A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Live Imaging of the Mitochondrial Glutathione Redox State in Primary Neurons using a Ratiometric Indicator
In This Article
Summary
This article describes a protocol to determine differences in basal redox state and redox responses to acute perturbations in primary hippocampal and cortical neurons using confocal live microscopy. The protocol can be applied to other cell types and microscopes with minimal modifications.
Abstract
Mitochondrial redox homeostasis is important for neuronal viability and function. Although mitochondria contain several redox systems, the highly abundant thiol-disulfide redox buffer glutathione is considered a central player in antioxidant defenses. Therefore, measuring the mitochondrial glutathione redox potential provides useful information about mitochondrial redox status and oxidative stress. Glutaredoxin1-roGFP2 (Grx1-roGFP2) is a genetically encoded, green fluorescent protein (GFP)-based ratiometric indicator of the glutathione redox potential that has two redox-state-sensitive excitation peaks at 400 nm and 490 nm with a single emission peak at 510 nm. This article describes how to perform confocal live microscopy of mitochondria-targeted Grx1-roGFP2 in primary hippocampal and cortical neurons. It describes how to assess steady-state mitochondrial glutathione redox potential (e.g., to compare disease states or long-term treatments) and how to measure redox changes upon acute treatments (using the excitotoxic drug N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) as an example). In addition, the article presents co-imaging of Grx1-roGFP2 and the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator, tetramethylrhodamine, ethyl ester (TMRE), to demonstrate how Grx1-roGPF2 can be multiplexed with additional indicators for multiparametric analyses. This protocol provides a detailed description of how to (i) optimize confocal laser scanning microscope settings, (ii) apply drugs for stimulation followed by sensor calibration with diamide and dithiothreitol, and (iii) analyze data with ImageJ/FIJI.
Introduction
Several important mitochondrial enzymes and signaling molecules are subject to thiol redox regulation1. Moreover, mitochondria are a major cellular source of reactive oxygen species and are selectively vulnerable to oxidative damage2. Accordingly, the mitochondrial redox potential directly affects bioenergetics, cell signaling, mitochondrial function, and ultimately cell viability3,4. The mitochondrial matrix contains high amounts (1-15 mM) of the thiol-disulfide redox buffer glutathione (GSH) to maintain redox homeostasis and mount antioxidant defenses5,6. GSH can be covalently attached to target proteins (S-glutathionylation) to control their redox status and activity and is used by a range of detoxifying enzymes that reduce oxidized proteins. Therefore, the mitochondrial glutathione redox potential is a highly informative parameter when studying mitochondrial function and pathophysiology.
roGFP2 is a variant of GFP that has been made redox-sensitive by the addition of two surface-exposed cysteines that form an artificial dithiol-disulfide pair7,8. It has a single emission peak at ~510 nm and two excitation peaks at ~400 nm and 490 nm. Importantly, the relative amplitudes of the two excitation peaks depend on the redox state of roGFP2 (Figure 1), making this protein a ratiometric sensor. In the Grx1-roGFP2 sensor, human glutaredoxin-1 (Grx1) has been fused to the N-terminus of roGFP29,10. Covalent attachment of the Grx1 enzyme to roGFP2 affords two major improvements of the sensor: it makes the sensor response specific for the GSH/GSSG glutathione redox pair (Figure 1), and it speeds up equilibration between GSSG and roGFP2 by a factor of at least 100,0009. Therefore, Grx1-roGFP2 enables specific and dynamic imaging of the cellular glutathione redox potential.
Grx1-roGFP2 imaging can be performed on a wide range of microscopes, including widefield fluorescence microscopes, spinning disc confocal microscopes, and laser scanning confocal microscopes. Expression of the sensor in primary neurons can be achieved by various methods that include lipofection11, DNA/calcium-phosphate coprecipitation12, virus-mediated gene transfer, or use of transgenic animals as the cell source (Figure 2). Pseudotyped recombinant adeno-associated viruses (rAAV) containing a 1:1 ratio of AAV1 and AAV2 capsid proteins 13,14 were used for the experiments in this article. With this vector, maximal sensor expression is typically reached 4-5 days after infection and stays stable for at least two weeks. We have successfully used Grx1-roGFP2 in primary hippocampal and cortical neurons from mice and rats.
In this article, rAAV-mediated expression of mitochondria-targeted Grx1-roGFP2 in primary rat hippocampal and cortical neurons is used to assess basal mitochondrial glutathione redox state and its acute perturbation. A protocol is provided for confocal live imaging with detailed instructions on how to (i) optimize laser scanning confocal microscope settings, (ii) run a live imaging experiment, and (iii) analyze data with FIJI.
Protocol
All animal experiments conformed to national and institutional guidelines, including the Council Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament, and had full Home Office ethical approval (University of Heidelberg Animal Welfare Office and Regierungspraesidium Karlsruhe, licenses T14/21 and T13/21). Primary hippocampal and cortical neurons were prepared from newborn mouse or rat pups according to standard procedures and were maintained for 12-14 days as previously described13.
1. Preparation of solutions
- Stock solutions for imaging buffer
- Prepare each stock solution according to Table 1 and keep them at 4 °C. For long-term storage (>3 months), keep aliquots at -20 °C.
| Component | MW | Concentration (M) | Amount (g) | Volume (mL) |
| NaCl | 58.44 | 5 | 14.61 | 50 |
| KCl | 74.55 | 3 | 1.12 | 5 |
| MgCl2·6H2O | 203.3 | 1.9 | 2 | 5 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 147.01 | 1 | 1.47 | 10 |
| Glycine | 75.07 | 0.1 | 0.375 | 50 |
| Sucrose | 342.3 | 1.5 | 25.67 | 50 |
| Sodium pyruvate | 110.04 | 0.1 | 0.55 | 50 |
| HEPES | 238.3 | 1 | 11.9 | 50 |
| Glucose | 180.15 | 2.5 | 45 | 100 |
Table 1: Stock solutions for imaging buffer.
- Stock solutions of drugs and dyes
- Dissolve diamide (DA; used for calibration of maximal 405:488 ratio) in water to obtain a 0.5 M stock solution (e.g., 1 g in 11.615 mL of water). Aliquot and store at -20 °C.
- Dissolve dithiothreitol (DTT; used for calibration of minimal 405:488 ratio) in water to obtain a 1 M stock solution (e.g., 5 g in 32.425 mL of water). Aliquot and store at -20 °C for a maximum of 3 months.
- Dissolve N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA; used to induce excitotoxicity and mitochondrial oxidation) in water to obtain a 10 mM stock solution (e.g., 25 mg in 16.991 mL of water). Store the aliquots at -20 °C. For long-term storage (>6 months), keep the aliquots at -80 °C.
- Tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester perchlorate (TMRE; a small-molecule indicator of the mitochondrial membrane potential)
- Dissolve TMRE powder in methanol to obtain a 20 mM stock (e.g., 25 mg in 2.427 mL of methanol).
- Dilute the 20 mM stock 1:1,000 in methanol to obtain a 20 µM stock.
- Aliquot the 20 mM and 20 µM stock solutions, seal with parafilm, and store protected from light at -20 °C.
NOTE: Both stock solutions are stable for several years. Use the 1,000x stock solution (20 µM) for experiments.
- Imaging buffer
- Prepare 100 mL of imaging buffer by adding all components from Table 2 to 80 mL of sterile water in a measuring cylinder. Bring the volume up to 100 mL with sterile water. Mix by carefully shaking the measuring cylinder until the solution appears homogeneous.
NOTE: It is recommended to use an osmometer to check the osmolarity of the buffer. It should be as close as possible to the growth medium of the cells. Here, this is 315 mOsmol/L. Increase or decrease the sucrose concentration as needed to match the osmolarity of the imaging buffer and growth medium. - Adjust the pH to 7.4. Make aliquots and keep them at 4 °C for up to two weeks. For long-term storage, keep the aliquots at -20 °C. Let the imaging buffer reach room temperature before use.
- Prepare 100 mL of imaging buffer by adding all components from Table 2 to 80 mL of sterile water in a measuring cylinder. Bring the volume up to 100 mL with sterile water. Mix by carefully shaking the measuring cylinder until the solution appears homogeneous.
| Component | Stock solution (M) | Final concentration (mM) | Volume (mL) |
| NaCl | 5 | 114 | 2.3 |
| KCl | 3 | 5.29 | 0.176 |
| MgCl2 | 1.9 | 1 | 0.053 |
| CaCl2 | 1 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Glycine | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Sucrose | 1.5 | 52 | 3.5 |
| Sodium pyruvate | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| HEPES | 1 | 10 | 1 |
| Glucose | 2.5 | 5 | 0.2 |
Table 2: Composition of imaging buffer. The indicated volumes are used for the preparation of 100 mL of imaging buffer.
- Solutions for stimulation and calibration
NOTE: Always prepare fresh stimulation solutions by adding stock solutions of indicated drugs to the imaging buffer just before the experiment. Solutions for stimulation and calibration will be added to the imaging chamber sequentially during an experiment (see sections 3-5). Depending on the type of experiment, different solutions are required to reach the same end concentration in the respective final volume in the imaging chamber.- Prepare 3x NMDA solution (90 µM; final concentration in the chamber: 30 µM) by adding 63 µL of a 10 mM NMDA stock to 6.937 mL of imaging buffer. Add 500 µL of the resulting solution to the chamber (final volume: 1.5 mL).
- Prepare 2x DA solution for steps 3 and 4 (1 mM; final concentration in the chamber: 0.5 mM) by adding 14 µL of a 0.5 M DA stock to 6.986 mL of imaging buffer. Add 1 mL to the chamber (final volume: 2 mL).
- Prepare 4x DA solution for step 5 (2 mM; final concentration in the chamber: 0.5 mM) by adding 28 µL of a 0.5 M DA stock to 6.972 mL of imaging buffer. Add 500 µL to the chamber (final volume: 2 mL).
- Prepare 1x DTT solution (5 mM; final concentration in the chamber: 5 mM) by adding 45 µL of 1 M DTT stock to 8955 µL of imaging buffer. Add 1 mL of this solution to the chamber after aspirating the imaging buffer (final volume: 1 mL).
2. Loading of cells with TMRE
NOTE: In this protocol, TMRE is used in non-quench mode15 at a final concentration of 20 nM. In general, the lowest possible concentration of TMRE that still provides sufficient signal intensity on the microscope of choice should be used. Due to uneven evaporation, the volume of medium in different wells can differ in long-term primary cultures. To ensure a consistent TMRE concentration in all wells, do not add TMRE directly to the wells. Instead, replace the medium in each well with the same amount of TMRE-containing medium. The protocol below is designed for primary neurons in 24-well plates containing ~1 mL of medium per well.
- Working in a tissue culture laminar flow hood, collect 500 µL of medium from each well into a single conical tube.
- Per well, add 0.5 µL of 20 µM TMRE stock into the conical tube (e.g., 12 µL for 24 wells).
- Carefully aspirate the remaining medium from the first well and replace it with 500 µL of TMRE-containing medium. Continue, well-by-well, with the remaining wells.
NOTE: Take care not to let the cells dry out and not to disturb the cells. - Return the cells to the incubator and wait for at least 60 min for dye equilibration.
NOTE: Loading time can be extended to several hours without adverse effects. - To ensure consistent TMRE concentrations and equilibration throughout the imaging experiment, make sure to include a final concentration of 20 nM TMRE in the imaging buffer and all stimulation solutions.
3. Optimization of scanning confocal microscope settings
NOTE: This step aims to find the best compromise between image quality and cell viability during live imaging. This section describes the optimization of settings for roGFP imaging. If multiparametric imaging is performed, similar optimization, including checking for a stable baseline without signs of bleaching or phototoxicity, needs to be performed for the additional indicators.
- Start the confocal microscope and load standard settings for GFP imaging (488 nm excitation, 505 - 550 nm emission).
- Set the detector to 12 bits or 16 bits.
NOTE: Usually, 8 bits are not sufficient for quantitative imaging. - Activate the sequential scan mode and add second sequence/track (405 nm excitation, 505 - 550 nm emission).
- For both channels, select a pseudocolor lookup table that indicates over- and under-exposed pixels (e.g., GLOW OU).
- Select an objective that is suitable for the object of interest.
NOTE: 10x-40x are suitable for single-cell analysis, 63x-100x are suitable for single-mitochondrion analysis. - Mount a coverslip with cells into the imaging chamber, add 1 mL of imaging buffer, and place the chamber on the microscope.
- Use the eyepiece and transmitted light to focus the cells.
NOTE: Do not use epifluorescence light to locate and focus cells. Even at low power, this will adversely affect the cells. - Record images with different pixel formats. Based on these images, select the lowest pixel number that gives an acceptable resolution of the structure of interest.
NOTE: Typically, 512 x 512 pixels work well for single-cell imaging with 20x and 40x objectives, and 1024 x 1024 or 2048 x2048 pixels typically work well for single-mitochondrion imaging with a 63x objective. - Record images with different pinhole sizes. Based on these images, select the largest pinhole size that gives an acceptable resolution of the structure of interest.
NOTE: Typically, 3-7 airy units work well. - Record images with different laser intensities.
- Adjust the detector gain and threshold accordingly. Based on these images, select the lowest laser intensity that gives acceptable signal intensity and signal-to-background ratio.
- To determine the signal-to-background ratio, measure the signal intensity in a region of interest (ROI) that contains cells or mitochondria (ROI1) and in an ROI without cells or mitochondria (ROI2). Then, divide the intensity of ROI1 by the intensity of ROI2.
NOTE: Aim for a signal-to-background ratio of >3 and signal intensities of individual ROIs of 200-1,000 for 405 nm excitation with 1-3% laser power and intensities of individual ROIs of 300-1,500 for 488 nm excitation with 1% laser power.
- To determine the signal-to-background ratio, measure the signal intensity in a region of interest (ROI) that contains cells or mitochondria (ROI1) and in an ROI without cells or mitochondria (ROI2). Then, divide the intensity of ROI1 by the intensity of ROI2.
- Adjust the detector gain and threshold accordingly. Based on these images, select the lowest laser intensity that gives acceptable signal intensity and signal-to-background ratio.
- Record images with different scan speeds and number of frame averages. Record 4-5 images for each combination of settings. Based on these image series, select the highest speed and lowest average settings that give acceptable image noise and image-to-image variability.
NOTE: A scan speed of 600 Hz and 1-2 frames for averaging work well in most cases. - Using a new coverslip, record a time-lapse series with the optimized settings.
NOTE: The duration and image interval of the series should resemble those of the planned experiments. - At the end of the time-lapse series, add 1 mL of 2x DA solution to the recording chamber. Image for additional 2 min.
- Aspirate the imaging buffer using a peristaltic pump or handheld pipette. Add 1 mL of 1x DTT solution. Image for additional 5 min.
- Analyze the time-lapse experiment (see section 5).
- Verify that none of the two channels gets over- or under-exposed during DA- and DTT-treatment with the optimized settings.
- Ensure that none of the two channels shows considerable bleaching during the time-lapse recording; aim for <2% loss of intensity between the first and last images.
- Verify that the 405:488 ratio does not change considerably during imaging.
- Repeat the whole procedure in an iterative manner, using several coverslips, until settings that consistently provide acceptable results have been defined.
4. Assessment of basal redox status
- Start the microscope and load the optimized settings from section 3.
- Set frame average to 3-5.
- Mount a coverslip with cells into the imaging chamber, add 1 mL of imaging buffer, and place the chamber on the microscope.
- Use the eyepiece and transmitted light to focus the cells.
NOTE: Do not use epifluorescence light to locate and focus cells. Even at low power, this will adversely affect the cells. - Switch to scanning mode and use the 488 nm channel in live view to focus and locate cells for imaging.
- Use the multipoint function to select 3-5 fields of view on the coverslip.
- Record a baseline image.
- Add 1 mL of 2x DA solution to the chamber.
- After 1, 2, and 3 min, use live view to confirm/adjust the focus and then record an image.
NOTE: Cells are typically fully oxidized after 2 min. - Replace the buffer in the imaging chamber with 1 mL of 1x DTT solution.
- After 3 and 5 min, use live view to confirm/adjust the focus and then record an image.
NOTE: Cells are typically fully reduced after 4-5 min.
5. Live imaging of acute treatments
NOTE: The protocol below describes imaging of the mitochondrial redox response to NMDA treatment. Image intervals and duration of the experiment might need to be adjusted for other treatments.
- Start the microscope and load the optimized settings from section 3.
- Set the time-lapse interval to 30 s and duration to 25 min.
- Mount a coverslip with cells into the imaging chamber, add 1 mL of imaging buffer, and place the chamber on the microscope.
NOTE: To avoid thermal focus drift, leave the cells on the microscope stage for 10-15 min before starting time-lapse imaging. - Use the eyepiece and transmitted light to focus the cells.
NOTE: Do not use epifluorescence light to locate and focus cells. Even at low power, this will adversely affect the cells. - Switch to the scanning mode and use the 488 nm channel in live view to focus and locate cells for imaging.
- Optional: To increase the number of recorded cells per run, use the multipoint function to image 2-3 fields of view per coverslip.
- Start the time-lapse acquisition and record 5 images as 2 min baseline recording.
- Add 500 µL of 3x NMDA solution to the chamber (final concentration 30 µM) and record additional 20 images as a 10 min NMDA response.
NOTE: Neurons are very sensitive to changes in osmolarity. Therefore, make sure to minimize evaporation of the imaging buffer. For longer treatments, the imaging chamber should be covered with a lid. - Add 500 µL of 4x DA solution to the chamber and record 6 more images (3 min maximum calibration).
- Aspirate the buffer from the imaging chamber and replace it with 1 mL of 1x DTT solution. Record 10 more images (5 min minimum calibration).
- End the recording and save the image series.
6. Data analysis
- Data import and image preprocessing in FIJI
- Use the Bio-Formats Importer to open a group of images from step 4 or an image file from step 5. Click on Plugins | Bio-Formats | Bio-Formats Importer. In the dialog box, use View stack with: Hyperstack, set Color mode: default, select Autoscale, and do not split into separate windows.
NOTE: Autoscale optimizes the display of the data on the computer screen. It does not change pixel intensities. - If individual images from step 4 were opened, click on Image | Stacks | Tools | Concatenate to merge them into a single-image stack.
- If there is XY-drift during the image series, click on Plugins | StackReg to register the images. In the dialog box, select Rigid Body or Translation.
- Change the image format to 32 bit by clicking on Image | Type | 32-bit.
- Split the color channels into separate windows by clicking on Image | Color | Split Channels.
- Select channel 1 (405 nm) and adjust the threshold to select the mitochondria for analysis by clicking on Image | Adjust | Threshold. In the dialog box, select Default, Red, Dark background, and Stack histogram and wait for the selected pixels to appear red. Click Apply. Select Set Background Pixels to NaN and Process all images.
NOTE: To avoid potential observer bias, automated threshold determination should be used. FIJI offers several automated methods (such as Default, Huang, Intermodes, Otsu) that can be selected from a dropdown menu in the threshold dialog box. Typically, the Default method gives a good result. It is recommended to compare several methods during the first analysis to find the best thresholding method for the given set of images. Once a method has been chosen, it needs to be applied to all images. - Repeat step 6.1.6 for channel 2 (488 nm).
- Create a ratio image to visualize the 405:488 nm ratio by clicking on Process | Image calculator. In the dialog box, select Image 1: channel 1, Operation: Divide, Image 2: channel 2, Create new window, Process all images.
- Change the lookup table of the ratio image to pseudocolor. For example, to change to Fire, click on Image | Lookup Tables | Fire.
- Use the Bio-Formats Importer to open a group of images from step 4 or an image file from step 5. Click on Plugins | Bio-Formats | Bio-Formats Importer. In the dialog box, use View stack with: Hyperstack, set Color mode: default, select Autoscale, and do not split into separate windows.
- Image analysis
- On the ratio image, draw ROIs around individual cells or mitochondria. After drawing each ROI, add it to the ROI Manager. Analyze | Tools | ROI Manager | Add. (keyboard shortcut: 'T') Select Show All.
NOTE: Because background pixels have been set to 'not a number' (NaN) in steps 6.1.6 and 6.1.7, they will not affect the result of the measurement. Therefore, it is acceptable to include some background pixels in the ROI. - Measure the 405:488 ratios of individual cells by clicking on ROI Manager | ctrl+A to select all ROIs | More | Multi Measure. In the dialog box, select Measure all slices and One row per slice.
- Export the measurements to spreadsheet software.
- Select the 405 nm image. Measure the intensities of all ROIs as in step 6.2.2. using the ROIs that are stored in the ROI manager.
- Export the measurements to spreadsheet software.
- Select the 488 nm image. Measure intensities of all ROIs as in step 6.2.2. using the ROIs that are stored in the ROI manager.
- Export the measurements to spreadsheet software.
- Save ROIs for future reference by clicking on ROI Manager | ctrl+A to select all ROIs | More | Save.
- Recommended: Generate intensity vs. time plots of the 405 and 488 nm traces. Verify that there is no marked bleaching in either of the channels (signal intensity at the end of the imaging series should be ≥98% of the first image) and that the two traces move into opposite directions during sensor responses (e.g., the 405 nm trace should increase during oxidation while the 488 nm trace should decrease).
- On the ratio image, draw ROIs around individual cells or mitochondria. After drawing each ROI, add it to the ROI Manager. Analyze | Tools | ROI Manager | Add. (keyboard shortcut: 'T') Select Show All.
- Data normalization
- For each ROI from the ratio image, determine the maximum value during DA treatment (Rmax) and the minimum value during DTT treatment (Rmin).
- Calculate the normalized ratio as follows:
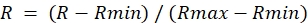
NOTE: This will set the maximum ratio to 1.0 and the minimum ratio to 0.
- Analysis of mitochondrial morphology
- To obtain measurements of mitochondrial morphology in parallel to roGFP intensities in step 6.2.6, go to Analyze | Set Measurements and check Shape descriptors and Fit ellipse.
NOTE: In addition to mean intensity, the measurements in the results window will include the length of the major axis (Major), the length of the minor axis (Minor), the aspect ratio (AR; major axis divided by minor axis; round mitochondria have an AR ~1, elongated mitochondria have a greater AR), as well as measurements of circularity (Circ.) and roundness (Round).
- To obtain measurements of mitochondrial morphology in parallel to roGFP intensities in step 6.2.6, go to Analyze | Set Measurements and check Shape descriptors and Fit ellipse.
Results
Quantification of differences in steady-state mitochondrial redox state after growth factor withdrawal
To demonstrate the quantification of steady-state differences in mitochondrial redox state, primary neurons grown in standard medium were compared to neurons cultured without growth factors for 48 h before imaging. Growth factor withdrawal results in apoptotic neuronal cell death after 72 h16. Cells were imaged after 48 h to test if this is preceded by changes in mitochondr...
Discussion
Quantitative and dynamic measurements of the mitochondrial redox state provide important information about mitochondrial and cellular physiology. Several fluorogenic chemical probes are available that detect reactive oxygen species, "redox stress," or "oxidative stress." However, the latter terms are not well-defined and often lack specificity9,17,18. Compared to chemical dyes, Grx1-roGFP2 offers several advantag...
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (BA 3679/5-1; FOR 2289: BA 3679/4-2). A.K. is supported by an ERASMUS+ fellowship. We thank Iris Bünzli-Ehret, Rita Rosner, and Andrea Schlicksupp for the preparation of primary neurons. We thank Dr. Tobias Dick for providing pLPCX-mito-Grx1-roGFP2. Experiments shown in Figure 4 were performed at the Nikon Imaging Center, University of Heidelberg. Figure 2 was prepared with BioRender.com.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| reagents | |||
| Calcium chloride (CaCl2·2H2O) | Sigma-Aldrich | C3306 | |
| Diamide (DA) | Sigma-Aldrich | D3648 | |
| Dithiothreitol (DTT) | Carl Roth GmbH | 6908.1 | |
| Glucose (2.5 M stock solution) | Sigma-Aldrich | G8769 | |
| Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | G7528 | |
| Glycine | neoFroxx GmbH | LC-4522.2 | |
| HEPES (1 M stock solution) | Sigma-Aldrich | 15630-080 | |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | H4034 | |
| Magnesium chloride (MgCl2·6H2O) | Sigma-Aldrich | 442611-M | |
| N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) | Sigma-Aldrich | M3262 | |
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Sigma-Aldrich | P3911 | |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | neoFroxx GmbH | LC-5932.1 | |
| Sodium pyruvate (0.1 M stock solution) | Sigma-Aldrich | S8636 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Sigma-Aldrich | P8574 | |
| Sucrose | Carl Roth GmbH | 4621.1 | |
| Tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester perchlorate (TMRE) | Sigma-Aldrich | 87917 | |
| equipment | |||
| imaging chamber | Life Imaging Services (Basel, Switzerland) | 10920 | Ludin Chamber Type 3 for Ø12mm coverslips |
| laser scanning confocal microscope, microscope | Leica | DMI6000 | |
| laser scanning confocal microscope, scanning unit | Leica | SP8 | |
| peristaltic pump | VWR | PP1080 181-4001 | |
| spinning disc confocal microscope, camera | Hamamatsu | C9100-02 EMCCD | |
| spinning disc confocal microscope, incubationsystem | TokaiHit | INU-ZILCF-F1 | |
| spinning disc confocal microscope, microscope | Nikon | Ti microscope | |
| spinning disc confocal microscope, scanning unit | Yokagawa | CSU-X1 | |
| software | |||
| FIJI | https://fiji.sc | ||
| StackReg plugin | https://github.com/fiji-BIG/StackReg/blob/master/src/main/java/StackReg_.java | ||
| TurboReg plugin | https://github.com/fiji-BIG/TurboReg/blob/master/src/main/java/TurboReg_.java |
References
- Roede, J. R., Go, Y. M., Jones, D. P. Redox equivalents and mitochondrial bioenergetics. Methods in Molecular Biology. 810, 249-280 (2012).
- Turrens, J. F. Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. Journal of Physiology. 552, 335-344 (2003).
- Lin, M. T., Beal, M. F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 443 (7113), 787-795 (2006).
- Manfredi, G., Beal, M. F. The role of mitochondria in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathology. 10 (3), 462-472 (2000).
- Mari, M., Morales, A., Colell, A., Garcia-Ruiz, C., Fernandez-Checa, J. C. Mitochondrial glutathione, a key survival antioxidant. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 11 (11), 2685-2700 (2009).
- Murphy, M. P. Mitochondrial thiols in antioxidant protection and redox signaling: distinct roles for glutathionylation and other thiol modifications. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 16 (6), 476-495 (2012).
- Dooley, C. T., et al. Imaging dynamic redox changes in mammalian cells with green fluorescent protein indicators. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (21), 22284-22293 (2004).
- Hanson, G. T., et al. Investigating mitochondrial redox potential with redox-sensitive green fluorescent protein indicators. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (13), 13044-13053 (2004).
- Gutscher, M., et al. Real-time imaging of the intracellular glutathione redox potential. Nature Methods. 5 (6), 553-559 (2008).
- Morgan, B., Sobotta, M. C., Dick, T. P. Measuring E(GSH) and H2O2 with roGFP2-based redox probes. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 51 (11), 1943-1951 (2011).
- Marwick, K. F. M., Hardingham, G. E. Transfection in primary cultured neuronal cells. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1677, 137-144 (2017).
- Kohrmann, M., et al. convenient, and effective method to transiently transfect primary hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 58 (6), 831-835 (1999).
- Depp, C., Bas-Orth, C., Schroeder, L., Hellwig, A., Bading, H. Synaptic activity protects neurons against calcium-mediated oxidation and contraction of mitochondria during excitotoxicity. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 29 (12), 1109-1124 (2018).
- Hauck, B., Chen, L., Xiao, W. Generation and characterization of chimeric recombinant AAV vectors. Molecular Therapy. 7 (3), 419-425 (2003).
- Brand, M. D., Nicholls, D. G. Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochemical Journal. 435 (2), 297-312 (2011).
- Zhang, S. J., et al. Nuclear calcium signaling controls expression of a large gene pool: identification of a gene program for acquired neuroprotection induced by synaptic activity. PLoS Genetics. 5 (8), 1000604 (2009).
- Winterbourn, C. C. The challenges of using fluorescent probes to detect and quantify specific reactive oxygen species in living cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1840 (2), 730-738 (2014).
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biology. 4, 180-183 (2015).
- Lukyanov, K. A., Belousov, V. V. Genetically encoded fluorescent redox sensors. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1840 (2), 745-756 (2014).
- Nietzel, T., et al. Redox-mediated kick-start of mitochondrial energy metabolism drives resource-efficient seed germination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (1), 741-751 (2020).
- Albrecht, S. C., et al. Redesign of genetically encoded biosensors for monitoring mitochondrial redox status in a broad range of model eukaryotes. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 19 (3), 379-386 (2014).
- Albrecht, S. C., Barata, A. G., Grosshans, J., Teleman, A. A., Dick, T. P. In vivo mapping of hydrogen peroxide and oxidized glutathione reveals chemical and regional specificity of redox homeostasis. Cell Metabolism. 14 (6), 819-829 (2011).
- Breckwoldt, M. O., et al. Multiparametric optical analysis of mitochondrial redox signals during neuronal physiology and pathology in vivo. Nature Medicine. 20 (5), 555-560 (2014).
- Ricke, K. M., et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction combined with high calcium load leads to impaired antioxidant defense underlying the selective loss of nigral dopaminergic neurons. Journal of Neuroscience. 40 (9), 1975-1986 (2020).
- Bjornberg, O., Ostergaard, H., Winther, J. R. Mechanistic insight provided by glutaredoxin within a fusion to redox-sensitive yellow fluorescent protein. Biochemistry. 45 (7), 2362-2371 (2006).
- Shokhina, A. G., et al. Red fluorescent redox-sensitive biosensor Grx1-roCherry. Redox Biology. 21, 101071 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved