A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Fabrication of Inverted Colloidal Crystal Poly(ethylene glycol) Scaffold: A Three-dimensional Cell Culture Platform for Liver Tissue Engineering
In This Article
Summary
This manuscript presents a detailed protocol for the fabrication of an emerging three-dimensional hepatocyte culture platform, the inverted colloidal crystal scaffold, and the concomitant techniques to assess hepatocyte behavior. The size-controllable pores, interconnectivity and ability to conjugate extracellular matrix proteins to the poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) scaffold enhance Huh-7.5 cell performance.
Abstract
The ability to maintain hepatocyte function in vitro, for the purpose of testing xenobiotics' cytotoxicity, studying virus infection and developing drugs targeted at the liver, requires a platform in which cells receive proper biochemical and mechanical cues. Recent liver tissue engineering systems have employed three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds composed of synthetic or natural hydrogels, given their high water retention and their ability to provide the mechanical stimuli needed by the cells. There has been growing interest in the inverted colloidal crystal (ICC) scaffold, a recent development, which allows high spatial organization, homotypic and heterotypic cell interaction, as well as cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) interaction. Herein, we describe a protocol to fabricate the ICC scaffold using poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) and the particle leaching method. Briefly, a lattice is made from microsphere particles, after which a pre-polymer solution is added, properly polymerized, and the particles are then removed, or leached, using an organic solvent (e.g., tetrahydrofuran). The dissolution of the lattice results in a highly porous scaffold with controlled pore sizes and interconnectivities that allow media to reach cells more easily. This unique structure allows high surface area for the cells to adhere to as well as easy communication between pores, and the ability to coat the PEGDA ICC scaffold with proteins also shows a marked effect on cell performance. We analyze the morphology of the scaffold as well as the hepatocarcinoma cell (Huh-7.5) behavior in terms of viability and function to explore the effect of ICC structure and ECM coatings. Overall, this paper provides a detailed protocol of an emerging scaffold that has wide applications in tissue engineering, especially liver tissue engineering.
Introduction
The liver is a highly vascularized organ with a multitude of functions, including detoxification of the blood, metabolism of xenobiotics, and the production of serum proteins. Liver tissue has a complex three-dimensional (3D) microstructure, comprising of multiple cell types, bile canaliculi, sinusoids, and zones of different biomatrix composition and different oxygen concentrations. Given this elaborate structure, it has been difficult to create a proper liver model in vitro1. However, there is a rising demand for functional in vitro models hosting human hepatocytes as platforms for testing drug toxicity2 and studying diseases associated with the liver3.
Current liver tissue engineering platforms have simplified the complexity of the liver by isolating one, or focusing on a few, of the liver's parameters, namely co-culture of cells4, biochemical composition of the zonal microenvironments5, flow dynamics6,7 and the configuration of the biomatrix8. Configuration of the biomatrix can be broken into parameters such as scaffold materials, composition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, matrix stiffness as well as the design and structure of the scaffold. There has been a rise in tissue engineering studies using synthetic hydrogels, especially poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels9, given the ability to tune the hydrogel's mechanical properties, bioactivity, and degradation rate. Regarding liver-related research, the biocompatible hydrogel was applied for virus infection study of liver disease3. As a hepatocyte platform design, numerous studies have utilized hepatocyte sandwich cultures10,11 and cell encapsulation within a hydrogel12,13 to provide the 3D environment and cell-ECM and cell-cell interaction which are essential to mimic in vivo microenvironment. However, these platforms do not possess a high degree of control and spatial organization, leading to non-uniform properties through the scaffold14.
The inverted crystal colloidal (ICC)14 scaffold is a highly organized 3D scaffold for cell culture that was first introduced in the early 2000s. The scaffold's unique structure can be attributed to the simple fabrication process using a colloidal crystal, an ordered lattice of colloidal particles of variable diameter. Briefly, to summarize the process, particles are neatly arranged and annealed using heat to form a lattice. The leaching of this lattice, by an organic solvent, in a polymerized hydrogel results in hexagonally packed spherical cavities15 with high surface area. This highly ordered scaffold has been previously made with both synthetic and natural materials, including but not limited to poly(acrylamide)16-21, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)15,22-30, poly(ethylene glycol)31,32, poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)21,33-35, and chitosan36-39. ICC scaffolds made of non-fouling materials tend to promote cellular spheroids within the cavities14,23,40. Multiple cell types have been shown to successfully proliferate, differentiate and function within this configuration, including chondrocytes41, bone marrow stromal cells42, and stem cells43,44. Regarding hepatocyte, studies have been conducted with ICC scaffolds made of Na2SiO3 and poly(acrylamide), but not PEG. With simple bioconjugation strategies (i.e., amine coupling through EDC/NHS), ECM proteins-conjugated PEG-based scaffolds can be fabricated, that can prove more cell binding sites to be a more in vivo like environment and enhance hepatic function.
In this manuscript and the associated video, we detail the fabrication of the ICC scaffold using poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) hydrogel and a polystyrene microsphere lattice, optimized for hepatocarcinoma (Huh-7.5) culture. We demonstrate the differences between the generally nonadhesive bare PEGDA ICC scaffolds and the collagen-coated PEGDA ICC scaffold in terms of scaffold topology and cell performance. Cell viability and function are measured qualitatively and quantitatively to assess Huh-7.5 cell behavior.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. ICC Scaffold Fabrication (Figure 1)
- Prepare the polystyrene (PS) lattices (diameter = 6 mm; 8-13 layers of beads).
- To prepare the mold, cut the tips off from 0.2 ml boil-proof microcentrifuge tubes at the 40 µl level. Adhere the top of the cut-tubes to 24 x 60 mm2 microscope cover glass slips with water-proof glue.
- Put the PS spheres (diameter = 140 µm) contained within a water suspension into a 20 ml vial, carefully pipette out the water suspension, and add 18 ml of 70% ethanol solution into the vial. Put the sphere solution into an ultrasonic bath to loosen aggregated spheres. Repeat this washing step several times in order to remove water and water-soluble components completely.
- Pipette 100 µl of ethanol into the molds.
- Cut the top of a 200 µl micropipette tip by 4 mm. Pipette 25 µl of the spheres into the mold twice using the 200 µl micropipette to achieve a total volume of 50 µl in each mold.
- Place the molds on a rocking shaker at 120 rpm overnight.
- Check the arrangement of the spheres in each mold under an optical microscope. If the spheres are not ordered hexagonally, add 50 µl of 70% ethanol and shake manually in the longitudinal and lateral axis direction to correct the arrangement.
- Let the ethanol evaporate at room temperature (RT) for two nights. Place the mold and bead complex in a 130 °C furnace for 6 hr to anneal the PS beads.
- Preparing bare and ECM-coated PEGDA scaffolds.
- Synthesize PEGDA macromers using established protocols45,46 for acrylating linear PEG macromers (Mw = 4.6 kDa).
- Prepare 50% (w/v) PEGDA solution in de-ionized (DI) water and allow the macromer to properly dissolve by centrifuging at 4,713 x g until it is completely dissolved.
- For ECM conjugated ICC scaffolds, dissolve an additional 10% (w/v) Acryloyl-PEG-NHS (Mw=3.4 kDa) in the 50% PEGDA solution.
- Prepare a 20% (w/v) stock solution of 2-hydroxy-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone (PI) in 70% ethanol.
- Add 50 µl of 20% (w/v) PI stock solution per 1 ml of 50 % (w/v) of PEGDA. Adjust the needed amount of PI stock solution based on the molecular weight of PEGDA.
- Vortex the mixture in centrifuge tube for 1 min to reach a homogenous solution.
- Peel the molds from the glass slide (from step 1.1.7), remove the glue from the molds, push the lattices out carefully using a spatula and place each of them into a 1.5 ml tube. Pipette 300 µl of the PEGDA solution and centrifuge at 845 x g for 5 min to allow proper PEGDA solution infiltration into the lattice.
- Remove the lattice from the tube using tweezers and carefully blot dry excess PEGDA solution on gloves. Place the lattice on a paraffin film-covered glass with the flat circular surface facing up.
- Expose the PEGDA solution infiltrated scaffold to 365 nm ultraviolet (UV) light (10.84 mW/cm2) for 5 min using a UV spot lamp.
- Place PEGDA-polymerized crystal lattices in new vials (around 10 lattices per vial) and add 20 ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF). Shake the vials on an orbital shaker at 300 rpm. Change THF at least 3 times with an interval of 1-2 hr.
Note: Do not remove THF completely when changing the THF in order to prevent bubbles from entering the scaffolds, which in turn can cause incomplete removal of PS. Leave enough solution to cover the lattices and add new THF.
Caution: THF is toxic. Wear gloves, a lab coat and goggles. Avoid inhalation by operating under the fume hood. - Check if PS spheres are dissolved by putting water into the used THF solution and observing the solution color. Repeat step 1.2.9 if the PS spheres are not properly dissolved.
Note: The solution color will change to white if there are any remaining PS spheres.
- Clean the scaffolds in the biosafety cabinet (BSC).
- To sterilize the scaffolds, prepare a 50 ml centrifuge tube with 2 ml of 70% ethanol per scaffold and place the scaffolds in the tube using a spatula. Allow the scaffolds to soak in ethanol for 1 hr. From this step forward, conduct all the procedures in the BSC.
- Carefully pour the ethanol out and replace with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (2 ml per scaffold) and centrifuge at 524 x g for 3 min to remove bubbles. Keep it in the refrigerator and change the PBS a few times with an interval of 1-2 hr.
- For Collagen type I-coated scaffolds, prepare another 50 ml centrifuge tube containing Collagen type 1 stock solution (1 ml per scaffold), transfer the sterilized scaffolds to this tube using a spatula, and centrifuge at 524 x g for 3 min. Shake the scaffolds at 400 rpm on an orbital shaker for 30 min and keep the tube in the refrigerator overnight.
- Wash the scaffolds with PBS twice before use by submerging the scaffolds in fresh PBS and then aspirating the PBS.
Note: Other ECM proteins can also be used instead of Collagen type I because the NHS chemistry requires an amine group to form the bond (Figure 2).
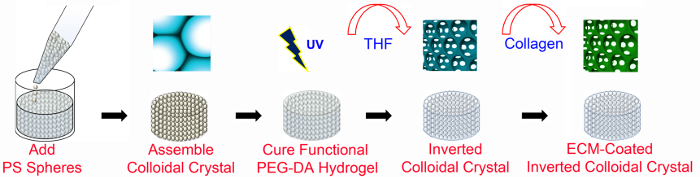
Figure 1. Overview of ICC fabrication. PEG-based ICC scaffolds are fabricated using microfabrication techniques with and without ECM-functionalization. ECM-coated ICC scaffolds require PEG-NHS as well as PEGDA (as detailed in Figure 2). The PS lattice has a diameter of 6 mm and a height of 8-13 bead layers. PS, polystyrene; PEGDA, poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate; UV, ultraviolet; THF, tetrahydrofuran; ECM, extracellular matrix. This figure has been modified and used with permission from Wiley47. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. ICC Structure Characterization
- To analyze ICC structure with or without conjugated proteins, use scanning electron microscopy (SEM)47.
- Fix the scaffolds with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), serially dehydrate them in 25, 50, 75, 95 and 100% ethanol solutions, and store them at -80 °C until the ethanol evaporates completely.
- Dry samples in a freeze drier for 48 hr.
- Affix the sample onto sample holder using carbon tape and place in a sputter coater.
- After automatic vacuuming, coat it with a Pt film of 10 nm thickness by sputtering for 60 sec at 20 mA.
- Image ICC scaffolds using SEM at a voltage of 5 kV (Figure 3A, Figure 4A).
- To measure the pore and interconnection diameter of cavities, analyze SEM micrographs using image analysis software48 (e.g., ImageJ; Figure 3B,C).
- To visualize the conjugated collagen to the scaffold without cells, fluorescently tag the collagen using antibodies (1:100) against the collagen type I and image with confocal laser scanning microscopy47 (CLSM; Figure 4B).
3. Huh-7.5 Cell Culture and Seeding
- Culture Huh-7.5 cells at a seeding density of 2-2.5 x 106 cells/ml in 100 mm cell culture dishes with 10 ml Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 U/ml penicillin-streptomycin (growth media) at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Change the media every three days in the BSC until they have reached 75-80% confluency.
- Prepare the scaffolds for cell seeding in the BSC.
- Carefully place the scaffolds in a 24-well plate with the flat surface facing up.
- To wash the scaffold, pipette 2 ml PBS to each well containing a scaffold. Aspirate the PBS and pipette 2 ml fresh PBS into each well.
- Aspirate the PBS and pipette 2 ml of growth media (see step 3.1) and leave for 30 min. Aspirate the media and allow the scaffold to dry for 1 hr.
- Detach confluent Huh-7.5 cells (from step 3.1) from the culture plate in the BSC using the trypsin digestion method.
- Aspirate media from plate, add 4 ml PBS to wash adherent cells and then aspirate PBS.
- Pipette 0.75-1 ml 0.25% trypsin and place in an incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 3 min.
- Remove plate from incubator and pipette 5 ml media to stop the trypsin reaction. Pipette media, detached cells, and trypsin mixture into a 15 ml tube.
- Centrifuge at 524 x g for 3 min, remove the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 5 ml media.
- Count cells using a hemocytometer and calculate the volume of the cell suspension that contains cells at target number, N0, per 25 µl (for standard experiment, N0 is 1 x 106 cells).
Volume of cell suspension=(target number of cells)/(concentration of cell suspension) - Slowly pipette 25 µl of cell suspension (containing N0 cells) directly on top of each scaffold (from step 3.1.4). Place the 24-well plate in the incubator.
- After 12 hr, transfer the scaffolds carefully with the use of a spatula into a new 24-well plate and pipette 2 ml of media into each well. Place the 24-well plate in the incubator.
- Change the media every 3 days or depending on when media is collected for protein secretion analysis (see Step 5.1).
4. Cell Viability
- To qualitatively analyze cell viability, use fluorescent live/dead staining kits to stain the cells and image using CLSM.
- Following kit instruction, prepare a solution with 4 µM calcein AM and 8 µM ethidium homo-dimer-1 in media (see step 3.1.3).
Note: Optimize depending on the cell number. Use double the amount of reagent if cells proliferate and double in number (around 2 million). - In the BSC, aspirate media in each well with a scaffold (step 3.7) and pipette 500 µl of the prepared solution. Incubate samples in a 37 °C incubator for 1 hr.
- Cover the plates in foil to protect the samples from light when removing the plate out of the incubator. Image samples using CLSM49.
- Following kit instruction, prepare a solution with 4 µM calcein AM and 8 µM ethidium homo-dimer-1 in media (see step 3.1.3).
- To quantitatively assess cell viability, measure enzymatic activity (in live cells) using colorimetric assays50 (i.e., 2-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (monosodium-salt reagent)).
- Create a standard curve for the ICC platform (i.e., a graph of absorbance (OD) versus given cell number).
Note: Cell seeding is not 100% efficient in comparison to other platforms, since cells can pass through the cavities of scaffolds.- Determine the cell seeding numbers, N0 that will be used to make the standard curve.
Note: Choose a range that includes cell numbers that are estimated in the experiment. For example, if the initial cell number is 5 x 105 cells and there is an estimated ~3 fold increase by the last day of the experiment, choose 2.5 x 105, 5 x 105, 1 x 106, and 2 x 106 cells as N0. - Perform cell seeding in the ICC scaffolds (one N0 per scaffold with seeding volume of 25 µl) as described in steps 3.1-3.6.
- After 6 hr, transfer the scaffolds to another 24-well plate well. Select a time that allows cell adherence but not cell proliferation.
- Perform cell counting on the transferred ICC scaffold.
- Dilute 10x monosodium-salt reagent (MSR) solution to 1x with media in the BSC and pipette 500 µl 1x MSR solution into each well with a scaffold. Incubate the 24-well plate at 37 °C for 1 hr.
- From each well, transfer 100 µl into a 96-well plate well. As a blank, pipette 100 µl of fresh 1x monosodium-salt reagent solution into different wells on the 96-well plate. Manually remove any bubbles present using a dry pipette tip and cover the 96-well plate in foil to protect it from light.
- Measure OD at λ = 450 nm reading using a spectrophotometer. Subtract the blank OD from other values to find the accurate OD51.
- Count the number of cells (NL) remaining in the well after transferring the scaffold (step 4.2.1.3) using a hemocytometer.
Note: Use 300 µl of trypsin to trypsinize the cells. - Calculate the actual cell number, NA.
actual = initial - left in well
NA=N0-NL - Make standard curve by plotting OD obtained in Step 4.2.1.4.3 vs. actual cell number (NA) and use this to estimate the cell number in the experiments.
Note: Make a new standard curve if any ICC parameters (i.e., porogen size, dimensions of the scaffold, ECM protein, etc.) are changed.
- Determine the cell seeding numbers, N0 that will be used to make the standard curve.
- Create a standard curve for the ICC platform (i.e., a graph of absorbance (OD) versus given cell number).
5. Cell Function
- Analyze protein secretion by the Huh-7.5 cells (i.e., albumin, urea) from the collected media (from step 3.7) by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)52.
Note: Dilute the media, depending on the number of cells seeded and the amount of media collected. For 5 x 105 cells seeded in ICC, use a ~1:25 ratio, before introducing it to the antibody-precoated wells. - To qualitatively analyze cell function, immunostain specific intracellular proteins (i.e., albumin), enzymes (i.e., CYP450), stain structural components (i.e., cellular actin) as well as the nuclei and image using CLSM49.
- Aspirate media (from step 3.7) and pipette 2 ml PBS to wash the cell-laden ICC scaffolds.
- Pipette 1 ml of 4% PFA and incubate for 5 min at room temperature for fixation.
- Wash 3x with 2 ml PBS.
- Permeabilize membranes by incubating the scaffolds in 1 ml of 0.1% 4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenyl-polyethylene glycol (surfactant) for 30 min.
- Wash 3x with 2 ml PBS to remove any leaking proteins.
- Pipette 500 µl 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and incubate at RT for 1 hr to block non-specific binding.
- Prepare diluted primary antibody (i.e., albumin, CYP450) solution.
- Pipette 500 µl of 1% BSA solution into a 15 ml tube and add 4.5 ml of 0.1% surfactant solution to prepare a total 5 ml of 0.1% BSA solution.
- Pipette 98 µl of the 0.1% BSA solution into a 200 µl microcentrifuge tube and 2 µl of the primary antibody to produce a 1:50 (primary antibody: 0.1% BSA) primary antibody solution.
- Pipette 40 µl of the primary antibody solution on the scaffold and cover the substrate with paraffin film. Wrap the 24 well plate with aluminum foil and store the dish at 4 °C overnight.
- Wash 3x with 2 ml PBS and shake the plate gently in between washing.
- Prepare diluted biotinylated secondary antibody (i.e., Anti-mouse antibody) stock solution.
- Pipette 198 µl 0.1% BSA solution and 2 µl second antibody to produce a 1:100 (secondary antibody: 0.1% BSA) secondary antibody solution.
- Prepare a 0.1% stock solution of rhodamine or fluorescein labeled phalloidin (to stain the cellular actin filaments) in the 0.1% BSA solution.
- Pipette 25 µl of each solution in a tube and mix well.
- Pipette 50 µl of the secondary antibody stock solution on the scaffold. Cover the scaffold with paraffin film, wrap the dish with aluminum foil and store at RT for 2 hr.
- Wash 3x with 2 ml PBS.
- Pipette 200 µl of 0.2% 4'-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; a nucleus stain) solution on the scaffold and keep at RT for 2-3 min. Cover the plate with aluminum foil.
- Wash 2x with 2 ml PBS.
- Using a dropper, place a drop of mounting media on the substrate.
- Carefully put the scaffold on a glass slide and image using CLSM47.
- Assess the gene expression by real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Use standard kits for reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR)53 and qPCR54 as per manufacturer's instructions. Extract the RNA from the cells as described below.
- Place the scaffold (from step 3.7) in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube.
- Pipette 1 ml of an RNA extraction solution into the tube and keep in a sonicator for 5 min at RT.
- Pipette 200 µl of chloroform into each microcentrifuge tube and shake the tube vigorously in hand for 15-20 sec. Keep the tubes at RT for ~3 min until the phases separate.
- Centrifuge the sample at 13,000 x g, 4 °C for 15 min and remove the tubes carefully so that phases do not mix.
- Carefully pipette 500-600 µl of the upper aqueous phase from the first tube into a second microcentrifuge tube.
- Add an equivalent volume (500-600 µl) of isopropanol to this second tube.
- Invert the tube 3-5 times and leave the tube standing at RT for 10 min.
- Centrifuge the sample at 13,000 x g, 4 °C for 15 min.
- If a pellet is not visible at the bottom of the tube, centrifuge again for 5 min.
Note: If there is still no visible pellet, the amount of RNA may be insufficient.
- If a pellet is not visible at the bottom of the tube, centrifuge again for 5 min.
- Invert tubes with the cap open to discard supernatant and pipette in 1 ml 70% ethanol diluted in DEPC water into the tube.
- Slightly vortex the tube so the pellet detaches from the wall of the tube and then let the tube air dry.
- Add 50 µl of DPEC water to resuspend the pellet.
- Keep pipetting until the pellet dissolves.
- Keep for 10 min at 55 °C in order to denature the double-stranded RNA into single-stranded RNA.
- Lightly drum fingers on the tube bottom and then centrifuge the tubes briefly (7,500 x g, 4 min, 4 °C).
- Keep the tubes in ice until performing reverse transcriptase55 and real-time PCR as described in 56.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The representative results for the structural characterization of the ICC scaffold and the comparison of each ICC scaffold condition's efficacy in culturing hepatocytes are shown and explained below. The ICC scaffold conditions used in these results are collagen coatings of 0 µg/ml (Bare), 20 µg/ml (Collagen 20), 200 µg/ml (Collagen 200), and 400 µg/ml (Collagen 400) and the initial Huh-7.5 cell seeding number is 1x106.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Tissue engineering scaffolds are rapidly evolving to provide all the physical and biochemical cues necessary to regenerate, maintain, or repair tissues for the application of organ replacement, studying disease, developing drugs, and many others57. In liver tissue engineering, primary human hepatocytes rapidly lose their metabolic functions once isolated from the body, creating a great need for engineering scaffolds and developing platforms to maintain the hepatic function. The current in vitro hepato...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no competing financial interests to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge support from a National Research Foundation Fellowship (NRF -NRFF2011-01) and Competitive Research Programme (NRF-CRP10-2012-07).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.2 ml PCR tube | Axygen Scientific | PCR-02D-C | Boil-proof |
| Gorilla Glue | Gorilla Glue, Inc. | Depends on vendor. This was purchased from a local store. | |
| Glass slides | VWR | 631-1575 | Dimensions: 24×60 mm2 |
| Polystyrene spheres | Fisher Scientific | TSS#4314A | Diameter = 140 µm; 3x104 particles per milliliter and 1.4% size distribution |
| Ethanol | Merck | 1.00983.1011 | absolute for analysis EMSURE; Dilute to 70% with Milli-Q water |
| Ultrasonic Bath | Elma | S10H | Equiment |
| Furnace | Nabertherm | N7/H | Equipment |
| 200 µl pipette tip | Axygen Scientific | T-210-Y-R-S | |
| Rocking shaker | VWR | 444-0142 | |
| Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) | Merck | 1.09727.0100 | Mw= 4 kDa; acrylation of PEG monomers and purification of the resulting precipitate produces a PEGDA macromer with Mw = 4.6 kDa |
| Centrifuge | Beckman Coulter | 392932 | Equipment |
| Acrylate-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) - Succinimidyl Valerate | Laysan Bio | ACRL-PEG-SVA-3400-1g | Mw = 3.4 kDa |
| 2-hydroxy-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone | Sigma Aldrich | 410896 | |
| Vortex | VWR | 58816-123 | Equipment |
| Microcentrifuge | Eppendorf | 5404 000.413 | |
| Paraffin Film | Parafilm M | #PM996 | Kept at 9" with allows intensity of 10.84 mW/cm2 |
| Bluewave 200 UV spotlight | Blaze Technology | 120008, 122300 | |
| Tetrahydrofuran (THF) | Merck | 107025 | |
| Orbital shaker | Heidolph | 543-123120-00-5 | |
| Collagen Type I | Sigma Aldrich | C3867-1VL | From rat. 1x, w/o CaCl2 & MgCl2; pH = 7.2 |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) | Gibco | 20012-027 | 16% W/V AQ. 10 x 10 ml |
| Paraformaldehyde | VWR | 43368.9M | Equipment |
| Freezone 4.5 freeze drier | Labconco | 7750020 | Equipment |
| Sputter coater | Jeol Ltd. | JFC-1600 | Equipment |
| Scanning Electron Microscope | Jeol Ltd. | JSM 5310 | |
| Anti-mouse primary antibodies against Collagen type I | Abcam | ab6308 | |
| Anti-mouse secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 | Life Technologies | A21121 | |
| Plate, Tissue Culture 24 Well, Flat Bottom (Nunclon) | Bio-Rev PTE LTD | 3820-024 | |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium(DMEM) 2.5 g/L Glucose w/ L-Gln | Lonza | 12-604F | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Gibco | A15-151 | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin (P/S) | Life Tchnologies | 15140-122 E | |
| 100 mm Corning non-treated culture dishes | Sigma Aldrich | CLS430591 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 25200-056 | Equipment; 37 °C, 5% Humidity |
| Forma Steri-Cycle CO2 Incubators | Thermofisher Scientific | 371 | |
| Hausser Bright-Line Phase Hemacytometer | Thermofisher Scientific | 02-671-6 | |
| Live/Dead Viability/Cytotoxicity Kit for mammalian cells | Life Technologies | L3224 | |
| CCK-8 Assay | Dojindo Laboratories | CK04-11 | Monosodium-salt reagent (MSR) |
| Infinite 200 PRO microplate reader | Tecan | ||
| Albumin Human ELISA kit | Abcam | ab108788 | |
| Triton X-100 | Bio-Rad | #1610407 | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | A2153-50G | |
| Anti-mouse primary antibodies (against CYP3A4, albumin) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-53850; sc-271605 | |
| DAPI | Life Technologies | D3571 | |
| Alexa Fluor 555 labeled Phalloidin | Life Technologies | A34055 | |
| Trizol | Life Technologies | 15596-026 | |
| Chloroform | VWR | 22706.326 | |
| Isopropanol | Fisher Scientific | 67-63-0 | |
| DPEC water | Thermofisher Scientific | AM9916 | |
| Nanodrop 2000c Spectrophotometer | Thermofisher Scientific | ND-2000 | |
| iScript Reverse Transcription Supermix | Bio-Rad Laboratories | 1708840 | |
| SYBR select Master Mix for CFX | Life Technology | 4472937 | |
| Primers (to be chosen) | |||
| CFX96 Real-Time System, C-1000 Touch Thermal Cycler | Bio Rad Laboratories | SOFT-CFX-31-PATCH |
References
- Yamada, M., et al. Controlled formation of heterotypic hepatic micro-organoids in anisotropic hydrogel microfibers for long-term preservation of liver-specific functions. Biomaterials. 33 (33), 8304-8315 (2012).
- Abboud, G., Kaplowitz, N. Drug-induced liver injury. Drug Safety. 30 (4), 277-294 (2007).
- Cho, N. J., et al. Viral infection of human progenitor and liver-derived cells encapsulated in three-dimensional PEG-based hydrogel. Biomed Mater. 4 (1), (2009).
- Revzin, A., et al. Designing a hepatocellular microenvironment with protein microarraying and poly (ethylene glycol) photolithography. Langmuir. 20 (8), 2999-3005 (2004).
- Sato, A., Kadokura, K., Uchida, H., Tsukada, K. An in vitro hepatic zonation model with a continuous oxygen gradient in a microdevice. Biochem Bioph Res Com. 453 (4), 767-771 (2014).
- Domansky, K., et al. Perfused multiwell plate for 3D liver tissue engineering. Lab Chip. 10 (1), 51-58 (2010).
- Hegde, M., et al. Dynamic interplay of flow and collagen stabilizes primary hepatocytes culture in a microfluidic platform. Lab Chip. 14 (12), 2033-2039 (2014).
- Flaim, C. J., Chien, S., Bhatia, S. N. An extracellular matrix microarray for probing cellular differentiation. Nat methods. 2 (2), 119-125 (2005).
- Underhill, G. H., Chen, A. A., Albrecht, D. R., Bhatia, S. N. Assessment of hepatocellular function within PEG hydrogels. Biomaterials. 28 (2), 256-270 (2007).
- Dunn, J., Tompkins, R. G., Yarmush, M. L. Hepatocytes in collagen sandwich: evidence for transcriptional and translational regulation. J cell biol. 116 (4), 1043-1053 (1992).
- Dunn, J. C., Tompkins, R. G., Yarmush, M. L. Long-term in vitro function of adult hepatocytes in a collagen sandwich configuration. Biotechnol progr. 7 (3), 237-245 (1991).
- Ling, Y., et al. A cell-laden microfluidic hydrogel. Lab Chip. 7 (6), 756-762 (2007).
- Kim, M., Lee, J. Y., Jones, C. N., Revzin, A., Tae, G. Heparin-based hydrogel as a matrix for encapsulation and cultivation of primary hepatocytes. Biomaterials. 31 (13), 3596-3603 (2010).
- Kotov, N. A., et al. Inverted Colloidal Crystals as Three-Dimensional Cell Scaffolds. Langmuir. 20 (19), 7887-7892 (2004).
- Shanbhag, S., Woo Lee, J., Kotov, N. Diffusion in three-dimensionally ordered scaffolds with inverted colloidal crystal geometry. Biomaterials. 26 (27), 5581-5585 (2005).
- Lee, Y. H., Huang, J. R., Wang, Y. K., Lin, K. H. Three-dimensional fibroblast morphology on compliant substrates of controlled negative curvature. Integr Biol. 5, 1447-1455 (2013).
- da Silva, J., Lautenschlager, F., Kuo, C. H. R., Guck, J., Sivaniah, E. 3D inverted colloidal crystals in realistic cell migration assays for drug screening applications. Integr Biol. 3, 1202-1206 (2011).
- da Silva, J., Lautenschlager, F., Sivaniah, E., Guck, J. R. The cavity-to-cavity migration of leukaemic cells through 3D honey-combed hydrogels with adjustable internal dimension and stiffness. Biomaterials. 31, 2201-2208 (2010).
- Lee, J., Lilly, G. D., Doty, R. C., Podsiadlo, P., Kotov, N. A. In vitro toxicity testing of nanoparticles in 3D cell culture. Small. 5, 1213-1221 (2009).
- Lee, J., Kotov, N. A. Notch ligand presenting acellular 3D microenvironments for ex vivo human hematopoietic stem-cell culture made by layer-by-layer assembly. Small. 5, 1008-1013 (2009).
- Liu, Y., et al. Rapid aqueous photo-polymerization route to polymer and polymer-composite hydrogel 3D inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res. Part A. 83, 1-9 (2007).
- Ma, P. X., Choi, J. W. Biodegradable polymer scaffolds with well-defined interconnected spherical pore network. Tissue Eng. 7, 23-33 (2001).
- Cuddihy, M. J., Kotov, N. A. Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) bone scaffolds with inverted colloidal crystal geometry. Tissue Eng Part A. 14, 1639-1649 (2008).
- Choi, S. W., Zhang, Y., Xia, Y. Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering: the importance of uniformity in pore size and structure. Langmuir. 26, 19001-19006 (2010).
- Choi, S. W., Zhang, Y., Thomopoulos, S., Xia, Y. In vitro mineralization by preosteoblasts in poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) inverse opal scaffolds reinforced with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Langmuir. 26, 12126-12131 (2010).
- Choi, S. W., Zhang, Y., Macewan, M. R., Xia, Y. Neovascularization in biodegradable inverse opal scaffolds with uniform and precisely controlled pore sizes. Adv Healthc Mater. 2, 145-154 (2013).
- Zhang, Y., Choi, S. W., Xia, Y. Modifying the Pores of an Inverse Opal Scaffold With Chitosan Microstructures for Truly Three-Dimensional Cell Culture. Macromol Rapid Commun. 33, 296-301 (2012).
- Cai, X., et al. Investigation of neovascularization in three-dimensional porous scaffolds in vivo by a combination of multiscale photoacoustic microscopy and optical coherence tomography. Tissue Eng. Part C, Meth. 19, 196-204 (2013).
- Zhang, Y. S., Yao, J., Wang, L. V., Xia, Y. Fabrication of Cell Patches Using Biodegradable Scaffolds with a Hexagonal Array of Interconnected Pores (SHAIPs). Polymer. 55, 445-452 (2014).
- Zhang, Y. S., Regan, K. P., Xia, Y. Controlling the Pore Sizes and Related Properties of Inverse Opal Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Macromol Rapid Commun. 34, 485-491 (2013).
- Stachowiak, A. N., Bershteyn, A., Tzatzalos, E., Irvine, D. J. Bioactive Hydrogels with an Ordered Cellular Structure Combine Interconnected Macroporosity and Robust Mechanical Properties. Adv Mater. 17, 399-403 (2005).
- Stachowiak, A. N., Irvine, D. J. Inverse opal hydrogel-collagen composite scaffolds as a supportive microenvironment for immune cell migration. J Biomed Mater Res. Part A. 85, 815-828 (2008).
- Liu, Y., Wang, S. 3D inverted opal hydrogel scaffolds with oxygen sensing capability. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces. 58, 8-13 (2007).
- Bryant, S. J., Cuy, J. L., Hauch, K. D., Ratner, B. D. Photo-patterning of porous hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 28, 2978-2986 (2007).
- Bhrany, A. D., Irvin, C. A., Fujitani, K., Liu, Z., Ratner, B. D. Evaluation of a sphere-templated polymeric scaffold as a subcutaneous implant. JAMA facial plastic surgery. 15, 29-33 (2013).
- Kuo, Y. C., Chiu, K. H. Inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds with laminin-derived peptides for neuronal differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 32 (3), 819-831 (2011).
- Yang, J. T., Kuo, Y. C., Chiu, K. H. Peptide-modified inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds with bone marrow stromal cells in the treatment for spinal cord injury. Colloids Surf. B, Biointerfaces. 84, 198-205 (2011).
- Kuo, Y. C., Tsai, Y. T. Inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds for uniform cartilage regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 11, 731-739 (2010).
- Choi, S. W., Xie, J., Xia, Y. Chitosan-Based Inverse Opals: Three-Dimensional Scaffolds with Uniform Pore Structures for Cell Culture. Adv Mater. 21, 2997-3001 (2009).
- Long, T. J., Sprenger, C. C., Plymate, S. R., Ratner, B. D. Prostate cancer xenografts engineered from 3D precision-porous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels as models for tumorigenesis and dormancy escape. Biomaterials. 35, 8164-8174 (2014).
- Kuo, Y. C., Tsai, Y. T. Inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds for uniform cartilage regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 11, 731-739 (2010).
- Kuo, Y. C., Chiu, K. H. Inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds with laminin-derived peptides for neuronal differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 32, 819-831 (2011).
- Lee, J., Cuddihy, M. J., Cater, G. M., Kotov, N. A. Engineering liver tissue spheroids with inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds. Biomaterials. 30 (27), 4687-4694 (2009).
- Galperin, A., et al. Integrated bi-layered scaffold for osteochondral tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2, 872-883 (2013).
- Waters, D. J., et al. Morphology of Photopolymerized End-linked Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogels by Small Angle X-ray Scattering. Macromolecules. 43 (16), 6861-6870 (2010).
- Elbert, D. L., Hubbell, J. A. Conjugate addition reactions combined with free-radical cross-linking for the design of materials for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2 (2), 430-441 (2001).
- Kim, M. H., et al. Biofunctionalized Hydrogel Microscaffolds Promote Three-Dimensional Hepatic Sheet Morphology. Macromol Biosci. , (2015).
- Ferreira, T., Rasband, W. ImageJ User Guide. , http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/docs/guide/146-30.html#toc-Subsection-30.1 (2012).
- JoVE Science Education Database. General Laboratory Techniques. Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy. , JoVE. Cambridge, MA. (2015).
- Tominaga, H., et al. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal Commun. 36 (2), 47-50 (1999).
- JoVE Science Education Database. General Laboratory Techniques. Introduction to the Microplate Reader. , JoVE. Cambridge, MA. (2015).
- JoVE Science Education Database. Basic Methods in Cellular and Molecular Biology. The ELISA Method. , JoVE. Cambridge, MA. (2015).
- Nolan, T., Hands, R. E., Bustin, S. A. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc. 1, 1559-1582 (2006).
- JoVE Science Education Database. Essentials of Environmental Microbiology. RNA Analysis of Environmental Samples Using RT-PCR. , JoVE. Cambridge, MA. (2016).
- JoVE Science Education. Essentials of Environmental Microbiology. , JoVE. (2015).
- Jeong, S., et al. The evolution of gene regulation underlies a morphological difference between two Drosophila sister species. Cell. 132 (5), 783-793 (2008).
- Griffith, L. G., Naughton, G. Tissue engineering--current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science. 295 (5557), 1009-1014 (2002).
- Hegde, M., et al. Dynamic Interplay of Flow and Collagen Stabilizes Primary Hepatocytes Culture in a Microfluidic Platform. Lab Chip. 14, 2033-2039 (2014).
- Kim, Y., Lasher, C. D., Milford, L. M., Murali, T., Rajagopalan, P. A comparative study of genome-wide transcriptional profiles of primary hepatocytes in collagen sandwich and monolayer cultures. Tissue Eng Pt C. 16 (6), 1449-1460 (2010).
- Baimakhanov, Z., et al. Efficacy of multi-layered hepatocyte sheet transplantation for radiation-induced liver damage and partial hepatectomy in a rat model. Cell Transplant. , (2015).
- Li, C. Y., et al. Micropatterned Cell-Cell Interactions Enable Functional Encapsulation of Primary Hepatocytes in Hydrogel Microtissues. Tissue Eng Pt A. 20 (15-16), 2200-2212 (2014).
- Shlomai, A., et al. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. P Natl A Sci USA. 111 (33), 12193-12198 (2014).
- Curcio, E., et al. Mass transfer and metabolic reactions in hepatocyte spheroids cultured in rotating wall gas-permeable membrane system. Biomaterials. 28, 5487-5497 (2007).
- Martinez-Hernandez, A., Amenta, P. The hepatic extracellular matrix. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat. 423, 1-11 (1993).
- Liu, Y., Wang, S., Lee, J. W., Kotov, N. A. A Floating Self-Assembly Route to Colloidal Crystal Templates for 3D Cell Scaffolds. Chem Mater. 17 (20), 4918-4924 (2005).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved