A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Combining Multiplex Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization with Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry on Fresh Frozen or Fixed Mouse Brain Sections
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a method for combining fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and fluorescence immunohistochemistry (IHC) in both fresh frozen and fixed mouse brain sections, with the goal of achieving multilabel FISH and fluorescence IHC signal. IHC targeted cytoplasmic and membrane attached proteins.
Abstract
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular technique that identifies the presence and spatial distribution of specific RNA transcripts within cells. Neurochemical phenotyping of functionally identified neurons usually requires concurrent labelling with multiple antibodies (targeting protein) using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and optimization of in situ hybridization (targeting RNA), in tandem. A "neurochemical signature" to characterize particular neurons may be achieved however complicating factors include the need to verify FISH and IHC targets before combining the methods, and the limited number of RNAs and proteins that may be targeted simultaneously within the same tissue section.
Here we describe a protocol, using both fresh frozen and fixed mouse brain preparations, which detects multiple mRNAs and proteins in the same brain section using RNAscope FISH followed by fluorescence immunostaining, respectively. We use the combined method to describe the expression pattern of low abundance mRNAs (e.g., galanin receptor 1) and high abundance mRNAs (e.g., glycine transporter 2), in immunohistochemically identified brainstem nuclei.
Key considerations for protein labelling downstream of the FISH assay extend beyond tissue preparation and optimization of FISH probe labelling. For example, we found that antibody binding and labelling specificity can be detrimentally affected by the protease step within the FISH probe assay. Proteases catalyze hydrolytic cleavage of peptide bonds, facilitating FISH probe entry into cells, however they may also digest the protein targeted by the subsequent IHC assay, producing off target binding. The subcellular location of the targeted protein is another factor contributing to IHC success following FISH probe assay. We observed IHC specificity to be retained when the targeted protein is membrane bound, whereas IHC targeting cytoplasmic protein required extensive troubleshooting. Finally, we found handling of slide-mounted fixed frozen tissue more challenging than fresh frozen tissue, however IHC quality was overall better with fixed frozen tissue, when combined with RNAscope.
Introduction
Proteins and mRNAs that neurochemically define subpopulations of neurons are commonly identified with a combination of immunohistochemistry (IHC) and/or in situ hybridization (ISH), respectively. Combining ISH with IHC techniques facilitates the characterization of colocalization patterns unique to functional neurons (neurochemical coding) by maximizing multiplex labelling capacity.
Fluorescent ISH (FISH) methods, including RNAscope, have higher sensitivity and specificity compared to earlier RNA detection methods such as radioactive ISH and non-radioactive chromogenic ISH. FISH enables visualization of single mRNA transcripts as punctate stained spots1. Furthermore, the RNAscope assay allows an increased number of RNA targets to be labeled at a time, using different fluorophore tags. Despite these advantages, technical limitations may affect the number of fluorophores/chromogens that can be used in a single experiment. These include availability of microscope filter sets; such considerations are compounded when neurochemical identification uses combined FISH and IHC, compared to using each technique in isolation, since inherent steps optimal for one method may be detrimental to the other.
Previous application of FISH combined with IHC has demonstrated the expression of specific cellular targets in human B-cell lymphomas2, chick embryos3, zebrafish embryos4, mouse retina5 and mouse inner ear cells6. In these studies, tissue preparation was either formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE)2,3,5 or fresh whole mount4,6. Other studies applied chromogenic RNAscope on fixed mouse and rat brain preparations7,8,9. In particular, Baleriola et al.8 described two different tissue preparations for combined ISH-IHC; fixed mouse brain sections and FFPE human brain sections. In a recent publication, we combined FISH and fluorescent IHC on fresh frozen sections, to simultaneously visualize low abundance mRNA (galanin receptor 1, GalR1), high abundance mRNA (glycine transporter 2, GlyT2) and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (vAChT) protein10 in the brainstem reticular formation.
The nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) is a major brain region involved in autonomic function. Located in the hindbrain, this heterogeneous population of neurons receives and integrates a vast number of autonomic signals, including those that regulate breathing. The NTS harbors several neuronal populations, which may be phenotypically characterized by the expression pattern of mRNA targets including GalR1 and GlyT2 and protein markers for the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and the transcription factor Paired-like homeobox 2b (Phox2b).
The RNAscope proprietor recommends fresh frozen tissue preparations, but tissue prepared by whole animal transcardial perfusion fixation, along with long term cryoprotection (storage at -20 °C) of fixed frozen tissue sections, is common in many laboratories. Hence, we sought to establish protocols for FISH in combination with IHC using fresh frozen and fixed frozen tissue preparations. Here, we provide for fresh frozen and fixed frozen brain sections: (1) a protocol for combined FISH and fluorescent IHC (2) a description of the quality of mRNA and protein labelling produced, when utilizing each preparation (3) a description of the expression of GalR1 and GlyT2 in the NTS.
Our study revealed that, when combined with RNAscope methodology, IHC success varied in fresh frozen and fixed frozen preparations and, was dependent upon localization of the target proteins within the cell. In our hands, membrane bound protein labelling was always successful. In contrast, IHC for cytoplasmic protein required troubleshooting even in cases where the cytoplasmic protein was overexpressed in a transgenic animal (Phox2b-GFP)11. Finally, while GalR1 is expressed in non-catecholaminergic neurons in the NTS, GlyT2 expression is absent in the NTS.
Protocol
A summary of tissue pre-processing steps may be found in Figure 1. All procedures were carried out in compliance with the Animal Care and Ethics Committee of the University of New South Wales in accordance with the guidelines for the use and care of animals for scientific purposes (Australian National Health and Medical Research Council).
1. Sample preparation of fresh frozen brain tissue
- Transcardial Perfusion
- Prepare heparinized (2500 U/L) 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB), pH 7.5. Make dry ice ethanol slurry by mixing dry ice with ethanol. This will have a temperature of approximately −72 °C and will be used for immediate freezing of the harvested tissue.
- Euthanize adult C57BL/6 and Phox2b-GFP11 (Mouse Genome Informatics database ID MGI:5776545) mice by anesthetizing with sodium pentobarbital (70 mg/kg, i.p.), using a 27.5 inch needle gauge.
CAUTION: Pentobarbital is a barbiturate. It is acutely toxic in high doses and may cause death by respiratory arrest. Consult local healthcare, legal and material safety guidelines before use. - Expose the heart and cannulate the left ventricle with a drawing-up needle (23 inch gauge). Perform transcardial perfusion with heparinized 0.1 M PB until the blood clears (2-3 minutes) at a flow rate of 11-13 mL/min. Determine blood clearing by monitoring the coloration of the liver and the effusate from the right atrium12.
- Isolate the brain from the skull cavity, immediately embed it in Optimal Cutting Temperature Compound (OCT) in a cryomold or aluminum foil and place it on the dry ice ethanol bath. Store the frozen embedded tissue in an airtight container at - 80 °C for up to 3 months.
- Sectioning of fresh frozen tissue
- Set the cryostat temperature to -20 °C. Leave the OCT-embedded tissue and a cryostat chuck in the cryostat for ~30 minutes to allow for equilibration to the new temperature.
NOTE: Keep the tissue frozen at all times; transport the tissue from the -80 °C freezer to the cryostat on dry ice. - Secure the tissue to the pre-chilled cryostat chuck using OCT compound. In this protocol, tissue blocks were mounted onto the chuck in the coronal plane.
NOTE: Trim excess OCT from the tissue, using a razor blade, to minimize the amount of OCT being cut by the cryostat and subsequently transferred onto the glass slide. - Cut 14 µm thick coronal sections and mount them onto charged glass microscopy slides.
- Warm the slides to room temperature before mounting the sections. Once the section has been mounted, keep the slides in a slide box in the cryostat.
- If more than one section needs to be mounted on one slide, warm the area for the second section by placing a finger on the opposite side of the slide for 5-10 seconds to aid adherence of the section to the slide. A cold tissue section will not attach to a cold slide. The sections should adhere to the slides flat; folding will cause them to fall off the slides during wash steps.
- If cracks are noticed in the sections, increase the cryostat temperature by 1-5 °C to avoid this. It is particularly important to place tissue sections in close proximity to one another on the same slide. This will prevent wastage of FISH probes and reagents during the assay.
- Store tissue sections mounted onto glass slides in an air-tight container at -80 °C for up to 6 months.
NOTE: Keep the sections frozen at all times and avoid freeze thaw cycles, to prevent RNA degradation. Transport the slide box from inside the cryostat to the -80 °C freezer on dry ice.
- Set the cryostat temperature to -20 °C. Leave the OCT-embedded tissue and a cryostat chuck in the cryostat for ~30 minutes to allow for equilibration to the new temperature.
- Fixation of fresh frozen tissue
- On the day the FISH probe assay is to be performed, prepare 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.5 (4% PFA solution). Filter by passing through filter paper (Grade 1: 11 µm, Table of Materials) in a Buchner funnel or crucible filter.
CAUTION : PFA is harmful and toxic by skin contact or inhalation. All procedures with PFA solution should be performed in a fume hood cabinet. PFA solution waste should be disposed of carefully following institutional safety protocols. - Cool the 4% PFA solution to 4 °C. Transport the slide-mounted tissue from the -80 °C freezer in dry ice and immediately immerse it in the pre-chilled fixative for 15 minutes.
NOTE: It is important that this fixation step does not exceed 15 minutes as over-fixation will result in non-specific background labelling.
- On the day the FISH probe assay is to be performed, prepare 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.5 (4% PFA solution). Filter by passing through filter paper (Grade 1: 11 µm, Table of Materials) in a Buchner funnel or crucible filter.
- Dehydration of fresh frozen tissue
- Dehydrate tissue sections by submerging the slides in graded concentrations of ethanol. In a Coplin jar, first submerge in 50%, then 70% and finally absolute ethanol, for 5 minutes each at room temperature. Repeat the final absolute ethanol incubation a second time.
- Air dry slides and, outline the group of sections using a hydrophobic barrier pen, ensuring that the internal area is kept to a minimum.
NOTE: Make sure that the glass slide is completely dry before drawing the hydrophobic barrier. The hydrophobic barrier should surround the tissue sections completely without gaps and must be dry before further processing.
2. Sample preparation of fixed frozen brain tissue
- Transcardial perfusion fixation
- Euthanize mice by anesthetizing with sodium pentobarbital (70 mg/kg, i.p) followed by transcardial perfusion, first with 0.1 M PB then 4% PFA solution. Fix with 10 minutes of perfusion at 11-13 mL/min.
- Isolate the brain from the skull cavity following perfusion-fixation and submerge overnight in 4% PFA solution, at 4 °C.
- Tissue sectioning of fixed tissue
- Rinse the brain in sterile 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS) before removing the meningeal layers, with the aid of a dissecting microscope, using fine forceps.
- Cut the brain precisely into blocks (separate the brainstem from the forebrain prior to vibratome sectioning) using a brain matrix (Table of Materials). Specifically, cut the brainstem caudally at the pyramidal decussation and dissect away the cerebellum. Similarly, cut the forebrain immediately rostral to the optic chiasm.
- Secure the tissue onto a vibrating microtome chuck using cyanoacrylate and embed in 2% agar solution.
- Cut 30 µm thick tissue sections using a vibrating microtome and store cut sections in cryoprotectant solution (30% RNase free sucrose, 30% ethylene glycol, 1% polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-40), in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.4). Tissue sections may be stored in cryoprotectant at -20 °C for up to 6 months.
- Preparation of fixed sections prior to FISH
- On the day of FISH, wash free floating sections three times, for 10 minutes per wash, to remove the cryoprotectant solution. To wash, place sections in 0.1 M PBS in a 12 well cell culture plate and agitate on a rotating platform shaker (90 - 100 rpm).
- After washes, use a paintbrush to mount sections on glass microscopy slides and air dry for at least 2 hours.
NOTE: The sections should adhere flat onto the slides as any pronounced folds will cause them to detach during washes. - Using a hydrophobic barrier pen, draw a barrier around the sections to restrict the FISH reagents to the sections. Once more, it is important to minimize the internal area of the outline drawn with the barrier pen.
POSSIBLE BREAK POINT: The sections could be stored at room temperature, overnight, to continue the assay the next day.
3. FISH assay
NOTE: The rest of the protocol applies to both fresh frozen and fixed frozen tissue.
- Prepare the reagents and instruments for hybridization and amplification steps.
- Set a benchtop incubator and water bath to 40 °C.
- Prepare a humidified, light-protected chamber for incubating slides. Humidification prevents drying of tissues - slides are securely located above a moist reservoir. Ideally, the chamber is made of heavy-duty polystyrene, it is light-proof and airtight to maintain a saturated water vapor atmosphere. Closure of the chamber relies on minimal friction to avoid movement. We used a slide box lined with wet laboratory wipes (Table of Materials) at the bottom. Place the slide box inside the incubator to prewarm it to 40 °C.
- Warm the 50x Wash Buffer (Table of Materials) and probes to 40 °C for 10 minutes, using the water bath, then cool to room temperature.
- Prepare 1 L of 1x Wash Buffer from the 50x stock concentration.
- Prepare probe mixture (Table of Materials): the C1 probe is ready to use at stock concentration whereas C2 and C3 probes are shipped as 50x concentration and require dilution with the diluent supplied in the kit.
NOTE: Probe mixtures can be stored at 4 °C for up to 6 months.
- Protease treatment
- Incubate sections with Protease III (Table of Materials) at room temperature for 30 minutes.
NOTE: Ensure that Protease III and incubation reagents in downstream processes (probe mixture, amplification solutions, blocking buffer and antibody sera) cover the sections entirely. A pipet tip may be used to spread the reagent onto the section to cover the entire area inside the hydrophobic barrier. - Wash slides twice with 0.1 M PBS, for 2 min each time, in a large plastic square Petri dish. Here a 245 mm x 245 mm square bioassay dish was used (Table of Materials). Hold from one side of the dish and tilt gently 3-5 times. After washes, flick excess 0.1 M PBS from slide and immediately add the next reagent. Do not let tissue sections dry.
NOTE: During each wash, the slides are immersed in solution at room temperature. This is the workflow for all subsequent wash steps. The fixed 30 µm thick sections dislodge from slides more easily than 14 µm thick sections, be gentle during the washes.
- Incubate sections with Protease III (Table of Materials) at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- Hybridization and amplification
- After washing off the protease solution, place the slides in the humidified, prewarmed chamber. Incubate sections with probe mixture (Table of Materials) for 2 hours at 40 °C inside a benchtop incubator.
NOTE: Ensure there are at least 2 sections set aside for positive and negative control probes to assess sample RNA quality and optimal permeabilization. Positive control probes target house-keeping genes; here, these were a cocktail of RNAs targeting ubiquitin C (UBC; high-abundance), peptidylpropyl isomerase B (PPIB; moderate-abundance) and RNA polymerase 2a (POLR2A; low-abundance). Negative control probes target the bacterial 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate reductase (DapB) gene, which is normally absent in mouse brain samples. Positive DapB signal indicates non-specific signal and/or bacterial contamination of the sample. - Following hybridization with the probe mixture, the signal amplification steps consist of incubation with Amp 1-FL (30 minutes), then with Amp 2-FL (15 minutes), followed by Amp 3-FL (30 minutes) and finally Amp 4-FL (15 minutes) - each at 40 °C. Using the dropper bottles provided, cover tissue sections with amplification solution. Proceed to IHC assay following the last amplification step.
- Rinse slides with Wash Buffer twice for 2 minutes between probe hybridization and each amplification step.
- After washing off the protease solution, place the slides in the humidified, prewarmed chamber. Incubate sections with probe mixture (Table of Materials) for 2 hours at 40 °C inside a benchtop incubator.
4. IHC Assay
- IHC blocking step
- To prevent non-specific binding of antibodies, incubate the sections for 1 h at room temperature with blocking solution containing 10% normal horse serum, 0.3% Tween20 in 1x TBSm (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% merthiolate) following the FISH assay. Prepare primary antibodies in a dilution buffer containing 1x TBSm, 5% normal horse serum and 0.1% Tween20. Primary antibody suppliers are listed in the Table of Materials.
- Immunohistochemistry
- Remove excess blocking buffer by flicking the slide and incubate sections with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C.
- Wash slides 3 times (5 minutes each) with 1x TBSm and incubate with secondary antibody in diluent containing 1x TBSm, 1% normal horse serum and 0.1% Tween20 for 2 hours at room temperature. Secondary antibodies used in this protocol are listed in the Table of Materials.
- Wash slides 3 times with 1x TBSm (5 minutes each) before coverslipping with mounting medium with or without DAPI (Table of Materials).
5. Imaging
- Examine immunostaining under an epifluorescence microscope equipped with a camera (see Table of Material for details). Acquire representative images at 20x magnification and save as TIFF files.
- Export representative images into an image processing software (Table of Materials) for brightness/contrast adjustment to increase the clarity and to reflect true rendering.
6. OPTIONAL: Quantitative analysis of target transcripts
NOTE: This is a methods article and quantitative results are not provided. The method of quantification presented here is sourced from Dereli et al.10.
- Acquire images from the regions of interest as explained in 5.1 and apply the same microscope and camera settings (such as exposure time and light intensity) to all images of the same fluorophore.
- Plot the neuronal profiles using an image analysis software (Table of Materials).
- Align the sections with reference to Bregma level according to a stereotaxic brain atlas13.
- Apply the same brightness and contrast to all the images of the same fluorophore. Only consider the neurons with DAPI-stained nuclei.
- Manually count the number of mRNA, protein expressing, mRNA/mRNA, protein/protein and mRNA/protein coexpressing cells within the region of interest.
- To decrease bias in the experimental results, have the person quantifying experimental outcomes blinded to the experimental groups.
- Apply Abercrombie correction14 to total cell counts by using the following Abercombie equation:
Corrected cell count = manual cell count x section thickness / (section thickness + nuclear size)
For example, for 14 µm thick sections, the average nuclear width is calculated to be 7.7 ± 0.3 µm and average section thickness is 14 ± 1 µm based on 30 cells and 10 sections respectively in 5 animals10. According to the Abercrombie equation, corrected cell count would be manual cell count x 14/(14+7.7).

Figure 1: Parallel workflow of tissue pre-processing steps for both fresh-frozen and paraformaldehyde fixed tissue. Processing steps for fresh-frozen tissue are displayed in the red outlined boxes, whereas those for paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixed tissue are displayed in the blue outlined boxes. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
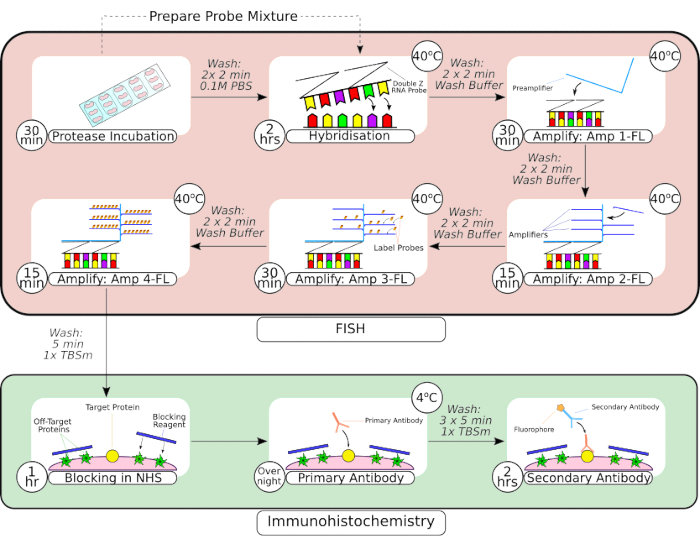
Figure 2: Summary of combined FISH probe and immunohistochemistry procedure. Following tissue pre-processing, the slide mounted tissue is encircled using a hydrophobic barrier pen, as seen in the first frame, and incubated in a protease solution at room temperature. Following washes, tissue is transferred to a benchtop incubator for hybridization for 2 hours before sequential amplification steps. The in situ hybridization system utilizes a proprietary 'Z probe' design, preamplifiers and amplifiers as seen in frames 3-66. Once tissue has undergone FISH probe processing, it is washed before blocking with normal horse serum. The primary antibody incubation is carried out overnight at 4 °C to maximize antibody-antigen binding. The secondary antibody incubation (2 hours) was carried out at room temperature. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
Here, we outline a method for combining multiplex FISH with fluorescent IHC to localize mRNA expression for GalR1 and GlyT2 using fresh-frozen and paraformaldehyde fixed tissues respectively in the mouse NTS. A pipeline of the tissue processing, FISH and IHC procedures described in the methods is displayed in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Table 1 provides a summary of the FISH probe and antibody combinations used in each figure.
Discussion
In the neurosciences, FISH and IHC are routinely used to investigate the spatial organization and functional significance of mRNA or proteins within neuronal subpopulations. The protocol described in this study enhances the capacity for simultaneous detection of mRNAs and proteins in brain sections. Our combined multiplex FISH-IHC assay enabled phenotypic identification of distinct neuronal subpopulations in the NTS in both fresh frozen and fixed brain preparations. FISH-IHC in fixed frozen tissue preparations produced r...
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Australian Research Council Discovery Project grant DP180101890 and Rebecca L Cooper Medical Research Foundation project grant PG2018110
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| ANIMALS | |||
| C57BL/6 mouse | Australian BioResources, Moss Vale | MGI: 2159769 | |
| Phox2b-eGFP mouse | Australian BioResources, Moss Vale | MGI: 5776545 | |
| REAGENTS | |||
| Cyanoacrylate | Loctite | ||
| Ethylene Glycol | Sigma-Aldrich | 324558 | |
| Heparin-Sodium | Clifford Hallam Healthcare | 1070760 | Consult local veterinary supplier or pharmacy. |
| Lethabarb (Sodium Pentabarbitol) Euthanasia Injection | Virbac (Australia) Pty Ltd | N/A | Consult a veterinarian for local pharmaceutical regulations regarding Sodium Pentabarbitol |
| Molecular grade agarose powder | Sigma Aldrich | 5077 | |
| OCT Compound, 118mL | Scigen Ltd | 4586 | |
| Paraformaldehyde, prilled, 95% | Sigma-Aldrich | 441244-1KG | |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average mol wt 40,000 (PVP-40) | Sigma-Aldrich | PVP40 | |
| ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant | Invitrogen | P36930 | With or without DAPI |
| RNAscope Multiplex Fluorescent Reagent Kit (up to 3-plex capability) | Advanced Cell Diagnostics, Inc. (ACD Bio) | ADV320850 | Includes 50x Wash buffer and Protease III |
| RNase Away | Thermo-Fisher Scientific | 7003 | |
| Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane | Sigma-Aldrich | 252859 | |
| Tween-20, for molecular biology | Sigma-Aldrich | P9416 | |
| EQUIPMENT | |||
| Benchtop incubator | Thermoline scientific micro incubator | Model: TEI-13G | |
| Brain Matrix, Mouse, 30g Adult, Coronal, 1mm | Ted Pella | 15050 | |
| Cryostat | Leica | CM1950 | |
| Drawing-up needle (23 inch gauge) | BD | 0288U07 | |
| Hydrophobic Barrier Pen | Vector labs | H-4000 | |
| Kimtech Science Kimwipes Delicate Task Wipes | Kimberley Clark Professional | 34120 | |
| Olympus BX51 | Olympus | BX-51 | |
| Peristaltic pump | Coleparmer Masterflex | L/S Series | |
| Retiga 2000R Digital Camera | QImaging | RET-2000R-F-CLR | colour camera |
| SuperFrost Plus Glass Slides (White) | Thermo-Fisher Scientific | 4951PLUS4 | |
| Vibrating Microtome (Vibratome) | Leica | VT1200S | |
| Whatman qualitative filter paper, Grade 1, 110 mm diameter | Merck | WHA1001110 | |
| SOFTWARES | |||
| CorelDRAW | Corel Corporation | Version 7 | |
| FIJI (ImageJ Distribution) | Open Source/GNU General Public Licence (GPL) | N/A | ImageJ 2.x: Rueden, C. T.; Schindelin, J. & Hiner, M. C. et al. (2017), "ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data", BMC Bioinformatics 18:529, PMID 29187165, doi:10.1186/s12859-017-1934-z and Fiji: Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I. & Frise, E. et al. (2012), "Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis", Nature methods 9(7): 676-682, PMID 22743772, doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019 |
| PRIMARY ANTIBODIES | |||
| Anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase Antibody | Millipore Sigma | AB1542 | Sheep polyclonal (1:1000 dilution), RRID: AB_90755 |
| Anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase Antibody, clone LNC1 | Millipore Sigma | MAB318 | Mouse monoclonal (1:1000 dilution), RRID: AB_2201528 |
| Anti-Vesicular Acetylcholine Transporter (VAchT) Antibody | Sigma-Aldrich | ABN100 | Goat polyclonal (1:1000 dilution), RRID: AB_2630394 |
| GFP Antibody | Novus Biologicals | NB600-308 | Rabbit polyclonal (1:1000 dilution), RRID: AB_10003058 |
| Phox2b Antibody (B-11) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-376997 | Mouse monoclonal (1:1000 dilution), RRID: AB_2813765 |
| SECONDARY ANTIBODIES | |||
| Alexa Fluor 488 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (min X Bov, Ck, Gt, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rat, Shp Sr Prot) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 711-545-152 | Donkey anti-Rabbit (1:400 dilution), RRID: AB_2313584 |
| AMCA AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) (min X Ck, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rb, Rat Sr Prot) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 713-155-147 | Donkey anti-Sheep (1:400 dilution), RRID: AB_AB_2340725 |
| Cy5 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Goat IgG (H+L) (min X Ck, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rb, Rat Sr Prot) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 705-175-147 | Donkey anti-Goat (1:400 dilution), RRID: AB_2340415 |
| Cy5 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) (min X Bov, Ck, Gt, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Rb, Rat, Shp Sr Prot) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 715-175-151 | Donkey anti-Mouse (1:400 dilution), RRID: AB_2619678 |
| Cy5 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Sheep IgG (H+L) (min X Ck, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rb, Rat Sr Prot) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 713-175-147 | Donkey anti-Sheep (1:400 dilution), RRID: AB_2340730 |
| RNASCOPE PROBES | |||
| Galanin Receptor 1 oligonucleotide probe | ACDBio | 448821-C1 | targets bp 482 - 1669 (Genebank ref: NM_008082.2) |
| Glycine transporter 2 oligonucleotide probe | ACDBio | 409741-C3 | targets bp 925 - 2153 (Genebank ref: NM_148931.3) |
| Phox2b oligonucleotide probe | ACDBio | 407861-C2 | targets bp 1617 - 2790 (Genebank ref: NM_008888.3) |
References
- Wang, F., et al. RNAscope: a novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Journal of Molecular Diagnostics. 14 (1), 22-29 (2012).
- Annese, T., et al. RNAscope dual ISH-IHC technology to study angiogenesis in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Histochemistry and Cell Biology. 153 (3), 185-192 (2020).
- Morrison, J. A., McKinney, M. C., Kulesa, P. M. Resolving in vivo gene expression during collective cell migration using an integrated RNAscope, immunohistochemistry and tissue clearing method. Mechanisms of Development. 148, 100-106 (2017).
- Gross-Thebing, T., Paksa, A., Raz, E. Simultaneous high-resolution detection of multiple transcripts combined with localization of proteins in whole-mount embryos. BMC Biology. 12, 55 (2014).
- Stempel, A. J., Morgans, C. W., Stout, J. T., Appukuttan, B. Simultaneous visualization and cell-specific confirmation of RNA and protein in the mouse retina. Molecular Vision. 20, 1366-1373 (2014).
- Kersigo, J., et al. A RNAscope whole mount approach that can be combined with immunofluorescence to quantify differential distribution of mRNA. Cell and Tissue Research. 374 (2), 251-262 (2018).
- Grabinski, T. M., Kneynsberg, A., Manfredsson, F. P., Kanaan, N. M. A method for combining RNAscope in situ hybridization with immunohistochemistry in thick free-floating brain sections and primary neuronal cultures. PLoS One. 10 (3), 0120120 (2015).
- Baleriola, J., Jean, Y., Troy, C., Hengst, U. Detection of axonally localized mRNAs in brain sections using high-resolution in situ hybridization. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (100), e52799 (2015).
- Fe Lanfranco, M., Loane, D. J., Mocchetti, I., Burns, M. P., Villapol, S. Combination of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and immunofluorescence imaging for detection of cytokine expression in microglia/macrophage cells. Bio-Protocol. 7 (22), (2017).
- Dereli, A. S., Yaseen, Z., Carrive, P., Kumar, N. N. Adaptation of respiratory-related brain regions to long-term hypercapnia: focus on neuropeptides in the RTN. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 13, 1343 (2019).
- Lazarenko, R. M., et al. Acid sensitivity and ultrastructure of the retrotrapezoid nucleus in Phox2b-EGFP transgenic mice. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 517 (1), 69-86 (2009).
- Gage, G. J., Kipke, D. R., Shain, W. Whole animal perfusion fixation for rodents. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (65), e3564 (2012).
- Paxinos, G., Franklin, K. B. . The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. , (2004).
- Abercrombie, M. Estimation of nuclear population from microtome sections. Anatomical Records. 94, 239-247 (1946).
- Kerr, N., et al. The generation of knock-in mice expressing fluorescently tagged galanin receptors 1 and 2. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences. 68, 258-271 (2015).
- Kachidian, P., Pickel, V. M. Localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in neuronal targets and efferents of the area postrema in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 329 (3), 337-353 (1993).
- Stornetta, R. L., et al. Expression of Phox2b by brainstem neurons involved in chemosensory integration in the adult rat. Journal of Neuroscience. 26 (40), 10305-10314 (2006).
- Gilmor, M. L., et al. Expression of the putative vesicular acetylcholine transporter in rat brain and localization in cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Journal of Neuroscience. 16 (7), 2179-2190 (1996).
- Fisher, J. M., Sossin, W., Newcomb, R., Scheller, R. H. Multiple neuropeptides derived from a common precursor are differentially packaged and transported. Cell. 54 (6), 813-822 (1988).
- Towle, A. C., Lauder, J. M., Joh, T. H. Optimization of tyrosine-hydroxylase immunocytochemistry in paraffin sections using pretreatment with proteolytic-enzymes. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 32 (7), 766-770 (1984).
- Biancardi, V., et al. Mapping of the excitatory, inhibitory, and modulatory afferent projections to the anatomically defined active expiratory oscillator in adult male rats. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 529 (4), 853-884 (2021).
- Matthews, D. W., et al. Feedback in the brainstem: an excitatory disynaptic pathway for control of whisking. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 523 (6), 921-942 (2015).
- Ramos-Vara, J. A. Principles and methods of immunohistochemistry. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1641, 115-128 (2017).
- Shi, S. R., Key, M. E., Kalra, K. L. Antigen retrieval in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: an enhancement method for immunohistochemical staining based on microwave oven heating of tissue sections. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 39 (6), 741-748 (1991).
- Yamashita, S., Katsumata, O. Heat-induced antigen retrieval in immunohistochemistry: mechanisms and applications. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1560, 147-161 (2017).
- Yamashita, S., Okada, Y. Mechanisms of heat-induced antigen retrieval: analyses in vitro employing SDS-PAGE and immunohistochemistry. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 53 (1), 13-21 (2005).
- Yamashita, S. Heat-induced antigen retrieval: mechanisms and application to histochemistry. Progress in Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 41 (3), 141-200 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved