A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Using the GAL4-UAS System for Functional Genetics in Anopheles gambiae
In This Article
Summary
The bipartite GAL4-UAS system is a versatile tool for modification of gene expression in a controlled spatiotemporal manner which permits functional genetic analysis in Anopheles gambiae. The procedures described for using this system are a semi-standardized cloning strategy, sexing and screening of pupae for fluorescent protein markers and embryo fixation.
Abstract
The bipartite GAL4-UAS system is a versatile and powerful tool for functional genetic analysis. The essence of the system is to cross transgenic 'driver' lines that express the yeast transcription factor GAL4 in a tissue specific manner, with transgenic 'responder' lines carrying a candidate gene/RNA interference construct whose expression is controlled by Upstream Activation Sequences (UAS) that bind GAL4. In the ensuing progeny, the gene or silencing construct is thus expressed in a prescribed spatiotemporal manner, enabling the resultant phenotypes to be assayed and gene function inferred. The binary system enables flexibility in experimental approaches to screen phenotypes generated by transgene expression in multiple tissue-specific patterns, even if severe fitness costs are induced. We have adapted this system for Anopheles gambiae, the principal malaria vector in Africa.
In this article, we provide some of the common procedures used during GAL4-UAS analysis. We describe the An. gambiae GAL4-UAS lines already generated, as well as the cloning of new responder constructs for upregulation and RNAi knockdown. We specify a step by step guide for sexing of mosquito pupae to establish genetic crosses, that also includes screening progeny to follow inheritance of fluorescent gene markers that tag the driver and responder insertions. We also present a protocol for clearing An. gambiae embryos to study embryonic development. Finally, we introduce potential adaptions of the method to generate driver lines through CRISPR/Cas9 insertion of GAL4 downstream of target genes.
Introduction
The bipartite GAL4-UAS system is the workhorse of functional characterization of genes in the insect model organism Drosophila melanogaster1,2,3. To use the GAL4-UAS system, transgenic driver lines, expressing the yeast transcription factor GAL4 under control of a regulatory sequence, are crossed with responder lines carrying a gene of interest or RNA interference (RNAi) construct controlled by an Upstream Activation Sequence (UAS) recognized by GAL4. The progeny of this cross express the transgene of interest in a spatiotemporal pattern dictated by the promoter controlling GAL4 expression (Figure 1). Phenotypes displayed by progeny of driver-responder crosses can be assessed to elucidate the function of candidate genes. Although D. melanogaster has been used to examine genes from other organisms4,5,6,7, the GAL4-UAS system has now been adapted for use in insects of medical and agricultural importance to provide direct analysis in the species of interest 8,9,10,11,12,13,14.
In the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, the GAL4-UAS system was first tested by cell line co-transfection9. Multiple constructs were assayed for efficiency in different pairwise combinations and found that 14 tandemly repeated UAS supplemented with a small artificial intron (UAS-14i) displayed the widest range of activation potential when used with a panel of GAL4 drivers. To demonstrate in vivo functionality, these constructs were then used to create two separate transgenic An. gambiae lines by PiggyBac transformation8: a driver line carrying GAL4 driven by a midgut specific promoter, and a responder line containing both the luciferase and enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) genes under regulation of UAS sequences. Gut specific luciferase activity and fluorescence in the progeny indicated that the system was efficient in Anopheles. Since then, driver lines have been created expressing transgenes in other tissues important for vectorial capacity and insecticide resistance, including oenocytes15 and hemocytes16, and in a close to ubiquitous pattern10. Numerous UAS lines have also been generated to assay genes thought to be involved in metabolism and sequestration mediated insecticide resistance, cuticular hydrocarbon synthesis and to fluorescently tag different cell and tissue types (Table 1). For the responder lines, site-directed integration of the transgene is now performed by ΦC31 catalyzed recombination cassette exchange17,18 to fix the genomic context of the UAS regulated genes. In this way, transgene expression is normalized regarding genomic insertion location, allowing for more accurate comparison of the phenotypic effects of different candidate genes.
The responder lines created to date are designed to either express the transgene either at elevated levels or to reduce gene expression through RNA interference (RNAi). Usually cDNA clones are fused to the UAS sequence to generate suitable expression plasmids, however full genomic sequences are also feasible assuming that they are not too large for cloning. To generate silencing constructs, we have used three different methods to obtain suitable tandem inverted sequences that form hairpin dsRNA that stimulates RNAi. These have included fusion PCR, asymmetric PCR and commercial synthesis of hairpin constructs. Common to each method is the inclusion of an intron sequence between the inverted sequences to provide cloning stability. Responder plasmids into which a gene of interest/RNAi construct can be inserted have been developed15. These plasmids also carry the required ΦC31 attB sites for RMCE (described in Adolfi accompanying JoVE paper which describes the RCME technique in detail). Protocols covering the important steps required when selecting the sequence for insertion into one of these plasmids for overexpression are included in this manuscript. Additionally, two protocols for RNAi hairpin construct creation are described and illustrated.
When creating new lines, identification of rare transgenic individuals is crucial to breed from to establish and maintain transgenic colonies. Most importantly for the GAL4-UAS system there is a necessity to distinguish the responder and driver lines to establish crosses and identify individual progeny that carry both transgenes. This is achieved by using different dominant selectable marker genes linked to the driver and responder cassettes. Most commonly these are fluorescent marker genes that are clearly distinguishable using optical filters (e.g., eYFP, eCFP, dsRed). It is important that markers are expressed in a known and reliable spatiotemporal pattern as this makes identification of abnormalities and contamination easier. Fluorescent marker gene expression is routinely regulated by the synthetic 3xP3 promoter, which causes eye and ventral ganglia specific expression in all stages of An. gambiae development19. Fluorescent markers controlled by 3xP3 are included in all transformation plasmids described in this article. A protocol detailing the common methods used to screen fluorescent An. gambiae pupae GAL4-UAS lines is included here.
One of the key elements of the GAL4-UAS system is the necessity to cross the differentially marked driver and responder lines. To do this male and females from each line must be separated prior to mating. Adults are readily distinguishable by sight, however, for establishing genetic crosses it is sensible to separate the sexes prior to adult emergence to ensure that mating has not occurred. The general size difference between male and female An. gambiae pupae is too variable to be an efficient and dependable method of sex determination20. Instead clear morphological differences in the external genitalia provide a reliable basis for sexing in An. gambiae. In this article, we describe a dependable method for sexing An. gambiae pupae to set up appropriate crosses.
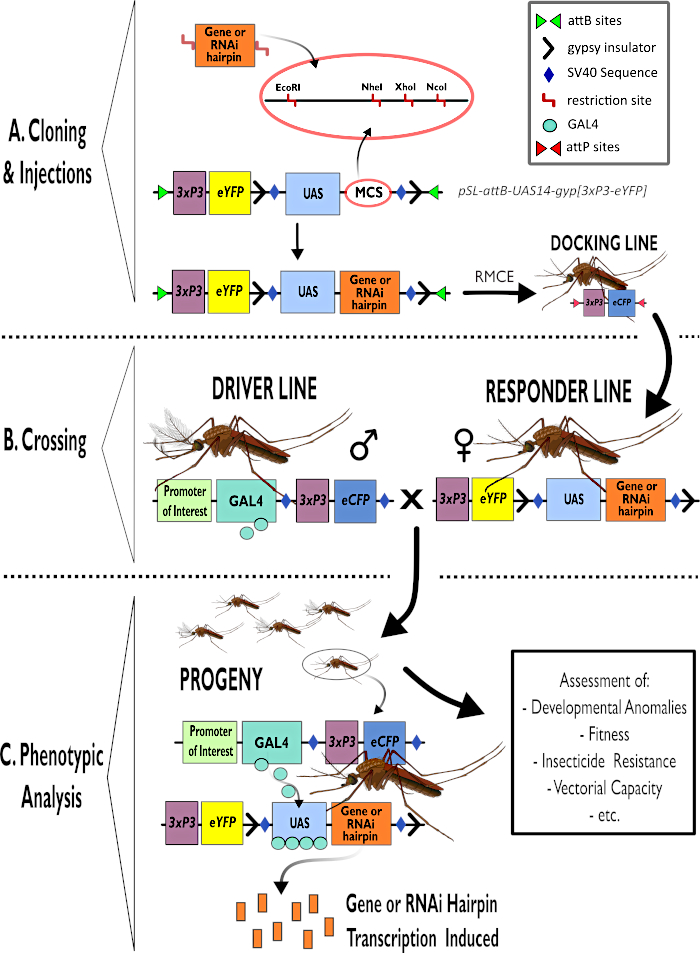
Figure 1 - Diagrammatic representation of process for using the bipartite GAL4-UAS System in Anopheles gambiae. (A) The major components of an example vector (pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xp3-eYFP]) are depicted, detailing the available restriction sites (EcoRI, NheI, XhoI and NcoI) within the multiple cloning sites that are suitable for use to insert the hairpin construct or coding sequence for the gene of interest. The structure of the docking line is also depicted. (B) The crossing step is illustrated indicating the use of males from the driver line (carrying GAL4 driver by a promoter of interest and eCFP driven by the 3xP3 promoter) and females from the responder line (carrying the gene of interest or hairpin construct controlled by a UAS promoter and an eYFP marker controlled by the 3xP3 promoter). (C) A diagrammatic representation of GAL4 driving expression of the gene of interest in the progeny of the cross in B and a list of some of the typical phenotypes that are assessed. Abbreviations: Multiple Cloning Site (MCS), Recombinase mediated cassette exchange (RMCE), Upstream Activator Sequence (UAS), enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP), enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (eCFP). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
It is the use of crosses that provides the bipartite nature of the GAL4-UAS system, which has distinct advantages over more linear approaches. For example, many more combinations of driver and responder lines can be assessed than would be feasible if a new transgenic line had to be generated and maintained for each promoter/gene combination. More importantly, it allows the analysis of genes that produce lethal or sterile phenotypes when their expression is perturbed which are difficult to create/maintain in a linear system. Such lethal phenotypes can manifest at all developmental stages, depending on the gene function and spatiotemporal expression, but are most often observed during embryonic development. Visualizing mosquito embryo development requires the clearing of the opaque chorion which coats the eggs. Following methods described in Trpiš (1970)21 and Kaiser et al. (2014)22, we describe the protocols we use to fix embryos, whilst maintaining structural integrity, and bleaching to clear the endochorion that allows microscopic visualization and imaging.
Protocol
1. Design and construction of UAS constructs
- Design and assembly of vectors for candidate gene expression
- Determine the sequence to be used for candidate gene upregulation.
- Sequence the cDNA/gDNA from the strain of interest and compare it to the published sequence to verify its identity and identify potential SNPs and restriction sites for diagnostic digest.
- Ensure that the forward primer used for gene amplification covers the native Kozak sequence and start codon, where appropriate. A primer with ~10 bp binding upstream of the start codon will encompass the Kozak sequence.
- Include the stop codon in the fragment amplified from the reverse primer in most circumstances. Use 3' termination sequences provided in the plasmid vectors described, or amplify from candidate gene genomic sequences.
- Order commercial sequences with specific codon bias if desired.
- Use standard subcloning procedures to insert gene cassettes in to UAS plasmid vectors, e.g., pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xP3-eYFP]15 (Figure 1) for both upregulation and RNAi constructs.
- Produce transgenic mosquitoes created using ΦC31 recombination mediated cassette exchange10,17,18,23.
- Determine the sequence to be used for candidate gene upregulation.
- Creation of RNAi hairpin constructs: single step amplification using asymmetric PCR15,24
- Extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from adult female An. gambiae carrying the desired candidate gene using the Livak method25.
- Design the forward primer to bind to target exon at the 5' of the desired fragment directed towards the neighboring intron. Design the 3' end of a bridge primer to bind to the end of the preceding exon to amplify the intron. The 5' end is complementary to a small fragment of the target exon immediately after the intron.
- Run an asymmetric PCR reaction as is described in Xiao (2006)24 (Figure 2).
- Clone the purified PCR product into a suitable vector carrying the UAS promoter (e.g., pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xP3-eYFP]15).
NOTE: Enzymes within the multiple cloning site which are appropriate for pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xP3-eYFP] cloning15 and the next steps required are indicated in Figure 1. Single enzyme digest is essential as only one restriction site is added. Dephosphorylation of the plasmid will improve cloning efficiency.
- Extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from adult female An. gambiae carrying the desired candidate gene using the Livak method25.
- Construction of RNAi hairpin constructs: Fusion PCR of cDNA and gDNA15
- Extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from adult female An. gambiae carrying the desired candidate gene using the Livak method25.
- Include gDNA in a PCR reaction to amplify the target area of the exon and intron sequences together (Figure 2).
- Design the 3' end of the forward primer to bind to the reverse target exon sequence to amplify towards the target intron sequence and the 5' end to carry a restriction site to facilitate cloning.
- Design reverse primer (1) to bind to the 5' end of the intron and the 5' end overhang carries the first bases of the forward sequence of the neighboring exon. This overhang is used in the fusion PCR.
- Purify the desired reaction product.
- Extract RNA, remove DNA using DNase's and prepare cDNA from adult female An. gambiae carrying the desired candidate gene following manufacturer's protocols.
- Use cDNA in an PCR reaction to amplify the target area of the exon only (Figure 2).
- Design forward primer (2) so that the 3' end binds at the 3' end of the complementary target exon sequence and the 5' end of the primer carries a restriction site for use in cloning.
NOTE: The forward primer from 1.3.1.2 can be used again in this second reaction. However, this will mean that a single enzyme digest is essential. Using a second forward primer with a different restriction site will permit double digest which may increase cloning efficiency. - Design reverse primer (2) - the 3' end binds to the 5' end of the neighboring exon amplifying the target exon. The 5' end binds to the 3' end of the introns forward strand. This overhang is used in the fusion PCR.
- Purify the desired reaction product.
- Design forward primer (2) so that the 3' end binds at the 3' end of the complementary target exon sequence and the 5' end of the primer carries a restriction site for use in cloning.
- Include the products of step 1.3.1 and 1.3.2 as templates for a fusion PCR reaction using standard concentrations with Forward primers 1 and 2. Purify the desired product.
- Digest the purified product to generate the overhangs for cloning. Clone into a suitable vector downstream of UAS promoter. Appropriate enzymes for pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xP3-eYFP] cloning15 and the next steps required are indicated in Figure 1.
- Extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from adult female An. gambiae carrying the desired candidate gene using the Livak method25.
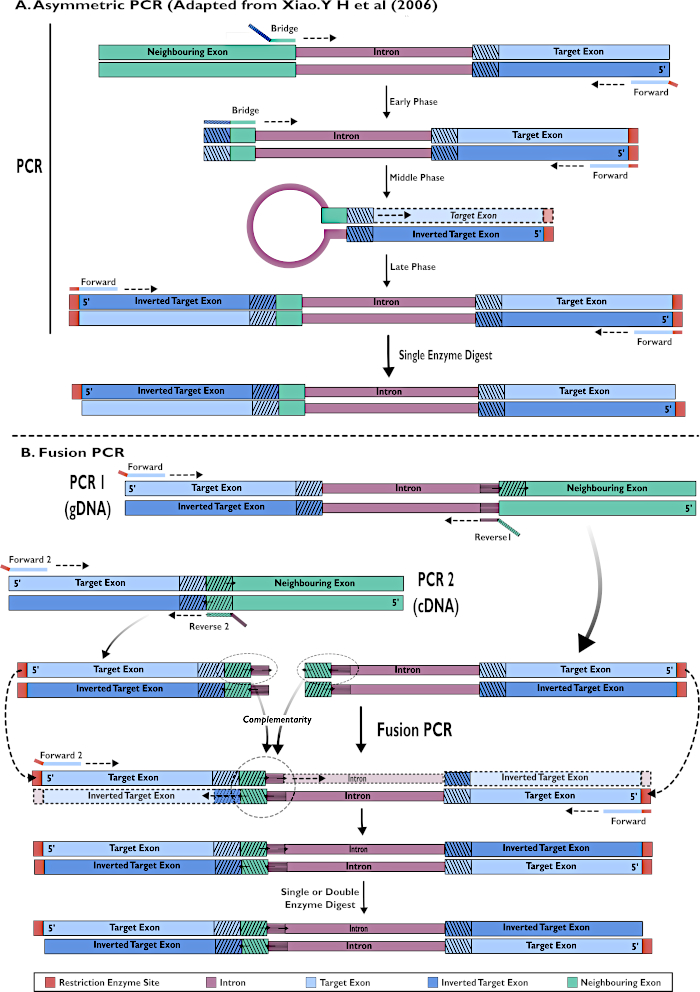
Figure 2 - Diagrammatic representation of the creation of RNAi constructs for insertion into pSL-attB-UAS14-gyp[3xP3-eYFP] by two methods: (A) Single step asymmetric PCR (adapted from Xiao. Y H et al (2006) and (B) multiple step fusion PCR. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. An. gambiae pupae screening
- Collection of pupae for microscopic characterization
NOTE: Throughout these protocols water refers to distilled water supplemented with 0.01% pond salt.- Rear An. gambiae mosquitoes using standard protocols (e.g.,MR426) to pupal stage.
CAUTION: Take care not to injure pupae throughout this process. - Collect pupae onto a clear flat dish suitable for use with a stereomicroscope (e.g., a 100 x 15 mm plastic Petri dish, avoiding the edges).
NOTE: To collect pupae we use a 3 mL plastic Pasteur pipette with about 10 mm cut from the end to widen the end and prevent injury to the mosquitoes. Screening and sexing can be completed on individuals, however, this is very slow. It is recommended to carry out screening and sexing on groups of 50-200 pupae (the size of group possible is limited by the size of dish used and is subject to personal preference). If a large number are being screened, efficiency can be increased by first aligning pupae about 4 to 5 deep in lines, and moving the target pupae out of this line. - Using a Pasteur pipette, carefully remove almost all the water from around the pupae. Leave just enough water around pupae so they are effectively immotile but can be moved easily with a fine brush. If they become difficult to move, then add more water.
NOTE: When enough water is removed, the pupae will lie on their side, permitting visualization of eyes for fluorescence detection and identification of dimorphic genitalia (Figure 4DE).
CAUTION: Ensure pupae do not desiccate. If only a very small volume of water is left it can reduce further with the heat from the lamp of the microscope and when split between pools of pupae. Additional water sometimes must be added during the process using a 3 mL Pasteur pipette to the desired group(s).
- Rear An. gambiae mosquitoes using standard protocols (e.g.,MR426) to pupal stage.
- Identification of fluorescent markers in pupae
NOTE: The use of a low magnification stereoscope allows wide field screening, sorting can be done on an inverted compound microscope, but has to be done individually.- When screening for a fluorescent marker it is first crucial to know the expected patterns of expression and inheritance. Consider the following:
- Color(s): determine which filter(s) to visualize the expression.
- Spatiotemporal expression pattern: Understand where and in what life stage you expect to see expression.
- Ratio of different phenotypes: establish what percentage of the population should carry the markers of interest.
- Conduct fluorescent screening in darkness, as even low light can interfere with resolution of fluorescence. However, use a lamp beside the stereoscope when light is required for other manipulations.
CAUTION: Ensure that the workspace around the fluorescent stereoscope is clear prior to turning off the lights. - Turn on fluorescent bulb and leave to warm for manufacturer's recommended period (Normally 10-15 min). Select the required filter on the fluorescent stereoscope and check that there is a colored beam of light visible that is directed at the center of the stage plate. If this is not visible or is very faint the fluorescent bulb may not have fully warmed, the shutter is closed, or the microscope optics are not well aligned.
- Using white light, center the pupae in the field of view and bring them into focus. This magnification may need to be changed when switching between different filters depending on the fluorescence intensity.
- Using a fine detailing paint brush ensure that the pupae examined do not overlap.
- Turn off the white light of the stereoscope and use the fine focus to bring the area of the pupae carrying the phenotype of interest into focus. The fluorescent pattern should be visible. Examples of 3xP3 promoter-controlled fluorescence are provided in Figure 3.
- Use the lowest magnification at which the expected fluorescent phenotype can be reliably distinguished from individuals with no fluorescene.
- For strains with bright fluorescence use a low intensity brightfield light as well while screening, if the fluorescent signal is still clearly identifiable.
- When finished primary screening, rapidly scan populations under other filters to detect potential contamination.
CAUTION: Ensure that there is a clear distance between the groups of sorted pupae to prevent contamination by pupae movement. Be aware that the size of the groups will change as pupae are sexed and that distances can appear bigger when looking under magnification. Take particular care when the pools are not within the field of view.
- When screening for a fluorescent marker it is first crucial to know the expected patterns of expression and inheritance. Consider the following:
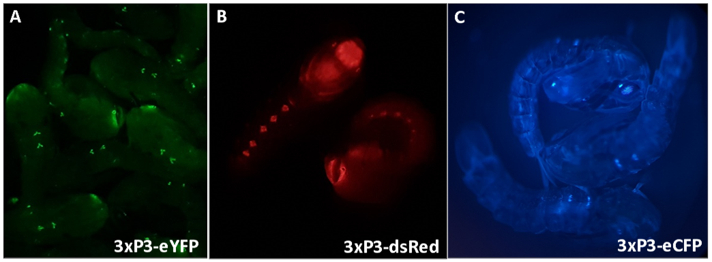
Figure 3 - Anopheles gambiae pupae expressing fluorescent markers driven by the 3xP3 promoter (A) eYFP, (B) dsRed and (C) eCFP. Magnification: A=16X, B,C=20X.
- Sexing Pupae
- Collect pupae. Remove excess water, but provide sufficient so that the anal paddles part slightly from the genitalia to aid visualization and morphological characterization (Figure 4D,E).
- If any pupa/e are not on their side, use a fine detailing paint brush to gently turn the pupa and move the anal paddles so that external genitalia can be identified.
- Separate pupae based on distinctive external genitalia; males have a long tube that extrudes from the final dorsal segment approximately half the length of the anal paddles (Figure 4B). The external genitalia of female pupae are considerably shorter and bifurcate (Figure 4A).
NOTE: On occasion, if the 4th instar larval exoskeleton remains attached or the external genitalia are damaged (Figure 4C), confident identification of the sex is more difficult. When the sex of a pupa is not clear, it is best practice to discard it. If the individual is to be kept, the pupa should be allowed to emerge in isolation and its sex determined using adult morphological features. It is likely that if its genitalia are damaged the individual may not mate successfully. - Make a pool for each sex at the opposite end of the dish to the unsexed pool, moving identified pupae across the dish using a fine detailing paint brush. Label the underside of the dish where the two pools will be gathered to identify them later.
- When both sexing and fluorescent screening is required, perform fluorescent screening first, since it is the quicker process of the two.
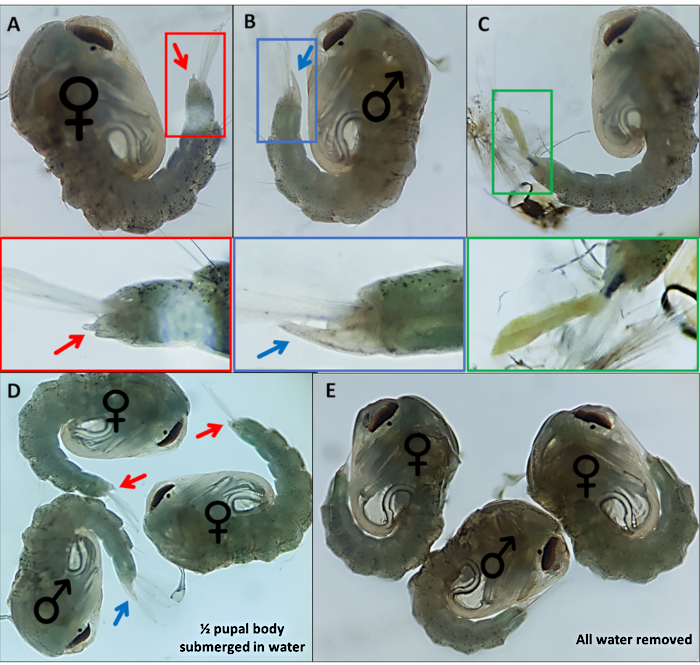
Figure 4 - Sexing Anopheles gambiae pupae. Individual pupae indicating the external genitalia of (A) a female (B) a male and (C) an individual which cannot be readily identified due to incomplete detachment of the larval exoskeleton. Enlarged images below highlighting the external genitalia. Pupae with ♀ (female) and ♂ (male) indicating the external genitalia of pupae with (D) ~50% of the pupa submerged in water and with (E) all water removed highlighting the difference in ease of visualization of the external genitalia. Magnification: A,B,C=40x, D,E=30x. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Sex confirmation as adults
- Until a very low error rate has been demonstrated, confirm pupae sexing by adult morphology after emergence. Separate sexed pupae into groups of 10 or less in a clear 20 mL tube with a few mL of water, sealing with a ball of cotton wool, labelled with the expected sex and allow to emerge overnight.
NOTE: As adults are transferred the following morning it is not necessary to supply emerging adults with food. - Confirm the sex of emerged adults using morphological features the following day.
- If any males are present in the female collections, discard the females, in case mating has already occurred.
- If any females are present in male collection, remove the female/s and keep the males for crossing.
- Until a very low error rate has been demonstrated, confirm pupae sexing by adult morphology after emergence. Separate sexed pupae into groups of 10 or less in a clear 20 mL tube with a few mL of water, sealing with a ball of cotton wool, labelled with the expected sex and allow to emerge overnight.
- Setting Up GAL4-UAS system crosses
- Aspirate the desired number of male and female adults from the tubes in step 2.4 into a cage or small bucket set up in the standard manner for An. gambiae rearing.
NOTE: Take care not to damage the adults during this transfer. - Use approximately 50 females with an equal number of males, when ~2000 adults are required from the progeny.
NOTE: Where a cross is to be fed multiple times to generate multiple batches up to 200 of each sex may be set up in 30cm x 30cm x 30cm cages. When only a small number of females (<20) are available for the cross, we add ~4x the number of males to increase the likelihood of successful mating. - Blood feed the crossed females and rear progeny to appropriate stage, following standard protocols26, to conduct phenotypic assessment (e.g., insecticide resistance, vectorial capacity and fitness cost assays).
- Where maternal effect of transgene expression is likely, set up reciprocal crosses of the driver and responder lines and assay expected phenotype.
NOTE: Crosses using 'heterozygous' or mixed populations of driver and responder lines, produce progeny with each of 4 possible genotypes. This provides wild type, UAS only and GAL4 only controls, as well as the transheterozygotes GAL4-UAS with which to analyze phenotype. If homozygous populations are crossed, set up additional crosses to provide appropriate controls to compare phenotypes. The progeny should be screened as above separating progeny carrying both or only either marker, as well as negatives, for phenotypic assessment.
- Aspirate the desired number of male and female adults from the tubes in step 2.4 into a cage or small bucket set up in the standard manner for An. gambiae rearing.
- Establishing homozygous populations from lines generated through RCME carrying alternative fluorescent markers
NOTE: It is essential that the fluorescent marker of both lines is present at the same genomic location and they are completely distinguishable.- Set up a parental cross of approximately 200 adults with equal numbers of differentially marked males of one line and females of the other line following screening to select individuals displaying correct fluorescence and sex, as described above. Around one-week later blood feed the cross using established protocols26.
- Rear the F1 progeny to pupae using standard protocols and collect pupae as described previously.
- Screen for fluorescence selecting those carrying both parental markers (transheterozygous). Set up a F1 intercross with these pupae.
- One week later, blood feed the F1 females and rear progeny to pupal stage following standard protocols.
- Screen the F2 pupae selecting those which display ONLY one of the markers. These will be homozygous for the insertion. Only 25% of the progeny will be homozygous for each insertion, so ensure that enough progeny are reared to provide a stock cage (400-500).
NOTE: The selection of transheterozygous progeny must be entirely rigorous otherwise the process becomes contaminated, and complete homozygosity may not be achieved. Double check all the progeny selected for the F1 intercross.
- Set up a parental cross of approximately 200 adults with equal numbers of differentially marked males of one line and females of the other line following screening to select individuals displaying correct fluorescence and sex, as described above. Around one-week later blood feed the cross using established protocols26.
3. An. gambiae embryo clearing protocol
- Blood feeding and maintenance
- Rear An. gambiae mosquitoes to adults following standard protocols (e.g.,MR4).
- Blood feed 5-7 day old female adults, ensuring most are fully engorged.
CAUTION: Throughout this protocol working quickly is essential to ensure that eggs are not allowed to desiccate.
- Induced egg laying
- 3 days after blood feeding collect eggs through induced laying.
- Assemble the oviposition chamber.
- Fill oviposition pot with water to a depth of approximately 5 mm. Attach the pot to one end of a 50 mL polypropylene tube, previously cut with a hacksaw so that both ends are open. (We use a plastic disc for a pot (Figure 5); however, the original lid of the tube can be used instead).
- Cover the other end of the cut polypropylene tube with material (hose/tights) or sections of latex glove secured with an elastic band, so adults can be introduced but cannot escape (Figure 5). Other alternative oviposition chamber designs exist and can be used26.
- Carefully introduce 10-15 females (blood fed in step 3.1.2) to the oviposition chamber. Cover the oviposition chamber to produce darkness and leave for 20 minutes.
CAUTION: Avoid moving the oviposition pot once eggs have been laid to prevent stranding and desiccation of eggs. - Carefully detach the 50 mL polypropylene tube from the oviposition pot, whilst ensuring not to release the mosquitoes. White eggs should be visible. Check that sufficient have been laid for proscribed purpose. Repeat if necessary.
- Cover the pot (for dust protection) and allow eggs to mature to the developmental stage of interest.
- Use a fine detailing paint brush to pick up eggs from the pot and place them on water in a 40 mm2 excavated glass block.

Figure 5 - Example of an Oviposition Chamber (A) dismantled to highlight the components and (B) assembled. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Embryo Fixing
CAUTION: Perform all fixing steps (step 3.3) in a fume hood due to use of formaldehyde.- Prepare FAA solution as described in Kaiser et al. (2014)22. FAA comprises 3.6 M formaldehyde, 0.87 M acetic acid and 8.5 M absolute ethanol made up to volume with distilled water (dH2O).
- For 10 mL of FAA combine 2.68 mL of 13.42 M formaldehyde, 4.96 mL of 17.14 M ethanol and 0.5 mL of 17.4 M acetic acid with 1.86 mL of distilled H2O. Fixative can be kept for at least 3 months in a tightly sealed glass container, kept in a designated chemical cupboard.
- Carefully remove the water from the glass block with a micropipette and cover eggs in 500 µL of FAA and oscillate gently (~25 RPM) on an orbital shaker at room temperature for 30 minutes. No color change is visible at this point.
- Rinse eggs thoroughly with distilled water. Perform rinsing 15 times to remove all traces of formaldehyde. Using a 1000 µL micropipette, add and then remove 1 mL of dH2O at a time ensuring not to damage the eggs while doing so.
- Store wastewater from rinses in a designated formaldehyde discard container for disposal according to safety guidelines.
- At this point, fixed eggs can be stored at 4 °C overnight in water to keep them hydrated.
- Prepare FAA solution as described in Kaiser et al. (2014)22. FAA comprises 3.6 M formaldehyde, 0.87 M acetic acid and 8.5 M absolute ethanol made up to volume with distilled water (dH2O).
- Embryo Bleaching
CAUTION: Perform all bleaching steps (step 4) in a fume hood due to the potential release of chlorine gas when sodium hypochlorite and acetic acid are combined.- Prepare bleaching solution (Trpiš solution - described in Trpiš (1970)21 and modified according to Kaiser et al. (2014)22). Trpiš solution is 0.59 M sodium hypochlorite and 0.35 M acetic acid dissolved in distilled H2O.
- For a 10 mL ovolume of Trpiš solution, combine 2.68 mL of 2.2 M sodium hypochlorite and 0.2 mL of 17.4 M acetic acid with 7.12 mL of distilled H2O.
NOTE:Trpiš solution can be stored for at least 3 months in a tightly sealed glass container and kept in a secure chemical cupboard. Solution may need to be vortexed after storage and should always be opened in a fume hood in case of release of chlorine gas.
- For a 10 mL ovolume of Trpiš solution, combine 2.68 mL of 2.2 M sodium hypochlorite and 0.2 mL of 17.4 M acetic acid with 7.12 mL of distilled H2O.
- Cover fixed eggs with 1 mL of Trpiš solution and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes. Eggs will start to develop pale patches after around 5 minutes of incubation, eventually reaching a milky white color once cleared.
- Rinse eggs as in step 3.3.3 to remove Trpiš solution.
- Store wastewater in a designated waste container and dispose with excess water down the drain.
- Prepare bleaching solution (Trpiš solution - described in Trpiš (1970)21 and modified according to Kaiser et al. (2014)22). Trpiš solution is 0.59 M sodium hypochlorite and 0.35 M acetic acid dissolved in distilled H2O.
- Storage
- Store in 500 µL of dH2O and keep between 2-8 °C for a few days. Remove most of the water carefully ahead of viewing and imaging on mass but avoid desiccation of the eggs by leaving a small volume of water in the watch glass. This will not disrupt photographing the eggs. Individual eggs can be placed on microscope slide for higher magnification imaging.
Results
3xP3 expression of eYFP, dsRed and eCFP provides reliable, readily distinguishable identification of individuals possessing the marker genes producing expression in eyes and ventral ganglia of An. gambiae pupae (Figure 3). The differential morphology observed in male and female external genitalia used for sexing and an example of an unidentifiable pupae are highlighted in Figure 4. Removal of all water from pupae increases sexing difficulty ...
Discussion
Understanding mosquito gene function is vital to develop new approaches to control Anopheles and impact malaria transmission. The GAL4-UAS system described is a versatile and powerful system for functional analysis of candidate genes and to date we have used the system to examine the genetic basis of insecticide resistance17 and cuticular hydrocarbon production15,23, as well as to fluorescently tag different mosquit...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge funding from LSTM and IVCC (Adriana Adolfi), BBSRC (New Investigator Award (AL), MRC (PhD studentship to BCP:MR/P016197/1), Wellcome (Sir Henry Wellcome Postdoctoral fellowship to LG: 215894/Z/19/Z) that have incorporated Gal4UAS analysis in the proposals.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 100 x 15 mm plastic Petri dish | SLS | 2175546 | Pack of 10 |
| 1000 µL Gilson Pipette | Gilson | F144059P | |
| 20/25 mL Universal Tubes | Starlab | E1412-3020 | Pack of 400 |
| 3 mL Pasteur Pipettes | SLS | G612398 | Greiner Pasteur pipette 3 mL sterile individually wrapped |
| 50 mL Falcon Tubes | Fisher Scientific | 11512303 | |
| Absolute Ethanol | Fisher Scientific | BP2818-500 | 500 mL |
| Acetic Acid | SLS | 45726-1L-F | 1 L |
| Cages | SLS | E6099 | 30x30x30 with screen port |
| Fine Paint Brushes | Amazon | UKDPB66 | KOLAMOON 9 Pieces Detail Painting Brush Set Miniture Brushes for Watercolor, Acrylic Painting, Oil Painting (Wine Red) |
| Fish food | Amazon | Tetra Min Fish Food, Complete Food for All Tropical Fish for Health, Colour and Vitality, 10 L | |
| Formaldehyde Solution | Sigma Aldrich | F8775 | |
| Mouth Aspirator | John Hock | 612 | |
| Pond Salt | Amazon | Blagdon Guardian Pond Tonic Salt, for Fish Health, Water Quality, General Tonic, pH Buffer, 9.08 kg, treats 9,092 L | |
| Pupae Pots | Cater4you | SP8OZ | 250 pots with lids |
| Small Plastic Buckets | Amazon | 2.5 L White Plastic Pail Complete with White Lid (Pack of 10) | |
| Sodium Hypochlorite | Fisher Scientific | S25552 |
References
- Brand, A. H., Perimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 118 (2), 401-415 (1993).
- Duffy, J. B. GAL4 system in drosophila: A fly geneticist's swiss army knife. Journal of Genetics and Development. 34 (1-2), 1-15 (2002).
- Dow, J. A. . ELS. , (2012).
- Edi, C. V., et al. CYP6 P450 Enzymes and ACE-1 Duplication Produce Extreme and Multiple Insecticide Resistance in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Genetics. 10 (3), 1004236 (2014).
- Daborn, P. J., et al. Using Drosophila melanogaster to validate metabolism-based insecticide resistance from insect pests. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 42 (12), 918-924 (2012).
- Riveron, J. M., et al. Genome-wide transcription and functional analyses reveal heterogeneous molecular mechanisms driving pyrethroids resistance in the major malaria vector Anopheles funestus across Africa. Genes Genomes Genetics. 7 (6), 1819-1832 (2017).
- Riveron, J. M., et al. A single mutation in the GSTe2 gene allows tracking of metabolically based insecticide resistance in a major malaria vector. Genome Biology. 15 (2), (2014).
- Lynd, A., Lycett, G. J. Development of the Bi-Partite Gal4-UAS System in the African Malaria Mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE. 7 (2), 31552 (2012).
- Lynd, A., Lycett, G. J. Optimization of the Gal4-UAS system in an Anopheles gambiae cell line. Insect Molecular Biology. 20 (5), 599-608 (2011).
- Adolfi, A., Pondeville, E., Lynd, A., Bourgouin, C., Lycett, G. J. Multi-tissue GAL4-mediated gene expression in all Anopheles gambiae life stages using an endogenous polyubiquitin promoter. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 96, 1-9 (2018).
- Kokoza, V. A., Raikhel, A. A. Targeted gene expression in the transgenic Aedes aegypti using the binary Gal4-UAS system. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 41, 637-644 (2011).
- O'Brochta, D. A., Pilitt, K. L., Harrell, R. A., Aluvihare, C., Alford, R. T. Gal4-based Enhancer-Trapping in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Genes Genomes Genetics. 2, 21305-21315 (2012).
- Zhao, B., et al. Regulation of the Gut-Specific Carboxypeptidase: A Study Using the Binary Gal4/UAS System in the Mosquito Aedes Aegypti. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 54, 1-10 (2014).
- Imamura, M., et al. Targeted Gene Expression Using the GAL4/UAS System in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Genetics. 165 (3), 1329-1340 (2003).
- Lynd, A., et al. Development of a functional genetic tool for Anopheles gambiae oenocyte characterisation: application to cuticular hydrocarbon synthesis. bioRxiv. , (2019).
- Pondeville, E., et al. Hemocyte-targeted gene expression in the female malaria mosquito using the hemolectin promoter from Drosophila. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 120, 103339 (2020).
- Adolfi, A., et al. Functional genetic validation of key genes conferring insecticide resistance in the major African malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (51), 25764-25772 (2019).
- Pondeville, E., et al. Efficient integrase-mediated site-specific germline transformation of Anopheles gambiae. Nature Protocols. 9 (7), 1698-1712 (2014).
- Horn, C., Schmid, B. G. M., Pogoda, F. S., Wimmer, E. A. Fluorescent transformation markers for insect transgenesis. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 32, 1221-1235 (2002).
- Clements, A. . A. Biology of Mosquitoes, Volume 1: Development, Nutrition and Reproduction. 1, (1992).
- Trpiš, M. A new bleaching and decalcifying method for general use in zoology. Canadian Journal of Zoology. 48, 892-893 (1970).
- Kaiser, M. L., Duncan, F. D., Brooke, B. D. Embryonic Development and Rates of Metabolic Activity in Early and Late Hatching Eggs of the Major Malaria Vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE. 9 (12), 114381 (2014).
- Grigoraki, L., Grau-Bové, X., Yates, H. C., Lycett, G. J., Ranson, H. Isolation and transcriptomic analysis of Anopheles gambiae oenocytes enables the delineation of hydrocarbon biosynthesis. eLife. 9, 58019 (2020).
- Xiao, Y. -. H., Yin, M. -. H., Hou, L., Pei, Y. Direct amplification of intron-containing hairpin RNA construct from genomic DNA. BioTechniques. 41 (5), 548-552 (2006).
- Livak, K. J. Organization and Mapping of a Sequence on the Drosophila melanogaster X and Y Chromosomes That Is Transcribed during Spermatogenesis. Genetics. 107 (4), 611-634 (1984).
- MR4, CDC, NEI & beiResources. . The MR4 Methods in Anopheles Research Laboratory Manual. 5th Edition. , (2015).
- Sik Lee, Y., Carthew, R. W. Making a better RNAi vector for Drosophila: use of intron spacers. Methods. 30 (4), 322-329 (2003).
- Cha-aim, K., Hoshida, H., Fukunaga, T., Akada, R., Peccoud, J. . Gene Synthesis: Methods and Protocols. , 97-110 (2012).
- Cavener, D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Research. 15 (4), 1353-1361 (1987).
- Wang, Y., Wang, F., Wang, R., Zhao, P., Xia, Q. 2A self-cleaving peptide-based multi-gene expression system in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Scientific Reports. 5, (2015).
- Galizi, R., et al. A synthetic sex ratio distortion system for the control of the human malaria mosquito. Nature Communications. 5, 3977 (2014).
- Kondo, S., et al. Neurochemical organisation of the Drosophila Brain Visualised by Endogenously Tagged Neurotransmitter Receptors. Cell Reports. 30 (1), 284-297 (2020).
- Lee, P. -. T., et al. A gene-specific T2A-GAL4 library for Drosophila. eLife. 7, 35574 (2018).
- Marois, E., et al. High-throughput sorting of mosquito larvae for laboratory studies and for future vector control interventions. Malaria Journal. 11, 302 (2012).
- Crawford, J. E., et al. Efficient production of male Wolbachia-infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes enables large-scale suppression of wild populations. Nature Biotechnology. 38 (4), 482-492 (2020).
- Goltsev, Y., et al. Developmental and evolutionary basis for drought tolerance of the Anopheles gambiae embryo. Developmental Biology. 330 (2), 462-470 (2009).
- Rezende, G. L., et al. Embryonic desiccation resistance in Aedes aegypti: presumptive role of the chitinized Serosal Cuticle. BMC Developmental Biology. 8 (1), 82 (2008).
- Vargas, H. C. M., Farnesi, L. C., Martins, A. J., Valle, D., Rezende, G. L. Serosal cuticle formation and distinct degrees of desiccation resistance in embryos of the mosquito vectors Aedes aegypti, Anopheles aquasalis and Culex quinquefasciatus. Journal of Insect Physiology. 62, 54-60 (2014).
- Chang, C. -. H., et al. The non-canonical Notch signaling is essential for the control of fertility in Aedes aegypti. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 12 (3), 0006307 (2018).
- Clemons, A., Flannery, E., Kast, K., Severson, D., Duman-Scheel, M. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Protein Expression during Aedes aegypti Development. Spring Harbor Protocols. 10, 1-4 (2010).
- Juhn, J., James, A. A. Hybridization in situ of Salivary Glands, Ovaries and Embryos of Vector Mosquitoes. Journal of Visualized Experiments. , e3709 (2012).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved