A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Setting Up a Stroke Team Algorithm and Conducting Simulation-based Training in the Emergency Department - A Practical Guide
In This Article
Summary
Every min counts in acute stroke care. This guide shows how to establish a Stroke Team algorithm and enhance its performance with regular simulation training. The principles of Crew Resource Management (CRM) facilitate a straight workflow, reduce door-to-needle times and increase staff satisfaction.
Abstract
Time is of the essence when caring for an acute stroke patient. The ultimate goal is to restore blood flow to the ischemic brain. This can be achieved by either thrombolysis with recombinant tissue-plasminogen activator (rt-PA), the standard therapy for stroke patients who present within the first hours of symptom onset without contraindications, or by an endovascular approach, if a proximal brain vessel occlusion is detected. As the efficacy of both therapies declines over time, every minute saved along the way will improve the patient's outcome.
This critical situation requires thorough work and precise communication with the patient, the family and colleagues from different professions to acquire all relevant information and reach the right decision while carefully monitoring the patient. This is a high fidelity situation. In nonmedical high-fidelity environments such as aviation, Crew Resource Management (CRM) is used to enhance safety and team efficiency.
This guide shows how a Stroke Team algorithm, which is transferable to other hospital settings, was established and how regular simulation-based trainings were performed. It requires determination and endurance to maintain these time-consuming simulation trainings on a regular basis over the course of time. However, the resulting improvement of team spirit and excellent door-to-needle times will benefit both the patients and the work environment in any hospital.
A dedicated Stroke Team of 7 persons who are notified 24/7 by a collective call via speed dial and run a binding algorithm that takes approximately 20 min, was established. To train everybody involved in this algorithm, a simulation-based team training for all new Stroke Team members was conceived and conducted at monthly intervals. This led to a relevant and sustained reduction of the mean door-to-needle time to 25 min, and enhanced the feeling of stroke readiness especially in junior doctors and nurses.
Introduction
The efficacy of thrombolysis with recombinant tissue-plasminogen activator (rt-PA) for acute ischemic stroke is highly time-dependent and decreases over time even in the therapeutic time window of 4.5 hr1. The same has been shown for endovascular stroke therapy2. The additional mechanical recanalization after thrombolysis has been shown to be highly effective in improving outcomes of patients with severe stroke due to Large Vessel Occlusion (LVO)3. This new therapy adds to the complexity and interdisciplinarity of acute stroke care since endovascular therapies require a neurointerventionalist, an anesthetist or neurointensivist and in many cases even the acute onward referral of the patient to a specialized center.
Therefore, concepts are needed to minimize the time to treatment without putting patient safety at risk. Since acute stroke care is delivered by interdisciplinary teams, a standardized algorithm and simulation-based training of technical and nontechnical skills appear to be a straightforward approach. In this context, not only "time is brain" but also "team is brain", since precious min and safety-relevant information can be lost by inefficient communication among team members. In nonmedical high-fidelity situations such as aviation, a concept called Crew Resource Management (CRM) has proven to be highly effective4.
A large share of fatal errors is not due to a lack of knowledge or technical skills, but to deficits in communication, interaction and decision-making. CRM emphasizes the importance of "nontechnical skills" and defines them as cognitive, social and personal resources that complement technical skills. The six key domains comprise clear communication, teamwork, situation awareness, decision-making, leadership and the management of stress5.
This concept has already been successfully implemented in professional cardiovascular life support6. A binding algorithm, a basic education in CRM for all Stroke Team members and regular simulation-based trainings for all new members of the high-fidelity Stroke Team offer ways to improve acute stroke care.
A dedicated Stroke Team of 7 persons who are notified by a collective call via speed dial and have precise tasks within a defined stroke algorithm was established to treat patients within the therapeutic time window. These are the 7 mandatory team members that are summoned to each stroke alarm:
1 resident in neurology from the Stroke Unit (SU)
1 resident in neurology from the Emergency Department (ED)
1 nurse from the ED
1 laboratory technician
1 resident specializing in neuroradiology
1 radiology technician
1 specialist in neurology (senior neurologist of the stroke unit)
Thus, a simulation-based Stroke Team training was conceived, which is conducted at monthly intervals for all new Stroke Team members and as a refresher for permanent staff. The simulation-based training transports the values of CRM and emphasizes the importance of nontechnical skills in an interdisciplinary multiprofessional team. To monitor the effects of this Stroke Team intervention consisting of the algorithm and the regular training, door-to-needle times, thrombolysis-associated complications, staff satisfaction and perceived safety in the emergency room (ER) are recorded continuously.
Protocol
1. Prenotification of the ED
- After the ED nurse hears an alarm, go to the computer screen immediately.
- Check the information above the incoming patient via the online platform (e.g., IVENA Ehealth)7. Find that the system announces a 66 year-old male patient with the tentative diagnosis of a stroke within the time window (stroke <6 hr) with the estimated time of arrival.
- Pre-notify the resident of the SU via phone call.
- As the SU resident hears the mobile phone ringing, have the SU resident take the phone call. Have the SU resident go to the ED at the estimated time of arrival.
2. Patient Arrives in the ED
- Bring the patient to the ED via paramedics. Have paramedics enter the ED with the patient on the stretcher and report to the stroke nurse and SU resident.
- SU resident: Perform a first initial check including the FAST-Test8 (F: facial droop, A: arm weakness, S: speech difficulties, T: exact time of symptom onset or time last seen well). Ask the patient or the paramedics about the intake of blood thinners. Find out about the characteristics and evolution of the symptoms, in order to exclude very obvious stroke mimics or patients that present beyond the therapeutic time window or have overt contraindications to thrombolysis. If the patient or the paramedics cannot answer these questions, contact relatives if available.
NOTE: The initial check reveals that the patient is a thrombolysis candidate. - ED nurse: Trigger the Stroke Team alert by a speed dial collective call, which simultaneously informs all members of the Stroke Team via their institutional mobile phones. Enter the insurance data of the patient into the hospital information system and perform the registration procedure. Check whether the patient has been treated at the hospital before and print out the latest discharge letter and laboratory values from the electronic hospital information and hand them to the SU resident.
- Have all Stroke Team members answer their phones to hear an automatic voice message saying "stroke within time window". Have all Stroke Team members immediately go to their workplaces as defined by the algorithm: ED resident, SU resident and senior neurologist meet at the emergency department, laboratory technician goes to the laboratory, radiology resident and technician meet at the CT scanner.
3. Rapid Blood Sampling and Clinical Examination
- ED resident: Obtain an intravenous access and perform blood sampling, either through an adaptor to the venous access or with a butterfly cannula, for coagulation parameters INR (prothrombin time in international normalized ratio), activated prothrombin time (aPTT) and thrombin time (TT) (3 ml, citrate plasma), hematology (1.6 ml, EDTA plasma), and clinical chemistry (7.5 ml, lithium heparinate plasma)9.
- SU resident: Inform the patient that he is examined for the suspicion of an acute stroke. Take a brief history including the questions on symptom onset, symptom evolution, prior disabilities, current medication intake (especially blood thinners), allergies and preexisting medical conditions. Ask whether the patient has had prior radiologic exams with contrast agents. When the patient cannot answer these questions, ask the relatives when available.
- Perform a focused neurological exam on the basis of the NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS)10. Free online-trainings of the NIHSS are available in several languages11.
- Senior neurologist: Review the patient's case and decide upon the appropriate imaging modality for the patient depending on the presenting symptoms and the time window. Preferentially consider Computed Tomography (CT) for patients with unequivocal stroke symptoms and a stroke onset clearly within the therapeutic time window because of speed and easy access. Preferentially consider Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for patients beyond the therapeutic time window or with unknown onset of stroke symptoms or patients with an atypical clinical presentation.
- Mark the blood samples as "vital" with pink coding caps and bring them to the laboratory. Reserve one centrifuge for Stroke Team samples. The complete analysis that is performed on an automated hemostasis analyzer, an automated hematology system, and an automated analyzer for clinical chemistry requires 15-20 min.
- Bring the patient to the CT scanner. The patient is still lying on the ambulance stretcher and is accompanied by the paramedics, the residents from the ED, the SU, and the senior neurologist from the SU.
- At the CT scanner, meet the resident specializing in neuroradiology and the radiology technician.
4. Cranial CT Scan and Acute Therapy
- Transfer the patient to the CT and connect a line with contrast agent (e.g., Ultravist-300) for the CT angiography to the venous access via Luer lock connection.
- ED nurse: Arrive at the CT scanner and bring along a stretcher with a thrombolysis kit (containing 10 mg rt-PA + aqua ad injectabilia, blood pressure medication suitable for intravenous (IV) application [e.g., urapidile], IV anti-vomiting medication [e.g., granisetron], IV sedative [e.g., lorazepam], 10 ml syringes and 0.9% NaCl solution to flush the venous access), monitoring equipment and portable oxygen.
- Radiology technician: Perform a cranial CT (to exclude intracranial hemorrhage) and CT angiography (to screen for LVO). Stroke-CT includes unenhanced CT with a slice thickness of 5 mm and CT angiography depicting brain supplying cervical and intracranial arteries.
- Neuroradiologist: Directly review the cranial CT. Unenhanced CT must exclude intracranial hemorrhage and intracranial tumor. For mechanical thrombectomy, CT angiography must prove proximal vessel occlusion, and infarct core on unenhanced CT should not be larger than Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS)12 of 5.
- Senior neurologist: Voice the decision to treat the patient with IV rt-PA.
- If the patient can reliably exclude the intake of blood thinners and prior problems with hemostasis, do not await coagulation parameters and administer the rt-PA bolus before the acquisition of the CT angiography.
- In case of an aphasic patient or an active oral anticoagulant therapy, await the laboratory values (15-20 min) and perform the CT angiography first.
- ED nurse: Prepare the appropriate dose for the rt-PA bolus and call the colleagues in the ED to prepare the remaining 90% of the dose for infusion via a pump over 1 hr. rt-PA is given at a dose of 0.9 mg/kg body weight. Have a table with appropriate doses for all body weights between 40 kg and >100 kg in discrete steps of 5 kg ready to prevent calculation errors. Patients weighing 100 kg and more should receive a total dose of 90 mg.
- SU resident: Administer the bolus of rt-PA (10% of the total dose) intravenously over 1 min directly on the CT table.
- Stroke team: Transfer the patient to the ED stretcher.
NOTE: The paramedics leave the scene. - Laboratory technician: Call the SU resident and disclose the coagulation parameters such as International Normalized Ratio (INR), thrombocytes, Thrombin Time (TT) and activated prothrombin time (aPTT).
- Neuroradiologist and senior neurologist of the SU: Examine the CT angiography for LVO. If LVO is present, directly notify the neuroradiologist, and the department of anesthesiology of the planned intervention.
- Stroke team: Transfer the patient back to the ED or directly to the angiography suite in case of LVO.
- Administer the remaining 90% of the rt-PA in the ED or in the angiography suite. Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation and neurological function on the NIHSS every 15 min and treat severely elevated blood pressure with IV medication (e.g., urapidil) to a target value below 185/90 mmHg.
- SU resident: Go to a computer and check the remaining laboratory parameters in the hospital information system.
5. Simulation-based Stroke Team Training
- Stroke Team trainers (2): Invite all new staff members that are involved in the care of acute stroke patients to the Stroke Team training, which is offered once a month.
- Before the training starts, prepare the remote-controlled manikin. Connect it to a real monitor, fill it with artificial blood (sugar-free red tea for example). Place the manikin on a stretcher with a head deviation to the left and a plegic position of the right arm and leg.
6. The Theoretical Course
- Sit a group of 4-10 staff members and medical students around a table. Invite everyone to introduce themselves, describe their professional background and share their experience in stroke care as well as the expectations towards the training.
- Stroke Team trainer 1: Give an oral presentation supported by illustrative slides, which covers the most frequent stroke symptoms and their detection by the FAST8 score, the basic principles of stroke pathophysiology and the current treatment modalities (IV thrombolysis and endovascular thrombectomy) as well as the Stroke Team algorithm of the hospital.
- Teach how to do a concise NIHSS exam and let the group practice on each other.
NOTE: At the end of the theoretical part which takes approximately 60 min, and in which the participants should understand the importance of the "time factor" and the significance of efficient teamwork, go to the ED.
7. The Hands-on Stroke Team Simulation
- Stroke Team trainer 2: Allocate the participants their roles in theStroke Team algorithm and advise them to treat the manikin as if it were a real patient.
- Tell the participants that a stroke patient is awaited. Leave them enough time to clarify a few questions and get together as a team.
- Bring the manikin into the ED, acting as a paramedic.
- Report that the patient is a 72 year-old female who collapsed during lunch and showed a loss of speech and a right-sided hemiparesis. State that the exact time of symptom onset is unknown, but there is the telephone number of the patient's daughter. Show the containers of aspirin and a beta blocker collected at the patient's home.
- Stroke team: Perform the Stroke Team algorithm on the manikin while Stroke Team trainer 1 notes the procedural times and positive and negative elements of the performance.
- Stroke Unit resident: Take the history from the paramedic and the daughter via the telephone and examine the NIHSS. Ask for the time of symptom onset, the intake of additional blood thinners, the preexisting medical conditions, especially recent operations, preceding hemorrhagic events and malignant diseases. Delegate some of the tasks (e.g., taking the history from the daughter by phone) to the team.
NOTE: The phone call reaches Stroke Team trainer 1. - Stroke Team trainer 1: Report that the symptoms began abruptly an hour ago, that her mother certainly did not take additional blood thinners ("… neither warfarin nor any of the new ones that her doctor proposed because her husband died from a brain bleeding when taking warfarin and she would not have that."), has recently been short of breath when climbing the stairs but is otherwise healthy except for a mild arterial hypertension.
- ED resident: Establish venous access, take a blood sample and cap it as 'vital', ensure that the blood sample is brought to the laboratory and order the imaging in the hospital information system.
- Stroke Team trainer 1: Display a systolic blood pressure of 210 mmHg.
- Stroke team: Decide if and how to treat this blood pressure, which is a contraindication to thrombolysis, communicate with the nurse and administer the right dose of a suitable IV drug.
- Transfer the patient to the CT scanner.
- Radiology technician: Perform a head CT of the manikin.
- Stroke Team trainer 1: Confront the neuroradiologist with a printed CT scan of a stroke patient brain without intracranial hemorrhage, without LVO and without early infarct signs.
- Neuroradiologist: Analyze the scan and convey the findings clearly to the residents of the stroke unit and the ED.
- Stroke team: Decide to treat the patient with thrombolysis and administer the bolus.
- Stroke Team trainers: Conduct a feedback session with discussion after the simulation.
- Stroke Team trainer 1: Name the door-to-needle time that was achieved during the training session which is usually 20-30 min and lower than expected by the participants.
- Stroke Team trainer 2: Conduct two rounds of feedback to each individual team member. Start the first one with the questions "What was done well? What would you personally do the same way in your next Stroke Team operation?" followed by a second round with the question "What did not work so well? What would you personally do differently next time?" and conclude with a feedback round to the complete team: "What are the essential factors for a successful Stroke Team operation?"
Results
Effect on the door-to-needle times and thrombolysis rate
The implementation of the Stroke Team algorithm in 2012 accompanied by regular simulation-based Stroke Team trainings led to a relevant increase in the patients treated with a door-to-needle time below 30 and 60 min and to an increase in our thrombolysis rate.
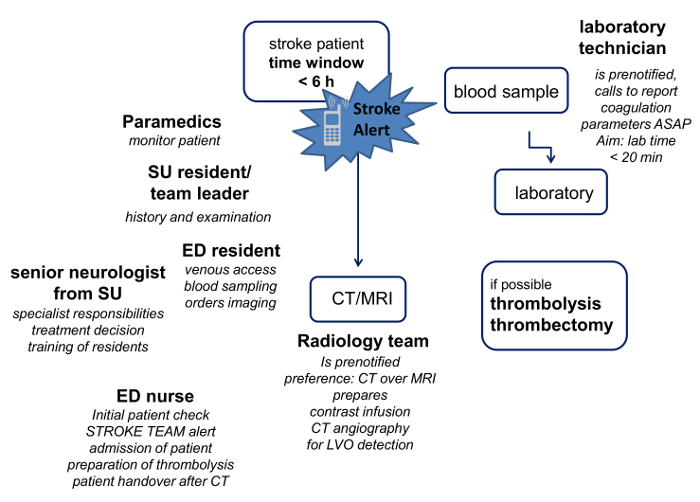
Figure 1: Stroke Team Algorithm of t...
Discussion
A binding stroke team algorithm and regular simulation-based stroke team trainings can lead to a long-term reduction of the door-to-needle time as the key benchmark process time for acute stroke treatment. Excellent examples of a set of measures that improve the acute stroke work flow, which also inspired our algorithm, have been described by the Helsinki group14,15. Another very innovative approach to shorten the time interval from symptom onset to thrombolysis are mobile stroke units such as the pioneering S...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Acknowledgements
The Stroke Team training was supported by a research grant of Boehringer Ingelheim to WP.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Drug | |||
| Alteplase (rtPA) | Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany | A licensed drug, which has proven effectiveness for acute ischemic stroke | |
| Urapidil 50 mg/10 ml | Takeda Pharma, Berlin, Germany | A licensed drug, antihypertensive | |
| Granisetron 3 mg/ml | Hameln Pharma, Hameln, Germany | A licensed drug, antiemetic | |
| Lorazepam 2 mg/ml | Pfizer, Berlin, Germany | A licensed drug, sedative | |
| Iopromid 300 mg/ml | Bayer Vital GmbH, Leverkusen, Germany | A licensed drug, non-ionic contrast agent for Computed Tomography (CT) | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Device | |||
| S-Monovette citrate 3 ml | Sarstedt, Nürnbrecht, Germany | For blood collection for coagulation assays | |
| S-Monovette EDTA 1.6 ml | Sarstedt, Nürnbrecht, Germany | For blood collection for hematology assays | |
| S-Monovette lithium heparinate 7.5 ml | Sarstedt, Nürnbrecht, Germany | For blood collection for clinical chemistry assays | |
| ACL Top 500 | Instrumentation Laboratory, Kirchheim, Germany | Automated hemostasis analyzer | |
| Sysmex XE 2100 | Sysmex Corporation, Norderstedt, Germany | Automated hematology analyzser | |
| Cobas 6000 | Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany | Automated clinical chemistry analyzser | |
| Resusci Anne Skillreporter | Laerdal, Stavanger, Norway | Remote-controlled manikin | |
| Ingenuity 128 | Philips, Hamburg, Germany | CT-scanner | |
| MEDRAD Stellant | Bayer Radiology, Leverkusen Germany | Contrast agent delivery system | |
| Universal 320 R | Hettich, Tuttlingen, Germany | Centrifuge | |
| Perfusor fm | Braun, Melsungen, Germany | Infusion pump | |
| Infinity Gamma | Dräger, Hamburg, Germany | Monitor | |
| Ivena ehealth | mainis IT-Service GmbH, Offenbach, Germany | Online prenotification platform | |
| Braun ThermoScan PRO 4000 | Welch Allyn, Hechingen, Germany | Ear thermometer |
References
- Emberson, J., et al. Stroke Thrombolysis Trialists' Collaborative Group. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 384 (9958), 1929-1935 (1929).
- Goyal, M., et al. HERMES collaborators. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 387 (10029), 1723-1731 (2016).
- Goyal, M., et al. SWIFT PRIME investigators. Analysis of Workflow and Time to Treatment and the Effects on Outcome in Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke: Results from the SWIFT PRIME Randomized Controlled Trial. Radiology. 279 (3), 888-897 (2016).
- Flin, R., Maran, N. Basic concepts for crew resource management and non-technical skills. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 29 (1), 27-39 (2015).
- Flin, R., O'Connor, P., Crichton, M. Safety at the sharp end. A guide to non-technical skills. , (2008).
- American Heart Association. . Adavanced Cardiovascular Life Support Provider Manual. ISBN 978-1-61669-010-6. , (2011).
- Kothari, R. U., Pancioli, A., Liu, T., Brott, T., Broderick, J. Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale: reproducibility and validity. Ann Emerg Med. 33 (4), 373-378 (1999).
- National Institute of Health. . NIH Stroke Scale. , (2016).
- National Institute of Health. . NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS). , (2016).
- Jauch, E. C., et al. American Heart Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; Council on Clinical Cardiology. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 44, 870-947 (2013).
- Pexman, J. H., et al. Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22, 1534-1542 (2001).
- Tahtali, D., et al. Crew resource management and simulator training in acute stroke therapy. Nervenarzt. , (2016).
- Meretoja, A., et al. Reducing in-hospital delay to 20 minutes in stroke thrombolysis. Neurology. 79 (4), 306-313 (2012).
- Meretoja, A., et al. Helsinki model cut stroke thrombolysis delays to 25 minutes in Melbourne in only 4 months. Neurology. 81 (12), 1071-1076 (2013).
- Ebinger, M., et al. Effect of the use of ambulance-based thrombolysis on time to thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 311 (16), 1622-1631 (2014).
- Ebinger, M., et al. Prehospital thrombolysis: a manual from Berlin. J Vis Exp. 26 (81), e50534 (2013).
- Itrat, A., et al. Cleveland Pre-Hospital Acute Stroke Treatment Group. Telemedicine in Prehospital Stroke Evaluation and Thrombolysis: Taking Stroke Treatment to the Doorstep. JAMA Neurol. 73 (2), 162-168 (2016).
- Fletcher, G., Flin, R., McGeorge, P., Glavin, R., Maran, N., Patey, R. Anaesthetists' Non-Technical Skills (ANTS): evaluation of a behavioural marker system. Br J Anaesth. 90 (5), 580-588 (2012).
- Youngson, G. G., Flin, R. Patient safety in surgery: non-technical aspects of safe surgical performance. Patient Saf Surg. 4 (1), (2010).
- Barzallo Salazar, M. J., et al. Influence of surgeon behavior on trainee willingness to speak up: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Surg. 219 (5), 1001-1007 (2014).
- Mata, D. A., et al. Prevalence of Depression and Depressive Symptoms Among Resident Physicians: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 314 (22), 2373-2383 (2015).
- Kleim, B., Bingisser, M. B., Westphal, M., Bingisser, R. Frozen moments: flashback memories of critical incidents in emergency personnel. Brain Behav. 5 (7), e00325 (2015).
- Rushton, C. H., Batcheller, J., Schroeder, K., Donohue, P. Burnout and Resilience Among Nurses Practicing in High-Intensity Settings. Am J Crit Care. 24 (5), 412-420 (2015).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved