Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Prospective, Randomized, and Controlled Study of a Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection for Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers
* Wspomniani autorzy wnieśli do projektu równy wkład.
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
The present protocol describes a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical study that evaluates a human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection for the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.
Streszczenie
With the development of society and the economy, the incidence of diabetic foot ulcers continues to increase. Currently, conventional debridement with dressing changes, hyperbaric oxygen, and vacuum sealing drainage are the main conservative treatments in clinical practice, and large wounds often require skin grafts or skin flap grafts. However, the treatment effects are not ideal, and many complications exist. Due to its complex pathogenesis, long treatment time, significant associated difficulties, and high disability rate, diabetic foot ulcers cause a heavy burden to patients, society, and medical care. According to our previous study, the pharmacological effects of human umbilical cord blood stem cells include nonspecific immune regulation; increased secretion of growth factors, vasoactive factors, and anti-inflammatory factors; enhanced anti-infectious ability of the human body; elimination of inflammation; and promotion of angiogenesis and ulcer healing. These effects suggest stem cells may be useful as an autologous or allogeneic treatment for refractory wounds. Therefore, we are conducting a clinical trial to treat refractory diabetic wounds with human umbilical cord stem cells in our clinic for diabetic foot ulcer patients who meet the inclusion criteria.
Wprowadzenie
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects individuals worldwide, and the World Health Organization (WHO) predicts that the number of people with diabetes mellitus will increase from 285 million in 2010 to 439 million in 20301. Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are one of the most serious complications of diabetes and are main contributors to non-traumatic lower-extremity amputations across the world2,3,4,5.
Recently, stem cells have flourished as a therapy due to their pluripotency, self-renewal, and ability to promote the secretion of regenerative cytokines6,7. A previous clinical experiment showed that fat-derived stem cell gels had a positive effect on the treatment of foot ulcers in chronic diabetes8. The authors verified the effectiveness of using stem cells to treat diabetic wounds in 59 patients. At week 12, the rate of complete wound closure in the treatment and control groups was 82% and 53%, respectively, which indicates that stem cells are effective for the treatment of refractory diabetic wounds. Overall, the ability of stem cells to regenerate, replace, repair, and differentiate has given infinite hope to the life science community9.
In 2008, Dulchavsky et al.10 used grafts containing autologous bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) to treat 20 cases of non-healing wounds of different causes. Histological examinations showed that the skin wounds of 18 patients were completely re-epithelialized. Similarly, the use of allogeneic non-diabetic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in gelatin scaffolds for the treatment of nonunion diabetic wounds can promote angiogenesis, increase re-epithelialization, and reduce the ulcer area11. However, there are few cases of stem cell treatment of diabetic foot wounds in domestic and foreign clinical research studies; most are only case reports or exploratory clinical research lacking a strict experimental design, and there are few large samples with good design or randomized controlled clinical trials. As stem cells are not common drugs or biological products, the preparation methods and quality controls differ between studies. Data from one study may not fully reflect the safety of all stem cells from the same species. Therefore, we further summarized the relevant basic research and preclinical experiments with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs) and systematically evaluated the safety and efficacy of their clinical application. On this basis, the injection of mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord to repair diabetic foot wounds was developed as a treatment. This study aims to verify the efficacy and safety of stem cell repair of diabetic foot wounds in clinical use.
In summary, stem cell therapy has a broad spectrum of applications and great potential and represents a promising new medical treatment method. With the continued support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81571901, No. 81501671, and No. 82172224), we conducted a series of studies on the treatment of diabetic wounds with HUCMSCs. We have published more than 20 related articles in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, Stem Cell Research and Therapy, and Cell Death and Disease and have applied for three national invention patents, thus accumulating a large foundation of research12,13. Here, we provide a standard approach to evaluate the injection of HUCMSCs for diabetic foot wound repair. This standard procedure has been approved by Chinese drug clinical trials (Trial registration number: Chinese drug clinical trials: MR-32-21-015759, [Initial Release: 10/20/2021]).
Protokół
This prospective, single-center, randomized, controlled clinical study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University (XYFY2021-KL124-02). The study started in July 2021 and will continue until July 2023; 60 patients were recruited in this experiment. All patients signed an informed consent that allowed the researchers to use their clinical materials and biological data.
1. Recruitment of patients
- Inclusion criteria:
- Ensure that the patients' ages are between 18 years and 80 years (inclusive), regardless of gender.
- Ensure that the patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic foot ulcers meet the 1999 WHO diagnostic criteria14 and have a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level ≤10% as detected during the screening period or within 3 months prior to randomization.
- Confirm that the ankle-brachial index15 of the target limb is at least 0.8 without intermittent claudication.
- Ensure that each patient's ulcer has the following characteristics:
Grade 1 or grade 2 according to the Wagner grading system16 for ulcers.
Location in the foot, ankle, or front shin.
Cross-sectional area after debridement of 2-5 cm2.
No pus or necrotic substance visible to the naked eye at least 4 weeks before randomization. - Do not include patients undergoing routine treatment of other wounds in the study.
- If multiple wounds are present, select the wound that meets the inclusion criteria and has the largest intervention and assessment area.
- If two or more wounds are similarly large, select the one with the most severe grade.
- If there are two or more wounds with the same area and grade, select the one with the longest wound duration.
- Participation in this clinical study is voluntary. Ensure that the patients cooperate with the physicians conducting the study and sign an informed consent form.
- Exclusion criteria:
- Exclude patients with clear surgical indications: vascular occlusion, bone exposure, abscess, osteomyelitis.
- Exclude patients with revascularization or angioplasty within 3 months prior to enrollment.
- Exclude patients with hepatic impairment; specifically, exclude patients with ALT (aspartate aminotransferase) and AST (alanine aminotransferase) levels three times higher than the upper limit of normal.
- Exclude patients with blood creatinine levels more than two times above the upper limit of normal; serum albumin <2.0 g/dL; immunosuppressive drug treatment; various malignant tumors; and pregnancy, breastfeeding, or a recent birth plan.
- Exclude patients with contraindications, allergies, or known allergies to any component of stem cell preparation products.
- Exclude patients in other situations that cause the investigator to believe the patient should not participate in this study:
- Exclude patients if it is discovered after admission that they do not meet the most important admission criteria.
- Exclude patients with serious adverse reactions, patients who request to withdraw from the study, and patients whose legal guardian requests for them to withdraw from the study.
- Exclude patients with a lack of medication or effective post-enrollment observational data.
- Randomization and blinding
- Randomize the patients recruited from the outpatient department of the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University on a 1:1 basis into the stem cell therapy group and the conventional wound treatment group.
- Conduct a double-blind trial for the treatment. Ensure a third party measures the wound area of each patient.
2. Preoperative treatment
- Perform routine pretreatment examinations for the patients after enrollment, including a routine blood test, urinalysis, a routine stool assessment, a biochemical function assessment, a coagulation function assessment, virology, etc. Ensure that patients are followed up in the same hospital to ensure the accuracy of the tests.
- Include patients who meet the inclusion criteria and have signed the written informed consent. Assign each subject randomly to either the stem cell therapy group or the conventional wound treatment group in a 1:1 ratio using a proportionate sampling technique.
3. Treatment procedures
NOTE: Patients in both groups receive systematic routine wound dressing changes every 3 days. For the stem cell treatment group, patients receive local injections of stem cells four times (on day 1, day 8, day 15, and day 22 after enrollment). In the conventional wound treatment group, the patients are treated with silver ion dressing four times (on day 1, day 8, day 15, and day 22 after enrollment). The specific steps are as follows.

Figure 1: Treatment process. In each group, 30 patients will undergo treatment strictly following the protocol described in this study. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Stem cell therapy group
- After locally disinfecting the wound with povidone-iodine and removing the necrotic tissue from the wound surface with surgical scissors, use a syringe to aspirate 50 mL of physiological saline to clean the wound surface inside and out.
- Measure the wound area using the sterile foil edge hook method17. Apply the sterile film transparent dressing with its coordinate grid to the wound surface, and outline the shape of the wound surface along its edge with a marker. Calculate the wound area according to the area of each coordinate grid of the film.
- Inject the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (2 x 105 cells/cm2; 0.4 mL/cm2) into the periphery and the base of the wound (injection spacing: 0.75 cm; injection volume: 0.1 mL/site).
NOTE: The number of injections for each patient depends on the wound area. - Trim the sterile dressing to appropriate size, cover it over the wound surface, and then bandage it.
- Conventional wound treatment group
- After locally disinfecting the wound with iodophor and removing the necrotic tissue from the wound surface with surgical scissors, use a syringe to aspirate 50 mL of physiological saline to clean the wound surface inside and out.
- Measure the wound area using the sterile foil edge hook method17. Apply the sterile film transparent dressing with its coordinate grid to the wound surface, and outline the shape of the wound surface along its edge with a marker. Calculate the wound area according to the area of each coordinate grid of the film.
- Trim the silver ion dressing to an appropriate size, cover it over the wound surface, and then bandage it.
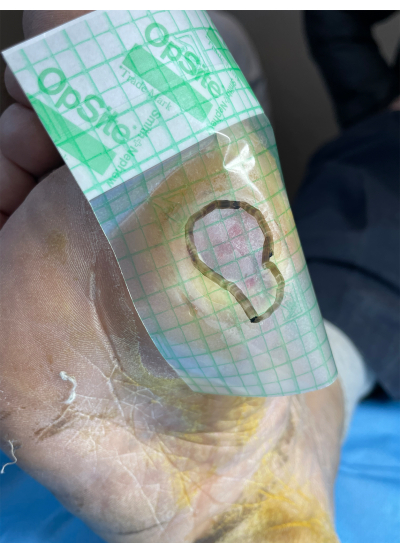
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of foot ulcer area measurement. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
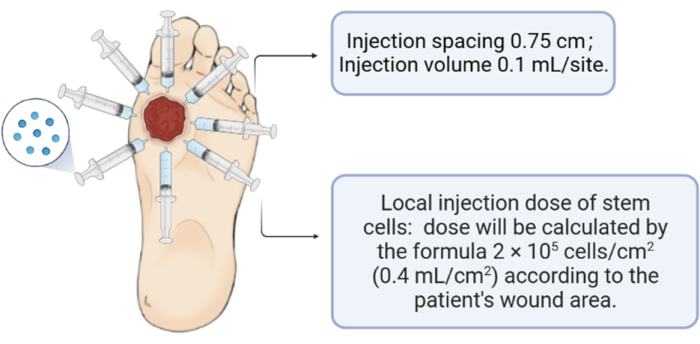
Figure 3: Schematic of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Observation indicators
- Obtain the demographic data of the subjects.
- Record the concomitant treatments; specifically, record the wound status (location, area, depth, infection, and ischemia), the wound healing rate, the healing time, and complications.
- Perform laboratory tests. Take the wound secretion for swabs and bacteriological culture. Conduct routine blood tests and tests for liver and kidney function.
5. Follow-up
- Examine the patients on the first day of therapy and during the follow-up visits 15 days and 30 days after the last therapy.
- Conduct follow-ups using both outpatient and telephone appointments to record the treatment effects, condition changes, recovery situation, and current living status.
6. Outcomes efficacy assessment
- Conduct the clinical evaluation according to the following criteria.
- Calculate the primary outcome index:
The 30 day wound healing rate = (original wound area − unhealed wound area at 30 days)/original wound area × 100%. - Calculate the secondary outcome index
- Wound healing time: Define the time of wound closure as the time at which the wound is completely re-epithelialized.
- Calculate the complete healing rate:
The complete healing rate = the number of complete healed cases/the total number of cases × 100%
- Calculate the surgical intervention rate:
Surgical intervention rate = the number of surgical interventions/the total number of cases × 100%.
NOTE: Subjects who underwent one of the following procedures are recorded as patients with surgical interventions: debridement and drainage, skin grafting, adjacent skin flap, distal skin flap, non-anastomotic skin flap, and amputation. - Perform the bacterial culture18 according to the standard clinical inspection procedures, and record bacterial culture results of ≥1 pathogen as positive. Calculate the pathogen positive rate:
Pathogen positive rate = the number of cases detected pathogen positive/the total number of cases × 100%.
- Calculate the primary outcome index:
7. Safety procedures
- In the case of an adverse event (any disease, new symptoms, signs, or laboratory examination abnormalities or the deterioration of the original symptoms and signs occurring during the stem cell clinical research, regardless of whether the event is related to the clinical research drug or not), take the necessary measures for treatment and rescue.
- Track and investigate all the adverse events and the treatment process, and record the results in detail until properly resolved or until the condition is stable. If a test is abnormal and has clinical significance, follow it up until it returns to normal.
Wyniki
At present, our research is still in the patient recruitment phase, and we have now completed three patients in the HUCMSCs treatment group and three patients in the control group with silver ion dressings, giving a total of six patients with chronic diabetic foot wounds. The average size of the ulcer area of a patient in the HUCMSCs treatment group was 3.5 cm2, and this was reduced to 2.6 cm2, 1.8 cm2, and 1.25 cm2 on the 8th, 15th, and 22nd days after treatment with HUCMSCs (...
Dyskusje
DFUs are a major global public health problem and a key cause of lower limb amputations and poor health-related quality of life19,20. At present, clinical management is still dominated by conventional debridement, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, vacuum sealing drainage (VSD), and conservative management. Larger wounds often require the transplantation of skin and skin flaps. Many patients suffer from long-term and repeated illnesses that cause severe physical and ment...
Ujawnienia
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Podziękowania
The authors thank the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University for its cooperation, including the recruitment and follow-up of patients with diabetic foot wounds. The authors also thank the patients who participated in the patient needs survey during the design of this study.
The author(s) announce the receipt of the following financial support for research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: National Natural Science Foundation of China 82172224, Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX22-1271), and the Innovation & Technology Commission (Health@InnoHK).
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silver Iin Wound Dressing | Shandong Cheerain Medical Co.,Ltd. | 20152640521 | Sterile silver ion dressing for medical use (Type F) 10 cm x 10 cm |
| Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Injection | Shandong Qilu Cell Therapy Engineering Technology Co., Ltd. | 32183185-X | Main components: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Pharmacological effect: non-specific immunomodulator can enhance the secretion of growth factor, vasoactive factor and anti-inflammatory factor, improve the anti infection ability of human body, eliminate inflammation, promote angiogenesis and ulcer healing. |
| Sterile mesh film transparent dressing | Smith & Nephew | 20162644490 | Sterile mesh film transparent dressing (used for wound area measurement) 6 cm x 7 cm |
Odniesienia
- Sun, H., et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 183, 109119 (2022).
- Volmer-Thole, M., Lobmann, R. Neuropathy and diabetic foot syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 17 (6), 917 (2016).
- Boulton, A. J. The pathway to foot ulceration in diabetes. The Medical Clinics of North America. 97 (5), 7755-7790 (2013).
- Kumar, S., et al. The prevalence of foot ulceration and its correlates in type 2 diabetic patients: a population-based study. Diabetic Medicine. 11 (5), 480-484 (1994).
- Margolis, D. J., Jeffcoate, W. Epidemiology of foot ulceration and amputation: Can global variation be explained. The Medical Clinics of North America. 97 (5), 791-805 (2013).
- Burgess, J. L., Wyant, W. A., Abdo Abujamra, B., Kirsner, R. S., Jozic, I. Diabetic wound-healing science. Medicina. 57 (10), 1072 (2021).
- Behr, B., Ko, S. H., Wong, V. W., Gurtner, G. C., Longaker, M. T. Stem cells. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 126 (4), 1163-1171 (2010).
- Moon, K. C., et al. Potential of allogeneic adipose-derived stem cell-hydrogel complex for treating diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes. 68 (4), 837-846 (2019).
- Bacakova, L., et al. Stem cells: Their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - A review. Biotechnology Advances. 36 (4), 1111-1126 (2018).
- Dulchavsky, D., et al. marrow-derived stromal cells (BMSCs) interact with fibroblasts in accelerating wound healing. Journal of Investigative Surgery. 21 (5), 270-279 (2008).
- Hu, Y., et al. Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 19 (1), 150 (2021).
- Meng, F., et al. CircARHGAP12 triggers mesenchymal stromal cell autophagy to facilitate its effect on repairing diabetic wounds by sponging miR-301b-3p/ATG16L1 and miR-301b-3p/ULK2. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 142 (7), 1976.e4-1989.e4 (2022).
- Shen, C., et al. Exosomal microRNA rectangle93 rectangle3p secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells downregulates apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 to promote wound healing. Bioengineered. 13 (1), 27-37 (2022).
- Alberti, K. G., Zimmet, P. Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine. 15 (7), 539-553 (1998).
- Lijmer, J. G., Hunink, M. G., vanden Dungen, J. J., Loonstra, J., Smit, A. J. ROC analysis of noninvasive tests for peripheral arterial disease. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. 22 (4), 391-398 (1996).
- Wagner Jr, F. W. The dysvascular foot: A system for diagnosis and treatment. Foot & Ankle. 2 (2), 64-122 (1981).
- Griffin, J. W., Tolley, E. A., Tooms, R. E., Reyes, R. A., Clifft, J. K. A comparison of photographic and transparency-based methods for measuring wound surface area. Physical Therapy. 73 (2), 117-122 (1993).
- Lipsky, B. A., et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 117 (7 Suppl), 212S-238S (2006).
- Huang, Y. Y., et al. Effect of a novel macrophage-regulating drug on wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Network Open. 4 (9), e2122607 (2021).
- Yarahmadi, A., et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma-fibrin glue dressing in combination with oral vitamin E and C for treatment of non-healing diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, clinical trial. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 21 (5), 687-696 (2021).
- Virador, G. M., de Marcos, L., Virador, V. M. Skin wound healing: Refractory wounds and novel solutions. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1879, 221-241 (2019).
- Um, S., Ha, J., Choi, S. J., Oh, W., Jin, H. J. Prospects for the therapeutic development of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. World Journal of Stem Cells. 12 (12), 1511-1528 (2020).
- Xiao, M., et al. Dynamic biological characteristics of human bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell senescence. Scientific Reports. 12, 17071 (2022).
- Zhang, Z., et al. Safety and immunological responses to human mesenchymal stem cell therapy in difficult-to-treat HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS. 27 (8), 1283-1293 (2013).
- Wu, M., et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell promotes angiogenesis via integrin beta1/ERK1/2/HIF-1alpha/VEGF-A signaling pathway for off-the-shelf breast tissue engineering. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 13 (1), 99 (2022).
- Li, K., et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via M2 macrophages. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 20 (1), 38 (2022).
- Qin, H. L., Zhu, X. H., Zhang, B., Zhou, L., Wang, W. Y. Clinical evaluation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after angioplasty for diabetic foot. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes. 124 (8), 497-503 (2016).
- Cai, J., et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell with autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in established Type 1 diabetes: A pilot randomized controlled open-label clinical study to assess safety and impact on insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 39 (1), 149-157 (2016).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone