelation reaction, as discussed below in step 1.5.
NOTE: Based on the chelation efficiency, use the minimum amount of DFO-Bn-NCS in steps 1.2.2 or 1.3.1 needed to achieve a ≥97% chelation efficiency without causing precipitation of DFO-Bn-NCS in the neutralized formulation of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4. Herein, [89Zr]Zr-DBN was synthesized in ≥97% radiochemical purity. - Prepare fresh 5.0 mM DFO-Bn-NCS in anhydrous DMSO (3.76 mg/mL) and add 4.0 µL of 5.0 mM DFO-Bn-NCS (20 nmol or 15 µg) to ~285 µL of neutralized [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 (10-25 MBq) from Step 1.2 and mix the solution by pipetting. Keep the final DMSO concentration in the chelation mixture below 2% of the total volume.
- To obtain the appropriate amount of DFO-Bn-NCS for steps 1.2.2 or 1.3.1 for different 89Zr formulations with a varied apparent specific activity of 89Zr, perform a set of chelation reactions using a fixed volume of a neutralized formulation of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4 with a range of DFO-Bn-NCS (7.5-15 µg). In the case of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, incubate the chelation reaction at 37 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 60 min. Whereas, in the case of [89Zr]ZrCl4, incubate the chelation reaction at 25 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 30 min. Discard the chelation reaction that shows precipitate during or at the end of incubation. At the end of incubation, perform radioactive thin layer chromatography (rad-TLC) with 100 mM diethylenetriamine pentaacetate (DTPA), pH 7.0, as a mobile phase to estimate the chelation efficiency of DFO-Bn-NCS for each chelation reaction, as discussed below in step 1.5.
- Take ~180 µL of [89Zr]ZrCl4 formulated in 0.1 N HCl (40-80 MBq) from step 1.1.2.4 and neutralize the resultant solution to achieve pH 7.5-8.0 with ~25 µL of 1.0 M Na2CO3.
- Prepare fresh 2.5 mM DFO-Bn-NCS in anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (1.88 mg/mL) and add 4.0 µL of 2.5 mM DFO-Bn-NCS (10 nmol or 7.5 µg) to ~205 µL of neutralized [89Zr]ZrCl4 (40-80 MBq) from step 1.3. Mix the solution by pipetting. Keep the final DMSO concentration in the chelation mixture below 2% of the total volume.
- Proceed with the chelation of 89Zr at 37 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 60 min in the case of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2, or at 25 °C in a shaker at ~550 rpm for 30 min in the case of [89Zr]ZrCl4.
- Determine the 89Zr chelation efficiency by rad-TLC with 100 mM DTPA (pH 7.0) as the rad-TLC mobile solvent. Expect [89Zr]Zr-DBN to show a Rf of ~0.021-0.035, [89Zr]ZrCl4 to show a Rf of ~1.0, and [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 to show a Rf of ~1.0. Calculate the chelation efficiency (%) using equation (1):
Percentage of 89Zr chelated to DFO-NCS to form [89Zr]Zr-DBN = [ (Radioactivity at Rf of [89Zr]Zr - DBN) / (Sum of the Radioactivities at Rf of [89Zr]Zr - DBN and at Rf of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4) ] × 100 (1)
NOTE: The acceptable 89Zr chelation efficiency to proceed with cell radiolabeling, as determined by rad-TLC, is ≥97%. The suggested ≥97% radiochemical purity of [89Zr]Zr-DBN was set as per the standard radiochemical purity requirement for other radiopharmaceuticals used in the field. See the representative rad-TLC in Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary Figure S2.

Figure 1: Schematic of [89Zr]Zr-DBN preparation. For the preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DBN, neutralize preformulated [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4 to a pH of 7.5-8.0. Incubate the neutralized solution with DFO-Bn-NCS. Check the chelation efficiency of 89Zr to DFO-Bn-NCS by rad-TLC. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Biocompatible formulation of [ 89Zr ]Zr-DBN for cell radiolabeling (Figure 2)
Timing: ~35 min
NOTE: Given the time it takes for the preparation of cells in step 3, start step 3 approximately 20 min before the beginning of step 2 for a ~30 min incubation. This allows cell radiolabeling in step 4 to start within ~5-10 min post-completion of steps 2-3.2.2.
- For [89Zr]Zr-DBN formulation made from the [89Zr]ZrCl4, add 50.0 µL of a cell-compatible mixture comprising ~27.0 µL of 1.2 M K2HPO4/KH2PO4 (pH 3.5) + ~23.0 µL of 1.0 M HEPES-KOH buffer (pH 7.5) to 50.0 µL of [89Zr]Zr-DBN. Incubate the [89Zr]Zr-DBN-cell compatible mixture for ~30 min at room temperature (25 °C).
NOTE: The [89Zr]Zr-DBN formulation made from [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 is biocompatible for the radiolabeling of cells and does not require step 2.
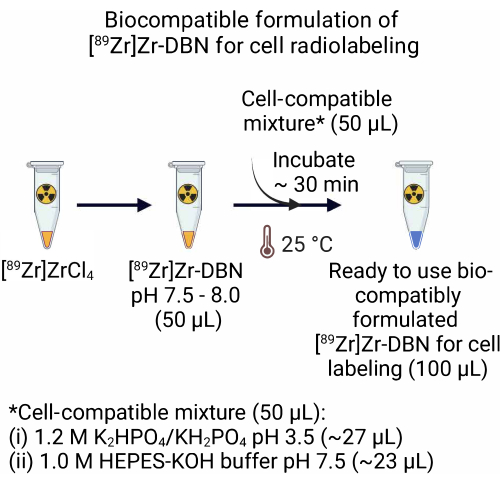
Figure 2: Preparation of the biocompatible formulation of the [89Zr]Zr-DBN for cell radiolabeling. For the preparation of a ready-to-use biocompatible formulation of the radiolabeling synthon, add an equal volume of cell compatible mixture, comprising 1.2 M K2HPO4/KH2PO4 (pH 3.5) + 1.0 M HEPES-KOH to an equal volume of [89Zr]Zr-DBN. Incubate at 25 °C for ~30 min. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Preparation of cells for radiolabeling
Timing: ~40-50 min
- Trypsinize ~12 × 106 adherent cells (stem cells, melanoma cancer cells, cardiopoietic stem cells, dendritic cells, or hepatocytes) and centrifuge the cells in a 15.0 mL conical centrifuge tube at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cell pellet in ~500 µL of PBS, and transfer the cell suspension to a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge the cells in a microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in ~500 µL of H-HBSS. Centrifuge the cells in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Repeat step 3.1.2 once more and proceed to step 4.1.1.
NOTE: H-HBSS is Hanks balanced salt solution with 0.01 M HEPES (pH 8.0).
- In the case of non-adherent cells, such as human white blood cells (freshly isolated human white blood cells from the blood), skip the trypsinization and centrifuge the cell suspension containing ~12 × 106 cells in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cell pellet in ~500 µL of PBS, and centrifuge the cells in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in ~500 µL of H-HBSS. Centrifuge the cells in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Repeat step 3.2.2 once more and proceed to step 4.1.1.
4. Radiolabeling of cells
Timing: ~125-155 min
- Initiation of cell radiolabeling (Figure 3)
- Use the cell suspension from step 3.1.2 or step 3.2.2 to prepare a ~500 µL cell suspension with approximately ~6 × 106 cells in ~500 µL of H-HBSS at pH 7.5-8.0 in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube.
- To this, add ~100 µL of the biocompatibly formulated [89Zr]Zr-DBN from step 2.
- Cell incubation for radiolabeling (Figure 4)
- Mix the biocompatibly formulated [89Zr]Zr-DBN and the cell suspension by gently pipetting up and down with a micropipette set at ~500 µL. Measure the amount of radioactivity in the incubation tube using a radioactivity dose calibrator at the 489 setting for 89Zr-isotope16.
- Incubate the cells and [89Zr]Zr-DBN mixture in a shaker at ~550 rpm at 25-37 °C for 30-45 min for cell labeling.
NOTE: The temperature of the incubation will vary depending on the cell types used for radiolabeling, as shown in Table 1. - After incubation in step 4.2.2, perform rad-TLC on the cell radiolabeling reaction using freshly prepared rad-TLC solvent (20 mM sodium citrate [pH 4.9-5.1]:methanol [1:1, V:V]). After the rad-TLC run, look for [89Zr]Zr-DBN and [89Zr]ZrCl4 around Rf = ~0.73-0.81 and Rf = ~0.01-0.02 for the radiolabeled cells. Calculate the percentage of radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 using equation (2).
Percentage of radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 = [ (Radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01 - 0.02) / (Sum of the Radioactivities at Rf = ~0.01 - 0.02 and Rf = ~0.73 - 0.81) ] × 100 (2)
NOTE: To understand the peaks visualized at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 and Rf = ~0.73-0.81, see the rad-TLC for white blood cell radiolabeling reaction in Supplementary Figure S3. - In a separate 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, mix ~100 µL of the biocompatibly formulated [89Zr]Zr-DBN with ~500 µL of H-HBSS at pH 7.5-8.0 for use as a no-cell control for background correction in step 4.2.5. After incubation at a similar temperature and time as used in step 4.2.2, perform rad-TLC. After the rad-TLC run, look for [89Zr]Zr-DBN and [89Zr]ZrCl4 around Rf = ~0.73-0.81. Calculate the percentage of radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 using equation (3).
Radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 = [ (Radioactivity at Rf = ~0.01 - 0.02) / (Sum of the Radioactivities at Rf = ~0.01 - 0.02 and Rf = ~0.73 - 0.81) ] × 100 (3)
NOTE: To understand the peaks visualized at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 and ~0.73-0.81, see the rad-TLC of no-cell control reaction in Supplementary Figure S4. - Calculate the effective cell radiolabeling (%) by subtracting the radioactivity percentage at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 (from rad-TLC from step 4.2.4) from the radioactivity percentage at Rf = ~0.01-0.02 (from rad-TLC from step 4.2.3).
- Quenching of radiolabeling and cell washing (Figure 5)
- After confirming the completion of radiolabeling by rad-TLC in step 4.2.5, perform quenching of the radiolabeling reaction by addition of ~600 µL of chilled, cell-appropriate complete medium, or by the addition of H-HBSS, as shown in Table 1.
- Centrifuge the cells in a microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant.
- Gently resuspend the pelleted cells in ~500 µL of chilled medium (Dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM) + 10% fetal bovine serum + 5% penicillin/streptomycin or Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 (RPMI-1640) + 10% fetal bovine serum + 5% penicillin/streptomycin or H-HBSS for a particular cell type, as shown in Table 1. Perform resuspension of the cell pellet by gently pipetting up and down with a micropipette set at ~500 µL.
- Centrifuge the cells in a microcentrifuge at ~96 × g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Repeat steps 4.3.2-4.3.4 twice to wash away the unbound radioactivity.
- Transfer the pellet to a fresh 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube with DMEM + 10% fetal bovine serum + 5% penicillin/streptomycin in the case of stem cells or H-HBSS and measure the radioactivity in the cell pellet using a dose calibrator at the 489 setting for 89Zr-isotope16.
- Calculate the final radiolabeling efficiency after all the washes using equation (4).
Radiolabeling efficiency = [(Decay corrected radioactivity in cell pellet at step 4.3.6) / (Decay corrected radioactivity in cell pellet and H-HBSS at step 4.2.1) ] × 100 (4) - To ensure the quality of the radiolabeled cells, first visually inspect the final suspension of radiolabeled cells for the presence of any clumps. If there are no clumps, proceed with this final suspension to the next step. If there are clumps, but they can be resuspended by pipetting or by gentle shaking, do so and proceed to the next step, as this passes the visual inspection. However, if the clumps are not resuspended either by pipetting or gentle shaking, discard the suspension and start over.
- If the visual inspection is passed, perform a trypan blue exclusion viability test using 0.4% trypan blue solution prepared in PBS within 1 h of radiolabeling and the washing steps (4.3.3-4.3.7) for assessing the cell viability of the radiolabeled cells.
- To perform the test, add 10.0 µL of 0.4% trypan blue solution to the 10.0 µL cell suspension of both radiolabeled and unlabeled cells and mix them by pipetting the trypan blue-cell suspension up and down with micropipette set at 10.0 µL.
- Load a hemacytometer with ~10.0 µL of the trypan blue-cell suspension mixture, immediately count the number of blue-stained cells and the total number of cells in the hemacytometer under a microscope at low magnification or using an automated cell counter. Calculate the percentage of viable cells using equation (5).
Percentage of viable cells = 100 - [(Number of blue - stained cells) / (Number of total cells)] × 100 (5)
- Use the radiolabeled cells if there is no change in the percentage of viable cells in the radiolabeled cell suspension as compared to the unlabeled counterpart. Discard the radiolabeled cells if the percentage of viable cells is less than unlabeled counterpart.
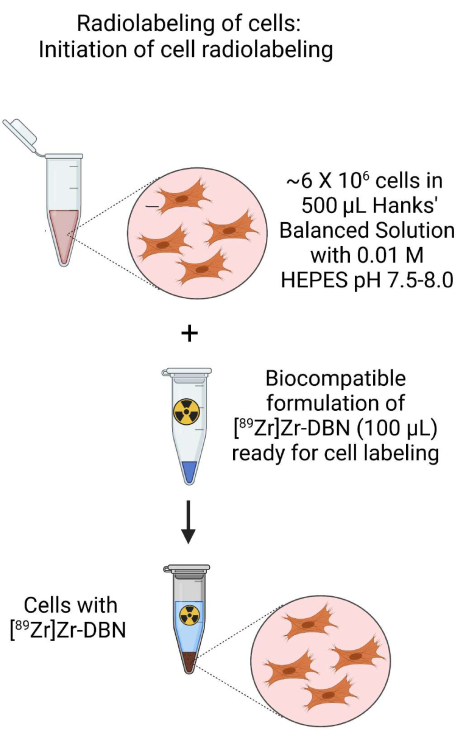
Figure 3: Schematic of the initiation of cell radiolabeling. Initiate radiolabeling of cells by the addition of the biocompatibly formulated [89Zr]Zr-DBN to the cell suspension prepared in HEPES buffered Hanks balanced salt solution. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
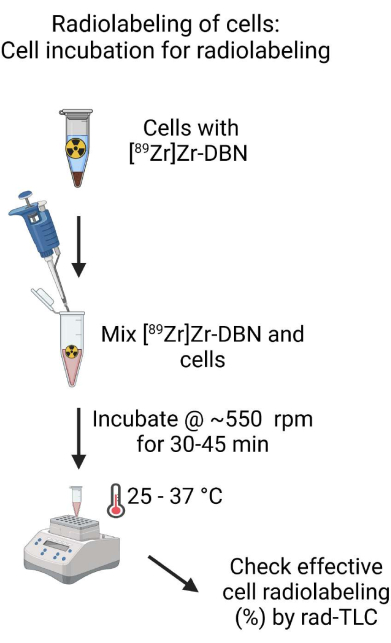
Figure 4: Schematic of cell incubation for radiolabeling. Thoroughly mix the biocompatibly formulated [89Zr]Zr-DBN with the cell suspension and incubate the cell suspension in a temperature-controlled heating block on a shaker for 30-60 min. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
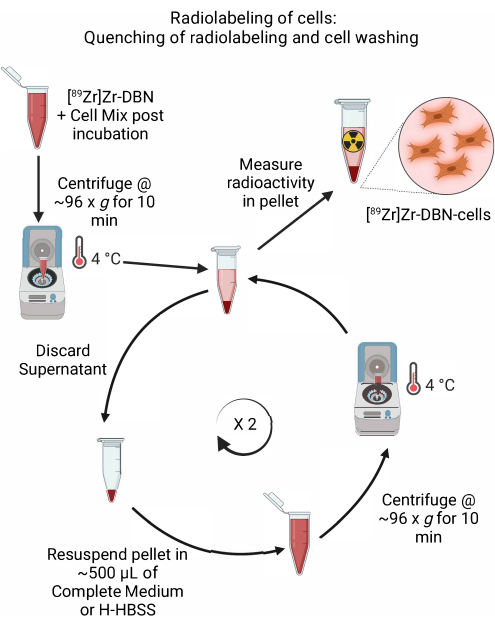
Figure 5: Schematic of the quenching of radiolabeling and cell washing. Quench the radiolabeling of cells by the addition of chilled cell medium or H-HBSS, followed by centrifugation at 4 °C. For cell washing, discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in ~500 µL of chilled cell medium or H-HBSS. Repeat the cycle of discarding the supernatant and resuspending the cell pellet in fresh medium to remove any unbound radiolabeling synthon. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Wyniki
The representative results presented in this manuscript were compiled from the previous [89Zr]Zr-DBN synthesis and cell radiolabeling studies18,19,22,23,24,25. In brief, 89Zr can be successfully complexed with DFO-Bn-NCS in ~30-60 min at 25-37 °C using 7.5-15 µg of DFO-Bn-NCS (Table 2
Dyskusje
Following are critical steps in the protocol that need optimization for effective cell radiolabeling. In protocol steps 1.2 and 1.3, depending on the volume of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 or [89Zr]ZrCl4 employed, an appropriate volume (microliters) of base must be used; 1.0 M K2CO3 solution must be used for the neutralization of [89Zr]Zr(HPO4)2 and 1.0 M Na2CO3 solution for the neutralization of [8...
Ujawnienia
Authors have no financial competing interest but are the inventors of this technology (Patent # US20210330823A1).
Podziękowania
This work was supported by NIH 5R21HL127389-02, NIH 4T32HL007111-39, NIH R01HL134664, and DOE DE-SC0008947 grants, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Mayo Clinic Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology, and Mayo Clinic Center for Regenerative Medicine, Rochester, MN. All figures were created using BioRender.com.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetonitrile | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | A996-4 | |
| Alpha Minimum Essential Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | 12571063 | |
| Anion exchange column | Macherey-Nagel, Inc., Düren, Germany | 731876 | Chromafix 30-PS-HCO3 SPE 45 mg cartridge |
| Conical centrifuge tubes (15 mL) | Corning Inc., Glendale, AZ, USA | 352096 | Falcon 15 mL high-clarity polypropylene (PP) conical centrifuge tubes |
| Dendritic cells | The American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA | CRL-11904 | |
| DFO-Bn-NCS | Macrocyclics, Inc., Plano, TX, USA | B-705 | p-SCN-Bn-Deferoxamine |
| DMSO | Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO | 276855 | |
| Dose calibrator | Mirion Technologies (Capintec), Inc., Florham Park, NJ, USA | 5130-3234 | CRC -55tR Dose Calibrator |
| Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium | The American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA | 30-2002 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | The American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA | 30-2020 | |
| Hanks Balanced Salt solution (HBSS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | 14025092 | For preparation of H-HBSS |
| Hydrochloric Acid (trace metal basis grade) | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | A508P212 | |
| Melanoma cells | The American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA | CRL-6475 | |
| Methanol | Sigma-Aldrich, Inc., St. Louis, MO | 34860 | |
| Microcentrifuge tube | Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany | 30108442 | Protein LoBind microcentrifuge tube |
| Murine GM-CSF | R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN USA | 415-ML-010 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | 15140-122 | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline without Ca2+ and Mg2+ | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA | 10010023 | For washing cells |
| Saline | Covidien LLC, Mansfield, MA, USA | 1020 | 0.9% Sterile Saline Solution |
| Shaker | Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany | T1317 | Thermomixer |
| Silica gel-rad-TLC paper sheet | Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA | SGI0001 | iTLC-SG |
Odniesienia
- Bhawnani, N., et al. Effectiveness of stem cell therapies in improving clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure. Cureus. 13 (8), e17236 (2021).
- Zakrzewski, W., Dobrzynski, M., Szymonowicz, M., Rybak, Z. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 10 (1), 68 (2019).
- Bukhari, A. B., Dutta, S., De, A. Image guidance in stem cell therapeutics: unfolding the blindfold. Current Drug Targets. 16 (6), 658-671 (2015).
- Momeni, A., Neelamegham, S., Parashurama, N. Current challenges for the targeted delivery and molecular imaging of stem cells in animal models. Bioengineered. 8 (4), 316-324 (2017).
- Gnecchi, M., Zhang, Z., Ni, A., Dzau, V. J. Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circulation Research. 103 (11), 1204-1219 (2008).
- D'Aloia, M. M., Zizzari, I. G., Sacchetti, B., Pierelli, L., Alimandi, M. CAR-T cells: the long and winding road to solid tumors. Cell Death & Disease. 9 (3), 282 (2018).
- Zhang, Q., et al. CAR-T cell therapy in cancer: tribulations and road ahead. Journal of Immunology Research. 2020, 1924379 (2020).
- Sterner, R. C., Sterner, R. M. CAR-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer Journal. 11 (4), 69 (2021).
- Shao, F., et al. Radionuclide-based molecular imaging allows CAR-T cellular visualization and therapeutic monitoring. Theranostics. 11 (14), 6800-6817 (2021).
- Sakemura, R., Can, I., Siegler, E. L., Kenderian, S. S. In vivo CART cell imaging: Paving the way for success in CART cell therapy. Molecular Therapy Oncolytics. 20, 625-633 (2021).
- Wang, Y., et al. Dendritic cell biology and its role in tumor immunotherapy. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 13 (1), 107 (2020).
- Bulte, J. W. M., Shakeri-Zadeh, A. In vivo MRI tracking of tumor vaccination and antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Molecular Imaging and Biology. 24 (2), 198-207 (2022).
- Holland, J. P., Sheh, Y., Lewis, J. S. Standardized methods for the production of high specific-activity zirconium-89. Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 36 (7), 729-739 (2009).
- Larenkov, A., et al. Preparation of zirconium-89 solutions for radiopharmaceutical purposes: interrelation between formulation, radiochemical purity, stability and biodistribution. Molecules. 24 (8), 1534 (2019).
- Pandey, M. K., et al. A new solid target design for the production of 89Zr and radiosynthesis of high molar activity [89Zr]Zr-DBN. American Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 12 (1), 15-24 (2022).
- Pandey, M. K., et al. Improved production and processing of 89Zr using a solution target. Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 43 (1), 97-100 (2016).
- Pandey, M. K., Engelbrecht, H. P., Byrne, J. P., Packard, A. B., DeGrado, T. R. Production of 89Zr via the 89Y(p,n)89Zr reaction in aqueous solution: effect of solution composition on in-target chemistry. Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 41 (4), 309-316 (2014).
- Bansal, A., et al. Novel 89Zr cell labeling approach for PET-based cell trafficking studies. EJNMMI Research. 5, 19 (2015).
- Bansal, A., et al. 89Zr]Zr-DBN labeled cardiopoietic stem cells proficient for heart failure. Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 90-91, 23-30 (2020).
- Friberger, I., et al. Optimisation of the synthesis and cell labelling conditions for [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [89Zr]Zr-DFO-NCS: a direct in vitro comparison in cell types with distinct therapeutic applications. Molecular Imaging and Biology. 23 (6), 952-962 (2021).
- Lee, S. H., et al. Feasibility of real-time in vivo 89Zr-DFO-labeled CAR T-cell trafficking using PET imaging. PLoS One. 15 (1), e0223814 (2020).
- Nicolas, C. T., et al. Hepatocyte spheroids as an alternative to single cells for transplantation after ex vivo gene therapy in mice and pig models. Surgery. 164 (3), 473-481 (2018).
- Yang, B., et al. Tracking and therapeutic value of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in reducing venous neointimal hyperplasia associated with arteriovenous fistula. Radiology. 279 (2), 513-522 (2016).
- Nicolas, C. T., et al. Ex vivo cell therapy by ectopic hepatocyte transplantation treats the porcine tyrosinemia model of acute liver failure. Molecular Therapy. Methods & Clinical Development. 18, 738-750 (2020).
- Bansal, A., Sharma, S., Klasen, B., Rosch, F., Pandey, M. K. Evaluation of different 89Zr-labeled synthons for direct labeling and tracking of white blood cells and stem cells in healthy athymic mice. Scientific Reports. 12 (1), 15646 (2022).
- Behfar, A., et al. Guided cardiopoiesis enhances therapeutic benefit of bone marrow human mesenchymal stem cells in chronic myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 56 (9), 721-734 (2010).
- Charoenphun, P., et al. 89Zr]oxinate4 for long-term in vivo cell tracking by positron emission tomography. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 42 (2), 278-287 (2015).
- Sato, N., et al. In vivo tracking of adoptively transferred natural killer cells in rhesus macaques using 89zirconium-oxine cell labeling and PET imaging. Clinical Cancer Research. 26 (11), 2573-2581 (2020).
- Volpe, A., Pillarsetty, N. V. K., Lewis, J. S., Ponomarev, V. Applications of nuclear-based imaging in gene and cell therapy: probe considerations. Molecular Therapy Oncolytics. 20, 447-458 (2021).
- Fogli, L. K., et al. Challenges and next steps in the advancement of immunotherapy: summary of the 2018 and 2020 National Cancer Institute workshops on cell-based immunotherapy for solid tumors. Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer. 9 (7), e003048 (2021).
- Li, X., Hacker, M. Molecular imaging in stem cell-based therapies of cardiac diseases. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 120, 71-88 (2017).
- Puges, M., et al. Retrospective study comparing WBC scan and 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with suspected prosthetic vascular graft infection. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 57 (6), 876-884 (2019).
- Butterfield, L. H. Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy clinical trials: are we making progress. Frontiers in Immunology. 4, 454 (2013).
- de Vries, I. J. M., et al. Magnetic resonance tracking of dendritic cells in melanoma patients for monitoring of cellular therapy. Nature Biotechnology. 23 (11), 1407-1413 (2005).
- Gosmann, D., et al. Promise and challenges of clinical non-invasive T-cell tracking in the era of cancer immunotherapy. EJNMMI Research. 12 (1), 5 (2022).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone