A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification (TRAP) to Investigate Arabidopsis thaliana Root Development at a Cell Type-Specific Scale
In This Article
Summary
Translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) offers the possibility to dissect developmental programs with minimal processing of organs and tissues. The protocol yields high-quality RNA from cells targeted with a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled ribosomal subunit. Downstream analysis tools, such as qRT-PCR or RNA-seq, reveal tissue and cell type-specific expression profiles.
Abstract
In this article, we give hands-on instructions to obtain translatome data from different Arabidopsis thaliana root cell types via the translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) method and consecutive optimized low-input library preparation.
As starting material, we employ plant lines that express GFP-tagged ribosomal protein RPL18 in a cell type-specific manner by use of adequate promoters. Prior to immunopurification and RNA extraction, the tissue is snap frozen, which preserves tissue integrity and simultaneously allows execution of time series studies with high temporal resolution. Notably, cell wall structures remain intact, which is a major drawback in alternative procedures such as fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based approaches that rely on tissue protoplasting to isolate distinct cell populations. Additionally, no tissue fixation is necessary as in laser capture microdissection-based techniques, which allows high-quality RNA to be obtained.
However, sampling from subpopulations of cells and only isolating polysome-associated RNA severely limits RNA yields. It is, therefore, necessary to apply sufficiently sensitive library preparation methods for successful data acquisition by RNA-seq.
TRAP offers an ideal tool for plant research as many developmental processes involve cell wall-related and mechanical signaling pathways. The use of promoters to target specific cell populations is bridging the gap between organ and single-cell level that in turn suffer from little resolution or very high costs. Here, we apply TRAP to study cell-cell communication in lateral root formation.
Introduction
Driven by the increasing application of next-generation sequencing techniques, spatial resolution in developmental biology could be augmented. Contemporary studies aim at dissecting tissues down to specialized cell types, if not single-cell level1,2,3,4. To this end, a plethora of different methods has been devised over the last fifty years (see Figure 1A)5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15.
Many tools in plant science have been adaptations of techniques that were pioneered in animal research. This is not the case for the method we are introducing in detail here. In 2005, equipped with a strong background in protein translation, the Bailey-Serres Lab set out to engineer ribosomal proteins for subsequent affinity purification16. Thus, they could avoid time-consuming and labor-intensive polysome profiling, which is based on ultracentrifugation with a sucrose gradient and was used to assess translating ribosomes since the 1960s17,18. The method has since been referred to as translational ribosome affinity purification (TRAP)16. After successful translatome studies in plants, Heiman et al. adapted TRAP for animals19 and others extended its application to yeast20, Drosophila21, Xenopus22 and zebrafish23,24.
Although genetic modification of the model system is a prerequisite for TRAP, which limits its application to species amenable to genetic transformation, one can simultaneously harness this objection to target subsets of cells that are of special interest and otherwise extremely difficult to isolate from the intact tissue/organ25 (e.g., highly branched dendritic cells in a mouse brain or fungal hyphae in infected plant tissue). In plants, all cells are held in place via cell walls that form the basis of the hydrostatic skeleton26. To free a plant cell from this matrix, scientists have either physically cut the cell out of its surrounding tissue through laser capture microdissection (LCM)27 or performed enzymatic digestion of the cell walls28. Among the latter cells, so-called protoplasts, the population of interest is fluorescently labeled and can be separated via fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)7. LCM usually requires a sample to be fixed and embedded in wax, which ultimately deteriorates the quality of its RNA29. FACS-based methods yield high-quality RNA, but the process of protoplasting itself introduces differences in gene expression30 and tissues with modified and thick secondary cell walls are notoriously difficult to treat. Moreover, many developmental processes in plants are assumed to rely on mechanically transmitted signals and therefore the integrity of the cell wall is of paramount importance31. Two methods, which use a shortcut to circumvent cell isolation by operating on the level of nucleii, are fluorescence-activated nuclear sorting (FANS) and isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types (INTACT). As in TRAP, they use cell type-specific promoters to mark nuclei, that subsequently get enriched via sorting or pull down, respectively8,15. A major challenge for all these approaches is to get sufficient RNA material from subsets of cells in a tissue. As TRAP captures only a fraction of the cellular RNAs, sample collection is a considerable bottleneck. Therefore, especially sensitive library preparation protocols are needed to produce high-quality data from low input amounts.
Since its establishment, TRAP has been either used in combination with DNA microarrays or, as sequencing costs dropped significantly in recent years, RNA-seq10,32,33. A multitude of research questions has already been elucidated as reviewed in Sablok et al.34. We are convinced that more reports will follow in coming years as the technique is very versatile when combining different promoters to target specific cell types. Eventually, this will be done even in an inducible way, and may be combined with probing the plant's reaction to many biotic and abiotic stress factors. Additionally, where stable transgenic lines are not available, hairy root expression systems have also been successfully used to perform TRAP in tomato and medicago35,36.
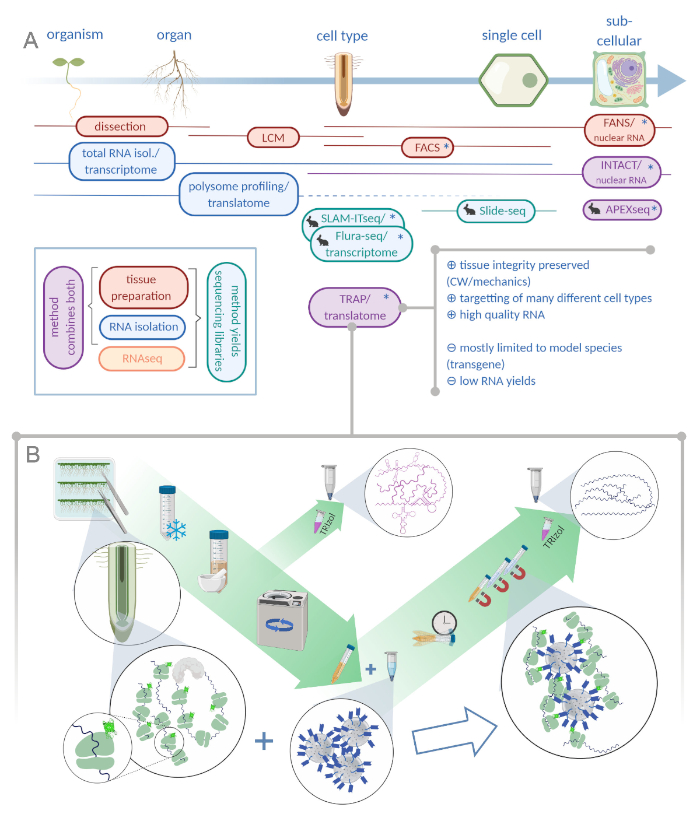
Figure 1: Translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) complements the "omics" analysis portfolio. A. Increasing levels of analytical precision, down to single-cell or even subcellular resolution can be achieved by a plethora of methods or combinations thereof. The scheme gives an overview of currently available tools in the plant and animal field. Tissue collection at cellular resolution can be achieved by protocols like LCM or FACS, which are then coupled to standard transcriptome or polysome profiling/translatome analysis. TRAP and INTACT integrate both tissue capture and RNA isolation as they are based on epitope-tagging. However, INTACT samples only cell nuclei and constitutes, therefore, a special case of transcriptome analysis. A small rabbit icon marks newly developed methods in the animal field: While SLAM-ITseq and Flura-seq rely on metabolic targetting of nascent RNAs with modified uracil bases in cells expressing the permissive enzyme, Slide-seq makes use of a coated glass slide with DNA barcodes that provide positional information in the cellular range. A proximity-labeling approach is followed in APEX-seq to sample RNAs in specific subcellular compartments. Notably, increased resolution often requires the generation of transgenic material (asterisks) and these methods are thus predominantly used for model species. TRAP is especially suited for plant science studies involving cell wall (CW) or mechanic signaling as well as cell species that are difficult to release from their CW matrix. B. Detailed wet-lab steps of the TRAP procedure: Seedlings expressing GFP-tagged ribosomal protein in distinct cell types (e.g. root endodermis) are grown on Petri dishes for seven days and root material harvested by snap freezing. A total RNA control sample is collected from the homogenized crude extract before pelleting the debris via centrifugation. Magnetic anti-GFP beads are added to the cleared extract to perform immunoprecipitation. After incubation and three wash steps, the polysome-associated RNA (TRAP/polysome RNA) is directly obtained via phenol-chloroform extraction. LCM: laser capture microdissection, FACS/FANS: fluorescence-activated cell/nuclear sorting, APEX-seq: method based on engineered ascorbate peroxidase, INTACT: isolation of nuclei tagged in specific cell types, SLAM-ITseq: thiol(SH)-linked alkylation for the metabolic sequencing of RNA in tissue, Flura-seq: fluorouracil-labeled RNA sequencing (Created with Biorender.com) Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The goal of this article is to supply a detailed description of the TRAP method, to highlight critical steps and to provide guidance for a possible library preparation method.
A generic TRAP experiment will essentially consist of the following steps (see also Figure 1B): (1) Preparation of plant material including cloning of ribosome-tagging construct, transgenic line production and selection, growing and bulking up of seeds, sterilization and plating, and stress application/treatment (optional) and tissue harvesting; (2) immunopurification including tissue homogenization and clearing of the crude extract, bead wash and immunopurification, and wash steps; (3) RNA extraction and quality assessment; and (4) library preparation.
The Arabidopsis root has been a model system to study plant development ever since its introduction as a model plant37,38. Here, the application of TRAP is showcased in the context of plant lateral root development. In plants, the buildup of the entire root system relies on the execution of this program and is therefore very important for the survival of the organism39. In Arabidopsis, lateral roots originate from pericycle tissue that resides next to xylem vessels and therefore is termed xylem pole pericycle (XPP; see Figure 2C)40. Some XPP cells, which are located deep inside the root, acquire a founder cell identity and, upon a local hormonal trigger, start to proliferate by swelling and dividing anticlinally41. However, due to the presence of a rigid cell wall matrix, this process exerts mechanical stress on the surrounding tissues. In particular, the overlying endodermis is affected, as it is in the way of the lateral root growth axis42,43,44. Indeed, the newly forming primordium will have to grow through the overlying endodermis cell (Figure 2C2) whereas cortex and epidermis cells are just pushed aside for the primordium to finally emerge45,46. Recent work in our lab has shown that the endodermis is actively contributing to accommodate the proliferation in the pericycle. Targeted blocking of endodermal hormonal signaling is sufficient to inhibit even the very first division in the XPP cells47. Hence, pericycle-endodermis communication constitutes a very early checkpoint for lateral root development in Arabidopsis. It is, however, not known how this crosstalk is performed. To unravel this mystery, we chose the TRAP-seq approach to target XPP and endodermal cells. To enrich for cells in the lateral root program, we mimicked the hormonal trigger by exogenously applying an auxin analog (1-naphthaleneacetic acid, NAA)48, which at the same time allowed to temporally resolve the initial phase of lateral root formation.
Protocol
1. Cloning of transgene, transgenic line production and selection
- Clone the promoter of choice in the appropriate entry vector. Use a recombination-based cloning method (Table of Materials) and recombine the promoters in pDONRP4-P1r. Clone RPL18 (with affinity tag or fluorescent protein of choice) using recombination-based cloning in pDONRP1-P249.
- Combine the entry vector containing RPL18 with the promoter-containing entry vector in a two fragment recombination reaction into the appropriate destination vector with FAST-red selection cassette50 to facilitate direct selection of transgenic seeds.
- Verify the recombined vector by sequencing and transform it into suitable, competent agrobacteria. Flower dip Arabidopsis plants and after 3-4 weeks harvest and select T1 seeds51.
- Use microscopy to identify well-expressing lines and verify expression patterns according to the reported promoter activity in multiple independent lines. Select lines showing a representative expression pattern with a single T-DNA insertion. This might help to minimize silencing and will be advantageous for genetic crosses.
- Select T3 offspring that is homozygous for the marker gene.
2. Propagation and sterilization
- Cell type-specific TRAP isolates RNA from a limited number of target cells per root. To generate the needed starting material, propagate homozygous lines. To this end, use standard growth conditions with a special focus on fungal growth control.
NOTE: If single insertion lines cannot be obtained, grow batches in large populations over few generations to avoid T-DNA-induced transgenerational silencing. - Sterilize large quantities of Arabidopsis seeds with one round of chlorine gas and one round of 70% EtOH.
- Spread seeds evenly on 12 cm x 12 cm square Petri dishes (less than 0.3 mL seeds/plate) and stack them into a desiccator or other suitable container. Avoid clump or heap formation as the seeds need to be accessible to the gas. Perform gas sterilization overnight with bleach and HCl volumes as reported52: 100 mL of bleach (13%) with 6 mL of conc. HCl in a 60 L desiccator. Defumigate for at least 1 h before collecting the seeds in a sterile container.
CAUTION: 37% HCl is highly corrosive and requires careful handling. Chlorine gas is toxic, use a fume hood. - Take 0.1 mL of dry, gas-sterilized seeds per plate and mix them with sterilization solution (70% EtOH, 0,01% Tween) at room temperature. Incubate for 20 min, decant EtOH and wash the seeds 3-4 times with sterile H2O.
- Transfer the soaked seeds into 50 mL tubes and dilute with sterile 0.1% agar to obtain 1 mL of imbibed seed slurry per plate (0.1 mL seed/1 mL slurry).
NOTE: Due to transgene integration events, plant lines can be susceptible to different sterilization techniques; especially EtOH incubation time was found to be critical. In our hands, the dual sterilization steps were necessary to avoid fungal contamination during the experiments. This is especially important when performing time series as contamination of a single time point hampers the whole experiment. It might well be that dual sterilization is not always needed, depending on local growing conditions.
- Spread seeds evenly on 12 cm x 12 cm square Petri dishes (less than 0.3 mL seeds/plate) and stack them into a desiccator or other suitable container. Avoid clump or heap formation as the seeds need to be accessible to the gas. Perform gas sterilization overnight with bleach and HCl volumes as reported52: 100 mL of bleach (13%) with 6 mL of conc. HCl in a 60 L desiccator. Defumigate for at least 1 h before collecting the seeds in a sterile container.
3. Plating
- Prepare these steps in advance. Pour ½ MS plates (pH 5.8) with 1% agar in the quantities needed for the experiment (20-30 per sample/time point). Cut 1 mL pipette tips to enlarge the tip diameter to ca. 3-4 mm with a razor blade. Autoclave the tips. Create a template holder for plating three rows of seeds per plate with square Petri dish lids. Prepare a laminar flow hood to provide a sterile work environment and label the plates to be processed.
NOTE: If many plates are processed at the same time, colored labels can speed up the labeling. - Place empty agar plates into the template holder and distribute 1 mL of imbibed seeds evenly onto three rows. Place the processed plates in stacks into the laminar flow until the seeds are dry (i.e., stick to the agar surface). Do not leave the plates longer as the agar will dry out as well.
- Once the seeds are sufficiently dry, close the lids and seal each plate with micropore tape. Stratify the seeds for two days at 4 °C in the dark and afterwards place them into a growth chamber.
4. Tissue treatment (optional)
NOTE: In this protocol, we outline the exogenous treatment of Arabidopsis roots with the synthetic auxin variant NAA. Depending on the experimental question at hand, this part needs to be adjusted or can be omitted entirely.
- Prepare strips of tissue paper of 1.5 - 2 cm in height and 10 cm in length. Extended incubation times require the tissue to be autoclaved prior to use.
- Remove the micropore tape from all plates that have to undergo the hormone treatment. Dilute 1 mL of 10 mM NAA (dissolved in DMSO) in 1 L of liquid, autoclaved ½ MS solution (pH 5.8) and soak the tissue paper in the solution (10 µM NAA).
- Use tweezers to apply a strip of tissue paper onto each row of roots. Gently use fingers to remove air bubbles. Empty excess liquid from the plate, close the lid and label the plate with the time. For extended incubation times, place the plates back into the growth chamber.
5. Harvesting
- Retrieve plates for each biological replicate/time point/treatment. Collect liquid nitrogen in a clean Dewar vessel and label tubes (15 or 50 mL) for the different tissue samples. Prepare a Styrofoam holder.
CAUTION: Become familiar with liquid nitrogen handling procedures (aeration, frostbites, potentially exploding tubes). - Open the plate and remove the tissue paper with forceps, being careful not to detach the roots from the agar surface. With a surgical blade, cut once per row along the shoot-root-junction in a single, determined stroke. Clean the blades between samples and exchange frequently to guarantee sharpness.
- With tweezers, swipe along the roots of each row to collect them in three bundles. Grab the roots and empty them into a 50 mL tube filled with liquid nitrogen to snap freeze.
NOTE: Do not try to assemble roots into dense structures (like balls) as they are difficult to grind in the next step. - Proceed with all plates that constitute one sample (in the order of incubation times) and pour out excess liquid nitrogen. Use the tube lid to prevent the roots from spilling. Then close the lid and collect all tubes in the Dewar vessel. Store the root tissue at -80 °C.
6. Immunopurification
NOTE: This step aims to obtain high-quality TRAP/polysome RNA. Therefore, strictly follow good practice advice for RNA handling. Perform all steps in this section in a sterile bench and clean all equipment and labware with an RNase-removing solution (Table of Materials). Wear gloves and change them immediately when contaminated with sample, ice, or other sources that have not been cleaned. Since this is a very crucial aspect, a section on equipment reuse together with waste disposal advice is included.
- Buffer preparation
- Prepare stock solutions according to Table 1 and autoclave (A) or filter sterilize (₳). Unless otherwise specified, the solvent is RNase-free water.
- Dissolve and aliquot dithiothreitol (DTT), phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), cycloheximide (CHX) and chloramphenicol (CAM) in their respective solvents as indicated in Table 1 and store them at -20 °C. All other stocks can remain at room temperature.
- Pre-mix the stocks - with ingredients 1-4 for wash buffer (WB) and 1-6 for polysome extraction buffer (PEB) - to avoid time-consuming buffer mixing prior to every extraction. Thus, only add water and the frozen ingredients (7-10) on the day of the extraction. Keep the pre-mixed stocks and RNase-free water at 4 °C.
NOTE: DTT concentration is 1/5 of the reported concentration from Zanetti et al. 2005, as the nanobody interaction with the GFP is sensitive to high DTT concentrations.
| Ingredients | Stock concentration | Add volume in mL for 50 mL of WB* | Add volume in mL for 50 mL of PEB* | ||
| 1 | Tris, pH 9 | A | 2 M | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | KCl | A | 2 M | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | EGTA | A | 0.5 M | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 4 | MgCl2 | A | 1 M | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| 5 | PTE | A | 20% (v/v) | 0 | 2.5 |
| 6 | detergent mix | A | 0 | 2.5 | |
| Tween 20 | 20% (v/v) | ||||
| Triton-X 100 | 20% (v/v) | ||||
| Brij-35 | 20% (w/v) | ||||
| Igepal | 20% (v/v) | ||||
| 7 | DTT | ₳ | 0.5 M | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 8 | PMSF | ₳ | 0.1 M (isopropanol) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 9 | Cycloheximide | ₳ | 25 mg/mL (EtOH) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 10 | Chloramphenicol | ₳ | 50 mg/mL (EtOH) | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Table 1: Buffer composition and mixing advice. Ingredients with the given stock concentrations mixed in the given amounts yield 50 mL of WB or PEB. Tris: tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane, EGTA: ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetra-acetic acid, PTE: Polyoxyethylene-(10)-tridecyl ether, A: autoclave, ₳: filter-sterilize; *fill up to 50 mL with RNase-free water.
- Tissue homogenization/grinding
- Cool down centrifuge and place homogenizers and centrifuge tubes on ice. Thaw aliquots of DTT, PMSF, CHX and CAM. Mix PEB and WB from the stock solutions in 50 mL tubes according to requirements of the day (# of samples) and cool on ice.
NOTE: Add PMSF only shortly before use, as the half-life of PMSF in water is only 30 min. - Prepare plenty of liquid nitrogen in a Dewar vessel and retrieve tissue samples from -80 °C storage. Wear cotton gloves underneath the standard lab gloves to prevent burns from cold mortars. Pour liquid nitrogen into mortars and pestles until they are cold enough to allow grinding. It is recommended to devise a system to distinguish mortars (label or keep in a certain order).
- Empty tissue sample into a mortar and grind carefully until all material is a white powder. If needed, add liquid nitrogen to keep the tissue frozen or to facilitate better grinding.
- Add 5 mL of PEB to the sample and quickly mix with the powder before the buffer freezes. While this sample thaws (mix from time to time) process another sample.
- As soon as the mixture can be transferred, empty the slurry into a glass homogenizer and keep on ice. With an additional 2 mL of PEB, rinse the mortar and pestle and add it to the sample in the homogenizer.
NOTE: Avoid a completely liquid sample as this allows RNA degradation. - Grind the slurry manually until the extract is homogenous. We recommend a minimum of 4 to 5 plunges.
NOTE: It may require some additional waiting time to allow the slurry to thaw further. Handling of homogenizers requires some diligence. Do not apply brute force and beware of suction forces. If not taken into account, this will lead to spillage, contamination or destruction of the homogenizer. - Pour the crude root extract into a 50 mL centrifuge tube (keep on ice).
NOTE: Usually several samples can be ground before transfer. Parallel handling of grinding, transferring and homogenizing is required. Try to work quickly but do not rush; stay calm. Always keep homogenized samples on ice.
- Cool down centrifuge and place homogenizers and centrifuge tubes on ice. Thaw aliquots of DTT, PMSF, CHX and CAM. Mix PEB and WB from the stock solutions in 50 mL tubes according to requirements of the day (# of samples) and cool on ice.
- Total RNA sample collection
- Transfer 200 µL aliquots of each crude sample to a clean microcentrifuge tube (labeled and cooled on ice beforehand).
- Proceed with the RNA extraction as detailed for TRAP samples in points 7.1 and 7.2. Do these steps while samples are clearing in the centrifuge.
- Perform a DNase treatment with the resuspended total RNA to eliminate DNA contamination and clean up the reaction using a commercial kit (Table of Materials).
NOTE: Total RNA extractions usually yield high concentrations and samples need to be diluted considerably. We recommend measuring the concentration after dilution by the sensitive Qubit protocol.
- Clearing the crude extract
- Take the ice bucket with samples from 6.2.7 and centrifuge them for 15 min at 16,000 x g and 4 °C.
NOTE: To balance out the centrifuge, pair samples accordingly. In case this is not entirely possible, adjust one sample by adding PEB. - Pour the supernatant to a fresh centrifuge tube (cooled on ice beforehand) and repeat centrifugation (15 min at 16,000 x g and 4 °C). This transfer can be quickly performed next to the centrifuge.
- While the crude extract is clearing, initiate the washing of GFP-beads for step 6.6.
NOTE: Keep this ice bucket for rocking on the shaker but do not place back into the sterile bench as it might be contaminated.
- Take the ice bucket with samples from 6.2.7 and centrifuge them for 15 min at 16,000 x g and 4 °C.
- Bead wash
- Aliquot magnetic GFP-beads (#samples x 60 µL, Table of Materials) into a 1.5 mL tube. Place on the magnetic stand. Once the beads have collected, remove the supernatant.
- Add 1 mL of cold WB, resuspend the beads and collect them again. Discard the wash buffer and repeat once more with 1 mL of WB.
- Ultimately, resuspend the beads in WB to the initial volume used in step 6.5.1.
- Immunopurification (IP)
- Immediately after centrifugation, pour the cleared supernatant into labeled 15 mL tubes and add 60 µL of washed beads per sample.
- Place all samples horizontally into the ice bucket and put it on a shaker. Let the mixture incubate for 2 h in order to bind the GFP-labeled polysomes to the beads.
- Collect the beads on the magnetic stand for 15 mL tubes (on ice) and add PMSF to the remaining PEB. Discard the supernatant. Pour approximately 5 mL of PEB to the beads and resuspend them by tilting. Shake the samples for 15 min in the same setup as in section 6.6.2.
- Repeat the washes with WB to a total of 3 washes (1 x PEB, 2 x WB). Before each buffer exchange, add PMSF.
- Collect the beads in 1 mL of WB and transfer them to a 1.5 mL tube. Finally, collect the beads one more time on the magnetic stand and remove all liquid. Close the tube and keep on ice until all samples are processed.
- Transport the samples to a fume hood for RNA extraction.
- Waste disposal and reconditioning of lab supplies.
- If performed according to good lab practice (see section 2.2.1), the sterilization procedure yields an aqueous NaCl solution. Leave the chlorine gas, as well as residual HCl and bleach, to defumigate in the fume hood.
- PEB and WB disposal: As CHX decomposes at high pH, collect all liquids and bring to pH>9. Dispose of the liquid waste in the halogenated chemical waste. All solids (tissues, serological pipettes, gloves, etc.) should be disposed of as chemical waste.
- Collect phenol-containing liquids separately, as well as phenol-contaminated material (tips, tubes and gloves).
- Hand-wash mortars, pestles and homogenizers (sponges and brush) with soap and rinse thoroughly. Subsequently, bake the material at >220 °C overnight. Either wrap in tin foil before the treatment or place into a heat-proof, covered container.
- Brush clean centrifuge tubes with detergent and then diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC)-treat in the fume hood. To this end, add liquid DEPC to deionized water (1 mL of DEPC to 1 L of H2O) and mix via shaking. Place the centrifuge tubes onto an autoclavable tray that catches spilled DEPC-water. Pour the suspension into the tubes and leave for 3 h or overnight. DEPC decomposes in the subsequent autoclaving process.
CAUTION: DEPC is highly toxic.
7. RNA extraction and QC
- RNA extraction
- Cool down the tabletop centrifuge to 4 °C.
- Add 1 mL of acid-guanidinium-phenol-based reagent (Table of Materials) to each sample, invert to resuspend the beads or total RNA slurry and incubate for 5 min on ice. Do not vortex!
- Add 200 µL of chloroform and incubate for 3 min on ice. Then thoroughly vortex the samples.
- To aid phase separation, centrifuge at max. speed for 10-15 min, 4 °C.
- Label 1.5 mL low-retention tubes (Table of Materials) and aliquot 650 µL of isopropanol into each.
- Carefully take the upper aqueous phase (ca. 650 µL) and transfer to the prepared tubes with isopropanol. Avoid touching the pink organic phase.
- Precipitate RNA overnight at -20 °C.
NOTE: It is recommended to store the samples in isopropanol at -20 °C or -80 °C and only solubilize in water when needed. Aqueous RNA degrades even at -80 °C when stored for weeks/months.
- RNA precipitation
- Cool down the tabletop centrifuge to 4 °C.
- Prepare fresh 80% EtOH with RNase-free water and cool down at -20 °C (5 min at -80 °C help to speed up the process).
- Centrifuge the samples at maximum speed (ca. 13,000 x g) for 30 min and discard the supernatant. The pellet will not be visible, so carefully pipette as if it was there. Add 1 mL of cold 80% EtOH and invert the tube one or two times.
- Centrifuge again for 30 min at maximum speed and repeat the wash to a total of two washes.
- Spin down for 2 min and remove all residual EtOH with a 10 µL tip. Leave the pellet to dry for 3-5 min (not more) at room temperature and resuspend in 20 µL RNase-free water.
- Keep the samples on ice and perform quality control as soon as possible. Proceed to store the samples at -80 °C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
- Quality control using dedicated equipment (Table of Materials) according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
8. Library preparation
- cDNA synthesis and amplification with the SMARTer v4 Ultra Low Input RNA Kit
- Calculate the dilution of each sample to have 1.5 ng of TRAP-RNA or total RNA in a volume of 4.75 µL. Perform all reactions in PCR-tubes and dilute samples with fresh aliquots of RNase-free water.
- Perform all steps according to the manufacturer's recommendations with ½ the reaction volumes. Amplify the cDNA with 12-13 PCR cycles.
- Clean up the PCR by adding 0.5 µL of 10x lysis buffer and 25 µL of SPRI beads (Table of Materials). If many samples are processed lysis buffer and beads can be pre-mixed. Make sure that the beads are evenly dispersed before pipetting.
- Proceed with the protocol in full reaction volumes (17 µL of elution buffer). Do not let the beads dry for more than 3 minutes. Overdried samples can potentially be rescued by prolonged incubation times.
- Measure the sample concentrations with the Qubit HS DNA kit.
NOTE: The SMARTer v4 kit can tolerate down to 200 pg input. We did obtain libraries in cases where Qubit values could not be determined (below 250 pg, detection limit) with a 16 cycle PCR. However, the limited input material might also yield less complex libraries.
- Fragmentation and adapter ligation PCR with the Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit
- Dilute the cDNA with RNase-free water to obtain a concentration of 200 pg/µl and pipette 1.25 µL in a PCR-tube.
- Perform all steps according to the manufacturer with ¼ the reaction volumes. Amplify the cDNA with 12 PCR cycles and compatible adapters for the samples that belong to one sequencing pool. With Illumina's Index Kits A and D up to 384 samples can be multiplexed.
- For the PCR clean up add 12.5 µL of resuspension buffer and 22.5 µL of SPRI beads (0.9x ratio). Elute the sample with 22 µL of elution buffer.
NOTE: QC and pooling was performed by the sequencing company (Table of Materials) and thus no bead-based normalization was needed. The enzymatic fragmentation reaction (tagmentation) is very sensitive to material input as every enzyme only cuts once. Therefore, do not exceed the concentration recommendation.
Results
For quality assessment, the above-mentioned procedure should be probed at several intermediate steps: expression pattern validation in planta, quality control of the isolated polysomal RNA as well as of the final libraries. qRT-PCR using known marker genes can, in addition, be performed to confirm the response to the treatment condition or to fine-tune the experimental conditions.
Confocal analysis of GFP signal distribu...
Discussion
Verification of RPL18 localization pattern
Crucial to avoid misinterpretation of data from any TRAP experiment is the proper expression pattern of the tagged ribosomal subunit. Therefore, the incorporation of GFP as an epitope tag to RPL18 very elegantly allows verification of the desired expression pattern and consecutively, pulldown of the polysome fraction from the same tissue. More invasive approaches to assure proper promoter patterns are followed by Jiao and Mayerowitz 2010, which requires GU...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Jean-Claude Walser of the Genetic Diversity Center Zurich for crucial expert advice in the early phase of this project. Work in the Vermeer lab was supported by an SNF Professorship grant (PP00P3_157524) and a R'EQUIP equipment grant (316030_164086) from the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) awarded to JEMV.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Sterilization | |||
| bleach, 13% | Sigma | 71696 | |
| beaker | VWR | 214-1172/74/75 | |
| desiccator with porcelaine plate (DURAN) | Sigma/Merck | Z317454-1EA/Z317594-1EA | |
| EtOH, p.a. | Honeywell | 02860-1L | |
| HCl, 37% | Roth | 4625.1 | |
| Tween 20 | Sigma | P9416 | |
| Plate growth + harvesting | |||
| MS salts, basal salt mixture, incl. MES buffer | Duchefa | M0254 | |
| agar plant for cell culture | Applichem/Panreac | A2111.1000 | |
| DMSO | Sigma | D4540 | |
| forcepts | Rubis Switzerland | 5-SA model | |
| KOH | Fluka | 60370 | |
| micropore/surgical tape | 3M | 1530-0 | |
| NAA | Duchefa | N0903 | |
| petri dishes 120x120 mm | Greiner bio-one | 688102 | |
| scalpel | VWR/Swann-Morton | 233-5454 | |
| tissues, neutral, two-layered | any supplier of your choice | ||
| Immunoprecipitation | |||
| GFP-beads: gtma-100 GFP-Trap_MA | Chromotek | e.g. gtma-100 | |
| Brij-35 | Sigma | P1254-500G | |
| centrifuge tubes (in accordance with centrifuge) | Beckman Coulter | 357001 | |
| Chloramphenicol | Applichem | C0378-25G | |
| cotton gloves | VWR | 113-7355 | |
| Cycloheximide, HPLC grade | Sigma | 01810-1G | |
| DEPC | VWR | E174 | might have long delivery times |
| DTT | Fluka | 43815 | |
| EGTA | Sigma | 3054.3 | |
| homogenizers DUALL 23 | KONTES GLASS CO (via VWR) | SCERSP885450-0023 (set) | SCERSP885451-0023 pestle only - SCERSP885452-0023 cylinder only; long delivery times |
| Igepal CA-360 | Sigma | I3021-100ml | |
| KCl | Sigma | 60130 | |
| MgCl2 hexahydrat | Roth | 2189.2 | |
| mortar and pestle | VWR | 470148-960 & 470019-978 | |
| PMSF | Roche | 10 837 091 001 | |
| Polyoxyethylene-(10)-tridecylether/PTE | Sigma | P2393-500G | |
| RNase-free water | Roth | T143.3 | |
| RNAZap | Thermo Fisher | AM9780/AM9782 | for cleaning surfaces |
| Tris, >99.3% | Roth | AE15.3 | |
| Triton X-100 | Fluka | T8787-250ml | |
| Tween 20 | Sigma | P9416-100ml | |
| RNA extraction | |||
| 2-Propanol, p.a. | Sigma | 33539-1L-GL-R | |
| Chloroform, HPLC grade | Scharlau | CL02181000 | |
| EtOH, p.a. | Honeywell | 02860-1L | |
| low-retention microcentrifuge tubes, 1.5 ml | Eppendorf/Sigma | Z666548-250EA | LoBind |
| RNase-free DNase set | Qiagen | 79254 | |
| RNeasy MiniElute Cleanup Kit | Qiagen | 74204 | |
| TRIzol reagent | ThermoFisher/Ambion | 15596018 | |
| Library preparation | |||
| 15/50 mL Tube Magnetic Separator | Abraxis | PN 472250 | |
| AMPure beads | Beckman Coulter | A63881 | |
| Index Kit A | Illumina | FC-131-2001 | |
| Index Kit D | Illumina | FC-131-2004 | |
| neodymium magnets | Amazon/other | 6 x 1.5 mm range: N42 (NdFeB) | |
| Nextera XT kit | Illumina | FC-131-1024/1096 | https://emea.support.illumina.com/ |
| PCR strips | ThermoScientific | AB-0266 | |
| SMARTer v4 kit | Takara Bioscience | 634892 | https://www.takarabio.com/ |
| Bioanalyzer | Agilent | 2100 Bioanalyzer Instrument | specialized equipment for RNA/DNA quality control |
| Tapestation | Agilent | 4200 Tapestation Instrument | specialized equipment for RNA/DNA quality control |
| Fragment Analyzer | Agilent | 5400 Fragment Analyzer System | specialized equipment for RNA/DNA quality control (high throughput) |
| LabChip | PerkinElmer | LabChip GX Touch Nucleic Acid Analyzer | specialized equipment for RNA/DNA quality control (high throughput) |
| Qubit 4 Fluorometer | ThermoFisher | Q33239 | specialized equipment for RNA/DNA concentration determination |
| qRT-PCR | |||
| GATA23 | Microsynth | fwd: AGTGAGAATGAA AGAAGAGAAGGG; rev: GTGGCTGCGAAT AATATGAATACC | |
| GH3.3 | Microsynth | fwd: CAAACCAATCCT CCAAATGAC; rev: ACTTATCCGCAA CCCGACT | |
| LBD29 | Microsynth | fwd: TCTCCAACAACA GGTTGTGAAT; rev: AAGGAGCCTTAG TAGTGTCTCCA | |
| UBC21 | Microsynth | fwd: TGCGACTCAGGG AATCTTCT; rev: TCATCCTTTCTT AGGCATAGCG | |
| SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR Green | Bio-Rad | #172-5270 | |
| iScript Adv cDNA Kit | Bio-Rad | #172-5038 | |
| miscellaneous | |||
| Falcon tubes 15 ml, Cellstar | Greiner bio-one | 188261 | |
| Falcon tubes 50 ml, Cellstar | Greiner bio-one | 210261 | |
| filter tips 1 ml | Axygen | TF-1000-R-S | |
| filter tips 10 µl | Axygen | TF-10-R-S | |
| filter tips 100 µl | Axygen | TF-100-R-S | |
| filter tips 20 µl | Axygen | TF-20-R-S | |
| filter tips 200 µl | Axygen | TF-200-R-S | |
| microcentrifuge tubes 1.5 ml | SARSTEDT | 72.690.001 | |
| Propidium iodide | Sigma | P4170-100MG | |
| sequencing company | Novogene | en.novogene.com |
References
- Van Verk, M. C., Hickman, R., Corné, M. J., Pieterse, M., Van Wees, S. C. RNA-Seq: Revelation Of The Messengers. Trends In Plant Science. 18 (4), 175-179 (2013).
- Libault, M., Pingault, L., Zogli, P., Schiefelbein, J. Plant Systems Biology At The Single-Cell Level. Trends In Plant Science. 22 (11), 949-960 (2017).
- Mustroph, A., et al. Profiling Translatomes Of Discrete Cell Populations Resolves Altered Cellular Priorities During Hypoxia In Arabidopsis. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America. 106 (44), 18843-18848 (2009).
- Karve, R., Iyer-Pascuzzi, A. S. Digging Deeper: High-Resolution Genome-Scale Data Yields New Insights Into Root Biology. Current Opinion In Plant Biology. 24, 24-30 (2015).
- Warner, J. R., Knopf, P. M., Rich, A. A Multiple Ribosomal Structure In Protein Synthesis. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America. 49 (1), 122-129 (1963).
- Gautam, V., Sarkar, A. K. Laser Assisted Microdissection, An Efficient Technique To Understand Tissue Specific Gene Expression Patterns And Functional Genomics In Plants. Molecular Biotechnology. 57 (4), 299-308 (2015).
- Bargmann, B. O. R., Birnbaum, K. D. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting Of Plant Protoplasts. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (36), e1673 (2010).
- Deal, R. B., Henikoff, S. The Intact Method For Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression And Chromatin Profiling In Arabidopsis Thaliana. Nature Protocols. 6 (1), 56-68 (2011).
- Dougherty, J. D. The Expanding Toolkit Of Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal Of The Society For Neuroscience. 37 (50), 12079-12087 (2017).
- Mustroph, A., Juntawong, P., Bailey-Serres, J. Isolation Of Plant Polysomal mRNA By Differential Centrifugation And Ribosome Immunopurification Methods. Methods in Molecular Biology. 553, 109-126 (2009).
- Matsushima, W., et al. SLAM-ITseq: Sequencing Cell Type-Specific Transcriptomes Without Cell Sorting. Development. 145 (13), (2018).
- Basnet, H., et al. Flura-Seq Identifies Organ-Specific Metabolic Adaptations During Early Metastatic Colonization. Elife. 8, (2019).
- Rodriques, S. G., et al. Slide-Seq: A Scalable Technology For Measuring Genome-Wide Expression At High Spatial Resolution. Science. 363 (6434), 1463-1467 (2019).
- Fazal, F. M., et al. Atlas Of Subcellular RNA Localization Revealed By Apex-Seq. Cell. 178 (2), 473-490 (2019).
- Slane, D., Bayer, M., Kaufmann, K., Mueller-Roeber, B. Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression Profiling Using Fluorescence-Activated Nuclear Sorting. Plant Gene Regulatory Networks: Methods And Protocols. , 27-35 (2017).
- Zanetti, M. E., Chang, I. F., Gong, F., Galbraith, D. W., Bailey-Serres, J. Immunopurification Of Polyribosomal Complexes Of Arabidopsis For Global Analysis Of Gene Expression. Plant Physiology. 138 (2), 624-635 (2005).
- King, H. A., Gerber, A. P. Translatome Profiling: Methods For Genome-Scale Analysis Of mRNA Translation. Briefings In Functional Genomics. 15 (1), 22-31 (2016).
- Mašek, T., Valášek, L., Pospíšek, M., Nielsen, H. Polysome Analysis And RNA Purification From Sucrose Gradients. RNA: Methods And Protocols. , 293-309 (2011).
- Heiman, M., et al. A Translational Profiling Approach For The Molecular Characterization Of Cns Cell Types. Cell. 135 (4), 738-748 (2008).
- Halbeisen, R. E., Scherrer, T., Gerber, A. P. Affinity Purification Of Ribosomes To Access The Translatome. Methods. 48 (3), 306-310 (2009).
- Thomas, A., et al. A Versatile Method For Cell-Specific Profiling Of Translated mRNAs In Drosophila. Plos One. 7 (7), e40276 (2012).
- Watson, F. L., et al. Cell Type-Specific Translational Profiling In The Xenopus Laevis Retina. Developmental Dynamics. 241 (12), 1960-1972 (2012).
- Lam, P. Y., Harvie, E. A., Huttenlocher, A. Heat Shock Modulates Neutrophil Motility In Zebrafish. Plos One. 8 (12), e84436 (2013).
- Fang, Y., et al. Translational Profiling Of Cardiomyocytes Identifies An Early Jak1/Stat3 Injury Response Required For Zebrafish Heart Regeneration. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America. 110 (33), 13416-13421 (2013).
- Mustroph, A., Zanetti, M. E., Girke, T., Bailey-Serres, J. Isolation And Analysis Of mRNAs From Specific Cell Types Of Plants By Ribosome Immunopurification. Methods In Molecular Biology. 959, 277-302 (2013).
- Monshausen, G. B., Gilroy, S. Feeling Green: Mechanosensing In Plants. Trends In Cell Biology. 19 (5), 228-235 (2009).
- Day, R. C., Grossniklaus, U., Macknight, R. C. Be More Specific! Laser-Assisted Microdissection Of Plant Cells. Trends In Plant Science. 10 (8), 397-406 (2005).
- Sheen, J. Signal Transduction In Maize And Arabidopsis Mesophyll Protoplasts. Plant Physiology. 127 (4), 1466-1475 (2001).
- Datta, S., et al. Laser Capture Microdissection: Big Data From Small Samples. Histology And Histopathology. 30 (11), 1255-1269 (2015).
- Birnbaum, K., et al. A Gene Expression Map Of The Arabidopsis Root. Science. 302 (5652), 1956 (2003).
- Hamant, O., Haswell, E. S. Life Behind The Wall: Sensing Mechanical Cues In Plants. BMC Biology. 15 (1), 1354 (2017).
- Vragović, K., et al. Translatome Analyses Capture Of Opposing Tissue-Specific Brassinosteroid Signals Orchestrating Root Meristem Differentiation. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (3), 923-928 (2015).
- Wang, Y., Jiao, Y. Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification (Trap) For Cell-Specific Translation Profiling In Developing Flowers. Methods In Molecular Biology. 1110, 323-328 (2014).
- Sablok, G., Powell, J. J., Kazan, K. Emerging Roles And Landscape Of Translating mRNAs In Plants. Frontiers in Plant Science. 8, 1443 (2017).
- Ron, M., et al. Hairy Root Transformation Using Agrobacterium Rhizogenes As A Tool For Exploring Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression And Function Using Tomato As A Model. Plant Physiology. 166 (2), 455-469 (2014).
- Reynoso, M. A., et al. Evolutionary Flexibility In Flooding Response Circuitry In Angiosperms. Science. 365 (6459), 1291-1295 (2019).
- Dolan, L., et al. Cellular Organisation Of The Arabidopsis Thaliana Root. Development. 119 (1), 71 (1993).
- Ristova, D., Barbez, E. . Root Development. , (2018).
- Shekhar, V., Stӧckle, D., Thellmann, M., Vermeer, J. E. M. The Role Of Plant Root Systems In Evolutionary Adaptation. Current Topics in Developmental Biology. 131, 55-80 (2019).
- Malamy, J. E., Benfey, P. N. Down And Out In Arabidopsis: The Formation Of Lateral Roots. Trends in Plant Science. 2 (10), 390-396 (1997).
- de Smet, I., et al. Bimodular Auxin Response Controls Organogenesis In Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America. 107 (6), 2705-2710 (2010).
- Péret, B., et al. Arabidopsis Lateral Root Development: An Emerging Story. Trends In Plant Science. 14 (7), 399-408 (2009).
- Vilches-Barro, A., Maizel, A. Talking Through Walls: Mechanisms Of Lateral Root Emergence In Arabidopsis Thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 23, 31-38 (2015).
- Porco, S., et al. Lateral Root Emergence In Arabidopsis Is Dependent On Transcription Factor Lbd29 Regulation Of Auxin Influx Carrier Lax3. Development. 143 (18), 3340-3349 (2016).
- Stoeckle, D., Thellmann, M., Vermeer, J. E. Breakout-Lateral Root Emergence In Arabidopsis Thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 41, 67-72 (2018).
- Banda, J., et al. Lateral Root Formation In Arabidopsis: A Well-Ordered Lrexit. Trends in Plant Science. 24 (9), 826-839 (2019).
- Vermeer, J. E. M., et al. A Spatial Accommodation By Neighboring Cells Is Required For Organ Initiation In Arabidopsis. Science. 343 (6167), 178-183 (2014).
- Vanneste, S., et al. Cell Cycle Progression In The Pericycle Is Not Sufficient For Solitary Root/Iaa14-Mediated Lateral Root Initiation In Arabidopsis Thaliana. The Plant Cell. 17 (11), 3035-3050 (2005).
- Marques-Bueno, M. M., et al. A Versatile Multisite Gateway-Compatible Promoter And Transgenic Line Collection For Cell Type-Specific Functional Genomics In Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal : For Cell and Molecular Biology. 85 (2), 320-333 (2016).
- Shimada, T. L., Shimada, T., Hara-Nishimura, I. A Rapid And Non-Destructive Screenable Marker, Fast, For Identifying Transformed Seeds Of Arabidopsis Thaliana. The Plant Journal : For Cell and Molecular Biology. 61 (3), 519-528 (2010).
- Clough, S. J., Bent, A. F. Floral Dip: A Simplified Method For Agrobacterium Mediated Transformation Of Arabidopsis Thaliana. The Plant Journal. 16 (6), 735-743 (1998).
- Lindsey, B. E., Rivero, L., Calhoun, C. S., Grotewold, E., Brkljacic, J. Standardized Method For High-Throughput Sterilization Of Arabidopsis Seeds. Journal Of Visualized Experiments. (128), e56587 (2017).
- Andersen, T. G., et al. Diffusible Repression Of Cytokinin Signalling Produces Endodermal Symmetry And Passage Cells. Nature. 555, 529-533 (2018).
- Schroeder, A., et al. The Rin: An Rna Integrity Number For Assigning Integrity Values To Rna Measurements. BMC Molecular Biology. 7, 3 (2006).
- Vragović, K., Bartom, E., Savaldi-Goldstein, S. Quantitation Of Cell Type-Specific Responses To Brassinosteroid By Deep Sequencing Of Polysome-Associated Polyadenylated RNA. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1564, 81-102 (2017).
- Bertin, B., Renaud, Y., Aradhya, R., Jagla, K., Junion, G. Trap-Rc, Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification From Rare Cell Populations Of Drosophila Embryos. Journal Of Visualized Experiments. (103), e52985 (2015).
- Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis Of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR And The 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25 (4), 402-408 (2001).
- Jiao, Y., Meyerowitz, E. M. Cell-Type Specific Analysis Of Translating Rnas In Developing Flowers Reveals New Levels Of Control. Molecular Systems Biology. 6, 419 (2010).
- Tian, C., et al. A Gene Expression Map Of Shoot Domains Reveals Regulatory Mechanisms. Nature Communications. 10 (1), 141 (2019).
- Townsley, B. T., Covington, M. F., Ichihashi, Y., Zumstein, K., Sinha, N. R. Brad-Seq: Breath Adapter Directional Sequencing: A Streamlined, Ultra-Simple And Fast Library Preparation Protocol For Strand Specific mRNA Library Construction. Frontiers in Plant Science. 6, 366 (2015).
- Song, Y., et al. A Comparative Analysis Of Library Prep Approaches For Sequencing Low Input Translatome Samples. BMC Genomics. 19 (1), 696 (2018).
- Basu, D., Haswell, E. S. Plant Mechanosensitive Ion Channels: An Ocean Of Possibilities. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 40, 43-48 (2017).
- Brady, S. M., et al. A High-Resolution Root Spatiotemporal Map Reveals Dominant Expression Patterns. Science. 318 (5851), 801 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved