A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Measuring Influenza Neutralizing Antibody Responses to A(H3N2) Viruses in Human Sera by Microneutralization Assays Using MDCK-SIAT1 Cells
In This Article
Summary
Influenza neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection of influenza infections. Microneutralization assays measure neutralizing antibodies in human sera and are often used for influenza human serology. We describe a microneutralization assay using MDCK-SIAT1 cells to measure neutralizing antibody titers to contemporary 3C.2a and 3C.3a A(H3N2) viruses following influenza vaccination or infection.
Abstract
Neutralizing antibodies against hemagglutinin (HA) of influenza viruses are considered the main immune mechanism that correlates with protection for influenza infections. Microneutralization (MN) assays are often used to measure neutralizing antibody responses in human sera after influenza vaccination or infection. Madine Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells are the commonly used cell substrate for MN assays. However, currently circulating 3C.2a and 3C.3a A(H3N2) influenza viruses have acquired altered receptor binding specificity. The MDCK-SIAT1 cell line with increased α-2,6 sialic galactose moieties on the surface has proven to provide improved infectivity and more faithful replications than conventional MDCK cells for these contemporary A(H3N2) viruses. Here, we describe a MN assay using MDCK-SIAT1 cells that has been optimized to quantify neutralizing antibody titers to these contemporary A(H3N2) viruses. In this protocol, heat inactivated sera containing neutralizing antibodies are first serially diluted, then incubated with 100 TCID50/well of influenza A(H3N2) viruses to allow antibodies in the sera to bind to the viruses. MDCK-SIAT1 cells are then added to the virus-antibody mixture, and incubated for 18 - 20 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2 to allow A(H3N2) viruses to infect MDCK-SIAT1 cells. After overnight incubation, plates are fixed and the amount of virus in each well is quantified by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using anti-influenza A nucleoprotein (NP) monoclonal antibodies. Neutralizing antibody titer is defined as the reciprocal of the highest serum dilution that provides ≥50% inhibition of virus infectivity.
Introduction
Influenza viruses continue to cause morbidity and mortality in the human population each year. HA is the major surface glycoprotein of influenza viruses. Neutralizing antibodies targeting HA are the main immune mechanism that correlates with protection of influenza infection1,2. Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assays and MN assays are two methods widely used to measure antibody responses in human sera after influenza infection or vaccination3. The HI assay measures antibody inhibition of virus hemagglutination of red blood cells and is considered a surrogate assay. Unlike HI, the MN assay can directly measure the levels of antibodies in human sera that neutralize influenza infection in cell cultures. MDCK cells are often used in influenza virus isolation and MN assays4.
Influenza viruses constantly undergo antigenic drift and shift, acquiring mutations on HA proteins that can alter the receptor binding specificity of viruses. Since 2014, new clusters of A(H3N2) viruses emerged and continued to circulate until the current season. The majority of these viruses belong to the genetic group 3C.2a and 3C.3a based on phylogenetic analysis of the HA proteins. Many of the circulating 3C.2a viruses had reduced ability to hemagglutinate red blood cells and therefore cannot be characterized by HI assays5. Neutralization assays must be used to measure the antibody responses to these viruses that do not hemagglutinate6. Furthermore, studies have shown that these contemporary A(H3N2) viruses have altered receptor binding properties compared with earlier A(H3N2) viruses and tend to accumulate culture adapted mutations and polymorphism when passaged in in vitro cell cultures7,8,9. Compared with conventional MDCK cells, MDCK-SIAT1 is a cell line developed by Matrosovich et al. through stable transfection of MDCK cells with cDNA of human α2,6-sialtransferase (SIAT1). This cell line expresses increased amounts of α2,6-sialic galactose moieties and decreased amounts of α2,3-sialic acid moieties than the parent MDCK cells10. MDCK-SIAT1 cells have shown to improve isolation rates for A(H3N2) viruses compared to MDCK cells11. Recently, Lin et al. reported that for newly emerged 3C.2a and 3C.3a human A(H3N2) influenza viruses, more faithful virus replications and better virus infectivity were achieved when viruses were cultured in MDCK-SIAT1 cell lines compared with MDCK cells7. Thus, the MDCK-SIAT1 cells are better suited in MN assays to characterize antibody responses to the recent clusters of A(H3N2) viruses.
Here we describe a MN assay using MDCK-SIAT1 cells to measure antibody responses to contemporary 3C.2a and 3C.3a A(H3N2) viruses in human sera. Viruses grown in either eggs or cells can be used in this assay. Heat inactivated sera containing neutralizing antibodies are first serially diluted, then incubated with 100 TCID50/well of influenza A(H3N2) virus to allow antibodies in the sera to bind to the virus. MDCK-SIAT1 cells are then added to the virus-antibody mixture, and incubated for 18 - 20 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2 to allow the A(H3N2) virus to infect MDCK-SIAT1 cells and replicate. After overnight incubation, the plates are fixed and the amount of virus in each well is quantified by an ELISA using anti-influenza A NP monoclonal antibodies. The detection of NP indicates the presence of virus infection and the absence of neutralizing antibodies. Neutralizing antibody titer is defined as the reciprocal of the highest serum dilution that provides ≥ 50% inhibition of virus infectivity.
Protocol
All influenza viruses should be handled according to appropriate biosafety level requirements (BSL-2 or higher) as defined in the Biosafety on Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (BMBL)12.
1. Preparation of Reagents and Starting Material
- Prepare MDCK-SIAT1 cells and sterile cell culture medium
- Prepare the MDCK-SIAT1 cell culture medium using 500 mL of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high glucose, 10% v/v heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2 mM L- glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 1 mg/mL G418 sulphate (e.g., geneticin), and 100 U/ml penicillin with 100 µg/mL streptomycin (optional). Sterilize by filtration through a 0.2 µM pore-size membrane. G418 sulphate is added to ensure plasmid stability in the MDCK-SIAT1 cells.
- Prepare the MDCK-SIAT1 cell line. In a 162 cm2- tissue culture flask(s) containing 30 mL of sterile cell culture media, seed flasks with 2 - 2.5 x 106 MDCK-SIAT1 cells and incubate at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 2 days; this will be used for tissue-culture infectious dose (TCID) determination and MN assays.
NOTE: MDCK-SIAT1 cells were kindly provided by Dr. M. Matrosovich, Marburg, Germany10. This cell line can also be obtained commercially (see the Table of Materials).
- Prepare the sterile virus propagation media using 500 mL of DMEM high glucose, 0.3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) fraction V, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 20 mM HEPES. Sterilize by filtration through a 0.2 µM pore-size membrane.
- Prepare 0.75% (v/v) guinea pig red blood cells (gpRBCs) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.01 M PBS, at pH 7.2.
- Prepare the sterile virus diluent using DMEM high glucose, 1% Bovine Albumin Fraction V (BSA), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 20 mM HEPES. Sterilize by filtration with a 0.2 µm pore-size membrane, and prepare fresh for each assay.
- Prepare the cold cell fixative as 80% cold acetone in PBS (0.01 M PBS, pH 7.2).
- Prepare the wash buffer using PBS (0.01 M PBS pH 7.2) and 0.3% (v/v) tween-20.
- Prepare the antibody diluent using PBS (0.01 M PBS, pH 7.2), 0.3% (v/v) tween-20, and 5% non-fat dry milk.
- Use anti-influenza A NP mouse monoclonal antibody clone A1 and A3 pool as the primary antibody. Dilute in the antibody diluent at the optimal concentration as determined by titration.
- Use goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to horse radish peroxidase (HRP) as the secondary antibody. Dilute in the antibody diluent at the optimal concentration as determined by titration.
- Prepare the peroxidase substrate using o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD) in 0.05 M phosphate citrate buffer at pH 5. Prepare 0.05 M phosphate citrate buffer by dissolving 1 capsule/100 mL deionized H2O. Dissolve 1 OPD tablet (10 mg)/20 mL of phosphate citrate buffer immediately before use.
- Use 0.5 M of sulfuric acid as the OPD stop solution. Add 28 mL of 18 M sulfuric acid stock to 972 mL deionized H2O in a chemical hood.
- Treatment of human and animal sera
- Heat inactivate the human sera used in the MN assays in a water bath at 56 °C for 30 min prior to the assay. Use immediately or if needed, store thawed sera at 4 °C for no more than 24 h; if longer storage period is needed, store sera frozen at -20 °C or colder.
- Treat the animal sera used in the MN assays with Receptor Destroying Enzyme (RDE) and heat inactivate prior to the assay as follows.
- Thaw the sera in a 37 ˚C water bath then place on ice. Mix 1 volume of animal serum sample with 3 volumes of RDE. Incubate at 37 ˚C for 18 - 20 h.
- Heat inactivate the RDE treated sera at 56 ˚C for 30 min. Add 6 volumes of PBS, pH 7.2 to each sample for a final pre-dilution of 1:10. If needed, store thawed sera at 4 °C for no more than 24 h; if longer storage period is needed, store sera frozen at -20 °C or colder.
NOTE: Animal sera may contain various sialic acid glycans which may bind to the HAs of influenza viruses and inhibit the binding of influenza-specific anti-HA antibodies. Therefore, it is necessary to RDE treat all animal sera prior to the MN assays to remove these non-specific viral HA binders in the serum samples.
2. Passage of MDCK-SIAT1 Cell Culture
Note: All cell cultures must be performed in a biological safety cabinet to prevent contamination.
- Decant the cell culture medium from the cell monolayer in 162 cm2 flasks. Trypsinize the cells by rinsing the monolayer with trypsin-EDTA. Add 5 mL trypsin-EDTA to cover the cell monolayer. Incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2 until the monolayer detaches (5-10 min). Add 15 mL of MDCK-SIAT1 cell culture media to each flask containing trypsinized cells, pipette up and down to separate cells.
- Use a hemocytometer and trypan blue to determine the cell counts and viability. Seed the cells in new 162 cm2 tissue culture flasks containing 30 mL of cell culture media with 2-2.5 x 106 cells /flask and incubate at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 2 days for use in TCID and MN assays. Seed cells at 4 - 5 x 106 cells/flask and incubate at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 2 days for use in virus propagation.
NOTE: The seeding density can be adjusted if shorter or longer culture periods are desired. For virus propagation, cells should reach over 100% confluency. For Tissue Culture Infection Dose (TCID) and MN assays, the cells should be at 75 - 95% confluency (Figure 1).
3. Propagation of A(H3N2) Viruses in MDCK-SIAT1 Cells
NOTE: A(H3N2) virus can be propagated either in 10 - 11 day old embryonated hen's eggs according to standard protocol3, or MDCK-SIAT1 cell cultures. MDCK-SIAT1 cells should reach over 100% confluency for virus inoculation. Virus seed stocks can be inoculated with multiple dilutions of inoculum. The inoculum dilutions with the best harvest HA and infectivity can be used for further MN assays.
- Remove the cell culture medium from the cell monolayer (>100% confluency) in 162 cm2 flasks. Wash the monolayer twice with 15 mL of sterile 0.01 M PBS, pH 7.2, and decant.
- Label 1 flask as control and add 20 mL of virus propagation media. Incubate flask at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Leave this flask untouched and use for comparison after day 1 of virus propagation.
- Add 10 mL of sterile virus propagation media to the flask(s) and incubate all flask(s) at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Thaw a vial of influenza virus stock at room temperature then place on ice. Dilute with the virus propagation media to the target dilutions.
NOTE: Target dilutions can be adjusted based on HA titers of virus stocks. To prepare a 1:1000 diluted inoculum, add 100 µL of virus to 9.9 mL of sterile virus propagation media. Invert gently, remove 1 mL of 1:100 dilution to 9 mL of sterile virus propagation media, invert gently for a 1:1000 diluted inoculum. Place on ice. - Remove all flasks except control flask from the incubator. Remove the virus propagation media from flask(s) of MDCK-SIAT1 cells and inoculate each flask with 10 mL of diluted virus. Incubate the flasks at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 1 h, rotating the flask(s) every 15 min.
- Remove 5 mL of inoculum from the flask(s) and replace with 15 mL virus propagation media containing 1 µg/mL TPCK-trypsin. Incubate the flask(s) at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 16-18 h.
- After the overnight incubation, observe the flask(s) under 100X microscope magnification and look for cytopathic effects (CPE) on the cells. Remove 15-17 mL of virus supernatant from the flask(s), and replace with 15 - 17 mL of freshly prepared virus propagation media containing 2 µg/mL TPCK-trypsin.
- Incubate the flasks at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Monitor the CPE of the monolayer (by comparison with the cell control flask) and check the HA periodically (every 4 h) with 0.75% gpRBC until harvest.
- Set up an HA 96-well microtiter plate. Add 50 µL of 0.01 M PBS, pH 7.2 to wells A2 - A12 and B2 - B12 (duplicates), and wells H1 - H12 for control.
- Add 100 µL of virus supernatant to A1 and A2, perform a 2-fold serial dilution from A1 and B1 through A12 and B12. Discard 50 µL after mixing in A12 and B12. Add 50 µL of 0.75% gpRBCs to Rows A, B, and H.
- Tap the plate and incubate at room temperature for 1 h.
- Determine HA of virus supernatant by tilting the 96-well microtiter plate at a 45° to 60° angle.
- Read plates for hemagglutination; the highest dilution of virus that achieves complete hemagglutination is considered the HA titration end point for the specific virus. Record the reciprocal of the highest virus dilution with complete hemagglutination as the HA titer of the virus.
NOTE: The settled RBCs in row H (controls) should start "running" and form a small teardrop-shape due to gravity. Wait till RBCs in control wells finish running, then read the RBC buttons in the virus titration wells. Those that exhibit RBC buttons and "run", do not achieve hemagglutination. Locate the highest dilution of virus that completely inhibit hemagglutination as the end point HA titer of the virus.
- Harvest the virus when the HA of the virus culture plateaus or the virus culture reaches the target HA (for example, >16 HAU), but before the cell monolayer starts to display significant CPE.
- Centrifuge the virus culture supernatant at 300 x g for 10 min at 4 °C to pellet the cellular debris. Transfer the clarified supernatant containing the virus harvest to a clean tube. Aliquot the supernatant containing the virus harvest into single-use sterile cryogenic vials and freeze immediately at -70 °C or colder.
NOTE: The virus stocks used for the MN assays should have high infectious titer and minimal defective particles. The minimum dilution of virus stocks to achieve 100 TCID50/50 µL for MN assay is 1:100.
NOTE: The virus stocks used in the MN assays should not be thawed and refrozen.
- Centrifuge the virus culture supernatant at 300 x g for 10 min at 4 °C to pellet the cellular debris. Transfer the clarified supernatant containing the virus harvest to a clean tube. Aliquot the supernatant containing the virus harvest into single-use sterile cryogenic vials and freeze immediately at -70 °C or colder.
4. Determination of TCID of the Virus
- Day 1: Virus titration
- Thaw a vial of virus at room temperature and immediately place on ice.
- Test the virus at two different starting dilutions: 10-2 and 10-3. Add 100 µL of virus to 9.9 mL of virus diluent for 10-2 dilution. Add 1 mL of 10-2 dilution to 9.0 mL of virus diluent for 10-3 dilution.
- Using two microtiter plates (plate 1 for 10-2 dilution and plate 2 for 10-3 dilution), add 100 µL of virus diluent to all wells except column 1 of the 96-well microtiter plate.
- Perform ½log10 dilutions (10-2, 10-2.5, 10-3, etc.). Add 146 µL of the virus starting dilution to all wells in column 1 and transfer 46 µL serially from column 1 through column 11 (Figure 2). Change pipette tips between wells. After mixing column 11, discard the tips with the 46 µL dilution.
- Use column 12 as the Cell Control (CC); it only contains virus diluent. Incubate for 1 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- Day 1: Preparation of MDCK-SIAT1 cells
Note: The MDCK-SIAT1 cell monolayer should reach 75 - 95% confluency for TCID and MN assays. One 162-cm2 flask at 95% confluency should yield enough cells to seed ~ 4 - 5 microtiter plates.- Wash the 75 - 95% confluent monolayer with 20 mL PBS to remove the FBS in the culture media. Trypsinize the cells as follows.
- Rinse the monolayer with sterile PBS, add 7 mL trypsin-EDTA to cover the cell monolayer. Lay the flask flat and incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2 until the monolayer detaches (approximately 5 - 10 min). Add 7 mL of virus diluent to each flask containing the trypsinized cells.
- Wash the cells with virus diluent to remove the FBS.
- Gently pipette up and down to separate the cells. Transfer the cells to a 50-mL conical tube; fill the tube with virus diluent.
- Centrifuge at 485 x g for 5 min. Decant the virus diluent, replace with fresh 50 mL virus diluent, and centrifuge at 485 x g for 5 min. Decant the virus diluent and replace with fresh virus diluent (10 mL/flask) to resuspend the pellet.
- Use a hemocytometer and trypan blue to determine the cell count and viability. Adjust the cell concentration with the virus diluent to 1.5 x 105 cells/mL.
- Add 100 µL of diluted MDCK-SIAT1 cells to each well of the microtiter plates (1.5 x 104 cells/well) and cover the plates. Incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 18 - 20 h.
- Wash the 75 - 95% confluent monolayer with 20 mL PBS to remove the FBS in the culture media. Trypsinize the cells as follows.
- Day 2: ELISA
- Fixation of cells
- Remove the medium from the microtiter plates. Wash each well with 200 µL of PBS. Add 300 µL cold 80% acetone to each well and incubate at room temperature for 10 min. Remove the fixative and allow the plates to air dry.
- ELISA
- Primary antibody addition
Note: Anti-influenza A NP monoclonal antibody should be used in excess as the primary antibody in ELISA. Determine the optimal antibody dilution for each lot of primary antibodies by performing antibody titrations in MN. Select the primary antibody concentration that is in excess and with the best signal to background ratio.- Dilute the anti-influenza A NP monoclonal antibody (primary antibody) to the target concentration in the antibody diluent (e.g. add 30 µL of primary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target dilution of 1:1000).
- Wash plates 3 times with 300 µL of wash buffer. Add 100 µL diluted primary antibody to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 1 h.
- Secondary antibody addition
Note: Goat anti mouse IgG conjugated to horse radish peroxidase (HRP) should be used in excess as the secondary antibody in ELISA. Determine the optimal antibody dilution for each lot of secondary antibodies by performing antibody titrations. Select the secondary antibody concentration in excess and with the best signal to background ratio.- Dilute the goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to HRP antibody (secondary antibody) to the target concentration in the antibody diluent (e.g. Add 7.5 µL of secondary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target 1:4000 dilution).
- Wash the plates 3 times with 300 µL wash buffer. Add 100 µL diluted secondary antibody to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 1 h.
- Substrate addition and plate reading
- Wash the plates 5 times with 300 µL wash buffer and tap on a lint-free wipe.
- Add 100 µL of freshly prepared substrate to each well and incubate at room temperature until the color development saturates and the optical density (OD) of cell control wells <0.2.
- Add 100 µL of stop solution to all wells. Read the OD of wells at 490 nm using a microplate spectrophotometer.
- Primary antibody addition
- Fixation of cells
- TCID 50 calculation
- Calculate the median OD490 of the cell controls (column 12).
- Consider any test well with an OD490 greater than twice the median OD490 of the CC wells as "positive"; otherwise, it is considered "negative".
- Calculate the TCID50 of the virus using the Reed-Muench method13.
- Determine the number of positives and negatives at each dilution.
- Calculate the "cumulative positive", "Cumulative negative", "Ratio", and "% positive" as illustrated in Table 1.
- Calculate the "proportional distance" between the dilution showing >50% positives and the dilution showing <50% positives using the following:
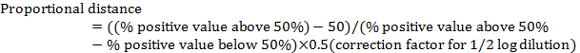
Note: The correction factor for ½ log dilution is 0.5. For example, in Table 1: (80 − 50)/(80 − 20) x 0.5 = 0.25 - Calculate the virus TCID50 by adding the proportional distance to the dilution showing > 50% positive.
NOTE: For example, in Table 2, TCID50 is 10-5+(-0.25) = 10-5.25. Note this is the TCID50 of the virus per 100 µL (or 10-5.25/100 µL).
- Calculate the virus dilution. For MN assays, dilute the virus to 200 TCID50/100 µL (equivalent to 100 TCID50/50 µL per well).
NOTE: In the example in Table 1, 1 TCID50 is 10-5.25 in 100 µL, and the dilution to achieve 200 TCID50/100 µL is 1:891 based on the calculations: 200 x 10-5.25 = 10-2.95 = 1/102.95 = 1/891
5. MN Assay Using MDCK-SIAT1 Cells
- Day 1: Test and control sera preparation and plate layout
- Thaw the sera in 37 °C water bath and remove immediately after thawing. Aliquot the amount of sera that needs to be tested; a minimum of 10 µL of original sera is needed to test with one virus in singlet. Test sera in duplicates if possible.
- Heat inactivate the human sera for 30 min in a 56 °C water bath as in step 1.12.1. Place sera on ice post heat inactivation, add the virus diluent to sera to achieve a 1:10 pre-dilution.
- RDE treat and pre-dilute animal sera to 1:10 to use for controls per 1.12.2.
NOTE: Thawed and treated human and animal sera can be stored at 4 °C for no longer than 24 h. Sera should be stored frozen at -20 °C or colder if longer storage period is needed prior to the assay. - To test with one virus, add 100 µL 1:10 diluted sera to columns A1 to A10 (Figure 4). Add 50 µL of virus diluent to rows B through H, except columns 11 and 12 (Figure 4). Perform a 2-fold serial dilution from rows A through H, and discard the last 50 µL at row H (Figure 4).
NOTE: When multiple viruses are to be tested, sera can be diluted in titer tubes. The dilution of serum, for the purpose of determining the serum titer, in well A is 1:10, well B 1:20, well C 1:40, well D 1:80, well E 1:160, well F 1:320, well G 1:640, well H 1:1,280 (Figure 4). - For the virus control, add 50 µL of virus diluent to wells A12, B12, C12, and D12 (no sera). For the cell control, add 100 µL of virus diluent to wells E12, F12, G12, and H12 (no virus, no sera).
- For the control sera (for example, ferret sera controls), add 100 µL of diluted control sera to well A column 11 and add 50 µL of virus diluent to wells B11 - H11. Serial dilute down.
- Cover the plates, incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2 until ready for the virus addition.
- Day 1: Virus addition
- Dilute the virus to 100 TCID50/50 µL with virus diluent.
- Add 50 µL diluted virus to all wells, except for column 11 on the back titration (BT) plates and the cell control wells E12, F12, G12, and H12 on all plates (Figure 4). For those plates with control sera at column 11, add virus to column 11.
- Back titration (BT)
- Include a BT in column 11 of one set of duplicate plates (for example, plate 1A and 1B). Add 50 µL of virus diluent to all wells in column 11. Add 50 µL of the virus at 100 TCID50/50 µL to the first well (A11). Mix by pipetting up and down.
- Mix and transfer 50 µL to successive wells to perform 2-fold serial dilutions. Change the pipette tips between wells to avoid virus carry-over. Discard 50 µL from well H11.
- Add 50 µL of virus diluent to column 11 to bring the final volume to 100 µL. Tap the plates to mix.
- Incubate plates at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 1 h.
- Perform MDCK-SIAT1 cell addition on day 1 and ELISA on day 2 as described in steps 4.2 and 4.3 (also described in 5.3 and 5.4)
- Day 1: MDCK-SIAT1 cell addition
- Prepare the MDCK-SIAT1 cells as described in step 4.2. Add 100 µL MDCK-SIAT1 cells at 1.5 x 105 cells/mL to each well (1.5 x 104 cells/well). Incubate the plates at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 18 - 20 h.
- Day 2: ELISA
- After overnight incubation, on the second day, fix the cells with 80% cold acetone as described in step 4.3.
- Primary antibody addition
- Wash the plates 3 times with 300 µL wash buffer. Dilute the anti-influenza A NP monoclonal antibody (primary antibody) to the optimal concentration as determined by titration in antibody diluent (e.g. add 30 µL of primary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target dilution of 1:1000).
NOTE: 100 µL of primary antibody is required per well. ~10 mL is needed per plate. - Add 100 µL diluted primary antibody to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 1 h.
- Wash the plates 3 times with 300 µL wash buffer. Dilute the anti-influenza A NP monoclonal antibody (primary antibody) to the optimal concentration as determined by titration in antibody diluent (e.g. add 30 µL of primary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target dilution of 1:1000).
- Secondary antibody addition
- Wash plates 3 times with 300 µL wash buffer. Dilute the goat anti mouse IgG conjugated to HRP antibody (secondary antibody) to the target concentration in antibody diluent (e.g. Add 7.5 µL of secondary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target 1:4000.)
NOTE: 100 µL of secondary antibody is required per 96 well. ~10 mL is needed per plate. - Add 100 µL diluted secondary antibody to each well. Incubate at room temperature for 1 h.
- Wash plates 3 times with 300 µL wash buffer. Dilute the goat anti mouse IgG conjugated to HRP antibody (secondary antibody) to the target concentration in antibody diluent (e.g. Add 7.5 µL of secondary antibody to 30 mL of antibody diluent for a target 1:4000.)
- Substrate addition and plate reading
- Wash the plates 5 times with 300 µL wash buffer and tap on lint-free wipe.
- Add 100 µL of freshly prepared substrate to each well and incubate at room temperature until the virus control wells reach an OD490 = 0.8 - 3, with the cell control at a low background OD490 <0.2.
- Add 100 µL of the stop solution to all wells. Read the OD of wells at 490 nm using a microplate spectrophotometer.
- Data analysis
NOTE: The MN calculations are determined for each plate individually.- Determine the neutralizing antibody titer of each serum sample.
- Calculate the OD490 cut-off of 50% virus neutralization for each plate using the following equation:
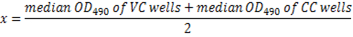
NOTE: Here x = 50% of the neutralization cut-off. The reciprocal serum dilution corresponding to the highest dilution with OD490 less than 50% of the cut-off (≥50% inhibition) is considered the neutralization antibody titer for that serum sample (Figure 5).
- Calculate the OD490 cut-off of 50% virus neutralization for each plate using the following equation:
- Check that the cell control wells have an OD490 <0.2 and the virus control wells have an OD490 = 0.8 - 3.
- Verify the virus infectivity in each assay (100x TCID50) by virus BT. The acceptable range of BT is 50, 100, or 200 TCID. If using the same cut-off as defined in step 4.4.2, the highest virus dilution in the BT column with OD above the cut-off should be in wells E11, F11, G11.
Note: The serum positive controls should give titers within 2-fold of the values obtained in the previous tests. The OD490 of the negative serum control should be similar to that observed for the virus control.
- Determine the neutralizing antibody titer of each serum sample.
Results
Determination of the infectivity of the virus stocks is the first step in the MN assay. Figure 2 illustrates the plate layout to determine the TCID50 of the virus stocks. For virus stocks with unknown infectivity, the virus can be titrated from multiple pre-dilutions, for example both 10-2 and 10-3, in order to capture the best titration curve to calculate infectivity of the virus. The virus amount used in the MN assay should ...
Discussion
The MN assay is one of the main assays used for influenza serology to detect antibody responses following influenza infection or vaccination. Titers generated from MN assays are often used as the primary outcome of many influenza seroepidemiology studies. MN assays are also widely used for sero-diagnosis, and the evaluation of vaccine immunogenicity. International inter-lab studies have been conducted to compare MN assays performed in multiple laboratories14.
In contras...
Disclosures
The authors report no conflict of interest. The findings and conclusions in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the funding agency.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Xiuhua Lu, Dr. Feng Liu, and Ms. Ashley Burroughs from the Influenza Division of the CDC for their critical review and assistance in preparation of this manuscript. We thank Dr. Adrian Reber from Influenza Division of the CDC for his assistance in preparing the graphics of Figure 3. Lastly, we thank Dr. M. Matrosovich, Marburg, Germany for providing the MDCK-SIAT1 cells.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high Glucose | Life Science | 11965 | A critical component of Sterile Cell Culture, Virus Propagation and Virus Diluent Media |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Hyclone | SH30070.03 | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Fraction V, Protase Free | Sigma-Aldrich | 3117332001 | |
| L-Glutamine | Life Science | 25030-081 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Life Science | 11360-070 | |
| Geneticin G-418 disulfate salt | Sigma-Aldrich | A1720-5G | |
| HEPES | Life Science | 15630-080 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Life Science | 15140-122 | |
| Acetone | VWR | 67-64-1 | Used at an 80% concentration |
| Phosphate-Citrate Buffer with Sodium Perborate | Sigma-Aldrich | SLBF2806V | |
| O-Phenylenediamine Dihydrochloride tablet | Sigma-Aldrich | SLBQ1086V | 1 tablet per 100ml of cell culture grade water |
| Sulfuric Acid | Fisher Scientific | A510-P500 | Used 0.5M final concentration |
| Ethanol, Denatured, 4L | VWR | EM-AX0422-3 | Used at an 70% concentration |
| Trypsin-EDTA | Life Science | 1748048 | |
| RDE II "Seiken" | Denka Seiken | 370013 | |
| Tween 20 | Sigma-Aldrich | P1379-500ml | |
| Anti-NP mouse monoclonal Ab | Millipore pool | MAB 8257 MAB 8258 | |
| Anti-mouse IgG HRP | KPL | 074-1802 | |
| 96-well flat-bottom plates | Thermo Scientific | 3455 | |
| Plate reader | Molecular Device | Spectromax 384 plus | |
| Cell Culture Flask 162 cm2/Vent Cap | Corning/VWR | 3151 |
References
- Reber, A., Katz, J. Immunological assessment of influenza vaccines and immune correlates of protection. Expert Rev of Vaccines. 12, 519-536 (2013).
- Li, C. K., Rappuoli, R., Xu, X. N. Correlates of protection against influenza infection in humans--on the path to a universal vaccine?. Curr Opin in Immunol. 25, 470-476 (2013).
- WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network. . Manual for the labratory diagnosis and virological surveillence of influenza. , (2011).
- Govorkova, E. A., Kodihalli, S., Alymova, I. V., Fanget, B., Webster, R. G. Growth and immunogenicity of influenza viruses cultivated in Vero or MDCK cells and in embryonated chicken eggs. Dev Biological Stand. 98, 39-51 (1999).
- Levine, M. Z., et al. Neutralizing Antibody Responses to Antigenically Drifted Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses among Children and Adolescents following 2014-2015 Inactivated and Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccination. Clin Vaccine Immunol : CVI. 23, 831-839 (2016).
- Lin, Y., et al. The characteristics and antigenic properties of recently emerged subclade 3C.3a and 3C.2a human influenza A(H3N2) viruses passaged in MDCK cells. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. , (2017).
- Lin, Y. P., et al. Neuraminidase receptor binding variants of human influenza A(H3N2) viruses resulting from substitution of aspartic acid 151 in the catalytic site: a role in virus attachment?. J of Virol. 84, 6769-6781 (2010).
- Skowronski, D. M., et al. Mutations acquired during cell culture isolation may affect antigenic characterisation of influenza A(H3N2) clade 3C.2a viruses. Euro Surveillance. 21, 30112 (2016).
- Matrosovich, M., Matrosovich, T., Carr, J., Roberts, N. A., Klenk, H. D. Overexpression of the alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase in MDCK cells increases influenza virus sensitivity to neuraminidase inhibitors. J of Virol. 77, 8418-8425 (2003).
- Oh, D. Y., Barr, I. G., Mosse, J. A., Laurie, K. L. MDCK-SIAT1 cells show improved isolation rates for recent human influenza viruses compared to conventional MDCK cells. J Clin Microbiol. 46, 2189-2194 (2008).
- US Department of Health and Human Services. . Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories. , (2009).
- Reed, H. M. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. The American Journal of Hygiene. 27, (1938).
- Laurie, K. L., et al. International Laboratory Comparison of Influenza Microneutralization Assays for A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2), and A(H5N1) Influenza Viruses by CONSISE. Clinical Vaccine Immunol : CVI. 22, 957-964 (2015).
- Lin, Y., Gu, Y., McCauley, J. W. Optimization of a Quantitative Micro-neutralization Assay. J Vis Exp : JoVE. , (2016).
- van Baalen, C. A., et al. ViroSpot microneutralization assay for antigenic characterization of human influenza viruses. Vaccine. 35, 46-52 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved