A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Radiotracer Administration for High Temporal Resolution Positron Emission Tomography of the Human Brain: Application to FDG-fPET
In This Article
Summary
This manuscript describes two radiotracer administration protocols for FDG-PET (constant infusion and bolus plus infusion) and compares them to bolus administration. Temporal resolutions of 16 s are achievable using these protocols.
Abstract
Functional positron emission tomography (fPET) provides a method to track molecular targets in the human brain. With a radioactively-labelled glucose analogue, 18F-fluordeoxyglucose (FDG-fPET), it is now possible to measure the dynamics of glucose metabolism with temporal resolutions approaching those of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). This direct measure of glucose uptake has enormous potential for understanding normal and abnormal brain function and probing the effects of metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Further, new advances in hybrid MR-PET hardware make it possible to capture fluctuations in glucose and blood oxygenation simultaneously using fMRI and FDG-fPET.
The temporal resolution and signal-to-noise of the FDG-fPET images is critically dependent upon the administration of the radiotracer. This work presents two alternative continuous infusion protocols and compares them to a traditional bolus approach. It presents a method for acquiring blood samples, time-locking PET, MRI, experimental stimulus, and administering the non-traditional tracer delivery. Using a visual stimulus, the protocol results show cortical maps of the glucose-response to external stimuli on an individual level with a temporal resolution of 16 s.
Introduction
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a powerful molecular imaging technique that is widely used in both clinical and research settings (see Heurling et al.1 for a recent comprehensive review). The molecular targets that can be imaged using PET are only limited by the availability of radiotracers, and numerous tracers have been developed to image neural metabolism receptors, proteins, and enzymes2,3. In neuroscience, one of the most used radiotracers is 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG-PET), which measures glucose uptake, usually interpreted as an index of cerebral glucose metabolism. The human brain requires a constant and reliable supply of glucose to satisfy its energy requirements4,5, and 70-80% of cerebral glucose metabolism is used by neurons during synaptic transmission6. Changes to cerebral glucose metabolism are thought to initiate and contribute to numerous conditions, including psychiatric, neurodegenerative, and ischemic conditions7,8,9. Furthermore, as FDG uptake is proportional to synaptic activity10,11,12, it is considered a more direct and less confounded index of neuronal activity compared to the more widely used blood oxygenation level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-fMRI) response. BOLD-fMRI is an indirect index of neural activity and measures changes in deoxygenated hemoglobin that occur following a cascade of neurovascular changes following neuronal activity.
Most FDG-PET studies of the human brain acquire static images of cerebral glucose uptake. The participant rests quietly for 10 min with their eyes open in a darkened room. The full radiotracer dose is administered as a bolus over a period of seconds, and the participant then rests for a further 30 min. Following the uptake period, participants are placed in the center of the PET scanner, and a PET image that reflects the cumulative FDG distribution over the course of the uptake and scanning periods is acquired. Thus, the neuronal activity indexed by the PET image represents the cumulative average of all cognitive activity over uptake and scan periods and is not specific to cognitive activity during the scan. This method has provided great insight into the cerebral metabolism of the brain and neuronal function. However, the temporal resolution is equal to the scan duration (often ~45 min, effectively yielding a static measurement of glucose uptake; this compares unfavourably to neuronal response during cognitive processes and common experiments in neuroimaging. Due to the limited temporal resolution, the method provides a non-specific index of glucose uptake (i.e., not locked to a task or cognitive process) and cannot provide measures of within-subject variability, which can lead to erroneous scientific conclusions due to Simpson's Paradox13. Simpson’s Paradox is a scenario, where brain-behavior relationships calculated across-subjects are not necessarily indicative of the same relationships tested within-subjects. Furthermore, recent attempts to apply functional connectivity measures to FDG-PET can only measure across-subjects connectivity. Thus, differences in connectivity can only be compared between groups and cannot be calculated for individual subjects. While it is debatable what exactly across-subject connectivity measures14, it is clear that measures calculated across-but not within-subjects cannot be used as a biomarker for disease states or used to examine the source of individual variation.
In the past five years, the development and wider accessibility of clinical-grade simultaneous MRI-PET scanners has sparked renewed research interest in FDG-PET imaging2 in cognitive neuroscience. With these developments, researchers have focused on improving the temporal resolution of FDG-PET to approach the standards of BOLD-fMRI (~0.5−2.5 s). Note that the spatial resolution of BOLD-fMRI can approach submillimeter resolutions but the spatial resolution of FDG-PET is fundamentally limited to around 0.54 mm full width at half maximum (FWHM) due to the positron range15. Dynamic FDG-PET acquisitions, which are often used clinically, use the bolus administration method and reconstruct the list-mode data into bins. The bolus dynamic FDG-PET method offers a temporal resolution of around 100 s (e.g., Tomasi et al.16). This is clearly much better compared to static FDG-PET imaging but is not comparable to BOLD-fMRI. Additionally, the window in which brain function may be examined is limited, because the blood plasma concentration of FDG diminishes soon after the bolus is administered.
To expand this experimental window, a handful of studies17,18,19,20,21 have adapted the radiotracer infusion method previously proposed by Carson22,23. In this method, sometimes described as 'functional FDG-PET' (FDG-fPET, analogous to BOLD-fMRI), the radiotracer is administered as a constant infusion over the course of the entire PET scan (~90 min). The goal of the infusion protocol is to maintain a constant plasma supply of FDG to track dynamic changes in glucose uptake across time. In a proof-of-concept study, Villien et al.21 used a constant infusion protocol and simultaneous MRI/FDG-fPET to show dynamic changes in glucose uptake in response to checkerboard stimulation with a temporal resolution of 60 s. Subsequent studies have used this method to show task-locked FDG-fPET (i.e., time-locked to an external stimulus19) and task-related FDG-fPET (i.e., not time-locked to an external stimulus17,18) glucose uptake. Using these methods, FDG-fPET temporal resolutions of 60 s have been obtained, which is a substantial improvement over bolus methods. Preliminary data show that the infusion method can provide temporal resolutions of 20−60 s19.
Despite the promising results from the constant infusion method, the plasma radioactivity curves of these studies show that the infusion method is not sufficient to reach a steady-state within the timeframe of a 90 min scan19,21. In addition to the constant infusion procedure, Carson22 also proposed a hybrid bolus/infusion procedure, where the goal is to quickly reach equilibrium at the beginning of the scan, and then sustain plasma radioactivity levels at equilibrium for the duration of the scan. Rischka et al.20 recently applied this technique using a 20% bolus plus 80% infusion. As expected, the arterial input function quickly rose above baseline levels and was sustained at a higher rate for a longer time, compared to results using an infusion-only procedure19,21.
This paper describes the acquisition protocols for acquiring high temporal resolution FDG-fPET scans using infusion-only and bolus/infusion radiotracer administration. These protocols have been developed for use in a simultaneous MRI-PET environment with a 90−95 min acquisition time19. In the protocol, blood samples are taken to quantify plasma serum radioactivity for subsequent quantification of PET images. While the protocol's focus is the application of infusion methods for functional neuroimaging using BOLD-fMRI/FDG-fPET, these methods can be applied to any FDG-fPET study regardless of whether simultaneous MRI, BOLD-fMRI, computed tomography (CT), or other neuroimages are acquired. Figure 1 shows the flowchart of procedures in this protocol.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
This protocol has been reviewed and approved by the Monash University Human Research Ethics Committee (approval number CF16/1108 - 2016000590) in accordance with the Australian National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research24. Procedures were developed under the guidance of an accredited Medical Physicist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, and clinical radiographer. Researchers should refer to their local experts and guidelines for the administration of ionizing radiation in humans.
1. Required equipment and personnel
- See the Table of Materials for the scanner room, radiochemistry lab, and general materials. A commercial supplier was used for the radiotracer.
- In the simultaneous MRI-PET environment, use four personnel: a radiographer (RG) to run the scan, a nuclear medicine technologist (NMT) to oversee the administration of the radiotracer and acquisition of blood samples, a laboratory assistant (LA) to spin blood, and a research assistant (RA) responsible to oversee the experimental design and stimulus presentation.
2. Preparation
- Tracer dose preparation by the NMT
- Calculate the infusion volume that will be administered over the course of the scan. In this protocol, the rate of infusion is 0.01 mL/s over 95 min. So, in a 95 min scan, participants receive 0.01 mL/s x 60 s x 95 min = 57 mL.
- Calculate the tracer dose that will be diluted into the administered saline solution. In this protocol, a total dose of 260 MBq is administered to the participant over 95 min. This dose was chosen to limit radiation exposure to 4.9 mSv, to keep within the 'low level risk' categorization according to Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA) guidelines for exposure of humans to ionizing radiation25. Decay correct 260 MBq from the mid-infusion point (47.5 min) back to T0. Using Equation 1, solve for A0
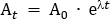
Where At is the radioactivity (MBq) at the mid-timepoint of the infusion, A0 is the initial radioactivity, and λ is the radioactive decay constant specific to the tracer. For FDG, the value of is λ ≈ 0.693/T1/2. T1/2 is the half-life of 18F (110 min).
NOTE: In this example, At = 260 MBq, λ = 0.693/110, and t = -47.5, so A0 = 350.942 MBq. - Calculate the required radiotracer dose for the 100 mL saline bag that will be used to administer the dose to the participant. The required radiotracer for the saline bag is diluted up to a total volume of 5 mL and drawn up in a 5 mL syringe. Therefore, for the 100 mL saline bag, the dilution factor is the volume of saline (100 mL) in addition to the 5 mL volume of the syringe with radiotracer. This total volume of 105 mL is divided by the infusion volume of 57 mL (i.e., 105 mL/57 mL = 1.842). So, the total radioactivity in a volume of 5 mL required for addition to the 100 mL bag is A0 x the dilution factor (i.e., 350.942 MBq x 1.842 = 646.44 MBq). Aseptically add the radiotracer to the saline bag.
NOTE: It is important to note that the calculated activity of 646.44 MBq that is added to the saline bag is the activity required at the commencement of the infusion. Generally, the doses for this protocol are prepared between 15 min to 1 h before administration. Therefore, it is important to factor in the decay of the radioisotope. Equation 1 in 2.1.2. can be used to account for this, where time (t) is the total number of minutes from the preparation of the dose to when the activity will be administered, At = 646.44 MBq, by solving for A0. - Prepare the priming dose. Withdraw 20 mL from the bag into a syringe and cap it. Calibrate this 20 mL syringe and label. The syringe is calibrated as a reference check to ensure that the radioactivity has evenly dispersed within the saline bag.
- Prepare the dose. Using a 50 mL syringe, withdraw 60 mL from the bag and cap with a red Combi stopper. This syringe is not calibrated, as the concentration of the radioactivity is known from the time it was added to the saline bag (step 2.1.3). Store both syringes in the radiochemistry lab until ready to scan.
NOTE: It is possible to draw a 60 mL volume in a 50 mL syringe, because Terumo syringes are marked to 20% above the labelled volume (i.e., a 50 mL syringe is marked to 60 mL). - Prepare the reference dose. Fill a 500 mL volumetric flask with approximately 480 mL of distilled water. Draw up 10 MBq of 18F-FDG into a syringe, decay-corrected to the scan start time (using Equation 1) and add it to the flask. Top the volume up to the 500 mL mark with more distilled water and mix thoroughly. Affix labels pre- and post-calibration for the syringe.
- Scanner room preparation by the NMT
- Once the participant is positioned in the scanner, there is very little room to manipulate or salvage the line for infusion or blood samples if blockage occurs. Prepare the scanner room to minimize the chance of line blockage.
- Ensure that all blood-collection equipment is within easy reach of the collection site. Place underpads at the end of the cannula and on any surface that will hold blood containers. Place bins for regular waste and biohazardous waste within easy reach of the blood collection site.
- Infusion pump preparation by the NMT
- Set up the infusion pump in the scanner room on the side that will be connected to the participant. Build lead bricks around the base of the pump and place the lead shield in front of the pump. Connect the tubing for the infusion pump that delivers the infusion to the participant and ensure the correct infusion rate has been entered. For this protocol, the rate is 0.01 mL/s.
- Prime the tubing before it is connected to the participant's cannula. Connect the 20 mL priming dose to the infusion pump. On the end of the tubing that will be connected to the participant, attach a three-way tap and an empty 20 mL syringe. Ensure that the tap is positioned to allow the 18F-FDG solution to flow from the priming dose through the tubing and collect only into the empty syringe.
- Preset the infusion pump to prime a volume of 15 mL. Select the Prime button on the pump and follow the prompts to prime the line.
- Attach the 50 mL dose syringe to the infusion pump in place of the priming dose. The 15 mL primed dose on the three-way tap can remain there until the participant is ready to be connected to the pump.
- Participant preparation by the NMT, RA, and RG
- Advise participants to fast for 6 h, and to consume only water (approximately two glasses), prior to the scan.
- Have the RA conduct the consent procedures and acquire additional measures (e.g., demographic surveys, cognitive batteries, etc.). Have the NMT and RG conduct the safety screens, the NMT review safety for PET scanning (e.g., exclusion for pregnancy, diabetes, chemotherapy or radiotherapy in the previous 8 weeks, and known allergies), and the RG review participant safety for MRI scanning (e.g., exclusion for pregnancy, medical or non-medical metallic implants, non-removable dental implants, claustrophobia).
- Cannulate the participant.
- Use two cannulas: one for dose administration and the other for blood sampling. The most appropriate cannula varies across participants, but the most suitable vein should be reserved for blood collection. A 22 G cannula is the preferred minimum size. Collect a 10 mL baseline blood sample while cannulating. Disconnect all saline flushes under pressure to maintain patency of the line.
- Test the participant's blood sugar level and other baseline blood measures (e.g., hemoglobin) from the baseline sample.
- Participant positioning in the scanner by the RG and NMT
- Have the RG position the participant in the scanner bore. For long scans, it is imperative to ensure comfort in order to reduce the risk of the participant dropping out and motion artefact due to discomfort. The participant should be covered with a disposable blanket to maintain a comfortable body temperature.
- Have the NMT flush the cannula to ensure it is patent with minimal resistance before connecting the infusion line. Once connected, the tubing can be lightly taped near the wrist. Instruct the participant to keep their arm straightened. Use supports such as foam or cushions for comfort. Have the NMT also check the cannula that will be used for plasma samples to ensure that it is able to withdraw blood with minimal resistance. It may be necessary to connect an extension tube primed with normal saline to make the cannula more accessible while the participant is in the scanner. If this is required, it should be checked for leakages.
- Once the subject is in the scanner bore, have the NMT check that they have suitable access to both cannulas.
- Have the NMT notify the RG and RA if there are any issues with the blood collection cannula, infusion cannula, or the infusion pump (e.g., occlusion, battery, extravasation) at any time during the scan.
3. Scan the participant
- Starting the scan with the NMT, RG, and RA
- At the start of the scan, situate the NMT in the scanner room to monitor the infusion equipment. Ensure the NMT is wearing hearing protection and using the barrier shield to minimize radiation exposure from the dose where possible.
- As the RG performs the localizer scan to ensure that the participant is in the correct position, check the details for the PET acquisition (e.g., scan duration, list-mode data collection, correct isotope).
- Design the protocol so that the PET acquisition will commence with the first MRI sequence. The RG prepares and starts the MRI sequence. The start time of the 95 min PET acquisition is time-locked to the start of the MRI sequence. If required, the NMT should deliver the bolus at the time of PET acquisition (Figure 1).
- Start the infusion pump. The RG should signal the NMT (e.g., via a thumbs-up sign) to start the pump 30 s after the start of the PET acquisition. This protocol starts the infusion pump 30 s after the scan start time to provide a safety buffer in case of scan failure. This also ensures that the first image taken during the PET scan indexes the brain prior to radiotracer administration for complete time activity curve data collection. Have the NMT observe the pump to ensure it has started to infuse the 18F-FDG and that there is no immediate occlusion of the line.
- Have the RA initiate any external stimulus at the agreed upon time (i.e., at the start of a functional run/experimental block) and calculate the times for blood samples. An example record form is shown in Supplement 1. Have the RA calculate the predicted time of each blood sample and provide copies to the NMT and lab assistant (LA). Have the RA ensure that the NMT takes the blood samples at approximately the correct time, and monitors equipment (e.g., infusion pump, stimulus) for any signs of errors.
- Take blood samples at regular time intervals
- Have the NMT and RA take one sample every 10 min. There are usually 10 samples in total, not including the baseline sample.
- If acquiring MRI scans simultaneously with PET scans, have the NMT wear hearing protection when entering the scanner room.
- Have the NMT wear gloves and swab the tip of the cannula clean. While the cannula site dries, open a 5 mL and a 10 mL syringe, vacutainer, and a 10 mL saline flush.
- Using the 5 mL syringe, withdraw 4-5 mL of fresh blood and discard the syringe in the biohazard waste.
- Using the 10 mL syringe, withdraw up to 10 mL of blood. The volume may be limited by how easily the blood can be withdrawn. It is important to minimize any resistance subsequently causing damage to the red blood cells that can hemolyze. At the midcollection point, have the NMT signal to the RA, who will mark this time on the record form (Supplement 1) as the 'actual' time of sample.
- Connect the 10 mL syringe to the vacutainer and then deposit the blood into the relevant blood tube.
- Quickly flush the cannula with 10 mL of saline, disconnected under pressure, to minimize any chance of line clotting.
- Immediately take the blood sample to the radiochemistry lab for analysis.
- Spinning the blood by the LA
- Have the LA get all the equipment ready (Table 1) and be wear gloves. Have three racks set out for the samples: one for blood tubes, one for pipetting the sample, and one for filled pipetted samples (pre- and post-counting).
- Have the LA regularly change gloves throughout the procedure, especially when handling the counting tube. If the LA has any radioactive plasma contamination on their gloves, it can be transferred to the counting tube and spuriously increase the number of recorded counts of the sample.
- The blood sample can be placed in the centrifuge as the availability of staffing resources permits, because the time that the blood sample was taken, and the time it was counted was noted. Spin all samples at a relative centrifugal force of 724 x g. The centrifuge settings used for this protocol are 2,000 rpm for 5 min with the acceleration and deceleration curves set to eight.
- Once the sample has been spun, place the tube in the pipetting rack. Remove the tube cap to not disturb sample separation. Place a labelled counting tube in the rack. The label should correspond to the blood tube.
- Ensure the tip is securely fastened to the pipette. Have a tissue ready for any drips. Steadily pipette 1,000 µL of plasma from the blood tube, transfer to the counting tube, and replace the lids on the counting tube and blood tube.
- Place the counting tube into the well counter and count for 4 min. Record the counting start time on the record sheet ('measurement time') for every sample. This is required for subsequent corrections to the PET acquisition start time. At later time points during the scan, have the LA perform each step in rapid succession to avoid a backlog of samples.
- Dispose of any blood product waste in biohazard bags.
- Have the LA get all the equipment ready (Table 1) and be wear gloves. Have three racks set out for the samples: one for blood tubes, one for pipetting the sample, and one for filled pipetted samples (pre- and post-counting).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Study-specific methods
Here, study-specific details for the representative results are reported. These details are not critical to the procedure and will vary across studies.
Participants and task design
Participants (n = 3, Table 2) underwent a simultaneous BOLD-fMRI/FDG-fPET study. As this manuscript focuses on the PET acquisition protocol, MRI re...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
FDG-PET is a powerful imaging technology that measures glucose uptake, an index of cerebral glucose metabolism. To date, most neuroscience studies using FDG-PET use a traditional bolus administration approach, with a static image resolution that represents the integral of all metabolic activity over the course of the scan2. This manuscript describes two alternative radiotracer administration protocols: the infusion-only (e.g., Villien et al., Jamadar et al.19,
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding source was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Acknowledgements
Jamadar is supported by an Australian Council for Research (ARC) Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DECRA DE150100406). Jamadar, Ward, and Egan are supported by the ARC Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function (CE114100007). Chen and Li are supported by funding from the Reignwood Cultural Foundation.
Jamadar, Ward, Carey, and McIntyre designed the protocol. Carey, McIntyre, Sasan, and Fallon collected the data. Jamadar, Ward, Parkes, and Sasan analyzed the data. Jamadar, Ward, Carey, and McIntyre wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved the final version.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Blood Collection Equipment | |||
| --12-15 vacutainers | Becton Dickinson, NJ USA | 364880 | Remain in sterile packaging until required to put blood in tube |
| --12-15 10mL LH blood collecting tubes | Becton Dickinson | 367526 | Marked with the sample number (e.g., S1, S2…) and subsequently marked with the sample time (e.g., time 0 + x min [T0+x]) |
| --2-15 10mL Terumo syringe | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS+10L | These are drawn up on the day of the study and capped with the ampoule that contained the saline |
| -- pre-drawn 0.9% saline flushes | Pfizer, NY, USA | 61039117 | |
| --12-15 5mL Terumo syringes | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS+05S | Remain in sterile packaging until ready to withdraw a blood sample |
| Safety & Waste Equipment | All objects arranged on a plastic chair inside the scanner room on the same side as the arm from which the blood samples will be taken. Biohazard and non-biohazard waste bags to be used. Gloves and waste bags to be easily accessible when preparing the radioactivity in the dispensing area and when pipetting the plasma samples. Biohazard and non-biohazard waste bags to be used. All waste generated is checked with the Geiger counter to ensure that radioactive contaminated waste is stored until it is safe to be disposed of according to Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (APRANSA) guidelines for Radiation protection series No.6 (2017). | ||
| -- Gloves | Westlab, VIC, Australia | 663-219 | |
| -- waste bags | Austar Packaging, VIC, Australia | YIW6090 | |
| --cello underpads ‘blueys’ Underpads 5 Ply | Halyard Health, NSW, Australia | 2765A | |
| --Blue Sharpie pen | Sharpie, TN, USA | S30063 | |
| Dose Syringes | Remain in sterile packaging until ready for use. All syringes used in this facility have an additional 20% volume capacity above the stated volume on the packaging. This is important for the 50mL syringe where the total capacity of 60mL is used | ||
| --5mL | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS+05S | |
| -- 20mL | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS+20L | |
| --50mL | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS*50LE | |
| --1 Terumo 18-gauge needle | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | NN+1838R | Remain in sterile packaging until ready to inject [18F]FDG into the saline bag |
| --100mL 0.9% saline bag | Baxter Pharmaceutical, IL, USA | AHB1307 | Remain in sterile packaging until ready to inject [18F]FDG |
| Radiochemistry Lab Supplies | |||
| --Heraeus Megafuge 16 centrifuge; Rotor Bioshield 720 | ThermoScientific MA, USA | 75004230 | Relative Centrifugal Force = 724 Our settings are 2000RPM for 5mins. Acceleration and deceleration curves set to 8 |
| --Single well counter | Laboratory Technologies, Inc. IL, USA | 630-365-1000 | Complete daily quality control (includes background count) and protocol set to 18F and 4mins. Cross calibration is performed between the well counter, dose calibrator and scanner on a bi-monthly basis. |
| --Pipette | ISG Xacto, Vienna, Austria | LI10434 | We use a 100-1000 μL set to 1000μL. It is calibrated annually. |
| --12-15 plasma counting tubes | Techno PLAS; SA Australia | P10316SU | Marked in the same manner as the LH blood tubes |
| --12-15 pipette tips | Expell Capp, Denmark | 5130140-1 | |
| --3 test tube racks | Generic | Checked with a Geiger counter to ensure there is no radiation contamination on them | |
| --500mL volumetric flask and distilled water | Generic | Need approximately 500mL of distilled water to prepare the reference for gamma counting | |
| --Synchronised clocks in scanner room, console and radiochemistry lab | Generic | Synchronisation checks are routinely completed in the facility on a weekly basis | |
| --Haemoglobin Monitor | EKF Diagnostic Cardiff, UK Haemo Control. | 3000-0810-6801 | Manufacturer recommended quality control performed before testing on participant’s blood sample. |
| --Glucometre | Roche Accu-Chek | 6870252001 | Accu-Chek Performa is used to measure participant blood sugar levels in mmol/L. Quality control is performed daily using high and low concentration solution control test. |
| Cannulating Equipment | Check expiry dates and train NMT to prepare aseptically for cannulation. | ||
| --Regulation tourniquet | CBC Classic Kimetec GmBH | K5020 | |
| --20, 22 and 24 gauge cannulas | Braun, Melsungen Germany | 4251644-03; 4251628-03; 4251601-03 | |
| --tegaderm dressings | 3M, MN USA | 1624W | |
| --alcohol and chlorhexidine swabs | Reynard Health Supplies, NSW Australia | RHS408 | |
| --0.9% saline 10mL ampoules; for flushes | Pfizer, NY, USA | 61039117 | |
| --10mL syringes | Terumo Tokyo, Japan | SS+10L | |
| --3-way tap | Becton Dickinson Connecta | 394600 | |
| --IV bung | Safsite Braun PA USA | 415068 | |
| --Optional extension tube, microbore extension set | M Devices, Denmark | IV054000 | |
| Scanner Room Equipment | |||
| --Siemens Biograph 3T mMR | Siemens, Erlangen, Germany | ||
| --Portable lead barrier shield | Gammasonics | Custom-built | MR-conditional lead barrier shield. Positioned at the 2000 Gauss line with the castors locked to provide additional shielding of the radioactivity connected to the infusion pump. |
| --Infusion pump BodyGuard 323 MR-conditional infusion pump | Caesarea Medical Electronics | 300-040XP | MR-compatible. This model is cleared for use on 1.5 and 3T scanners at 2000 Gauss with castors locked. |
| --Infusion pump tubing | Caesarea Medical Electronics | 100-163X2YNKS | Tubing is administration set with an anti-siphon valve and male luer lock (REF 100-163X2YNKS). |
| --Lead bricks | Custom built | Tested for ferromagnetic translational force | |
| Other Equipment | |||
| --Syringe shields | Biodex, NY USA | Custom-built | There is a 5mL tungsten syringe shield that is MR-safe, as well as a 50mL lead shield that has been tested for ferromagnetic attraction prior to use in the MR-PET scanner. It is used to transport the radioactive dose from the radiochemistry lab into the scanner to minimise radiation exposure to the NMT. |
| --Geiger counter Model 26-1 Integrated Frisker | Ludlum Measurements, Inc. TX USA | 48-4007 | This is calibrated annually and used to monitor potential contamination and waste. It is not taken into the MR-PET scanner. |
References
- Heurling, K., et al. Quantitative positron emission tomography in brain research. Brain Research. 1670, 220-234 (2017).
- Chen, Z., et al. From simultaneous to synergistic MR-PET brain imaging: A review of hybrid MR-PET imaging methodologies. Human Brain Mapping. 39 (12), 5126-5144 (2018).
- Jones, T., Rabiner, E. A. The development, past achievements, and future directions of brain PET. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 32 (7), 1426-1454 (2012).
- Kety, S. S. Metabolism of the nervous system. , Elsevier. 221-237 (1957).
- Sokoloff, L. The metabolism of the central nervous system in vivo. Handbook of Physiology, section I, neurophysiology. 3, 1843-1864 (1960).
- Harris, J. J., Jolivet, R., Attwell, D. Synaptic energy use and supply. Neuron. 75 (5), 762-777 (2012).
- Mosconi, L., et al. FDG-PET changes in brain glucose metabolism from normal cognition to pathologically verified Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 36 (5), 811-822 (2009).
- Pagano, G., Niccolini, F., Politis, M. Current status of PET imaging in Huntington's disease. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 43 (6), 1171-1182 (2016).
- Petit-Taboue, M., Landeau, B., Desson, J., Desgranges, B., Baron, J. Effects of healthy aging on the regional cerebral metabolic rate of glucose assessed with statistical parametric mapping. Neuroimage. 7 (3), 176-184 (1998).
- Chugani, H. T., Phelps, M. E., Mazziotta, J. C. Positron emission tomography study of human brain functional development. Annals of Neurology. 22 (4), 487-497 (1987).
- Phelps, M. E., Mazziotta, J. C. Positron emission tomography: human brain function and biochemistry. Science. 228 (4701), 799-809 (1985).
- Zimmer, E. R., et al. [18 F] FDG PET signal is driven by astroglial glutamate transport. Nature Neuroscience. 20 (3), 393(2017).
- Roberts, R. P., Hach, S., Tippett, L. J., Addis, D. R. The Simpson's paradox and fMRI: Similarities and differences between functional connectivity measures derived from within-subject and across-subject correlations. Neuroimage. 135, 1-15 (2016).
- Horwitz, B. The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage. 19 (2), 466-470 (2003).
- Moses, W. W. Fundamental limits of spatial resolution in PET. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 648, S236-S240 (2011).
- Tomasi, D. G., et al. Dynamic brain glucose metabolism identifies anti-correlated cortical-cerebellar networks at rest. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 37 (12), 3659-3670 (2017).
- Hahn, A., et al. Quantification of task specific glucose metabolism with constant infusion of 18F-FDG. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 57 (12), 1933-1940 (2016).
- Hahn, A., et al. Task-relevant brain networks identified with simultaneous PET/MR imaging of metabolism and connectivity. Brain Structure and Function. 223 (3), 1369-1378 (2018).
- Jamadar, S. D., et al. Simultaneous task-based BOLD-fMRI and [18-F] FDG functional PET for measurement of neuronal metabolism in the human visual cortex. Neuroimage. 189, 258-266 (2019).
- Rischka, L., et al. Reduced task durations in functional PET imaging with [18F] FDG approaching that of functional MRI. Neuroimage. 181, 323-330 (2018).
- Villien, M., et al. Dynamic functional imaging of brain glucose utilization using fPET-FDG. Neuroimage. 100, 192-199 (2014).
- Carson, R. E. PET physiological measurements using constant infusion. Nuclear Medicine and Biology. 27 (7), 657-660 (2000).
- Carson, R. E., et al. Comparison of bolus and infusion methods for receptor quantitation: application to [18F] cyclofoxy and positron emission tomography. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 13 (1), 24-42 (1993).
- National Health and Medical Research Council. National statement on ethical conduct in human research. , (2007).
- Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. Code of practice for the exposure of humans to ionizing radiation for research purposes. , (2005).
- Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., Smith, S. M. FSL. Neuroimage. 62 (2), 782-790 (2012).
- Tustison, N. J., et al. N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 29 (6), 1310(2010).
- Avants, B., Klein, A., Tustison, N., Woo, J., Gee, J. C. 16th Annual Meeting for the Organization of Human Brain Mapping. , (2010).
- Avants, B. B., Epstein, C. L., Grossman, M., Gee, J. C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis. 12 (1), 26-41 (2008).
- Klein, A., et al. Mindboggling morphometry of human brains. PLoS Computational Biology. 13 (2), e1005350(2017).
- Tustison, N. J., et al. Large-scale evaluation of ANTs and FreeSurfer cortical thickness measurements. Neuroimage. 99, 166-179 (2014).
- Avants, B. B., et al. A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage. 54 (3), 2033-2044 (2011).
- Burgos, N., et al. Attenuation correction synthesis for hybrid PET-MR scanners: application to brain studies. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 33 (12), 2332-2341 (2014).
- Panin, V. Y., Kehren, F., Michel, C., Casey, M. Fully 3-D PET reconstruction with system matrix derived from point source measurements. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 25 (7), 907-921 (2006).
- Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage. 17 (2), 825-841 (2002).
- Bludau, S., et al. Cytoarchitecture, probability maps and functions of the human frontal pole. Neuroimage. 93, 260-275 (2014).
- Amunts, K., Malikovic, A., Mohlberg, H., Schormann, T., Zilles, K. Brodmann's areas 17 and 18 brought into stereotaxic space-where and how variable? Neuroimage. 11 (1), 66-84 (2000).
- Malikovic, A., et al. Cytoarchitectonic analysis of the human extrastriate cortex in the region of V5/MT+: a probabilistic, stereotaxic map of area hOc5. Cerebral Cortex. 17 (3), 562-574 (2006).
- Wilms, M., et al. Human V5/MT+: comparison of functional and cytoarchitectonic data. Anatomy and Embryology. 210 (5-6), 485-495 (2005).
- Eickhoff, S. B., Heim, S., Zilles, K., Amunts, K. Testing anatomically specified hypotheses in functional imaging using cytoarchitectonic maps. Neuroimage. 32 (2), 570-582 (2006).
- Eickhoff, S. B., et al. Assignment of functional activations to probabilistic cytoarchitectonic areas revisited. Neuroimage. 36 (3), 511-521 (2007).
- Eickhoff, S. B., et al. A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage. 25 (4), 1325-1335 (2005).
- Everett, B. A., et al. Safety of radial arterial catheterization in PET research subjects. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 50 (10), 1742-1742 (2009).
- Takagi, S., et al. Quantitative PET cerebral glucose metabolism estimates using a single non-arterialized venous-blood sample. Annals of Nuclear Medicine. 18 (4), 297-302 (2004).
- Zanotti-Fregonara, P., Chen, K., Liow, J. S., Fujita, M., Innis, R. B. Image-derived input function for brain PET studies: many challenges and few opportunities. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 31 (10), 1986-1998 (2011).
- O'Loughlin, S., Currie, G. M., Trifonovic, M., Kiat, H. Ambient temperature and cardiac accumulation of 18F-FDG. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology. 42 (3), 188-193 (2014).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved