A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Induction and Assessment of Levodopa-induced Dyskinesias in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease
In This Article
Summary
This article describes methods to induce and evaluate levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. The protocol offers detailed information regarding the intensity and frequency of a range of dyskinetic behaviors, both dystonic and hyperkinetic, providing a reliable tool to test treatments targeting this unmet medical need.
Abstract
Levodopa (L-DOPA) remains the gold-standard therapy used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD) motor symptoms. However, unwanted involuntary movements known as L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) develop with prolonged use of this dopamine precursor. It is estimated that the incidence of LIDs escalates to approximately 90% of individuals with PD within 10–15 years of treatment. Understanding the mechanisms of this malady and developing both novel and effective anti-dyskinesia treatments requires consistent and accurate modeling for pre-clinical testing of therapeutic interventions. A detailed method for reliable induction and comprehensive rating of LIDs following 6-OHDA-induced nigral lesioning in a rat model of PD is presented here. Dependable LID assessment in rats provides a powerful tool that can be readily utilized across laboratories to test emerging therapies focused on reducing or eliminating this common treatment-induced burden for individuals with PD.
Introduction
Although it has been more than 50 years since levodopa (L-DOPA) was first introduced as a treatment for individuals with PD1,2, it remarkably remains the most effective therapy for parkinsonian motor symptoms. The clinical motor symptoms associated with PD stem from the loss of dopamine (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) pars compacta, resulting in the dramatic decrease in available dopamine in the striatum. L-DOPA effectively restores striatal DA levels, resulting in motor benefit early in the disease3,4. Inopportunely, with long-term treatment, most individuals with PD will develop L-DOPA induced dyskinesias (LID), including chorea, dystonia, and athetosis, which often significantly impact activities of daily living5,6,7.
While several behavioral models of LID in rodents exist, differences in modeling and behavioral assessment of LIDs have called into question the reproducibility of results between labs as well as the reliability of these experimental tools for pre-clinical PD research. Developed in association with a clinical movement disorder specialist8, the current protocol is a straightforward method for LID induction and rating and is appropriate for use in a rat model of PD utilizing 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced unilateral nigral lesioning9,10. The LID rating scale provided here includes scoring for both the intensity and frequency of dyskinetic behavior in various individual body parts. Pertinent information regarding workflow optimization of experiments and the appropriate care and handling of parkinsonian and dyskinetic animals is also provided.
Protocol
The animals presented here were maintained and handled in compliance with the institutional guidelines. All animal procedures were approved by the Michigan State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) in compliance with federal and state regulations.
1. Drug-free confirmation of 6-OHDA lesion status
- Postural Tail hang test11,12,13
NOTE: Assess lesion status at least 1 week following 6-OHDA lesion induction (See9,10,35 for details on lesioning) in experimental subjects (e.g., male or female, adult Sprague Dawley or Fisher 344 rats).- Suspend the rat approximately 6 cm above its cage, firmly holding at the base of the tail, for ~5 s.
- Record the direction of body contortion as + for a successfully lesioned animal twisting contralateral to the lesioned side and - for lack of twisting or twisting in both directions.
- NOTE: These tests are optional but recommended. See14,15,16,17 for additional drug-free testing options/variations.
- Step adjusting drag test (adapted from16)
NOTE: Assess lesion status at least 1 week following unilateral 6-OHDA lesion induction in experimental subjects (e.g., male or female, adult Sprague Dawley or Fisher 344 rats).- Hold the rat by the base of its tail, elevating the back feet off the surface by ~6 cm; drag backward across a flat, smooth but not slippery surface, ~75 cm, over 5–10 s.
- Observe and record the number of tapping/step adjusting movements of each forepaw over three repeated tests.
- Score the subject as + for successful unilateral lesioning when 0–2 forepaw taps are observed contralateral to the lesioned side, together with rapid tapping (~10 taps) from the forepaw ipsilateral to the lesioned side (e.g., animals unilaterally lesioned on the left side show tapping deficit (0–2 taps) with the contralateral right forepaw).
- Conversely, score moderate to rapid tapping (5–10 taps) from both forepaws as - to indicate incomplete or unknown lesion status.
NOTE: An anxious animal can show rapid tapping/step adjusting even if successfully lesioned. If this is suspected, place the rat back in their home cage and re-test ≥30 mins later.
2. Preparation of reagents and supplies
- Determine L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride (levodopa or L-DOPA) and benserazide hydrochloride, a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor (see Table of Materials) dose, rating frequency, and experimental timeline that is appropriate for the investigational question12,18,19,20 (Figure 1).
NOTE: Investigational questions can be posed to seek any number of questions ranging from asking whether a specific therapy might reduce existing LID or prevent induction of LID. They can also explore whether therapeutic efficacy is dependent on the dose of levodopa or whether LID expression and/or therapeutic efficacy varies depending on the sex, species, and age of the subject.
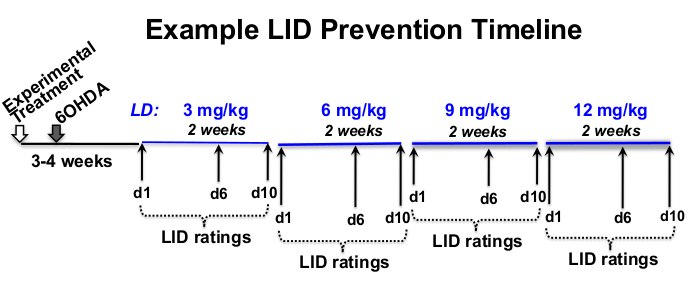
Figure 1: Example of treatment timeline. Example L-DOPA dose-escalation timeline of 12 weeks in total length, with 8 weeks of L-DOPA injections beginning 3 weeks after 6-OHDA lesioning and 4 weeks following experimental treatment. In this example, L-DOPA is subcutaneously injected 5x per week (Monday–Friday) at approximately the same time each day, for 2 weeks at each prescribed L-DOPA dose (3, 6, 9, and 12 mg/kg). Behavioral LID ratings take place on days 1, 6, and 10 of each L-DOPA dosage level. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Weigh rats weekly to calculate the appropriate drug quantity based on the ongoing weight changes during the study.
NOTE: Due to increased activity in LID+ rats, there is potential for weight loss with long-term L-DOPA treatments. If weight loss occurs provide rats with nutritionally complete, highly palatable treats (see Table of Materials) following L-DOPA injections. - Calculate the amount of L-DOPA and benserazide required for each weekly concentration, weighing out lyophilized aliquots for each day of injection, and storing in combination for 1–2 weeks at -20 °C in glass amber vials until the day of treatment.
NOTE: Target dose is 12 mg/kg or 12 mg L-DOPA/1000 g body weight. Example of calculations for determining the amount of L-DOPA and saline needed for each day of a week using 12 mg L-DOPA/kg body weight at an injection volume of 1 cc/kg of rat weight is given in Supplementary File 1.
3. Room and cage set up
- On the first day of L-DOPA treatment 3-4 weeks following 6-OHDA lesion surgery, transfer rats to single housing, including IACUC-approved enrichment.
- Maintain in single housing throughout the study to avoid peer interference with behavioral assessments.
- On LID rating days, place the home cages on a steel wire rack, turned at an approximately 45° angle for optimal viewing of the rat (Figure 2A). Flip the identification tags (Figure 2B) upward and remove water bottles, food racks, and all types of enrichment in the cage (Figure 2C) to avoid interference with behavioral assessments.

Figure 2: Example of the cage set up for LID ratings of large-scale rat experiments. (A) Multiple cages can be set up for LID rating using large metal racks that allow for optimal viewing of each animal. Cages should be spread apart at a 45° angle with ID cards flipped upward (B), food, water bottles, nesting materials, and other enrichment removed to limit visual obscureness of the rat and distractions to the rat while examining dyskinetic behaviors (C). The metal racks need to be a few feet away from any wall to allow the rater to examine the rat at the front or back of the cage as needed. It is essential to label enrichment apparatuses (e.g., C- red rat retreat houses) with individual animal IDs to replace them into the same cage from which they came. This is particularly important when using animals of different sexes not to increase stress to the experimental subjects. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Levodopa injections and dyskinesia rating
- Subcutaneous injections of L-DOPA21,22
- Immediately preceding the daily injection of L-DOPA, add the appropriate volume of sterile saline to the pre-weighed lyophilized L-DOPA and benserazide mix in the amber vial and shake well for 10 s (step 2.3).
NOTE: Target injection volume is 1 mL/1000 g body weight (with 12 mg L-DOPA per mL). The volume of the sterile saline will depend on the number of animals per study. - Fill individual syringes (e.g., 1.0 or 0.5 mL with 26 G needle) with the required volume for each animal (1 mL/kg rat weight) and label each syringe with individual animal identification.
NOTE: Keep the filled syringes protected from light in sterile pouches until the time of injection. L-DOPA rapidly oxidizes in the presence of oxygen and light in an aqueous environment23,24,25,26. - Bring the first cage to the injection bench.
- Remove the rat from its cage and place it on the injection surface.
- Gently restrain the head and shoulders against the surface on which the rat is resting with the palm of the non-dominant hand.
- Gently, scruff the skin on the back overlying the scapulae with the thumb and forefinger of the non-dominant hand, inject L-DOPA volume with the dominant hand into the subcutaneous space between/below the fingers, keeping the needle as parallel to the body as possible to avoid intramuscular injection.
NOTE: The rats are not anesthetized before injection. - Dispose of each used individual syringe in a sharp's container.
- Replace the rat into its individual cage and add nutritionally complete treats except on LID rating days to avoid interference with behavioral assessments until after ratings are complete.
- Set the timer for 1–2 min depending on the rating time desired and the number of rats in the study on rating days. Retrieve the next cage and inject the next rat when the timer indicates.
- Repeat this, injecting one rat every 1–2 min, until all the rats are injected.
- Immediately preceding the daily injection of L-DOPA, add the appropriate volume of sterile saline to the pre-weighed lyophilized L-DOPA and benserazide mix in the amber vial and shake well for 10 s (step 2.3).
- Levodopa-induced dyskinesia rating post-injection
- Rate the intensity (Table 1) and frequency (Table 2) of dystonic and hyperkinetic dyskinesia movements at the desired number of timepoints, which should include the initial onset of LID behavior, peak behavior, and the phase of decline (see Supplementary File 2 for an example of LID rating log sheet).
- For male and female adult Sprague Dawley or Fisher 344 rats, and a sample size of N = 40 rats, begin the dyskinesia ratings 20 min after the first L-DOPA injection, and then at 50 min intervals until 220 or 270 min post-injection, depending on when LID behaviors have discontinued in 90%–100% of rats.
- If using 1 min rating intervals, set a timer for 1 min. Rate the first rat for one minute. Move to the next rat and rate it for 1 min. Continue through all the rats, rating for 1 min intervals.
- Have a timer positioned next to the cage visibly so that the LID behavior intensity (Table 1) can be observed while estimating the frequency of any given behavior (Table 2) during the rating period.
- After ratings for the first time point are completed start again with the first rat at the next time point (e.g; 70 min post-injection) and continue at the desired interval (e.g., every 50 min) until all time points are completed.
NOTE: Due to the overlap of L-DOPA injection and LID rating tasks, two persons are needed on the rating days, one for injecting and one for behavioral ratings.
Results
LIDs in parkinsonian rats can manifest as a range of abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs), including dystonic, hyperkinetic, and stereotypic behaviors. LID rating criteria for such behaviors are presented here to include both intensity (Table 1) and frequency (Table 2). This provides an overall LID severity score for each rat that reflects both the quality (intensity) and quantity of time spent engaging (frequency) in these behaviors at each rating timepoint. The final LID severity scor...
Discussion
Presented here are details for the reproducible induction and rating of LIDs in a parkinsonian rat model following unilateral 6-OHDA lesioning of the nigrostriatal DA system. While it was once thought that rodents did not develop LID and that rotational asymmetry may be the analog of LID in rats31, rat and mouse models have been characterized over the past two decades and are a well-accepted tool for LID research15,32,
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Acknowledgements
We want to acknowledge the struggles of all those with Parkinson's disease and the strength and resilience they show every day, especially the beloved father of KSC, Mark Steece. The work represented here was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NS090107, NS110398) and the Parkinson Disease Foundation International Research Grant Program, now the Parkinson Foundation. We also would like to acknowledge Molly VanderWerp for her excellent editorial assistance.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 100 Minutes Digital Timer | Staples | 1111764 | |
| Compass CX Compact Scale | Ohaus | 30428202 | |
| 5-(2-aminoethyl)-1,2,4-benzenetriol, monohydrobromide | Cayman Chemicals | 25330 | 6-OHDA is a catecholaminergic neurotoxin that is used to induce dopaminergic lesions and parkinsonian symptoms in rodents. |
| Allentown cages | Allentown, LLC | Rat900 | Allentown cages provide the ability to view the rats from all sides. |
| BD Allergist Trays with Permanently Attached Needle | BD | BD 305540 | For subcutaneous L-DOPA injections |
| Benserazide hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | B7283 | Benserazide is a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor used with L-DOPA to to induce dyskinesia in rodent models of PD. |
| Glass amber scintillation vials | Thermo Scientific | B7921 | Used for storage of L-DOPA/benserazide at -20 °C until mixed with sterile saline. |
| L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | D1507 | L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine methyl ester is a precursor to L-DOPA that crosses the blood-brain barrierand use to treat parkinsonian symptoms in rodents. |
| Paper Mate Sharpwriter Mechanical Pencils | Staples | 107250 | |
| Rodent nutritionally complete enrichment treats | Bio-Serv | F05478 | |
| Round Ice Bucket with Lid, 2.5 L | Corning | 432129 | |
| Standard Plastic Clipboard | Staples | 1227770 | |
| Steel wired 6' long movable shelving units | Uline | H9488 | Width/Height can be adjusted to need/number of rats per experiment |
| Sterile Saline 0.9% | Covidien/Argyle | 1020 | For mixing with L-DOPA/benserazide prior to subcutaneous injections. |
References
- Cotzias, G. C., Papavasiliou, P. S., Gellene, R. L-dopa in parkinson's syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 281, 272 (1969).
- Yahr, M. D., Duvoisin, R. C., Schear, M. J., Barrett, R. E., Hoehn, M. M. Treatment of parkinsonism with levodopa. Archives of Neurology. 21 (4), 343-354 (1969).
- Bastide, M. F., et al. Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson's disease. Progress in Neurobiology. 132, 96-168 (2015).
- Sellnow, R. C., et al. Regulation of dopamine neurotransmission from serotonergic neurons by ectopic expression of the dopamine D2 autoreceptor blocks levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 7 (1), 8 (2019).
- Bastide, M. F., Bezard, E. L-dopa induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease]. Bulletin de l'Académie Nationale de Médecine. 199 (2-3), 201-212 (2015).
- Hauser, R. A., et al. ADS-5102 (Amantadine) extended-release capsules for levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's Disease (EASE LID 2 study): Interim results of an open-label safety study. Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 7 (3), 511-522 (2017).
- Huot, P., Johnston, T. H., Koprich, J. B., Fox, S. H., Brotchie, J. M. The pharmacology of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacological Reviews. 65 (1), 171-222 (2013).
- Steece-Collier, K., et al. Embryonic mesencephalic grafts increase levodopa-induced forelimb hyperkinesia in parkinsonian rats. Movement Disorders. 18 (12), 1442-1454 (2003).
- Thiele, S. L., Warre, R., Nash, J. E. Development of a unilaterally-lesioned 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (60), e3234 (2012).
- Simola, N., Morelli, M., Carta, A. R. The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease. Neurotoxicity Research. 11 (3-4), 151-167 (2007).
- Borlongan, C. V., Hida, H., Nishino, H. Early assessment of motor dysfunctions aids in successful occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Neuroreport. 9 (16), 3615-3621 (1998).
- Fleming, S. M. Behavioral outcome measures for the assessment of sensorimotor function in animal models of movement disorders. International Review of Neurobiology. 89, 57-65 (2009).
- Borlongan, C. V., Sanberg, P. R. Elevated body swing test: a new behavioral parameter for rats with 6-hydroxydopamine-induced hemiparkinsonism. Journal of Neuroscience. 15 (7), 5372-5378 (1995).
- Chang, J. W., Wachtel, S. R., Young, D., Kang, U. J. Biochemical and anatomical characterization of forepaw adjusting steps in rat models of Parkinson's disease: studies on medial forebrain bundle and striatal lesions. Neuroscience. 88 (2), 617-628 (1999).
- Lundblad, M., et al. Pharmacological validation of behavioural measures of akinesia and dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neuroscience. 15 (1), 120-132 (2002).
- Olsson, M., Nikkhah, G., Bentlage, C., Bjorklund, A. Forelimb akinesia in the rat Parkinson model: differential effects of dopamine agonists and nigral transplants as assessed by a new stepping test. Journal of Neuroscience. 15 (5), 3863-3875 (1995).
- Monville, C., Torres, E. M., Dunnett, S. B. Comparison of incremental and accelerating protocols of the rotarod test for the assessment of motor deficits in the 6-OHDA model. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 158 (2), 219-223 (2006).
- Steece-Collier, K., et al. Striatal Nurr1, but not FosB expression links a levodopa-induced dyskinesia phenotype to genotype in Fisher 344 vs. Lewis hemiparkinsonian rats. Experimental Neurology. 330, 113327 (2020).
- Steece-Collier, K., et al. Genetic silencing of striatal CaV1.3 prevents and ameliorates levodopa dyskinesia. Movement Disorders. 34 (5), 697-707 (2019).
- Tayarani-Binazir, K. A., Jackson, M. J., Strang, I., Jairaj, M., Rose, S., Jenner, P. Benserazide dosing regimen affects the response to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat. Behavioral Pharmacology. 23 (2), 126-133 (2012).
- Lindgren, H. S., Rylander, D., Ohlin, K. E., Lundblad, M., Cenci, M. A. The "motor complication syndrome" in rats with 6-OHDA lesions treated chronically with L-DOPA: relation to dose and route of administration. Behavioural Brain Research. 177 (1), 150-159 (2007).
- Suckow, M. A., Stevens, K. A., Wilson, R. P. . American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine series xvii. , 1268 (2012).
- Zhou, Y. Z., Alany, R. G., Chuang, V., Wen, J. Studies of the Rate Constant of l-DOPA Oxidation and Decarboxylation by HPLC. Chromatographia. 75, 597-606 (2012).
- Stroomer, A. E., Overmars, H., Abeling, N. G., van Gennip, A. H. Simultaneous determination of acidic 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine metabolites and 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Clinical Chemistry. 36 (10), 1834-1837 (1990).
- . PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6047, Levodopa Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Levodopa (2021)
- Merck. . The Merck Index 13th edn. , (2021).
- Ortner, N. J., et al. Lower affinity of isradipine for L-Type Ca(2+) channels during substantia nigra dopamine neuron-like activity: Implications for neuroprotection in Parkinson's Disease. Journal of Neuroscience. 37 (228), 6761-6777 (2017).
- Hazra, A., Gogtay, N. Biostatistics series module 3: Comparing groups: Numerical variables. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 61 (3), 251-260 (2016).
- Mishra, P., Pandey, C. M., Singh, U., Keshri, A., Sabaretnam, M. Selection of appropriate statistical methods for data analysis. Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia. 22 (3), 297-301 (2019).
- Divito, C. B., et al. Loss of VGLUT3 produces circadian-dependent hyperdopaminergia and ameliorates motor dysfunction and l-Dopa-Mediated dyskinesias in a model of Parkinson's Disease. Journal of Neuroscience. 35 (45), 14983-14999 (2015).
- Henry, B., Crossman, A. R., Brotchie, J. M. Characterization of enhanced behavioral responses to L-DOPA following repeated administration in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease. Experimental Neurology. 151 (2), 334-342 (1998).
- Andersson, M., Hilbertson, A., Cenci, M. A. Striatal fosB expression is causally linked with l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements and the associated upregulation of striatal prodynorphin mRNA in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiology of Disease. 6 (6), 461-474 (1999).
- Cenci, M. A., Lee, C. S., Bjorklund, A. L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the rat is associated with striatal overexpression of prodynorphin- and glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA. European Journal of Neuroscience. 10 (8), 2694-2706 (1998).
- Dekundy, A., Lundblad, M., Danysz, W., Cenci, M. A. Modulation of L-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements by clinically tested compounds: further validation of the rat dyskinesia model. Behavioural Brain Research. 179 (1), 76-89 (2007).
- Collier, T. J., et al. Interrogating the aged striatum: robust survival of grafted dopamine neurons in aging rats produces inferior behavioral recovery and evidence of impaired integration. Neurobiology of Disease. 77, 191-203 (2015).
- Maries, E., et al. Focal not widespread grafts induce novel dyskinetic behavior in parkinsonian rats. Neurobiology of Disease. 21 (1), 165-180 (2006).
- Mercado, N. M., et al. The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism (rs6265) enhances dopamine neuron graft efficacy and side-effect liability in rs6265 knock-in rats. Neurobiology of Disease. 148, 105175 (2021).
- Cenci, M. A., Crossman, A. R. Animal models of l-dopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders. 33 (6), 889-899 (2018).
- Lindenbach, D. Behavioral and cellular modulation of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia by beta-adrenoceptor blockade in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 337 (3), 755-765 (2011).
- Petzinger, G. M. Reliability and validity of a new global dyskinesia rating scale in the MPTP-lesioned non-human primate. Movement Disorders. 16 (2), 202-207 (2001).
- Fox, S. H., Johnston, T. H., Li, Q., Brotchie, J., Bezard, E. A critique of available scales and presentation of the Non-Human Primate Dyskinesia Rating Scale. Movement Disorders. 27 (11), 1373-1378 (2012).
- Cenci, M. A., Ohlin, K. E. Rodent models of treatment-induced motor complications in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 15, 13-17 (2009).
- Cenci, M. A., Whishaw, I. Q., Schallert, T. Animal models of neurological deficits: how relevant is the rat. Nature Reviews: Neuroscience. 3 (7), 574-579 (2002).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Aberrant restoration of spines and their synapses in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: involvement of corticostriatal but not thalamostriatal synapses. Journal of Neuroscience. 33 (28), 11655-11667 (2013).
- Konradi, C., et al. Transcriptome analysis in a rat model of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Neurobiology of Disease. 17 (2), 219-236 (2004).
- Morin, N., Jourdain, V. A., Di Paolo, T. Modeling dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson disease. Experimental Neurology. 256, 105-116 (2014).
- Cenci, M. A., Riggare, S., Pahwa, R., Eidelberg, D., Hauser, R. A. Dyskinesia matters. Movement Disorders. 35 (3), 392-396 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved